Components of a circuit, ohms law
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Electric Field
The field around charged particles that exerts a non-contact force on other charged particles.
Current
Rate of flow of charge
Non-Contact Force
A force that one object can apply to another object without touching it
Line of Force
The path that a positive charge would follow due to the electric field
Cell
Pushes electrons around a complete cicuit
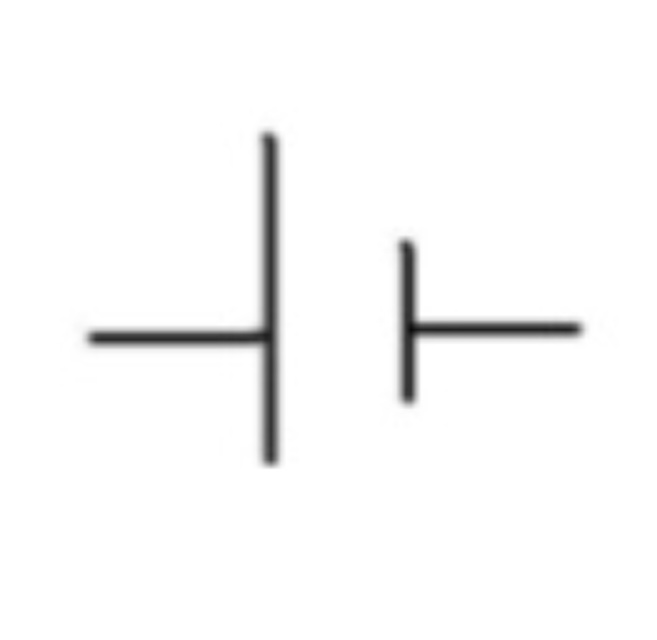
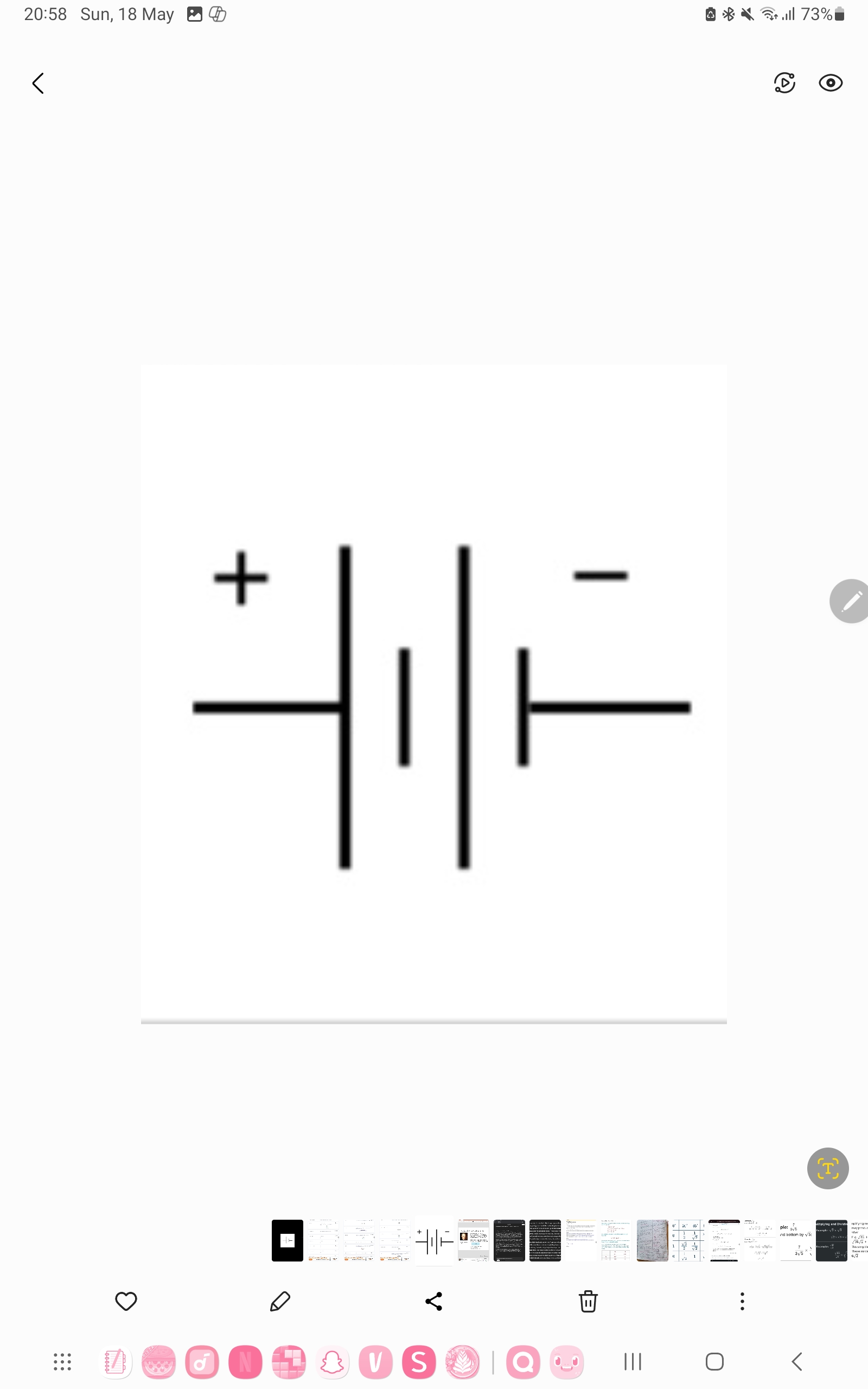
Battery
Two or more cells
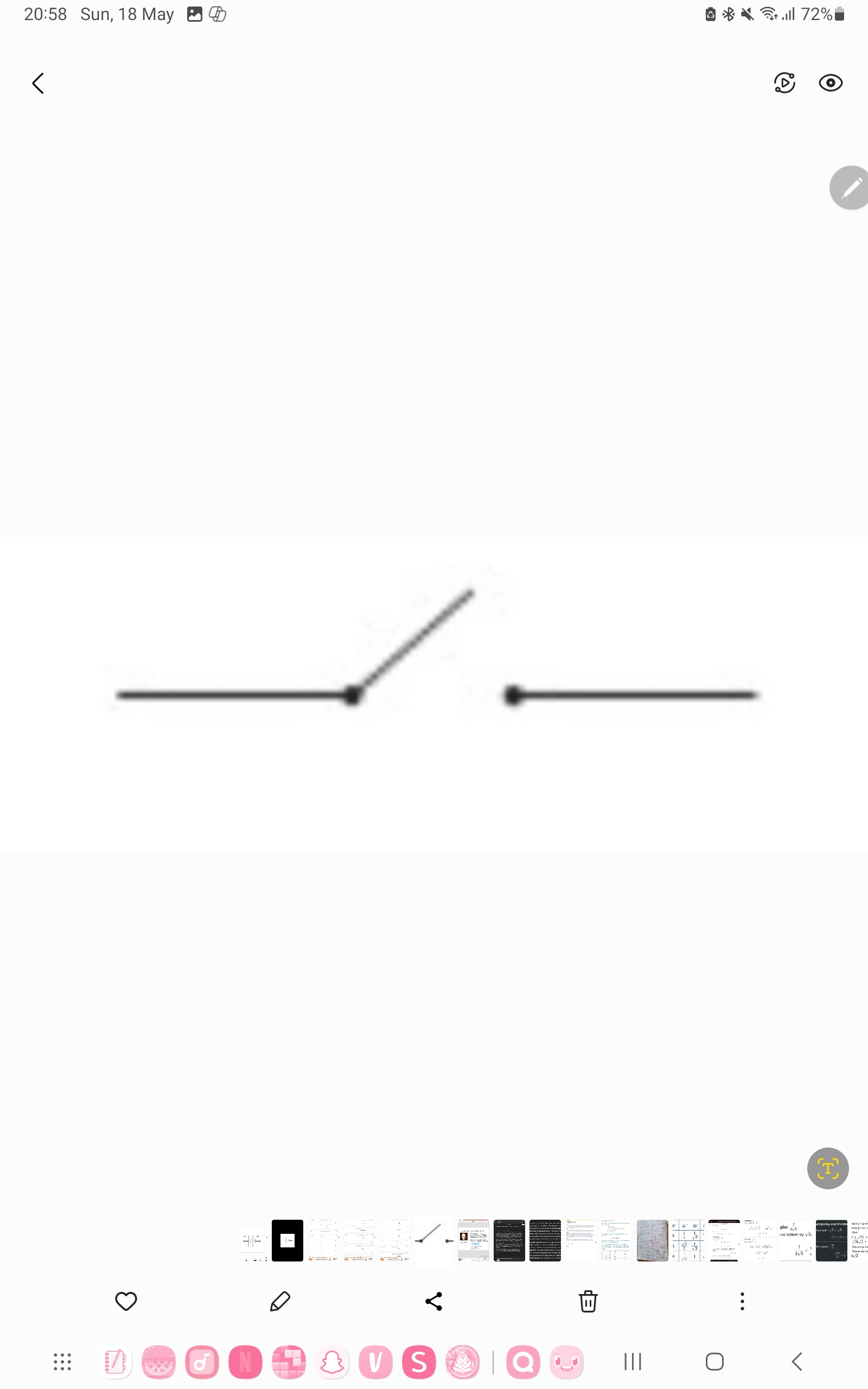
Switch
Enable the current in a circuit to be turned on or off
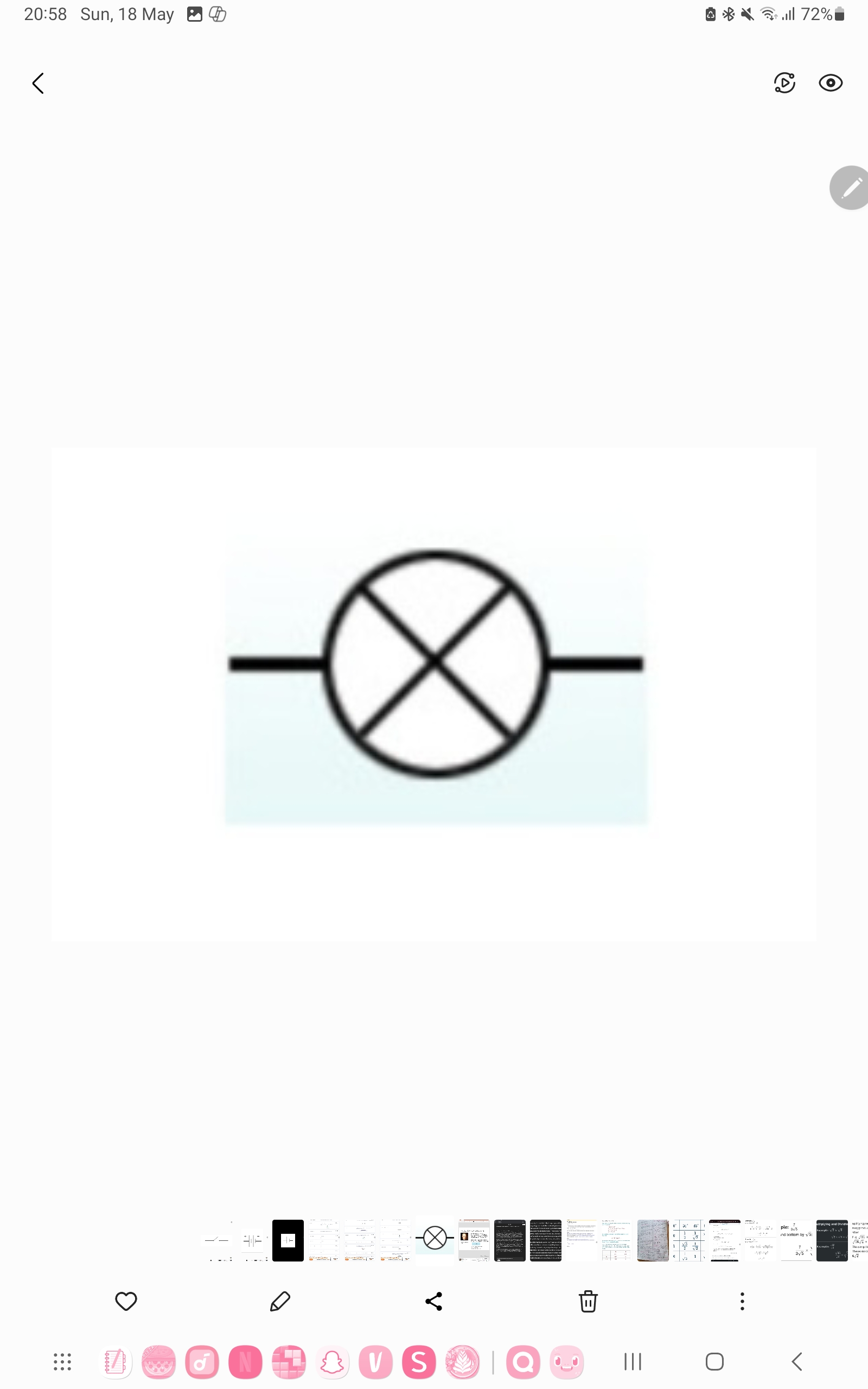
Lamp
Emits light when current passes through it
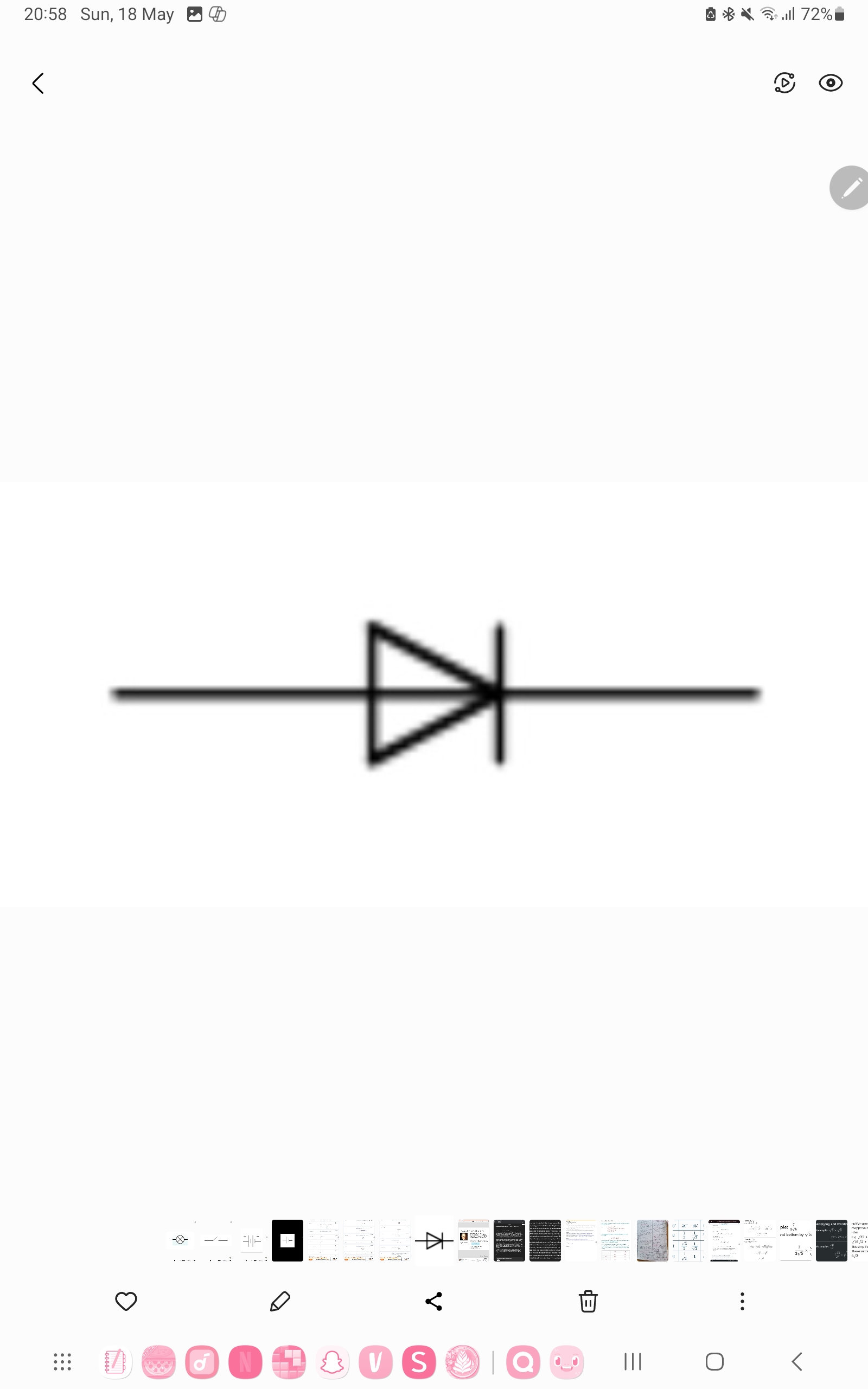
Diode
A device that permits current to flow through it in only one direction.
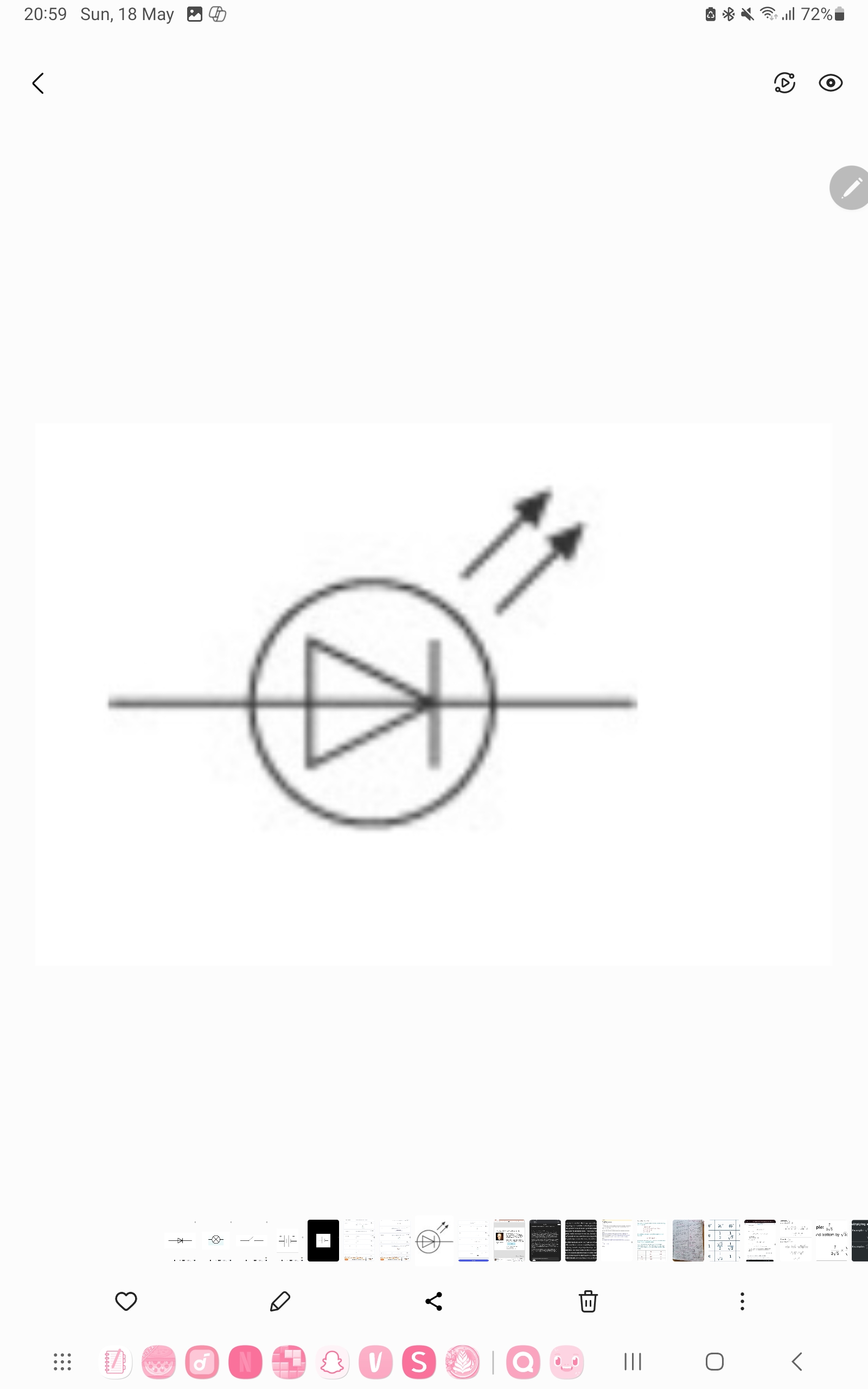
Light-emitting Diode (LED)
combines the propertied of a diode and a lamp
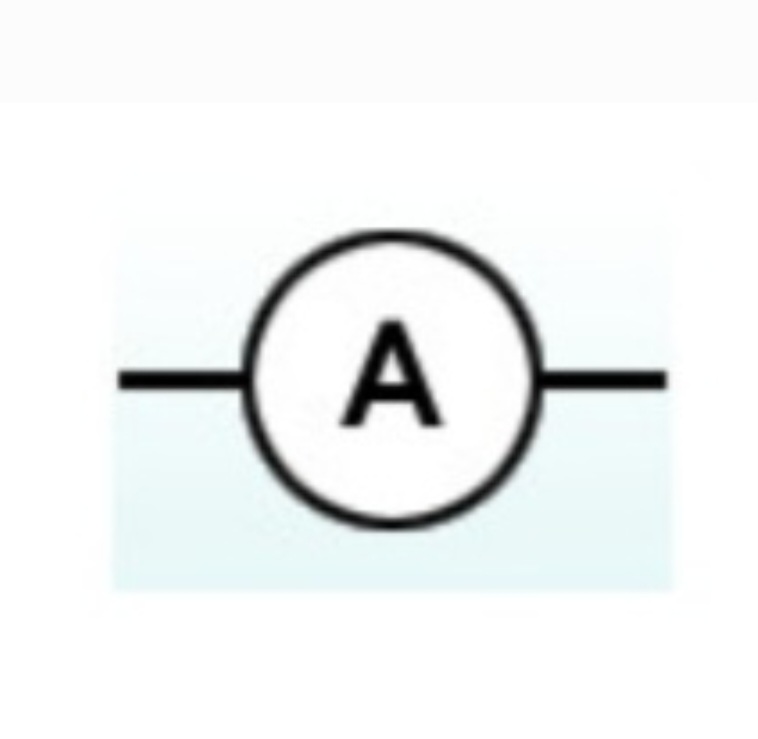
Ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit
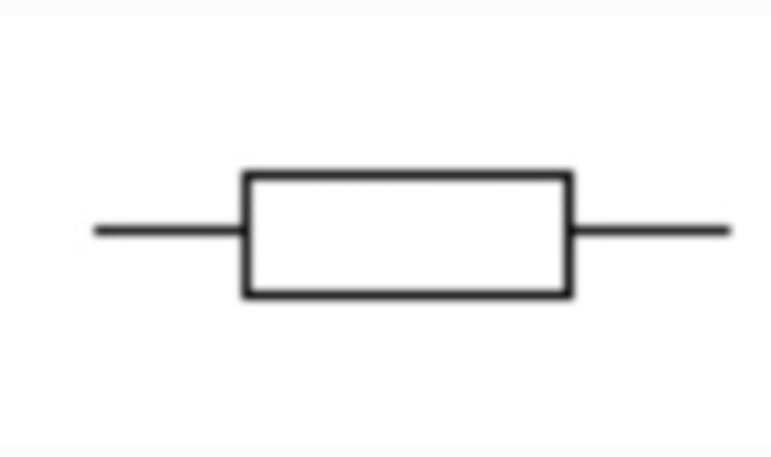
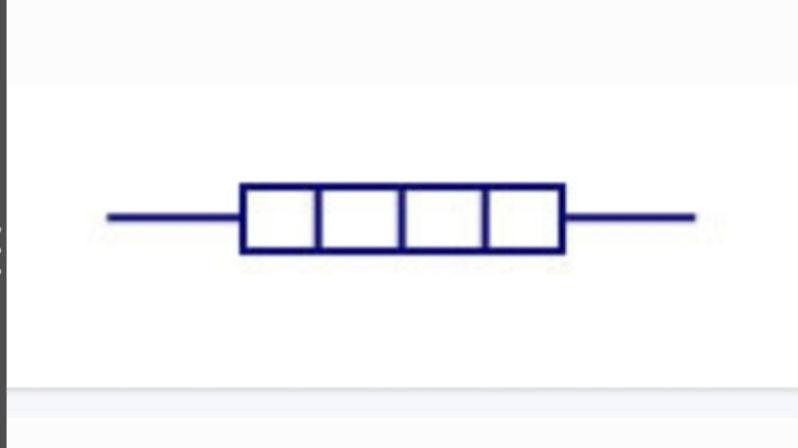
Fixed Resistor
limits the current in a circuit
Variable Resistor
Allows current to be varied
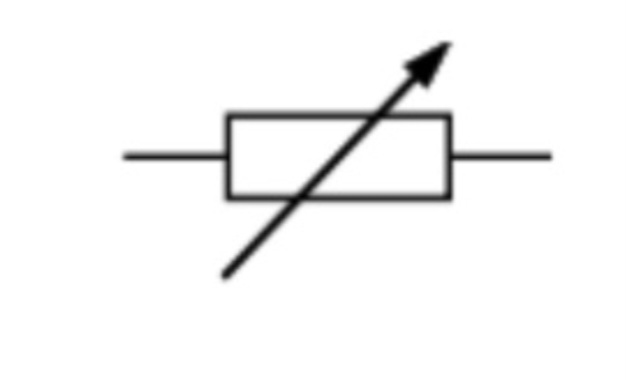
Fuse
A safety device with a thin metal strip that will melt if too much current passes through a circuit
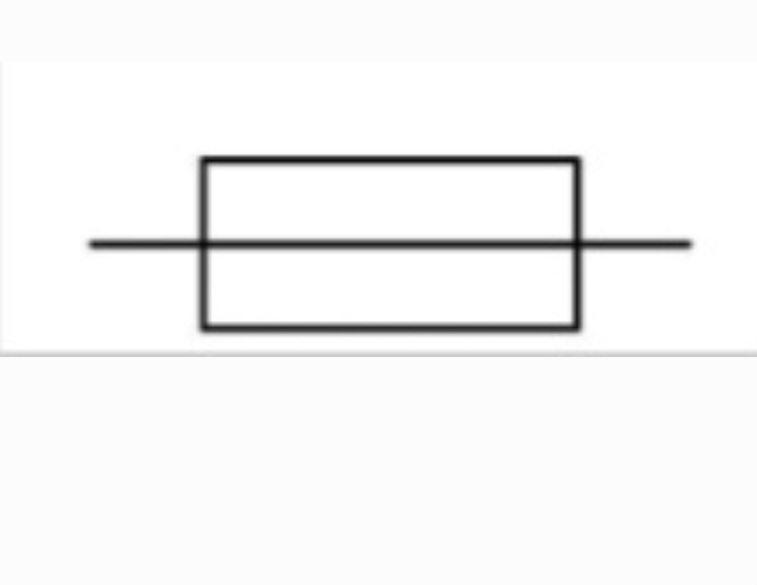
Heater
Designed to transfer energy from an electric current to heat the surroundings
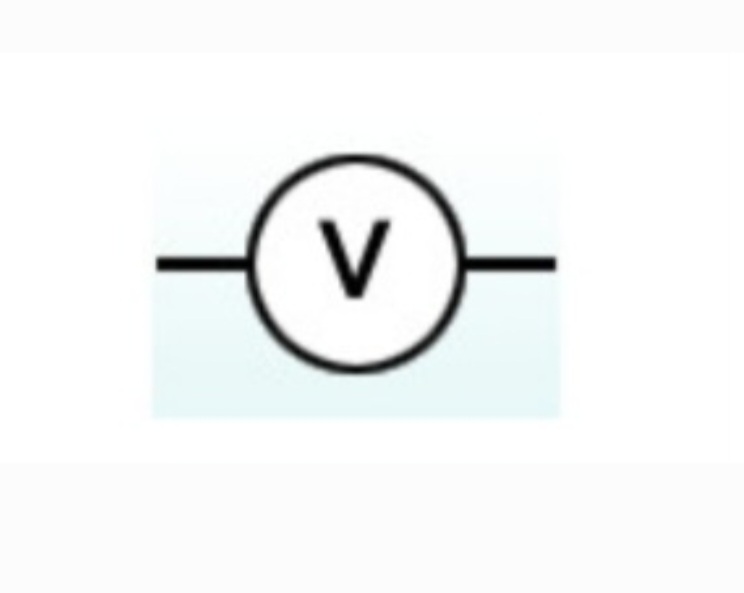
Voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particles
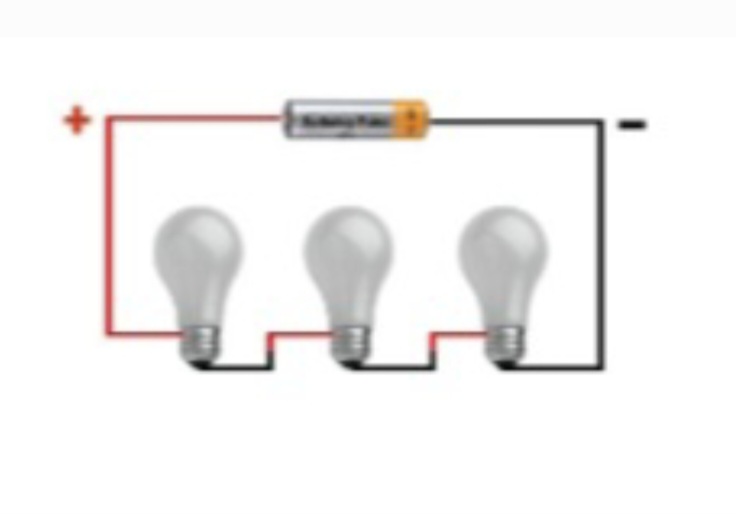
Series
A circuit in which all parts are connected end to end to provide a single path of current.
Potential Difference
The work done by each Coulomb of charge
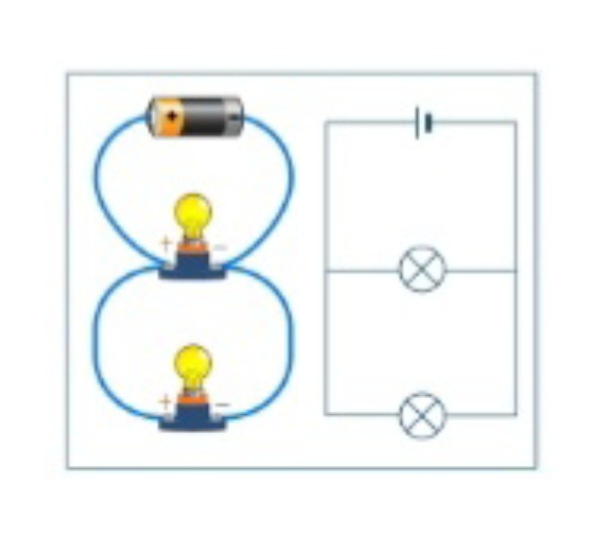
Parallel
A circuit in which parts are connected in separate circuits to each other to provide a single path of current.
Charge Equation
=Energy Transferred÷Potential Difference
Unit of Charge
Coulomb(s)
Unit of Current
Amps
Unit of Potential Difference
Volt(s)
Unit of Resistance
Ohm(s)
equation that links resistance, potential difference and current
resistance = potential difference ÷ current
Ohm's Law
The current through a resistor at a constant temperature is directly proportional to the Potential difference across the resistor
Thermistor
A resistor that changes its resistance with a change of temperature.
Light Dependent Resistor
A resistor which has high resistance in the dark, and low resistance in bright light
Total Resistance of a series circuit
Sum of the resistances of every component
Total potential difference of a series circuit
Sum of the potential differences of every cell
Current of a series circuit
The same current passes through each component
Potential difference in a series circuits
Potential difference is shared between the components
Total Current in a parallel circuit
The sum of the currents through each branch
Total resistance of a parallel circuit
Always less than the resistor with the least resistance
Live Wire
The brown wire in a cable or plug.
Neutral Wire
A wire that carries current away from the component; it is coated in blue plastic.
Three-Pin Plug
connects an appliance to the mains
Short circuit
When the live wire in an appliance touches the neutral wire