Blood Donation & Blood Component Preparation
1/243
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
c
Which of the following information is not required for whole blood donors?
a. Name
b. Address
c. Occupation
d. Sex
e. Date of birth
d
Which of the following would be cause for deferral?
a. Temperature of 99.2 degrees Fahrenheit
b. Pulse of 90 beats per minute
c. Blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg
d. Hematocrit level of 37%
e. None of the above
e
Which of the following would be cause for permanent deferral?
a. History of hepatitis after 11th birthday
b. Positive hepatitis C test result
c. Positive HTLV-I antibody
d. Positive anti-HBc test result
e. All of the above
a
Immunization for rubella would result in a temporary deferral for:
a. 4 weeks
b. 8 weeks
c. 6 months
d. 1 year
e. no deferral required
a
Which of the following donors is acceptable?
a. Donor who had a first-trimester therapeutic abortion 4 weeks ago
b. Donor whose husband is a hemophiliac who regularly received cryoprecipitate before 1989
c. Donor who was treated for gonorrhea 6 months ago
d. Donor who had a needlestick injury 10 months ago
e
Which of the following tests is not required as part of the donor processing procedure for allogeneic donation?
a. ABO
b. Rh
c. STS
d. Anti-HTLV I
e. Anti-CMV
a
Which of the following lists the correct shelf-life for the component?
a. Deglycerolized RBCs, 24 hours
b. RBCs (CPD), 35 days
c. Platelet concentrate, 7 days
d. FFP, 5 years
e. RBCs (CPDA-1), 21 days
b
Each unit of cryoprecipitate prepared from whole blood should remain approximately how many units of AHF activity?
a. 40 IU
b. 80 IU
c. 120 IU
d. 160 IU
e. 180 IU
c
Platelet concentrates prepared by apheresis should contain how many platelets?
a. 5.5 x 10^10
b. 6 x 10^10
c. 3 x 10^11
d. 5.5 x 10^11
e. 6 x 10^11
e
The required storage temperature for frozen RBCs using the high-glycerol method is:
a. 4 degrees Celsius
b. -20 degrees Celsius
c. -18 degrees Celsius
d. -120 degrees Celsius
e. -65 degrees Celsius
c
How does irradiation affect the shelf-life of red blood cells?
a. Irradiation has no effect on the shelf-life.
b. The expiration date is 28 days from the date of irradiation or the original outdate, whichever is later.
c. The expiration date is 28 days from the date of irradiation or the original outdate, whichever is sooner.
d. The expiration date is 25 days from the date of irradiation or the original outdate, whichever is later.
e. The expiration date is 25 days from the date of irradiation or the original outdate, whichever is sooner.
e
Once thawed, FFP must be transfused within:
a. 4 hours
b. 6 hours
c. 8 hours
d. 12 hours
e. 24 hours
b
Quality control for RBCs requires a maximum hematocrit level of:
a. 75%
b. 80%
c. 85%
d. 90%
e. 95%
b
AHF concentrates are used to treat:
a. Thrombocytopenia
b. Hemophilia A
c. Hemophilia B
d. von Willebrand disease
e. Factor XIII deficiency
a
Prothrombin complex concentrates are used to treat which of the following?
a. Factor IX deficiency
b. Factor VIII deficiency
c. Factor XII deficiency
d. Factor XIII deficiency
e. Factor V deficiency
d
How is the antibody screen test different for donors than for patients?
a. In donors, a 2-cell screen is used.
b. In donors, a 3-cell screen is used.
c. In donors, a pooled cell is used.
d. There is no difference in testing.
c
RBCs that have been leukoreduced must contain less than ________ and retain at least ___ of original RBCs.
a. 8 x 10^6/85%
b. 8 x 10^6/90%
c. 5 x 10^6/85%
d. 5 x 10^6/80%
a
Random-donor platelets that have been leukoreduced must contain less than ___________ leukocytes.
a. 8.3 x 10^5
b. 8 x 10 ^6
c. 5 x 10^6
d. 3 x 10^11
c
A single unit of FFP or PF24 should contain _______ mL of plasma.
a. 100-150
b. 200-400
c. 150-250
d. 50-150
c
Cryoprecipitate that has been pooled must be transfused within __ hours.
a. 24
b. 6
c. 4
d. 8
Blood donation
- Occurs when a person voluntarily has blood draw & used for transfusion.
Blood donation
- Involves collecting blood from a donor so it can be used to treat someone else.
Directed
Allogenic
Autologous
Apheresis
4 Types of Blood Donation
Directed
- Blood is intended for the use of specific px.
Directed
- A donation in which the recipient chooses the donor. (donor is known, as compared to mass blood donation)
yellow, salmon
tag for the directed unit is a distinct color is _ to differentiate it from autologous tags
T
Directed (t/f)
- Blood from directed donors is no safer than blood from the volunteer blood supply.
Directed
- Selected donor that is non-relative
whole blood donation
Allogenic is commonly referred to as
Allogenic
- Blood donated is intended for the use of general px population.
Allogenic
- For mass donation, anyone that needs blood.
Allogenic
- For hospital consumption
Mass blood donation
Example of Allogenic
• Form / Interview
Proces of Blood donation of Allogenic
Autologous
- Blood donated by the owner for future use.
donor-patient
- Autologous donor Is referred to as the -
Autologous
For rare blood types
Apheresis
- Blood donation in which a specific component of the blood is only extracted, & the remaining components are returned to the donor.
2-3 hrs
Apheresis takes place for how many hrs
specific gravity / weight
Apheresis
- Separation of components is based on
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
Continuous Flow Centrifugation
Centrifugation Methods

Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
- Blood is processed in batches / cycles (passes).

Draw
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
• – whole blood is drawn with a pump.

Spin
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
– components are centrifuged.

Dwell & Surge
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
– separation of desired & undesired components.

Return
Intermittent Flow Centrifugation
– reinfusion of undesired components
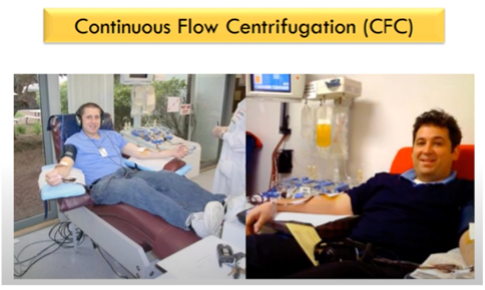
Continuous Flow Centrifugation
- The process of withdrawal, processing & reinfusion of the blood is performed simultaneously on a continuous manner.
2 venipuncture sites are needed.
Continuous Flow Centrifugation requires how many sites
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
Plasmapheresis
Leukapheresis
Erythrocytapheresis
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis
Types of Apheresis
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- ≥ 75% of platelets transfusions
Single Donor Platelet (SDP) –
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
a unit
6–8 random donor platelets
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- One plateletpheresis unit is equivalent to
Plateletpheresis donors may donate more often. The interval between donations is at least 2 days, not to exceed more than twice a week or more than 24 times a year.
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- Plateletpheresis donors may donate more often. The interval between donations is at least - days, not to exceed more than - a week or more than - times a year.
Donors who have ingested aspirin, Feldene, or aspirin containing medications should be deferred for 48 hours, because these medications interfere with platelet adhesion, & all of the platelets in a given therapeutic dose would be affected.
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- Donors who have ingested aspirin, Feldene, or aspirin containing medications should be deferred for - hours, because these medications interfere with platelet adhesion, & all of the platelets in a given therapeutic dose would be affected.
In addition, donors on Plavix (clopidogrel) or Ticlid (ticlopidine) should be deferred for 14 days, which is the time required for the medication to clear the system & the platelet function to return to normal. If the donor has donated whole blood, or if 100 mL or more of red cells were not able to be returned to the donor on the previous pheresis procedure, the donor must be deferred for 8 weeks
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- In addition, donors on Plavix (clopidogrel) or Ticlid (ticlopidine) should be deferred for - days, which is the time required for the medication to clear the system & the platelet function to return to normal.
If the donor has donated whole blood, or if 100 mL or more of red cells were not able to be returned to the donor on the previous pheresis procedure, the donor must be deferred for 8 weeks
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- If the donor has donated whole blood, or if 100 mL or more of red cells were not able to be returned to the donor on the previous pheresis procedure, the donor must be deferred for -
It is required if the interval between donations is less than 4 weeks; in that case, the platelet count must be above 150,000/µL
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- It is required if the interval between donations is less than ; in that case, the platelet count must be above -
- Apheresis or single-donor platelets contain at least 3 × 1011 platelets (therapeutic equivalent of four to six random donor platelets), are stored at 22°C – 24°C with continuous agitation, contain approximately 300 mL of plasma, & have a shelf-life of 5 days.
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- Apheresis or single-donor platelets contain at least - (therapeutic equivalent of four to six random donor platelets), are stored at - with -, contain approximately 300 mL of plasma, & have a shelf-life of 5 days.
Apheresis or single-donor platelets contain at least 3 × 1011 platelets (therapeutic equivalent of four to six random donor platelets), are stored at 22°C – 24°C with continuous agitation, contain approximately 300 mL of plasma, & have a shelf-life of 5 days.
Plateletpheresis / Thrombocytopheresis
- Apheresis or single-donor platelets contain at least 3 × 1011 platelets (therapeutic equivalent of four to six random donor platelets), are stored at 22°C – 24°C with continuous agitation, contain approximately - of plasma, & have a shelf-life of - days.
Apheresis
is the only effective method for collecting leukocytes, specifically, granulocytes
• Hydroxyethyl starch (HES)
• Prednisone
• Dexamethasone
• Growth Factors
Leukapheresis
- Donors are given drugs / sedimenting agents to increase the recovery of WBCs:
Hydroxyethyl starch (HES)
– not a WBC sedimenting agent, but an RBC sedimenting agent, act as it allows better separation of layers during centrifugation resulting in improved yield, or reduced RBC contamination. Meaning only the target cells are collected.
Circulatory volume expansion with headaches & peripheral edema.
Side effect of Hydroxyethyl starch (HES)
Prednisone & Dexamethasone
are oral med- function as it increase the number of circulation granulocytes for easy collection of targets cells.
Growth Factors
– specifically the colony stimulating factors this is a recombinant hematopoietic growth factor – it increases granulocyte yield.
muscle & skeletal pain
Side effect of Growth Factors
Erythrocytapheresis
- Also used for therapeutic by removing excess volume of RBC (polycythemia vera), sickle cell disorder (↓ the number of hemoglobin as containing RBCs thereby treating or preventing any complications.
Erythrocytapheresis
- Also used to remove incompatible RBCs from a patient circulation (ex. Rh + to rh -)
Double RBC Pheresis
2 units of Red cells are collected using apheresis.
16 weeks
Erythrocytapheresis - Donation Frequency
Successful Completion
<8 weeks
Erythrocytapheresis - Donation Frequency
Red Cell Loss <200 mL
8 weeks
Erythrocytapheresis - Donation Frequency
Red Cell Loss >200 mL but 300 mL
16 weeks
Erythrocytapheresis - Donation Frequency
Red Cell Loss >300 mL
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis
- Collection of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) or peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs)
GCSF
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis
- Hematopoietic growth factors, particularly -, is used to increase the # of circulating stem cells prior to the procedure.
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis
- Procedure use to collect stem cells (Stem cells normally live in bone marrow. Medicine is used to help release stem cells from the bone marrow into the bloodstream where they can be collected)
F
Drug Given to Stem Cell Donors: For 5 days leading up to your PBSC donation, you will be given injections of a drug called filgrastim to increase the number of blood-forming cells (also called blood stem cells) in your bloodstream.
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis (t/f)
- Drug Given to Stem Cell Donors: For 7 days leading up to your PBSC donation, you will be given injections of a drug called filgrastim to increase the number of blood-forming cells (also called blood stem cells) in your bloodstream.
T
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis (t/f)
- Although there are very few peripheral blood stem cells, their numbers can be increased through administering medications such as growth factors (including granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) [filgrastim]), chemotherapy, & agents like Mozobil (plerixafor) injection.
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis
- Are found in the upper portion of the buffy coat.
F
At least 2-3 apheresis procedure is needed to produce acceptable amount. 4 – 6hrs per procedure.
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis (t/f)
- At least 10-30 apheresis procedure is needed to produce acceptable amount. 5 – 10 hrs per procedure.
16 weeks
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of 2RBC
Every 2 days (≤2x in 7 days)
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of Plasma (frequent)
Every 4 weeks (≤13x / year)
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of Plasma (infrequent)
Every 2 days (≤2x / in 7 days; ≤24x / year )
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of Platelets, Single Apheresis Unit
Every 7 days
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of Platelets, Double / Triple Apheresis Unit
Every 2 days
Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells (HPC) Pheresis - Apheresis
Frequency of Donation of Granulocytes
Voluntary, non-remunerated
Professional / Commercial
Family / Replacement
Walk-in Donor
Walking Donor
Types of Blood Donor
Voluntary, non-remunerated
- Donates on his own free will without receiving any payment
Professional / Commercial
- Donates blood for the sake of money
Family / Replacement
- Donates blood for somebody in the community.
Family / Replacement
- Allows family & friends to make donations to replace blood that was utilized by you.
Walk-in-Donor
- More common in allogenic donations.
Walking Donor
- Waiting for the signal to donate ; they already passed the screening test.
Walking Donor
- For patients who need fresh blood.
Donor Recruitment & Registration
Donor Selection & Screening
Blood Extraction / Bleeding
Blood Storage
Steps in Blood Donation
• Name (first, last, MI)
• Date & time of donation
• Address
• Contact information
• Gender
• Age / date of birth
Donor Recruitment & Registration includes
18 (legal age) & 17 yrs old can be accepted given with a parent’s consent. 65 is the maximum blood donation age.
Age that is acceptable for blood donation
65
what is the maximum age for blood donation
Donor Selection & Screening
- Essential to ensure the benefit of both donor & recipient
Donor Selection & Screening
- In a form of questionnaires