Unit 2 - Central Dogma of Biology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
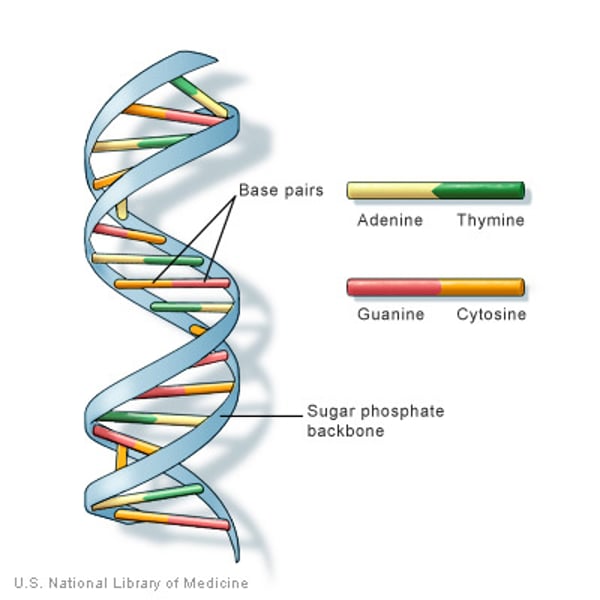
DNA
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
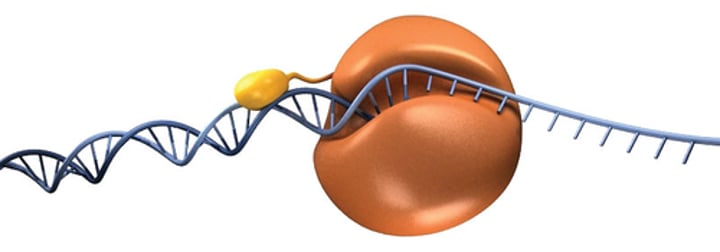
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins complementary bases (A-T, C-G) to single-stranded DNA
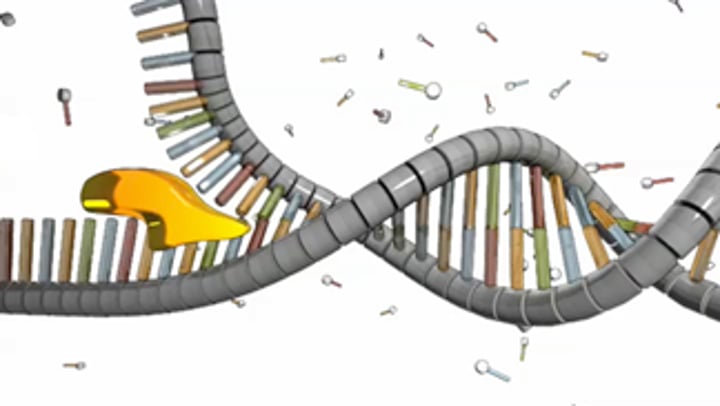
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a phosphate, sugar (deoxyribose) and a base (A,T,C,G).
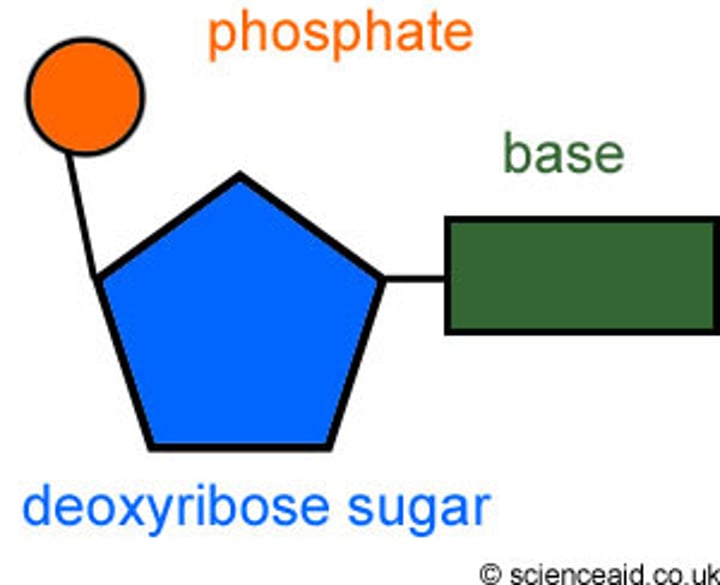
Complementary pairs
A-T or C-G ; the DNA bases that "match" or join together as a double-stranded molecule
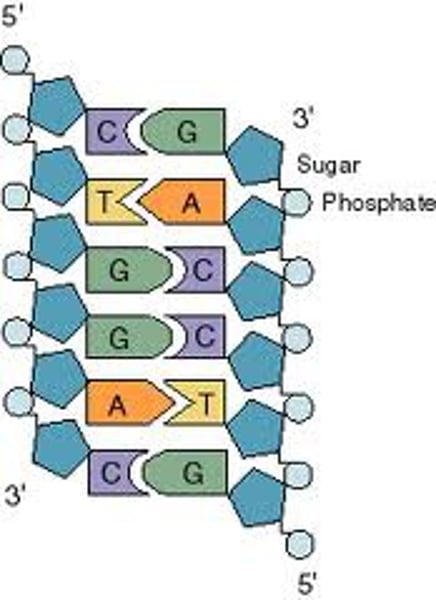
Double Helix Model
DNA is double stranded and forms a ladder-like structure similar to a spiral staircase

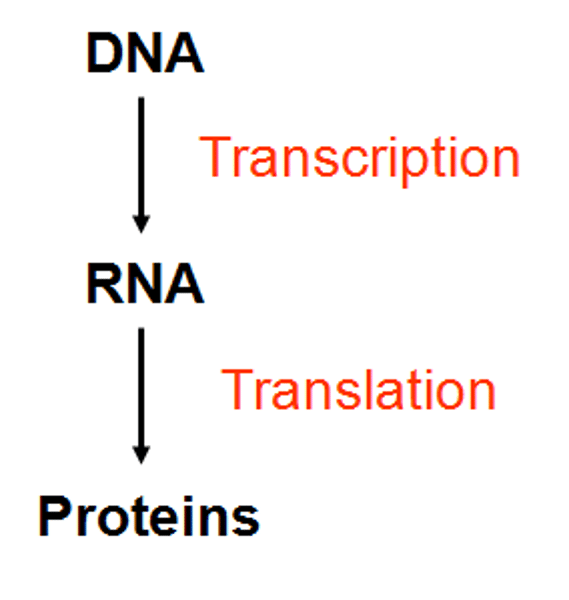
Central Dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
mRNA (messenger RNA)
a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein
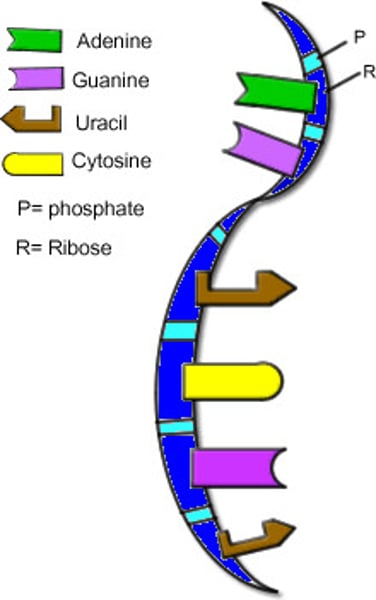
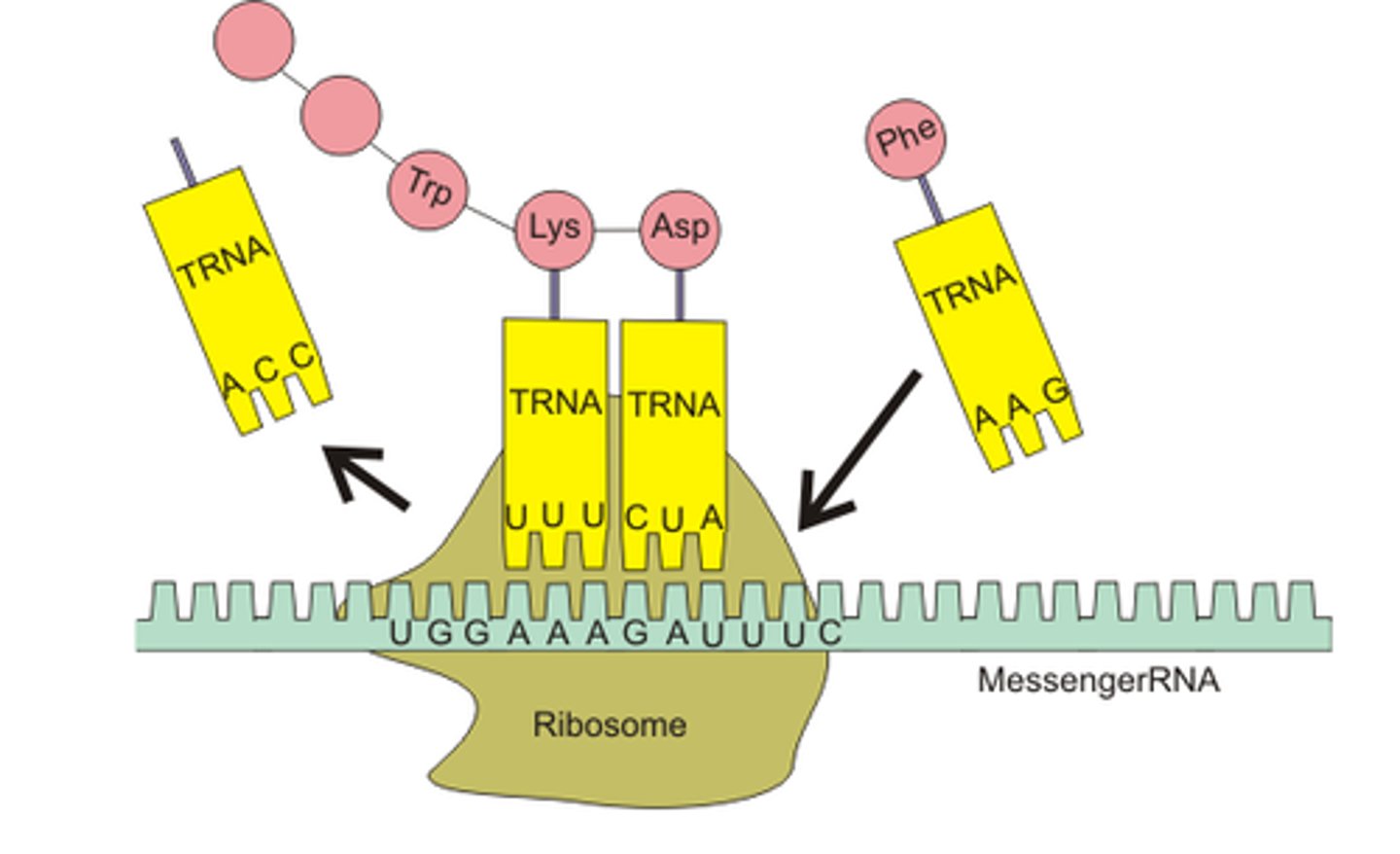
tRNA (transfer RNA)
type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
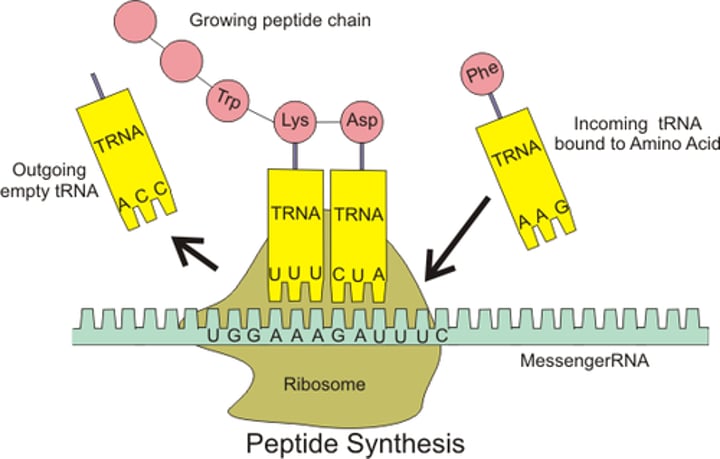
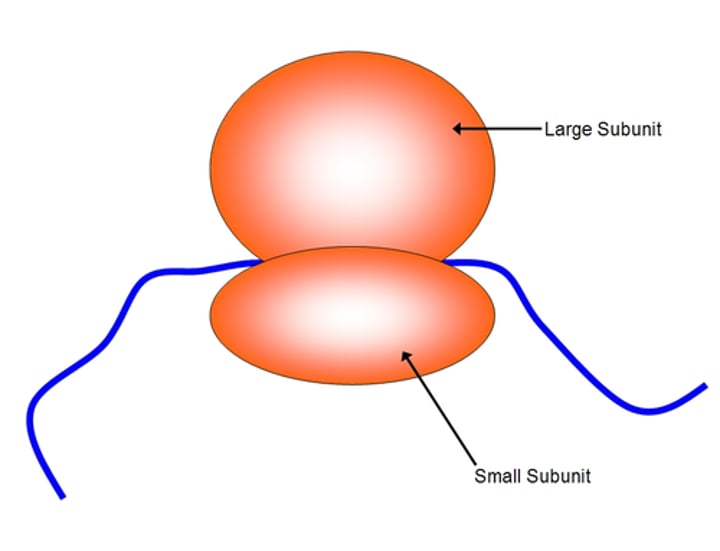
Ribosome
An organelle in the cytoplasm that reads mRNA one codon at a time
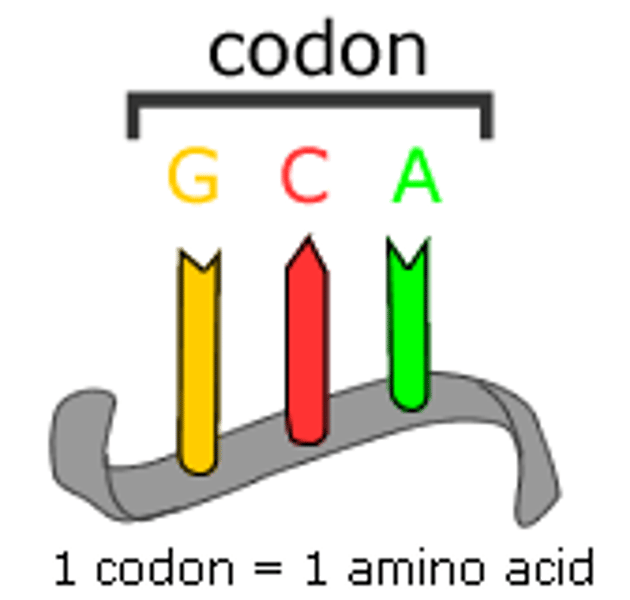
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of mRNA that provides the code for a particular amino acid
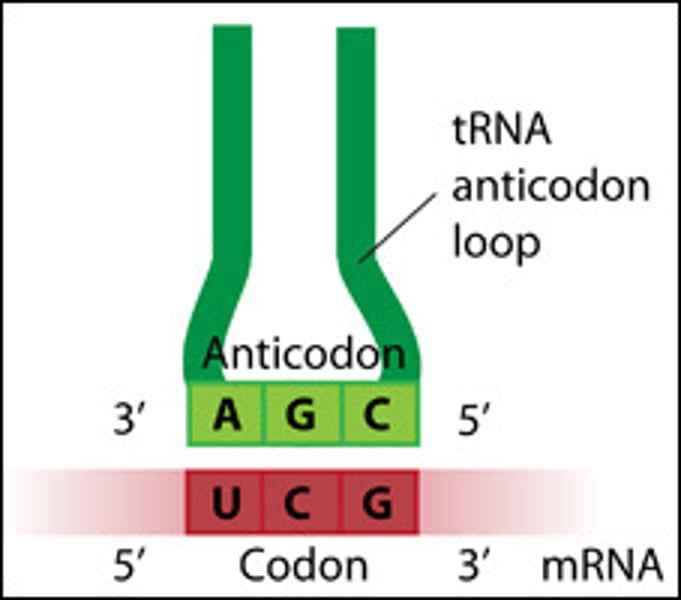
Anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
Amino acids
building blocks of proteins
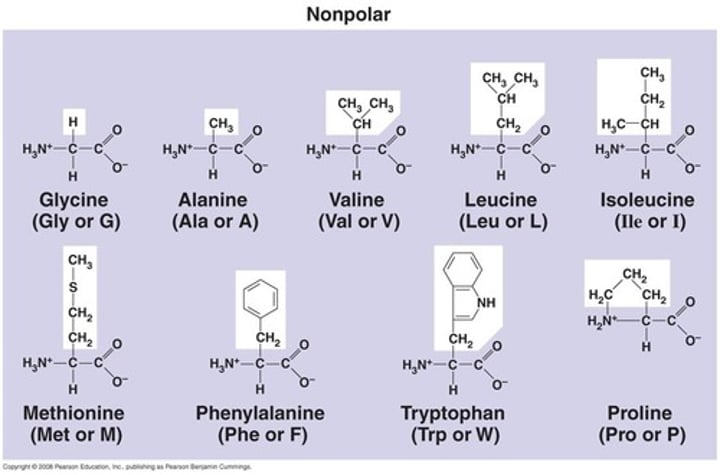
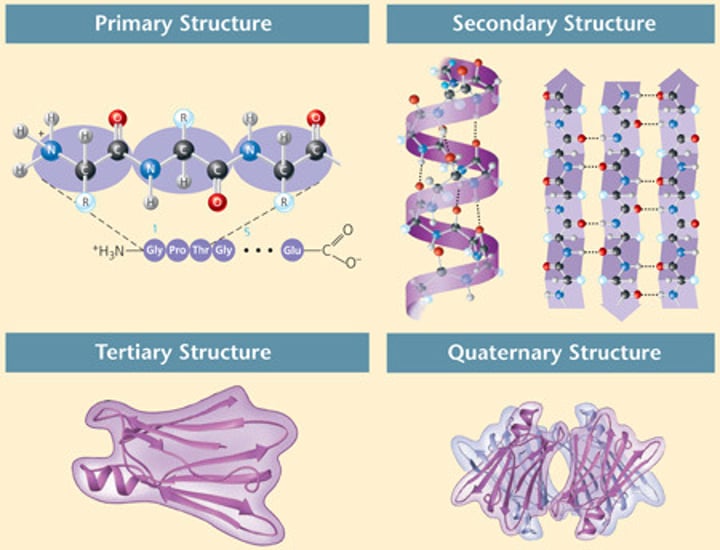
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids; Traits coded for by DNA
DNA mutations
Changes to genes due to changes in nucleotide base sequences.
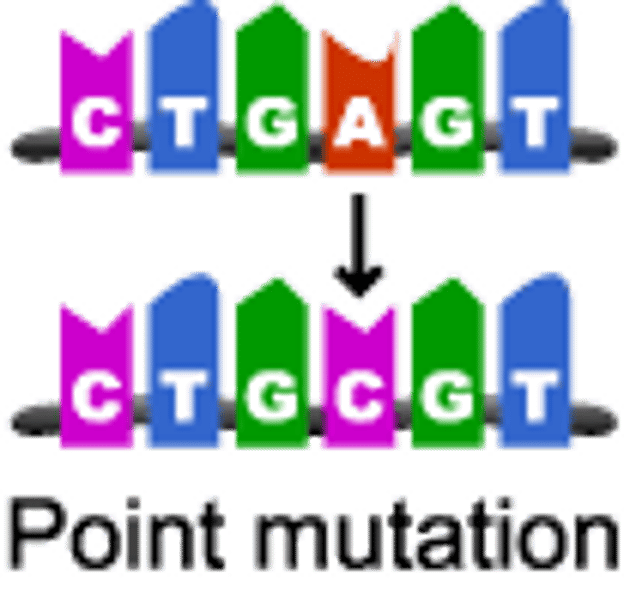
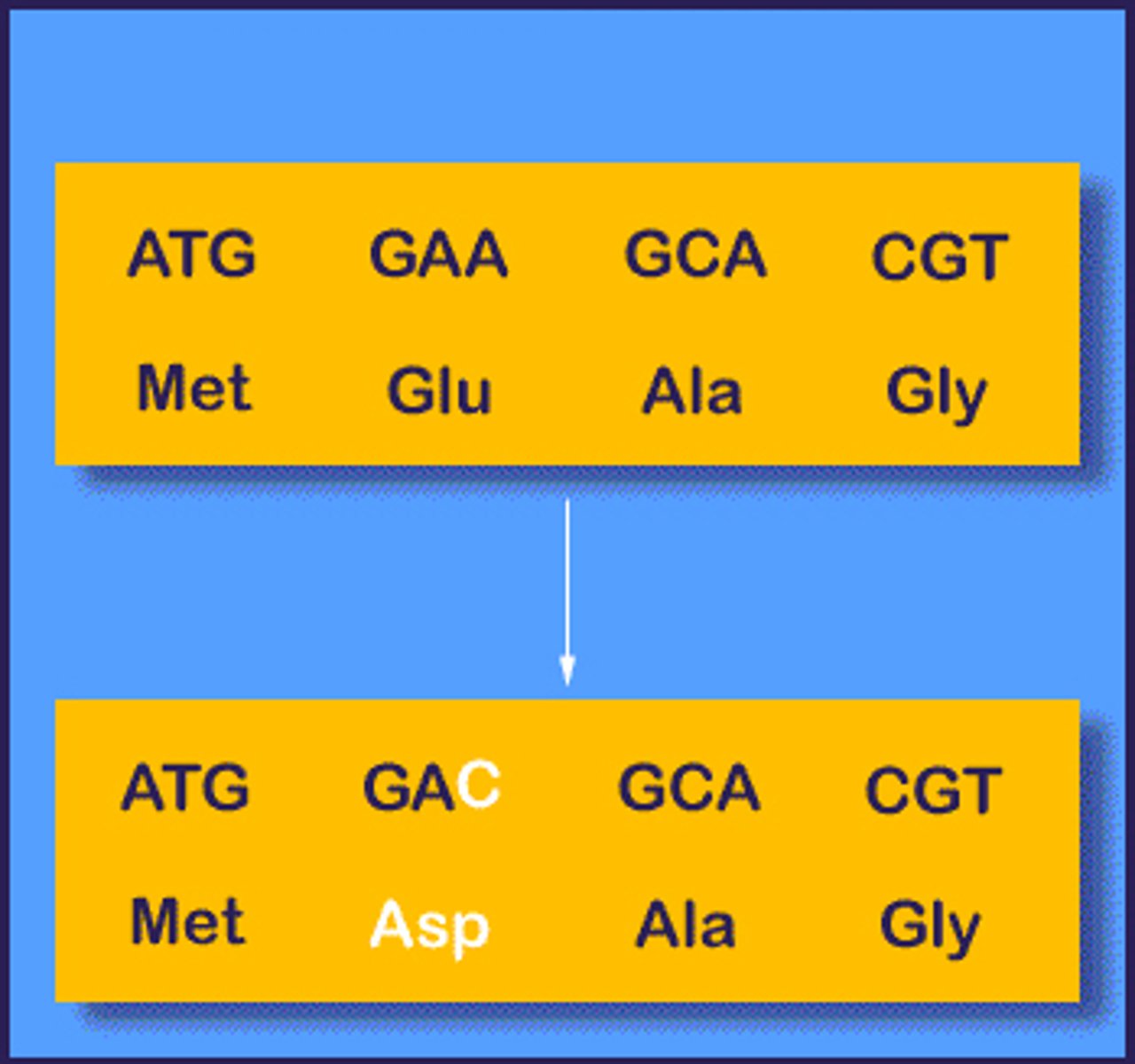
Missense mutation (substitution)
one nucleotide is replaced with a different nucleotide
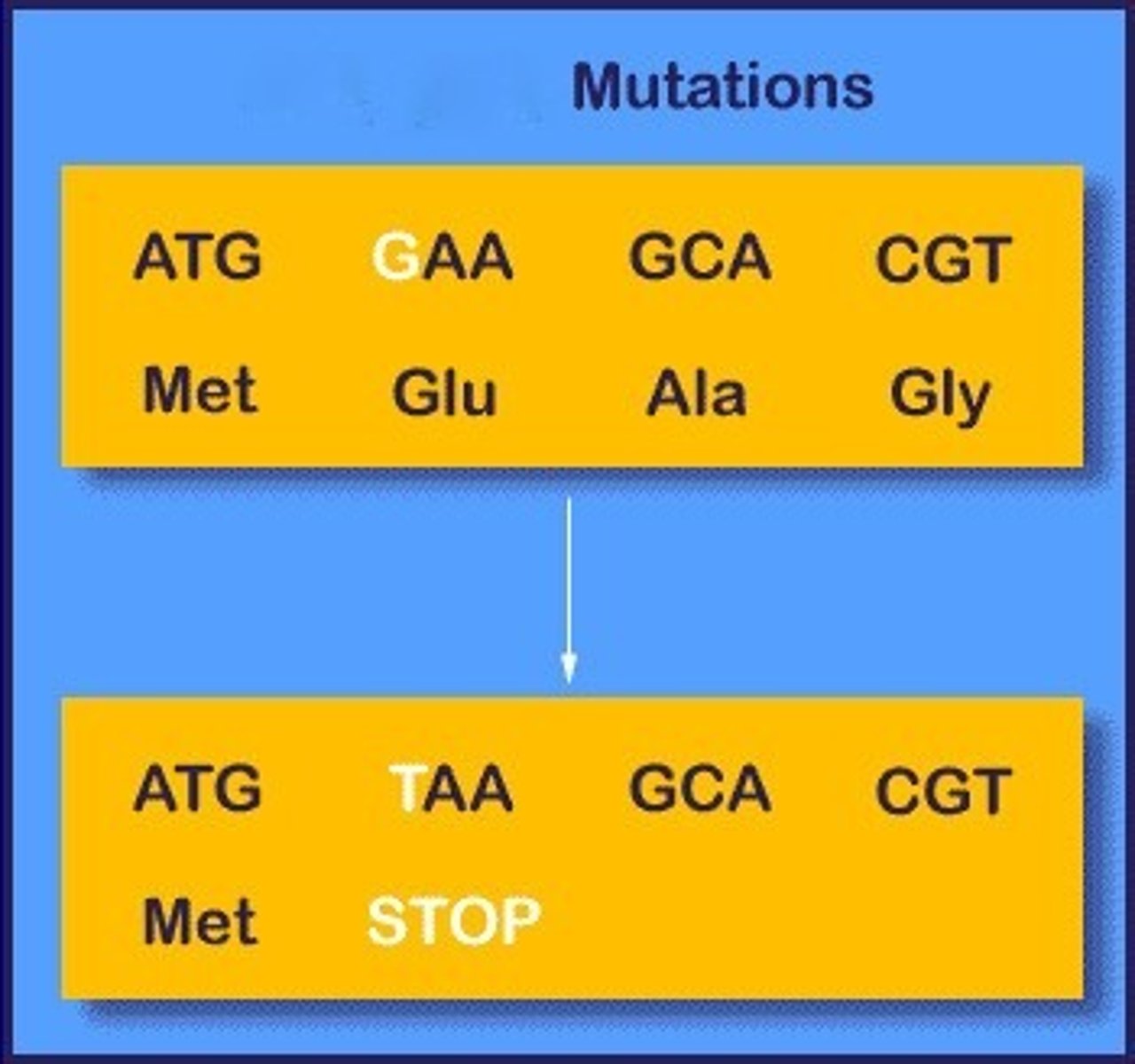
Nonsense mutation
Changes a normally working codon into a stop codon that does not code for an amino acid
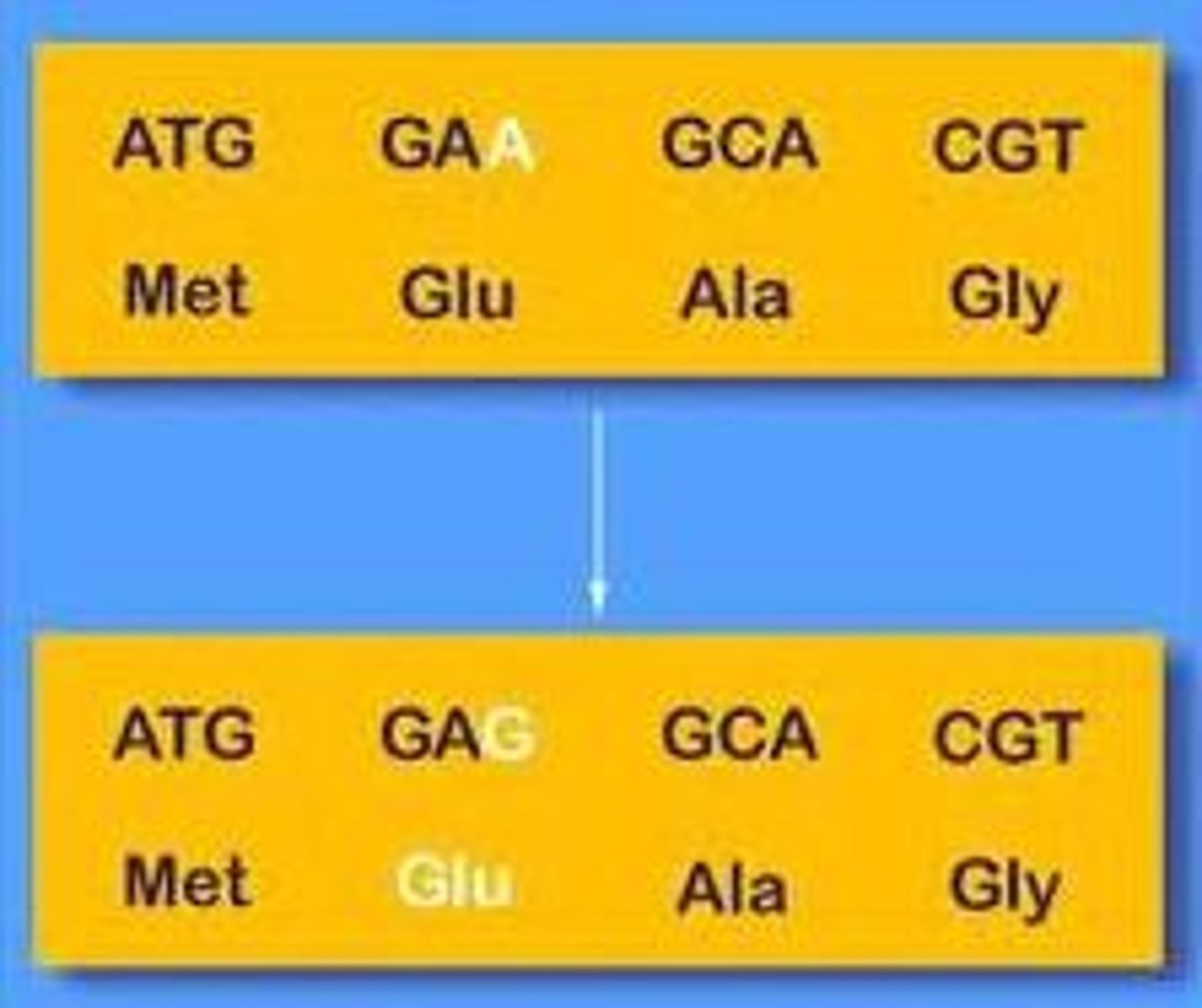
Silent mutation
Changes a base within a codon but does not change the amino acid and thus the protein is made as usual
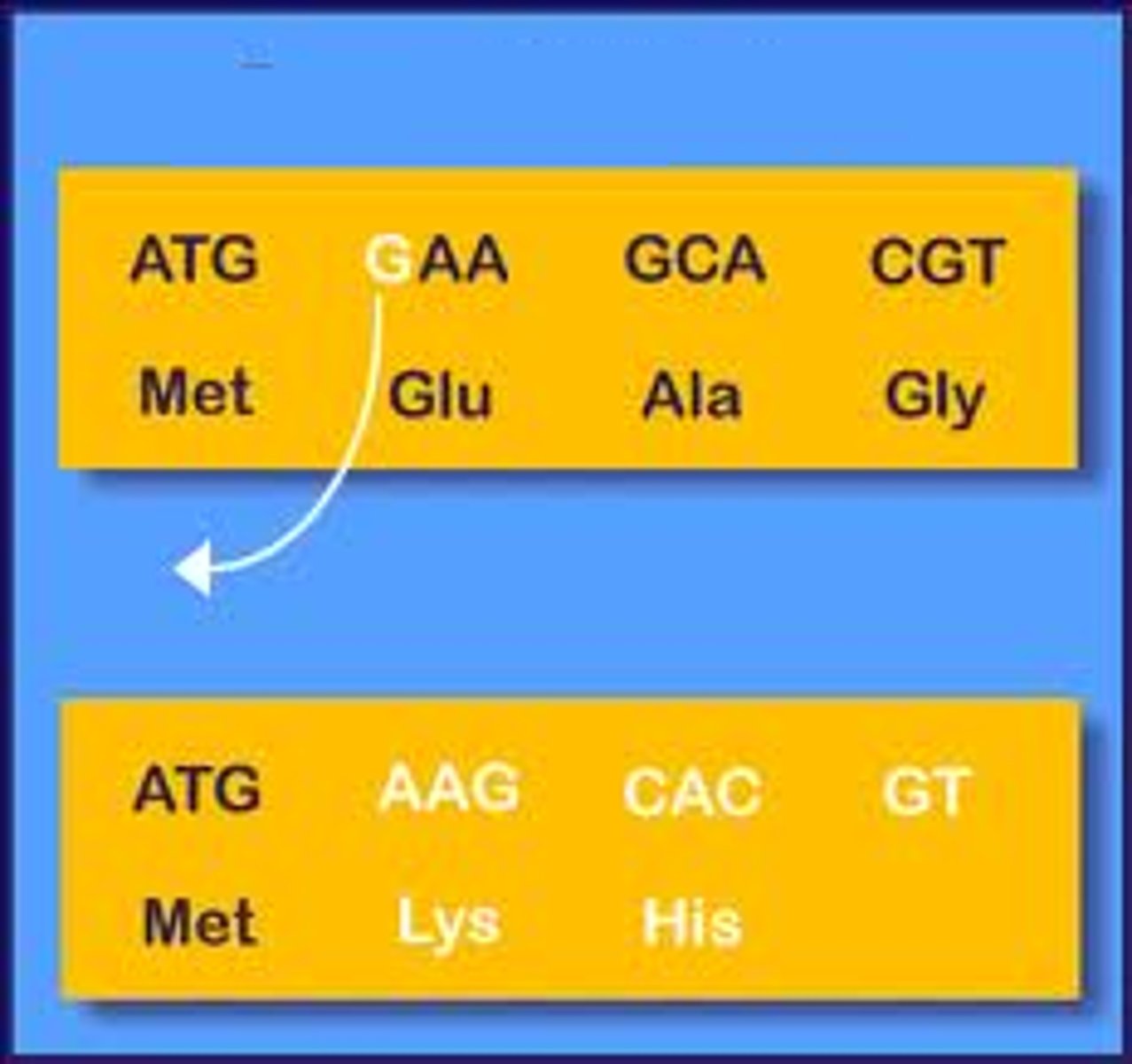
Frameshift mutation
Involves the insertion or deletion of a base in the DNA sequence that ultimately shifts the "reading" frame of the mRNA and thus alters the final protein product
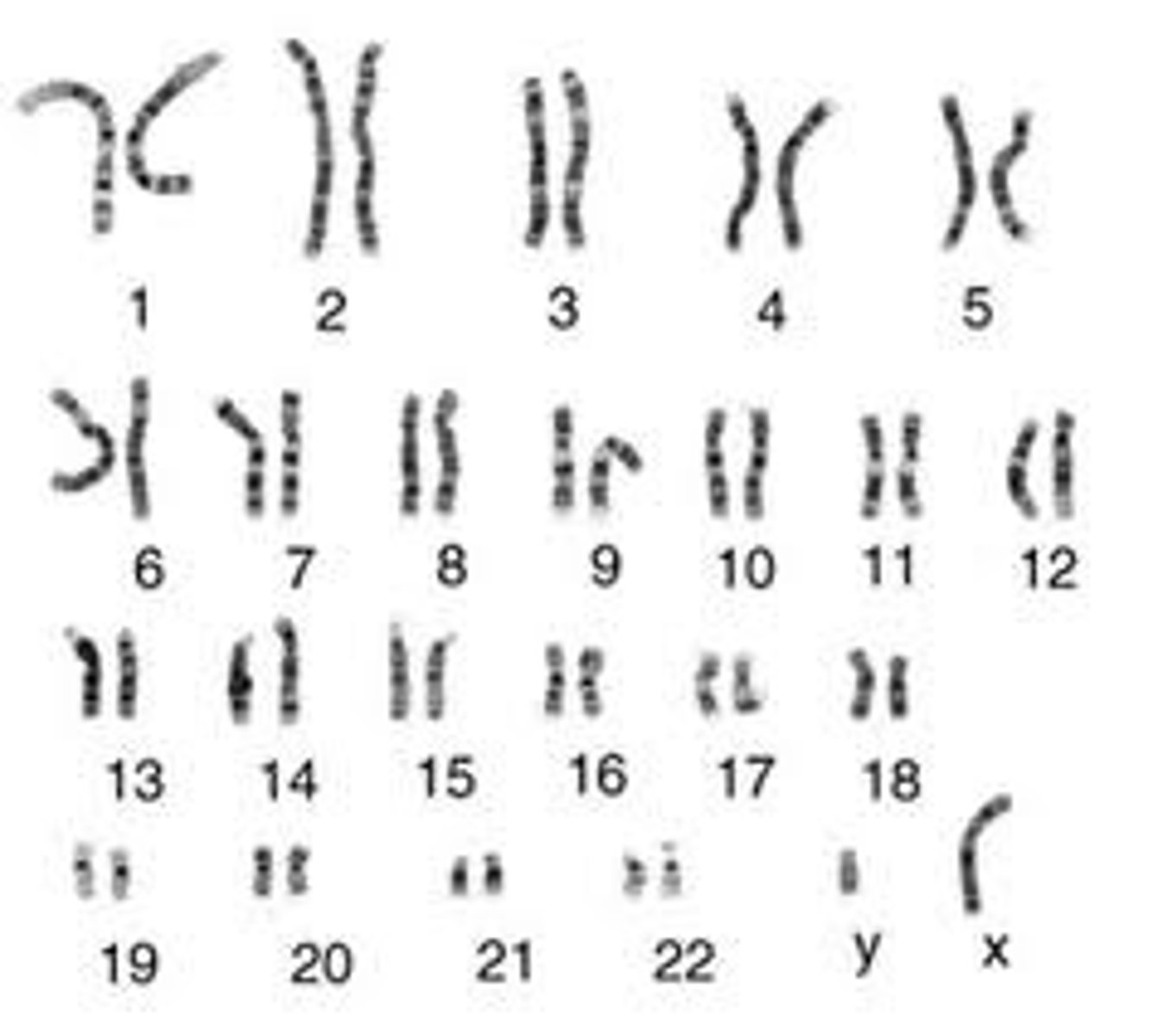
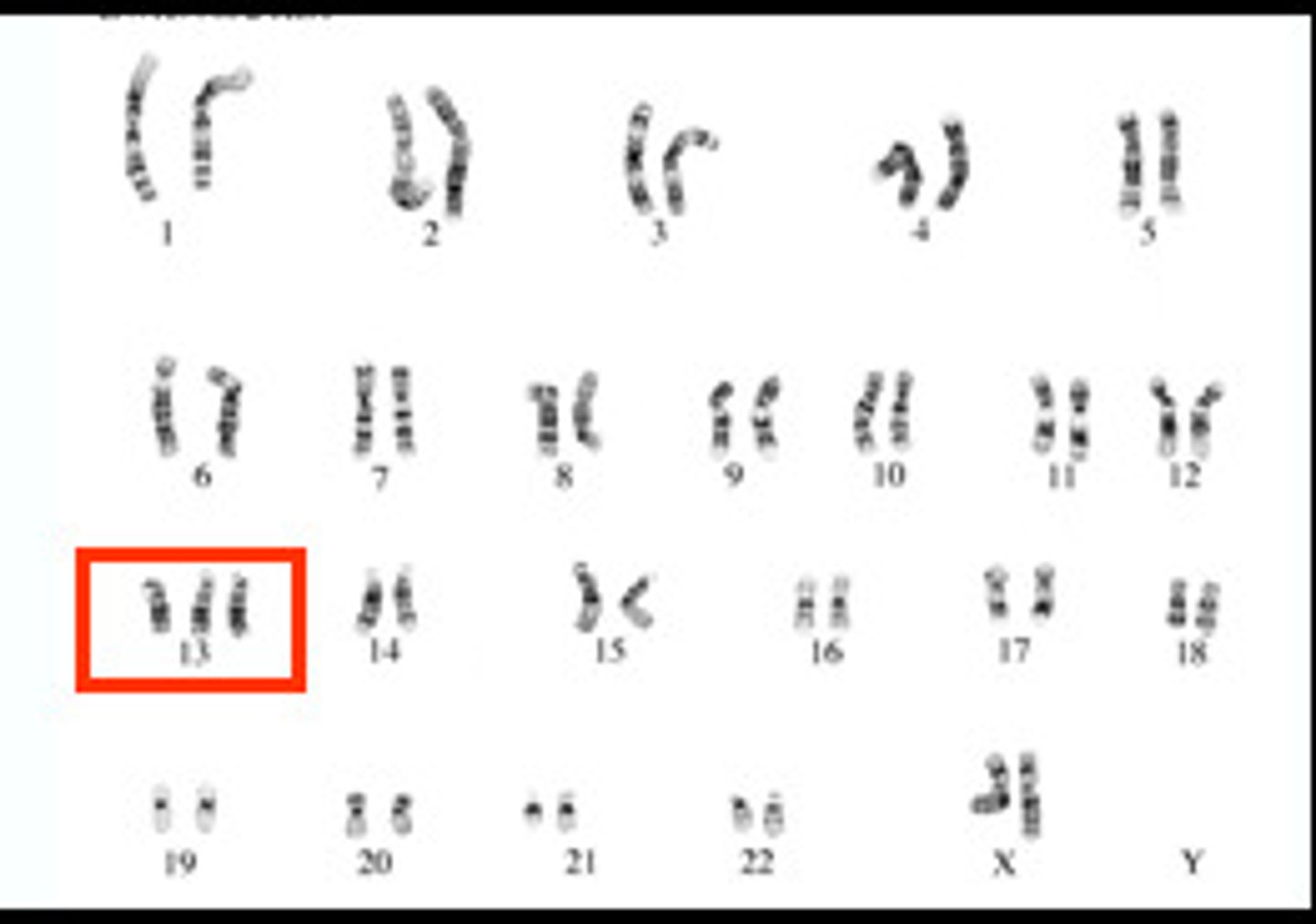
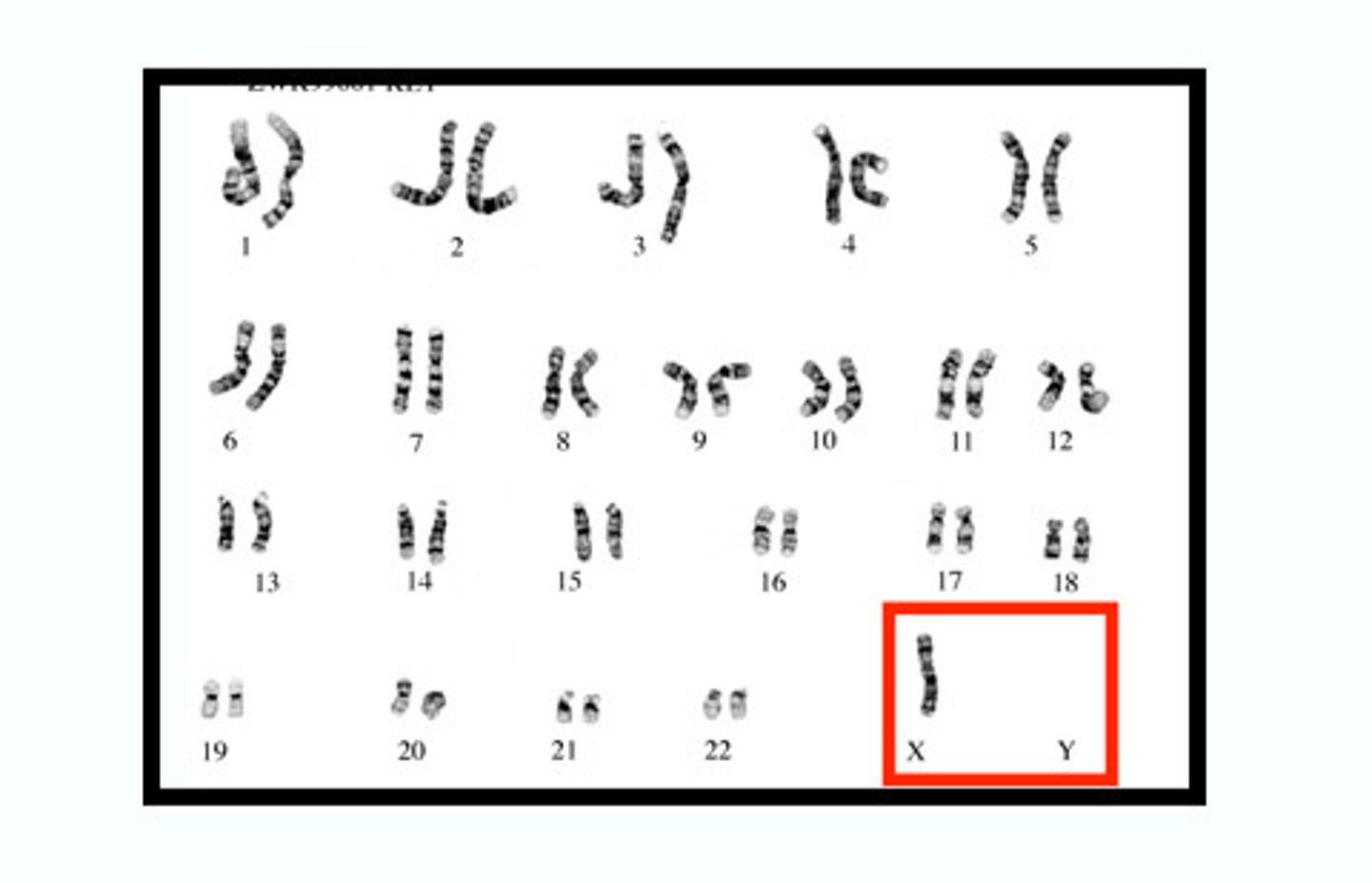
Karyotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
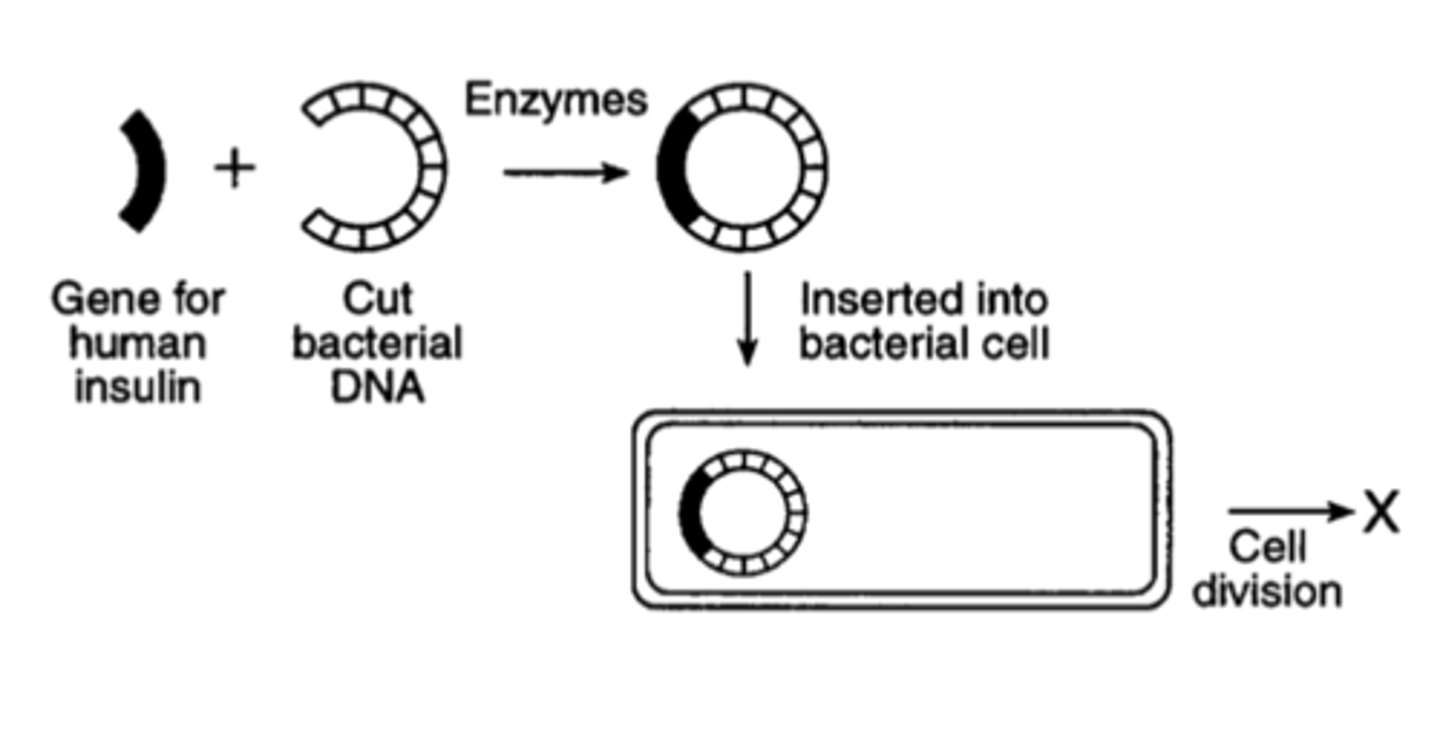
Genetic engineering (gene splicing)
Inserts genes of one organism into the genes of another in order to obtain a desired protein or trait
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
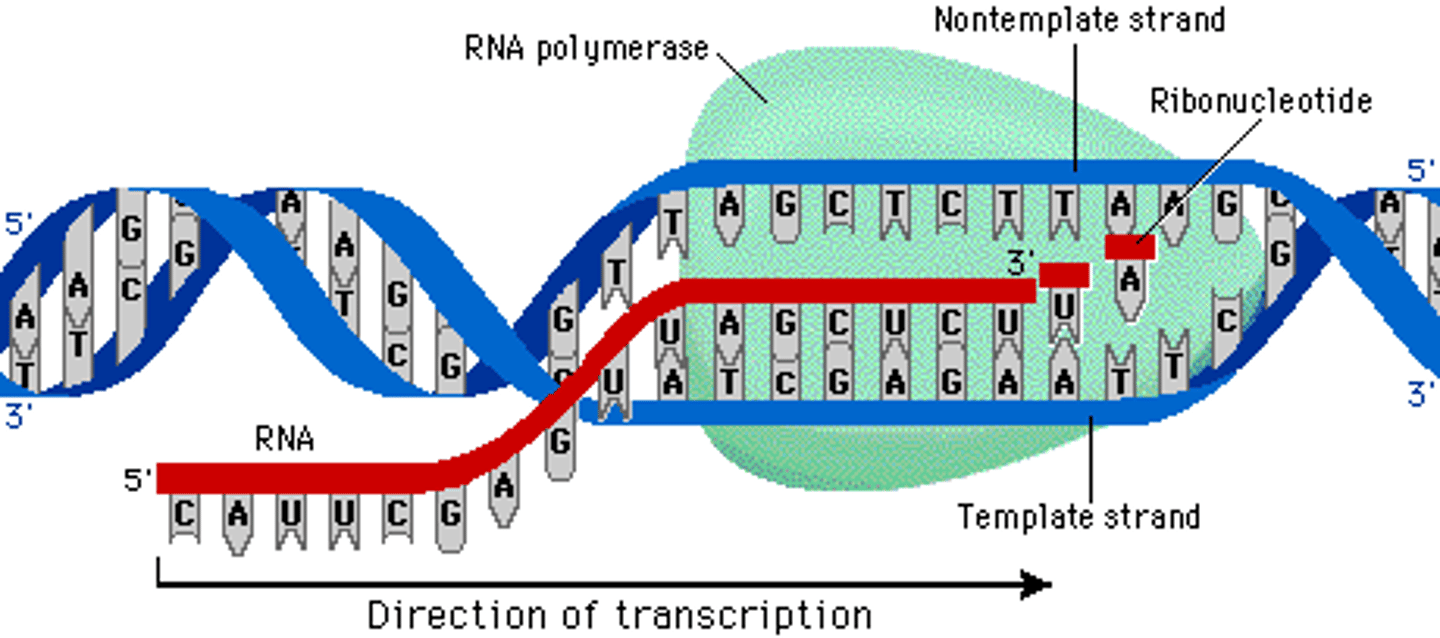
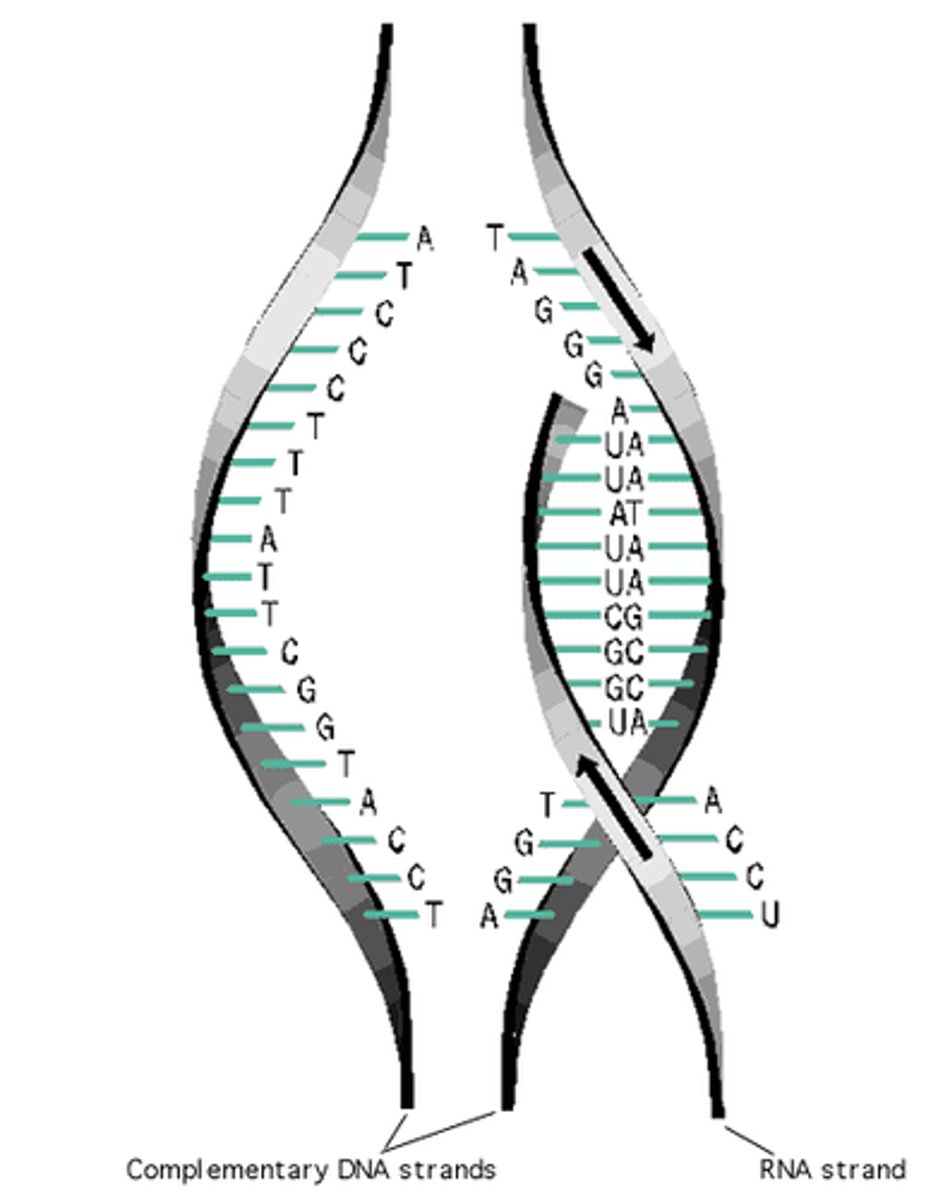
Transcription
The synthesis of a single-stranded RNA molecule from a DNA template
Translation
The decoding of mRNA into a polypeptide chain by the ribosome
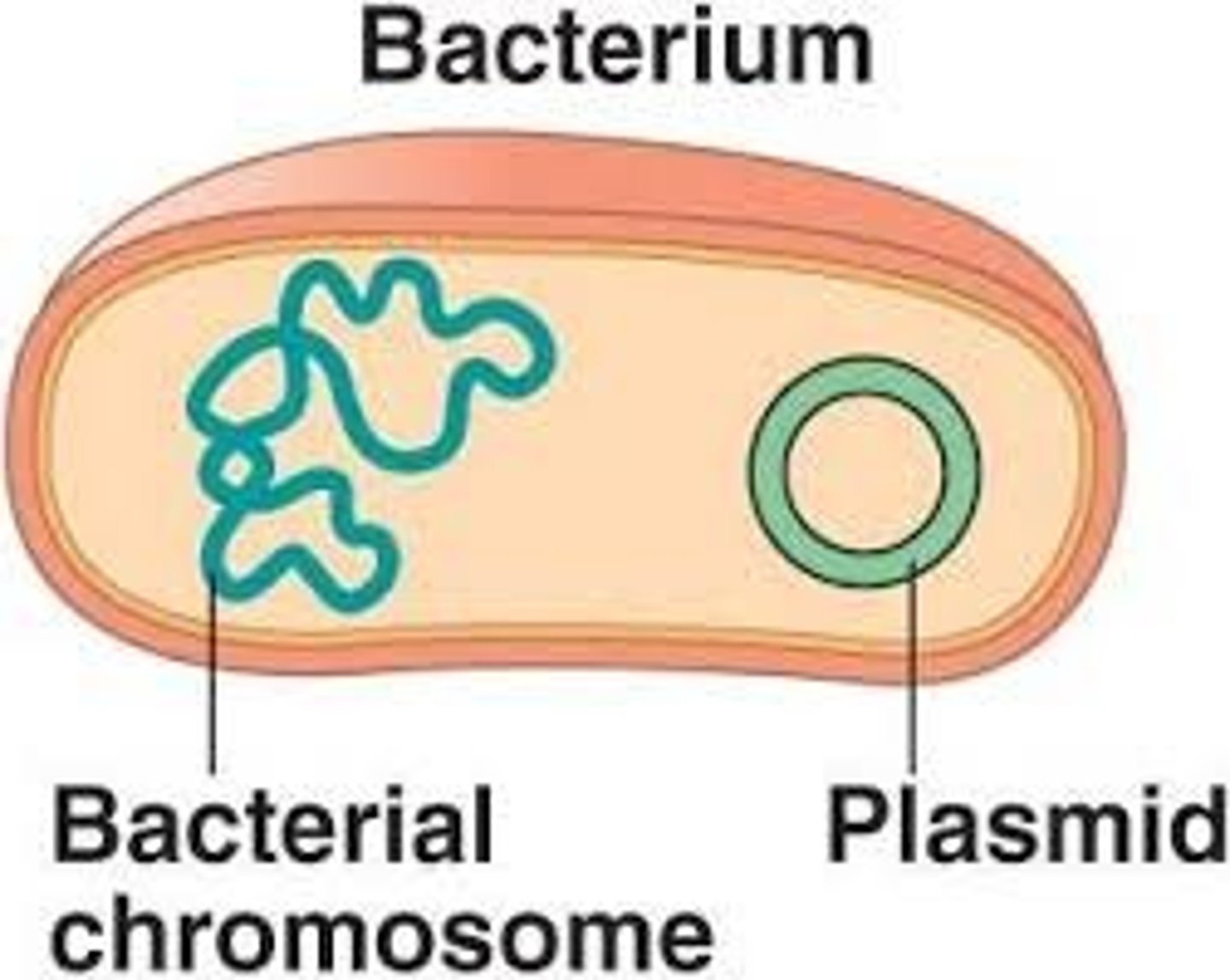
Plasmid
Circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
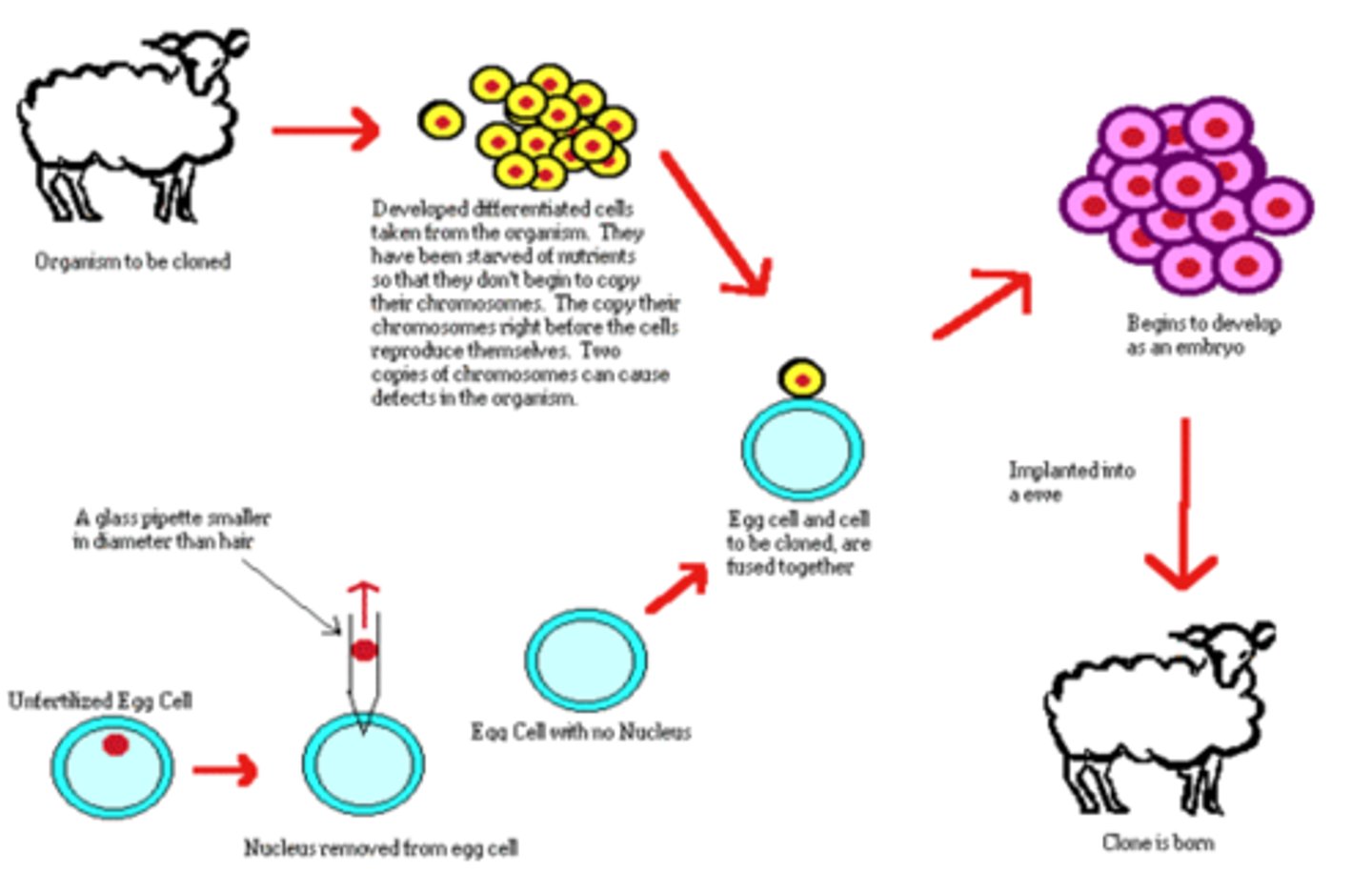
Cloning
Making a genetically identical copy of DNA or of an organism.
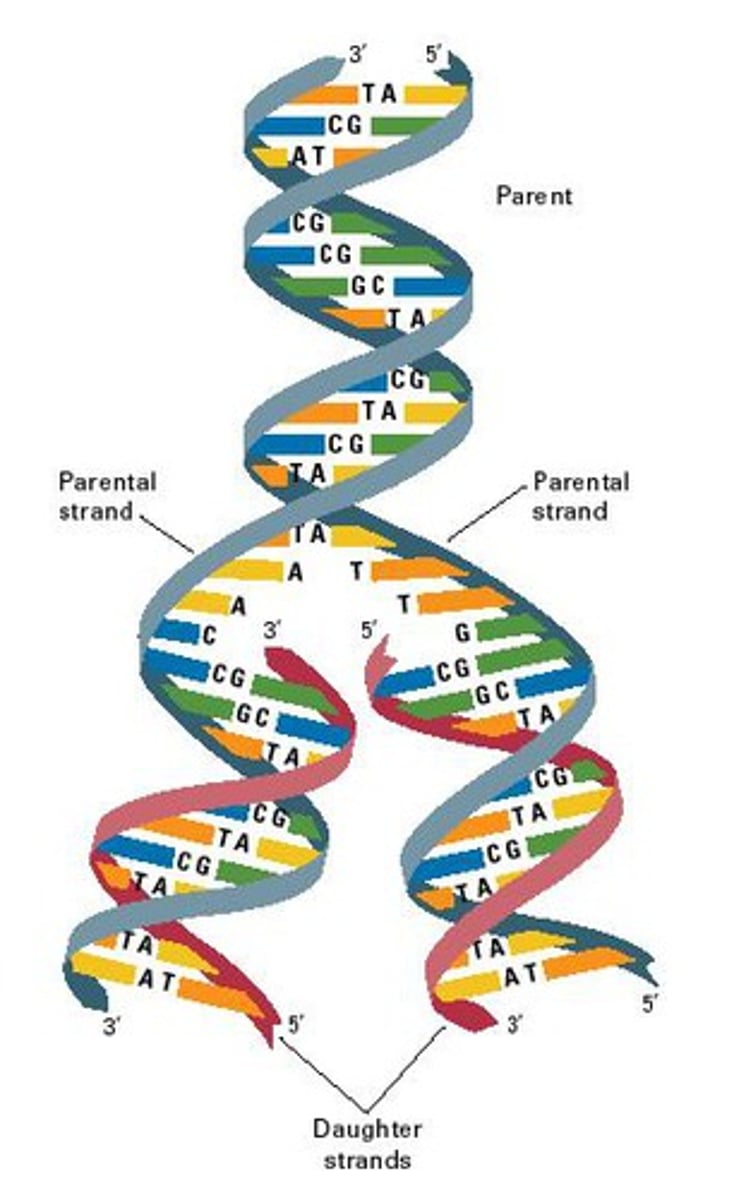
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
Trisomy
a condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nucleus, causing developmental abnormalities
Monosomy
Chromosomal abnormality consisting of the absence of one chromosome from the expected number
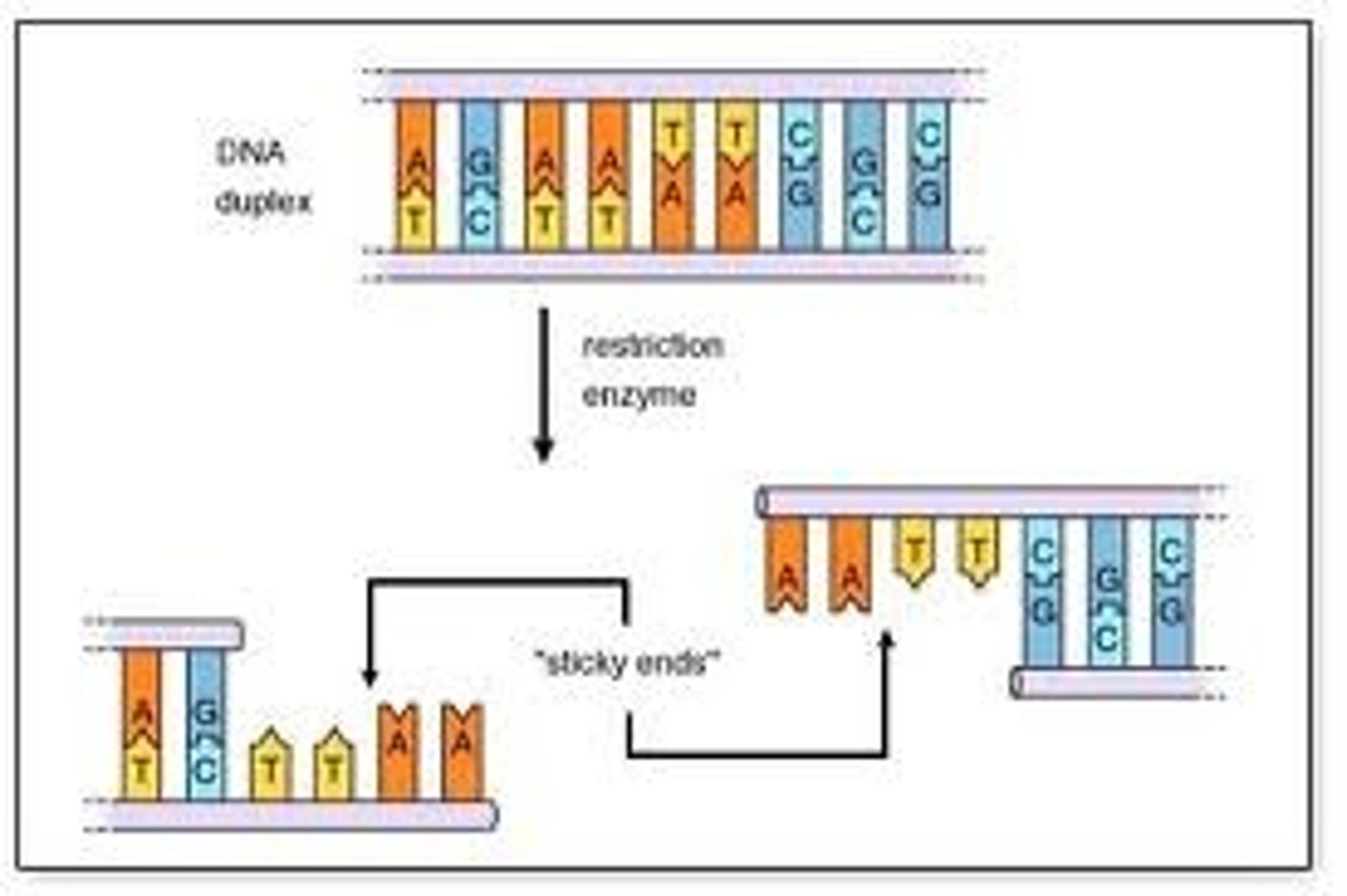
Restriction enzymes
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides usually resulting in "sticky ends"