ANAT1101 Module 2 Chemistry of Life
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Elements
Pure substances that cannot be broken down.
It consists of particles called atoms.
Molecules
Chemical combinations of two or more elements.
Compounds
Combination of two or more different elements.
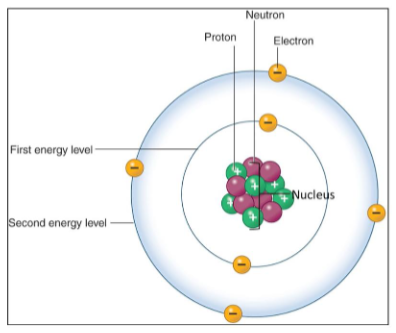
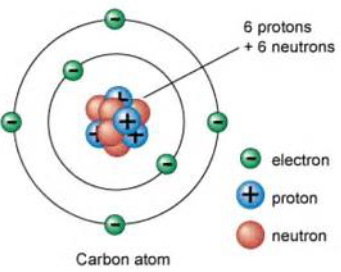
Atoms
Contains:
Nucleus
It contains: protons and neutrons.
Outer shells (or rings)
It contains: electrons.
It can hold a maximum number of electrons.
Atoms is stable when the outermost shell is full.
It is achieved by donating, accepting, or sharing electrons.
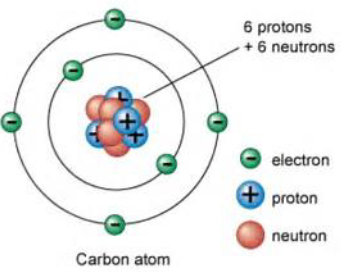
Protons
It is inside the nucleus of an atom.
It carry a positive charge.
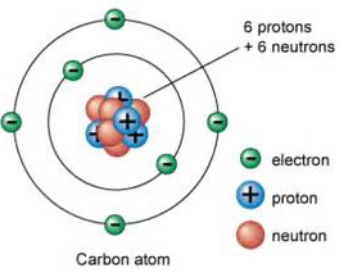
Neutron
It is inside the nucleus of an atom.
It carries no charge.
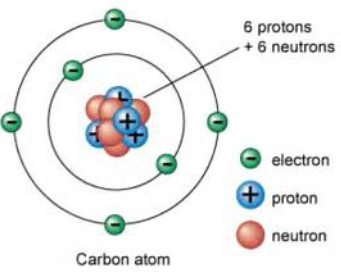
Electron
It is on the outer shell of an atom.
It carries a negative charge.
Ionic Bond
It is when an electron transfers to the outer shell of one atom to another.
The positively charged ion is attracted to the negatively charged ion, forming an ionic bond.
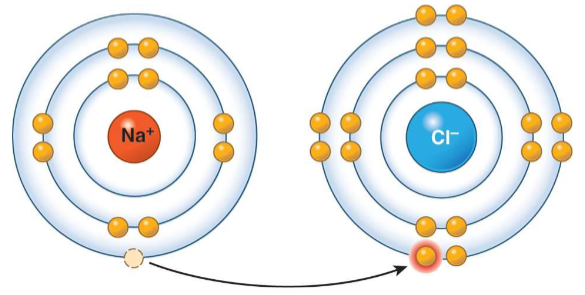
Cation
A positive charged ion.
Anion
A negative charge ion.
Ionization
It is the process by which ionic bonds break and release ions capable of conducting electricity.
Electrolytes
These are compounds that ionize in water to produce ions that can conduct electricity.
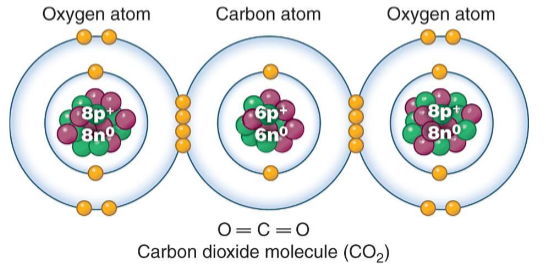
Covalent Bonds
It is formed when atoms share one or more pair of electrons.
Electrons are shared so that each element has a full shell.
It is stronger than ionic bonds.
Energy
It is needed by the body to function.
It is stored in bonds of molecules.
Breaking bonds releases energy.
Forming bonds requires energy.
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions that occur within the body to maintain life, including the conversion of food into energy.
Catabolism
It is the breaking of bonds.
It releases energy.
Some energy released as heat while some are transferred to ATP for storage.
Anabolism
It is the building of new bonds.
It requires energy.
The energy is obtained from the ATP.
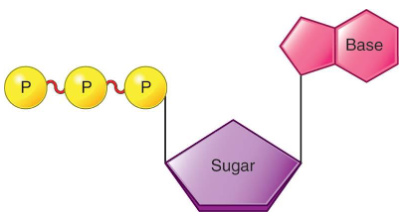
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
It is the body’s storage molecule for energy.
It consists of a base, sugar, and a three phosphate groups.
Phosphate groups are connected with high-energy bonds.
Breaking one of these bonds releases energy.
Energy from nutrients is used to reattach the broken bonds.
Organic Compounds
It contains carbon.
Four Major Groups:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Inorganic Compound
It includes:
Water
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
Acids and Bases
Solution
It is a mixture of a solvent and solute.
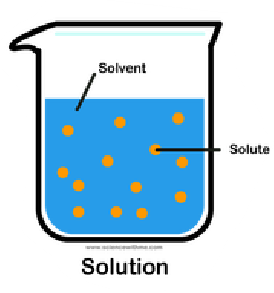
Solute
It is the substance that is being dissolved.
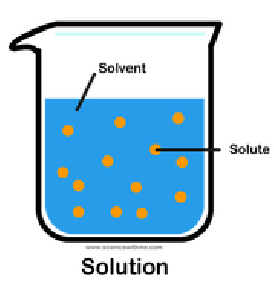
Solvent
It is the fluid within a substance dissolves.
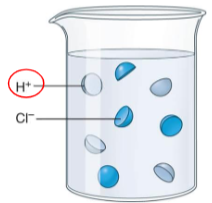
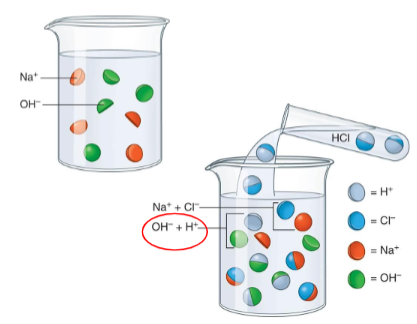
Acids
These are substances that releases hydrogen ion (H+) when dissolved in water.
If the pH scale is less than 7.
Bases
It is a substance that can accept a hydrogen ion (H+) from another substance.
If the pH scale is more than 7.
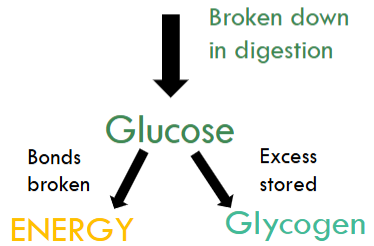
Carbohydrates
It is made up of saccharides/sugars.
It is the body’s main energy source.
It is broken down into glucose.
Bonds in glucose broken down to release energy.
If glucose is not immediately broken down, it is stored as glycogen.
Lipids
It is made up of fatty acids and glycerol.
It provide structure to cells (make up cell membrane)
It is a reserve energy supply.
It cushions organs.
Protein
It is made up of amino acids.
The structure and metabolic functions of every cell depends on proteins.
Nucleic Acid
It is made up of base, sugar, and phosphate.
It stores genetic information and energy.
Important nucleic acids in the body:
DNA
RNA
ATP