ch. 12: the effects of hormones on learning and memory
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
epinephrine (adrenaline)
a hormone and neurotransmitter involved in the body’s response to stress
secreted by adrenal glands in response to stressors
plays a key role in physiological arousal and cognitive functions, particularly memory
Walter Cannon’s emergence theory(1915)
Proposed that exposure to stress increases epinephrine secretion.
This hormonal response helps the body adapt to stress.
Early research in the 1920s and 1930s demonstrated the physiological effects of epinephrine.
Figure Placement: Historical timeline of epinephrine research.
what does research say about epinephrine & behavior post WW2
Fear-induced paralysis in soldiers linked to adrenal hormone discharge.
Animal studies on aversive conditioning revealed links between epinephrine and learning/memory.
These studies laid the foundation for research on hormonal influences on cognitive processes.
epinephrine’s role in learning and memory
the most extensively studied hormone in relation to memory
reliable assays and selective agonists/ antagonists allow precise measurement of its effects
released during learning, enhancing memory retention
epinephrine and the Yerkes-Dodson curve (memory and performance)
epinephrine’s effect on memory follows a u-shaped curve
low and high levels impair memory
moderate levels enhance memory
optimal level for avoidance memory in rats: 1500 pg/ml
what is the optimal dose of epinephrine to enhance memories in avoidance memory rats
1500 pg/ml
what do findings show about memory and epinephrine related to foot shocks
mild foot shocks increase blood epinephrine levels
combining foot shocks with exogenous epinephrine enhances memory
rat study: stressed out rats with a shock at varied time points, this raised levels of epinephrine
memory enhancement was time-dependent :
most effective if administered immediately after training
delayed administration reduces effectiveness
the stress hormones take a while before they reach their optimal level. it will take some time. The most effective time in enhancing memory, was after 1 minute of training, perfect for the stress hormone levels to rise.
how does epinephrine enhance memory
it influences encoding, storage and retrieval
**its best effects occur at consolidation
what are epinephrine’s challenges
it does not cross BBB easily (very little makes it to the brain)
must act in peripheral receptors that influence brain function
how does epinephrine enhance memory if it does not easily cross BBB
activates peripheral adrenergic receptors
adrenergic receptors communicate with the CNS
what is the role of the amygdala in memory modulation
crucial role in emotionally charged memory formation
electric stimulation enhances memory retention
evidence: intra-amygdala injections of epinephrine/ norepinephrine modulate memory
integration of peripheral and central mechanisms (epinephrine
Epinephrine acts via β-noradrenergic receptors.
Activates neurons in the vagus nerve → nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) releases norepinephrine →amygdala. (how epinephrine directly affects memory)
blocking this pathway prevents memory enhancement
what are the human studies on epinephrine and emotional memory
First way to measure epinephrine’s involvement in memory: block the activity of adrenergic receptors with propanol
Study: Participants read emotional vs. neutral stories.
Findings: Propranolol (β-adrenergic blocker) impaired recall of emotional stories but not neutral ones.
Implication: β-adrenergic activation is critical for emotional memory consolidation
imaging evidence involving amygdala activation and memory
FMRI and PET studies
higher amygdala activation correlates with better recall of emotionally intense stimuli
sex diffs: women show greater left amygdala activation; men show greater right amygdala activation
images that were more emotional or provocative were remembered better
salivary a-Amylase (sAA) and memory
second way to measure activity of epinephrine and memory
a-amylase is a marker of epinephrine
sAA as a biomarker for adrenergic activity
more SAA= more epinephrine activity
Increased sAA after emotional image viewing linked to improved emotional memory recall (**individuals are tested on how well they remember the images)
Gender differences in sAA response: Stronger response in women
"Increase in sAA vs. Emotional Memory" (emphasize the upward trend in women, and the weak response in men)
there is only an increase in epinephrine when there is emotionally arousing information
what is a-amylase
a marker of epinephrine
an enzyme produced in the saliva
mechanisms of epinephrine and memory
epinephrine’s role: elevates blood glucose and enhances memory
direct action on neurons: improves synaptic function
glucocorticoid secretion: additional hormones involved in stress and memory
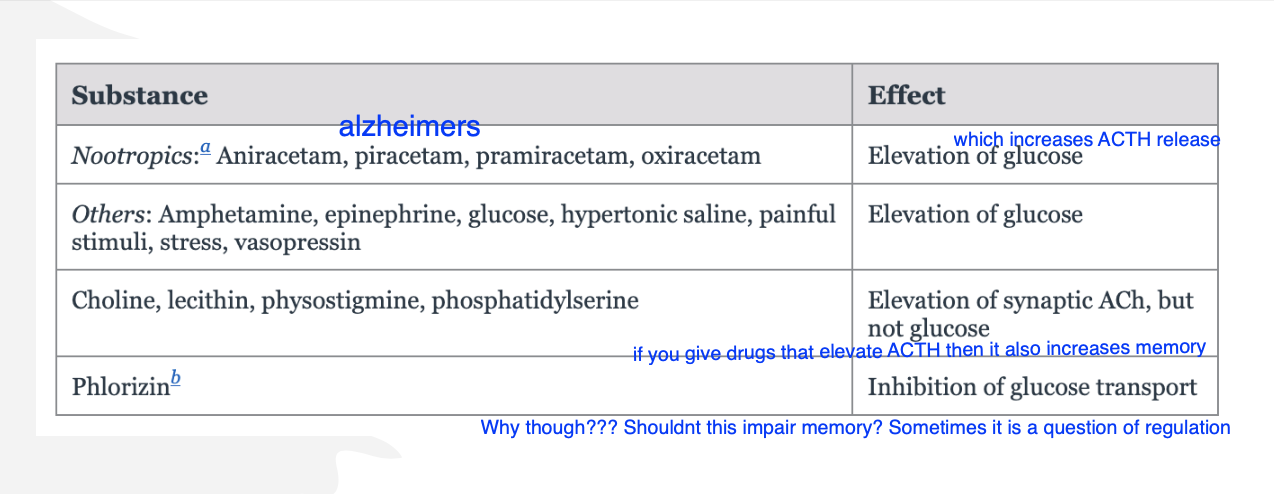
ACTH: not necessary for memory enhancement induced by epinephrine
blocking ACTH does not impair memory
the glucose hypothesis of memory enhancement
glucose increases neuronal glucose entry: enhances ACTH release
epinephrine (I think) increases levels of glucose. Liver releases glucose during fight or flight response
inverse u-shaped dose-response: optimal memory enhancement at 100 mg/kg glucose
delayed glucose injection ineffective: timing of glucose intake is crucial for memory enhancements
glucose enhances memory for avoidance learning
the effects of glucose are time dependent
epinephrine and glucose synergy
Epinephrine stimulates glucose release, which enhances memory
Adrenergic antagonists block epinephrine but do not block glucose effects
drugs also enhance memory by elevating glucose
cognitive enhancers effect on epinephrine and glucose in memory enhancement
Agents that elevate blood glucose levels enhance memory (e.g., glucose, epinephrine)
how can drugs contribute to memory enhancement
**both glucose and ACTH increase memory
insulin’s role in cognitive function
Regulates glucose metabolism and affects memory
Insulin receptors in the brain, particularly in the hippocampus
Impaired insulin signaling linked to cognitive impairments (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease)
how does glucose affect memory in elderly people
Glucose improves memory in elderly individuals
Elderly individuals: Improved memory after consuming glucose (compared to
saccharin)
Cognitive decline in elderly linked to impaired glucose regulation
memory relapses occur sometimes because glucose naturally goes down and dysregulates
**did not improve cognitive functioning, working memory, or word recognition in young subjects
improved their attentional skills
enhances both storage and retrieval of memory
insulin-dependent vs non-insulin dependent diabetes
insulin-dependent= type 1: insulin cells in the liver are being destroyed
non-insulin dependent type 2: cells don’t take up the insulin (can be cured)
**both types of diabetes impair cognitive functioning
more pronounced in elders but still present in young people
cognitive impairement and diabetes
verbal memory is most affected
hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia contribute to cognitive decline
Yerkes law: too much or too little of something isn’t good→ optimal amount
metabolic syndrome: linked to both cognitive decline and diabetes
insulin receptors in alzheimer’s disease
insulin receptors and link to Alzheimers disease
insulin receptor function: disruption linked to memory impairment
alzheimer's: reduced brain insulin receptors in severe memory impairment
insulin treatment: improves memory in Alzheimer’s patients
**brain insulin not body (body insulin is the one that decreases glucose)
streptozotocin
Induces diabetes and cognitive impairment in rodents, artificially
a drug that artificially creates diabetes, it destroys insulin cells (insulin-secreting beta cells in the pancreas)
what is some evidence from a study that insulin is important to memory
Streptozotocin-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Rodents
Memory test: Passive avoidance learning impaired in diabetic rats
• Phlorizin: Enhances memory performance in diabetic rats
lowers blood glucose, but enhances memory despite lowering blood glucose. How is that? this is about the regulation of glucose levels
• "Streptozotocin and Passive Avoidance Task" (showing latency to enter dark compartment)
rats either in control or STZ condition and we are testing their latency to enter dark room compartments
findings:
those in STZ condition : would cross over more easily= shorter latency=worse memory. They don’t remember being shocked in the dark compartment
control rats who did not receive STZ have good memory of getting shocked in the dark. They take a long time to cross over. (long latency)
measuring effects of diabetes on spatial memory — Morris water maze
study where rats are put into a pool of water with a platform, and at first they are stressed cuz they hate water. Eventually they learn that there is a platform in the water (they have to rely on their memory). When the platform is removed, we expect the rats to swim real where the platform usually is. We measure how well they learned where the platform is based on how long they spend in that area
STZ induces diabetes in rats, impairing spatial memory
Conditions:
STZ-treated rats with no insulin
STZ-treated rats with insulin from the onset (replaced right away so diabetes never developed)
STZ-treated rats with insulin after diabetes onset (replaced 10 weeks after treatment began)
insulin affects spatial memory in diabetic rats only if provided from the onset of diabetes
findings of morris water study on spatial memory deficit
Insulin treatment at the onset prevents learning deficits, but post-onset treatment does not reverse cognitive impairments
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
major candidate for how learning occurs. when neurons are continuously stiumulated, it facilitates neuronal communication
enhances neuronal connectivity, linked to learning
the hippocampus is important for processing memory, especially for spatial information
LTP in diabetic rats findings (morris water study)
Diabetic rats show impaired hippocampal LTP
Insulin treatment from the onset prevents LTP impairments (treatment and began at the same time as STZ)
Diagram showing hippocampal LTP in normal vs. diabetic rats
what is the role of fructose in memory enhancement
• Fructose enhances memory despite not being metabolized by neurons
• Higher doses of glucose (e.g., 2.0 g/kg) found to be more effective than lower doses
• Different sugars act on memory via peripheral sites or neural pathways
impaired glucose metabolism in Alzheimers patients
metabolism is significantly lower
regional glucose metabolism is observed in brain regions but it decreases
early decrease in cortical glucose utilization occurs in the same brain regions that later demonstrate the greatest density of senile plaques and tangles
how does acute stress enhance memory
• Acute stress and glucocorticoids promote lasting memory formation.
• Treatment with glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol, corticosterone) before learning improves recall.
• Short-term exposure to glucocorticoids enhances learning and memory.
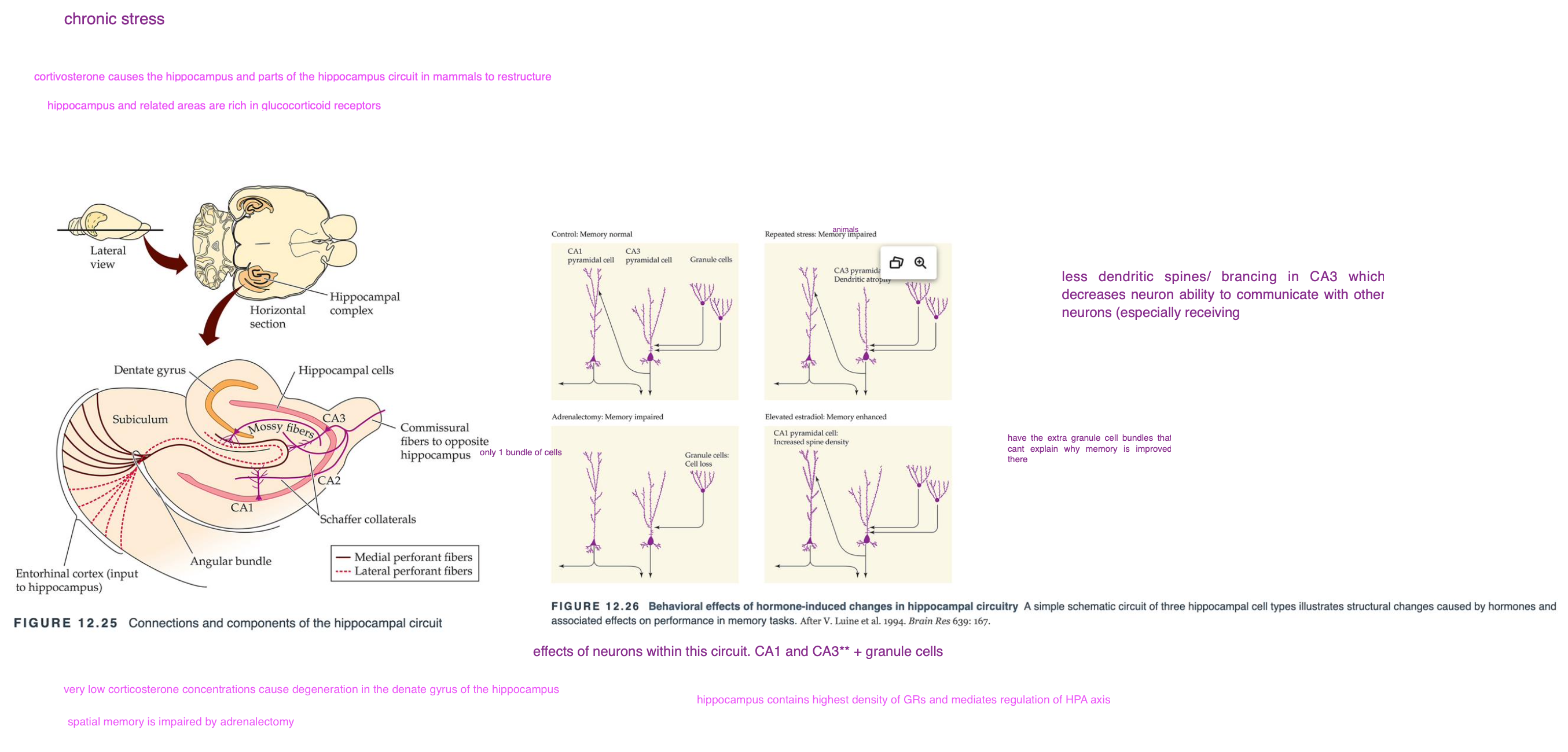
how does chronic stress impair memory
Chronic stress or long-term glucocorticoid (corticosterone) treatment impairs memory.
• Chronic exposure to glucocorticoids functions as an amnestic agent (promotes forgetting).
inverted u-shape curve in stress and memory
Both arousal and glucocorticoid levels influence learning in an inverted U-shape.
Low to moderate glucocorticoid concentrations enhance learning.
High concentrations of glucocorticoids impair memory.
how is recognition memory associated to cortisol
Cortisol treatment improves recall, especially for negative stimuli.
The relationship between cortisol and recognition memory is dose-dependent.
the radial arm maze task
Common test of spatial memory in rats.
Tests both short-term (working) to remember which rows have been visited already on a given trial and long-term (reference) memory to remember which of the 8 rows are baited
Rats must remember which arms of the maze are baited for successful navigation.
food at the end of each arm (in middle)
what are the effects of chronic stress on spatial memory (ex. radial maze)
Chronic stress impairs spatial memory in low-arousal tasks (e.g., radial arm maze)
High-arousal conditions(e.g., water maze), meaning that the task is already stressful may mitigate (make less severe) the negative effects of stress.
how does corticosterone impact spatial memory
• High corticosterone levels correlate with more errors in spatial tasks.
• Long-term corticosterone treatment impairs spatial learning.
• RU 38486 (progestin and a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist) can improve performance in spatial tasks.
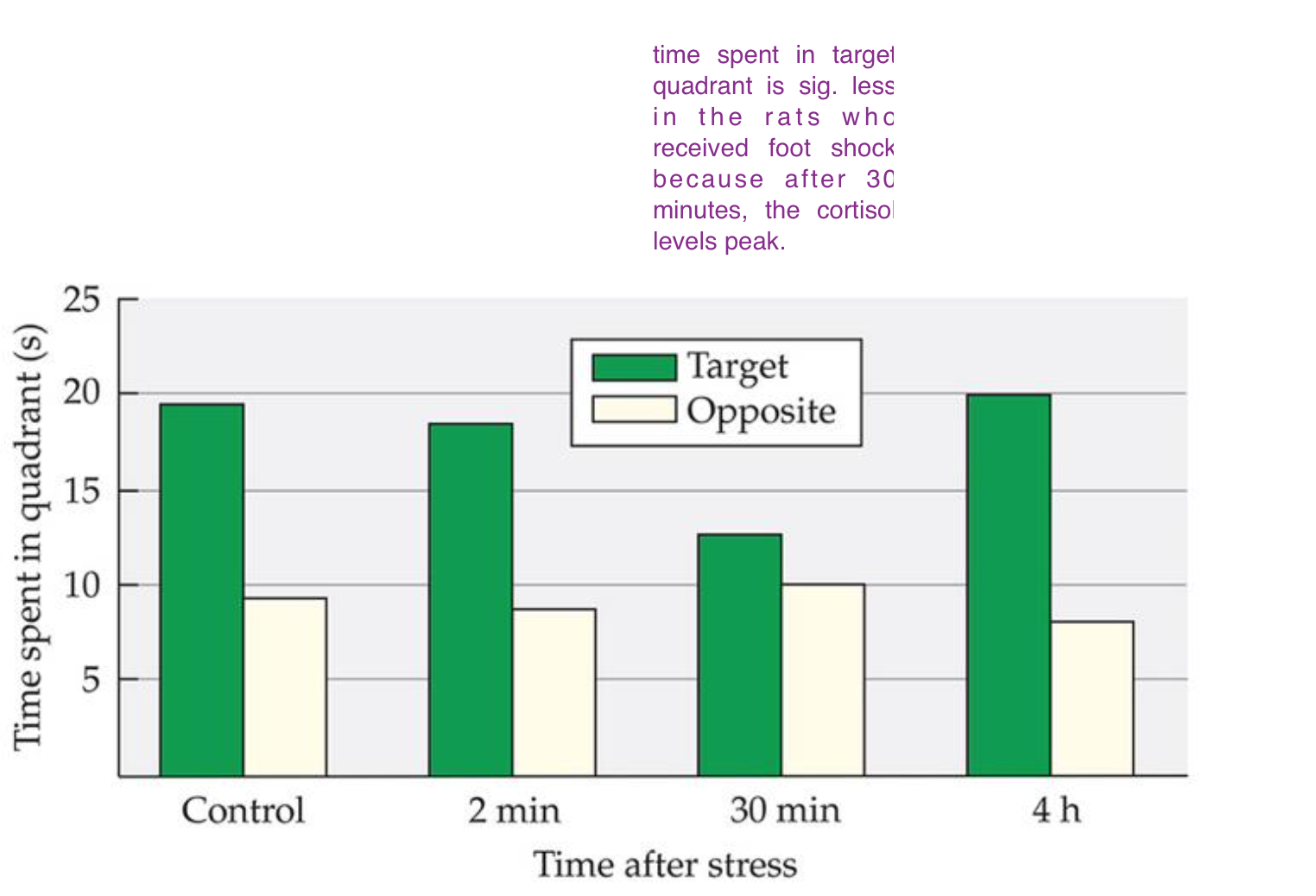
acute stress and its influence on memory retreival in the foot shock study
Acute stress can impair memory retrieval.
after training, mice were given foot shocks before memory retrieval (in a Morris water maze) impair recall, especially when stress occurs 30 minutes before testing.
because shock results in elevated glucocorticoid concentrations about 30 mins later, it impairs performance
how can acute stress facilitate learning
Acute stress can enhance learning in
classical conditioning tasks (e.g., eyeblink conditioning). in both hippocampus-dependent and hippocampus-independent learning and memory
Glucocorticoids are necessary for stress-evoked
facilitation of learning.
adrenalectomy blocked the stress-evoked facilitation learning
The facilitation effect is short-lived; memories are not
sustained after 24 hours.
how do glucocorticoids influence memory consolidation
injections of natural glucocorticoids mimic acute stress and tend to facilitate memory consolidation
Glucocorticoids facilitate memory consolidation by acting on glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) in the brain.
Blocking GRs impairs memory, while activating GRs enhances memory.
drugs that blocked either GRs or MRs were infused into the brains of rats right before or right after the rats learned a spatial water maze
blocking GRs but not MRs impaired performance on this spatial memory task
rats who don’t have GRs also experienced memory deficits
what is the amygdala’s role in memory
• The basolateral amygdala (BLA) mediates the memory-enhancing effects of glucocorticoids.
• Lesions in the BLA block the memory-facilitating effects of stress.
how is amygdala involved in glucocorticoids and fear memory extinction
cortisol interferes with the extinction of fear memories, allowing them to persist
corticosterone and food-hoarding birds
Elevated corticosterone levels improve spatial memory in birds, particularly in food-hoarding species.
Stressful conditions and unpredictable food supply lead to higher corticosterone levels, which enhance spatial memory. They also search less sites bc they remember where they hid their food
on the other hand, the birds who have unlimited food supply will search more sites and have impaired spatial memory
birds implanted with corticosterone also displayed improved spatial memory
Corticosterone may help birds recover cached food by improving memory under challenging conditions.
half the birds maintained a limited and unpredictable food supply while the rest provisioned with unlimited food supplies for 60 days
hippocampal circuit