waves
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
key terms in waves
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is a wave
A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through matter or space without the transfer of matter itself
Name the main properties of a wave.
Wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed.
What is the wavelength of a wave?
is the distance between a point on a wave and the same point on the next cycle of the wave, e.g. two crests, or two troughs
What is frequency?
the number of complete wave cycles per second
How do you calculate the speed of a wave?
v=f×λ
Q: What's the difference between a transverse and a longitudinal wave?
A: In a transverse wave, the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of travel (e.g., light waves). In a longitudinal wave, the oscillations are parallel to the direction of travel (e.g., sound waves).
Q: What happens when a wave reflects off a boundary?
The wave changes direction but stays in the same medium. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Q: What happens when a wave refracts?
The wave changes direction as it passes from one medium to another, due to a change in speed.
What is diffraction?
The bending of waves around obstacles or through gaps, which results in spreading out of the wave.
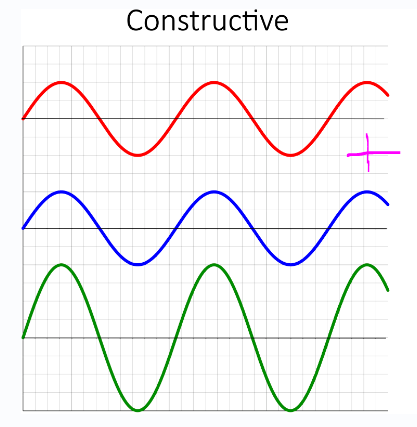
What is the superposition principle?
When two or more waves overlap, the resultant displacement is the algebraic sum of the displacements of the individual waves.
What is a stationary wave?
A wave that results from the interference of two traveling waves with the same frequency and amplitude, moving in opposite directions.
Q: What are nodes and antinodes in stationary waves?
Nodes are points of zero displacement, and antinodes are points of maximum displacement.
Q: What does the de Broglie equation describe?
It relates the wavelength of a particle to its momentum
What are electromagnetic waves?
Waves that are made of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, and travel through space at the speed of light.
Name some uses of electromagnetic waves
Communication, medical imaging, cooking (microwaves), and safety (X-rays).
Waves are said to be coherent if they have:
The same frequency
A constant phase difference
define amplitude
is the magnitude of the maximum displacement reached by an oscillation in the wave
define period
period is the time taken for one complete oscillation at one point on the wave
Interference is only observable if produced by a coherent source
coherent
when does constructive interference happen?
Constructive interference happens when the resultant wave has a larger amplitude than any of the individual waves