Lecture 2 - Trypanosomes (Haemoflagellates)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the order, family, and genus of trypanosomes?
-Order: Kinetoplastida
-Family: trypanosomatidae
-Genus: Trypanosoma/Leishmania
What do trypanosomes contain cellularly that allow for diagnosis? What is its function?
Kinetoplast - rudimentary mitochondria
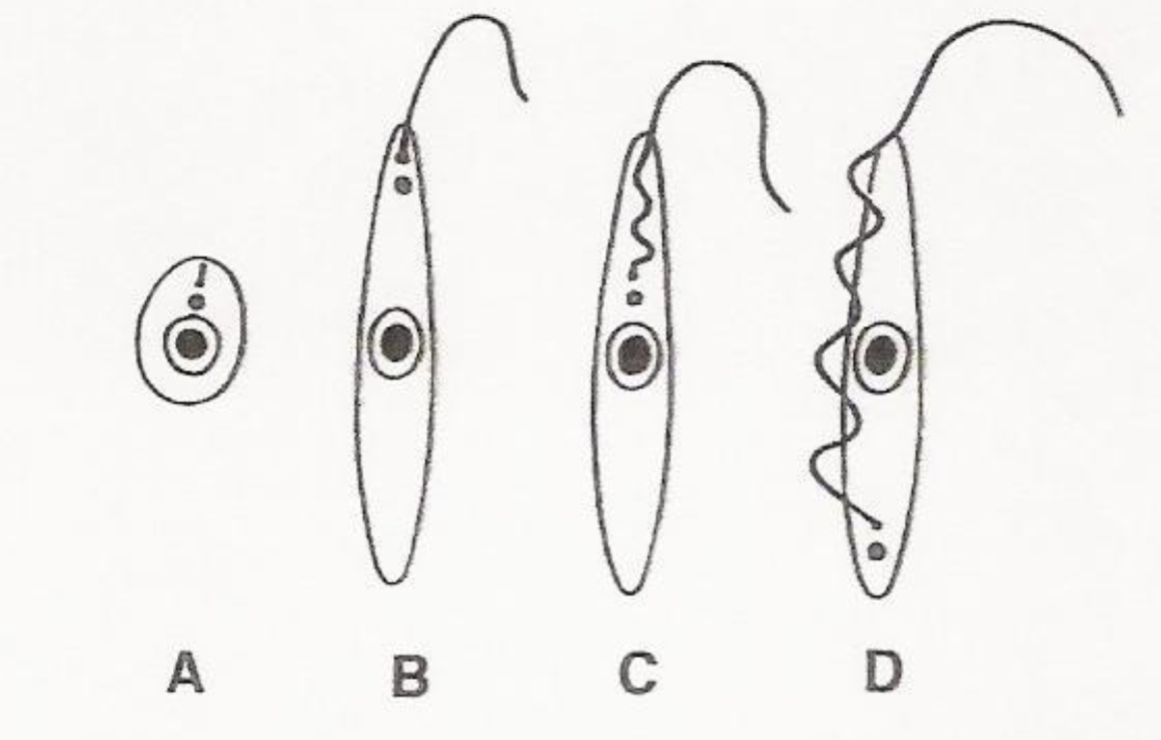
What is a? Where is it found? What species is it found in?
-Amastigote stage
-Intracellular form
-Found in Leishmania and T. cruzi
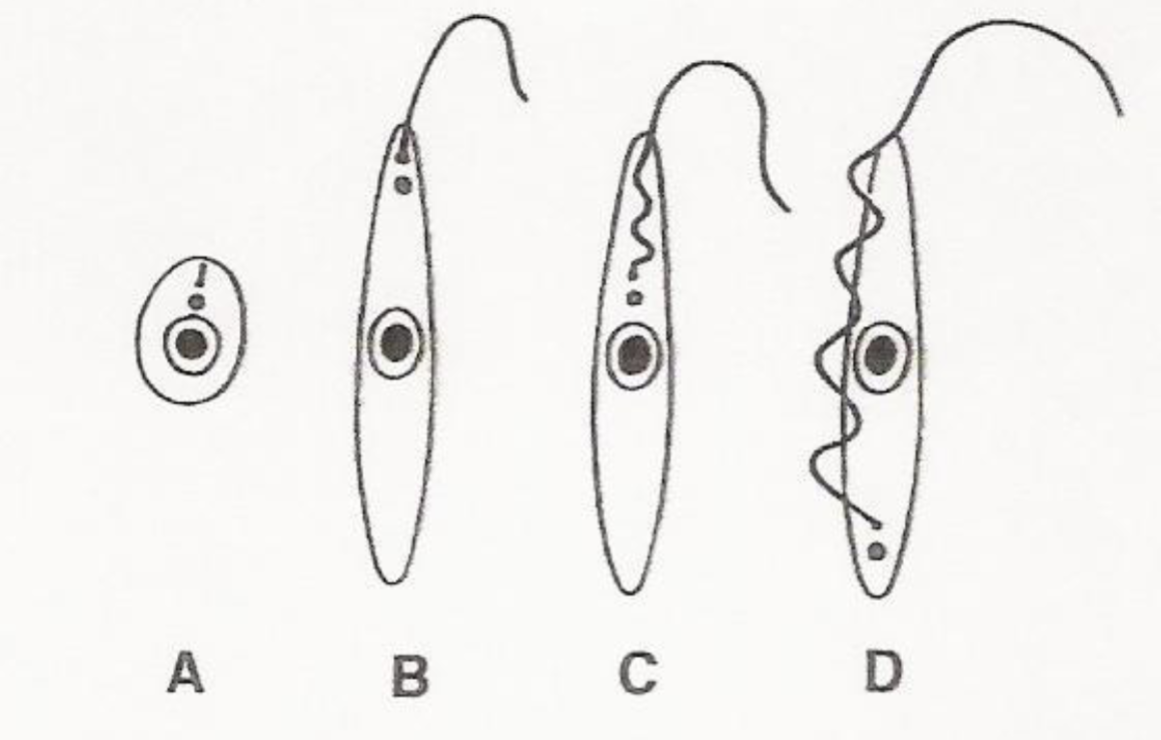
What is b? Where is it found? What species is it found in?
-Promastigote stage
-Extracellular form found in insects
-Leishmania
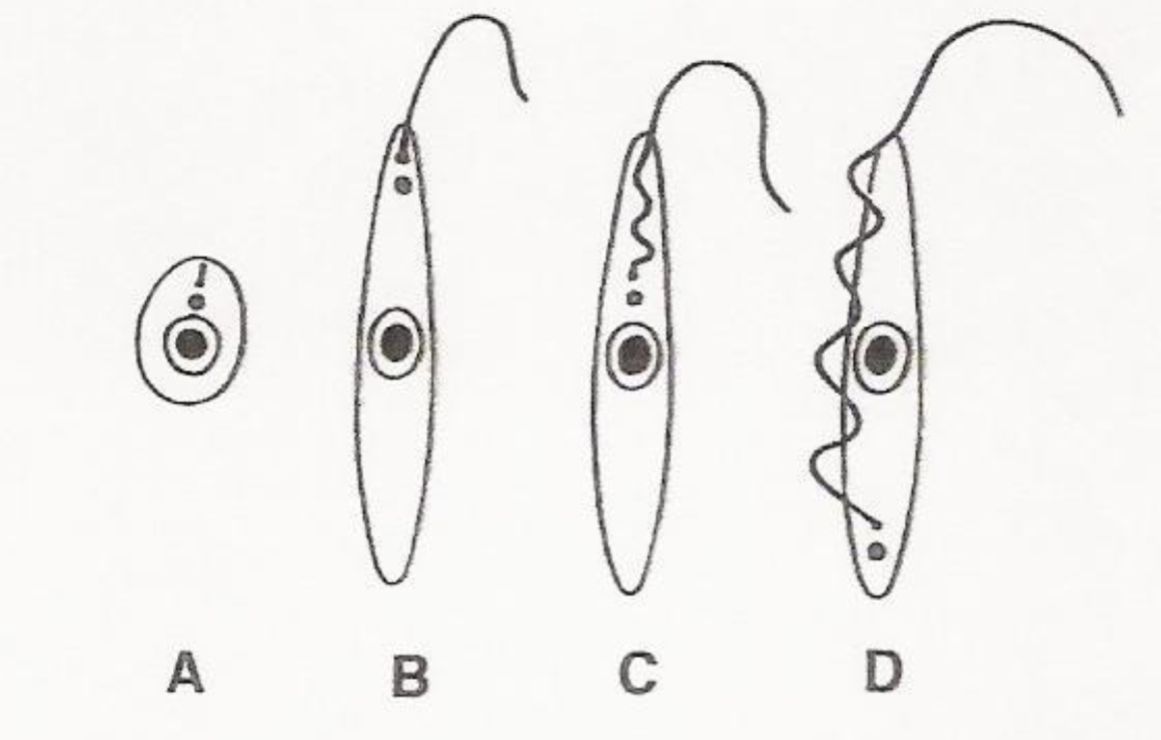
What is c? Where is it found? What species is it found in?
-Epimastigote
-Extracellular form found in insects
-Trypanosomes (except leishmania)
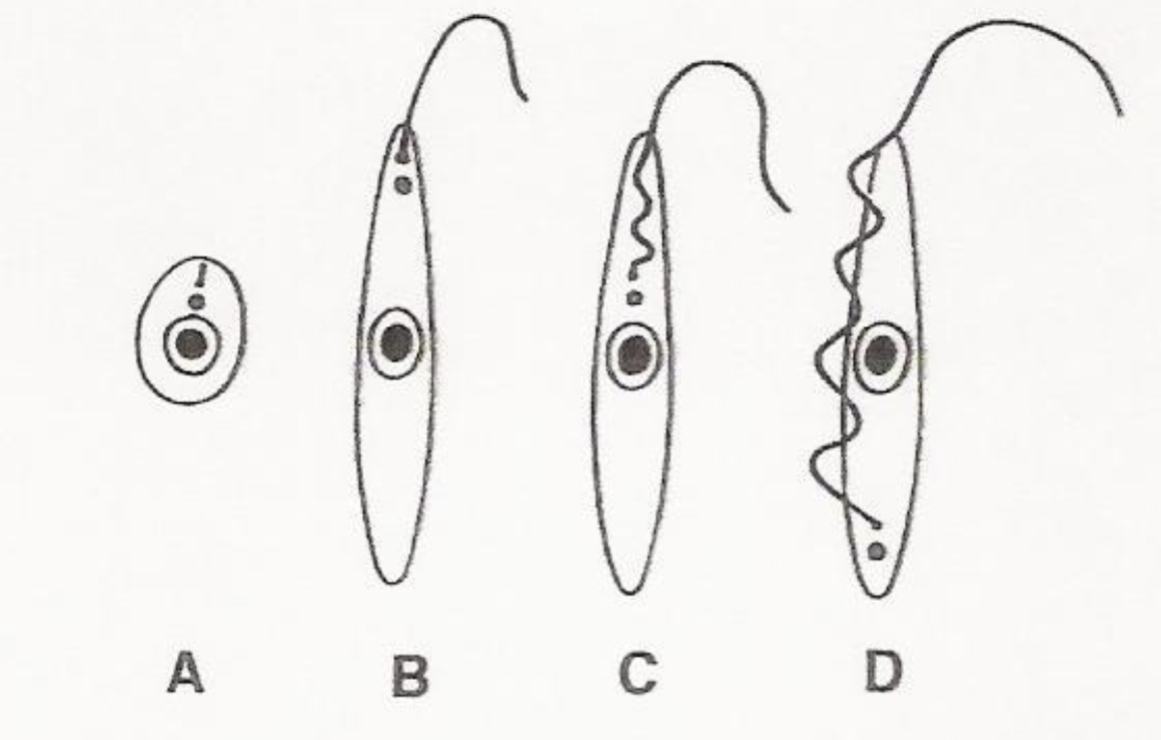
What is d? Where is it found? What species is it found in?
-Trypomastigote
-Extracellular in blood stream
-Both Leishmania and Trypanosomes
What are the three African Trypanosomes of veterinary importance?
Trypanosoma brucei brucei
Trypanosoma congolense
Trypanosoma vivax
How is Trypanosoma brucei brucei transmitted? Who does it affect? What is the reservoir?
-Transmitted by tsetse flies
-Affects livestock and humans
-Wildlife (buffalo) reservoirs
How is Trypanosoma congolense transmitted? Who does it affect? What is the reservoir?
-Transmitted by tsetse flies
-Affect livestock (particularly cattle)
-Wildlife (buffalo) reservoirs
How is Trypanosoma vivax transmitted?
-Transmitted by tsetse flies and hematophagus dipterans
For the African trypanosomes, what are the clinical signs?
-Anemia
-Intermittent fever
-Edema
-Chronic wasting
-Swollen lymph nodes
-Death
How are the african trypanosomes diagnosed?
-Giesma stain of blood smear
-Lymph node biopsy
-ELISA test
-PCR
What is the treatment and control for the African Trypanosomes?
-Treatment: diminazene aceturate, melarsomine dichlorhydrate, suramin, isometamidium chloride
-Control: insecticide treated traps
What animals does Trypanosoma evansi affect?
horses (most importantly), mules, buffalo, deer, camels, llama, cattle
What are the clinical signs of Trypanosoma evansi?
nervous signs, weight loss, progressive anemia, icterus
What are the species affected and transmission of Trypanosoma equiperdum?
-Species affected: horses, donkeys, mules, zebras
-Transmission: sexually
What are the clinical signs of Trypanosoma equiperdum?
Genital edema, mucopurulent discharge, and neurological signs
What are the affected species of Trypanosoma cruzi? What transmits it?
-Humans and canines
-Transmitted by Triatoma (kissing bug) through feces
What are the clinical signs of the acute phase in Trypanosoma cruzi? Chronic phase?
-Acute phase: fever, localized/generalized lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy
-Chronic phase: right-side CHF, myocarditis, arrhythmias, bilateral cardiac dilation
What is the diagnosis and treatment of trypanosoma cruzi?
-Diagnosis: travel history, Giesma stain of blood smear or lymph node biopsy, serology, PCR, culture
-Treatment: Benznidazole (not available in the US)