ACS Analytical Chemistry
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
standard deviation (s)
the square root of the variance
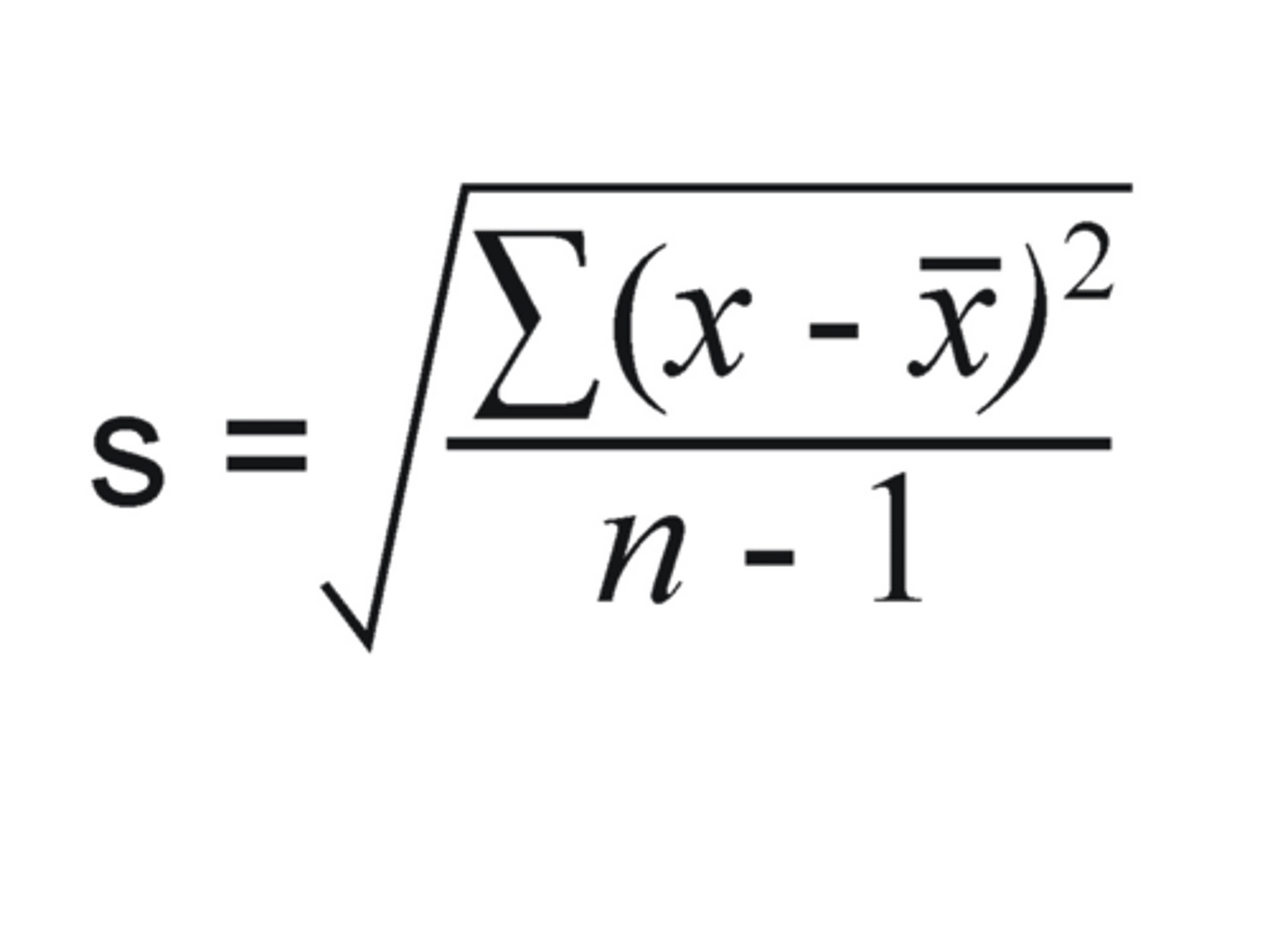
% relative standard deviation (%RSD)
Standard deviation divided by mean times 100
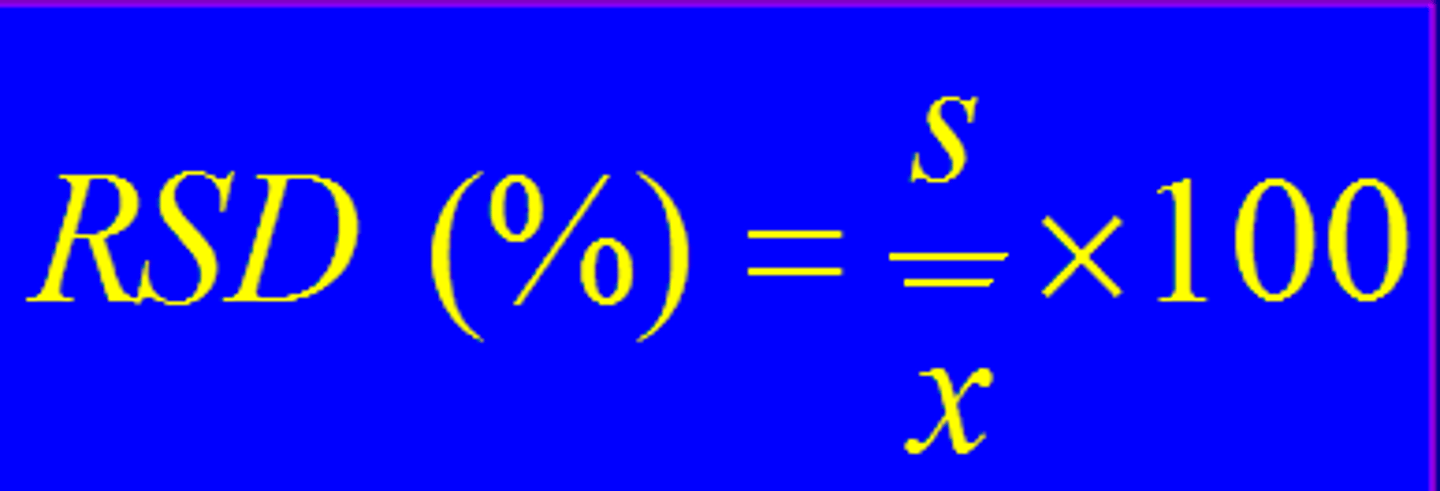
Grubbs test (Gcalc)
|Questionable value - mean/ std dev|
If that is larger than the Gtable value then the value is thrown out. Locate Gtable value based on number of values in data set.
Used to define outliers
z score
(x- xavg)/s
F Test
used to compare precision
(s2)^2/(s1)^2 (should always be >1)
Use n-1 to find on table.
Fcalc> Ftable -- There is some noise or error
External standard
use standard solutions spanning a range of conc, measure response
Internal standard
substance similar to analyte (ie deuterated); used to normalize signal by reducing random error
Standard Addition
ideal for analyzing sample in a complex matrix; add known standard to constant amount of sample; x-int =[sample]
Box car average
minimizes distance between data points and best fit line/ minimizes standard deviation
Limit of detection (LOD)
3*std dev
Limit of quantitation (LOQ)
10* std dev
sigma--> sigma* absorbs at
~100nm
proteins absorb at
~ 280 nm (bc of aromatic R groups)
d-->d absorb
visible light
(transition metals)
IR spectroscopy
responds to change in dipole moment
Raman
responds to change in polarizability
photomultiplier tube
detects single photon, is highly sensitive
Jablonski Diagram
shows movement from ground state to excited state
Fluorescence
occurs when LUMO--> HOMO releases energy;
generally occurs in rigid molecules
X ray fluorescence
Useful when sample cannot be put into sol'n
capacity factor (k')
tells efficiency of a separation
k'= time in SP /time for MP to elute= mol SP/mol MP
Van Deemter Equation
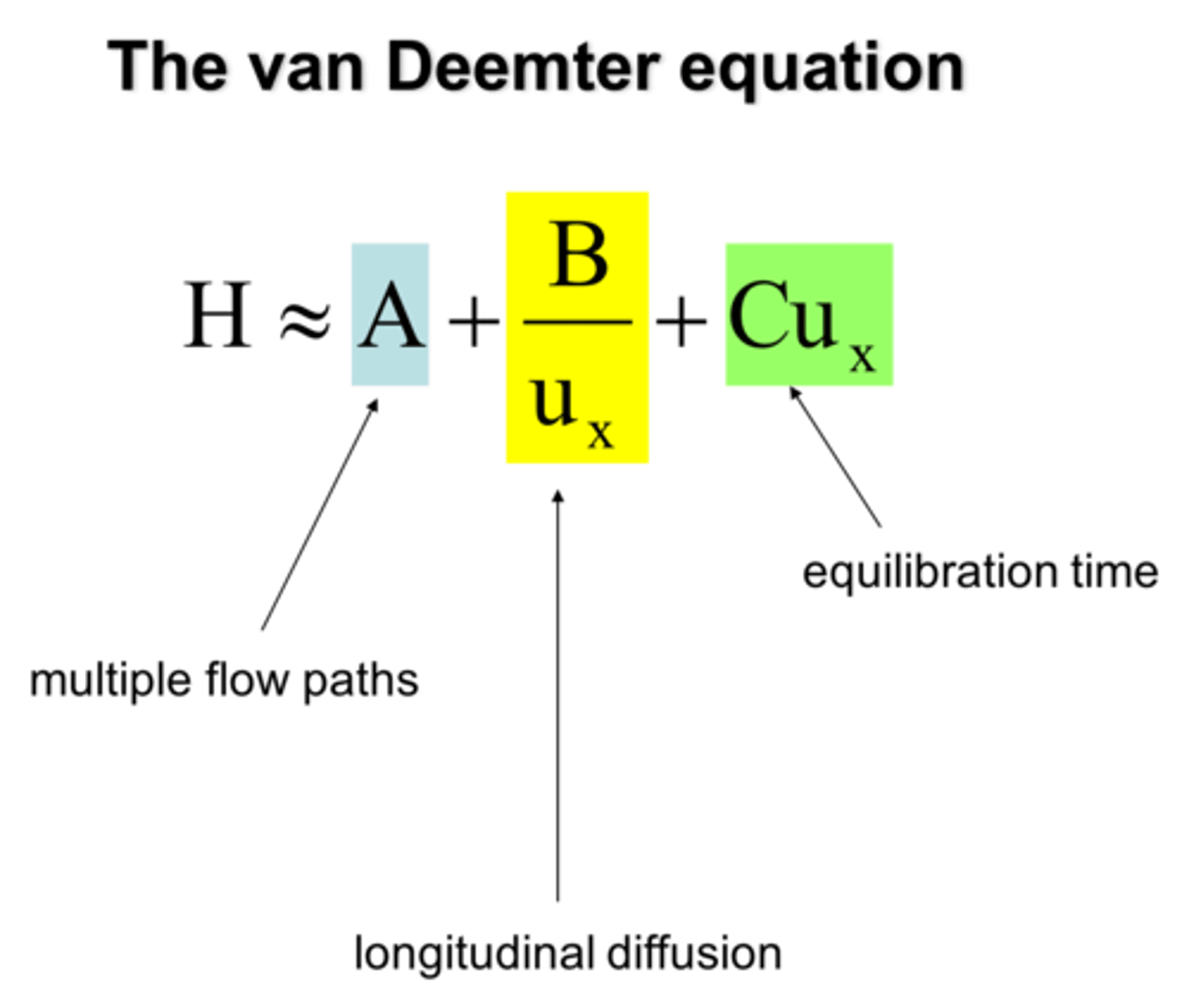
A (in van deemter Eq)
accounts for path
A=2(lambda)dp
decrease particle diameter, increase speed of separation
B (in van deemter Eq)
accounts for diffusion
B= 2(gamma) Dm
affected by temp, [ ], solubility, density, viscosity,
gamma-- channel uniformity
C (in van deemter Eq)
accounts for equilibration
Cs = f'(k') * (df^2/Ds)
Cm = f(k') * (r^2/Dm)
Gas chromatography
A term is eliminated
Liquid chromatography
no terms eliminated
capillary electrophoresis
A and C terms eliminate; VERY efficient
electrophoretic mobility
allows separation based on charge
electroosmotic flow
'drag' of analyte because of friction
apparent mobility
= electrophoretic mobility + electroosmotic flow
thermal conductivity detector
non destructive, but not sensitive
electron capture detector
e- emitted from Ni, analyter accepts e-, decreased current
works well for halogens, organometallics, and nitriles
very sensitive
Flame ionization detector
best for organic cmpds
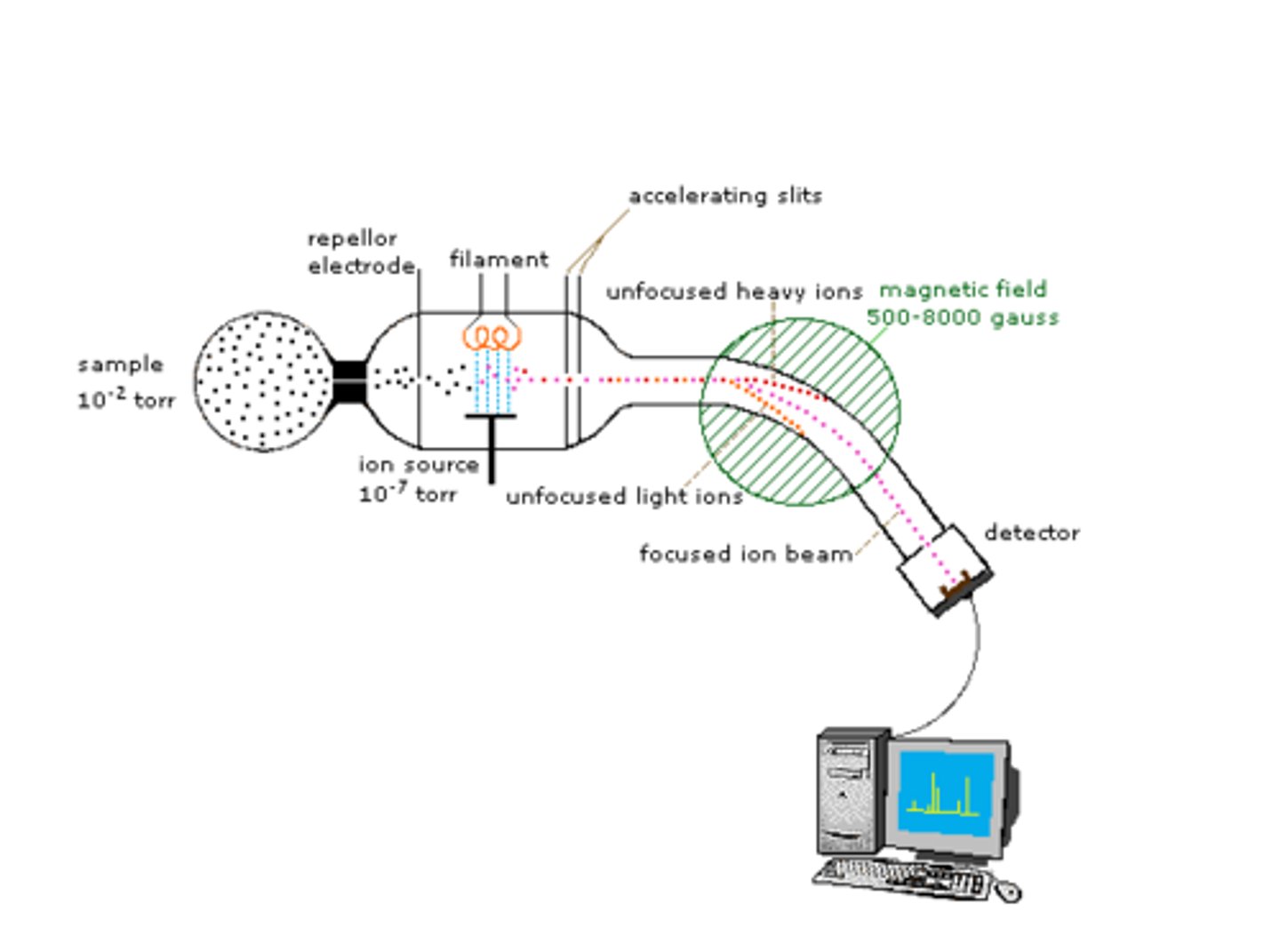
Mass Spec instrument set up
reduction potential > 0
desire for e-
reduction potential < 0
desire to lose e-
Nerst Equation
Delta G= -nFEcell
nonspontaneous electrochemical reaction
Ecell < 0
spontaneous electrochemical reaction
Ecell > 0
Students t test
compares two means from two different samples
compare t to alpha
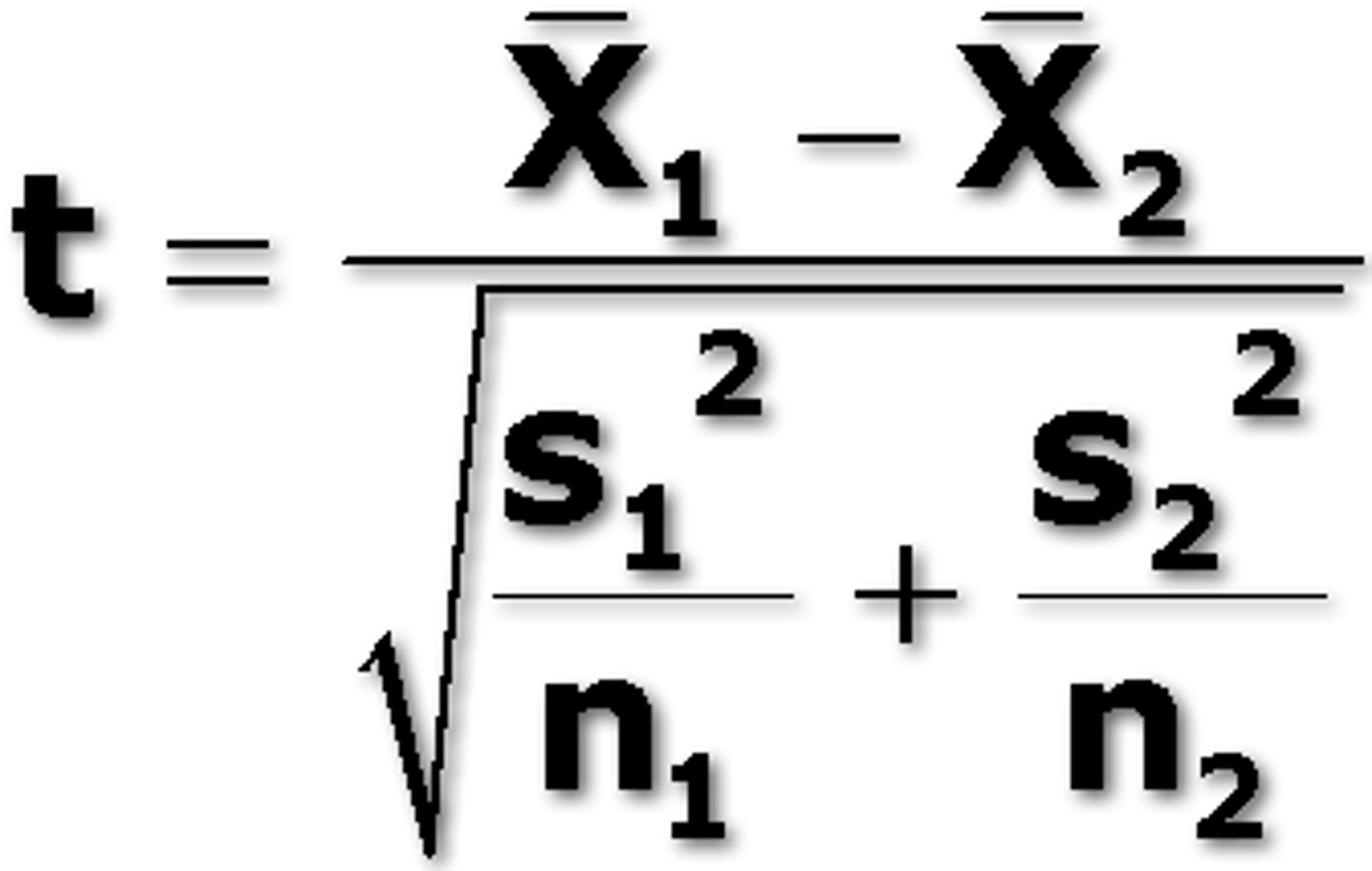
determinate error (systematic error)
Sampling, method, measurement or personal errors. Can be traced to a source. Affect accuracy.
indeterminate error (random error)
Affect precision. Can be traced to sample collection, manipulation and or measurement.
uncertainty
The range of possible values for a measurement. can be added or subtracted via squaring each standard deviation, performing the necessary operations (+,-) and taking the square root.
relative uncertainty
Uncertainty of a quantity divided by the value of the quantity. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the measured quantity.
multiplying or dividing uncertainty
use relative uncertainty. Square, add, then square root. Absolute uncertainty can be obtained by multiplying by R.
Binomial Distribution
The probability distribution of X with parameters n and p. Homogenous mixtures.
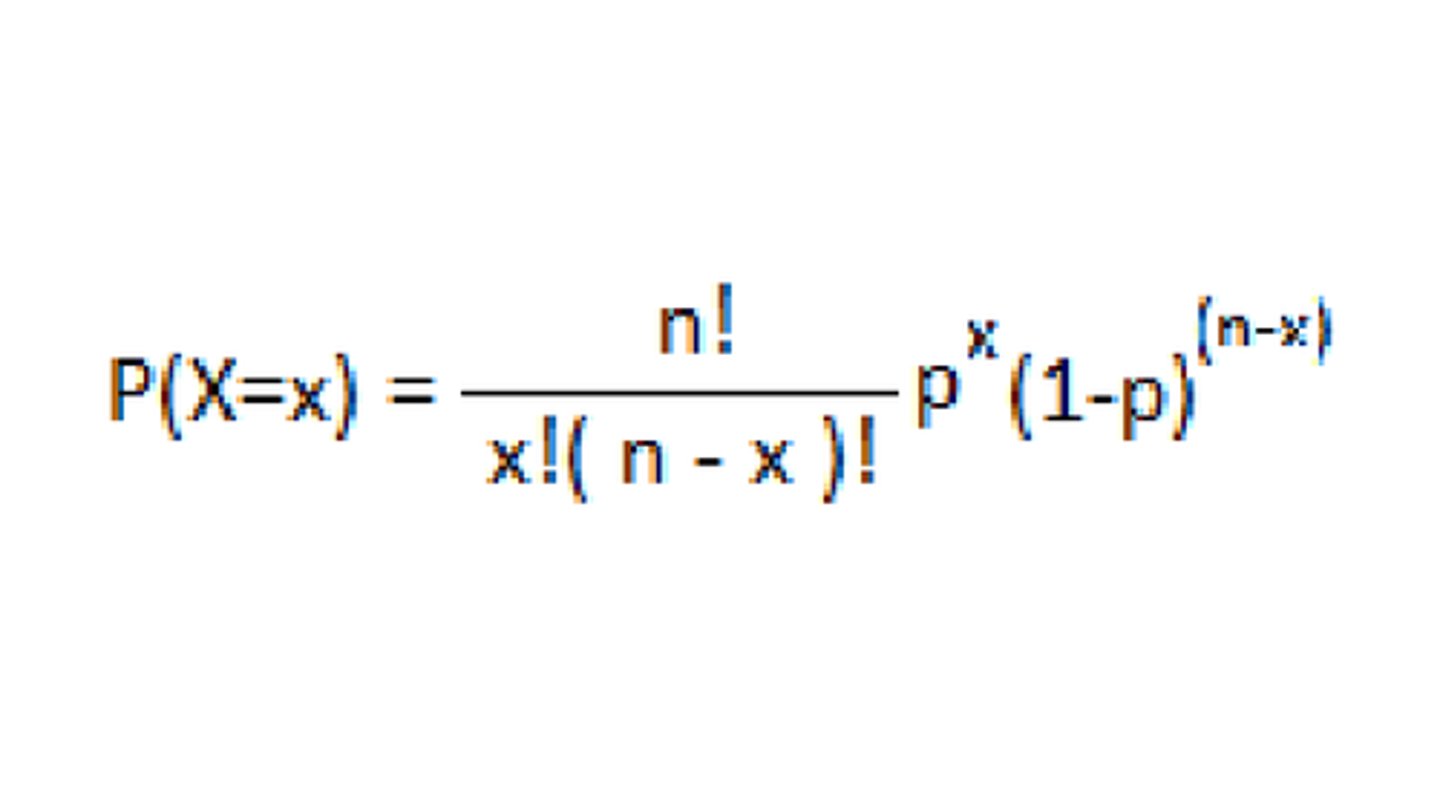
confidence interval
a range of values so defined that there is a specified probability that the value of a parameter lies within it. Xi = µ ± zσ : Where z is from a table.
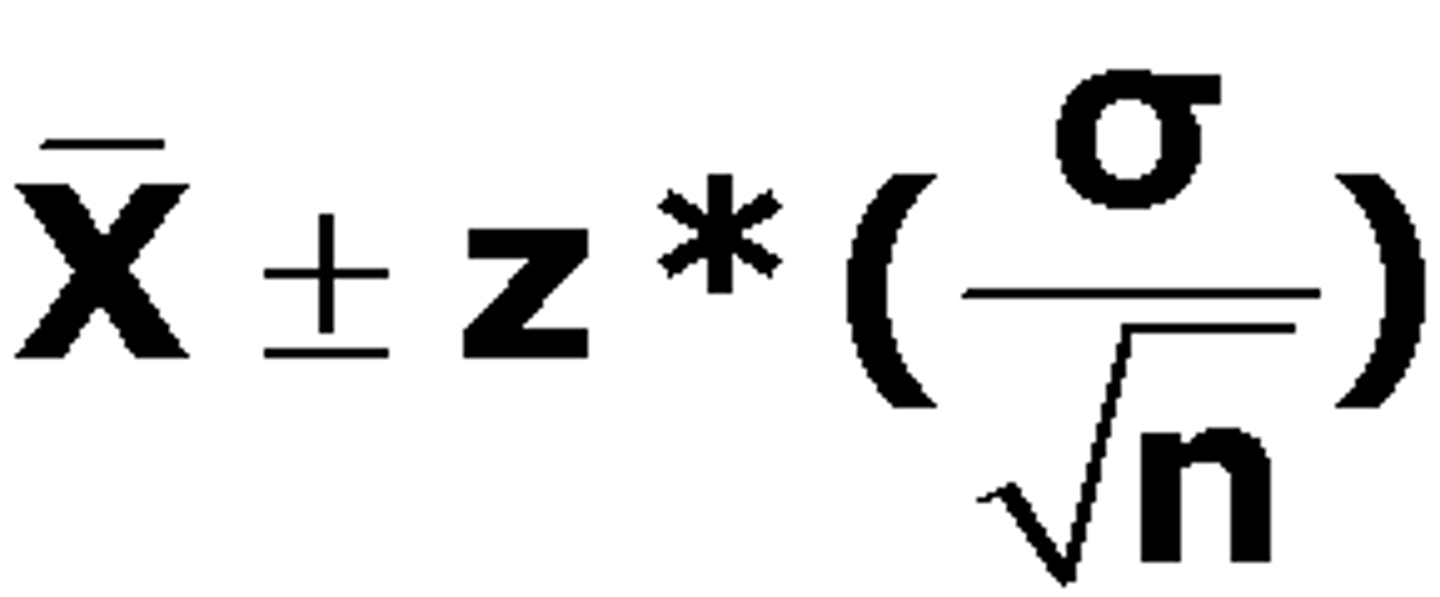
degrees of freedom
The number of individual scores that can vary without changing the sample mean. Statistically written as 'N-1' where N represents the number of subjects.
Normal Phase HPLC
polar stationary phase, non-polar mobile phase. Therefore non-polar will come out first, polar last.
Reverse phase HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography)
Non-polar stationary phase, polar mobile phase. This polar comes out first.
Gradient elution
Faster separation
standard solution
a solution whose concentration is accurately known
matrix effect
is a change in the analytical signal caused by anything in the sample other than analyte
For Gaussian distribution of points...
2/3 of points lie in +/- 1 std deviation
Q test
A rough test to justify ejecting an outlying data point from a set