Excretion
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is excretion?
The removal of waste products from metabolism
What 2 waste products do plants excrete?
Oxygen (a waste product from photosynthesis)
Carbon dioxide (a waste product from respiration)
Give 3 waste products that the human body excretes
Urea
Carbon dioxide
Excess water & salts
Where is carbon dioxide excreted from?
The lungs
Where is excess water & salts excreted from?
The skin via sweat
It can also be excreted from the kidneys
Where is urea excreted from?
The kidneys
What is the function of the kidneys?
- To regulate the volume & concentration of urine
- To remove nitrogenous waste products
- To maintain a balanced content of water in the body
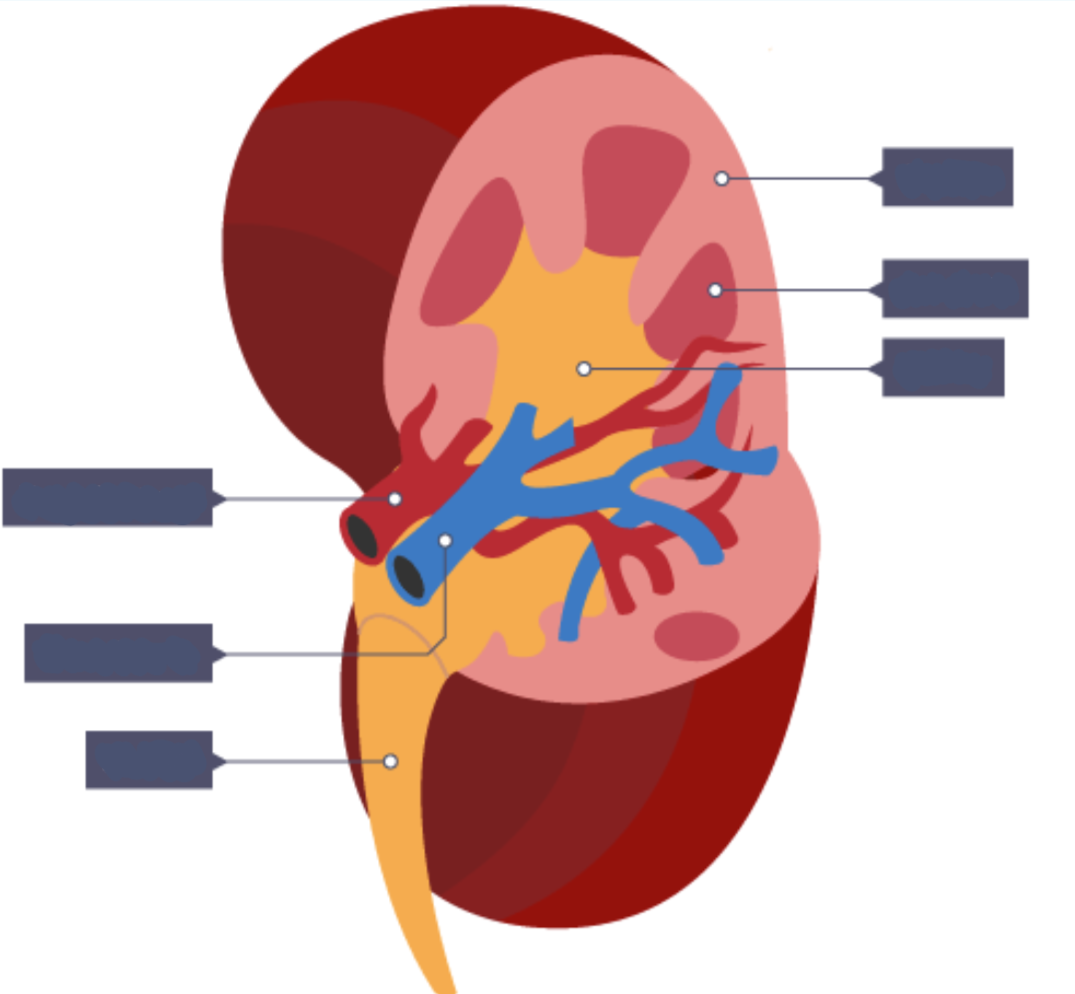
Label this diagram of the kidneys
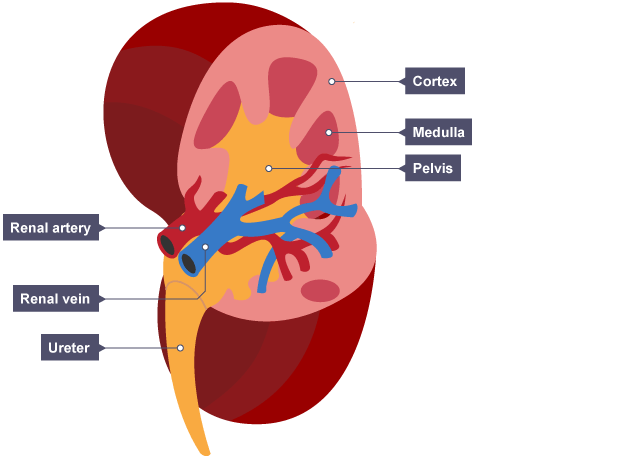
The inner part of the kidney is called…
The medulla
The outer part of the kidney is called…
The cortex
What is the function of the pelvis?
To collect urine & carry it to the ureter
What is the function of the ureter?
To carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder so it can be excreted out the body
What is the difference between the ureter & the urethra?
The ureter connects the kidneys to the bladder whereas the urethra connects the bladder to outside the body
Blood is carried to the kidney by…
The renal artery
Blood is carried away from the kidney by…
The renal vein
What are the 4 roles of the kidneys?
Ultrafiltration
Selective re-absorption
Excretion
Osmoregulation
What is ultrafiltration?
The filtering out of waste products at a high pressure to form urea
What is selective re-absorption?
When useful substances such as water, ions, glucose & amino acids are reabsorbed back into the blood
What is osmoregulation?
The controlling & maintaining of a balanced water content in the body
Each kidney contains millions of tubules, also known as…
Nephrons
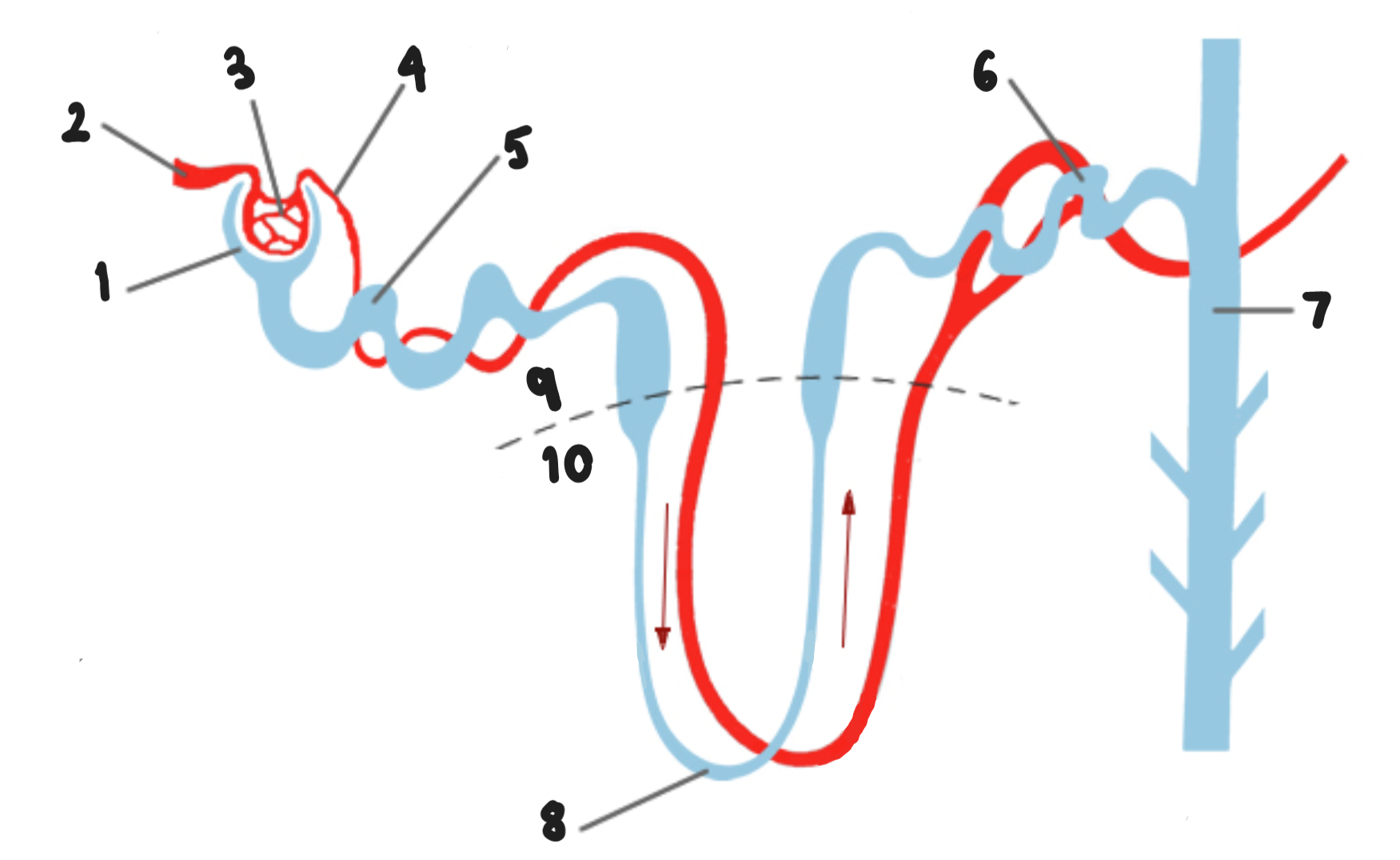
Label this diagram of a nephron
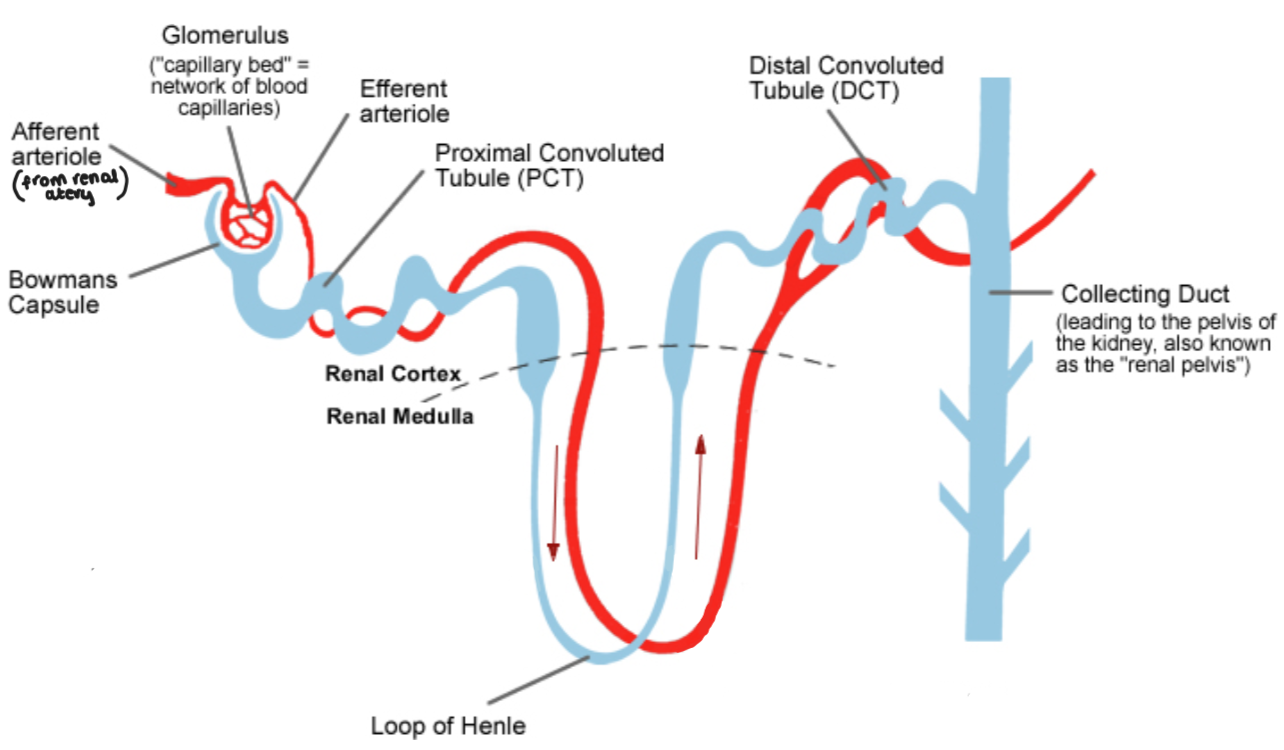
Where does ultrafiltration happen?
In the glomerulus
How does ultrafiltration work?
The renal artery transports oxygenated blood to the Bowman’s capsule at a high pressure
In the glomerulus the pressure increases even further as the efferent arteriole (where the blood exits) is narrower than the afferent arteriole (where the blood enters)
Therefore, only small substances can squeeze through, leaving behind the bigger molecules (e.g. proteins & blood cells)
What is the glomerular filtrate?
The mixture of small substances that were able to squeeze through the efferent arteriole during ultrafiltration
Give 4 components that are in the glomerular filtrate
Urea
Water
Salt
Glucose
What is the purpose of selective reabsorption?
To prevent useful substances such as glucose being excreted
Where is glucose reabsorbed?
At the proximal convoluted tubule
Why does the proximal convoluted tubule contain lots of mitochondria?
So that it can provide enough energy for active transport which is needed to reabsorb glucose back into the blood
Where is salt reabsorbed?
In the Loop of Henle
Where is water reabsorbed?
In the collecting ducts (depending on the levels of water in the body)
After all the useful substance have been reabsorbed, the remaining filtrate in the collecting duct will…
Form urine which is then transported from the kidney to the bladder via the ureter
The urine is then stored in the bladder until it leaves the body via the urethra
Give 3 components of urine
Water
Urea
Ions
What is ADH?
A hormone which is involved in the control of water loss by urine
ADH = anti-diuretic hormone
When is ADH released?
When the osmo-receptors detect that the blood is too concentrated due to a lack of water
Where is ADH released from & to?
Pituitary gland → nephrons
What does ADH do when it is released?
It makes the collecting duct more permeable to water so that more water is reabsorbed back into the blood from the filtrate & less is lost as urine
What happens to urine when ADH is released?
There are smaller volumes of it & it is more concentrated (giving it a dark yellow colour)
Describe the negative feedback loop when dehyration is detected
The concentration of the blood increases so more ADH is released, meaning that water is retained & highly concentrated urine is produced
Describe the negative feedback loop when overdehyration is detected
The concentration of the blood decreases so less ADH is released, meaning that salts are retained & dilute urine is produced
In high temperatures, increased sweating can lead to ____. This can result in ____ via sweat, meaning that the kidneys may try to compensate by ____ salt retention. The ____ detects this & makes us feel that we are ____ so we drink more water to ____ the salts in our blood.
1 = Dehydration
2 = Salt loss
3 = Increasing
4 = Brain
5 = Thirsty
6 = Dilute
What is kidney failure?
When your kidneys stop functioning properly & therefore cannot filter waste products from the blood
What are the symptoms of kidney failure?
Protein & glucose in urine
Swollen hands & feet
Nausea
Drowsiness
What can short-term kidney failure be caused by?
Infections
Blockage of ureter
What can long-term (chronic) kidney failure be caused by?
Diabetes
High blood pressure
Tumors in the abdomen
Short-term kidney failure can be treated by…
Antibiotics or surgery
Long term kidney failure can be treated by…
Dialysis or a kidney transplant
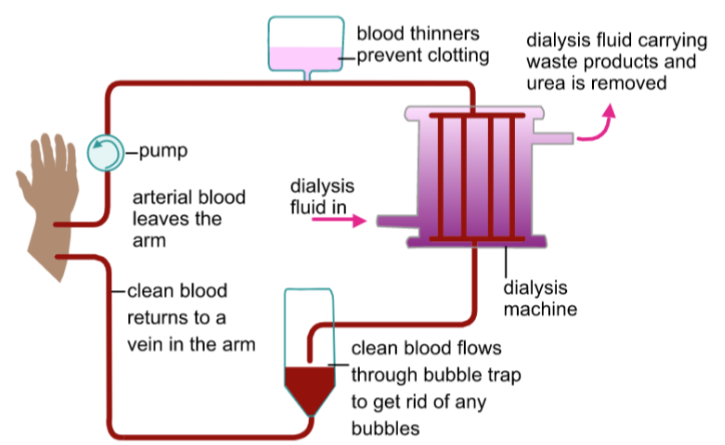
Explain how a dialysis machine works
Blood is pumped into the dialysis machine & passes through tubes with a partially permeable membrane
Dialysis fluid surrounds the tubes, containing the same concentration of salts & sugars as the blood, however it contains no urea
Therefore urea diffuses from the blood into the dialysis fluid because particles are moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Proteins & blood cells are too big to pass through the partially permeable membrane, so they remain in the blood
The ‘cleaned’ blood then is pumped back into the patient
What are the negatives of being treated by dialysis?
- Treatment by dialysis is expensive
- The patient has to be connected to the dialysis machine for 4-5 hours several times a week
- The patient should control the amount of protein they have in their diet to help reduce urea production
What are the negatives of being treated with a kidney transplant?
- Kidney transplants are expensive
- The supply of suitable donor kidneys are limited
Suggest why suitable donor kidneys are hard to find
Because kidneys have antigens on their surface & the immune system recognises strange & foreign cells, often meaning that the donor kidney will be rejected
Therefore, a donated kidney must have very similar antigens to the patients cells, limiting the amount of suitable donor kidneys
Why is a kidney transplant put in lower down in the abdomen instead of where the original kidneys are?
Because it is closer to the bladder which means that the tubes connecting the new kidney to the bladder can be shorter, making the surgery less complicated