by 124L - repro, excretory & endo systems
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
what do hormones mimic and how?
neurotransmitters; by binding to metabotropic receptors
do hormones produce short or long term responses?
both
what are hormones?
chemicals secreted by endocrine glands
what are the endocrine glands that produce hormones?
pineal gland
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
thyroid and parathryoids
adrenal glands
pancreas
ovaries
testes
where is the hypothalamus (1) located and what does it produce?
location: post pituitary
releases oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone
where is the pituitary gland (2) located and what does it produce?
location: hypothalamus (both posterior and anterior are connected to)
posterior: stores hormones
stores hormones:
ADH
oxytocin
anterior: makes and releases hormones, under guidance of hypothalamus
makes hormones:
ACTH
GH
MSH
TSH
FSH, LH (gonadotropins)
prolactin
where is the thyroid gland (3) located and what does it produce?
location: sternum
releases calcitonin, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
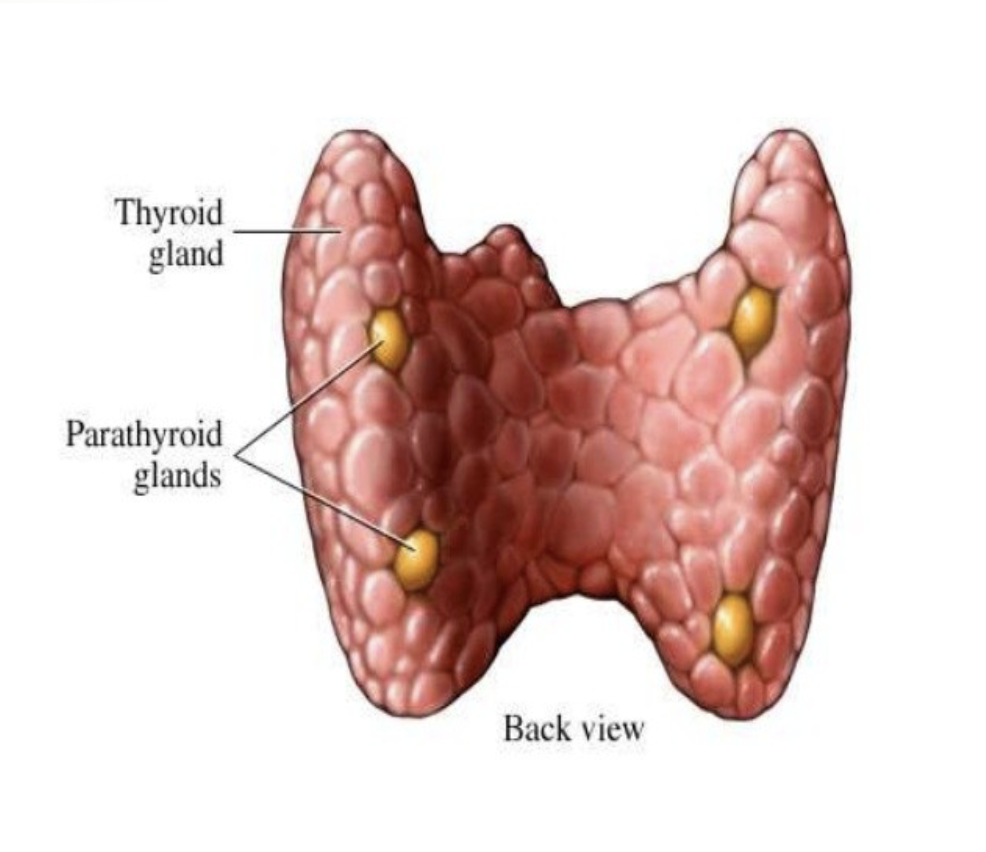
what is a deformity that occurs in the thyroid?
lack of iodine in diet causes goiter (visibly enlarged thyroid gland)
where is the parathyroid gland (4) located and what does it produce?
location: within thyroid
releases parathyroid hormone (pTH)
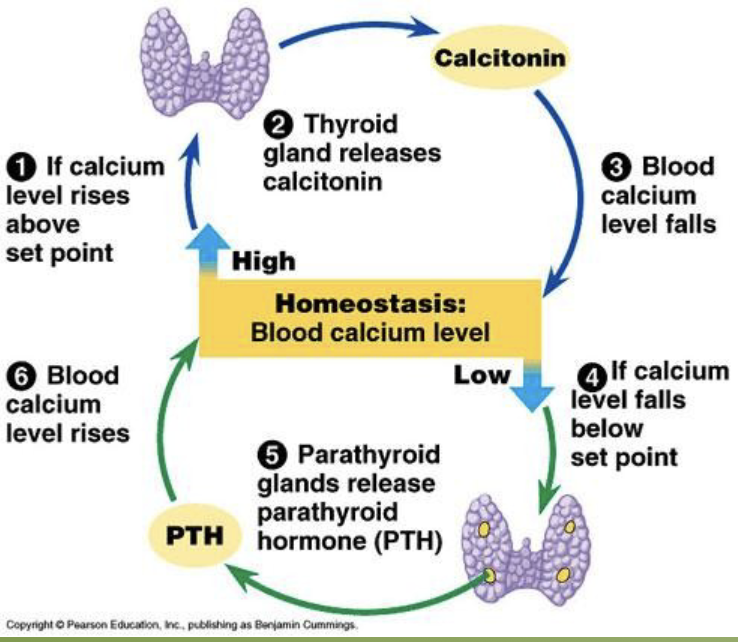
be able to explain the feedback loop for thyroid and parathyroid glands
what does the pancreas (5) produce and from where?
releases:
glucagon (from alpha cells)
insulin (from beta cells)
somatostatin (from delta cells)
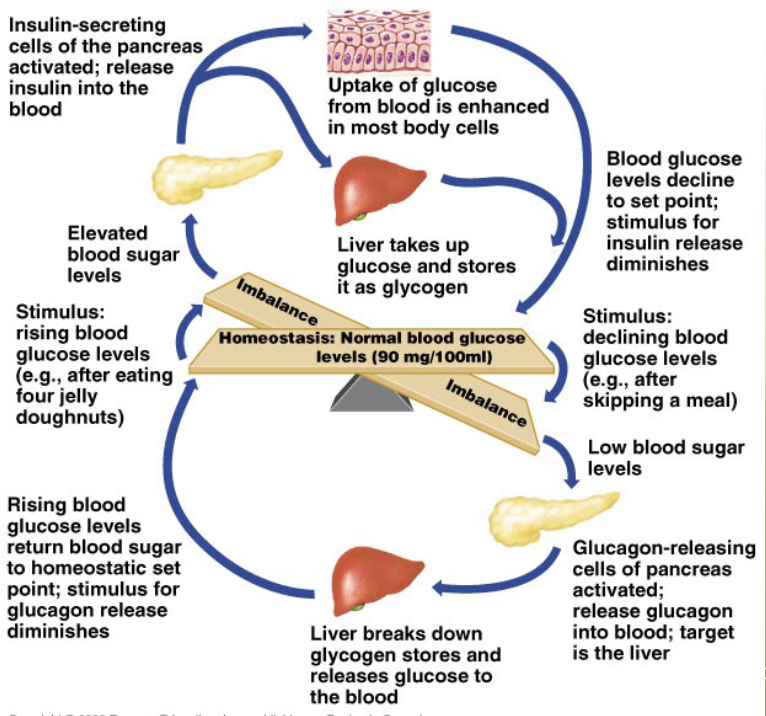
be able to describe the blood glucose feedback loop
where are the adrenal glands (6) located and what do they produce?
locations: cortex and medulla
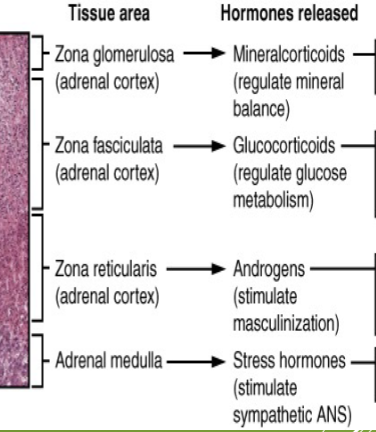
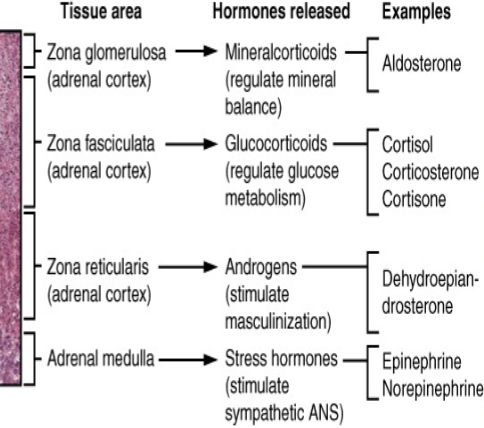
cortex releases: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens
medulla releases: epinephrine and norepinephrine
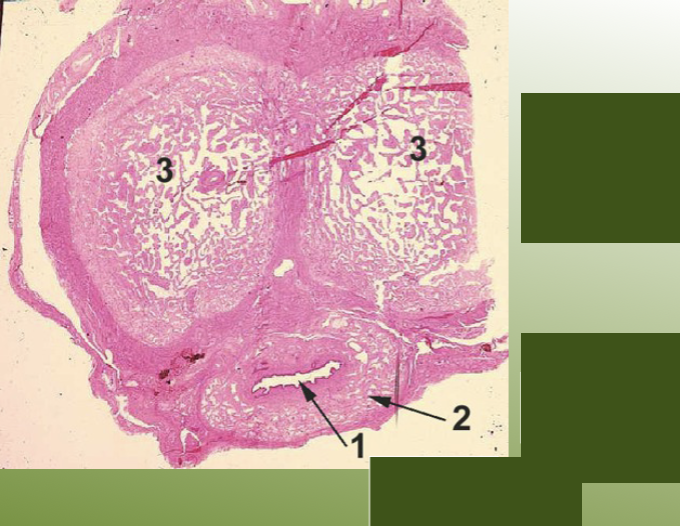
identify the different tissue areas present in a microscope picture of the adrenal gland.
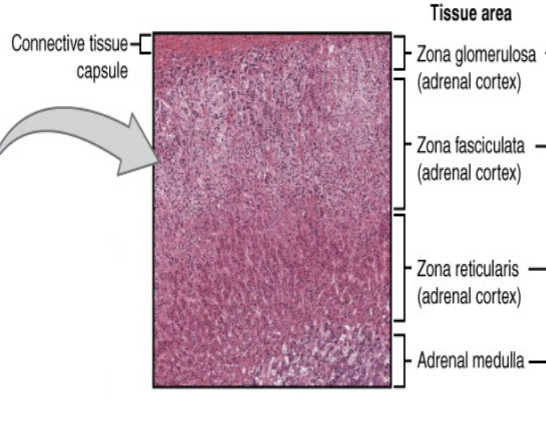
what hormones are released by each tissue area in a microscope picture of the adrenal gland?
give an example for each hormone that’s released by each tissue area in a microscope picture of the adrenal gland.
what do the testes (7) produce?
releases androgens as well as the adrenal cortex
what do the ovaries (8) produce?
releases estrogen and progesterone
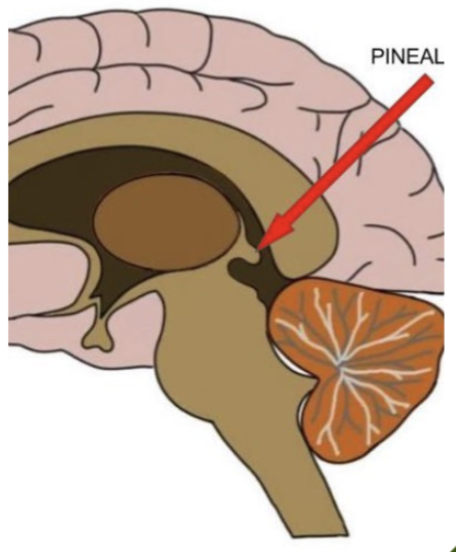
what does the pineal gland (9) produce? what is the function of this hormone?
releases melatonin
function: affects biological rhythms (light/dark cycles) & causes sleepiness
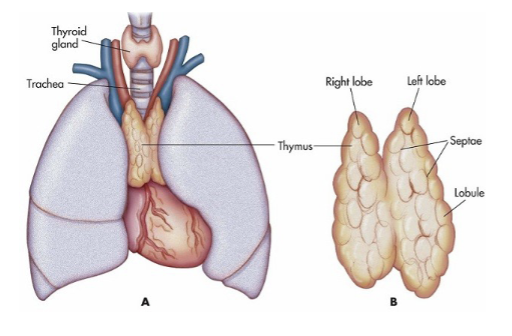
what does the thymus (10) produce? what is the function of this hormone?
releases thymosin
function: stimulates T lymphocyte development (found in immune system)
where is the thymus (10) located?
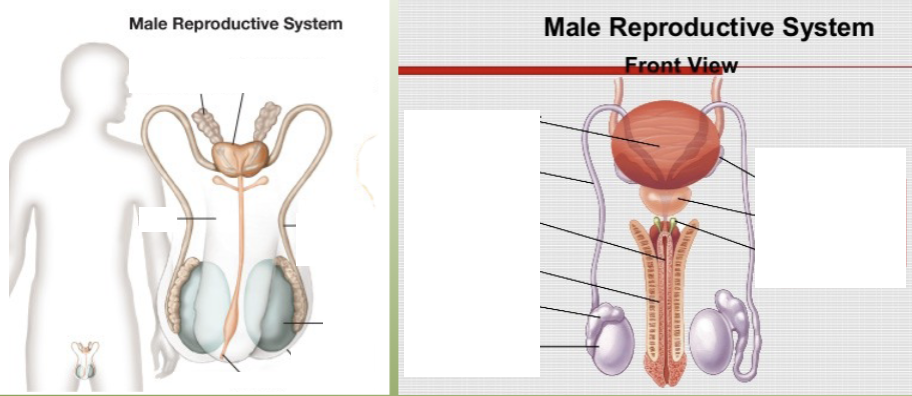
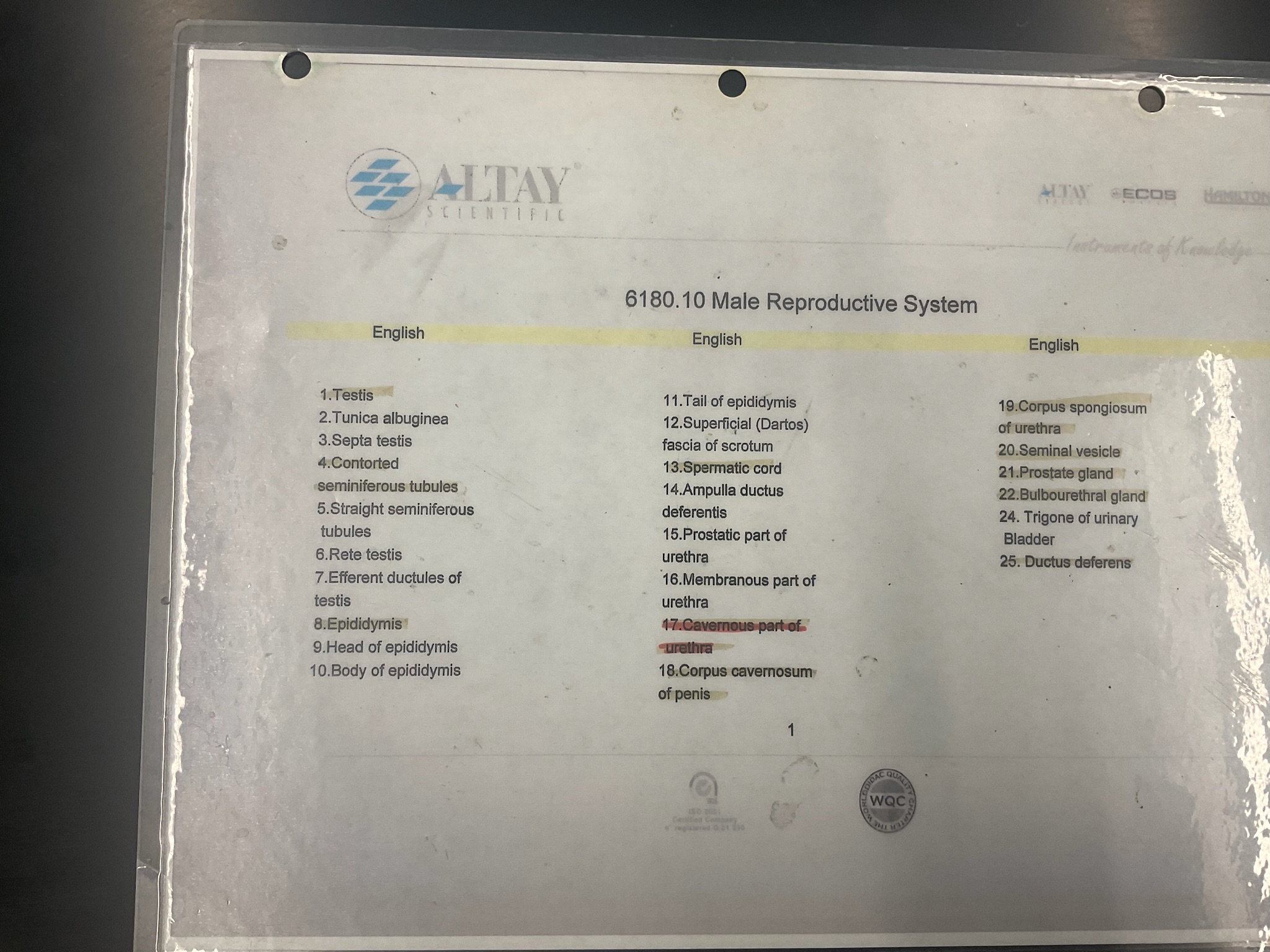
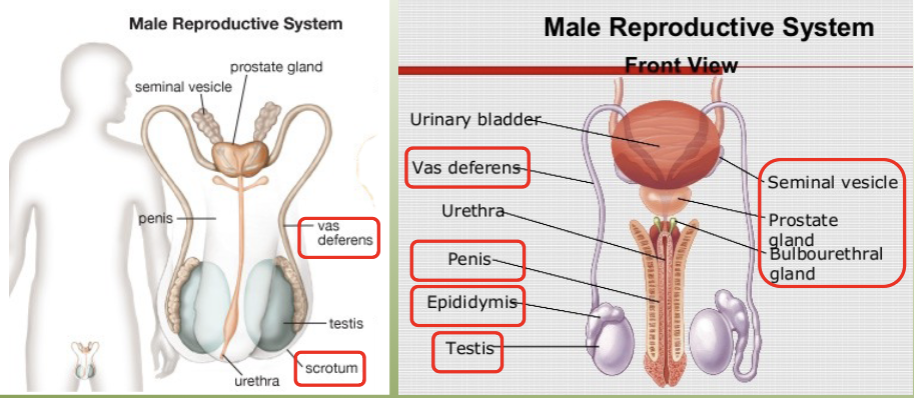
label the key structures of the male reproductive system.
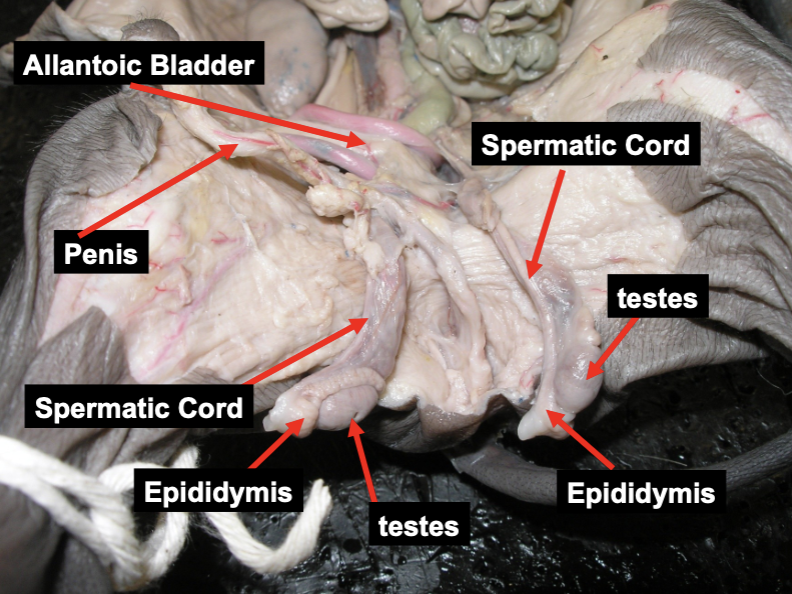
label the key structures of the male reproductive system on a male pig.
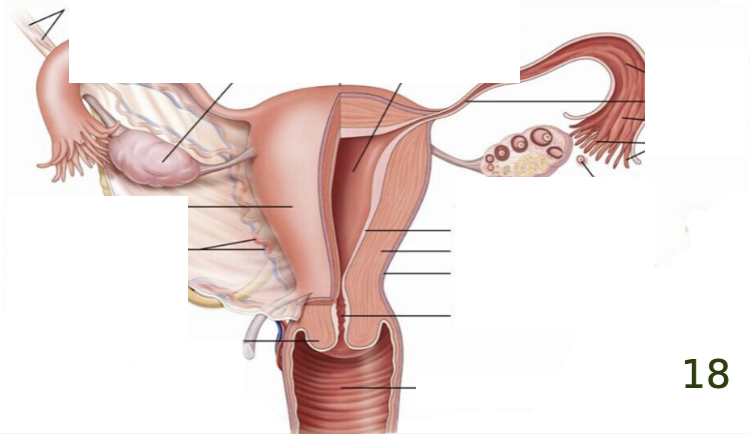
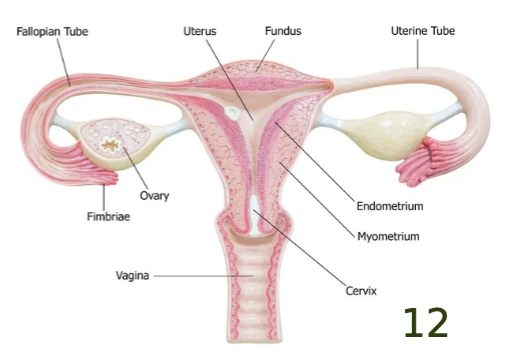
label the key structures of the female reproductive system.
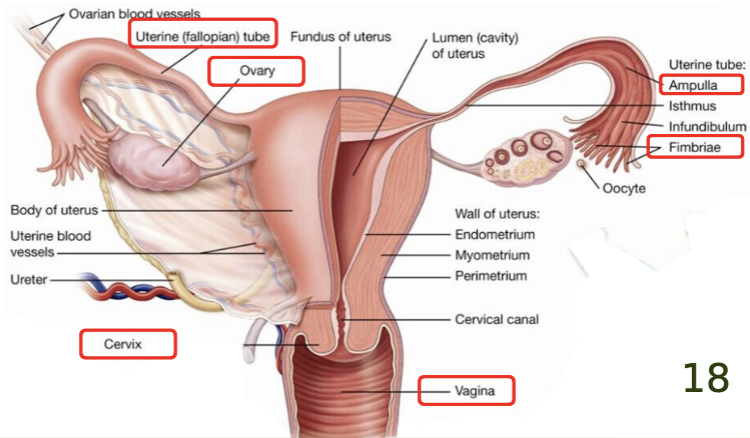
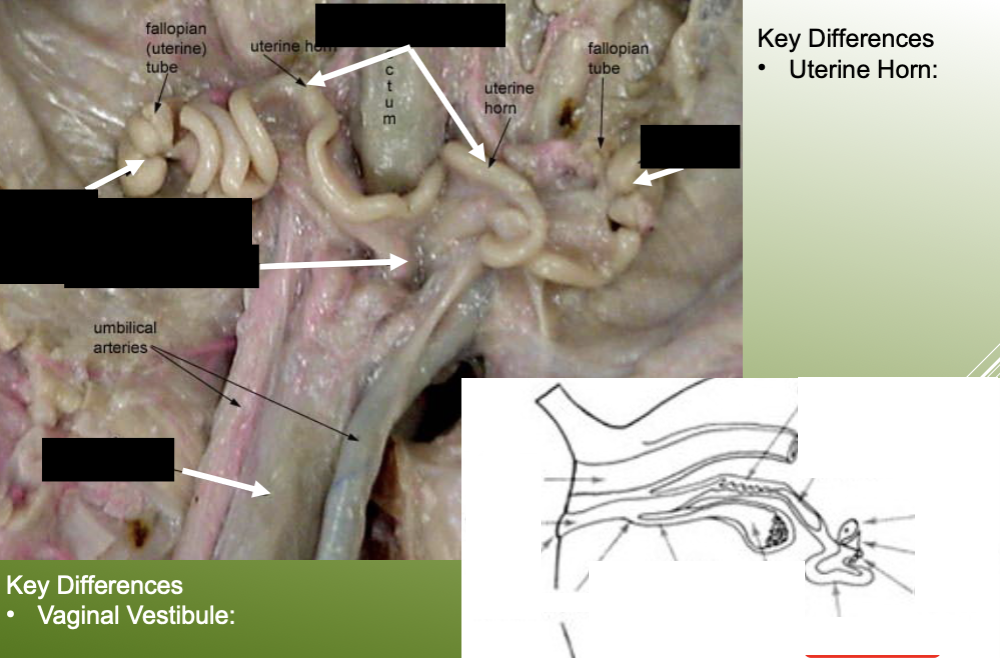
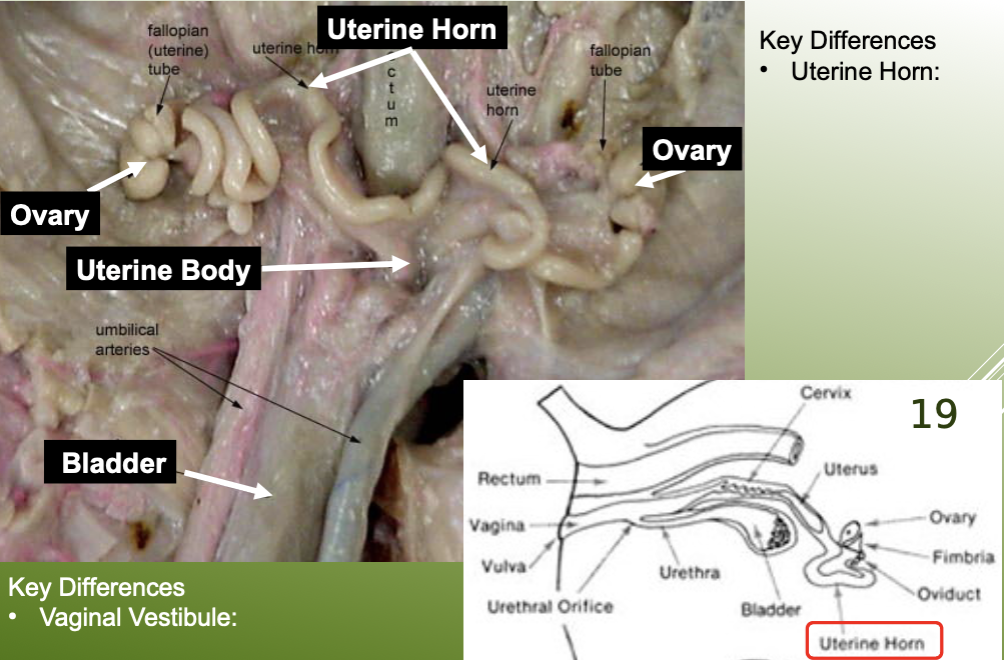
label the key structures of the female reproductive system on a female pig.
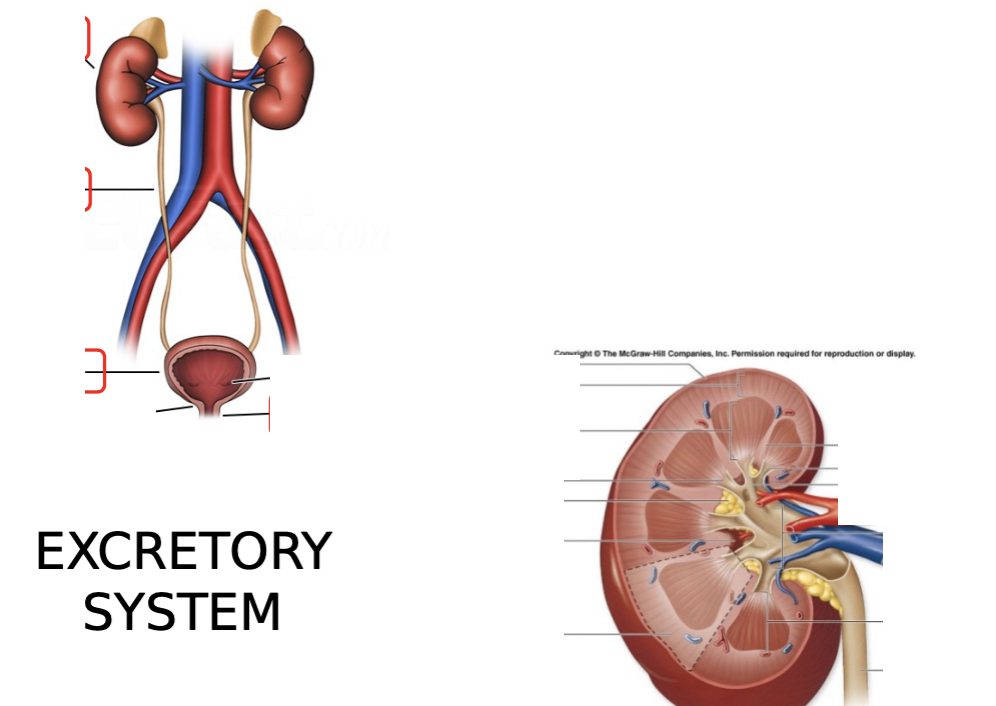
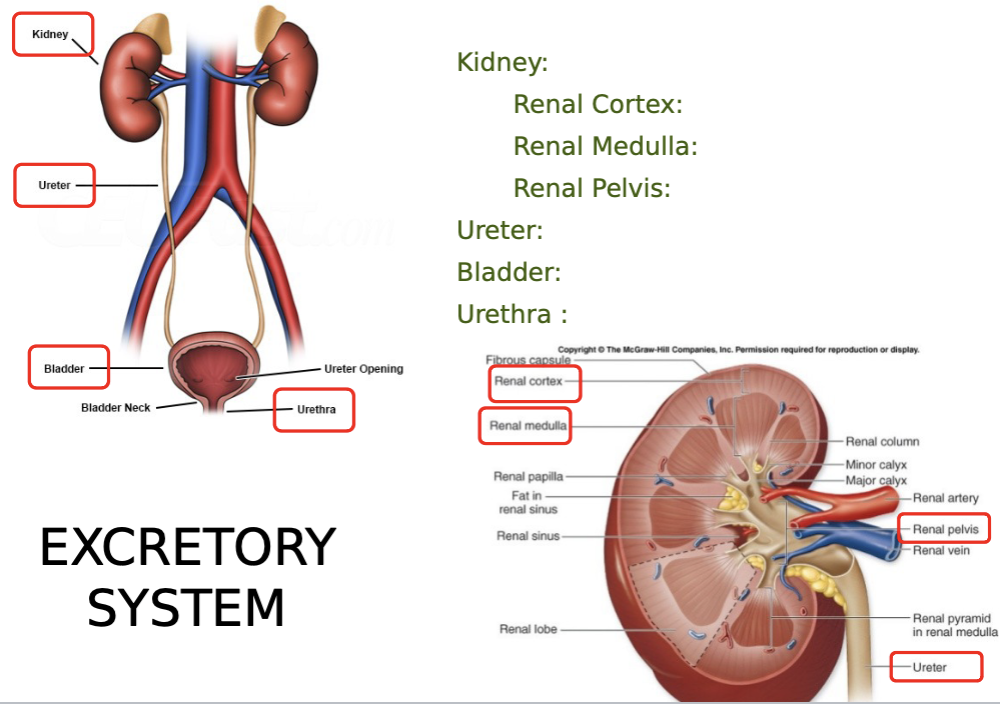
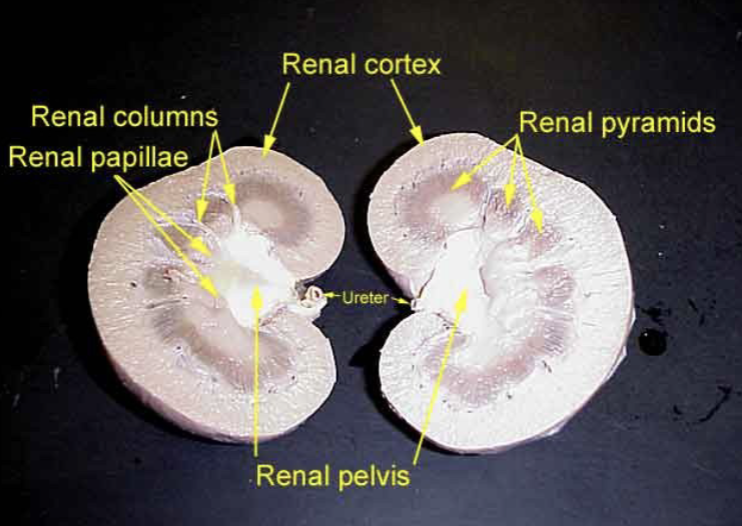
what are the key structures of the excretory system? be able to label them on diagrams.
kidney: renal cortex, renal medulla, renal pelvis
ureter
bladder
urethra
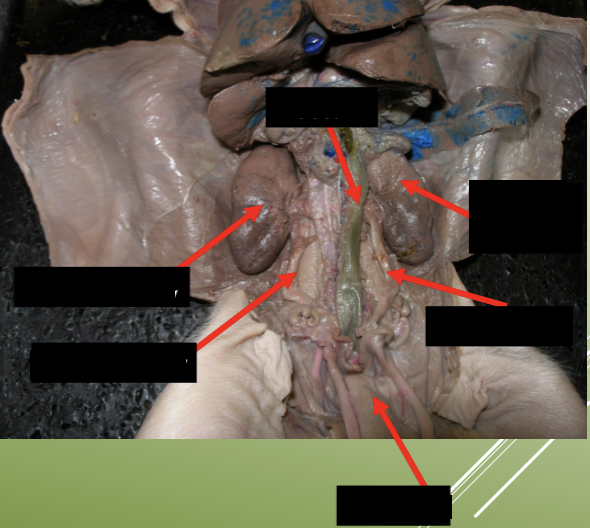
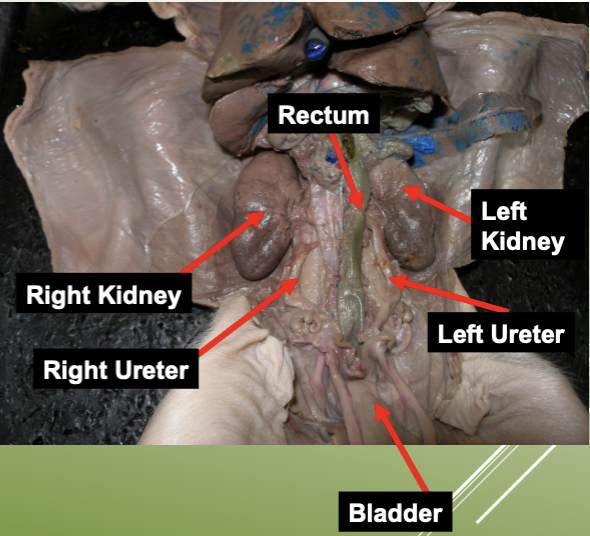
label the urinary system on a pig.
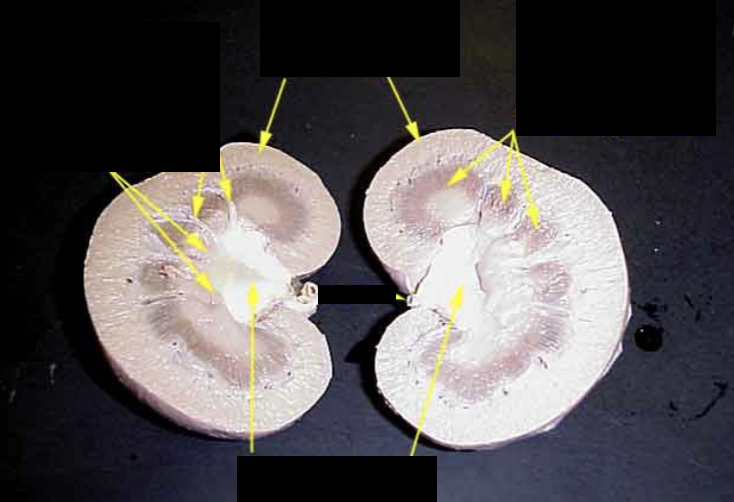
label the dissection cut of a kidney.
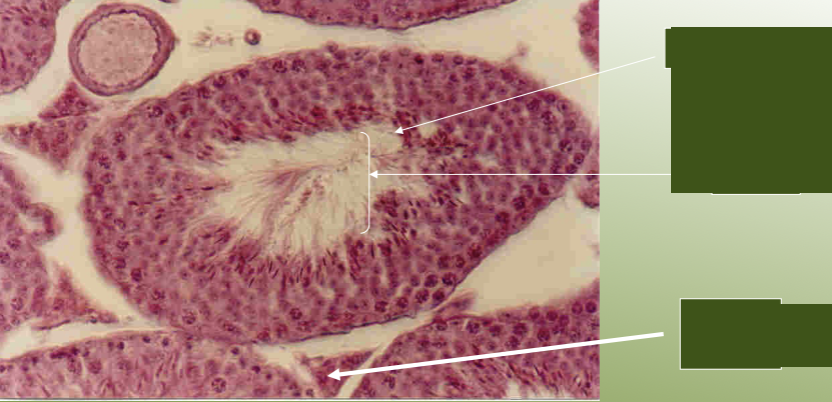
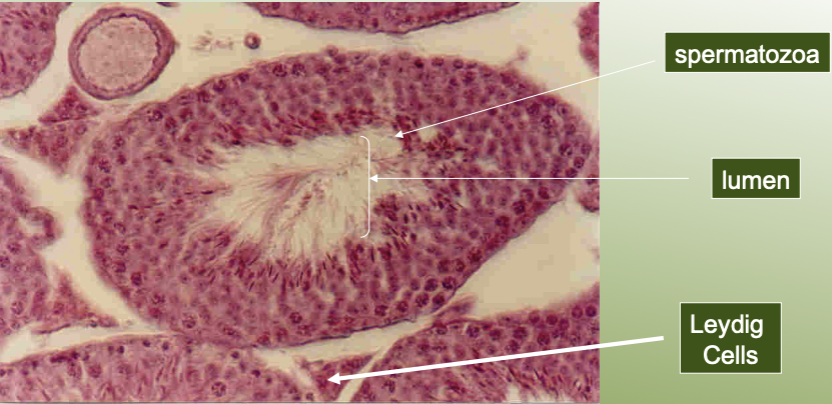
label the structures of the testis under a microscope.
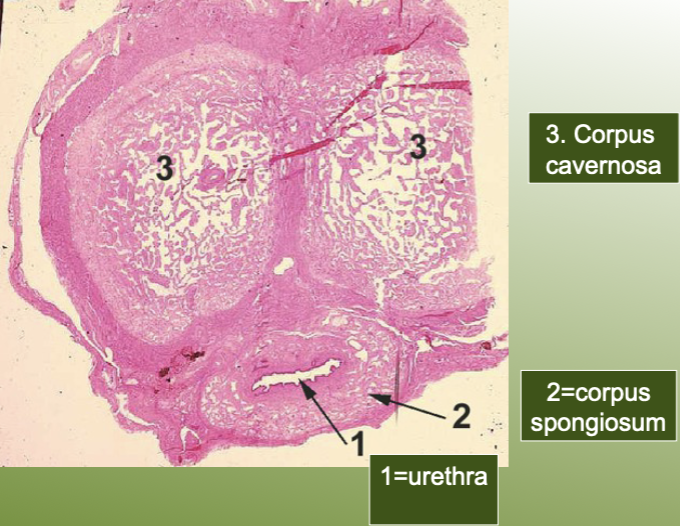
label the structures on the human penis slide.
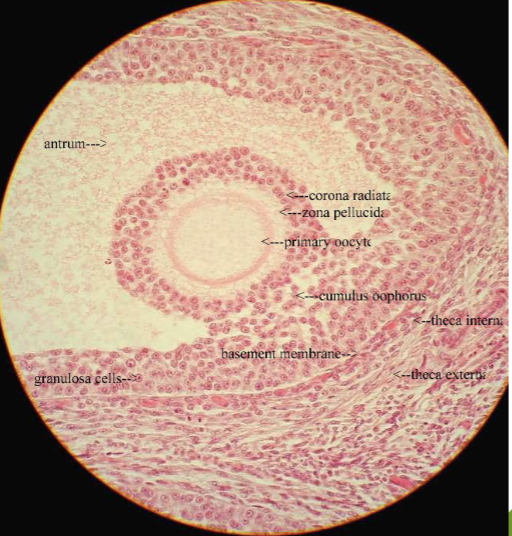
what does this microscope slide represent?
graafian follicle
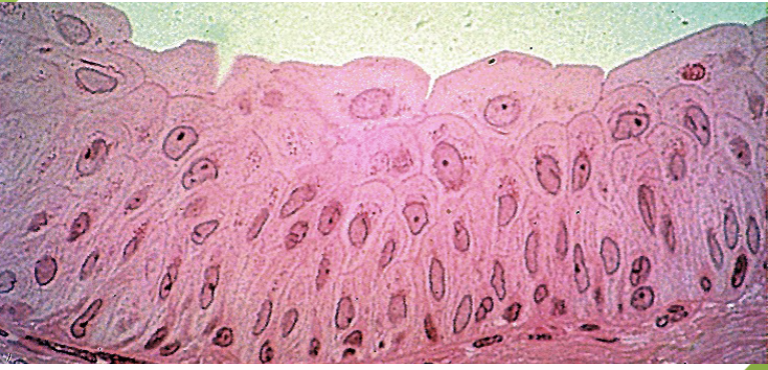
what does this microscope slide represent?
transitional epithelium
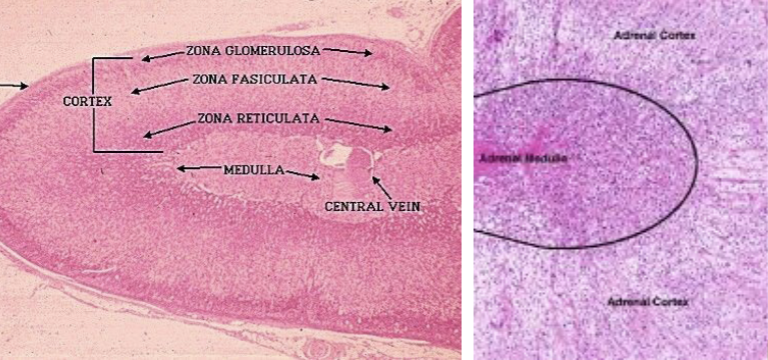
what does this microscope slide represent?
adrenal gland
what hormones fall under the peptide chemical class?
oxytocin
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
calcitonin
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
what hormones fall under the protein chemical class?
growth hormone (GH)
prolactin (PRL)
what hormones fall under the glycoprotein chemical class?
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
what hormones fall under the amine chemical class?
triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
calcitonin
what is the function of oxytocin?
stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary gland cells
smooth muscle contraction (ex. contractions of uterus at birth)
constricts ducts in breast to allow milk flow
what is the function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
promotes retention of water by kidneys by working on distal convoluted ducts of kidney
alcohol can inhibit the release of this hormone
what is the function of the growth hormone (GH)?
stimulates growth (especially long bones) and metabolic functions
responsible for growth spurt during puberty
what is the function of PROlactin (PRL)?
females: stimulates milk PROduction and secretion
males: causes testosterone to have more potent effects
what is the function of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)?
stimulates production of ova (female) and sperm (males)
what is the function of luteinizing hormone (LH)?
females: on day 14 of a monthly cycle, increased LH —> ovulation
males: LH causes Leydig/interstital cells of testes to make testosterone
what is the function of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)?
stimulates thyroid gland to make triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), higher levels of these increases metabolism
iodine is very important for the body as the element is required for both these hormones
what is the function of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
stimulates adrenal cortex (Zona Fasiculata) to secrete glucocorticoids
what are the functions of the triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) hormones?
stimulate and maintain metabolic processes
higher levels makes the body more active, low levels makes someone rly tired and it’s easier to gain weight
what is the function of the calcitonin hormone?
lowers blood calcium level
stores excess calcium in the bone
what is the function of the parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
raises blood calcium level by breaking down bones
what is oxytocin regulated by?
nervous system
what is antidiuretic hormone (ADH) regulated by?
water/salt balance
what is growth hormone (GH) regulated by?
hypothalamic hormones
what is prolactin (PRL) regulated by?
hypothalamic hormones
what is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) regulated by?
hypothalamic hormones
what is luteinizing hormone (LH) regulated by?
hypothalamic hormones
what is thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) regulated by?
thyroxine in blood & hypothalamic hormones
what is adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) regulated by?
glucocorticoids & hypothalamic hormones
what are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) hormones regulated by?
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
what is calcitonin regulated by?
calcium in blood
what is parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulated by?
calcium in blood
know the general structures of the hormones.
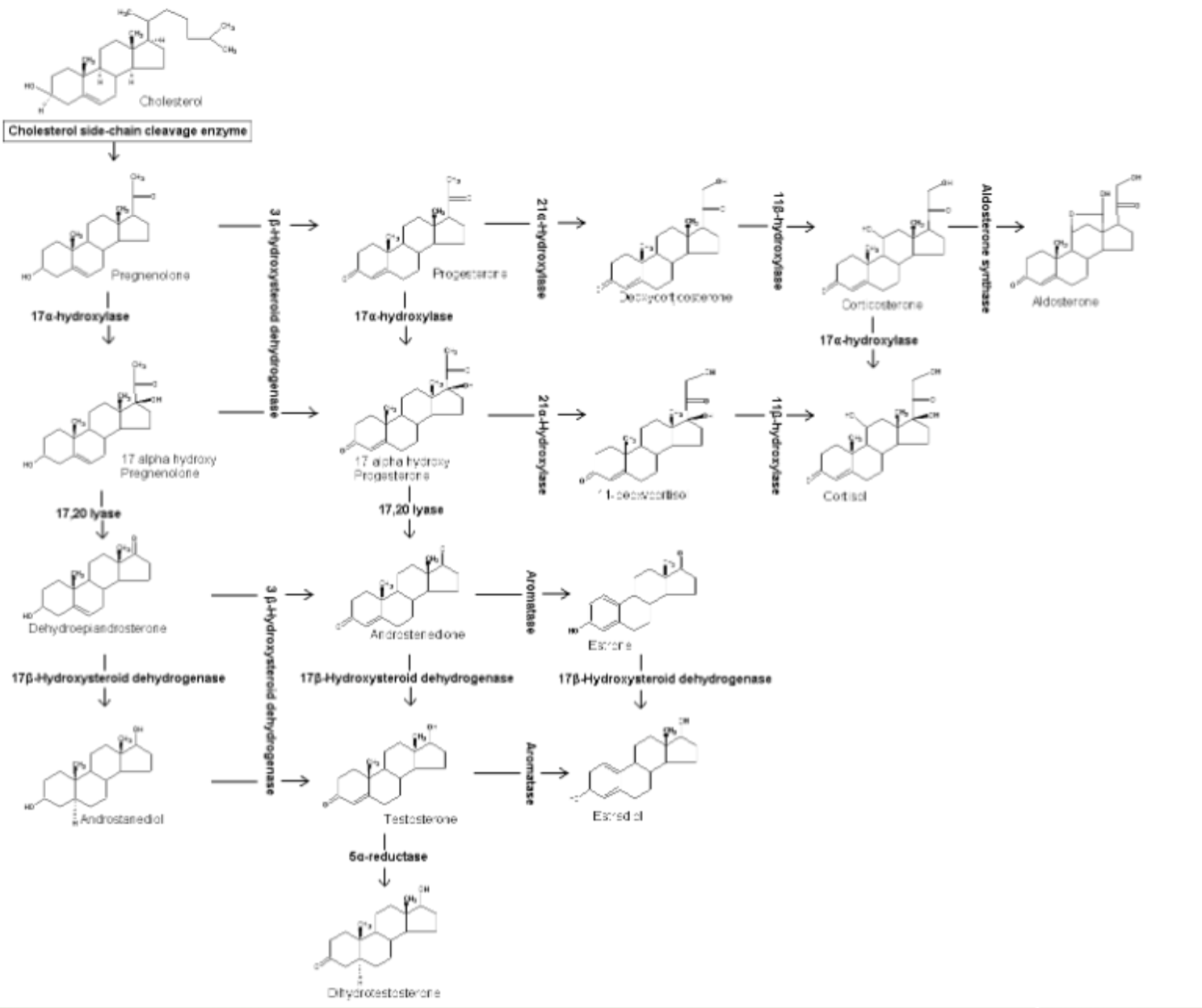
what is the function of the melanocyte stimulating hormone and where is it produced?
function: causes melanocytes of skin to spread melanin over broader areas of each cell (skin darkens) upon exposure to UV
production location: anterior pituitary
what is the function of endorphins and where are they produced?
function: body’s natural pain killer
receptor for this hormone can also be bound by opioids bc they’re similar in molecular structure
production location: anterior pituitary
what is the function of the glucagon hormone and where is it produced?
function: raises blood glucose by having the liver breakdown glycogen and release the glucose units into the blood
production location: released by the alpha cells of the Islet of Langerhans (pancreas)
what is the function of the insulin hormone and where is it produced?
function: lowers blood glucose by having the liver uptake the excess and store it in the polymer form of glycogen
production location: released by the beta cells of the Islet of Langerhans (pancreas)
what is the function of the somatostatin hormone and where is it produced?
function: inhibits the release of both insulin and glucagon when blood glucose is within optimal range
production location: released by the delta cells of the Islet of Langerhans (pancreas)
what is the function of epinephrine and norepinephrine/noradrenaline hormones? where are they produced?
functions:
cause the “flight or fight” collectively
shunts blood away from digestive system and gives most blood to brain, heart, skeletal muscle, and lungs
production location: medulla of adrenal gland
what is the function of the androgens hormone in females? where is it produced in females?
functions:
has effects of testosterone (doesn’t effect males, only females)
production location: zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
up against the adrenal medulla
what is the function of the glucocorticoids hormone? where is it produced? what is the hormone triggered by?
functions:
causes a reduction in inflammation (THINK cortisone shot)
raises blood glucose by breaking lipids and proteins (dif. from pancreatic hormones which break down the carb stores of glycogen)
production location: zona fasiculata of adrenal cortex (middle of cortex)
trigger: triggered by adrenocorticotropic hormone from anterior pituitary
what is the function of the mineralocorticoids hormone? where is it produced?
function: causes an increase of sodium to be reabsorbed in the kidneys, causing more water to be retained.
more fluid in a confined space builds pressure
production location: zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex (outer most zona)
what is the function of androgens in males? where is it produced in males?
functions:
proper sperm production
maintains secondary sex characteristics (hair pattern (facial, chest, limbs, pubic), upper chest development (more muscle mass), vocal cords lengthen and thicken, sex drive, enlargement of genitalia during puberty)
production location: produced by LH influencing Leydig cells of the testes
what is the function of progesterone? where is it produced?
function: as pregnancy hormone, keeps uterus lining in thickened state
production location: ovary
why do progesterone levels matter during pregnancy?
they must be kept high during pregnancy, or if they’re lowered, the fetus will be aborted
what is the function of estrogen? where is it produced?
function: maintenance of the secondary sex characteristics (causes fat deposition in mammary glands, causes fat deposition in hips, causes pelvic girdle bones to shallow and widen for child bearing years, hair pattern (arms, legs, pubic))
production location: ovary
define the testes as a part of the male reproductive system.
sperm is produced via meiosis
contain highly convoluted tubes called seminiferous tubules
outside tubules are special cells, Leydig (interstital cells), that produce testosterone
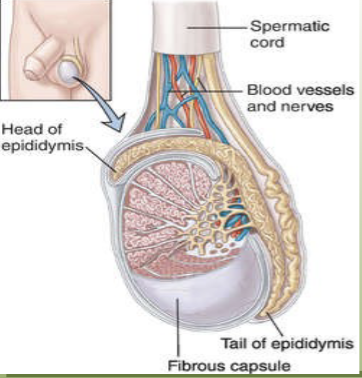
define the epididymis as a part of the male reproductive system.
coiled structure which hugs around the testes like the letter “C”
where sperm mature (newly made sperm at the head and more mature at tail)
define the vas deferens as a part of the male reproductive system.
tube which brings sperm into the body and empties them into the urethra
define the urethra as a part of the male reproductive system.
tube which carries sperm and urine out of the body
define the penis as a part of the male reproductive system.
organ containing urethra, organ for copulation
define the seminal vesicles as a part of the male reproductive system.
accessory organ/gland
produces about 60% of total contribution to semen
secretes fructose (powers sperm)
prostaglandins (causes uterine contractions, mucus)
define the prostate as a part of the male reproductive system.
accessory organ/gland
secretes enzymes which help buffer the acidity of vagina
define the bulbourethral (Cowper’s) as a part of the male reproductive system.
accessory organ/gland
secrete little fluid that may provide small amount of lubrication during intercourse
usually released as pre-ejaculate (which can sometimes contain sperm)
define the scrotum as a part of the male reproductive system.
sac of skin which contains testes
define the inguinal canal as a part of the male reproductive system.
hole (passage) in the abdominal muscle through which the vas deferens passes
define the ovary as a part of the female reproductive system.
organ which produces the eggs
define the oviduct/fallopian tube as a part of the female reproductive system.
acts as a collecting tube for the egg(s)
contains finger-like projections at the lateral end (near the ovary) called fimbriae
cause sweeping movements which draw the eggs into the oviduct
site of fertilization
there is no physical link between the ovary and the oviduct
define the uterus as a part of the female PIG reproductive system.
divided into 3 parts:
horns: one from each ovary, provides an increased surface area for embryo attachment
human uterus has no horns
body: occurs at the junction of the two horns
cervix: semi-cartilaginous ring of tissue
define the vagina as a part of the female reproductive system.
tube which provides frictional surface to stimulate male ejaculation
provides passage for birth
define the urogenital sinus (aka vaginal vestibule) as a part of the female reproductive system.
common tube that receives from both the urethra and vagina
define the genital papillae as a part of the female PIG AND HUMAN reproductive system.
projection that lies just ventral to the urogenital opening in the female pig
clitoris in human female
define the kidney as a part of the urinary system.
structure responsible for filtration of the ammonia wastes from the blood
what are the three regions of the kidney? describe each.
cortex - outer layer of kidney
medulla - contains renal pyramids (calyces)
pelvis - area where collecting ducts drain urine, connects to ureter
define the ureter as a part of the urinary system.
tube that drains urine to the urinary bladder
define the urinary bladder as a part of the urinary system.
reservoir for urine to be expelled from the body
define the urethra as a part of the urinary system.
tube responsible to drain the urine out of the body
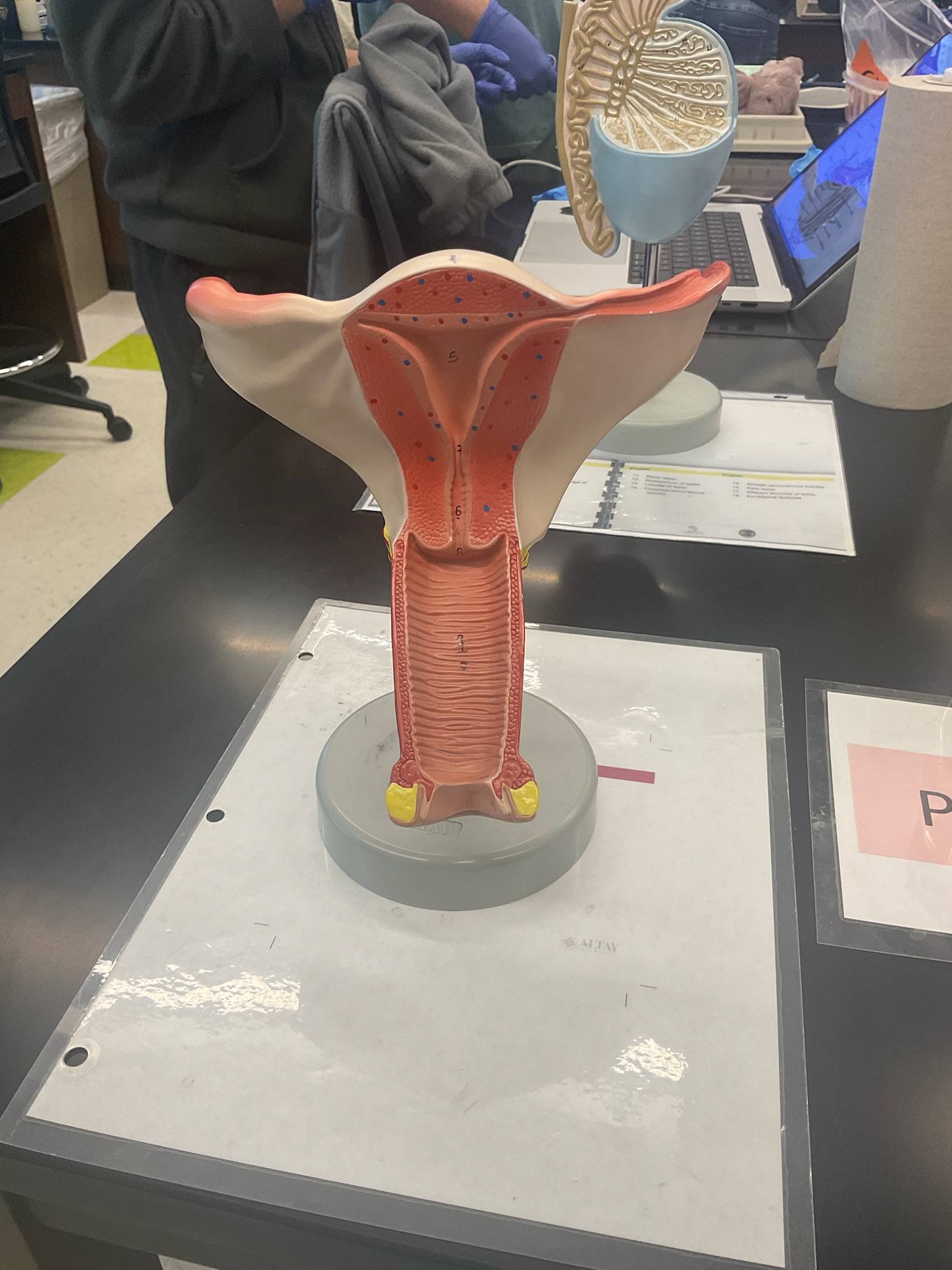
what does this model represent? label the numbered structures.
internal female reproductive organs

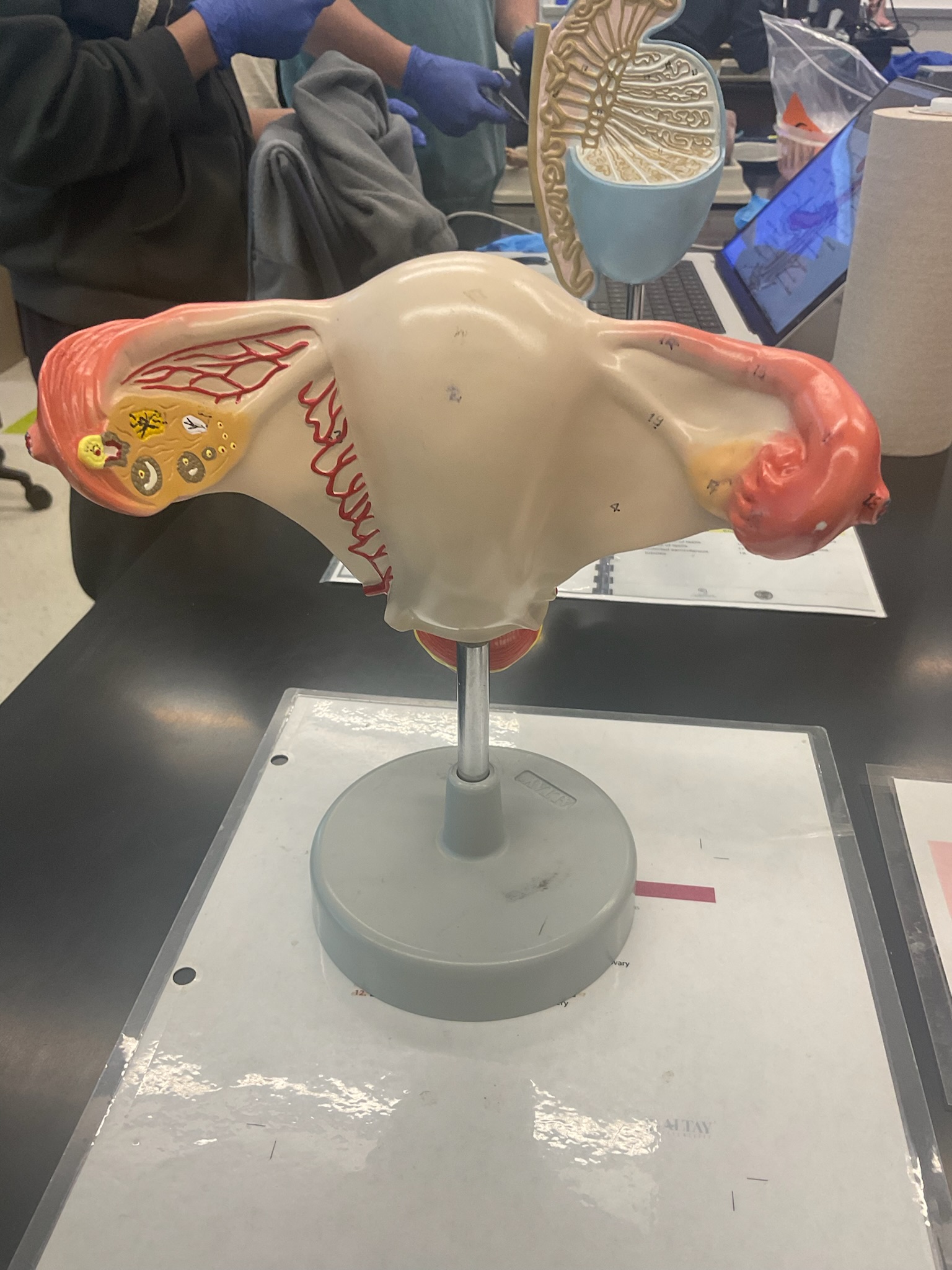
what does this model represent? label the numbered structures.
internal female reproductive organs
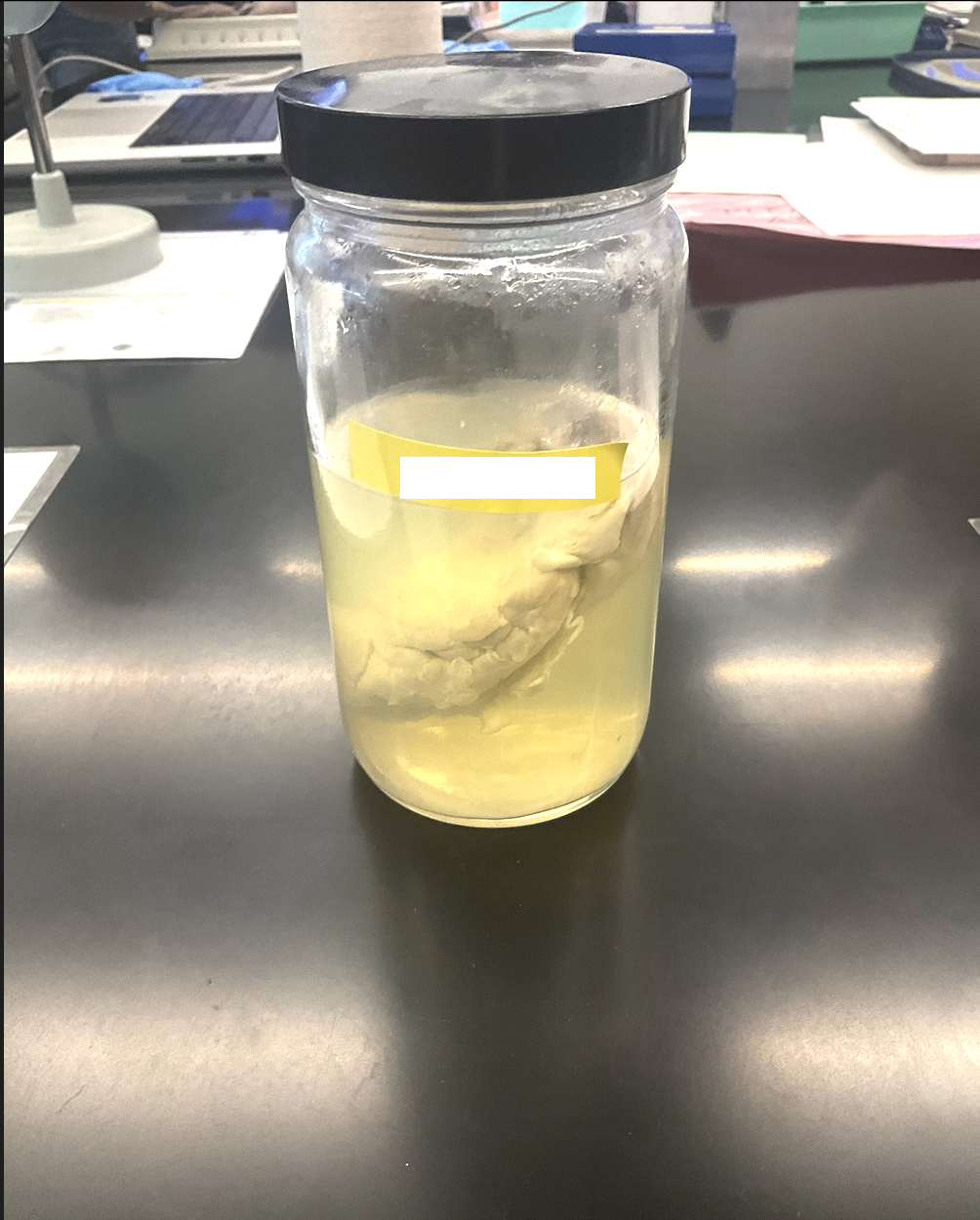


what is this structure?
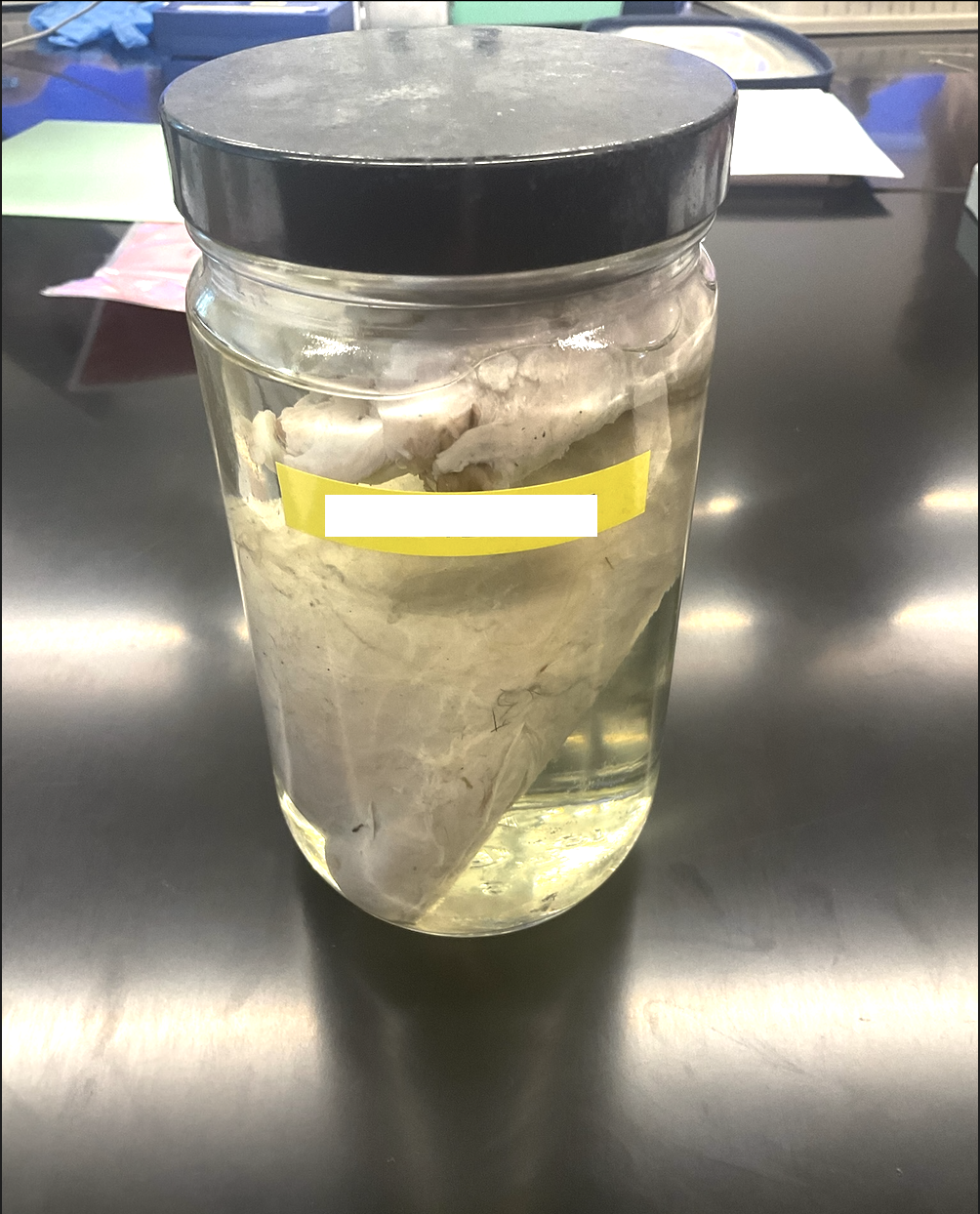


what is this structure?
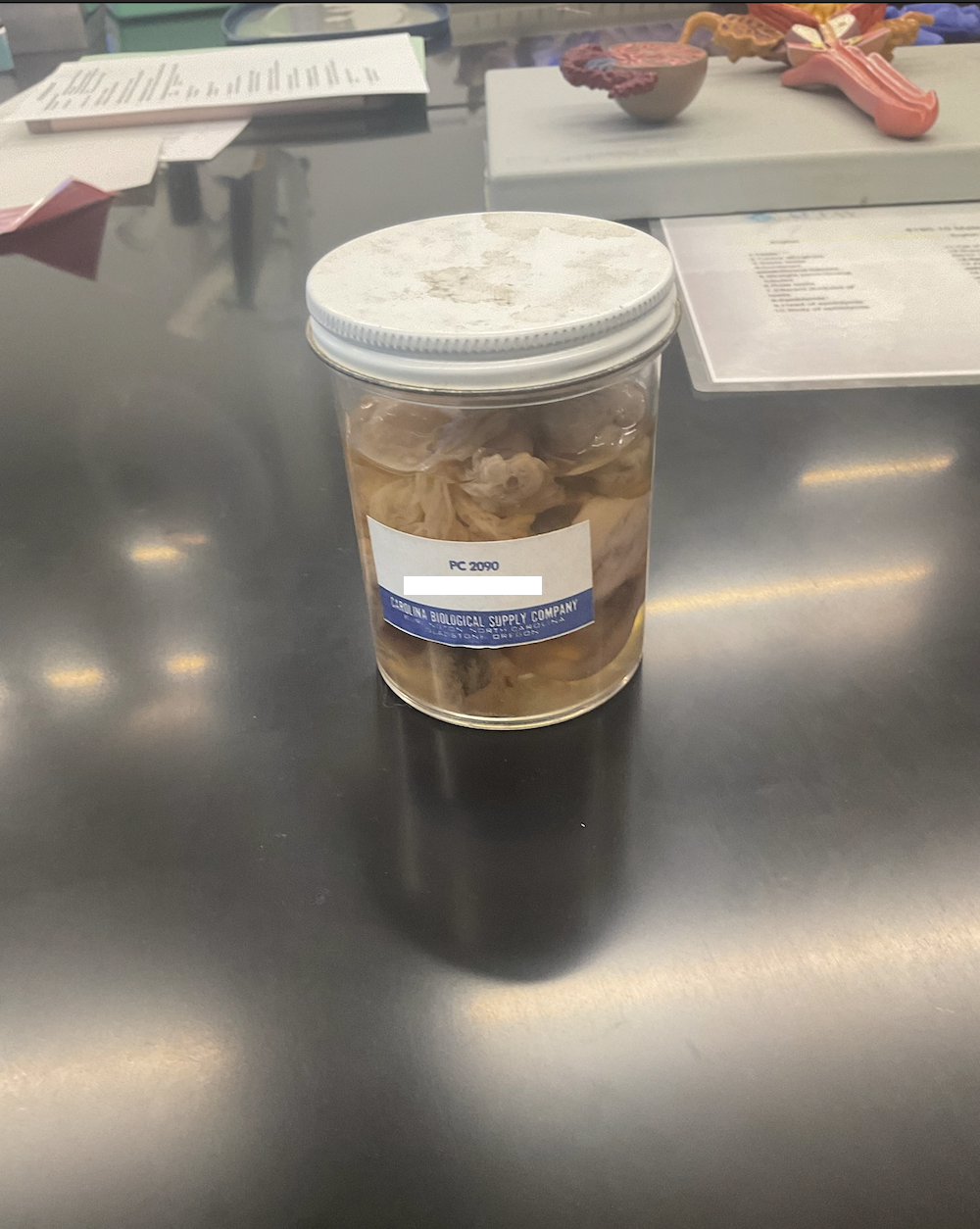

what is this structure?
pig ovary
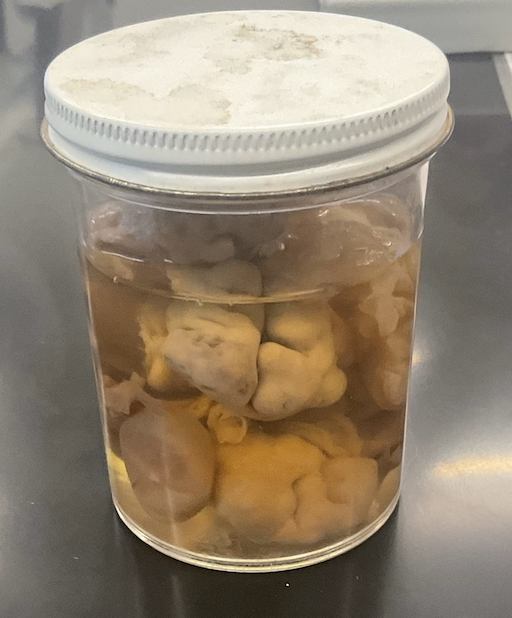

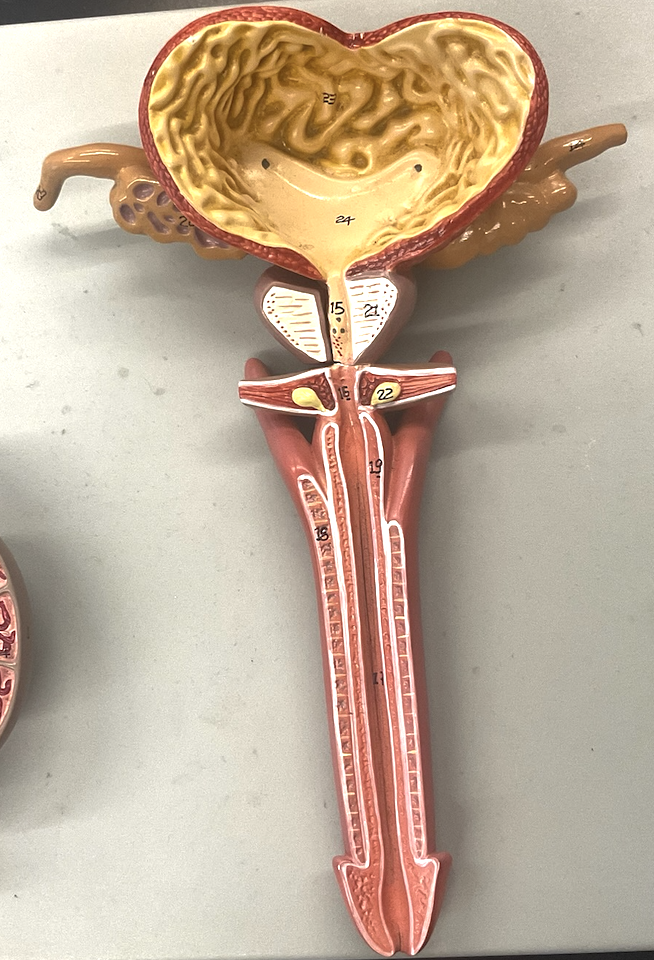
what does this model represent? label the numbered structures.
male reproductive system