1 scope of lexicology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
object of lexicology
vocabulary
words
word-forming morphemes
complex morphemes
define vocabulary
a system of all the lexemes in a language or a field; all the words used by a person
approaches to the study of vocabulary
synchronic
diachronic
contrastive
synchronic study of vocab
syn = together
descriptive —> vocab at particular time
diachronic study of vocab
dia = through, across
historical/comparative —> history and evolution of words
contrastive study of vocab
correlation between the vocabs of 2 langs
what is the minimum free form
a word = a simple lexeme
define a simple lexeme
the basic unit of lang resulting from the connection of a specific meaning w a given sequence of sounds/letters capable of a particular grammatical employment
what characterizes a simple lexeme
indivisibility
positional mobility
uninterruptability
2 types of words based on meaning
lexical —> denote ideas (mental reflections of reality)
grammatical —> express specific features of lexical words (gram cat) and syntactically organize words
word-forming morphemes
the smallest meaningful units
the basic constituent of the word
complex lexeme
lexical unit consisting of 2+ words
fixed phrases, proper names, technical terms
define extralinguistic reality
set of impressions/mental images organized by our minds into concepts
everything imaginable in our mind expressible by language
not same for all the languages
differences in extralinguistic realities
phenomenon is:
the same
absent (halušky)
slightly different = prototype
the same but differently categorized (hand, arm - ruka)
the same but its different features are linguistically processed (bedroom - spáľňa)
model of sign - Ch. S. Peirce
language units are signs representing something
types of signs - Ch. S. Peirce
symbols
icons
indexes
symbol
conventionalized, arbitary sign
linguistic - arbitary word = table
non-linguistic - traffic sign
icon
casual, natural sign
linguistic - onomatopoeia = splash
non-linguistic - pictogram
index
casual, symptomatically dependent on another phenomenon
context dependent
linguistic - deictic expressions = that
non-linguistic - smoke indicating fire
model of linguistic sign - F. de Saussure
bilateral conception
signifié (concept, mental image) associated with signifiant (the physical trace of the sound)
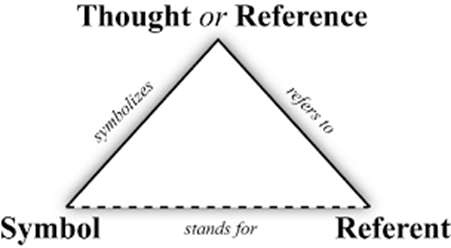
model of linguistic sign - Ch. Ogden & I. Richards
symbol doesn’refer to the referent/object of reality directly but through thought/the idea in our mind
basic features of a word
displacement
arbitrairness vs motivation - phonological, semantic, morphological
universality vs reference
discreteness - effect vs affect
duality
semanticity
cultural transferability