Cognitive Psychology: Knowledge Representation, Mental Imagery, and Language Comprehension
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What are the two main types of knowledge?
Procedural and Declarative knowledge.
How is procedural knowledge acquired?
Through repeated practice or exposure.
What is an example of procedural knowledge?
Muscle memory.
What characterizes declarative knowledge?
It is specific to facts and events and is acquired with organization.
What are the two types of declarative knowledge?
Episodic and Semantic knowledge.
What is episodic knowledge?
Autobiographical knowledge with temporal tags.
What is semantic knowledge?
Factual knowledge about words and concepts, not tied to personal experiences.
What did Cohen & Corkin (1982) study?
The difference between explicit episodic learning and implicit procedural learning.
What task did Cohen & Corkin use to compare normals and amnesics?
The Tower of Hanoi puzzle.
What was a key finding regarding normals in the Tower of Hanoi task?
Normals learn procedures and have episodic memory.
What was a key finding regarding amnesics in the Tower of Hanoi task?
Amnesics can learn the task but do not have episodic memory.
What is semantic memory?
Permanent memory of general world knowledge.
Which brain areas are involved in episodic and semantic memory?
Episodic memory involves the hippocampus and anterior prefrontal cortex; semantic memory involves the lateral temporal lobes and posterior prefrontal cortex.
What is the Feature Model in semantic memory?
A model that represents knowledge as sets of features weighted in an n-dimensional space.
What are defining features in the Feature Model?
Important features that characterize a category, such as 'wings' for birds.
What are characteristic features in the Feature Model?
Less important features, such as the color of a bird.
What is the decision process in the Feature Model?
It involves global feature comparison followed by defining feature comparison.
What is the Hierarchical Network Model?
A model that organizes semantic memory in a hierarchy of nodes and links.
What is cognitive economy in the Hierarchical Network Model?
Storing common information at only one level to save cognitive resources.
What is the Spreading Activation Model?
A model where related nodes are connected, and activation spreads along these connections.
How does the strength of connection in the Spreading Activation Model vary?
The strength of the connection weakens with distance between nodes.
What is a problem identified in the Semantic Feature Comparison Model?
Responses to disconfirming sentences are slower than expected.
What evidence supports the Hierarchical Network Model?
Faster response times for true/false statements based on the hierarchy of concepts.
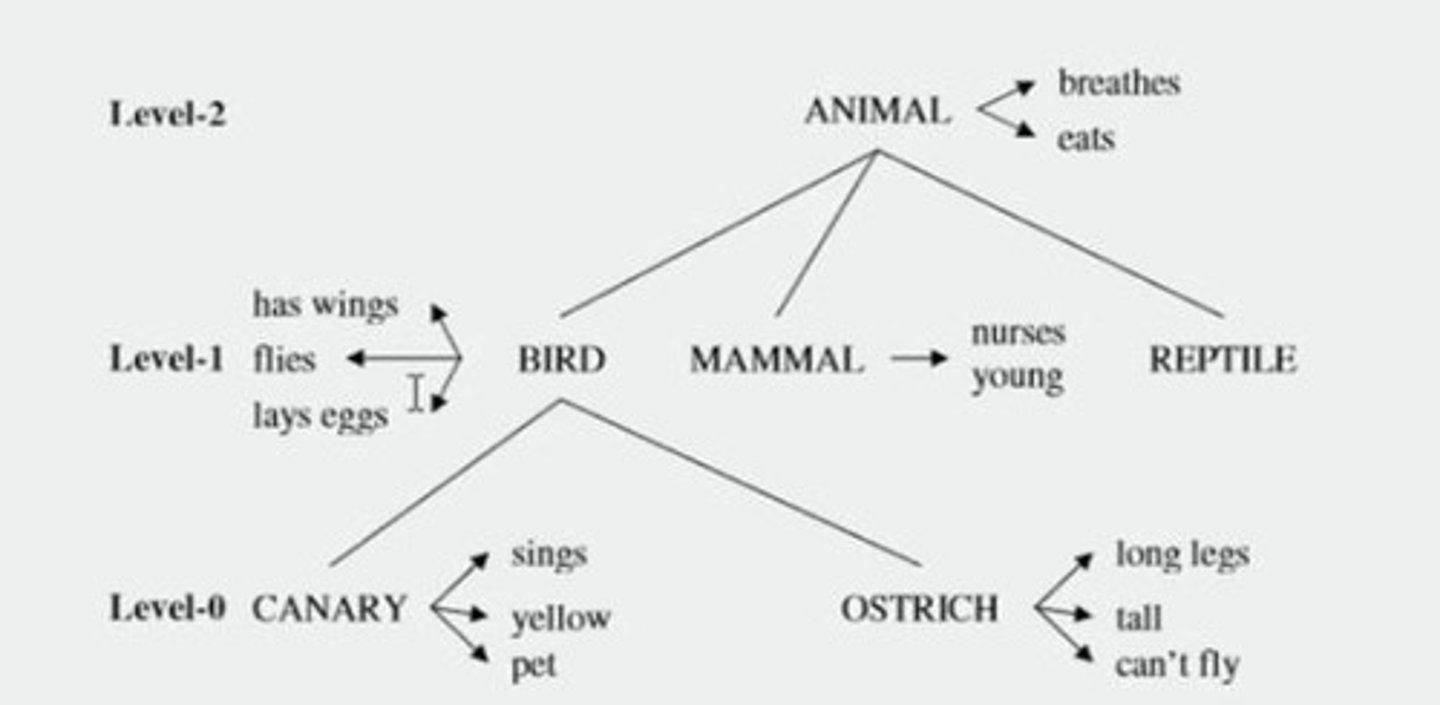
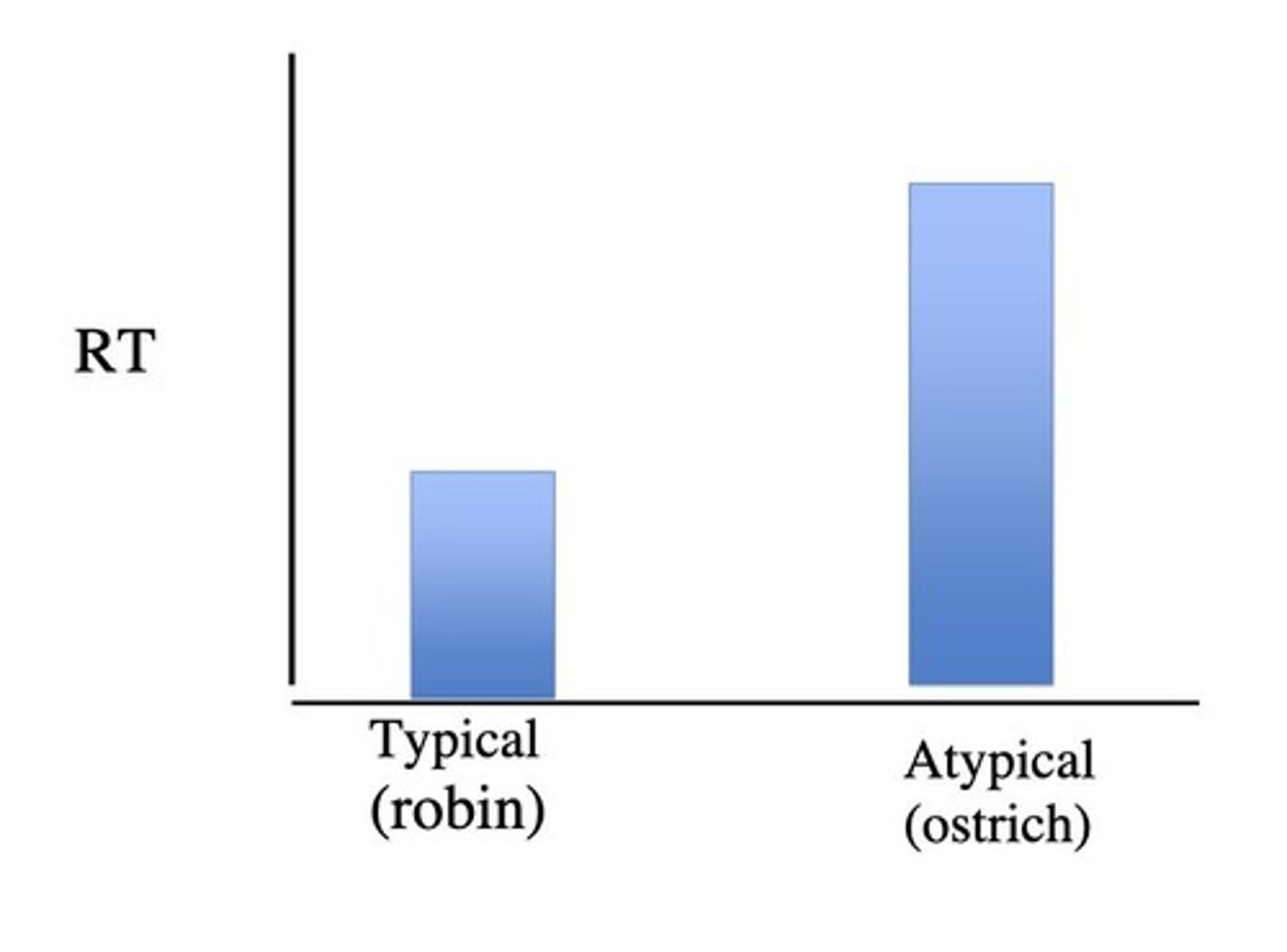
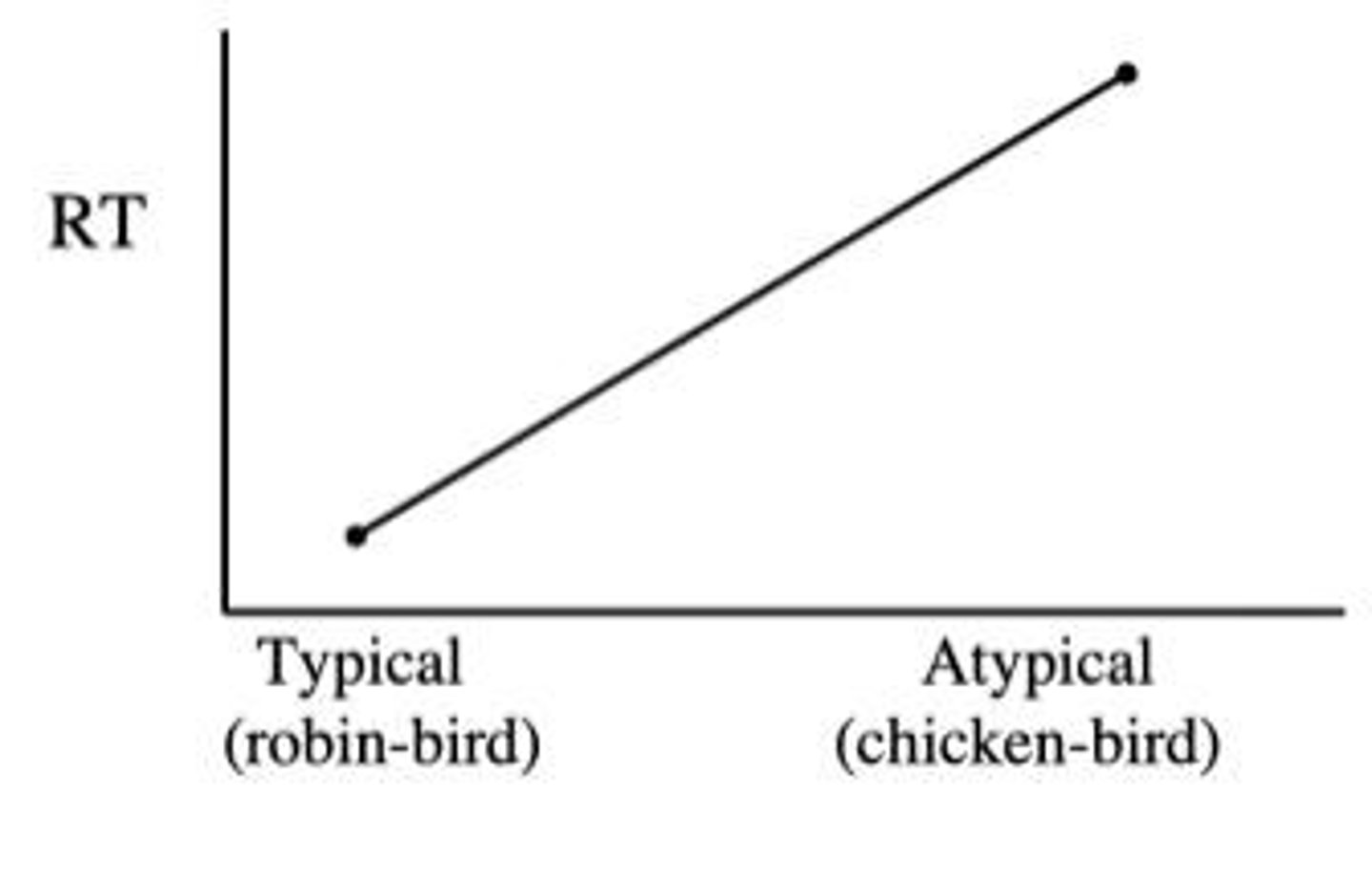
What is the significance of typicality effects in semantic memory models?
Different types of birds are verified at different rates, affecting response times.
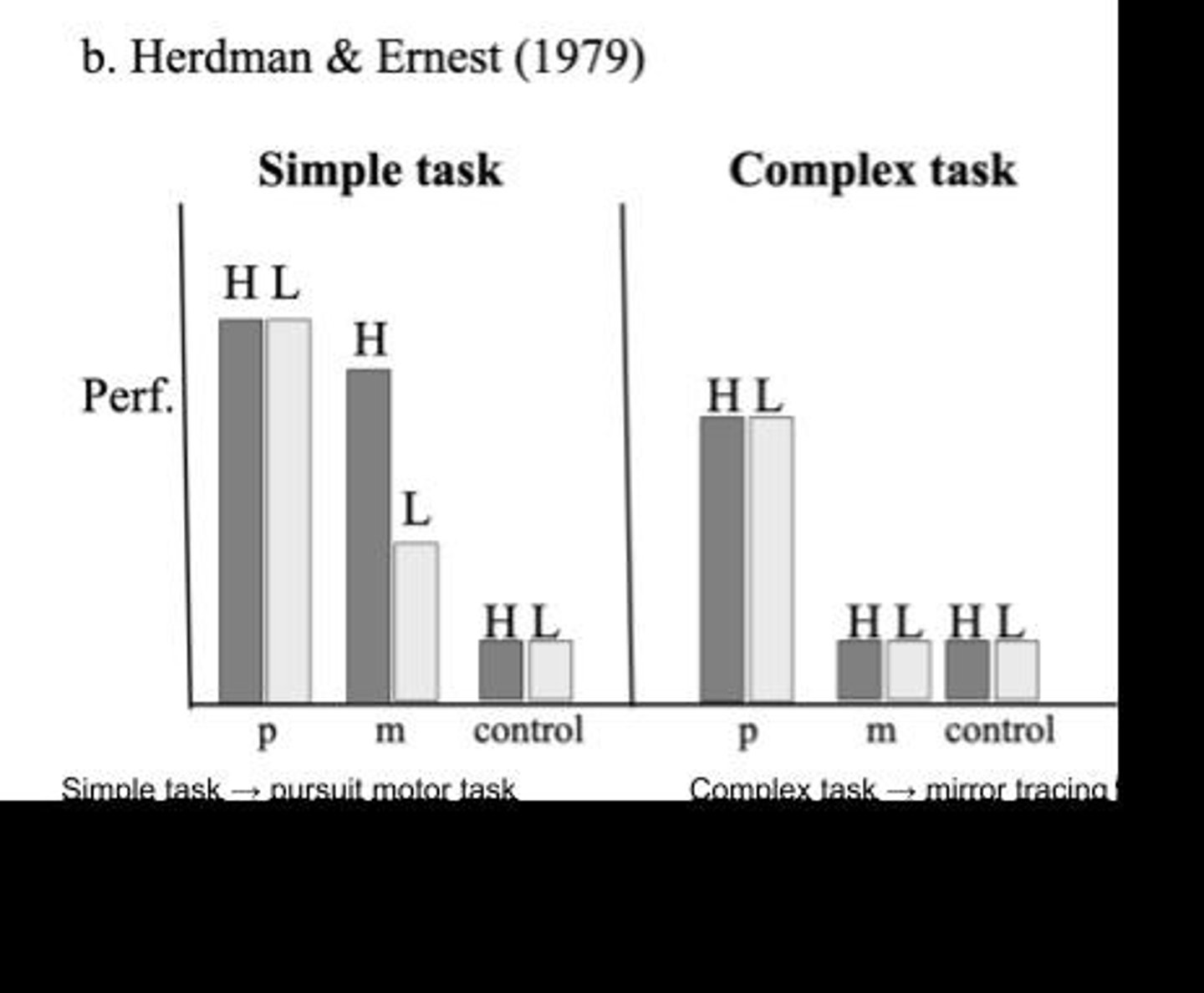
What is the role of the Mirror Tracing Task in studying HM?
It demonstrated implicit learning and memory despite HM's lack of episodic memory.
What does the term 'subjective organization' refer to in semantic memory?
Personal organization of information as proposed by Tulving (1962).
What is the main focus of psychoanalysis in relation to semantic memory?
Examining and formalizing the organization of semantic memory.
What is the primary difference between episodic and procedural knowledge?
Episodic knowledge is about personal experiences, while procedural knowledge is about skills and tasks.
What is the purpose of evaluating at intersections in cognitive psychology?
To determine the strength of activation and whether a concept is categorized as ISA or ISNOTA.
What does verification time indicate in semantic memory?
It indicates how quickly a statement can be confirmed as true or false, with shorter connections being verified faster.
What is semantic priming?
A phenomenon where the activation of one concept facilitates the retrieval of a related concept.
What are the two main categories of long-term memory (LTM)?
Declarative and Procedural memory.
What are the subcategories of declarative memory?
Episodic and Semantic memory.
What is procedural knowledge?
Knowledge of how to perform tasks, which is often difficult to extinguish once learned.
What are the three models of knowledge proposed by Tulving?
Semantic-feature comparison, Hierarchical network, and Spreading activation model.
What does the hierarchical network model suggest about information retrieval?
It suggests that retrieval takes longer as one moves up levels of the hierarchy.
What was the main finding of Sheppard's (1967) recognition memory study?
Participants recognized 98% of 200 pictures seen for a few seconds.
What did Nickerson's (1965) study on picture memory reveal?
Participants recalled 92% of 600 pictures one day later and 63% one year later.
What is hemispheric specialization?
The concept that the left and right hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions.
How does the right hemisphere process pictures compared to the left hemisphere?
The right hemisphere processes pictures better when presented to the left visual field.
What is dual-coding theory?
The theory that information can be represented in two ways: verbally (left hemisphere) and visually (right hemisphere).
What factors influence the type of code used in dual-coding theory?
The nature of the information, the task, and individual differences in abilities.
What is the Vividness of Mental Imagery Questionnaire (VVIQ)?
A scale that rates how clear individuals can form mental images in their minds.
What does functional equivalence refer to in cognitive psychology?
The idea that mental images are abstract-analog representations that can simulate continuous change.
What evidence supports the concept of mental rotation?
Shepard & Metzler's study showed that the time to decide if two 3D objects were the same varied with the degree of rotation needed.
What did Kosslyn's experiments on mental images reveal?
They showed that internal visual images are functionally analogous to perception, with response times varying based on the size of mental objects.
What is the main idea behind the concept of mental scanning?
It suggests that the time taken to mentally scan an image reflects the properties of the image itself.
What is the difference between first-order and second-order isomorphism in mental imagery?
First-order isomorphism refers to direct structural representation, while second-order isomorphism refers to relational similarities between cognitive systems and the physical world.
What is the significance of the paired associated task in Paivio's research?
It demonstrated how concrete words activate compound images more effectively than abstract words.
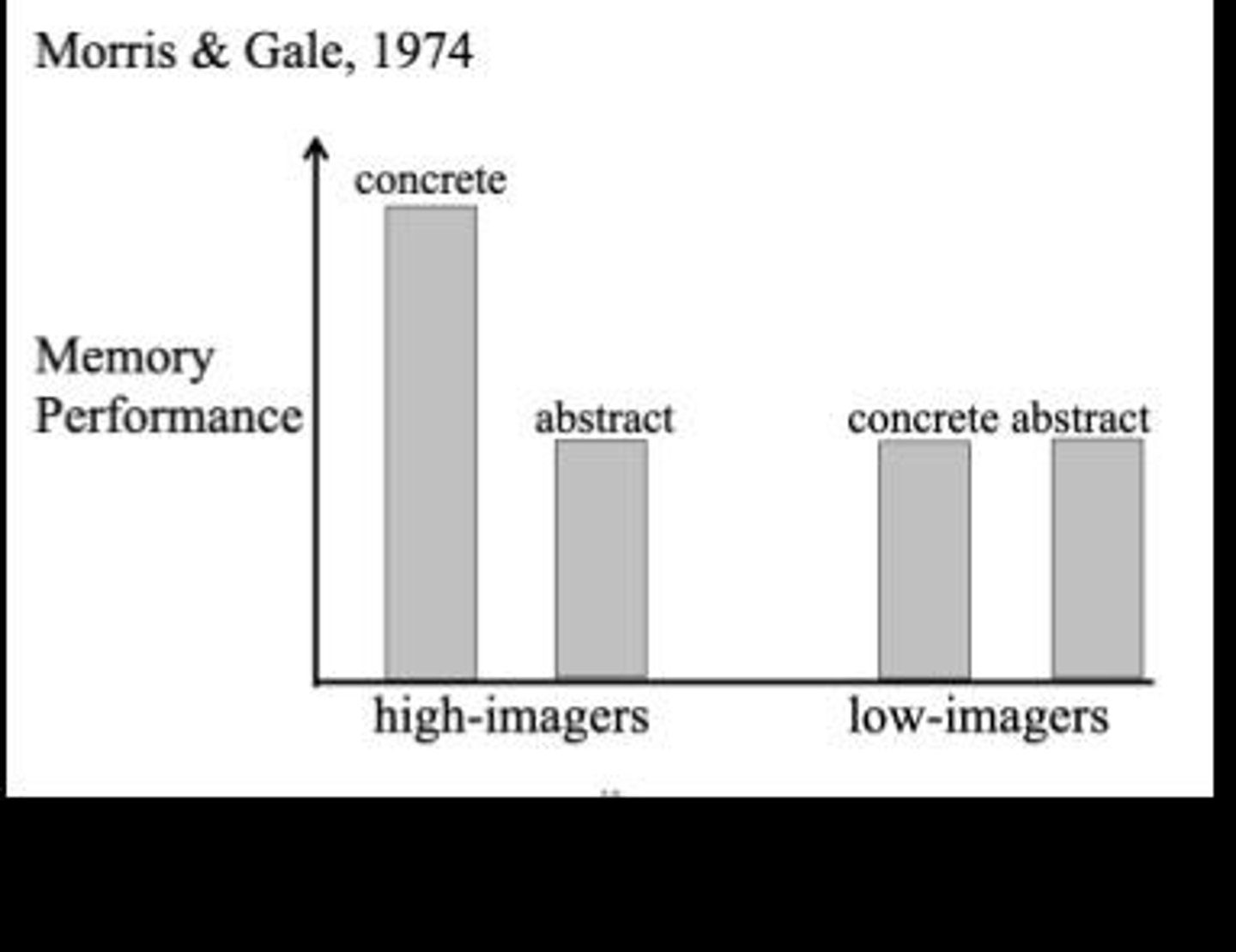
What does the term 'imagability' refer to in the context of dual-coding theory?
It refers to how easily a word can evoke a mental image, influencing memory recall.
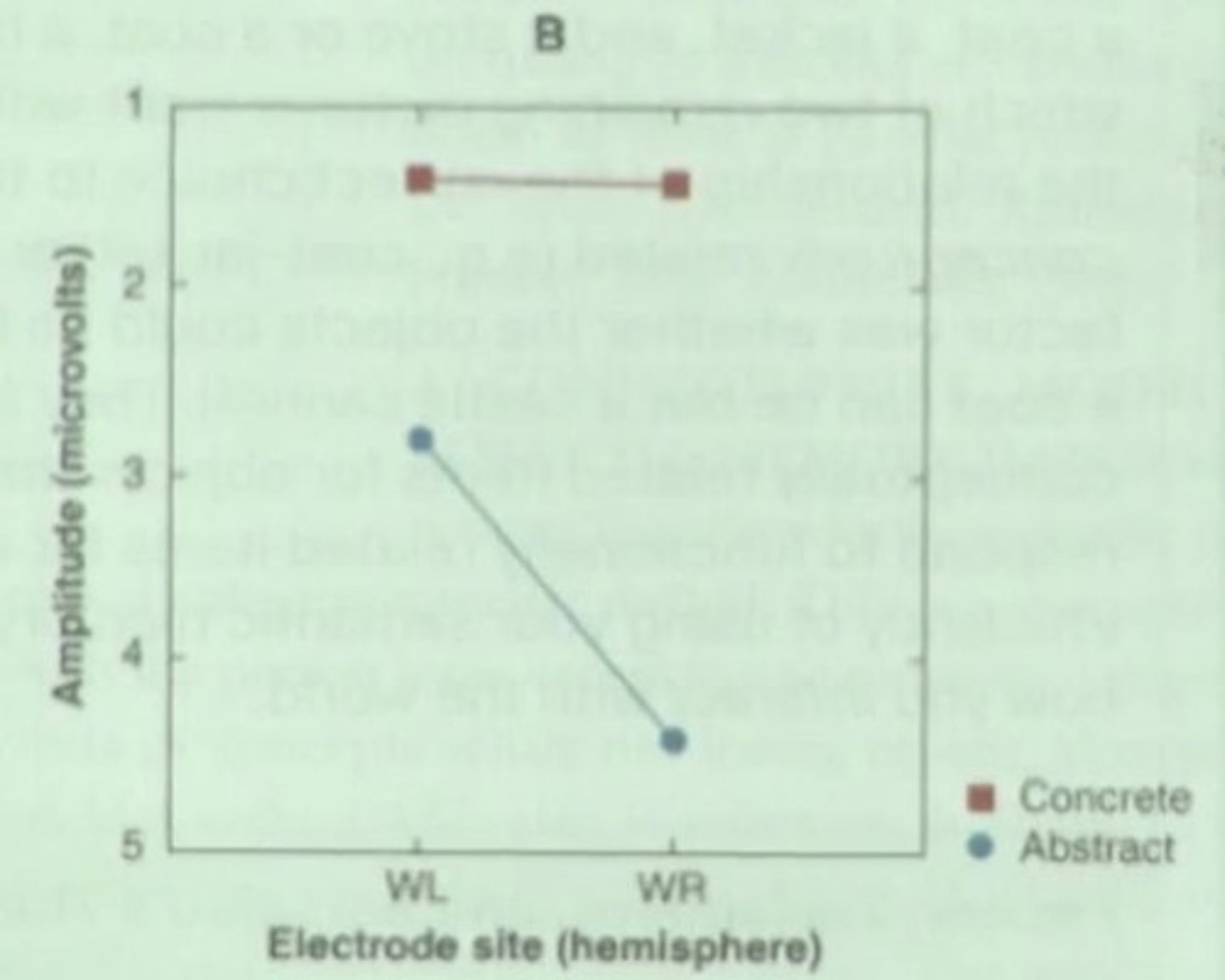
What is the role of individual differences in mental imagery?
They affect how vividly and controllably individuals can form mental images.
What is the relationship between verbal and nonverbal stimuli in cognitive processing?
They are processed using different codes and brain structures, with verbal stimuli favoring the left hemisphere and nonverbal stimuli favoring the right hemisphere.
What is the main process involved in visual processing?
Translation of written symbols into meaning.

What are the two types of eye movements during reading?
Fixations and saccades.
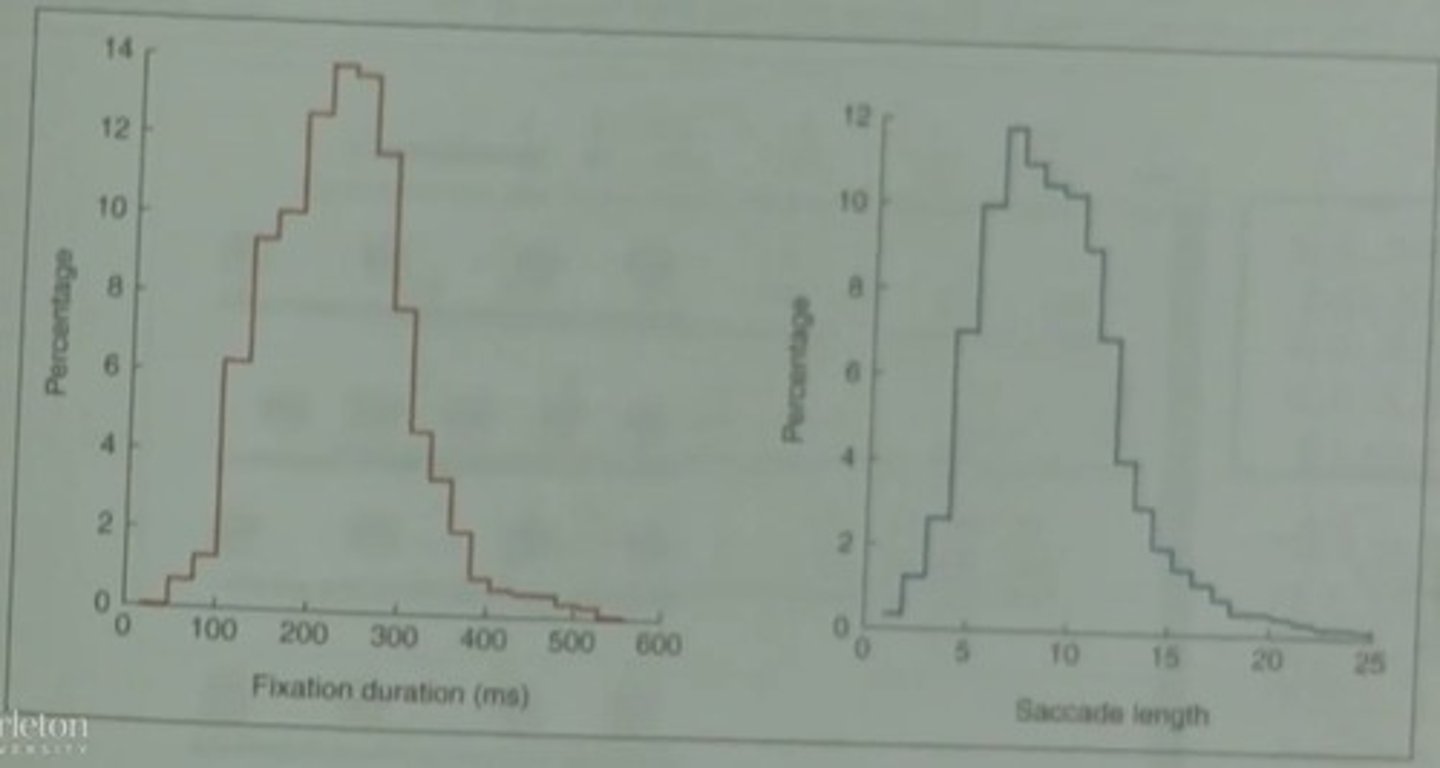
How long does a typical fixation last?
Approximately 200-250 milliseconds.
What percentage of content words are typically fixated on?
80% of content words.
What is the duration of a saccade?
Approximately 20-40 milliseconds.
What is the purpose of fixations in reading?
To process symbols in the foveated area for comprehension.
What happens during saccadic suppression?
No information is processed while the eyes are moving.
What does the immediacy assumption in reading suggest?
Readers attempt to interpret each content word fully as it is fixated.
What does the eye-mind assumption state?
The eye remains fixated on a word as long as it is being processed.
What was the finding of the gaze-contingent paradigm study by Rayner (1998)?
Reading rate drops significantly when foveated letters are covered.
What is the typical behavior regarding skipping words during reading?
Words skipped are usually function words like 'the' and 'and'.
What is the impact of changing a word during a saccade?
Readers typically do not notice the change.
How do fixation patterns differ between high and low skill readers?
Lower skill readers show more fixations, backtracking, and longer fixations per word.
What is visual word recognition?
Encoding of words and activation of their corresponding representations.
What three tasks are commonly used to study word recognition?
Eye tracking, lexical decision, and naming.
What is a marker effect in word recognition?
Variables that have a strong reliable effect on word recognition, such as word frequency.
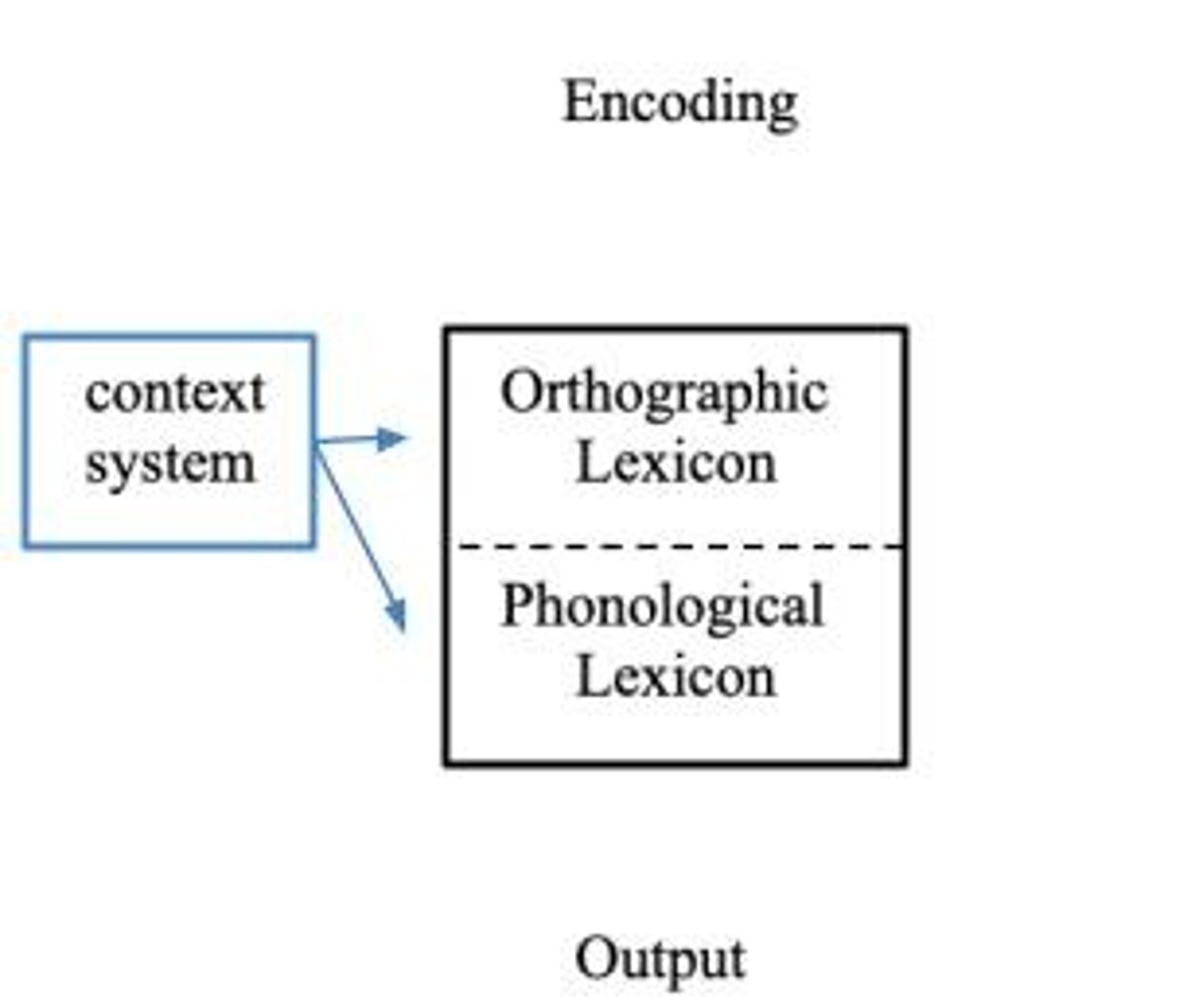
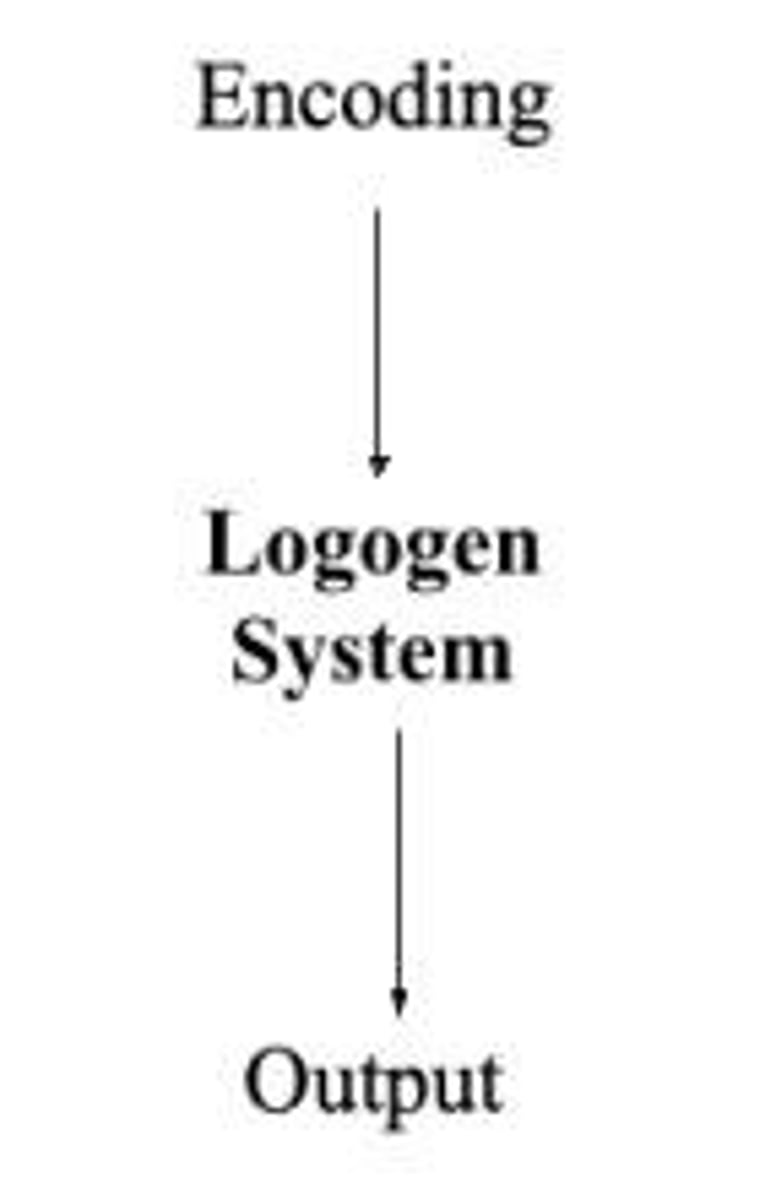
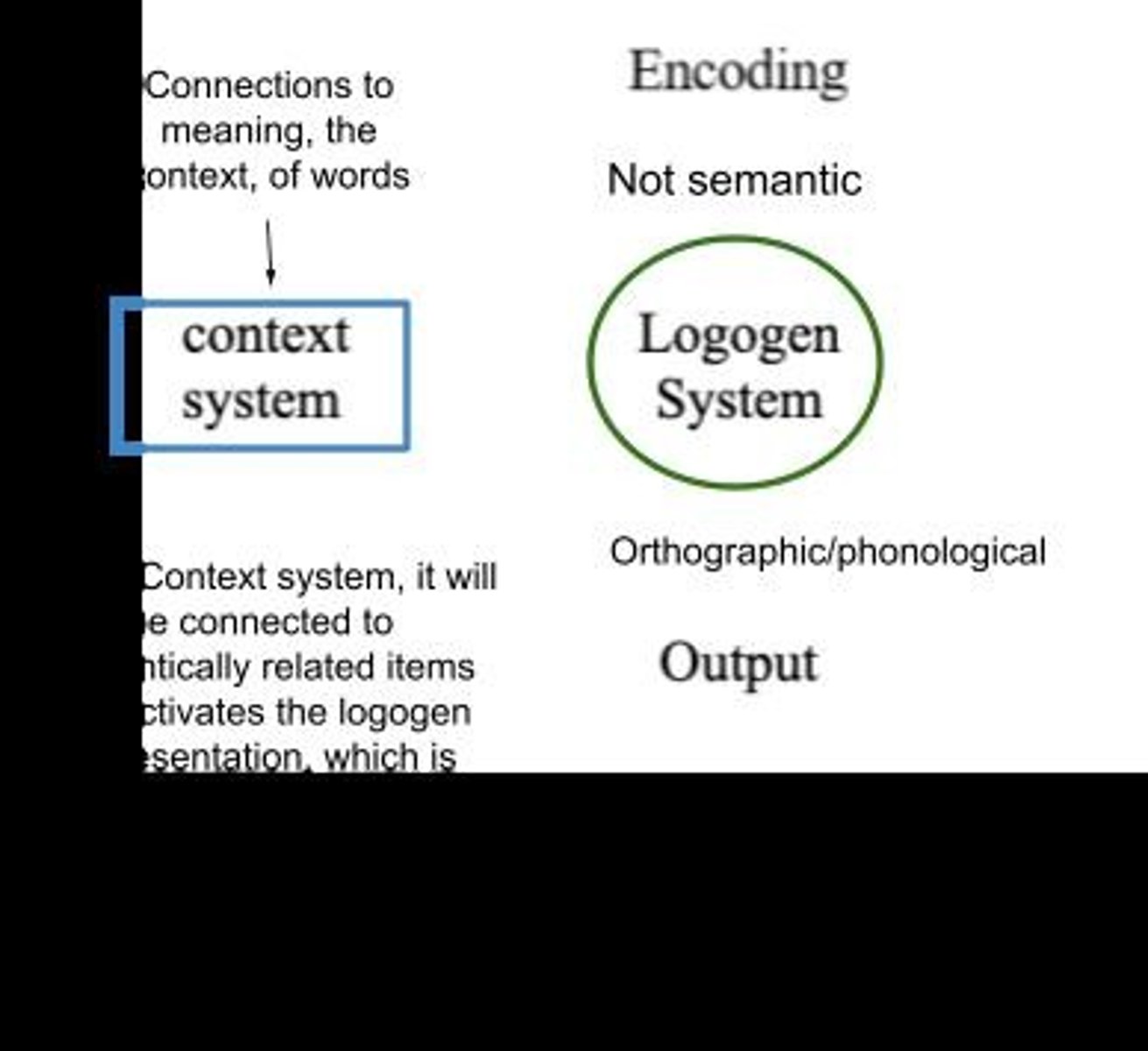
What is Morton's Logogen Model?
A model where each known word has a logogen that accumulates information for activation.
How does word frequency affect processing time?
Common words have a lower activation threshold and are processed more quickly.
What are context effects in word recognition?
Effects that occur due to the context in which a word is presented, influencing recognition.
What is the role of phonological coding during reading?
It helps keep information active in working memory and derive meaning from words.
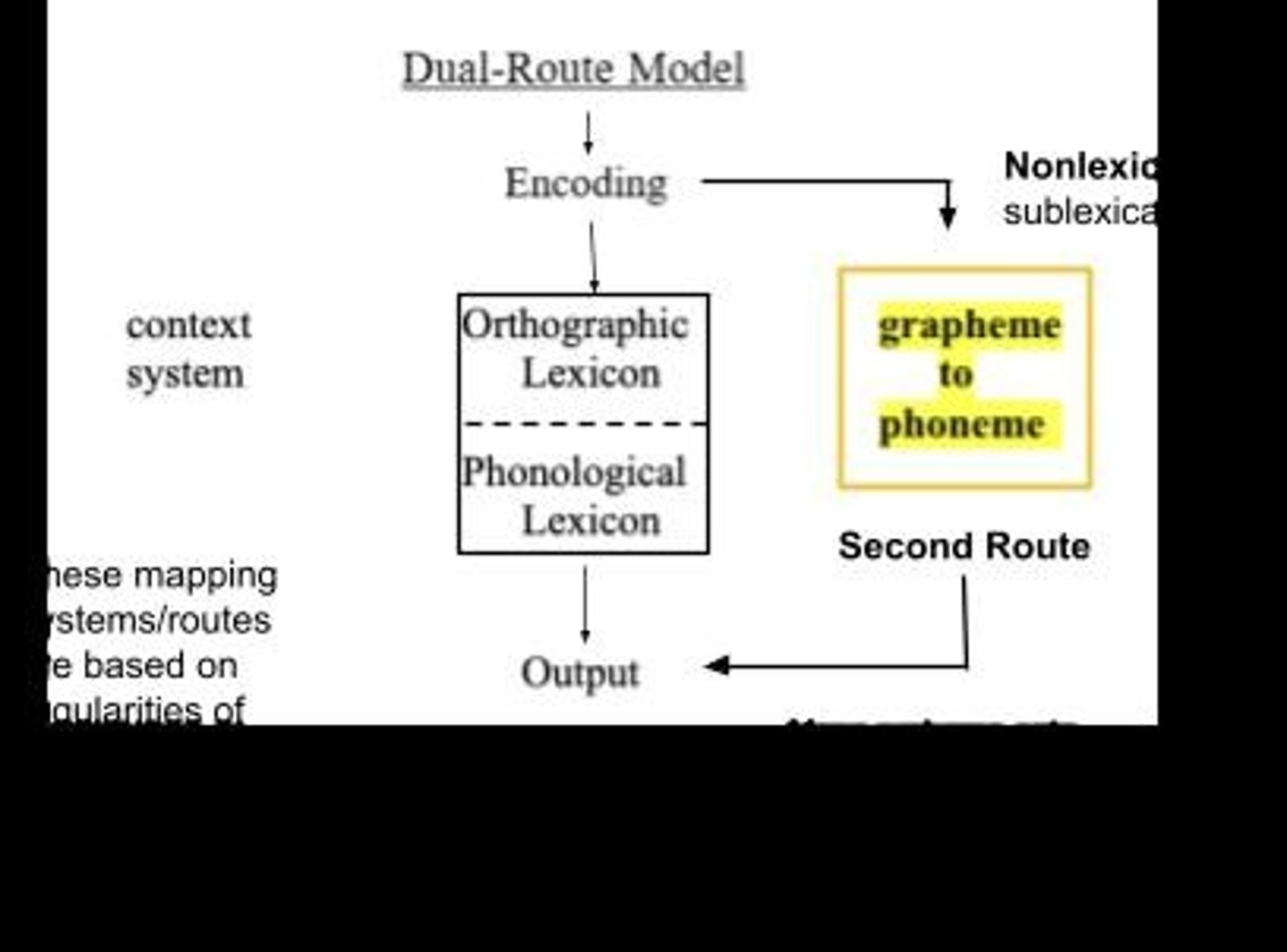
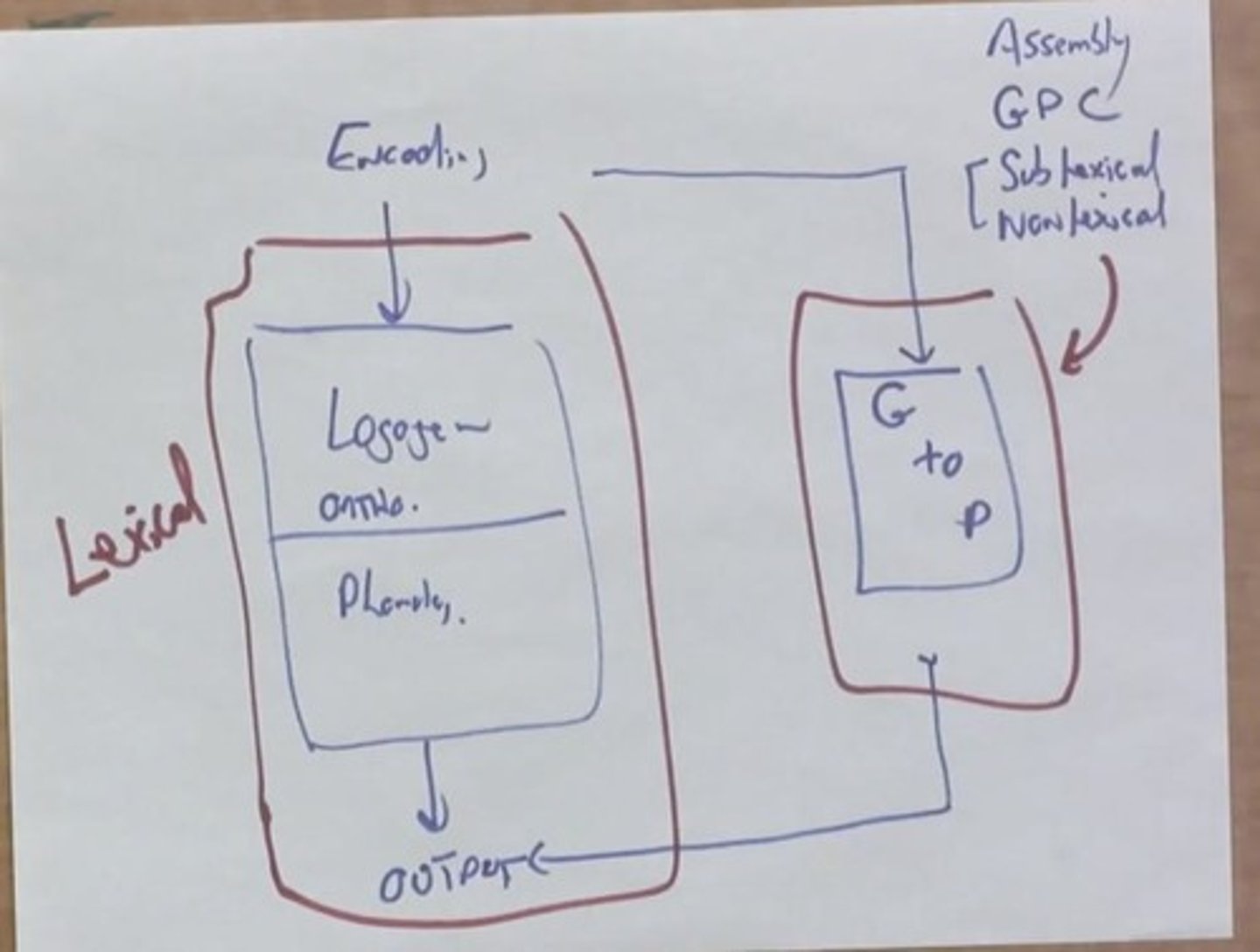
What is the dual route explanation in reading?
It describes two pathways: a lexical route sensitive to frequency and a nonlexical route for regular words.
What is the difference between high-frequency (HF) and low-frequency (LF) words?
HF words are processed more quickly than LF words due to their commonality.
What is the significance of word regularity in reading?
Regular words follow predictable spelling patterns, while irregular words do not.
What is the whole word vs. phonics debate in learning to read?
It concerns whether to teach reading through whole words or by phonetic decoding.
What is the effect of degraded stimulus quality on word recognition?
It results in longer reaction times in lexical decision and naming tasks.
How do repetition effects manifest in word recognition?
Recognition is faster for words that have been previously encountered.
What is change blindness?
Change blindness is when a change in a visual stimulus is not detected, even though you are looking for a change.
What is inattentional blindness?
Inattentional blindness is the failure to notice an object that is fully visible due to a lack of attention.
How can inattentional blindness be minimized?
By allocating attention appropriately, such as focusing fully on driving and avoiding distractions like texting.
What is the purpose of Head-Up Displays (HUDs) in aircraft?
HUDs maximize head-up displays, allowing pilots to keep their eyes outside while accessing critical flight information.
What is a potential downside of using HUDs?
HUDs may cause inattentional blindness, leading pilots to miss important external events.
What is the Lexical Decision Task?
A task where participants quickly determine if a string of letters forms a valid word.
What does the Logogen Model account for?
It accounts for word frequency effects in word recognition through a system of logogens that activate based on input.
What is the difference between regular and irregular words?
Regular words follow consistent grapheme to morpheme conversion, while irregular words do not have predictable correspondences.
What is cognitive tunneling?
Cognitive tunneling occurs when attention is focused on a HUD, potentially at the expense of noticing other important information.
What are fixations and saccades in visual processing?
Fixations are periods of focused attention on a stimulus, while saccades are quick eye movements between fixations.
What is the significance of high frequency and low frequency words in the Logogen Model?
High frequency words have lower activation thresholds and are recognized faster than low frequency words, which require more input.
What is the impact of degrading stimulus quality on word recognition?
Degrading stimulus quality leads to slower identification responses.
What is the role of the assembly route in word recognition?
The assembly route processes low frequency words by converting graphemes to phonemes, allowing for word output.
What is the flicker paradigm used for in studying change blindness?
It introduces transients to help identify changes in visual stimuli during eye movements.
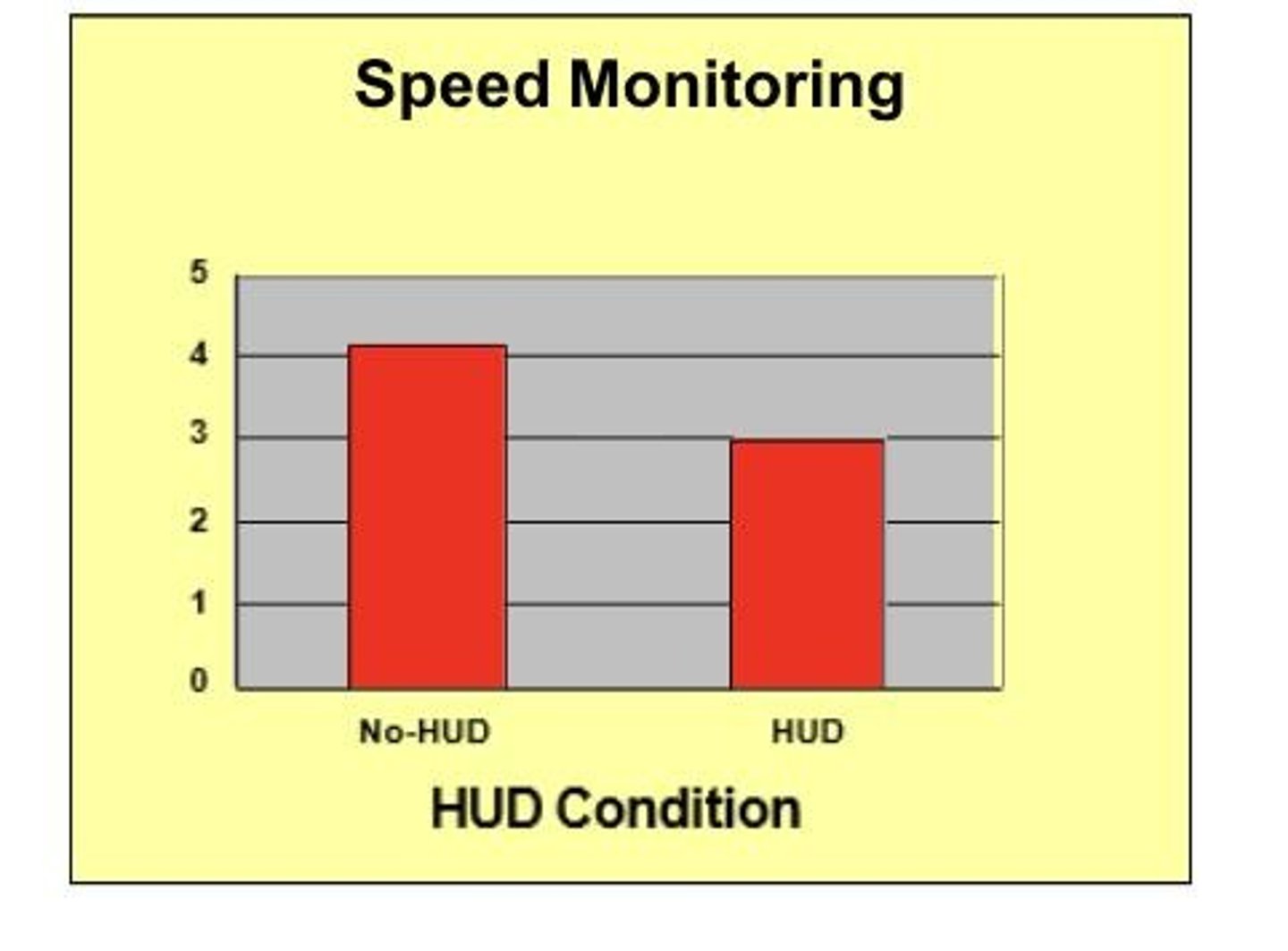
How do HUDs affect driver behavior in automobiles?
HUDs improve speed monitoring but may lead to larger lane deviations due to decreased attention to the external scene.
What is the relationship between object-based attention and cognitive tunneling?
Cognitive tunneling occurs when attention is focused on a perceptual object, such as a HUD, which can hinder awareness of other stimuli.
What are the two main tasks involved in cognitive psychology?
Information processing and memory, including knowledge representation, abilities, and limitations.
What is the significance of the activation threshold in the Logogen Model?
Each logogen has an activation threshold that determines how much input is needed for it to activate and recognize a word.
What is the main focus of the final exam in this course?
The exam focuses on lectures 9, 10, 11, & 12, with no aids allowed.
What should students bring to the final exam?
A pencil for the scantron and their Carleton ID card.
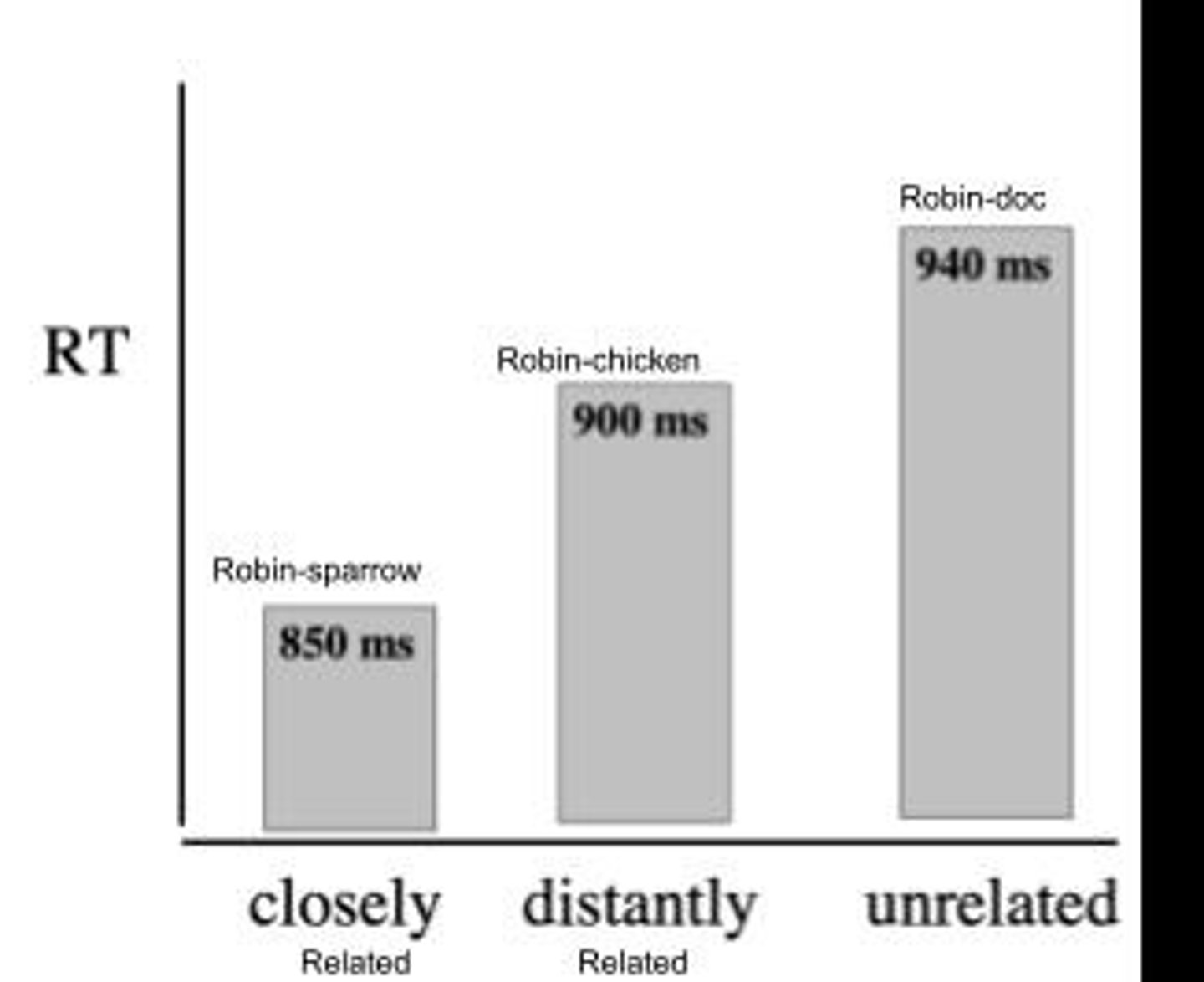
What is the purpose of semantic priming in naming tasks?
To determine how quickly participants can name semantically related or unrelated items.
What is the effect of stimulus quality on the logogen system?
If stimulus quality interacts with frequency effects, it may affect the logogen system's performance.