Honors Bio Aerobic and Anaerobic Cellular Respiration (Finn)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
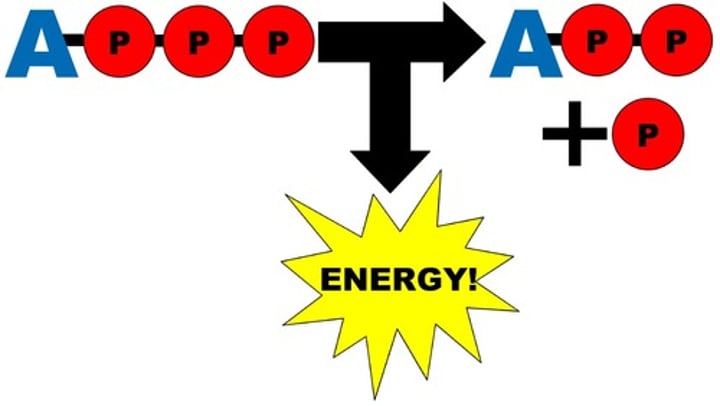
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
main energy source that cells use for most of their work
oxygen
molecule used in aerobic respiration. If not present, cells will do anaerobic respiration.
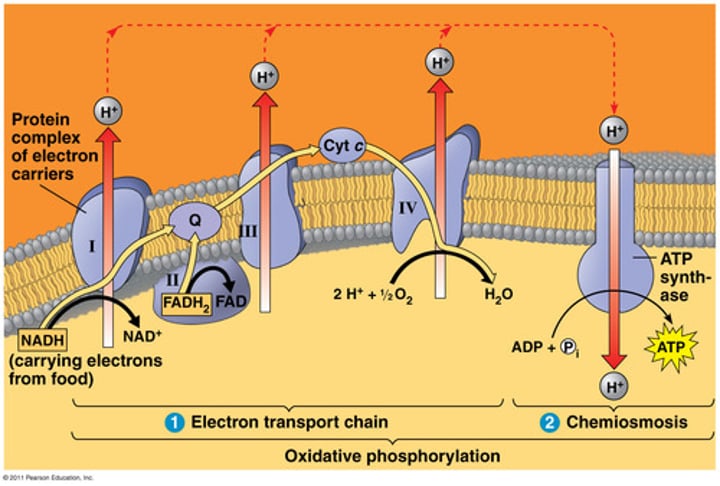
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons through the inner membrane to make ATP.
fermentation
A process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose; no oxygen required; only glycolysis occurs; no Krebs Cycle or ETC ; end products are such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
aerobic respiration
Pathway in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel (glucose)
NADH and FADH2
An energy-carrying molecule produced by glycolysis and the Citric Acid cycle. Carries energy to the electron transport chain, where it is stored in ATP.
glycolysis
The splitting of 6-carbon sugar glucose into 2 organic carbon compounds (pyruvate). Glycolysis is the one pathway that occurs in all living cells, serving as the starting point for fermentation or aerobic respiration.
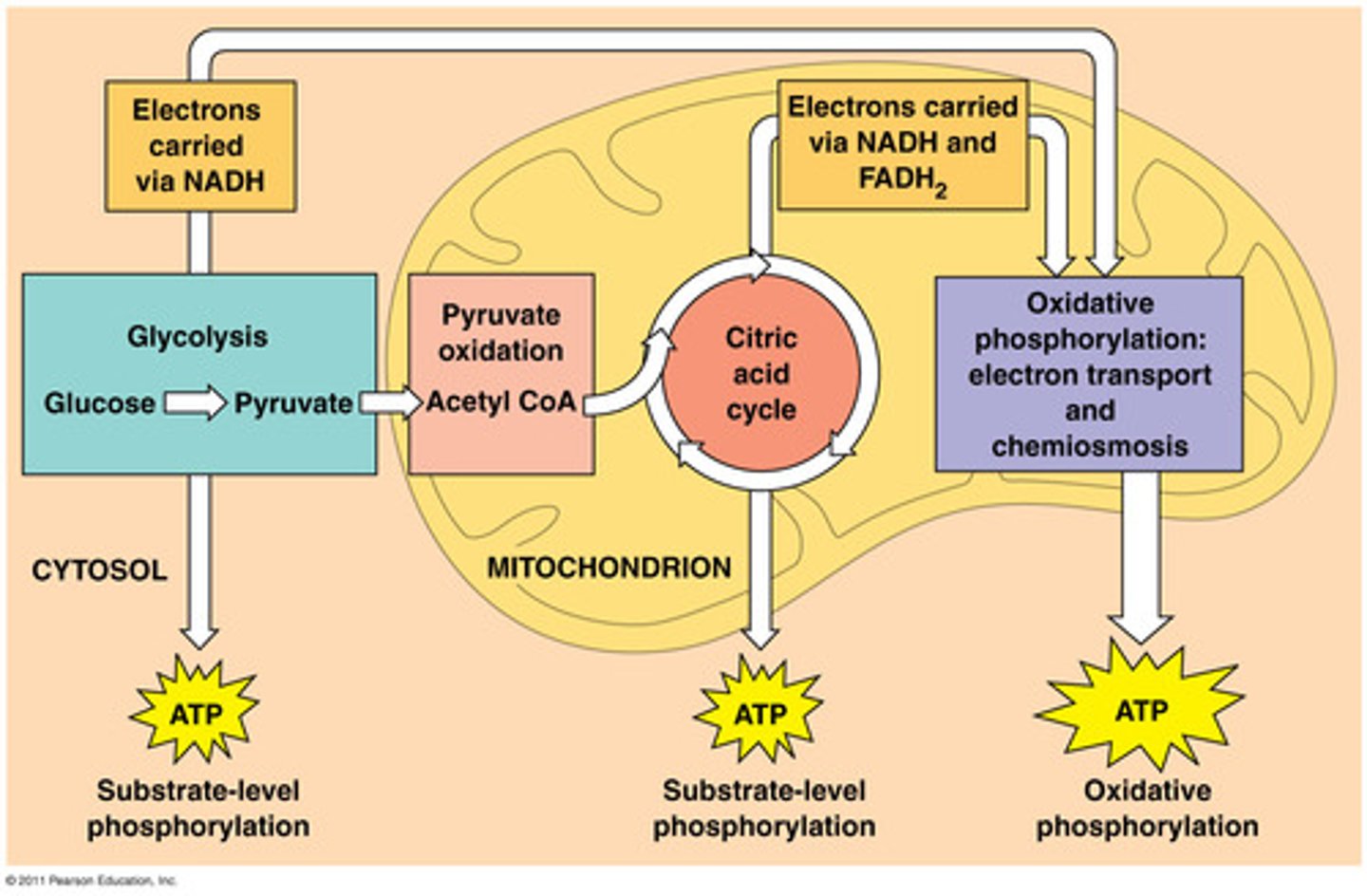
pyruvate
Three-carbon compound that forms as an end product of glycolysis.
anaerobic fermentation
Enables cells to produce ATP in the absence of oxygen. Yields 2 ATP and lactic acid or ethanol.
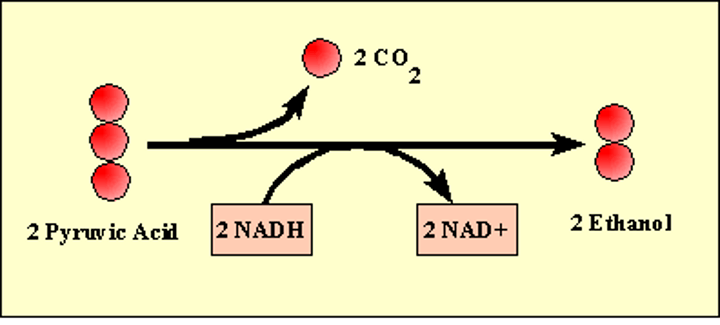
alcohol fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol; form of anaerobic respiration
lactic acid fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to lactate with no release of carbon dioxide; form of anaerobic respiration