Urology Boards Images
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is this?
contrast extravasation at Right Ureter
What is this?
"Drooping Lily” sign seen at the Right kidney. Occurs in a duplicated system when the obstructed/dilated upper moiety pushes down on the lower moiety creating a drooping Lily appearance.
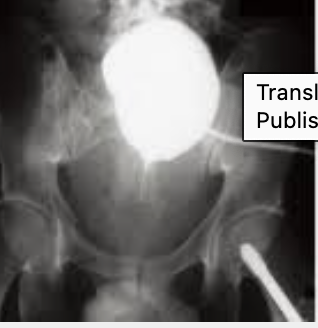
What is this?
“Pie in the sky” - high bladder after trauma suggesting pelvic hematoma. Raises concern for urethral injury.
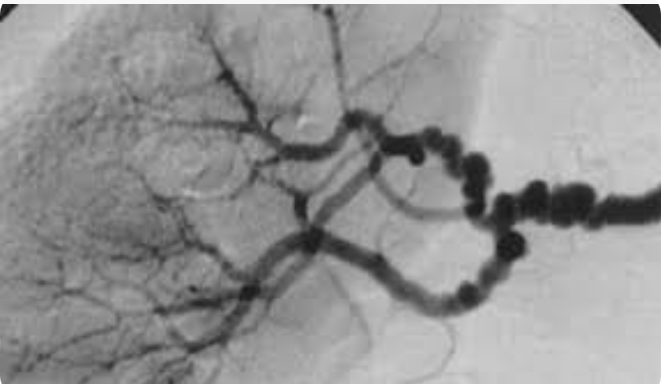
What is this?
Angiography showing “string of pearls” = Fibromuscular Dysplasia
What is this called and why does it happen?
Dromedary HUmp, usually occurs on the left side as the spleen pushes down on the kidney causing it to buldge, Just compression, not a tumor.
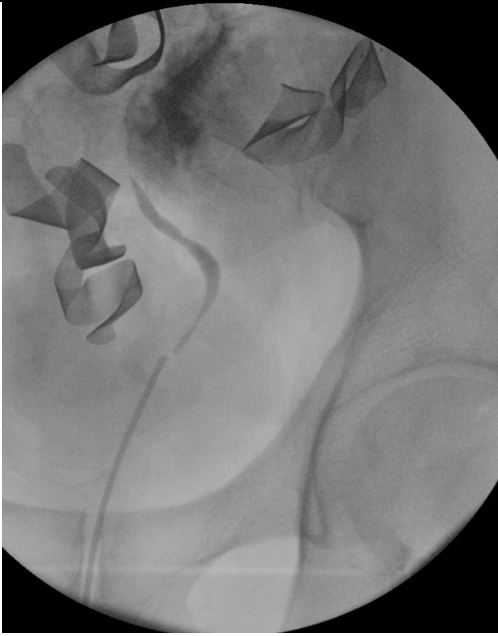
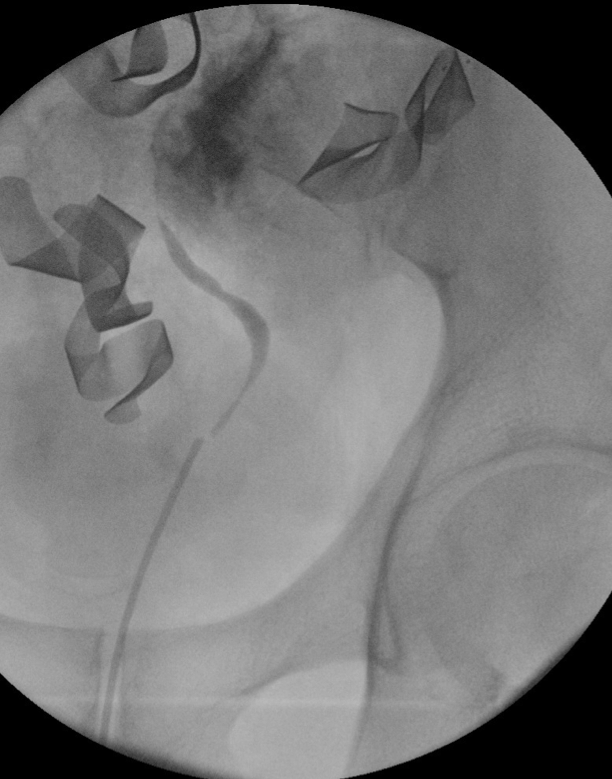
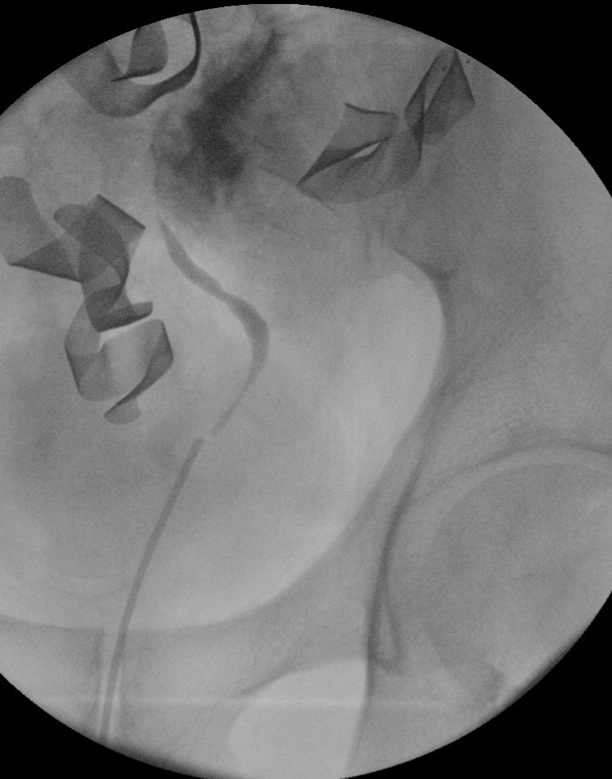
Intraoperative retrograde pyelography revealing left sided ureteral defect from blast injury
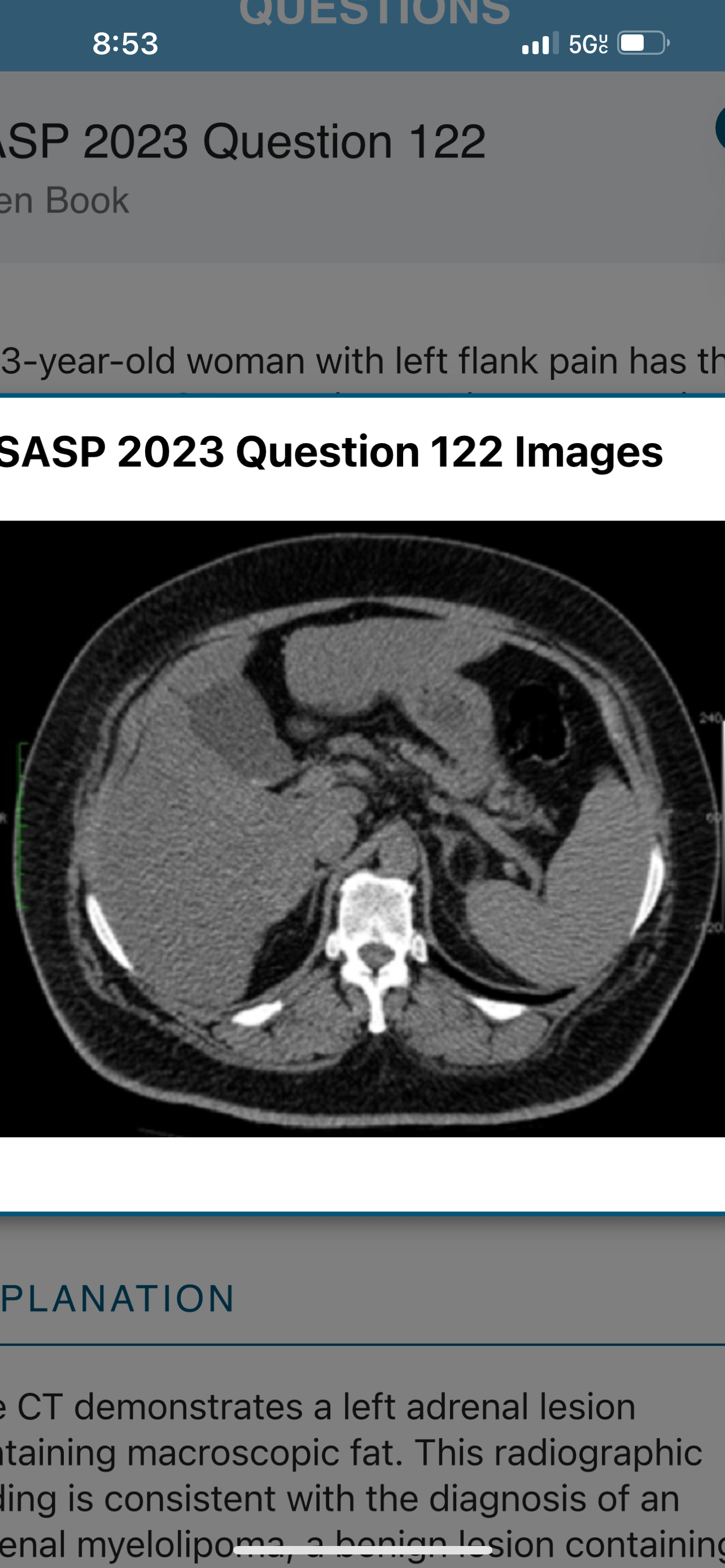
What is this?
T2 image of the MRI shows an abnormality in the anterior prostate which is dark
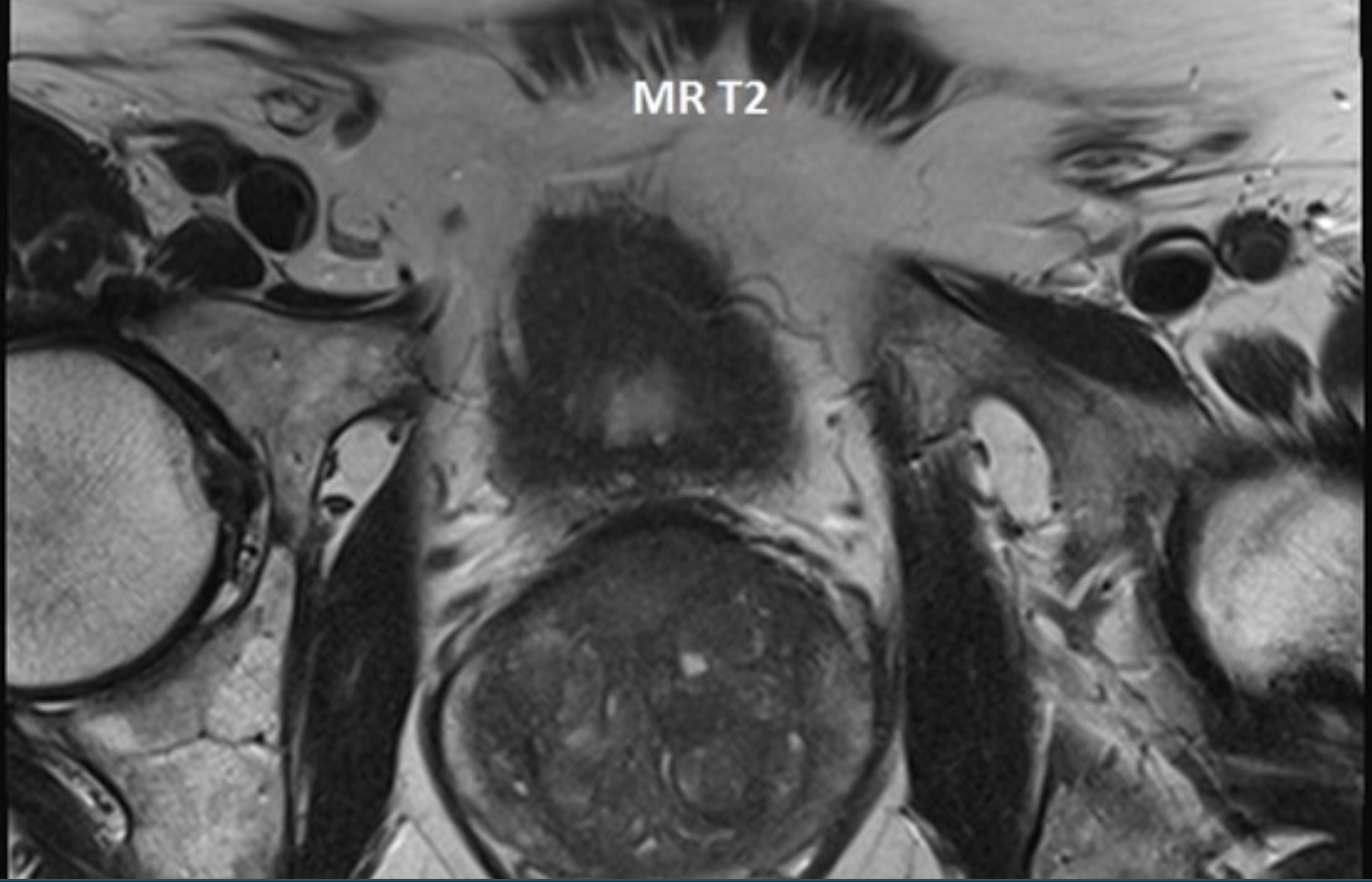
What is this?
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Map (ADC) for prostate cancer, demonstrating suspicious pirads 4 lesion in anterior prostate also dark
ON T2 imaging how do pca lesions appear?
DARK
On DWI images how do pca lesions appear?
BRIGHT WHITE
ON ADC (apparent diffusion coefficient) how do pca lesions appear?
Dark
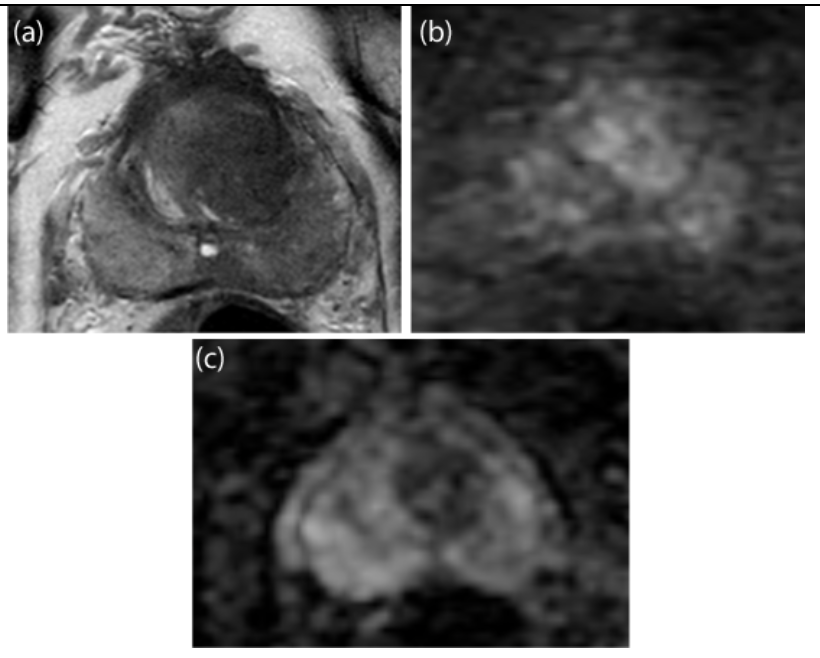
Describe the lesions in a) T2 imaging b) DWI c) ADC
Axial T2 weighted image (a) demonstrate an hypointense mass (arrows) with ill-defined, “smudgy” lesional margins. The mass restricts diffusion as it is bright on high b value (b1400) diffusion weighted image (arrows) (b) (arrow) and is dark on the ADC map (arrows) (c).
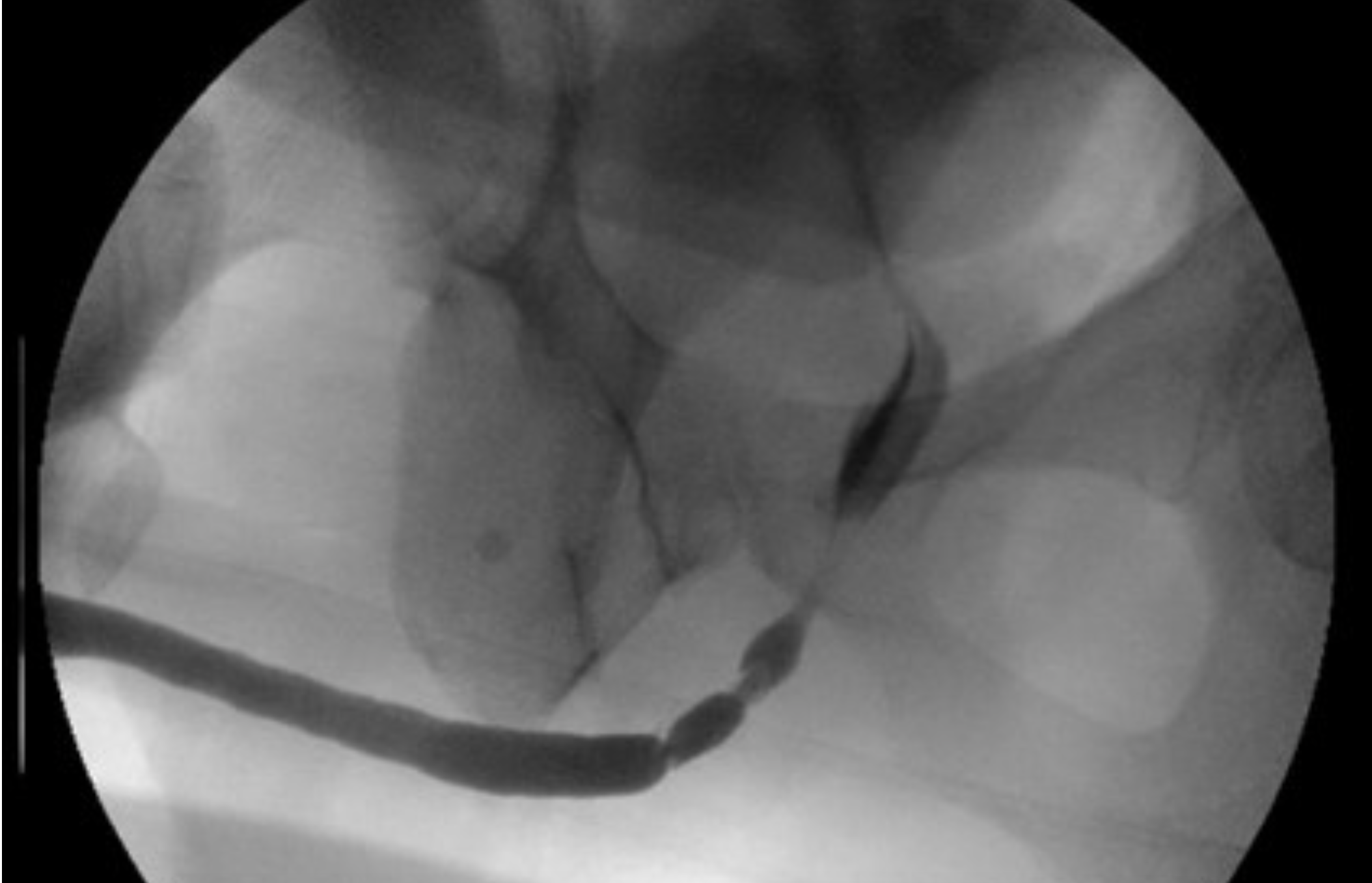
What is this?
5 cm mid- to proximal bulbar urethral stricture
What’s is this ?
Fourniers on scrotal US
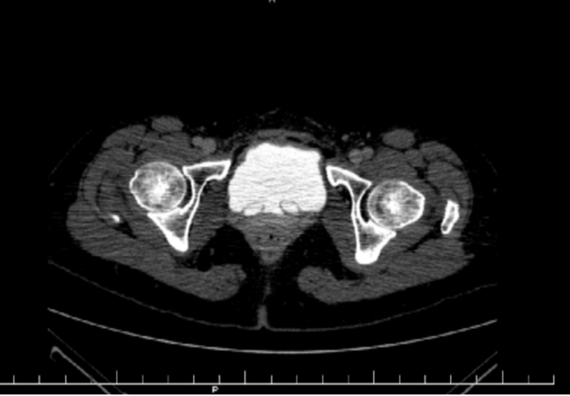
What is this?
B/l ureteroceles
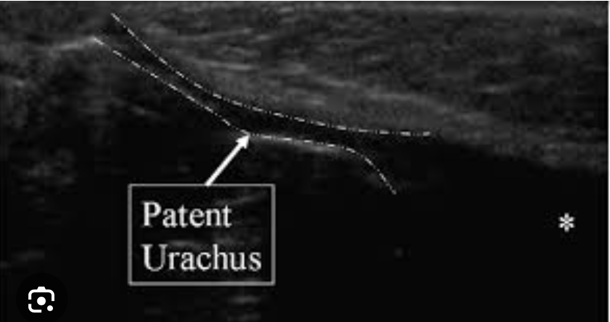
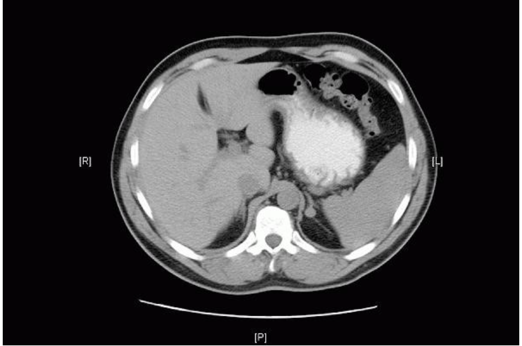
What is this depicting?
Left adrenal mass
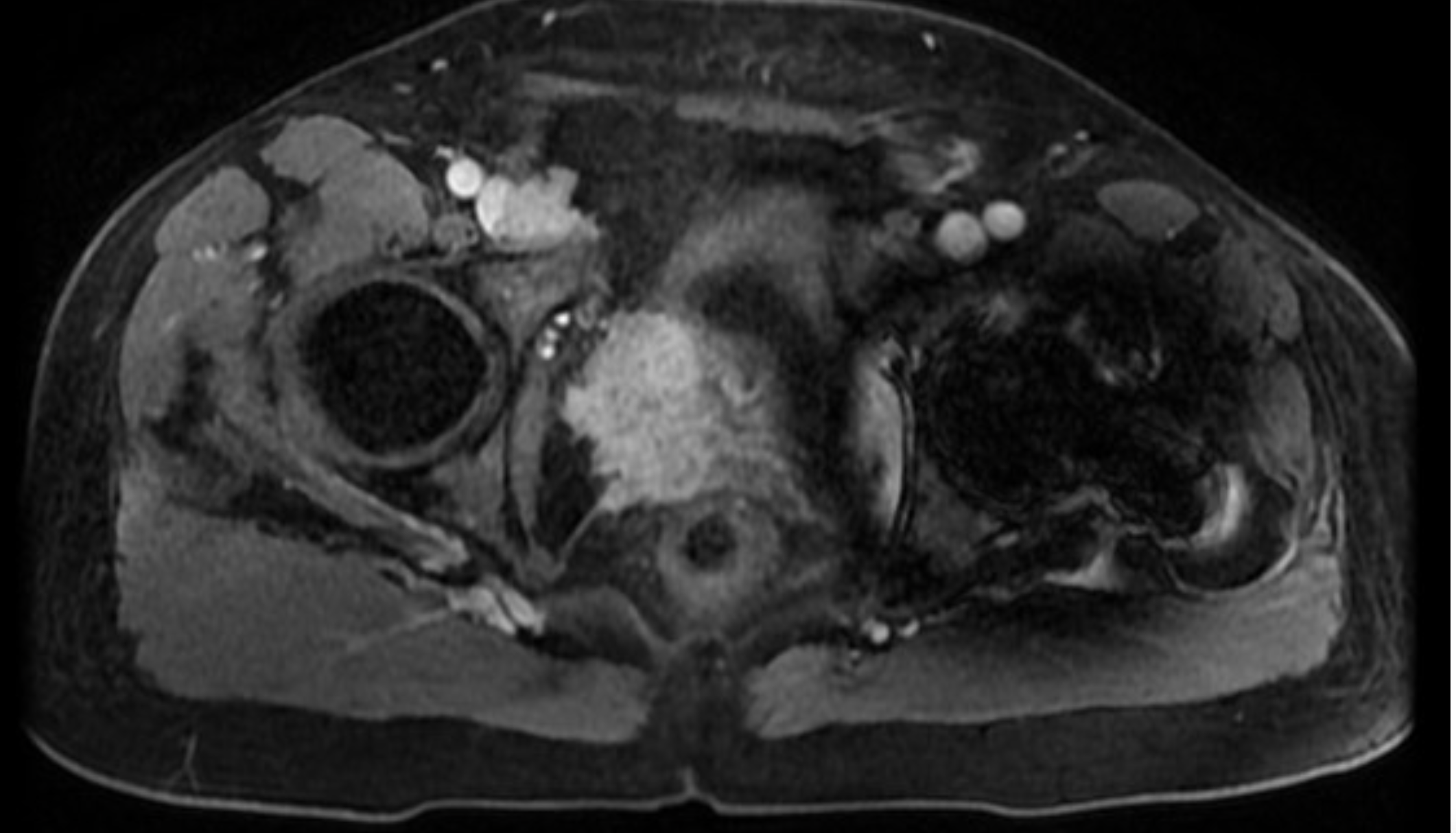
What is this MRI showing?
Prostate cancer on the right with extra capsular extension. And Large right lymph node.
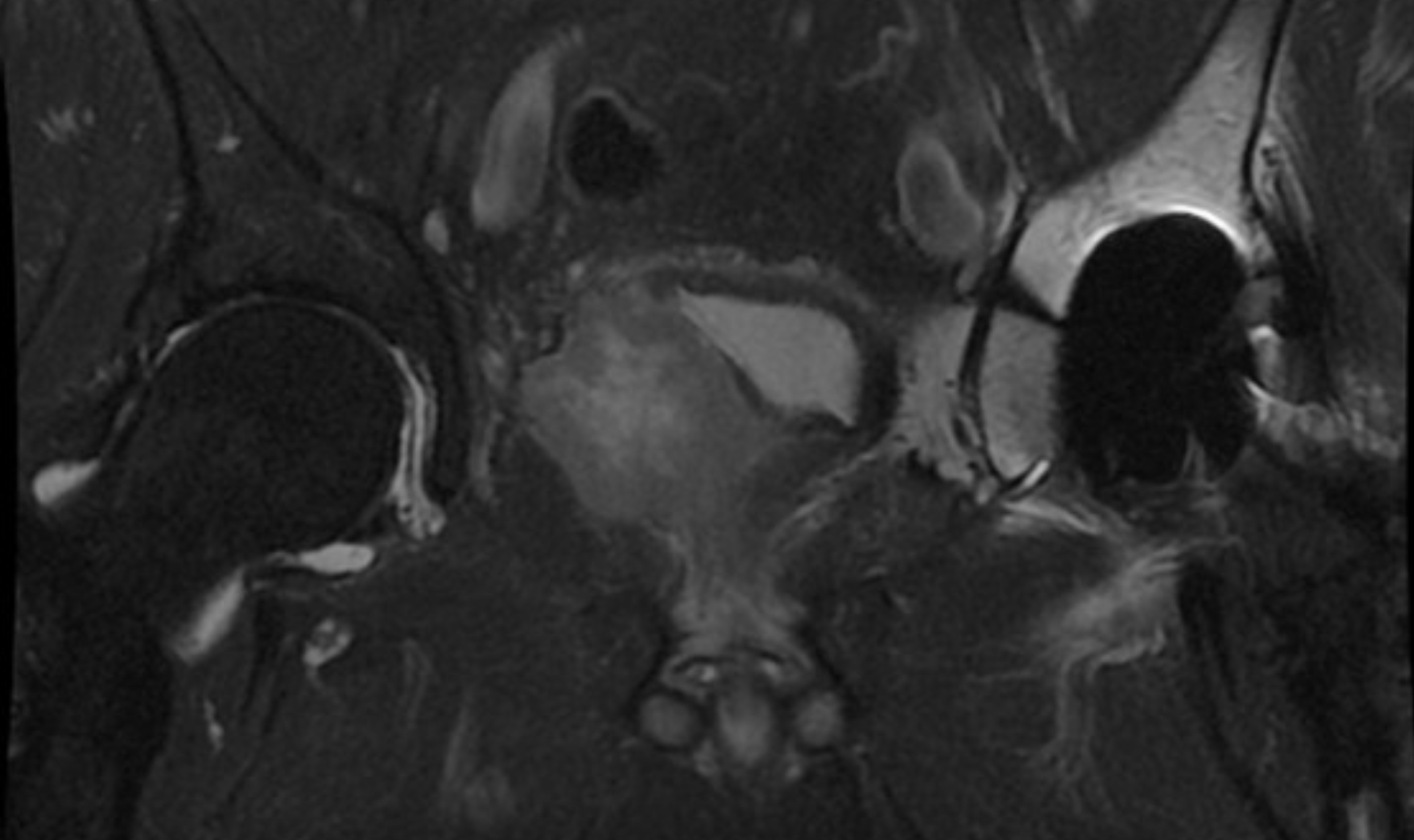
What is this MRI depicting?
Prostate cancer extending into the bladder.
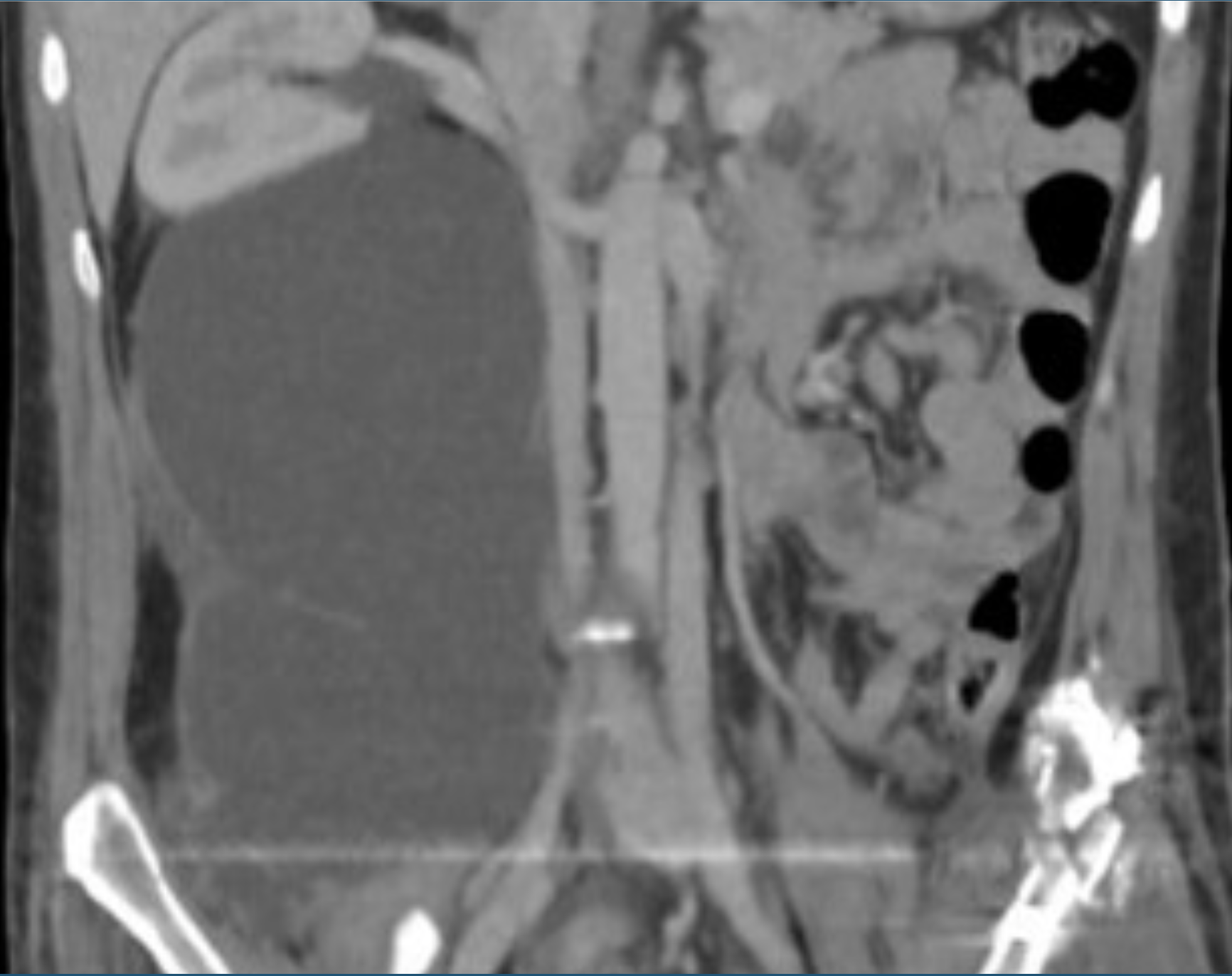
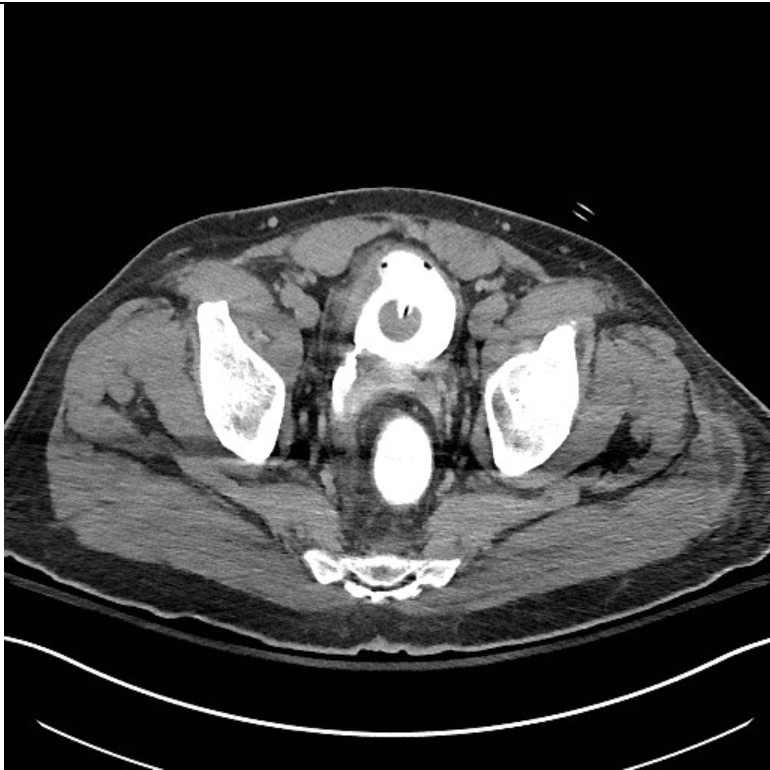
Ct scan shows what?
large retroperitoneal fluid collection and right hydronephrosis
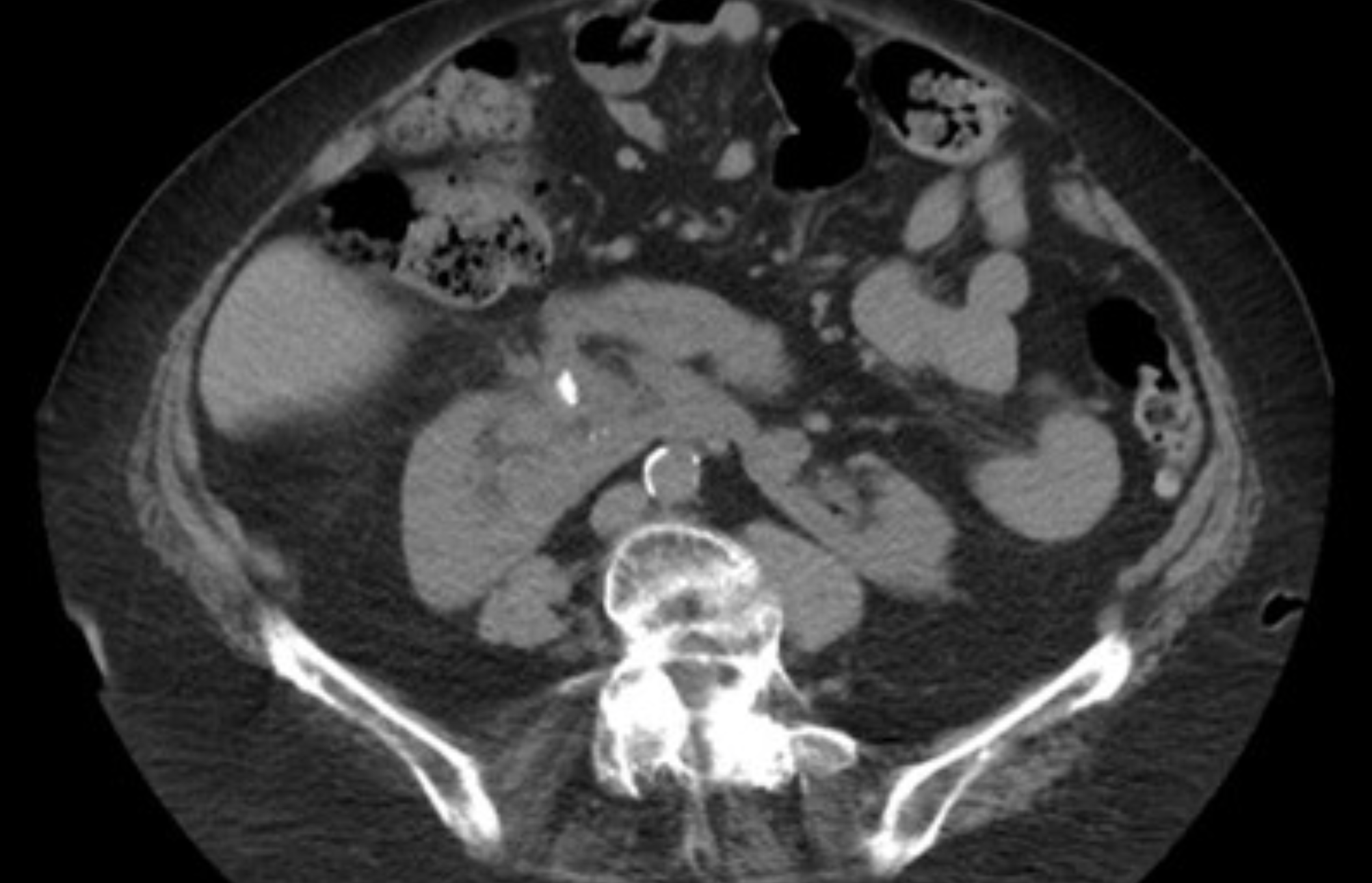
What I this showing? What is The safest method to maximize stone clearance when accessing this kidney 1.5 cm lower pole partial staghorn stone extending to the renal pelvis?
Horseshoe kidney. With large stone burden PCNL is preferred, and for horseshoe kidneys this is via US guided upper pole access!
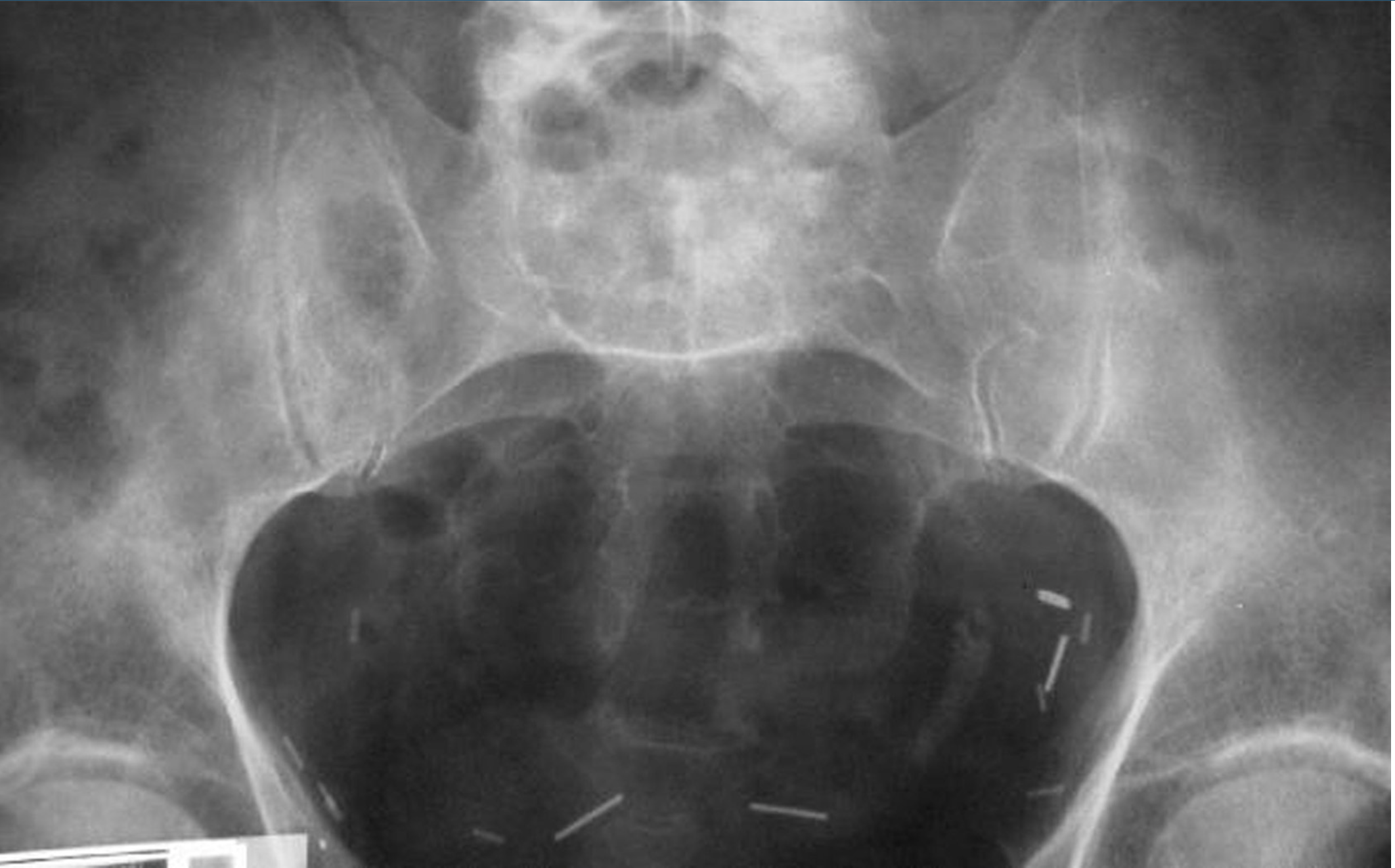
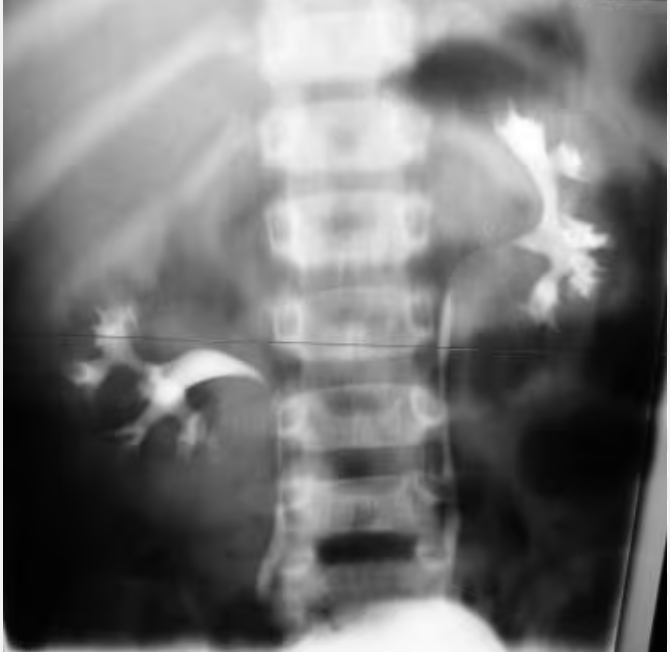
KUB of Patient with ESWL last wee, what do you see?
steinstrasse in the distal left ureter
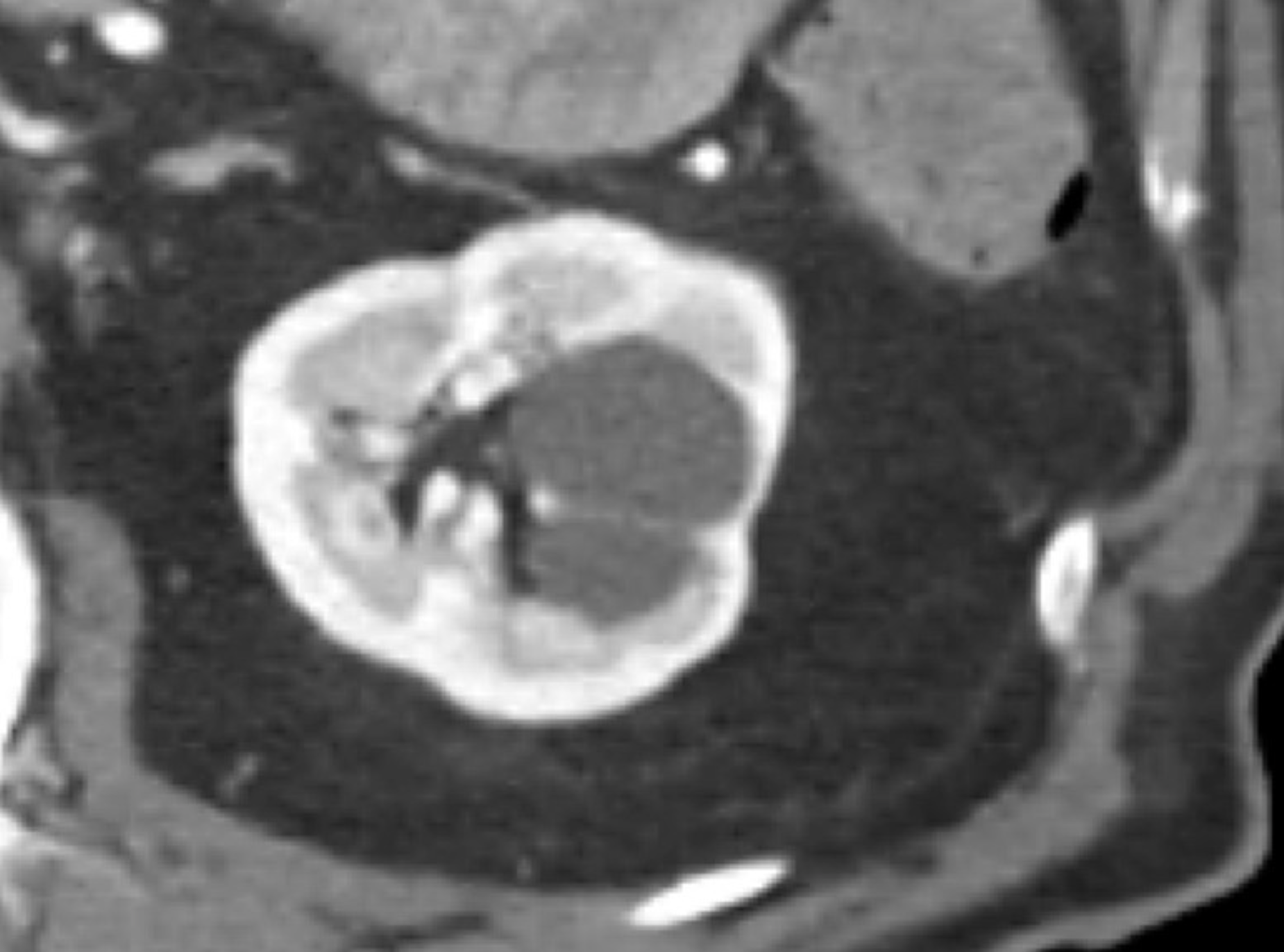
Describe the Bosniak system and Name what class this image is.
Bosniak 1: Well-defined, thin (≤ 2mm) smooth wall, homogenous fluid, no septa or calcification
Bosniak 2: Well-defined, thin (≤ 2mm) smooth walls with: few (1-3) septa (may enhance)
Bosniak 2F: Cystic masses with smooth, minimally thickened (3 mm) enhancing wall or more enhancing septa or many smooth thin (≤ 2mm) enhancing septa.
Bosniak 3: One or more enhancing thick (≥ 4 mm) or irregular enhancing walls or septa.
Bosniak 4: One or more enhancing nodules (≥ 4 mm)
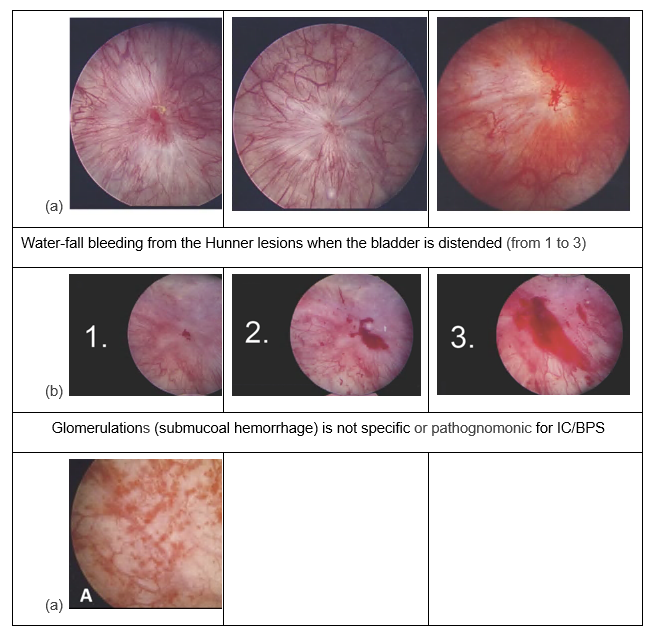
Hunner lesions - classic appearance is blood vessels radiating from a central area of inflammation.
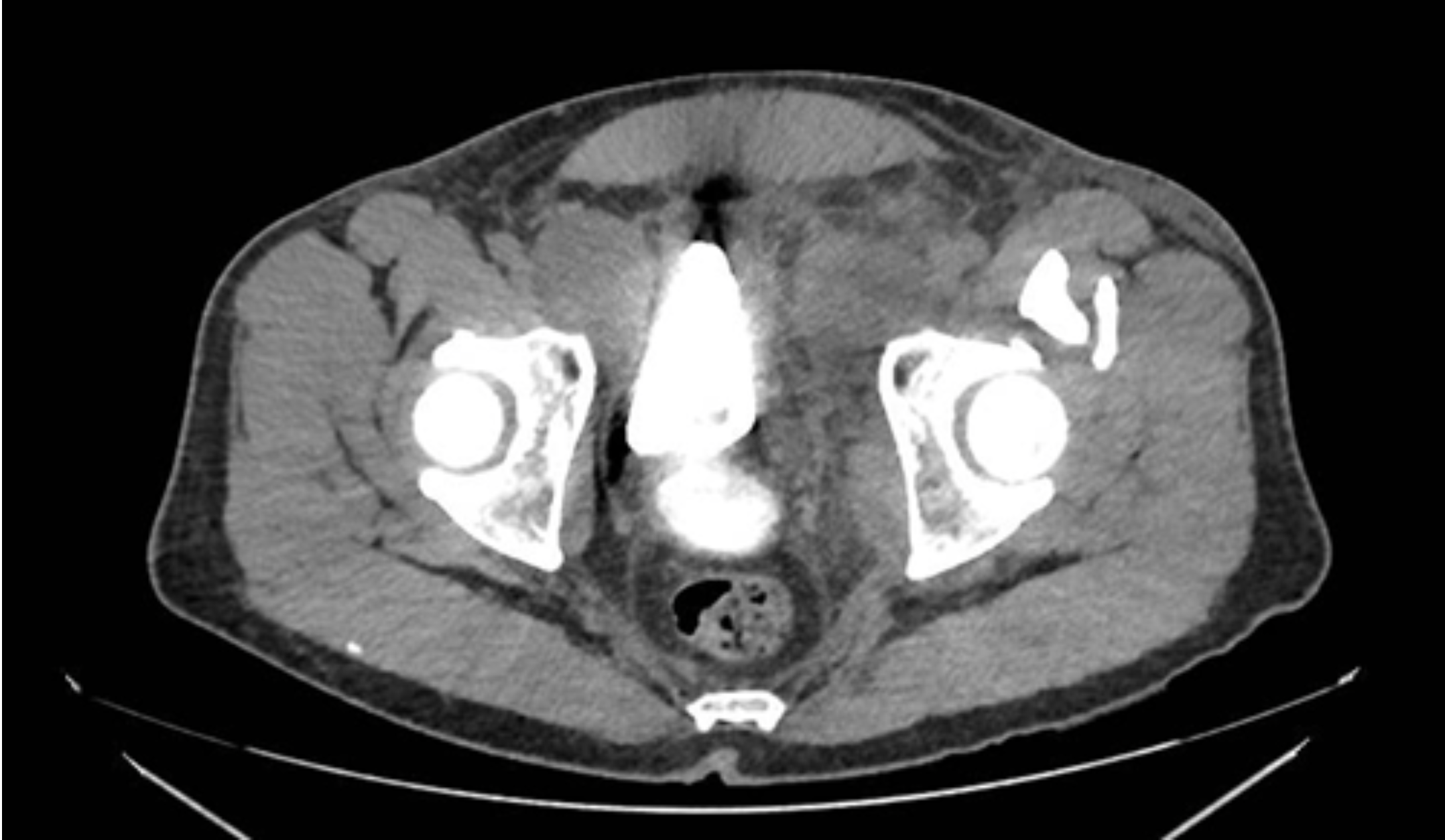
2 weeks post prostatectomy, patient n/v, abdominal pain, and wbc what do we see in the imaging
This patient has a posterior urethrovesical anastomotic leak with bilateral lymphoceles. The left lymphocele has stranding and is mildly enhancing, concerning for infection.
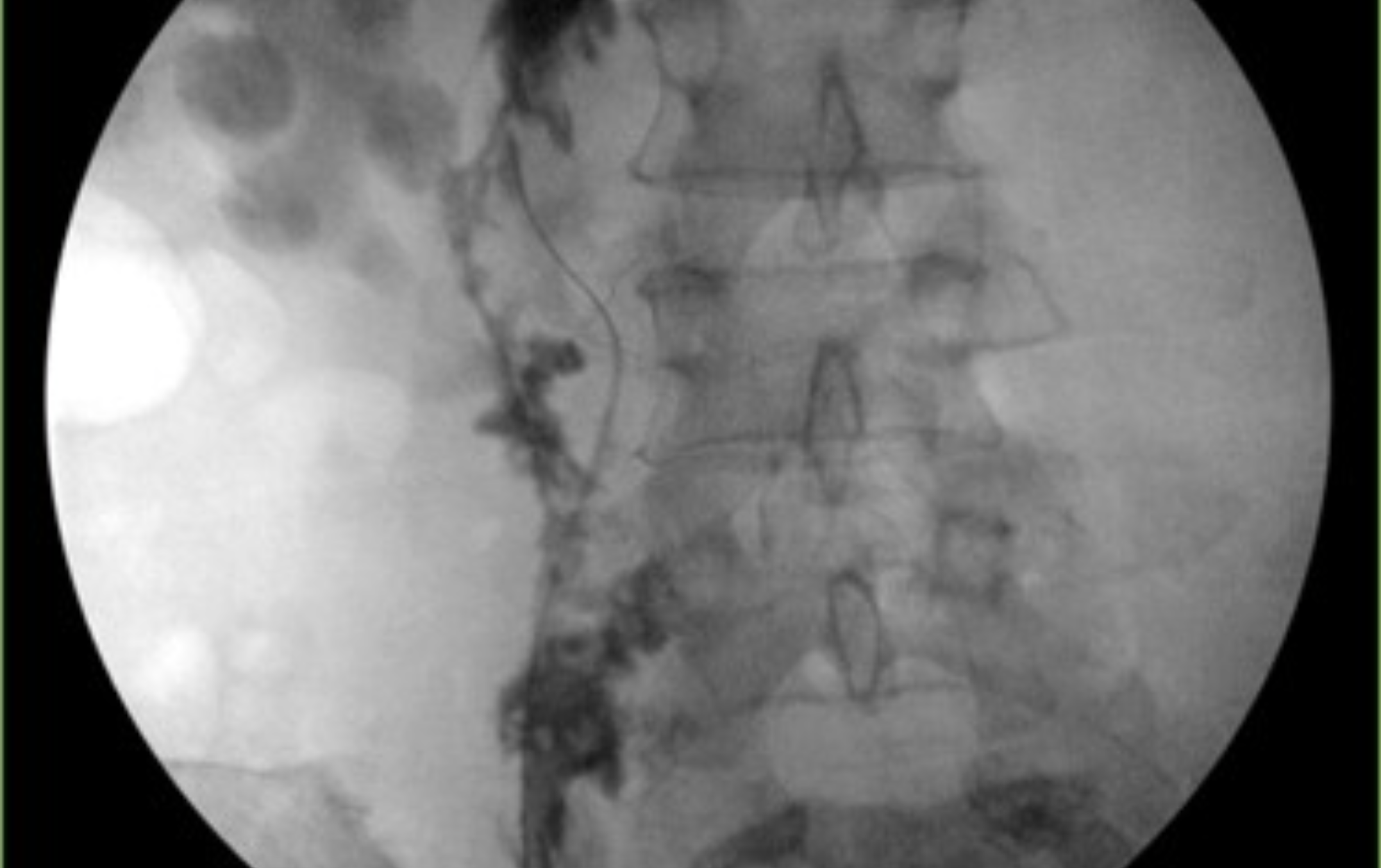
What does this retrograde pyelogram show?
Retrograde pyelogram demonstrates a complete ureteral avulsion
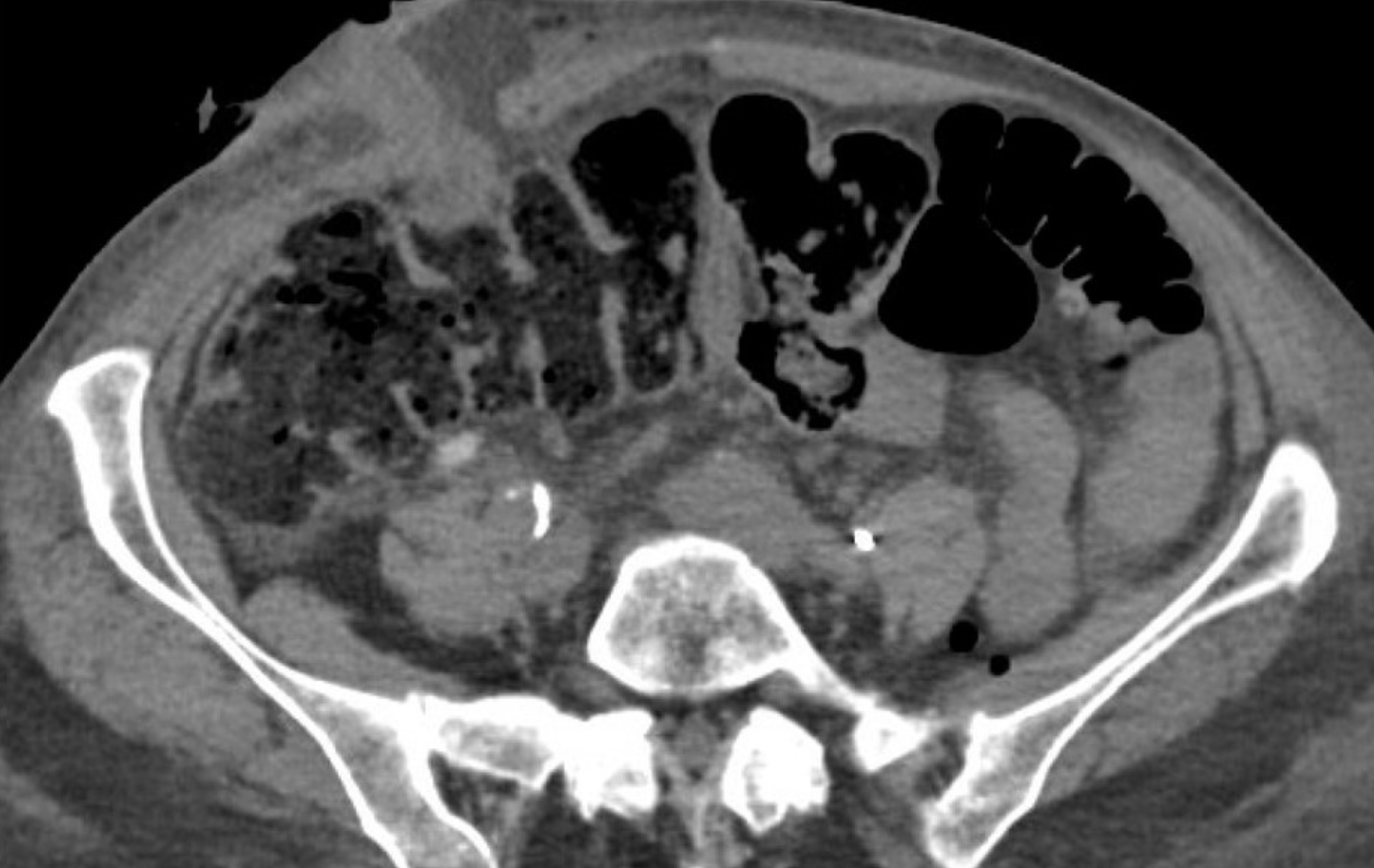
Five days after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit, a 72-year-old woman has mild pain around the stoma. CT is shown
Omentum seen protruding alongside urostomy = stomal dehiscence.
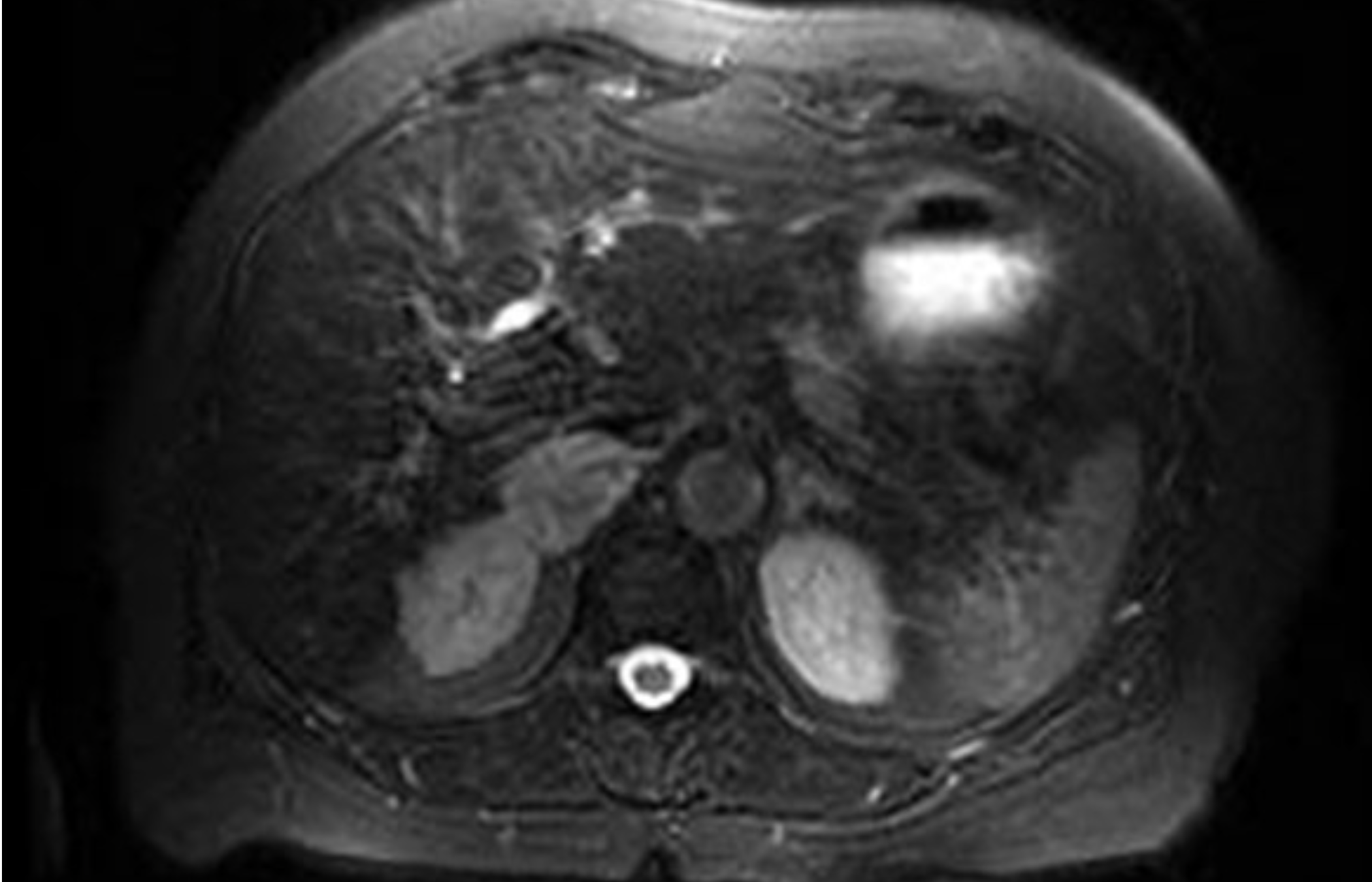
Asymptomatic woman who underwent a right partial nephrectomy for a grade 2 pT1b clear cell RCC has an MRI scan with T2 shown and and out-of-phase sequence images without signal drop-out. What do we think is going on?
She has a right adrenal lesion of moderately increased signal uptake on T2 imaging and without signal drop-out on out-of-phase sequence. These characteristics are found both with adrenal metastases and pheochromocytoma. Must get labs to r/o phew
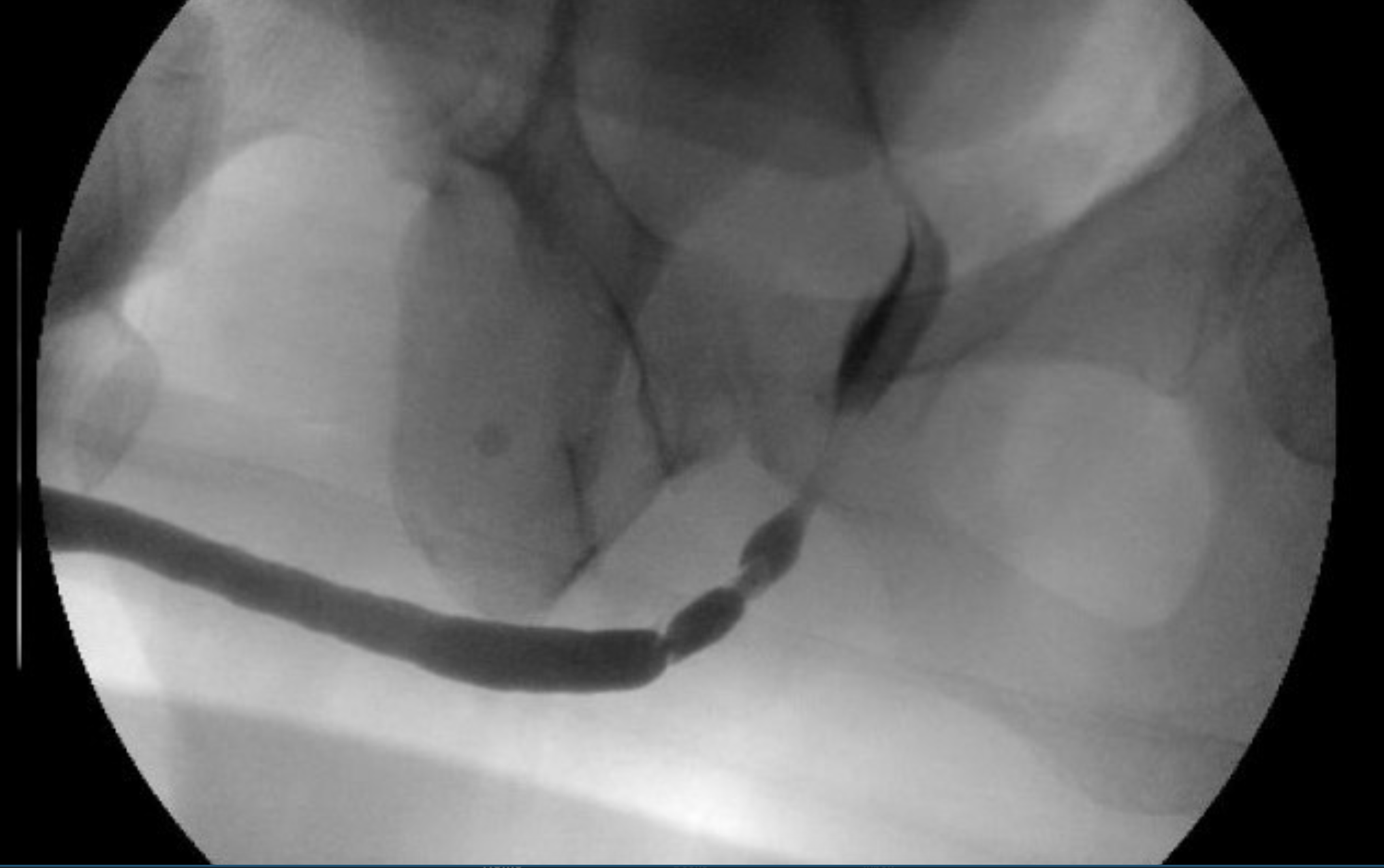
What is the study and what does it show?
study shows a 5 cm mid- to proximal bulbar urethral stricture
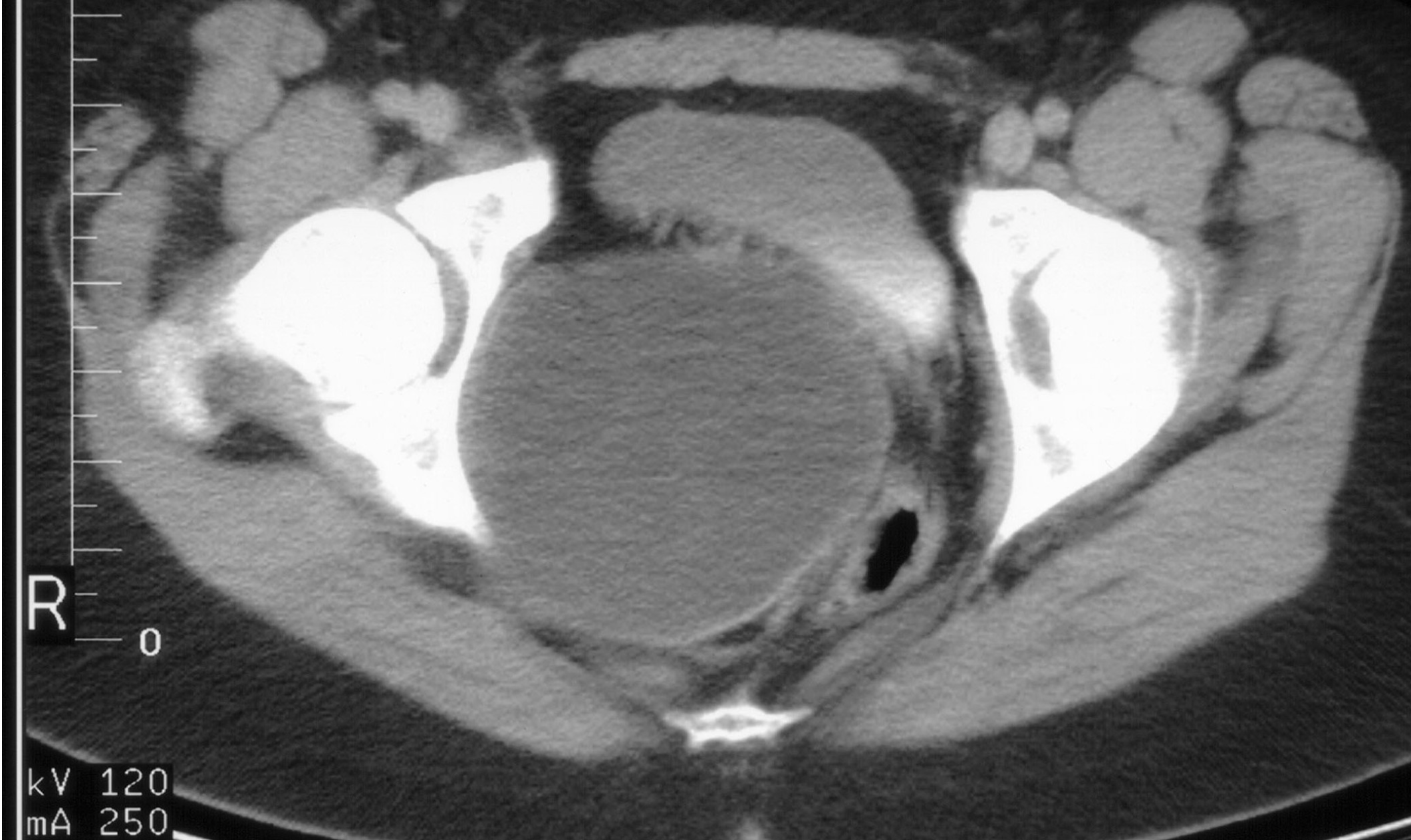
18 y/o with amenorrhea has CT scan shown…what it is it?
CT image demonstrates a large spherical structure filled with fluid containing internal densities consistent with liquefied blood. This patient has a hematocolpos due to vaginal obstruction.
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome occurs in 1:4000 female births and is defined as vaginal agenesis or absence, a rudimentary uterus, normal ovaries, and external genitalia.
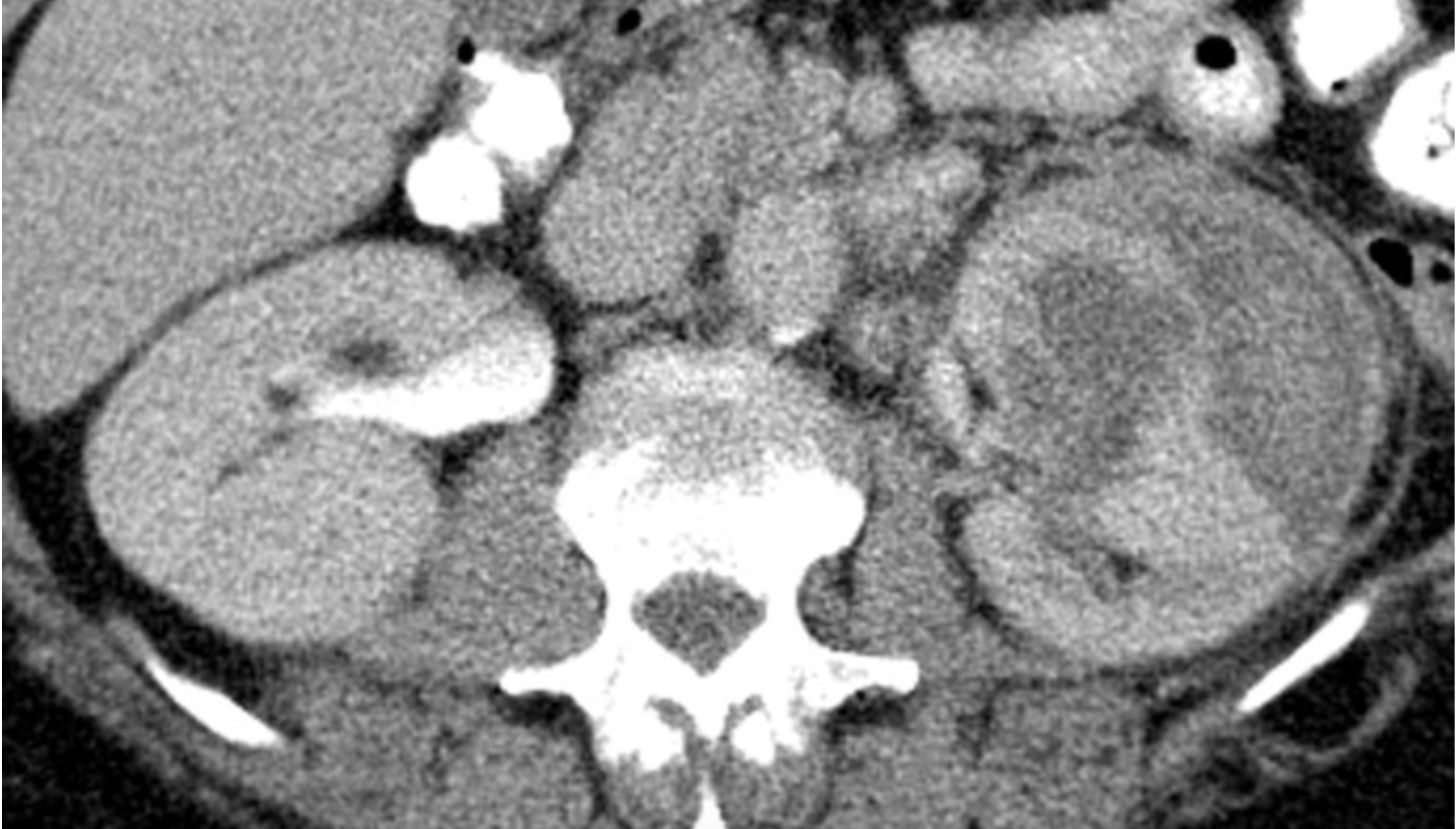
What is being shown here?
Subcapsular hematoma.
While subcapsular hematoma can occur in the absence of renal malignancy, the clinician should always be suspicious of an underlying tumor as a cause for the bleeding. In those cases in which an underlying tumor is not evident, delayed imaging is advised as it can allow evaluation for tumor after the hematoma is reabsorbed.
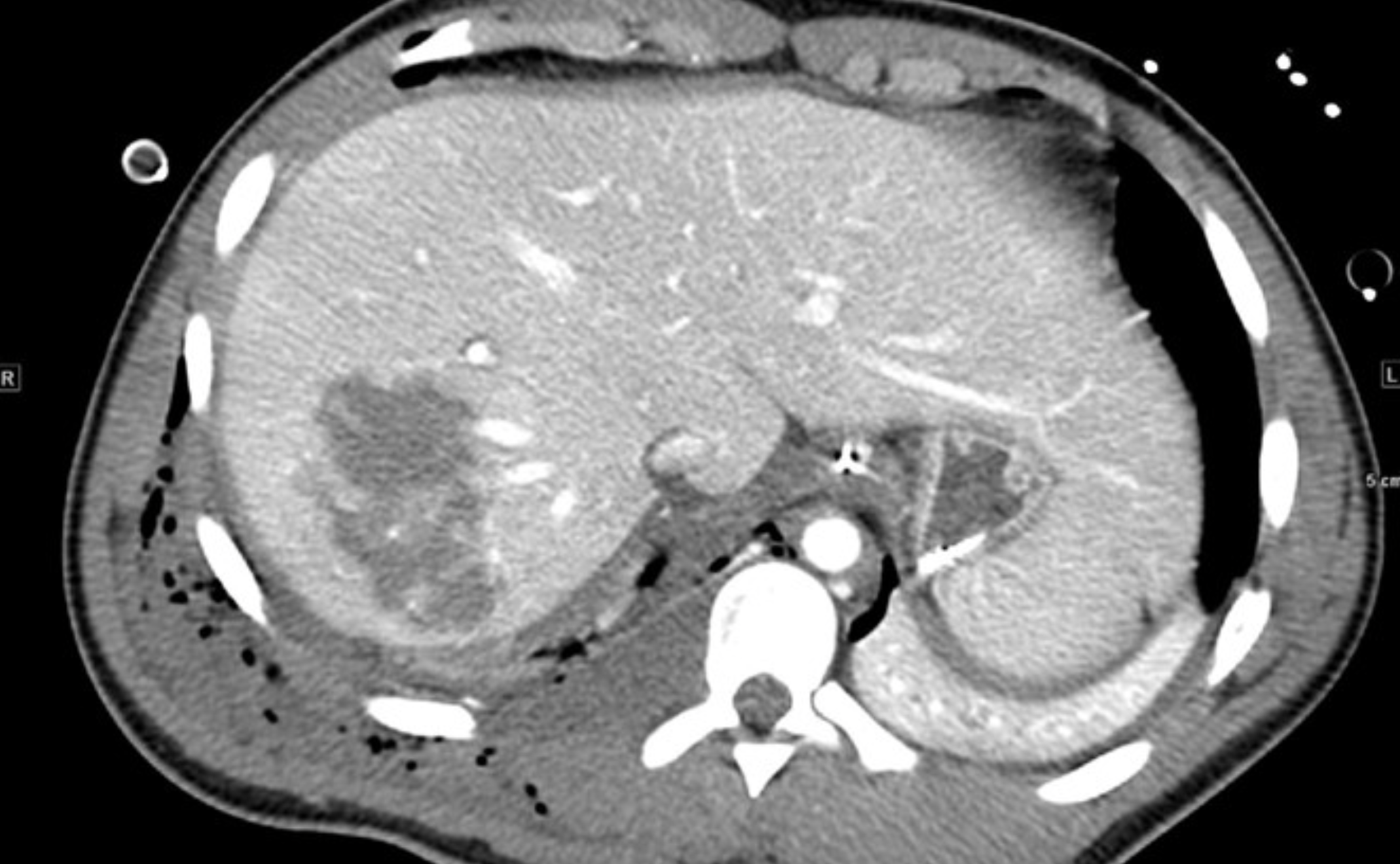
What is CT showing?
The CT scan demonstrates a significant liver injury
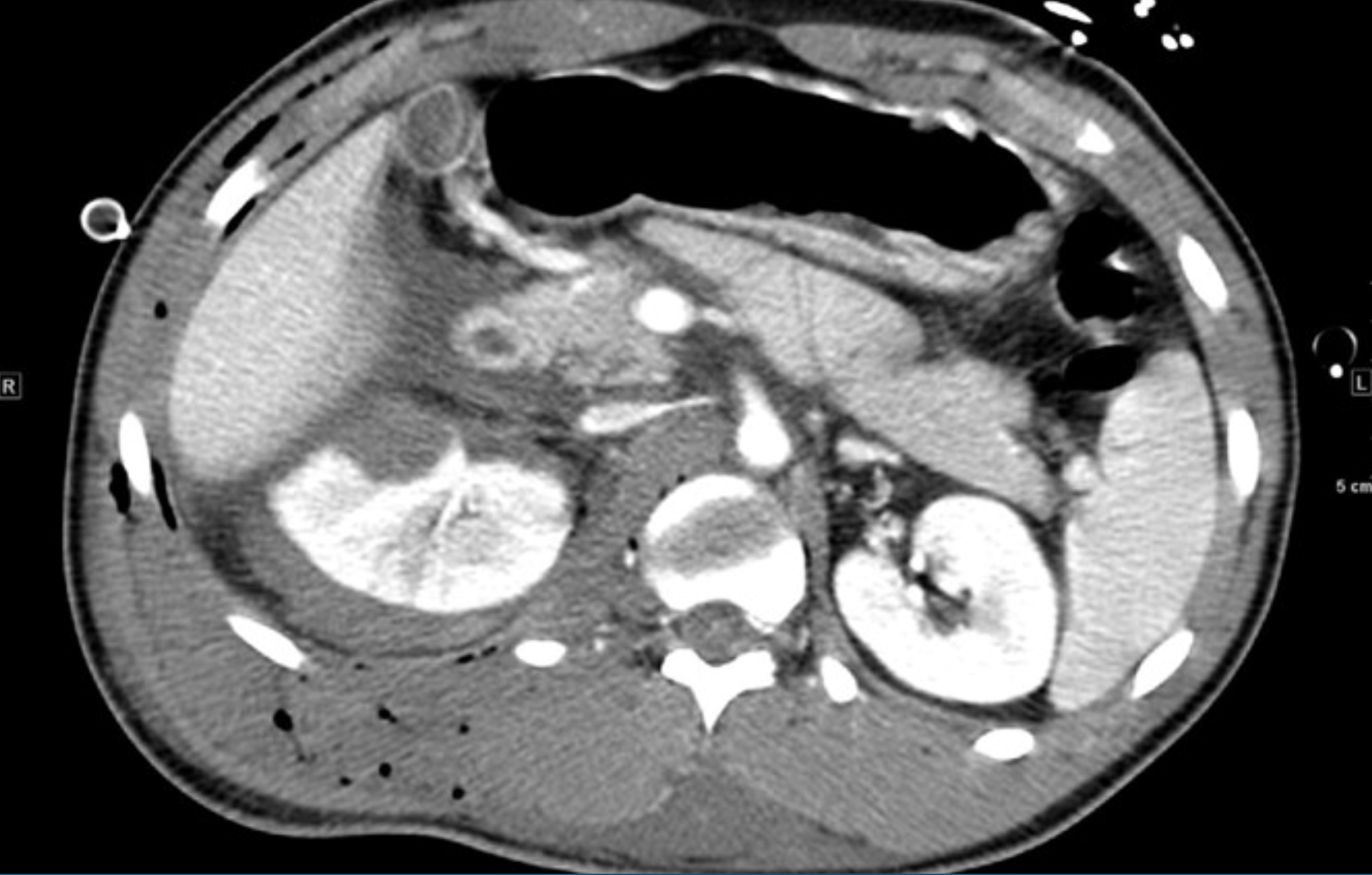
What is CT showing?
A partially devascularized right kidney (in this case due to blunt trauma).
The apical segment is intact and perfused.
The potential causes include intimal tear, distal renal arterial thrombosis, and or vasospasm. Many of these injuries will regain partial reperfusion without intervention.
Brushite stone pathognomonic for
hypercalciuria and elevated urinary pH
Symptoms of storage LUTS
Urinary frequency
Urinary urgency
nocturia
urge urinary incontinence