Exam 3 CHEM 241
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Term: Reagent, Definition: Action
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
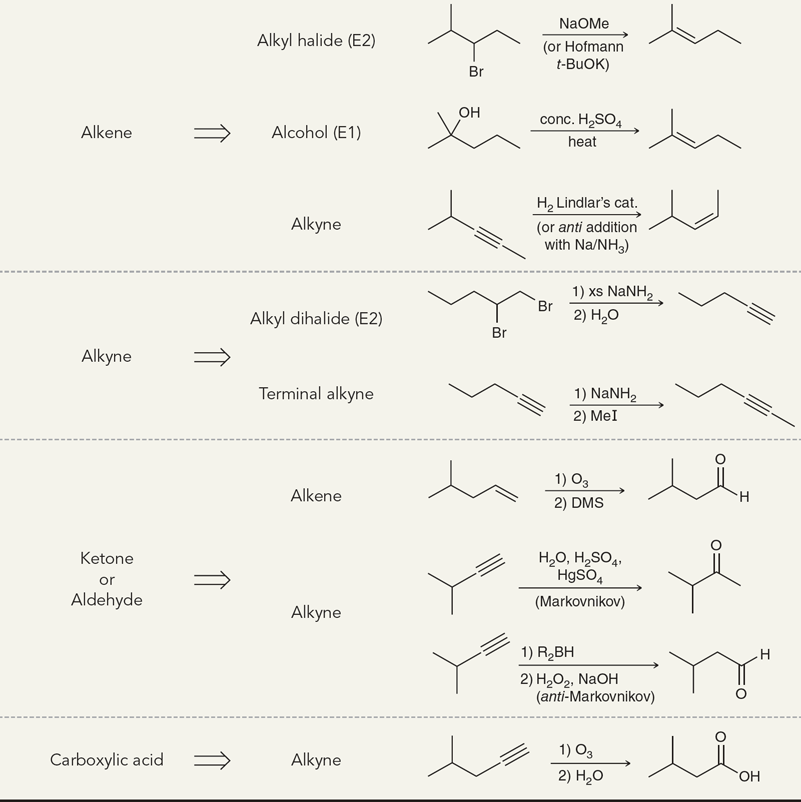
Alkenes Addition Map
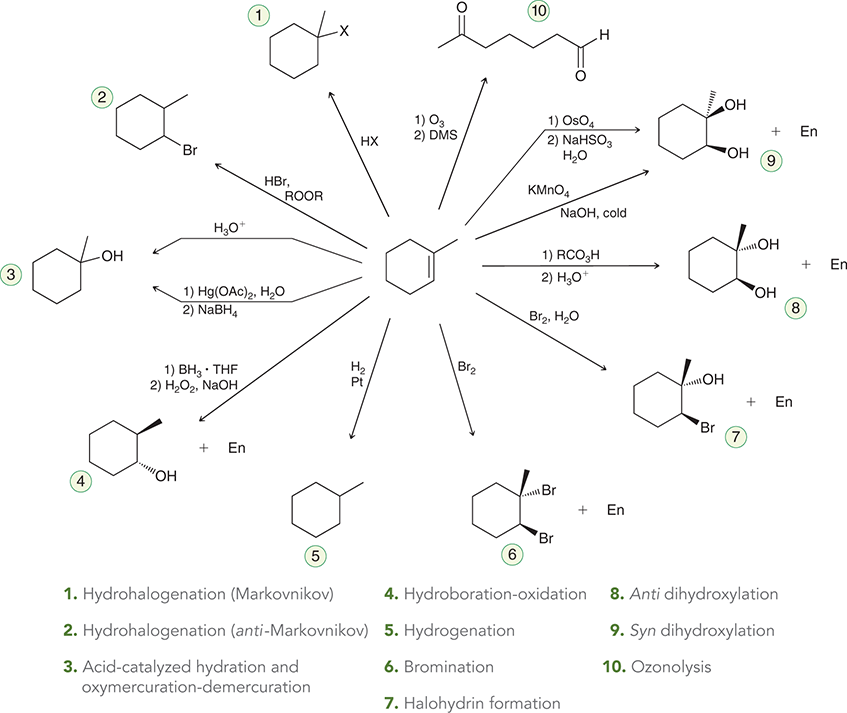
Alkynes Addition Map
Radical Steps
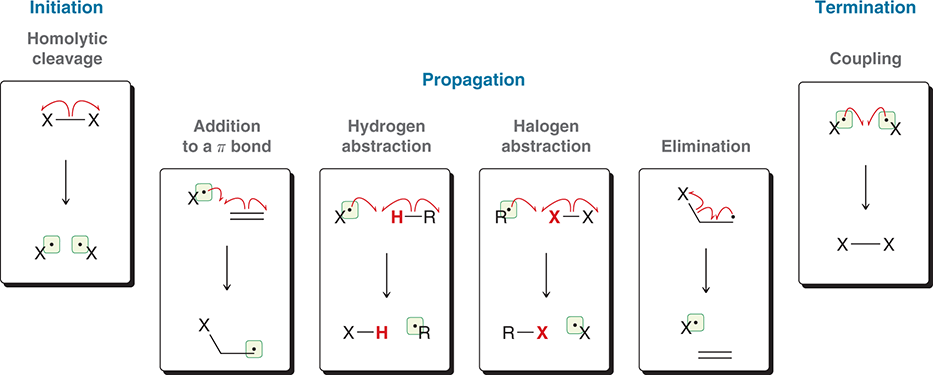
Cl2/hv
same use as Br2/v except installation of Cl at the most substituted position
Br2/hv
installation of Br (replacing a hydrogen atom) at the most substituted position

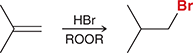
HBr/ROOR
Alkene undergoes anti-Markovnikov addition of H and Br
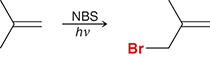
NBS/hv
install a bromine atom at the allylic position of an alkene
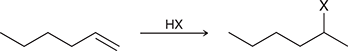
HX
Treating an alkene with this reagent gives Markovnikov addition of H and X across the alkene.
(Hydrohalogenation)

H3O+
Treating an alkene with this reagent gives Markovnikov addition of H and OH across the alkene.
(Acid-cat. hydration)

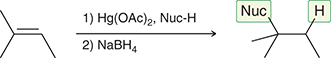
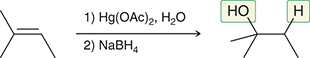
1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O (H2O can be replaced with a nucleophile)
2) NaBH4
Treating an alkene with these reagents gives Markovnikov addition of H and OH across the alkene, without any carbocation rearrangements.
(Oxymercuration-demercuration)
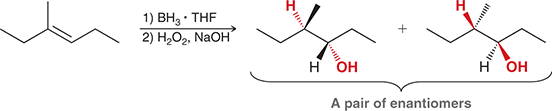
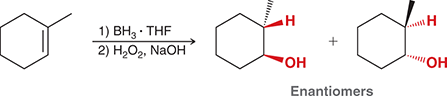
1) BH3 • THF
2) H2O2, NaOH
Treating an alkene with these reagents gives anti-Markovnikov addition of H and OH across the alkene. The reaction proceeds exclusively via a syn addition.
(hydroboration-oxidation)
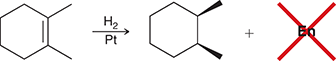
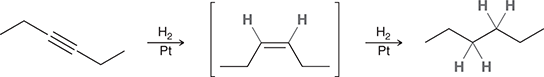
H2, Pt
Treating an alkene with these reagents gives syn addition of H and H across the alkene.
(Hydrogenation)
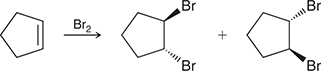
Br2
Treating an alkene with this reagent gives anti addition of Br and Br across the alkene.
(bromination/halogenation)
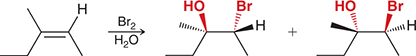
Br2, H2O
Treating an alkene with these reagents gives anti addition of Br and OH across the alkene, with the OH group being installed at the more substituted position.
(Halohydrin formation)


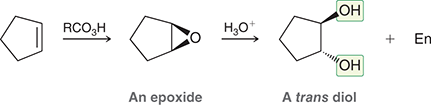
1) RCO3H
2) H3O+
Treating an alkene with a peroxy acid (RCO3H) converts the alkene into an epoxide, which is then opened upon treatment with aqueous acid to give a trans-diol.
(anti-dihydroxylation)
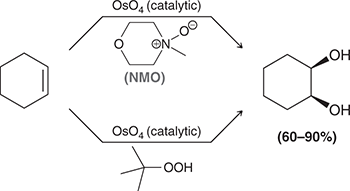
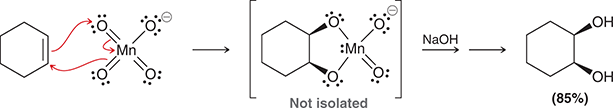
KMnO4, NaOH, cold or
1) OsO4
2) NaHSO3, H2O
Treating an alkene with these reagents gives syn addition of OH and OH across the alkene.
(syn-dihydroxylation)
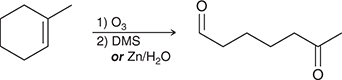
1) O3
2) DMS
Ozonolysis of an alkene causes cleavage of the C=C bond, giving two compounds, each of which possesses a C=O bond.
(ozonolysis)
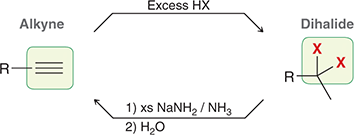
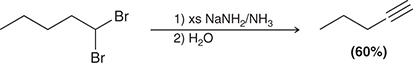
1) excess NaNH2
2) H2O
When treated with these reagents, a vicinal or geminal dibromide is converted to an alkyne.
(elimination)
1) R2BH
2) H2O2, NaOH
When treated with these reagents, a terminal alkyne undergoes anti-Markovnikov addition of H and OH to give an enol, which quickly tautomerizes to give an aldehyde.
(Hydroboration-oxidation)
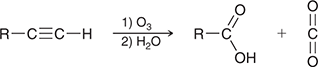
1) O3
2) H2O
When treated with these reagents, an alkyne undergoes oxidative cleavage of the C≡C bond. Internal alkynes are converted into two carboxylic acids, while terminal alkynes are converted into a carboxylic acid and carbon dioxide.
(ozonolysis)
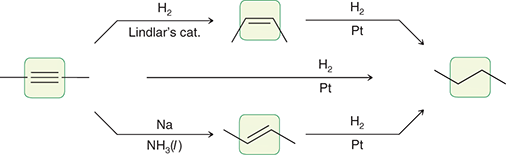
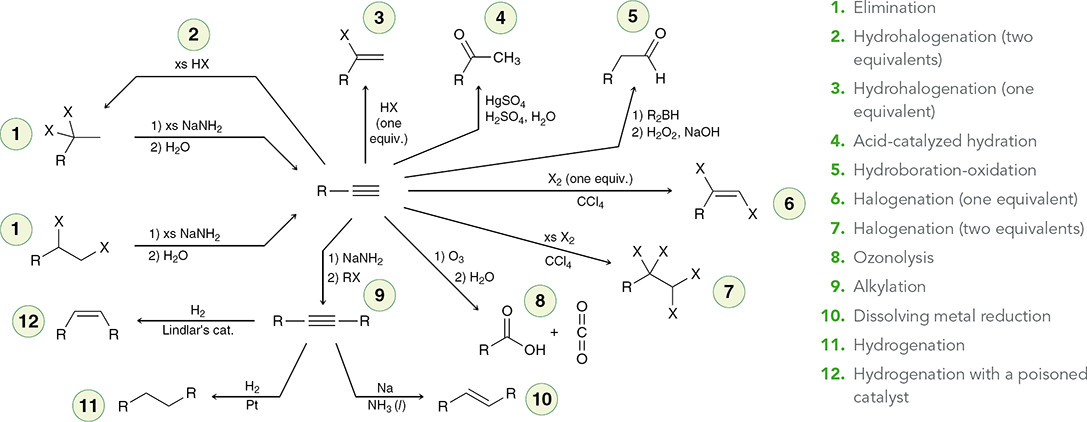
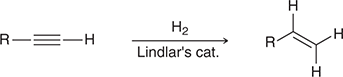
H2, Lindlar’s catalyst
When treated with these reagents, an alkyne is converted to a cis alkene.
(hydrogenation)
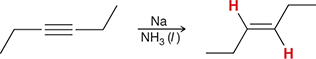
Na, NH3 (l)
When treated with these reagents, an internal alkyne is converted to a trans alkene.
(dissolving metal reaction)
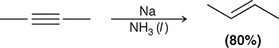
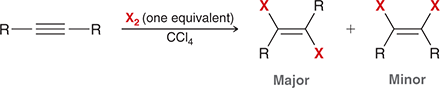
X2
When treated with this reagent, an alkyne undergoes addition of X and X (excess X2 gives a tetrahalide).
(halogenation)

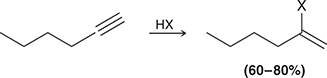
HX
When treated with HX, an alkyne undergoes Markovnikov addition (excess HX gives two addition reactions to afford a geminal dihalide).
(hydrohalogenation)

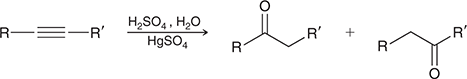
H2SO4, H2O, HgSO4
When treated with these reagents, a terminal alkyne undergoes Markovnikov addition of H and OH to give an enol, which quickly tautomerizes to give a ketone.
(Acid-cat. hydration)
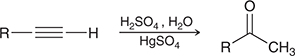
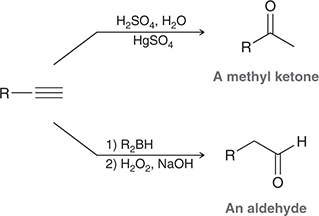
Relationship between H2SO4 and R2BH
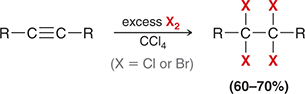
Excess vs one equivalent halogenation
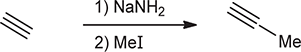
NaNH2/H2O
adds group before/after triple bond
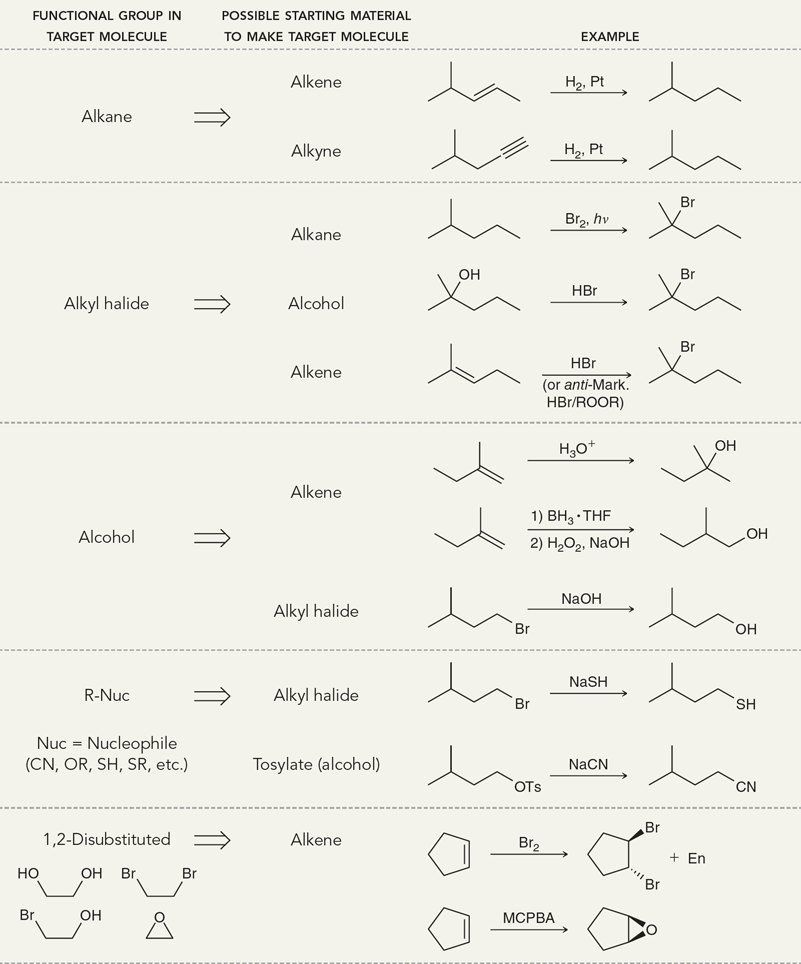
Table 11.1