Pre-Implanatation and Implantation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is implantation?
The process by which the blastocyst embeds itself to uterine lining (endometrium)
To establish a connection for nutrient and waste exchange
Between developing embryo and mother
What occurs if the embryo doesn’t implant properly?
Results in growth defects and death of embryo
What are the 4 stages of the pre-implantation period (0-12 days)
Uterus structural and functional remodeling #4fdff6
Migration of embryo #2a8fee
Spacing of embryo (in multiparous species) #2b5ced
Maternal recognition of pregnancy
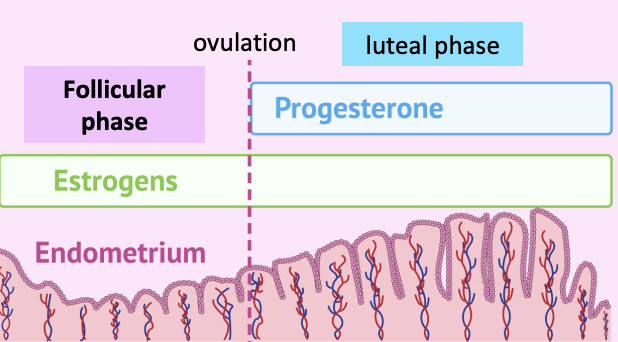
Pre-Implantation Period: Utero Structural and Functional Remodeling (uterine receptivity) #4fdff6
What are the 2 hormones that causes structural changes
In which phase released
What does it cause
Estrogen: Prepares uterus for pregnancy
Released in: Follicular phase
Builds and maintain endometrium
Increase
Endometrium size
Cell number
Blood flow
Protein and enzyme content
Progesterone:
Released in: Luteal phase
Maintains and controls endometrium
Allow embryo to stick/implant
Stimulates growth of blood vessels that supply endometrium
Stimulates glands in endometrium to secrete nutrients
Pre-Implantation Period: Migration of the Embryo #2a8fee
Embryo migrates through and into
By
Importance
Embryo migrates: Through oviduct and into uterine cavity
By: Peristalsis
Importance: Allows embryo to reach site in uterus that is ready for implantation
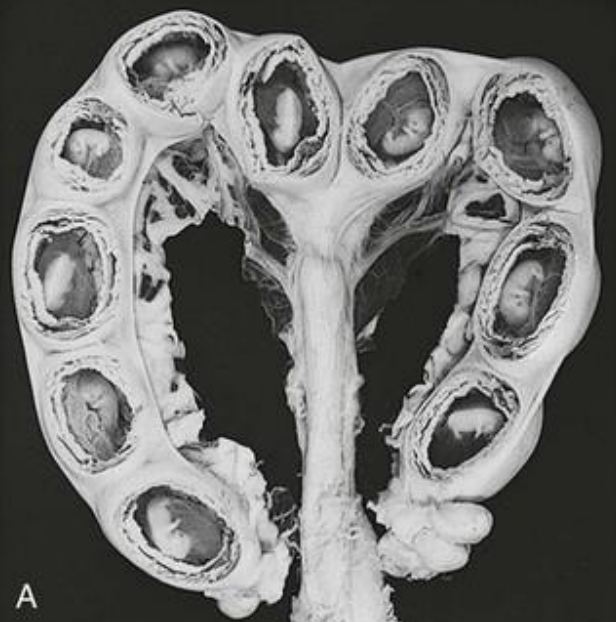
Pre-Implantation Period: Spacing of Embryos #2b5ced
Only occurs in
To ensure
Reduces
Develop
Only occurs in: Multiparous species (species that give birth to more than 1 offspring; pigs, cats, dogs)
To ensure: Proper development and growth as all embryos have room and access to nutrients
Reduces: Risk of overcrowding
Develop: Embryos also develop individual placentas to allow efficient nutrient and gas exchange
Pre-Implantation Period: Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy
What occurs
By
To prevent
What occurs: Embryo signals presence to maternal system
By: Producing specific chemical signals (IFNT) that are recognised by maternal body
Prevents: Regression of corpus luteum (uterine lining)
Implantation (Day 12-21) #b600ff
What occurs
What serves as attachment site for fetal membranes
Typical site of implantation
Different is horse, so where does implantation occur
Types of implantation
What occurs: Hatched blastocyte moves through uterus and attaches to uterine wall
What serves as attachment site for fetal membranes: Caruncles that become large and vascularised only during pregnancy
Typical site of implantation: Uterine horns
Different is horse, so where does implantation occur: Uterine horns and body
Types of implantation:
Invasive
Non-invasive
Invasive Implantation
Occurs in which species
What occurs
Pattern of implantation
Phases
Occurs in: Rodents and primates
What occurs: Trophectoderm of blastocyst invade through uterine stroma
Pattern of implantation: Eccentric and interstital
Phases:
Apposition
Adhesion
Invasion
Invasive Implantation
What occurs in these phases of implantation:
Apposition
Adhesion
Invasion
Apposition:
Blastocyst reach uterus
Loosely aligns with endometrial epithelium (uterine lining)
But doesn’t attach firmly
Adhesion:
Trophectoderm firmly attached to endometrial epithelium
Invasion:
Trophectoderm cross luminal epithelium (LE)
Invade stroma
This establishes contact between maternal blood and embryo for nutrient and gas exchange
Non-Invasive Implantation
Occurs in which species
What occurs
Pattern of implantation
Phases
#1bd700
Occurs in: Domestic animals (cats, dogs, cow, sheep, goat, pig)
What occurs: Trophectoderm of blastocyst attaches to uterine epithelium without deeply invading the uterine stroma
Pattern of implantation: Centric
Phases:
Apposition
Adhesion (interdigitated microvilli)
Non-Invasive Implantation
What occurs in these phases
Apposition
Adhesion
Apposition:
Trophectoderm loosely aligns with endometrial epithelium
But doesn’t attach firmly
Adhesion:
Interdigitated microvilli formed at interface between trophectoderm and uterine epithelial cells
Microvilli from trophectoderm and uterine epithelial cells interlock with each other
This facilitates nutrient and gas exchange while maintaining superficial attachment
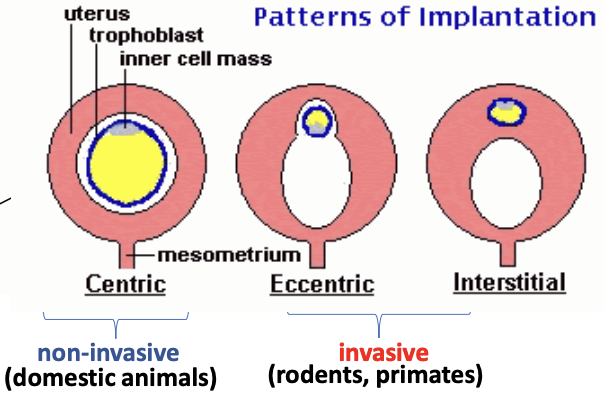
Pattern of Implantation
What
Categorised based on
Types
#9000ff
What: How the embryo attaches to and interacts with endometrium during pregnancy establishment
Categorised based on: Position and degree of invasion
Types:
Centric #00c0ff
Eccentric
Interstitial
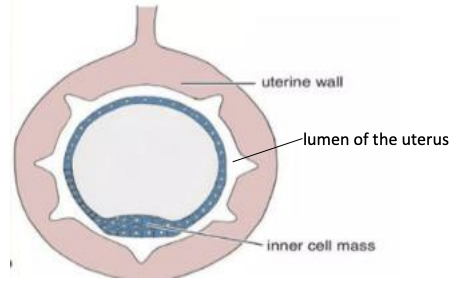
Centric Pattern of Implantation
What occurs
In what type of implantation
#00c0ff
What occurs: Blastocyst remains within central lumen of uterus and attaches to endometrium superficially
Type of implantation: Non-invasive (domesticated animals)
Eccentric Pattern of Implantation
What occurs
In what type of implantation
What occurs: Blastocyst becomes lodged in uterine cleft (crypts) with proliferation of surrounding uterine mucosa
Type of implantation: Invasive (rodents and primates)
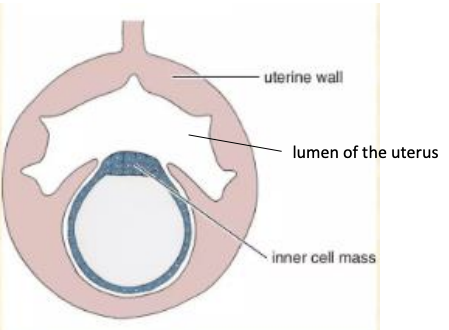
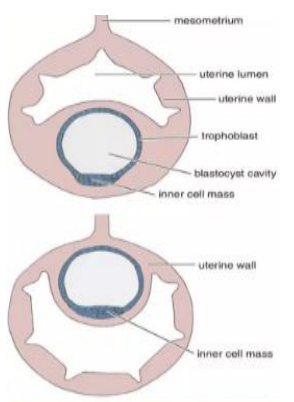
Interstitial Pattern of Implantation
What occurs
In what type of implantation
What occurs: Blastocyst burrows through the uterine epithelium to the uterine stroma where the embryo develops
Type of implantation: Invasive (rodents and primates)
Establishing Maternal-Fetal Connection
Embryo initially nourished by
What is histotroph
Contains
What occurs as the embryo continue to grow
Therefore to meet nutritional needs, what occurs
Allows
Occurs due to
Embryo initially nourished by: Histotroph (uterine milk)
Histotroph: Fluid secreted by uterine lining
Contains: Nutrients and growth factors that support early embryo development
As embryo continue to grow: Histotroph no longer sufficient to meet embryo’s needs for nutrients, oxygen and waste removal
Therefore: A close relationship between extraembryonic tissues (tissues outside embryo) and maternal circulatory system needs to be established
Allows: Embryo to import maternal nutrients, oxygen and export waste products
Occurs due to: Formation of the placenta