ALL YEAR 8 SCIENCE
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ALL YEAR 8 SCIENCE <3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
inherited variation
due to genetic information inherited from parents- genes
environmental variation
due to the environment
continuous variation
where differences between living things are grouped into categories and given a name/ label
discontinuous variation
where difference between living things are given a numerical/ number valueg
gene
a section of dna which determines a characteristic
how many chromosomes are in a cell
46
how many chromosomes are in a egg/ sperm cell
23
what is a different version of a gene
allele
how old is the earth
4.5 billion
survival of the fittest
the idea that only the strong can survive and breed
population
group of organisms of the same kind living in the same place
natural selection
theory that animals and plants living today descended from species that existed in the past
extinct
when no more individuals of a species remain
biodiversity
the variety of living things. it is measured as the differences between individuals of the same species or the number of different species in an ecosystem
competition
when two or more living things struggle against each other to get the same resource
evolution
process by which species change over time in response to environmental changes and competition for rescources
what are the 4 causes of extinction
destruction of habitat, predators, disease, mutations
what are changes in genes called
mutations
how can you increase the strength of an electromagnet
have a large iron core, add more turns/coils, increase the current
electromagnet
a type of magnet that is powered by electricity
what are some everyday electromagnets
bell, loudspeaker, car park barrier
alternating currents
a current that goes back and forth
what’s the abbreviation for alternating current
a.c
how many layers is the earth’s atmosphere split into
5
what are the 5 layers of the earth’s atmosphere called
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
how thick is the troposphere
10km
how thick is the stratosphere
40km
how thick is the mesosphere
50km
how thick is the thermosphere
300km
how thick is the exosphere
10,000km
how much percent of the atmosphere is made up of nitrogen
78%
how much percent of the atmosphere is made up of oxygen
21%
how much percent of the atmosphere is made up of other gases
1%
what is the word equation for rusting
iron + water + oxygen = hydrated iron oxide
fossil fuel
a fuel that is made over millions of years under pressure and is mined from the earth. they will run out
how was coal formed
dead plants under pressure
how was oil and gas formed
dead animals under pressure
what are the main 3 greenhouse gases
carbon dioxide, methane, water vapour
global warming
the long term heating of the earth by co2
climate change
the long term shift of the earth’s climate
300, 000 km per second
how fast does light travel
8 mins
how long does it take for light from the sun to reach earth
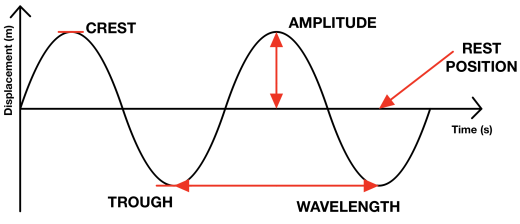
transverse wave
what type of wave is this
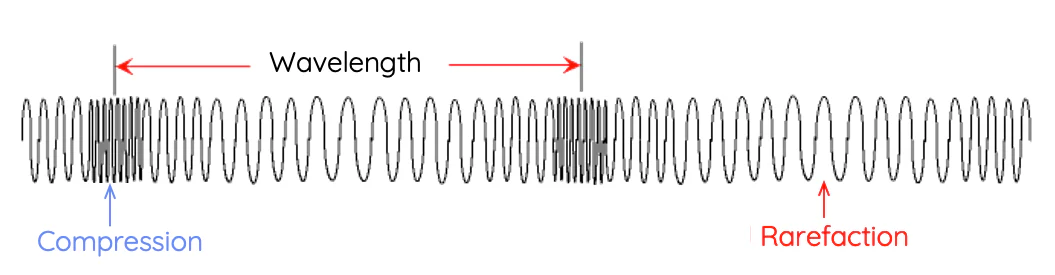
longitudinal wave
what type of wave is this
red, blue, green
what are the primary colours in science
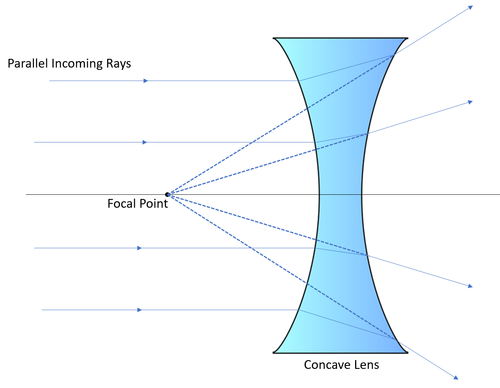
concave lens
what is this?
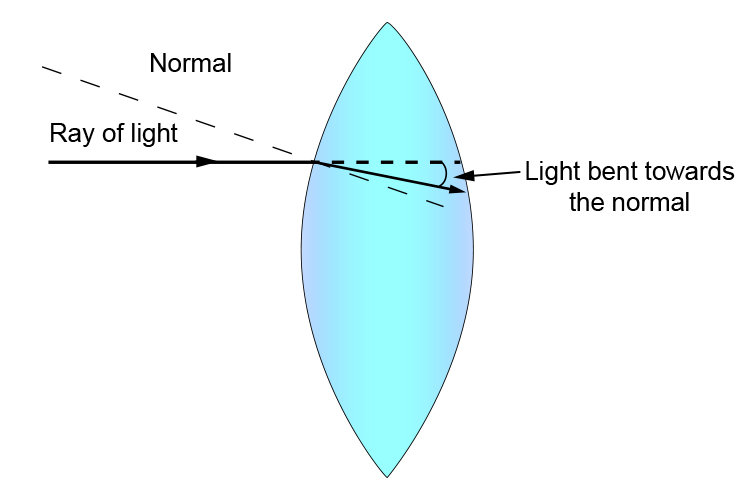
concave lens
what is this?
goes through the object
transmitted
absorbed
light goes into the object
causation of shadows
when light is blocked by an object and causes a dark area, because light cannot go through the object in front
by light reflecting off objects into our eyes
how do we see
amplitude
the distance the particles move each side, measured from their rest position
to either side of their rest position
how do sound waves vibrate the particles
echolation
the use of echos to measure distances
between 20HZ and 20 000 HZ
what frequencys can human ears detect
Hertz (Hz)
what do you measure frequency in
frequency
the speed of the vibration of a sound wave
there are no particles to vibrate
why can’t sound travel through a vaccum
mechanical waves
what type of waves are sound waves
electromagnetic waves
what type of waves are light waves
incident ray
a ray of light that hits a surface
reflect, refract or absorb
what are the 3 things light rays do when they hit a surface
reflection
when light bounces off an object into your eyes
transparent
allows light to pass through
translucent
allows some light through
opaque
allows no light to pass through
what are the five groups of animals
fish, amphibian, reptiles, birds and mammals.
joint
when 2 or more bones meet allowing movement when 2 or more bones meet allowing movement
what do muscles do
they allow the bones to move by contracting and relaxing
what do bones do
they provide support to the body
tendon
attaches muscle to bone. Doesn’t stretch
how many bones does an adult have
206
what are the 2 types of tissue that a bone is made of
living and non living
define non living tissue
hard material that supports the weight of the body and is pulled by the muscles to cause movement.
define living tissue
where the body makes blood cells, it is called bone marrow. red blood cells carry oxygen around the body and white blood cells fight diseases
what would happen if 2 bones moved against each other
they would wear away
what do ligaments do
join 2 bones and can stretch.
name the 3 types of muscle
cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
the heart
smooth muscle
intestines and oesophagus have walls that are made from layers of muscle. these muscles allow the food to be churned and pushed through the digestive system
skeletal muscle
pull upon bones and cause movements of the organism in vertebrates
word equation for respiration
sugar+oxygen>carbon dioxide+water
rib muscle
allow the rib to move. increases the volume of thoracic activity
rib
protects lungs and provides sctructure
trachea
allows air to travel from mouth to lungs
diaphragm
contracts and flattens when we breath in
journey of air from outsde to inside our body
atmosphere> nasal passages> larnyx> trachea> bronchus> bronchioles> alveoli
alveoli
singular form of alveolus. each of your lungs contains millions of alvioli and they help diffuse carbon dioxide into the blood.
gaseus exchange
he movement of oxygen from the alveoli the the capillary and the movement of carbon dioxide from the calillerary into the alveoli
where does respiration happen
mitochondria
what does respiration do
provides energy
what respires
all living cells
hinge joint
A joint that moves simply, like a door opening and closing. Knees, elbows
ball and socket joint
Allows more movement in more directions. Shoulder.
flower
the reproductive organ of plants, often attractive or sweet smelling to insects
fruit
the ripe part of a seed-bearing plant, often fleshy and edible to animals
seed
the part that the plant will lose and can then develop into a new plant
leaf
where photosynthesis occurs. contains chlorophyll and absorbs light energy
stem
supports the plant, holding it upright and growing taller