Compiled Knowt Notes For Bu111 Midterm Exam
1/619
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
620 Terms
Diamond E Model: (Definition)
Matches internal characteristics with external solutions. It is the plan the business uses to pursue opportunities & avoid threats. Determined using Diamond-E, KSF, or Porter’s Generic Strategies.
Internal Strategy: What CAN we do?
External Strategy: What SHOUD we do?
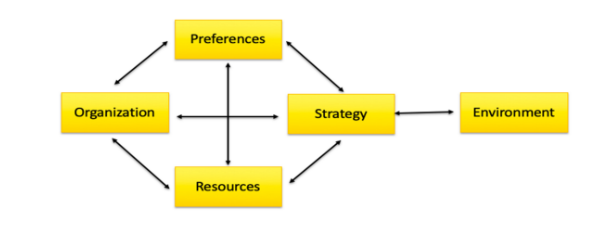
Diamond E Model (connecting internal qualities of the company to the external environment)
Internal Qualities (Strengths/Weaknesses)
Management Preferences
Organization
Strategy
Resources
External Environment (Opportunities/Threats)
Determined using PEST or Five Forces
Diamond E Model Application
1- Is the current strategy aligned with future opportunities and threats?
2- What new strategies are feasible and worthwhile?
3- What are our strengths and how can we use them for competitive advantage in the environment?
4- What do we need to execute a strategy? Can we get it? Where are we inconsistent?
Diamond E Model Steps
1- Look Internally, i.e. What do we want and what can we do?
Management Preferences:
What does management want? Ambitions? Objectives? Vision? Biases?
What are its Priorities?
How comfortable is it with Risks?
Does it value some strategies over others?
Does it value some resources over others?
Organization:
Company Culture - “Who we are”
Company Capabilities - “ What are we good at” ex: Marketing, supply chain, etc.
Specialist (efficiency) vs Generalist (integrative)
Innovation vs Stability
Resources:
Financial: Cash on hand, equity, debt, ability to take out loans
Intangibles: Human Capital, reputation, patents, knowledge
2- Deal with Strategy - Environment Linkage
Assess forces at work and their implications
Adjust internal or adjust strategy, because there are variables we can change
3- Create a Strategy
Once you have examined all internal factors, create strategy to tackle the external factors, i.e Environment
Business Situation Framework #1 (Customer)
Customer:
Who buys, uses, why, how much, how often, and in what context?
Segments (size, growth, % of market)
How do they make buying decisions?
Distribution channel preference
Business Situation Framework #2 (Company)
Company:
Capabilities, expertise, resources, distribution channels
Financial situation
Organizational structure
Preferences, vision, mission
Intangibles (reputation, brand equity, human capital)
Business Situation Framework #3 (Competition)
Competition:
Market share concentration
Strategy (position/target, products, pricing, distribution)
Best practices (are they doing something we aren’t/can’t)
Barriers to entry - new competitors?
Regulations
Business Situation Framework #4 (Product)
Product:
Nature of product (how it’s used, why it’s valuable?
Differentiated?
Complementary goods needed?
Substitutes
Life cycle stage
Principle Logic (ICE-A)
Internal Consistency:
Good management/execution of internal business practices
External Allignement:
Correct strategy, optimized for the environment
P+G Strategy-Structure (2000)
Internally inconsistent and externally misaligned strategy
Wrongly focused on diversifying their product lineup
Customers lost interest, too much variety for target audience
Suppliers were also short on resources for the expansion, causing shortages
Ikea Strategy-Structure
Internally consistent and externally aligned strategy
Noticed many customers did not have the space for large furniture in their smaller apartments/homes
Adapted to environment, shipping furniture in pieces so it could be fit in any home and built there.
Consider their financial resources, they were able to use large buildings as retail warehouses and create different product lines to appease their target audience.
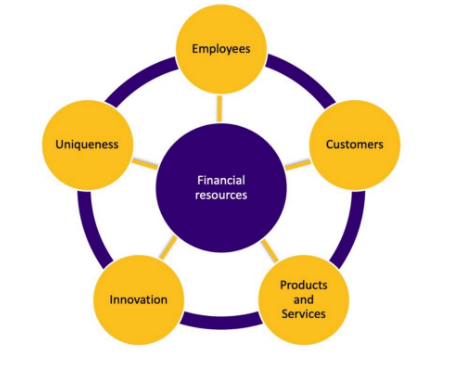
Success Key Factors (SKF)
SKF - Financial Resources (3 KPI)
Financial Resources:
Profits
Growth
ROI
Key Performance Indicators:
Revenue/Profits: Describes net profit. Higher is better, growth is better.
ROI: Returned revenues on initial investment
Firm Value: The value of the company if sold today
SKF - Employees (4 KPI)
Employees:
Enable Firm Operation
Hire qualified personnel that enjoy working for you
Give your employees chances to succeed, ex promotions
Motivate them with profit sharing, flexibility, development, opportunities, etc.
Key Performance Indicators:
Employee Commitment: Describes the loyalty, passion, and commitment of employees. These workers are significantly more productive.
Employee Turnover: Amount of employees you have to replace, year over year (Lower is better)
Productivity: The amount of output the company’s employees generate
Application: Employees tend to be attracted to work at companies with good employee relations.
SKF - Customers (5KPI)
Customers:
Provide Revenue
Create brand loyalty
What do you have to offer?
Who needs/wants it the most?
Key Performance Indicators:
Customer Satisfaction: When a company anticipates their target market’s needs.
Market Share: Percentage of overall market you control/own in $ influenced by firm size
Share of Wallet: the % of money that consumers regularly spend on a company’s products rather than their competitors. (Higher is better)
Net Promoter Score: Measuring advocacy of your customers, such as if customers regularly recommend a company’s products to others. (Higher is better)
Churn: % of customers the firm loses every year. Measures customer loyalty. (Lower is better)
SKF - Products/Services (7 KPI)
Products/Services:
The “Means of Revenue”
Concerns perceived quality
Optimize your inputs, production process
Key Performance Indicators:
Quality: Concerns the product’s perceived value, consistency and reliability
Reliability: Products expected life span is directly related to its perceived value
Returns: Happens when consumers are not satisfied with product (Lower is better).
Defects: Products that are not up to company’s quality quality standards. High defect rates creates perception of inconsistent product quality.
Warranty Claims: Higher number of warranty claims show product does not live up to its expected life cycle
Waste: Inefficiencies in manufacturing process, usually due to low quality inputs
Value: You get what you pay for and are okay with it because you expect it.
SKF - Innovation (6KPI)
Innovation:
Improves Environmental Alignment
Culture, structure, and rewards
Includes small things like the WAY you serve customers.
Can create valuable change
Key Performance Indicators:
New Products: New forms of the product, new approaches to selling the products, etc.
Idea Generation: New ideas are encouraged and are being explored by employees in the company
Cycle Time: How long it takes to go from idea generation to full implementation (Faster is better, indicates better and more efficient organization).
Company Culture: Can be accepting of change, gives employees rewards for pushing innovative ideas/
Company Structure: Can provide employees opportunities to explore change/creativity.
Rewards: Employees can be rewarded for thinking outside the box
SKF - Uniqueness (3KPI)
Uniqueness:
Creates market advantage
R&D needed
What’s going to attract employees and customers to your business instead of your competitors?
Key Performance Indicators:
Distinctive Competitive Advantage: Valuable & sustainable differentiation from competitors
Strong Unique Reputation: Extracted from market research. How the market (consumers, competitors, employees) perceives the firm
Superior Competitive Performance: Is the firm able to produce cheaper, faster, is the firm able to charge more, attract better employees, compared to competition.
Why Consider KSF?
- Guide strategic and daily actions. like a daily checklist
- Ensure long-term success
- Ensure holistic thinking
Reminds you that KSF are connected. Organizations are made up of interconnected components.
Porter’s Generic Strategies (Definition)
Offers insights on competitive position strategies a firm can take and what is needed to pursue them.
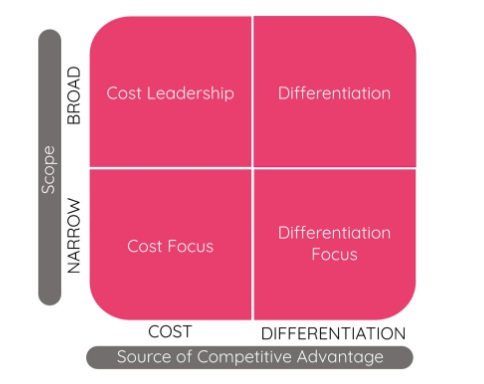
Porter’s Generic Strategies
Competitive Scope (Y):
Broad Target: Appeal to a broad group of customers
Narrow Target: Identify an underserved niche market, and target them.
Competitive Advantage (X):
Cost: Advantage resides in offering products cheaper than competitors. Can the firm deliver goods at the lowest cost and still turn a profit?
Differentiation: Advantage resides in how firm’s products are distinct from competitors. How can the firm make consumers pay more for their product?
PGS #1: Cost Leadership
Description:
Appeals to BROAD market at LOW price
Has the capacity to produce at large volumes and has the capabilities to produce more cheaply than others
Does the large portion of the overall market value lower priced offering?
PGS #2: Differentiation
Description:
Appeals to BROAD market at HIGH price
Products provide unique features that consumer pay extra for, and has the capacity to product at a large capacity
Are the unique features broadly appealing?
PGS #3: Cost Focus
Description:
Appeals to NARROW market at LOW price
Serves their niche at the lowest price possible
Does a simpler, lower performance, cheaper product appeal to small but enough portion of the market
PGS #4: Differentiation Focus
Description:
Appeals to NARROW market at HIGH price
Company targets small group that are willing to pay substantially more.
Would customers be willing to pay a lot more?
PEST Factors: Look For’s in External Analysis
Present:
Current Environmental situation
Firm should constantly look for ways to adapt to its current environment
Trends:
Observable Environmental changes that will come in the future
Firms should anticipate changes and adapt ahead of time. Ex: Society’s social structure changer over time
Quick Changes:
Predictable or surprising changes
Anticipate and plan contingency strategies
Predictable Changes: Interest rates changes
Surprising Changes: Covid-19, natural disasters
PEST Factor #1: Political
Descriptions:
Laws
Regulations
International Trade Laws
Trade Agreements
Opportunities/Threats:
Expansion. Ex. If governments negotiate trade agreements with foreign countries a business will have opportunities to expand into foreign markets
Barriers. Ex. Regulations bar the average Canadian from creating their own chartered banks.
Competition. Ex. If trade agreement reduced tariffs, foreign companies are now competing with you for the same population
PEST Factor #2: Economic
Descriptions:
GDP
Inflation
Employment
Exchange Rate
Interest Rates
Opportunities/Threats:
Input Cost. Ex. When inflation is high, input costs are higher. When CAD exchange rate is high, input costs are lower.
Demand. Ex. If firm wants to expand into country with high GDP, demand will be higher because citizens have plenty of money.
Funding. Ex. Higher interest rates lower access to easy loans
Competitive Pricing. Ex. High CAD is better for importers as it allows them to import for for the same amount of money. Low CAD is better for exporters as it makes them more competitive, people with a stronger currency can buy more of the Canadian firm’s products.
PEST Factor #3: Social
Descriptions:
Values/Attitudes
Customs
Habits
Demographics
Opportunities/Threats:
Customers. Ex. Values, attitudes, customs and habits affect what they demand and how the firm communicates with them in marketing material
Employees. Ex. Canadian’s attitudes towards working in an office post COVID have changed. Many Canadians prefer working from home, at least more than they did pre-Covid.
CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility). Ex. Management, who control CSR plan, are constrained by the morals and values of their society. Many companies in the east would not promote pro-LGBTQ initiatives because of public backlash.
PEST Factor #4: Technology
Descriptions:
IT
Internet
Materials & Equipment
Has Biggest Impact on Organizations
Opportunities/Threats:
Barriers. Ex. Tech can create or reduce barriers of entry to many industries. Airbnb entered hotel industry by using technology, instead of buying lots of real estate.
Innovation. Ex. Changes in steel production allowing steel to be lighter but just as resilient.
Strategy. Ex. Companies use technology to adapt new trends, such as retailers integrating e-commerce capabilities in their business model.
Questions to Answer From PEST Analysis
Are social factors changing how I hire or what customers want? How are customers different in foreign markets?
Can I use tech to improve product quality, meet customer needs, or increase profitability?
Will changes in laws, regulations or tech reduce barriers to entry?
What legal protection do I have or what laws do I have to comply with?
What do future economic conditions look like and how will they impact my firm?
Porter’s Five Forces: Focus
- Focuses on evaluating INDUSTRY environment
- Helpful on identifying COMPETITION in industry
- Identifies challenges or constraints
- Identifies what the competitive environment look like
- Identifies external factors affecting the industry
- Identifies the industries that might be worth entering
- What barriers will a firm face if they choose to expand into this industry?
Caveat: Power and influence of each force will vary by industry. One weakness of Five Forces.
PORTER’S 5 Forces:
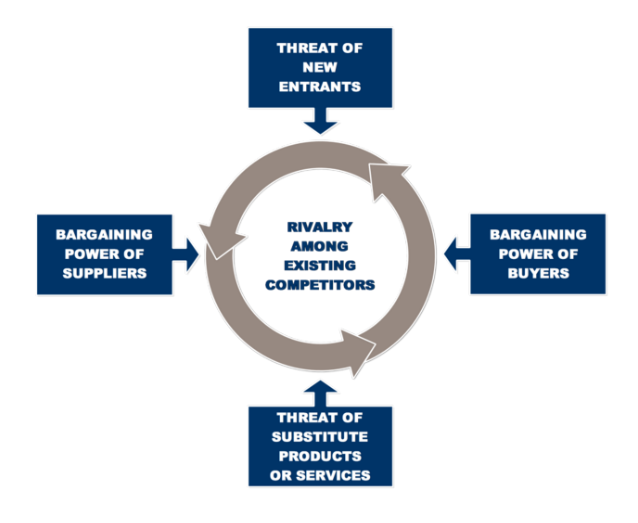
P5F Breakdown: Existing Competitors (6)
Existing Competitors:
Biggest factor
More competition = less profit, no above-normal returns
Includes all current competitors
Factors:
Homogenous Competitors:
When competitors are similar to each other
Lack of competitive advantage
Companies have to work extra hard to gain market share
Very aggressive competition
Ex: Bread, Milk, etc.
Low Industry Growth Rate:
Lower volume long term
More aggressive competition
Low profitability n
Niche markets like umbrella market
The capacity of Competitors:
If competitors are at max production capacity, competition is not aggressive
High profitability
Ex. Lemonade stands are at max production capacity on hot days’ they will run out of lemons
Low Consumer Switching Costs:
If consumers can switch easily (churn), competition is more aggressive
Low profitability
Ex. Gum, many brands have similar flavors, so low switching costs
Products viewed as Commodities or Perishable:
If consumers view the product as a commodity (homogenous), they will not care which brand they buy
Price competition is much more aggressive
Very low profitability
Ex. Fruits and Vegetables
Exit Barriers:
Low exit barriers allow customers to leave the market whenever they want.
Aggressive competition to retain customers.
Ex. Companies make leaving subscription plans complicated to create exit barriers.
Solutions:
Grow Market Share
Acquisition of competitors
Create/increase consumer switching costs
Differentiation
Look at Diamon-E to determine the best solution
P5F Breakdown: Threat of New Entrants (3)
The threat of New Entrants:
The easier it is for new competitors to enter the market, the more profitability declines.
The market will become saturated
The ability to keep future competitors out determines profitability long term
Determined by barriers to entry
New entrants often use innovation to permeate the market, such as Airbnb and UBER.
Barriers To Entry:
Cost Related:
Economies of scale (high output)
Capital requirements
Other cost advantages such as learning curves, specialized assets like tech
Ex. Entry may require large capital requirements such as the automobile industry
Customer Related:
Differentiation: Customers are either brand loyal or have high switching costs.
Distribution Channels: Firms secure contracts with distributors. Ex Lays will secure a contract with Sobeys to secure shelf space, making it harder for other potato chip manufacturers to enter the market.
Ex. Apple has high brand loyalty and switching costs
Ex. Sobeys may negotiate an exclusive distribution deal with Lays.
Government Regulations:
Regulations make entering the market harder.
Ex. Banking and cell phone service. Government has to give you permission to create a bank.
Solutions:
Grow to achieve scale
Control distribution network
Lobby government to create regulations
Differentiate, and create brand loyalty and identity
Lock customers in
P5F Breakdown: Threat of Substitutes (4)
The threat of Substitutes:
More substitutes = less profit
Cheap substitutes eat away at the bottom end of your market
Not as convenient, or comfortable, but since it is cheaper people make do.
The cheaper and better the substitute, the more likely it steals market share
Substitutes put a cap on your prices (price ceiling)
Factors:
Many Good Substitutes:
Consumers have many good options
Aggressive competition
Low profits
Ex. Ritz Crackers, have many different substitutes like cookies or chips
Low Switching Costs:
Consumers can switch easily or cheaply
Aggressive competition
Lowe profits
Ex. Switching from one gum brand to another is really easy, consumers do not think twice
High Buyer Propensity to Substitute:
The likelihood that consumers will substitute for a competitor rather than your product
Consumers are more likely to switch to other substitutes instead of you
Firms will spend more money on marketing
Aggressive competition
Low Profits
Ex. Butter can easily be substituted for margarine
Improvements in Price vs Performance Trade-Off:
Over time, substitutes innovate and improve
Substitutes become better, but the price stays the same
Lowers price ceiling
Ex. One Plus Phones, cheaper for better
Solutions:
Strong marketing/differentiation
Create switching costs
Lock in customers
P5F Breakdown: Bargaining Power of Suppliers (5)
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Provides the key inputs for the firm
Changes in cost of inputs affects market as a whole
The more power suppliers have to negotiate prices, the less profitability in industry
Factors:
Few Suppliers:
Suppliers know you need them, since there is less choice
Can negotiate higher prices
There may be many good substitutes for this input
Less supply for required inputs, causes aggressive competition and bidding wars
Low profits
Ex. Diamond Mines, can be substituted for other gems
Few Good Substitute Suppliers:
More supplier negotiating power, as there are no alternatives
Low profits
Ex. In the automobile industry there are no rubber tire substitutes
High Switching Costs:
If cost to change inputs are high, you will be resistant to switching supplier
Unique inputs usually have high switching costs
Low profits
Ex. Factory can give bulk discounts, or can lock a buyer into contracts
Low Importance:
You will be less likely to negotiate low prices if you are unimportant
You need supplier, but supplier does not need you
Ex. Walmart has a lot of negotiating power with suppliers because they are a huge chain
Threat of Forward Integration:
Concern that the supplier may enter industry and become a direct competitor
Ex. Disney and Netflix. Disney stopped supply Disney movies to Netflix and instead launched their own streaming service.
Solutions:
Form strategic alliance with supplier
Internal supply, create your own products, like Netflix making shows.
Long run: redesigned product or reevaluate inputs
P5F Breakdown: Bargaining Power of Buyers (5)
Bargaining power of Buyers:
Who pays for your product?
Effects: Reduces price that you can charge; increases costs.
Factors:
Few/Concentrated Buyers:
If buyers are few in number, they have more bargaining power over you, and can demand lower price
Low profit
Ex. Niche markets like designer umbrella market
Discretionary Purchase; Purchase Significance:
Non essential items people buy if they have extra money
Low purchase significance = it is not a need
Keep prices low to motivate buyers
Ex. Includes recreational activities like yoga classes are non essential
Ex. Life threating meds like insulin are essential
Standardized Products; Switching Costs:
These products have low switching costs, reducing profitability
Makes it easy to switch between brand, company has to work harder to keep customer loyal
Ex. Commodities such as milk or gas.
Financially Motivated:
Determines motivation of the buyers to buy your product
Cost Significance: As things get more expensive consumers try to negotiate the price. Ex. Cars, houses.
Profitability: If you affect buyer’s profitability, they will not negotiate the price. Ex: A gumball from a gumball machine
Cost Savings: How much the consumer saves when they buy from you vs competition. Ex. Consumers love to shop at stores when they are running sales.
Threat of Backwards Integration:
If buyer may become competitor, that is a problem
You lose a buyer as well as gain a competitor
Gives buyer more bargaining power
Lower profits
Ex. Apple bought intel chips, then decided to create their own chips
Solutions:
Form alliance with other sellers (illegal, price fixing)
Strong marketing/differentiation
Create high switching costs, lock customers in
Application of Porter’s Five Forces
Expansion Questions:
- How profitable is this industry? Do I enter or not?
- Can I enter? What are the barriers to entry?
Profitability Questions:
- What factors are affecting our revenues and costs?
- What can we do to be more profitable?
Competition Questions:
- Concerns reducing rivalry to improve profitability
- What barriers to entry can we create?
- What are our competitors and how do we reduce head-to-head competition?
Steps to Connect Models to Solve Issues
1- Identity KSF affected by the problem
2- Identify KPI that affect the KSF
3- User Porter’s Five Forces and PEST to determine if the issue is industry-wide
If it is an industry issue, analyze competitors to determine the strategy
If it isn’t an industry issue, use DIamond-E or Generic Strategies to reevaluate strategy
Connecting The Models
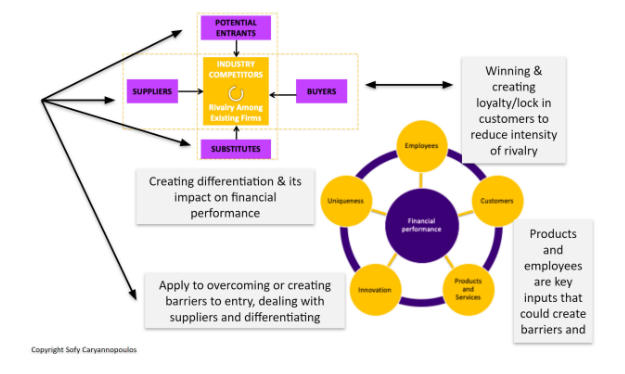
Key Success Factors:
Apply to overcome or create barriers to entry
Am I doing a poor job in one or more KSF or KPI?
What tactics/strategies can I Implement to fix this?
Porter’s Five Forces:
Is the cause an industry factor? Compare your situation to competitors.
What tactics/strategies can I implement to fix this?
PEST Factors:
Has something changed in one of these factors? Is this change an underlying cause of issues identified above?
Cross Model Connections:
Under what conditions does pursuing a broad versus narrow target make sense? How does the Diamond-E inform the selection among the four generic strategies?
How can you harness insights from Porter’s Five Forces to understand the significance and the impact of key success factors by profitability? How do actions recommend for KSF’s align with strategies recommended by Porter’s Five Forces?
What KPI’s might be affected (and in what way) by factors related to Porter’s Five Forces? How might they indicate SWOT in Diamond-E?
Identify some key success factors that are related to reducing the negative forces on profitability that you might identify using Porter’s.
How does the Diamond-E connect to Porter’s Five Forces? Provide an example of how you would apply Diamond-E to identify strategies for dealing with challenges using Porter’s Five Forces.
How can changes in PEST impact each of Porter’s Five Forces? Identity specific elements of PEST that might change and explain the connection to the Porter’s Force and the effect it will have.
PEST - Social Factor Elements
customs, habits, values/attitudes, demographic characteristics
Significance of social factors
affect customer preferences and worker attitudes and behaviour, standards of business conduct, and corporate social responsibility
what are demographics
study of human populations
cohorts
homogeneous groups within the larger population
why are demographics important
powerful predictor of behaviour/trends, certainty and simplicity of age data, predicts supply and demand and informs environmental analysis and human resource decisions
4 elements of demographics (diamond)
cohort size, cohort characteristics, cohort participation, future and trends
size of cohort
number of people in each age group
factors affecting cohort size
fertility rate, birth rate
activity participation rate
percentage of cohort that engages in a behaviour
cohorts in order
WWI, roaring twenties, depression babies, WWII, baby boom, gen x, millennials, gen z
implications of aging boomers, fewer youth
increased elder care needs, increased number of vulnerable seniors
cohort characteristics - factors
economics, technology, world events/news, parenting
cohort characteristics - characteristics
values and priorities, lifestyle, habits (digital and other), mindset
cohort characteristics - implications
how to attract retrain motivate, what makes a product appealing, how to attract as consumers, how much they spend and what they spend on
boomers characteristics
prefer in-person transactions, long hrs in office, 1 career and company
gen x characteristics
research online but buy in store, brand loyal, flexible work, perfect career
millenials characteristics
digitally savvy, quality over brand, want authenticity, access over ownership, will change jobs
gen z characteristics
digitally savvy, value uniqueness, want to know brand, frugal and avoid debt, several careers
Financial Institutions
facilitate the flow of money from sectors with surpluses to those with deficits
4 Financial Pillars
1) chartered banks
2) alternate banks (trust companies, credit unions)
3) specialized lending & saving intermediaries
4) investment dealers
Financial pillar #1: chartered banks
-a privately owned, profit-seeking financial intermediary that serves individuals, businesses & non-business organizations
-main source of short-term loans for business firms
Financial Pillar #2: alternate banks
-trust companies - safeguards funds and estates entrusted to it; may also serve as trustee, transfer agent, and registrar for corporations
ex: a corporation selling bonds to investors appoints a trustee, usually a trust company to protect the bondholders interests
OR
-credit unions - cooperative savings and lending association formed by a group with common interests
ex: lend money to businesses & consumers who use the money to buy durable goods
Financial Pillar #3: specialized lending & saving intermediaries
- Life insurance companies -shares risk with its policyholder in return for payment of a premium from policyholders
- factoring companies - buys accounts receivable from a firm for less than their face value then collects the face values of receivables
Financial Pillar #4: Investment dealers
-primary distributors of new stock and bond\ issues
-facilitate secondary trading of stocks and bonds, both on exchanges and over the counter stock and bond markets
Bonds
-Certificates of debt that carry a promise to buy back the bonds at a higher price
-a company/ government borrows money from you (investor). they pay interest (coupon) each year and pay off the debt (face value) on an agreed date (maturity date)
Yield
- percentage return on any investment
-helps compare investments
- yield = what you made/ what you paid
Interest on a bond
coupon rate x face value
Capital gain on a bond
face value - purchase price
Approximate yield to maturity
(coupon rate x (face value + (face value - price paid)/ years to maturity) / price paid
What impacts the coupon rate at bond issue
-environment: prevailing interest rates
-company: credit rating of issuer
-product: features
What impacts bond price when traded?
- environment: changes in prevailing rates of interest; inflation
-company: changes in credit rating
- product: coupon rate relative to the return on other equally risky investments
Stocks
Securities that represent part ownership or equity in a corporation
Common stock
the most basic form of ownership, including voting rights on major issues, in a company
preffered stock
Preferred stock typically has limited or no voting rights, but its holders are paid dividends or receive repayment priority in the event the corporation is liquidated
Impacts of stock price
-present value of expected future cash flows
-anything that effects demand and supply of stock
What effects expected future returns?
- environment: economy, interest, PEST, industry conditions, changing dynamics
-company: choices, strategies & changes in diamond E
Leverage
value of initial investment is greater than dollars available to invest
Buying on margin
paying a small percentage of a stock's price as a down payment and borrowing the rest
Going Long
purchase stock with your money only
Selling short
selling stock that has been borrowed from a brokerage firm and must be replaced at a later date
-buy low, sell high
elements of technology (PEST)
internet, information technologies, materials and equipment
5 industries changed by tech
music, travel, transportation, publishing, retail
complementary goods
goods and services that enhance the value of the product and service you're selling
technology standard
enables compatibility of complementary good
installed base
number of users
network effect
value increases as user base grows
vicious/virtuous cycle
availability of complementary good, attractiveness to users, number of users, attractiveness to producers of complementary good
solutions for virtuous/vicious cycle
compatibility, partnerships, incentives for complementary goods suppliers, build base
lock-in
extent to which a customer is committed to a product or service
big data and analytics
collection and analysis of large amounts of data
big data and analytics - benefits
deeper insights, better and faster decisions, predictive capabilities, foundation of AI and machine learning
big data and analytics - use examples
customization, automation, optimized operations, personalization
e-commerce
online research and shopping
omnichannel
seamless experience between platforms, online and physical experience
ecommerce and omnichannel benefits
enhanced marketing and service, improved efficiency, higher margins
ecommerce and omnichannel use examples
customization, optimized operations, automation
VR/AR
replicates an environment or maps over reality
VR/AR benefits
experience without purchase or proximity, reduced cost, enhanced experience