Meiosis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Prophase I
Each chromosome comes near its replicated chromosome pair. Nucleus dissolves at this stage. Crossing Over (exchange of genetic material) occurs at this phase.

Metaphase I
The pairs of homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. The centromere of each chromatid pair attaches to one spindle fibre.
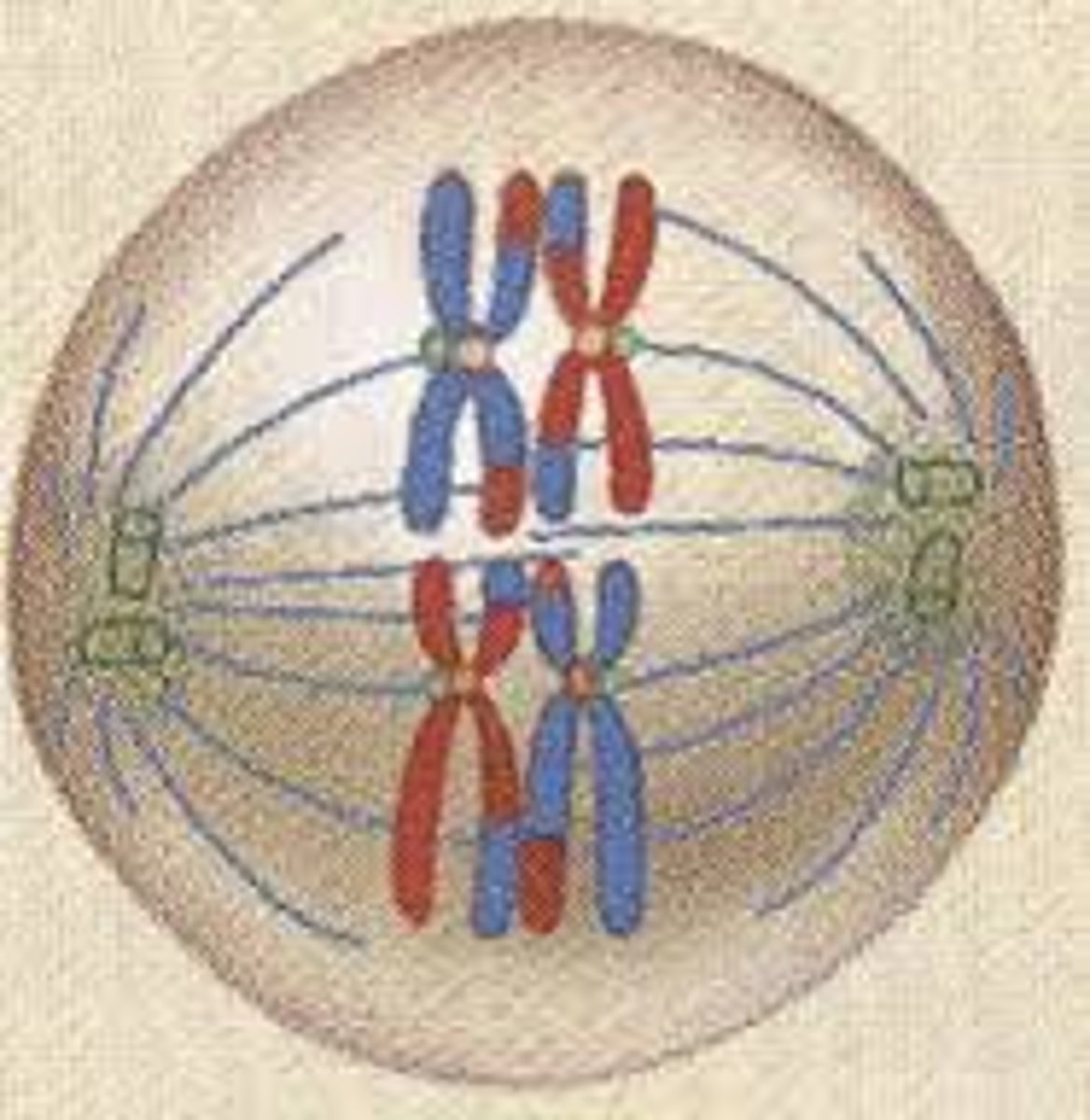
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell. Note that chromatids do not separate - each duplicated chromosome still has two chromatids.
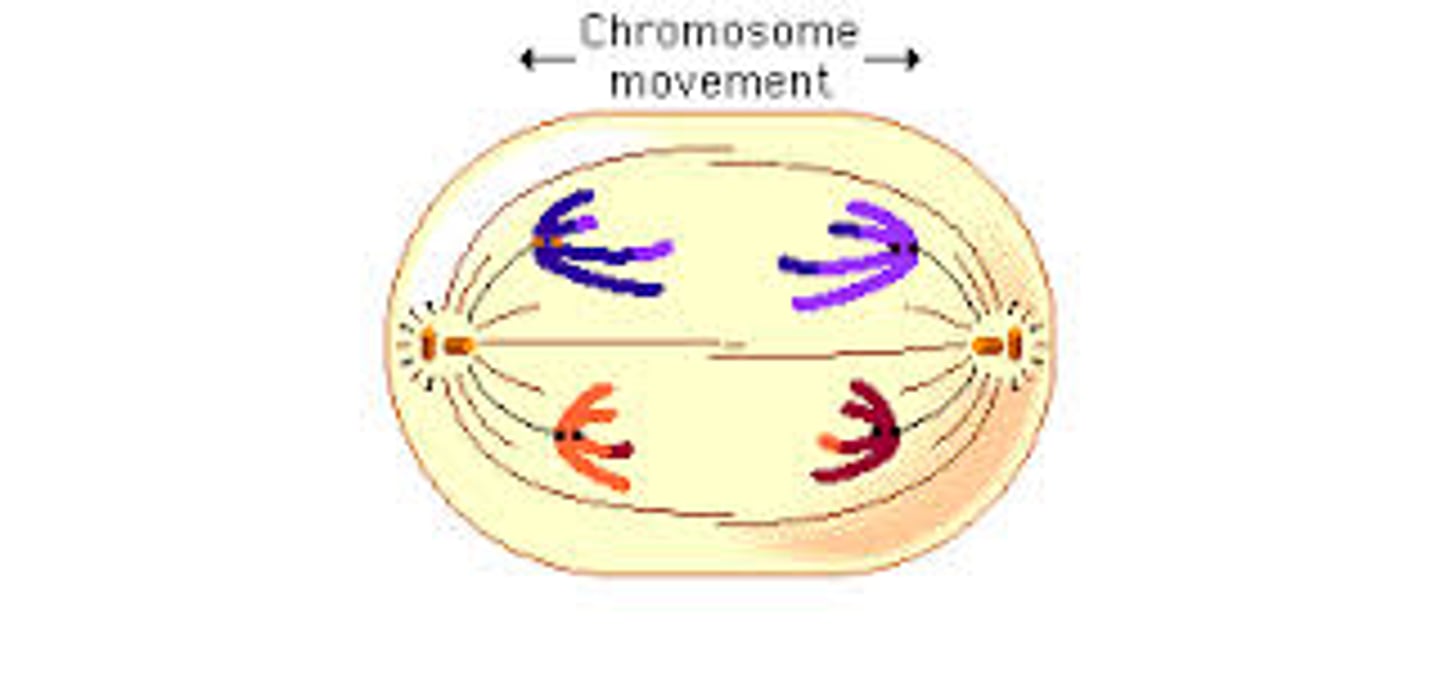
Telophase I
The cytoplasm divides and two new cells form. Each new cell has one duplicated chromosome from each similar pair.
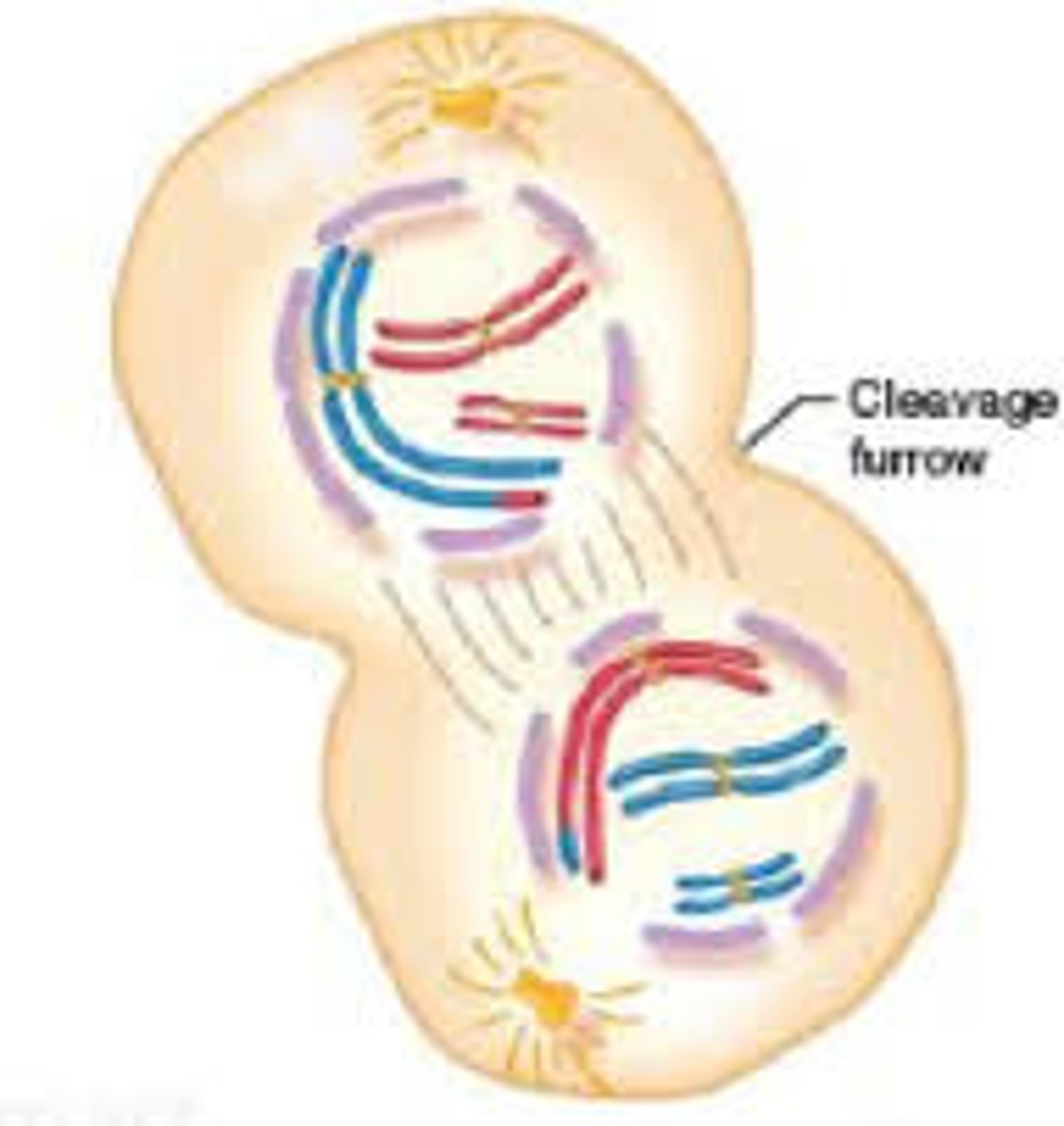
Prophase II
The duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell.
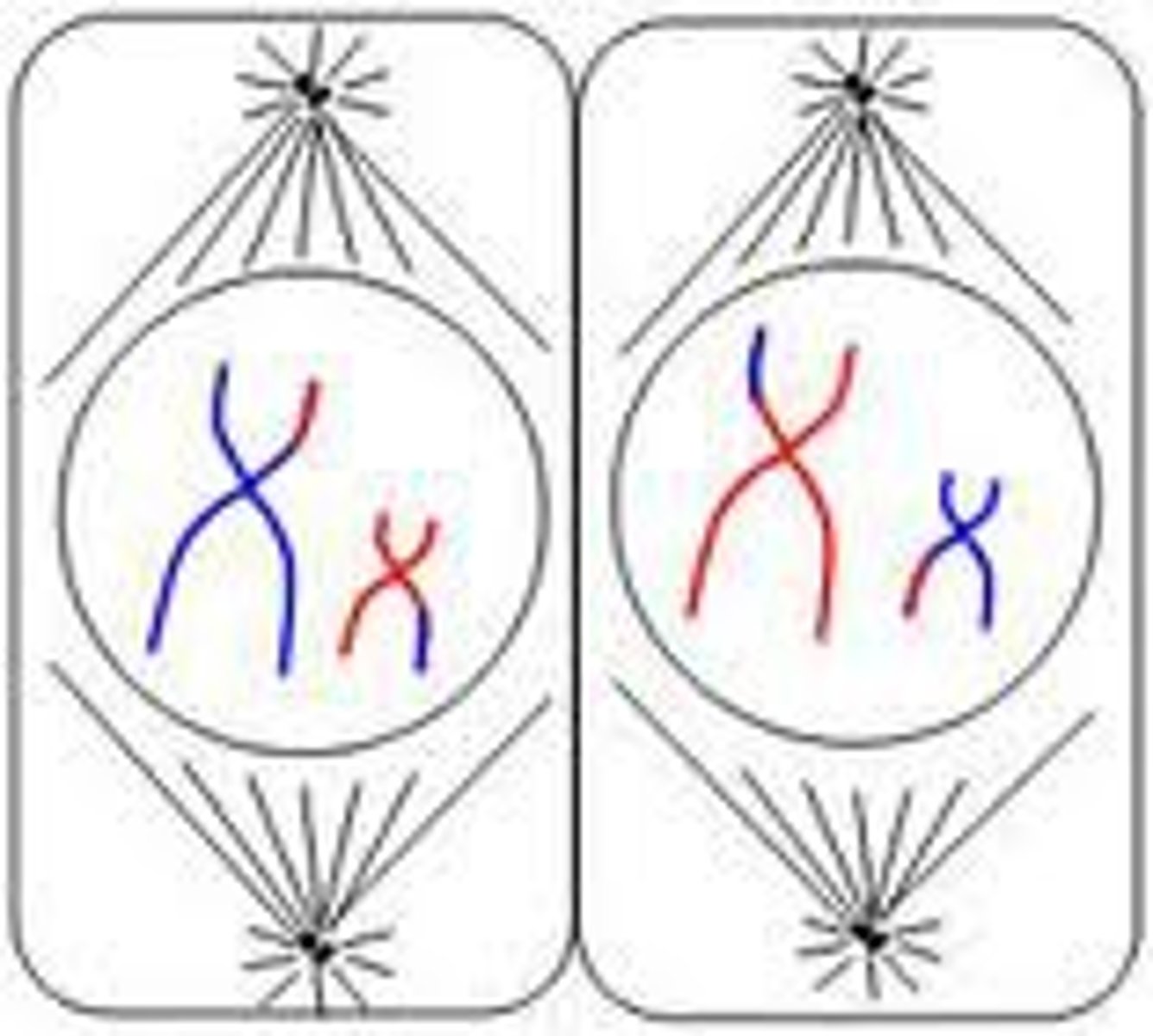
Metaphase II
The duplicated chromosomes move to the centre of the cell. Each centromere attaches to two spindle fibres instead of one.
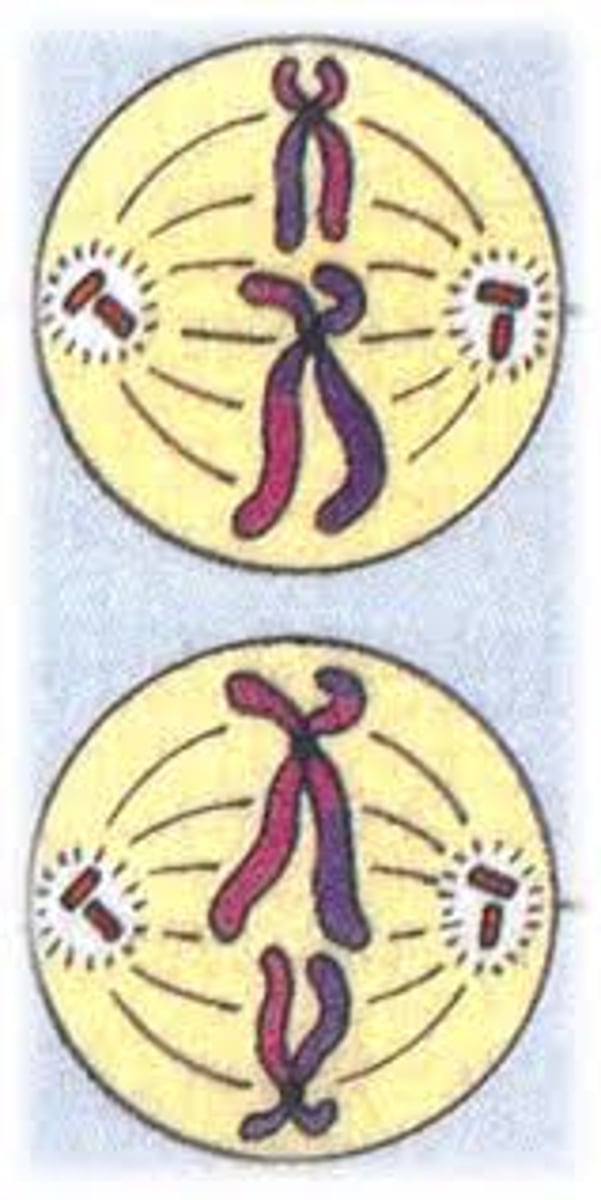
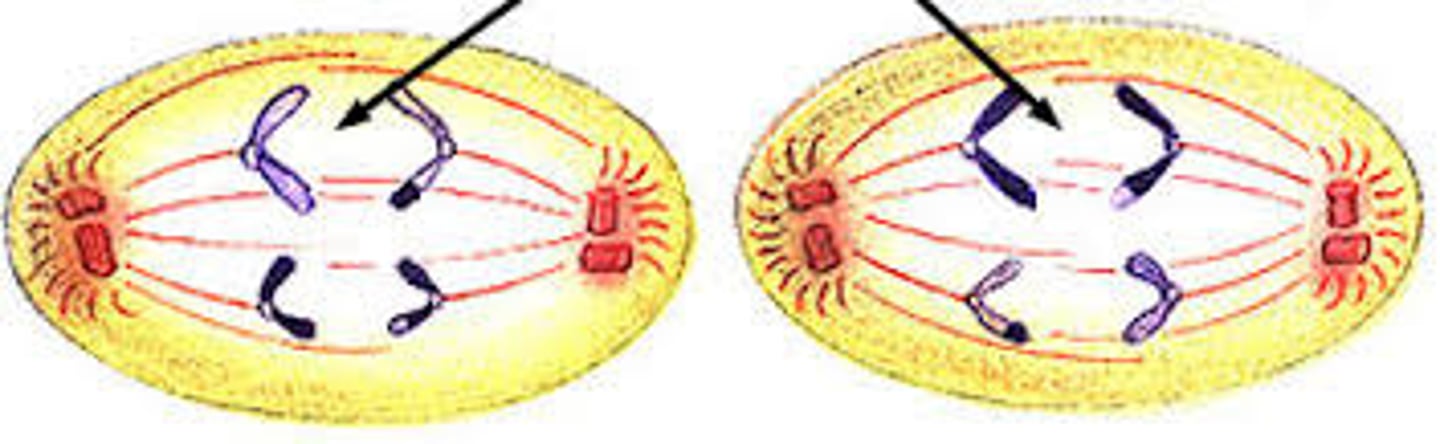
Anaphase II
The centromere divides. The chromatids seperate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Each chromatid is now an individual chromosome.
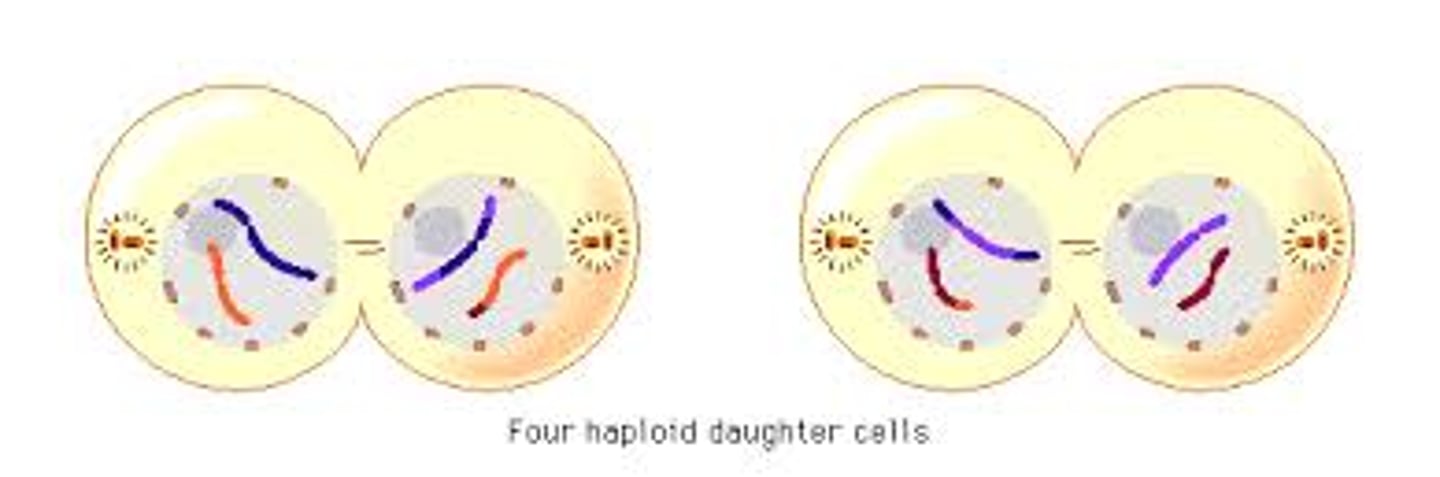
Telophase II
The spindle fibres disappear, and a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes.
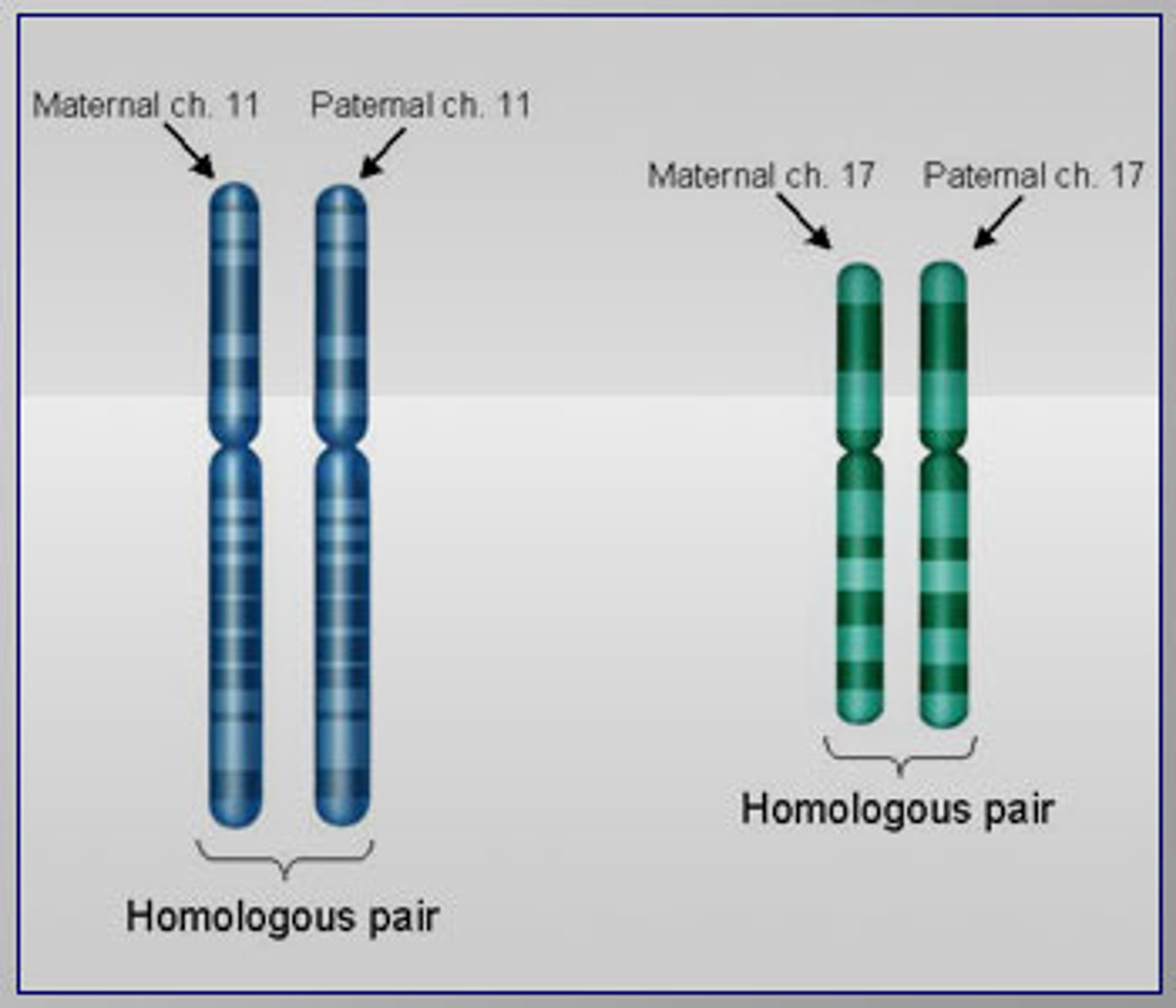
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes, that have the same structure, and that pair during meiosis.
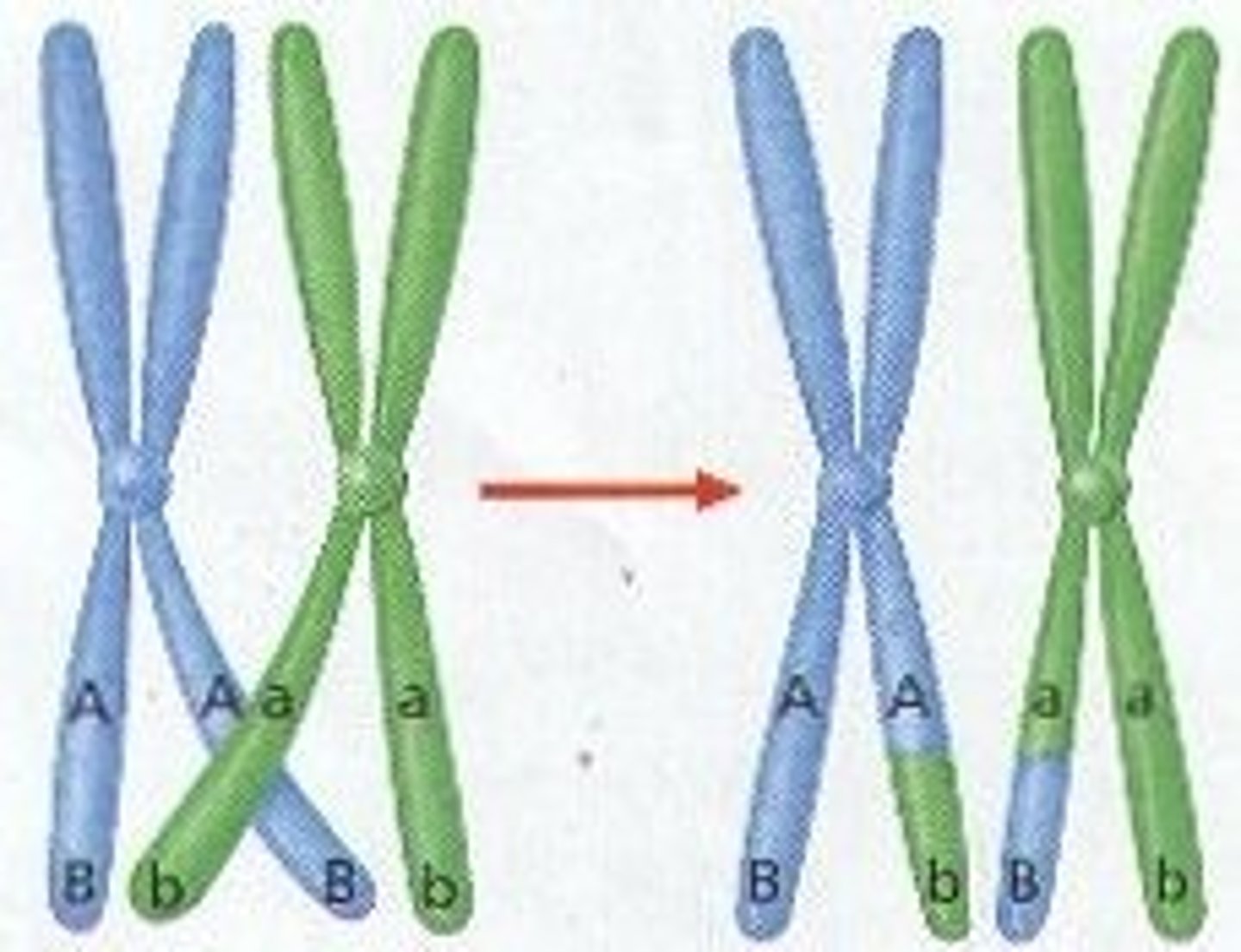
Crossing Over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis. This increases genetic variation.
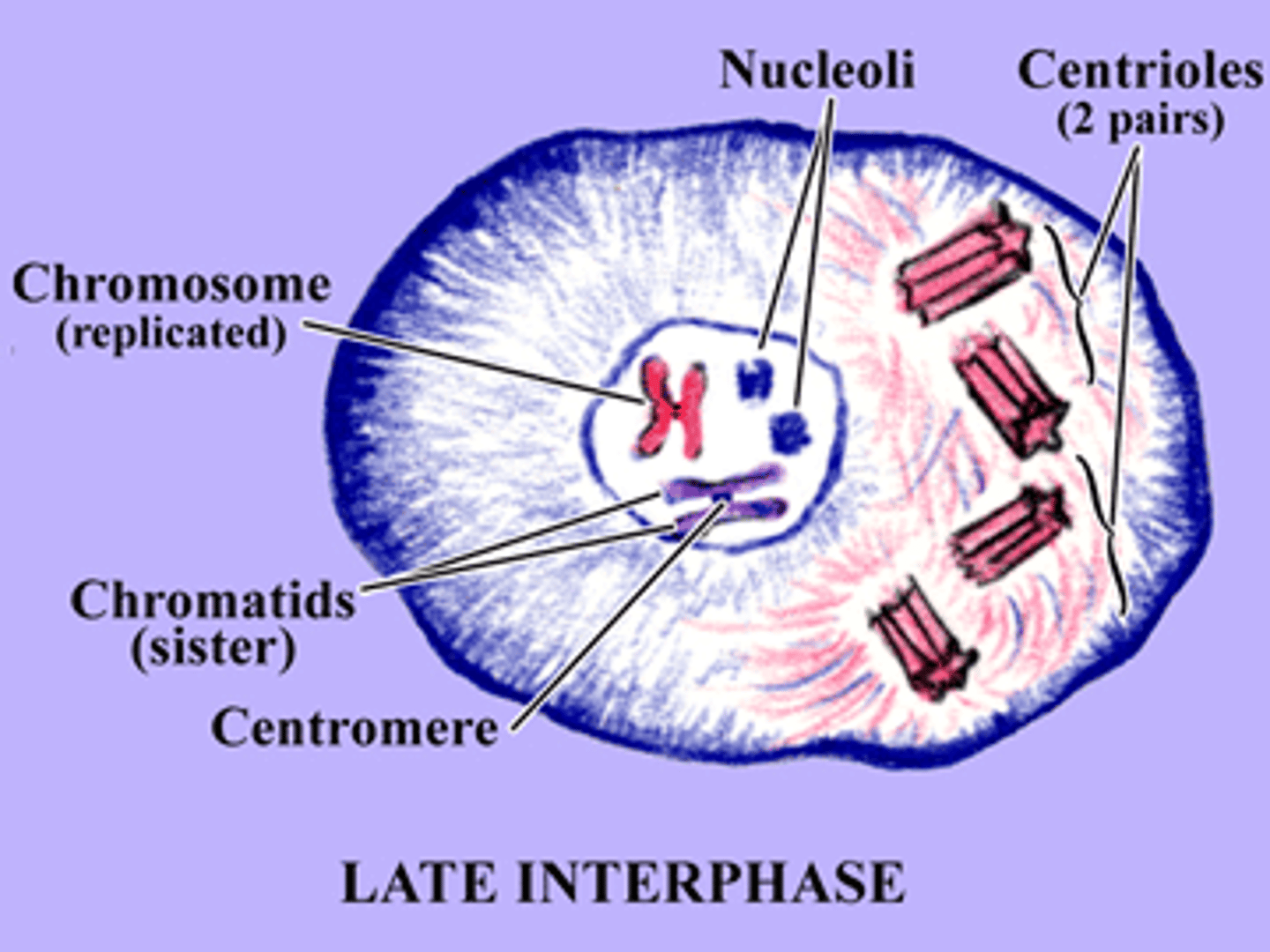
Interphase
Chromosomes (uncondensed in this phase) replicate in preparation for meiosis. At this point they are long and thing and called "chromatin".
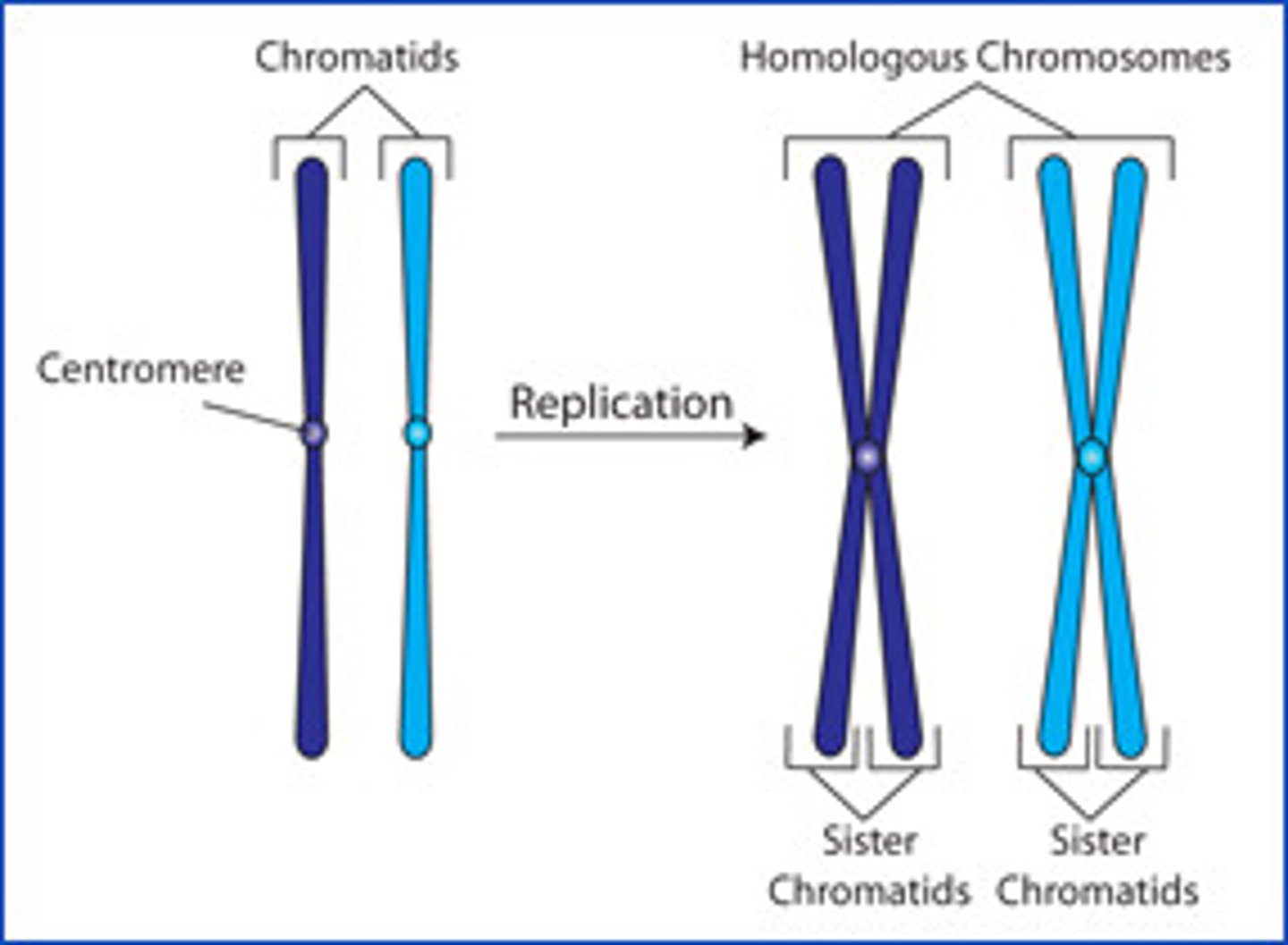
Replication
Chromosomes duplicate before dividing in meiosis.
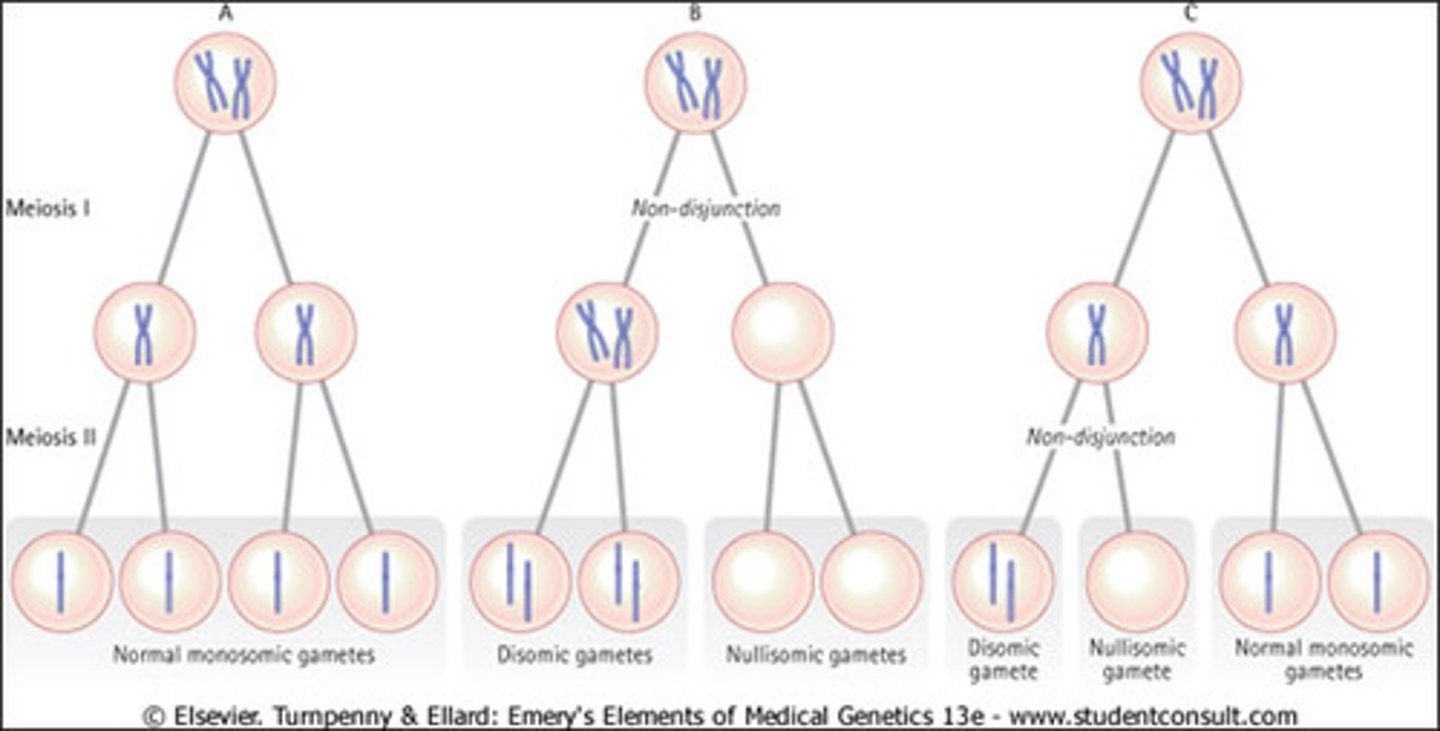
Non-Disjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate, resulting in gametes with too many or too few chromosomes
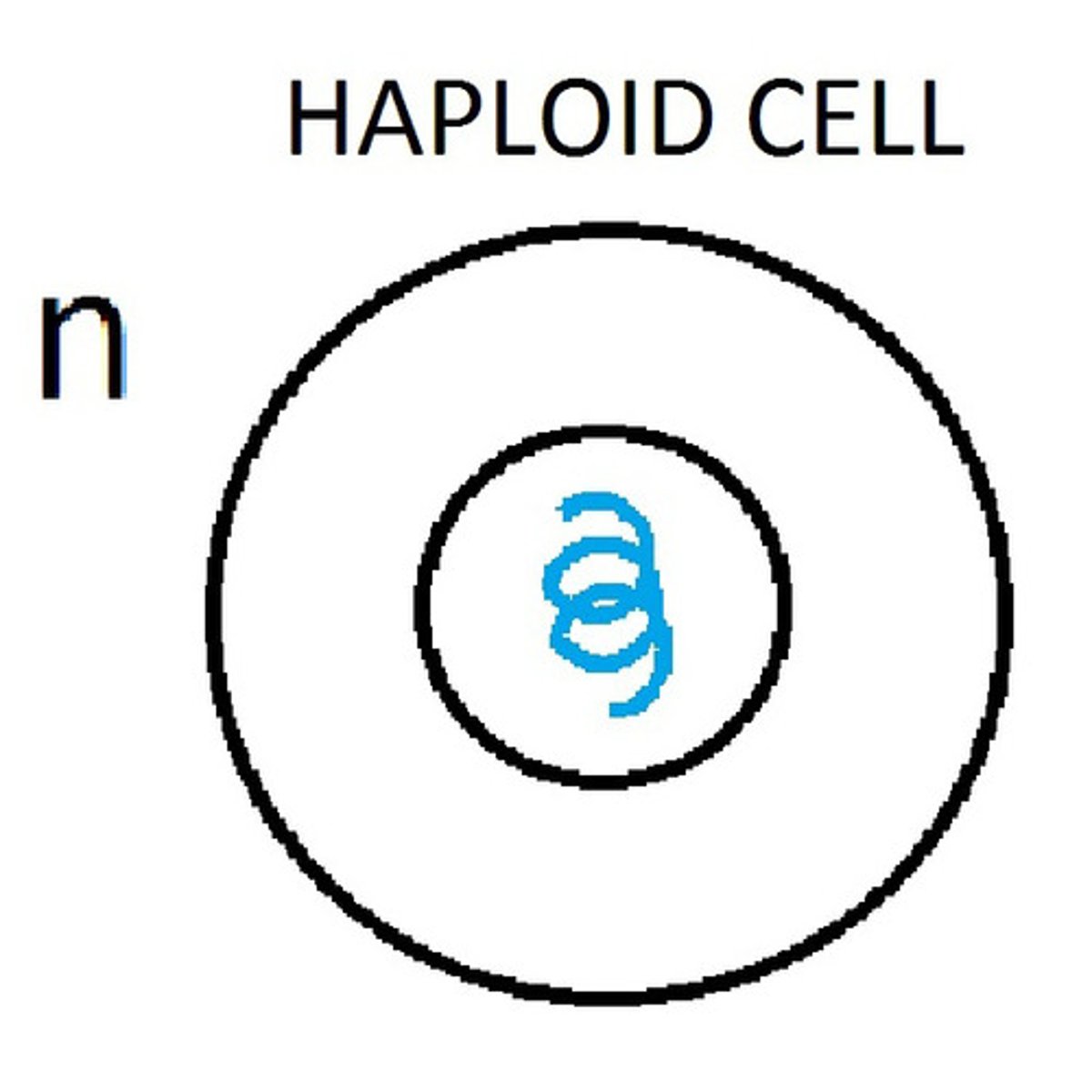
Haploid
A cell that contains only one set of chromosomes instead of the normal pair. Gametes, which are sex cells like sperm and eggs, are haploid cells.
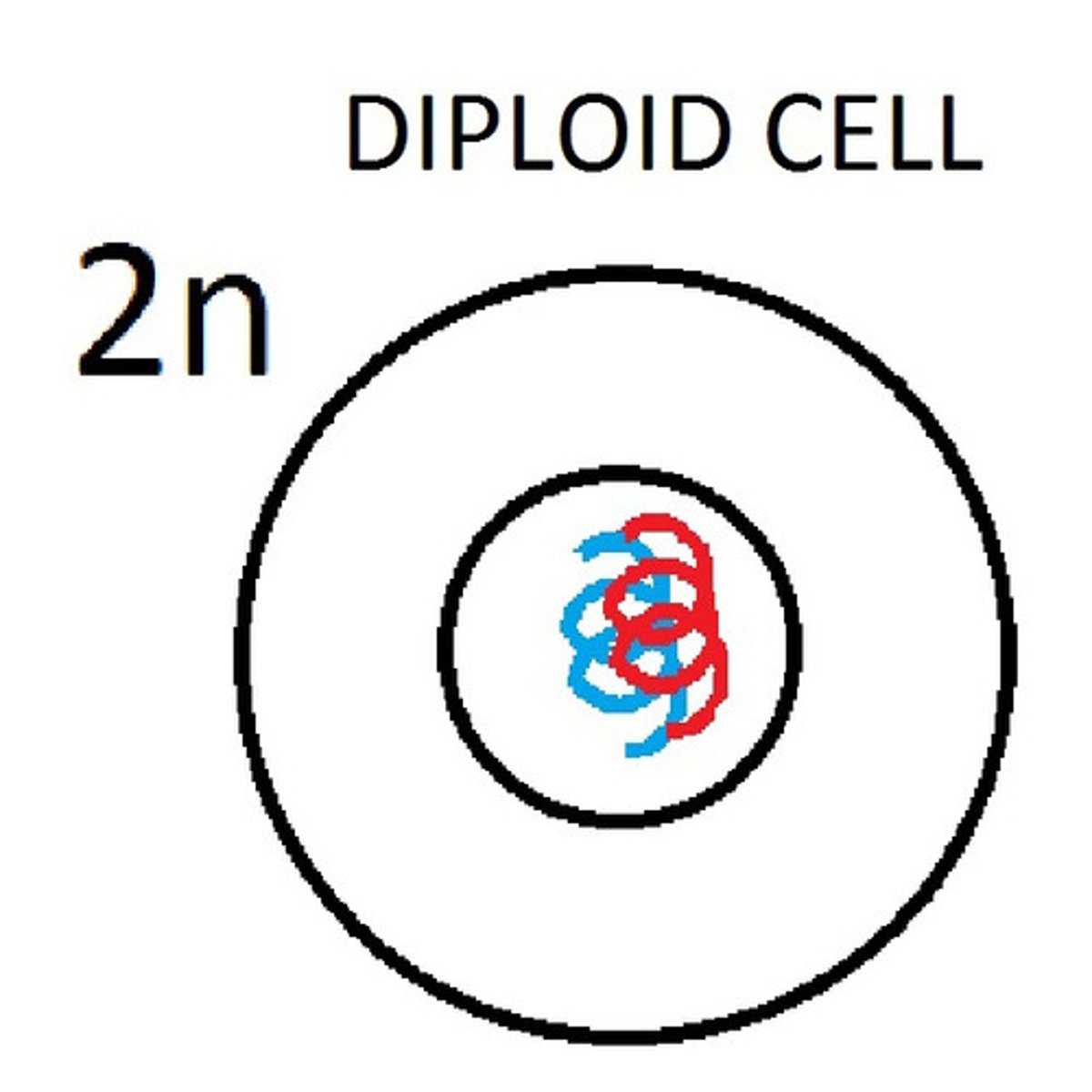
Diploid
A cell that contains two sets of chromosomes; one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father. Most body cells (nerve, brain, muscle, skin, etc.) are considered diploid cell.
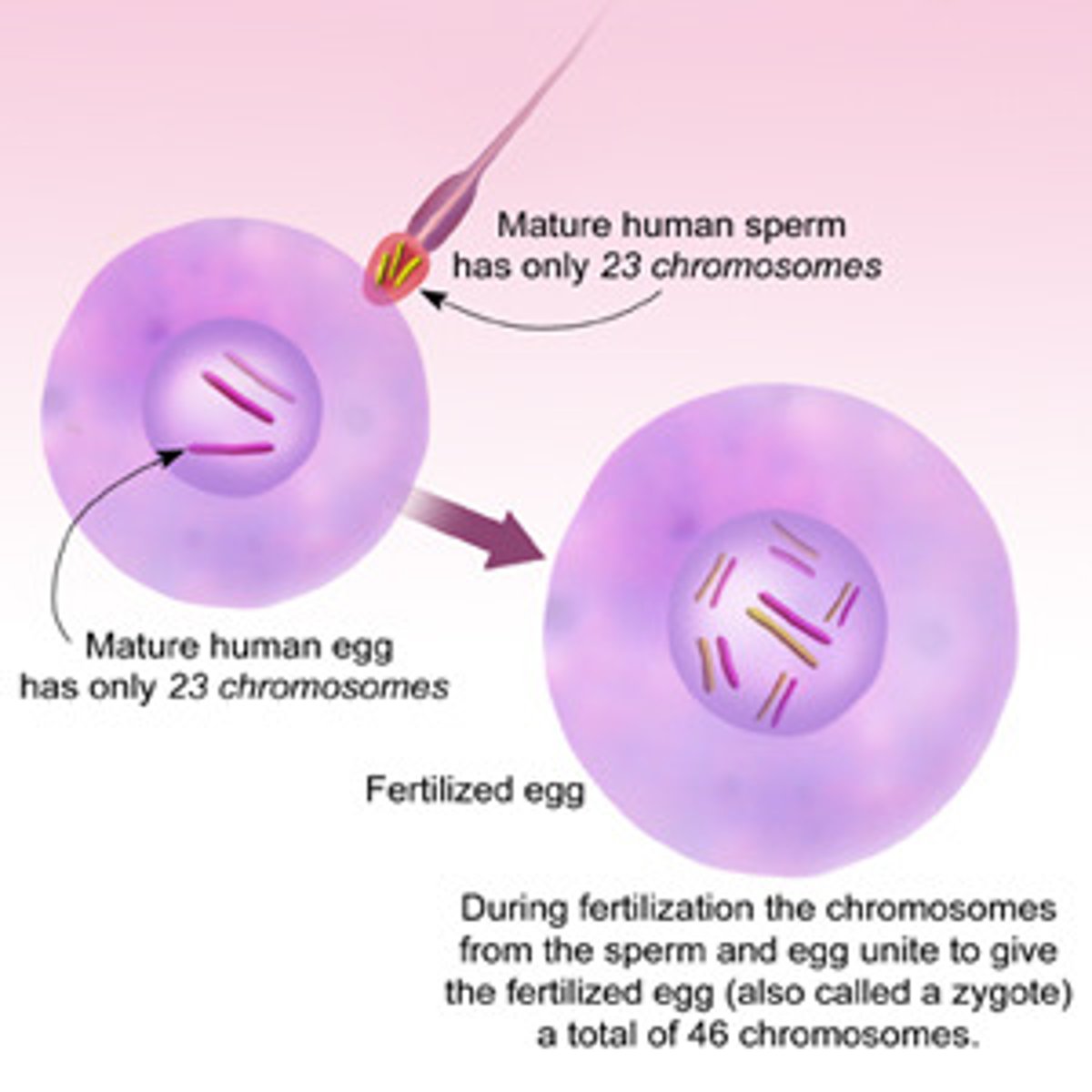
Sperm
Male gamete (sex cell)
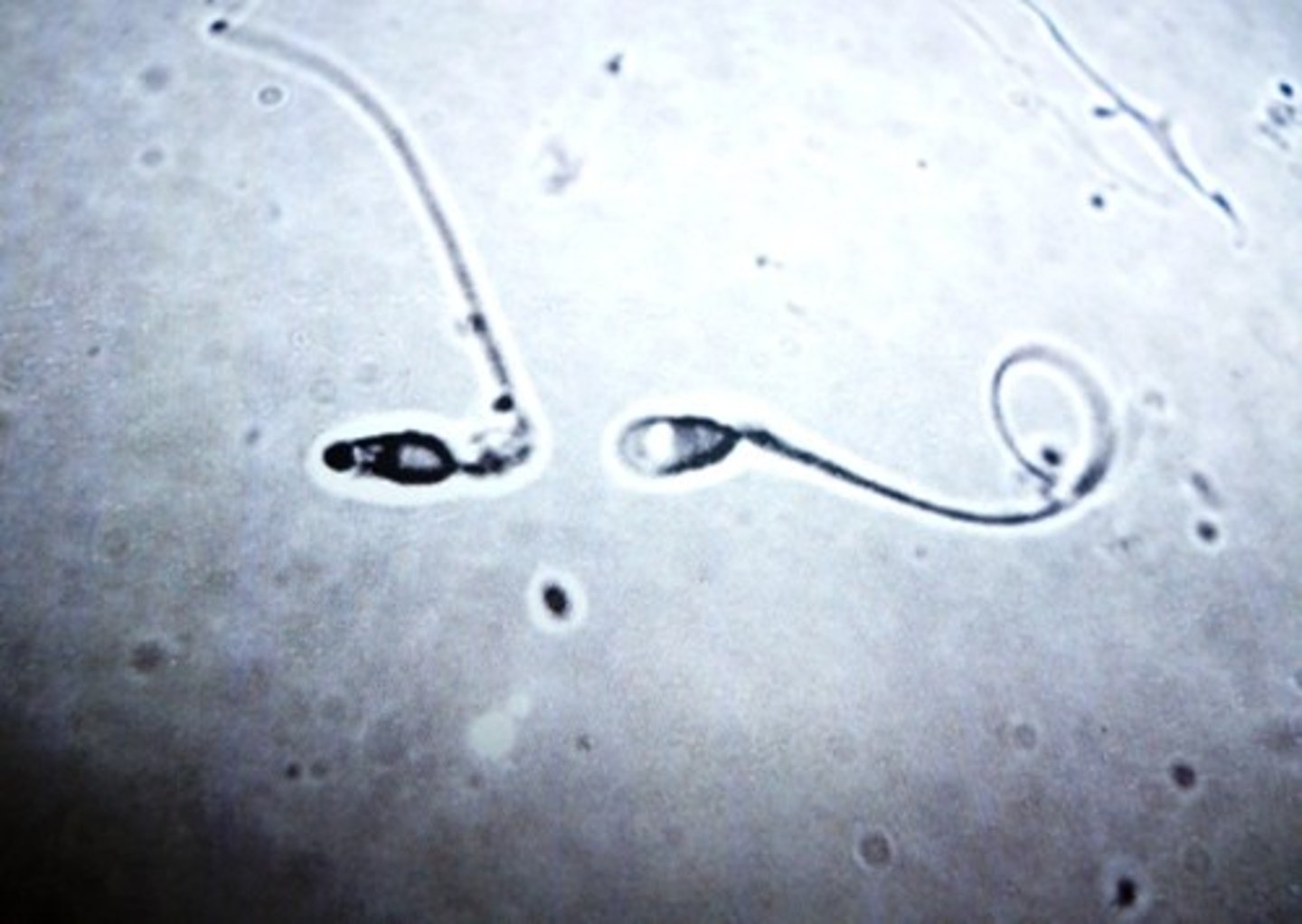
Egg
Female gamete (sex cell)
Gamete
The result of meiosis is 4 gametes, or sex cells, that each contain half of the genetic information in the parent organism.
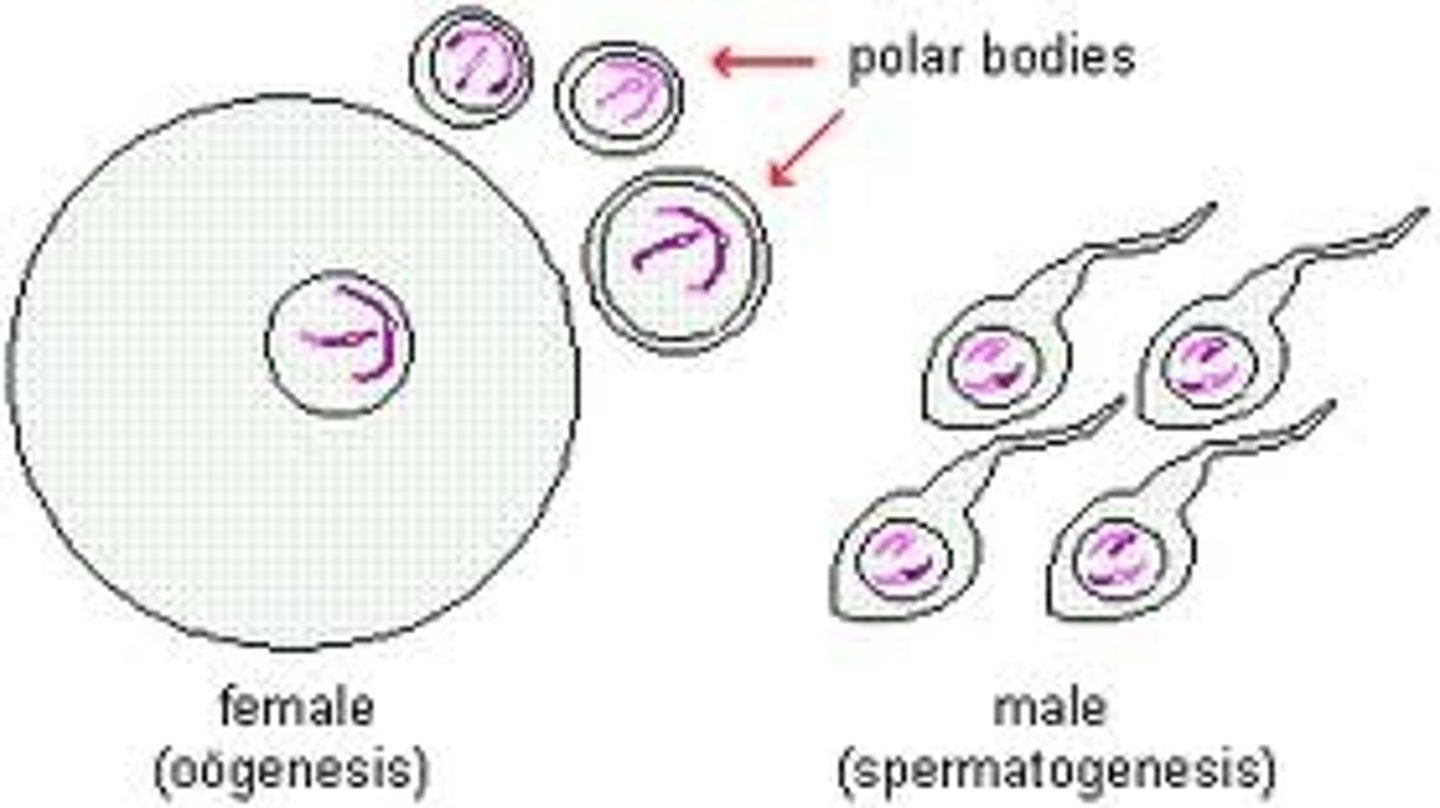
Meiosis
A process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number. It occurs by two divisions of the nucleus and results in the production of 4 sex cells (gametes).
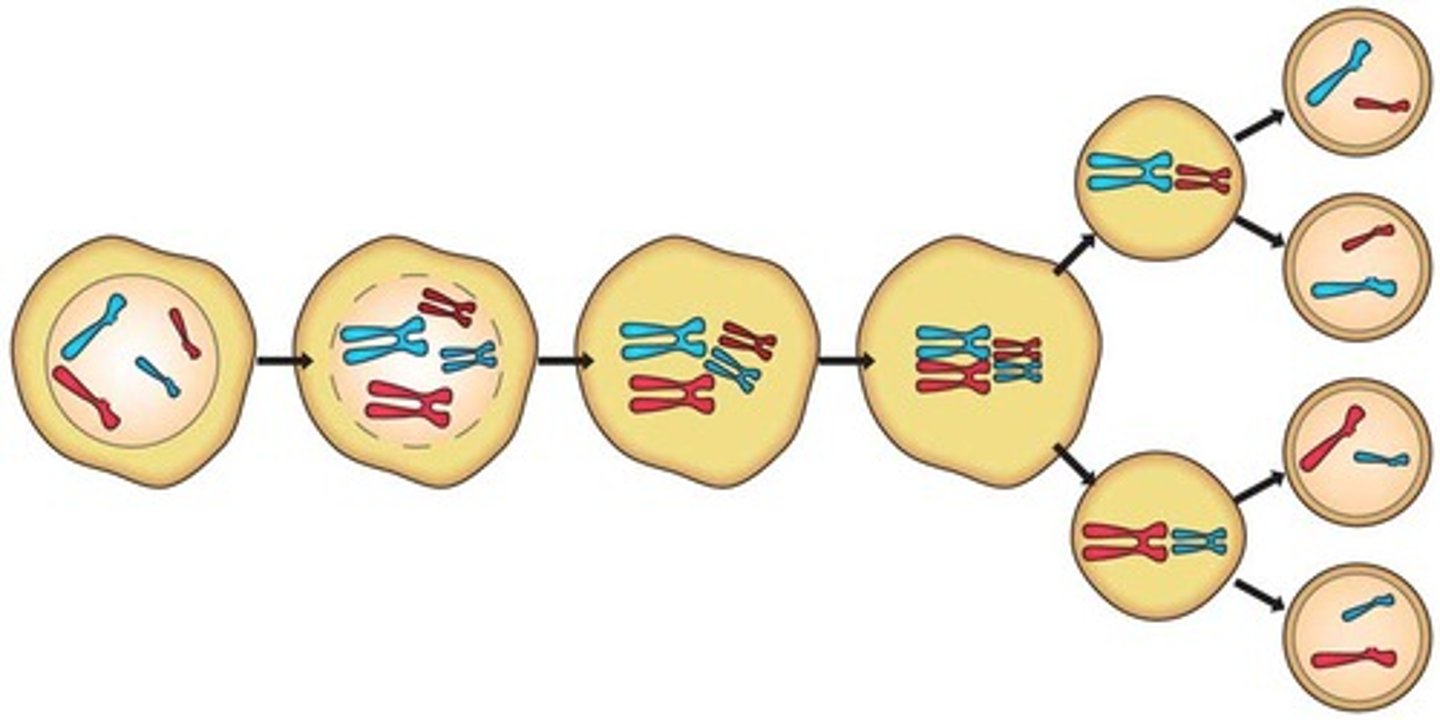
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.