genetics unit 2-SLU
1/204
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
Coupling or the cis configuration
w+ m+/ w m
Repulsion or the trans configuration
w+ m/ w m+
Two-point testcrosses
a double heterozygous female is crossed with a homozygous recessive male for gene mapping
Three-point testcross:
A cross of a triple heterozygote with a triple homozygous recessive Use previous example and add a third gene Vestigial (vg), Black body (b), Purple eyes (pr)
testcross from 3 point
Parental cross: vg b pr / vg b pr (F) x vg+ b+ pr+ / vg+ b+ pr+(M)
F1 trihybrid: vg b pr / vg+ b+ pr+
Testcross F1 trihybrid: (F) x tester (M)(vg b pr / vg b pr)
Drosophila: always use hybrid (F) & tester (M)
NO RECOMBINATION IN MALES! = XY
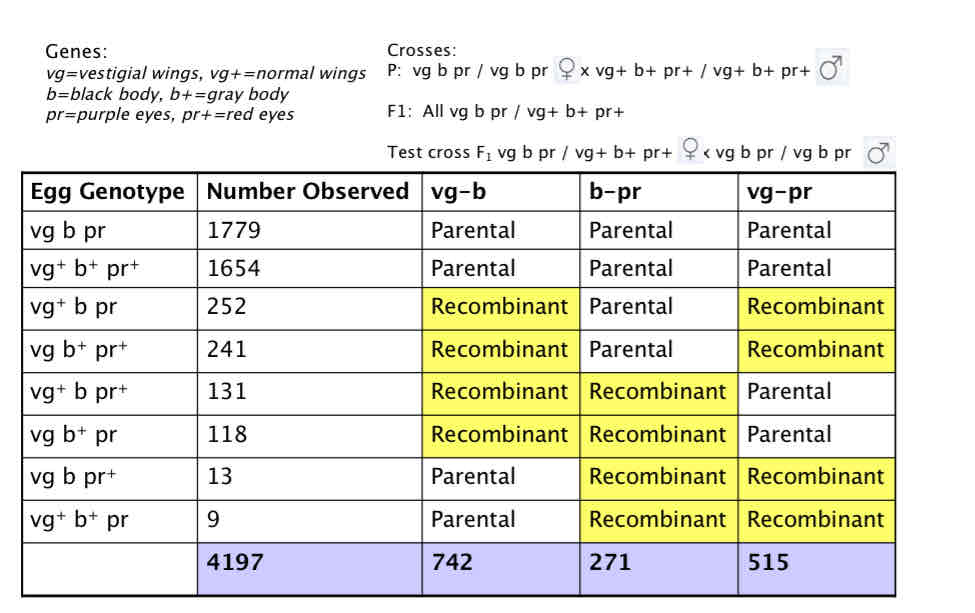
Genes:vg=vestigial wings, vg+=normal wings, b=black body, b+=gray body, pr=purple eyes, pr+=red eyes
crosses:
P: vg b pr / vg b pr(F) x (M)vg+ b+ pr+ / vg+ b+ pr+
F1: All vg b pr / vg+ b+ pr+
Test cross F1 vg b pr / vg+ b+ pr+(F) x (M)vg b pr / vg b pr
Rf(vg g-b) = (252 +241 + 131 +118)/ 4197 ×100 = 17.7m.u..
Rf(vg-pr) = (252+241+13+9)/4197 × 100= 6.4 m.u.
RF(b-pr) = (131+118+13+9)/4197 × 100= 6.4 m.u
Is the test cross from the drosophila example displaying linkage? Vg-pr= 12.mu,pr-b= 6.4 m.uc.,total= 17.7 mu, all summed = 18.7 mu
Double Crossovers
Expect 0.123 x 0.064 = 0.0079 = 0.79%
Observed (13 + 9) / 4197 = 0.0052 = 0.52%
Interference
the presence of one crossover interferes with formation of another crossover nearby
Coefficient of Coincidence (coc):
the extent of interference coc = Observed double crossover frequency/ Expected double crossover frequency = 0.52 / 0.79 = 0.66
Interference (I):
I = 1 – coc = 1 – 0.66 = 0.34
Single crossovers
between non-sister chromatids can be detected as recombinants.
double crossover
can occur in several ways. Consequences depend on which chromatids are involved.
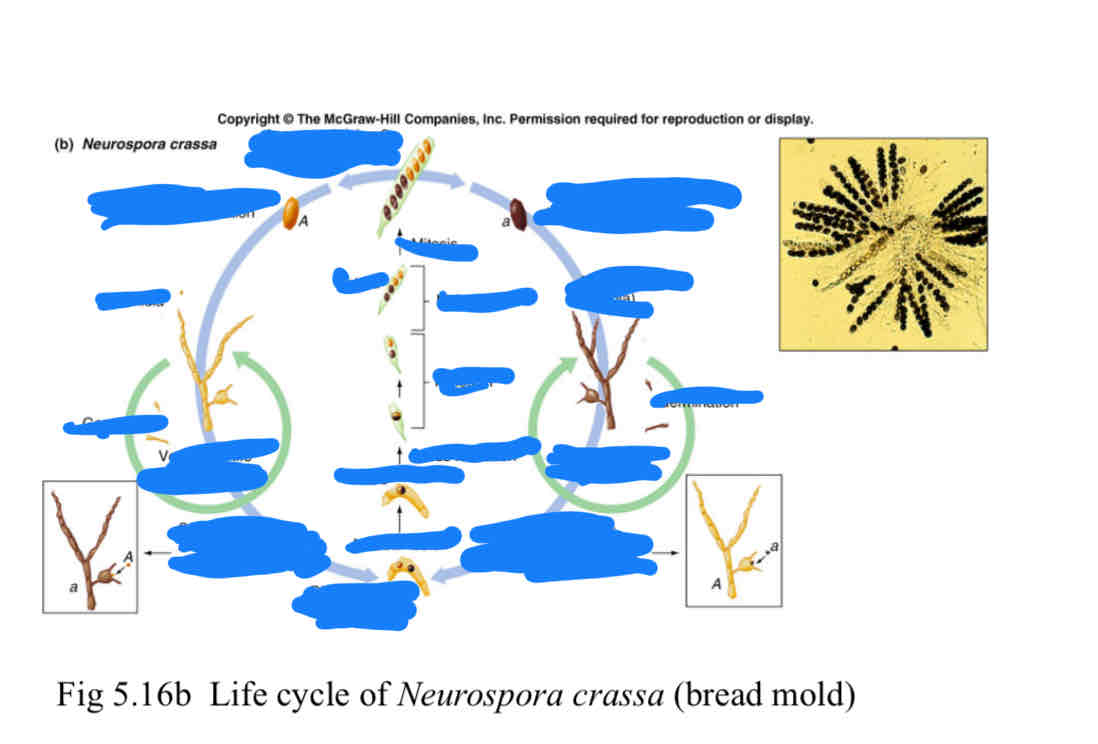
Ascus (pl, asci):
a sac that houses all four haploid products of each Meiosis
Ascospores (haplospores):
the haploid cells in an ascus that can germinate and survive as viable individuals.
HIS4
WT; his4, mutant, cannot grow in the absence of AA histidine.
Tetrad
after meiosis, the assemblage of four ascospores (or four pairs of ascospores) in a single ascus is called a tetrad.
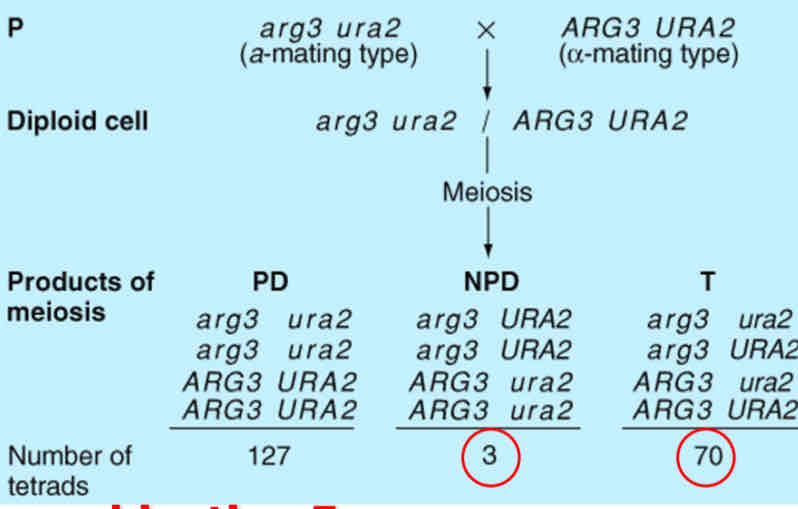
Parental ditype (PD):
a tetrad that contains four parental classhaploid cells (his4 TRP1 or HIS4 trp1).
Nonparental ditype (NPD):
a tetrad that contains four recombinant haploid cells (two his4 trp1 and two HIS4 TRP1).
Tetratype (T)
a tetrad carrying four kinds of haploid cells: two different parental class spore (one his4 TRP1 and one HIS4 trp1)and two different recombinants (one his4 trp1 and one HIS4 TRP1)
label this diagram of fungi(yeast) life cycle
check the image if you are right
no crossing over, double stranded
parental ditype
single crossover,3 strand, DCO 3 strand
tetratype
DCO 4 strand
Nonparent ditypes
recombination and tetratype trend
Recombination occurs at the 4-strand stage Tetratypes (T) > Non-Parental Ditypes (NPD) for linked genes. Small number of NPD tetrads = recombination after replication. Otherwise # NPD would be higher
what is recombination
usually reciprocal (exceptions molecular – cover later), shuffles alleles, does not create new alleles
Recombination Frequency
RF = (NPD + ½ T) / total # Asci * 100 (3 + ( ½ ) (70) / 200 * 100 = 19 m.u. All NPD spores are recombinant!½ T spores are recombinant!
label this diagram
check this
human genome size
3,000 mb
take a look at sep 23 for amy examples about clculatimg m. u.
pg.3 and 4
human traits
Single-gene traits – Mendelian – recessive & dominant Most traits are complex, Many genes, Inheritance patterns – obscure
genetucs of human traits
Cannot set up a testcross for mapping genes by recombination analysis
pedigrees
Pedigrees (a family history) used to analyze traits, but only for some limited traits. The rarity of suitable pedigrees makes it hard to test for linkage and calculate map distance between genetic markers
Determine whether two genes / markers are linked
Examine a number of families which are informative for the loci in question.For each family we must find the genotype (marker) of each parent and of each of the offspring. Now for the tricky part, we must decide whether it is more likely that we have observed the particular progeny in that family because the genes are linked and are tending to be inherited together than that we have observed those progeny through the chance - Mendelian independent assortment of alleles at the two genes. For this we use Lod score.
pototroph
(wild-type strains) can grow on minimal medium (sugar, some salts and trace elements)
auxotroph
(nutritional mutants) cannot grow on minimal medium, but can grow on complete mudium E. coli: genotype à trp ade thi+ Has mutations for tryptophan and adenine biosynthesis No growth on minimal medium Must be supplied with tryptophan and adenine
utilization pathways
Some genes are not involved in biosynthetic pathway, but in utilization pathways, i.e. prevent use of nutrients, E. coli: genotype lac+ bacterium, wild type, is able to use lactose; the mutant lac cannot
conjugation
is a process in which is a unidirectional transfer of genetic information through direct cellular contact between a donor bacterial cell and a recipient one Segment of donor chromosome is transferred The part transferred integrates into recipient’s chromosome. Homologous recombination
conjugation pathway
Conjugation → direct contact→type of mating system→Transfer of genetic material → unidirectional
what is the recipiant of conjuagation
transcomjugant
Lederberg & Tatum (1946) – bacterial conjugation
E. coli – 2 auxotrophic mutant strains
Strain A: met bio thr+ leu+ thi+ Requires: methionine & biotin
Strain B:met+ bio+ thr leu thi Requires: threonine, leucine, thiamine
what siss a photorophic colony results from
recombination
bacteria cells cannot
pass through a filter and requires cell to cell (bernard davis)
william Hayes, 1953
showed genetic transfer is unidirectional: donor to recipient, proposed that it is mediated by a sex factor called F. the donor cell possesses Sex Factor (F+); the recipient cell lacks (F- ). Factor is a plasmid containing a region of DNA called Origin (O) and a number of genes, including F-pili specifying hairlike host cell surface components which permit the physical union of F+ and F- cells.
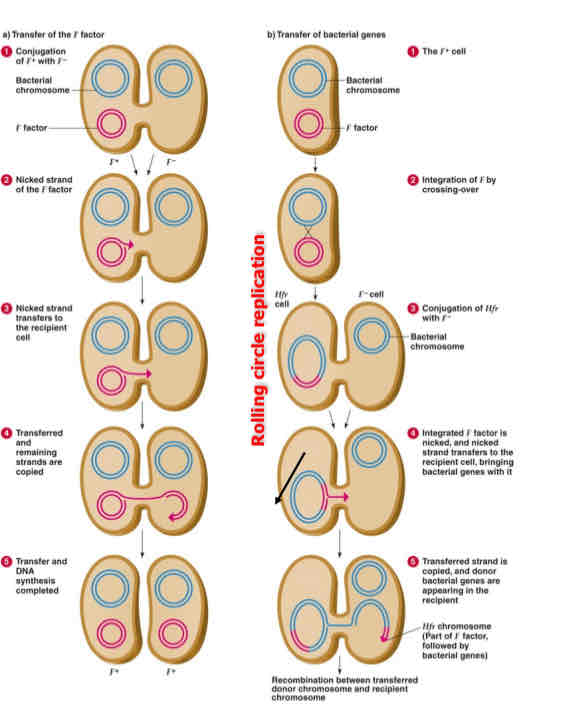
describe the image
Single strand to recipient; complimentary strand is synthesized; Replication in donor maintains double strand. Both cells are now F+, F+; plasmid integrated into bacterial chromosome, Hfr replicates F plasmid as part of bacterial chromosome
Hfr (high-frequency recombination) strains:
originate by a rare crossover event in which F factor integrates into the bacterial chromosome, and produce recombinants for chromsomal gene
Map bacterial genes by conjugation
Hfr (Host): prototrophic thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal+ str, F- (Recipient): auxotrophic thr leu aziS tonS lac gal strR
aziR
Resistant to growth inhibition by sodium azide
tonR
resistant to infection by the bacteriophage T1
strS
sensitve to streptomycin
Jacob & Wollman (1950s)
interrupted-mating experiments
F’ Factors:
Excision of F plasmid →may take part of bacterial chromosome with it.
F’ (F prime):
F factors containing bacterial genes, In this example, the lac+ gene goes with the F plasmid called F’ (lac)
Merodiploid
having two copies of one or a few genes and only one copy of all the others (F’ cells conjugate with F- cells). This conjugation is called F-duction or Sexduction
ø
the recomination efficencey, Ø= 0.1, equivalent to 10 cM.
ø= 0.5, i.e. unlinked
z
lod score
When to accept or reject a hypothesis
The value of Zmax is a measure of our confidence in the result.
• If Zmax > 3, then we conventionally think the linkage to have been proved.
• Conversely, if Z < -2, we take the linkage to have been disproved.
cystic Fibrosis
autosomal recessive genetic disorder About 70% of mutations observed in CF patients result from deletion of three base pairs in CFTR's nucleotide sequence. This deletion causes loss of the amino acid phenylalanine located at position 508 in the protein; therefore, this mutation is referred to as delta F508
CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane
conductance regulator)
The Gene Associated with Cystic Fibrosis, is a type of protein classified as an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter or traffic ATPase.
locus of CF
7q31.2 - The CFTR gene is found
in region q31.2 on the long (q) arm of
human chromosome 7.
Gene Structure of CF
The normal allelic variant for this gene is about 250,000 base pairs (bp) long and contains 27 exons.
mRNA of CF
The intron-free mRNA transcript for the CFTR gene is 6129 bp long
Mapping and cloning of BRCA1
The BRCA 1 gene encodes a predicted protein of 1863 amino acids. BRCA 1 is expressed in numerous tissues, including breast and Ovary. This protein contains a zinc finger domain in its amino-terminal Region. Identification of BRCA1 has facilitated early diagnosis of breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility in some individuals as well as a better understanding of breast cancer biology
Genetic Maps of the Human Genome
The total genetic map length of the human genome is about 3,000 cM
• By a lucky coincidence, the total genome length is about 3,000 million base pairs.
• So on average, 1 cM is equivalent to 1 Mb (1 Mb = 1 million base pairs).
QTL mapping:
identify genomic regions associated with phenotypic differences between individuals, Need a population with a detailed linkage map, substantial phenotypic variation, and a large number of individuals. For example, inbred lines BCF1 or F2., Clone the QTL, Molecular markers, statistical tools, and genomic information has enable geneticists to clone QTL much faster.
what will the map of quantitative traits look like
bell curve
Transformation
unidirectional transfer of extracellular DNA into cells, resulting in a phenotypic change in the recipient Recipients whose phenotypes are changed by the transformation are called transformants Donor DNA → extracted →purified →broken into fragments. Fragments are added to a recipient strain
Competent cells
cells prepared to take up DNA by transformation.Cells can be treated chemically or are exposed to a strong electric field in a process called electroporation.
Transduction
process by which bacteriophages (bacterial viruses, phages) transfer genes from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient), such phages are called phage vectors.phage usually can only carry less than 1% of DNA in the bacterial chromosome. Once the donor genetic material has been introduced into the recipient, it may undergo genetic recombination with the homologous region of the recipient chromosome. The recombinant recipients are called transductants.
The 1918 flu pandemic (the Spanish Flu)
The pandemic lasted from March 1918 to June 1920, Kill 50 and 100 million ( about 3% of the world's population (1.6 billion at the time), 500 million (1/3) were infected. one of the deadliest natural disasters in human history
H1N1
The swine-origin (H1N1) is a subtype of influenza virus A that has emerged in humans in early 2009 and raised concerns about pandemic developments. In experiments with ferret and mice, the 2009 A(H1N1) influenza virus was found to be more pathogenic than a seasonal A (H1N1) virus, with more extensive virus replication occurring in the respiratory tract, and with more abundant for Virus shedding from the upper respiratory tract. Studies suggest that the 2009 A(H1N1) influenza virus has the ability to persist in the human population, potentially with more severe clinical consequences.
Genetic Characteristics of Swine-Origin 2009 A (H1N1) Influenza Viruses Circulating in Humans
In April 2009, a previously undescribed A (H1N1) influenza virus was isolated from humans in Mexico and the United States. As of 18 May 2009, there have been 8829 laboratory-confirmed cases in 40 countries, resulting in 74 deaths
bacteriophage carry genees via
transduction
generized transdunction
Any genes can be transfer between bacteria, Lederberg & Tatum (1952),Salmonella typhimurium, Bacterial cells separated that is similar to the, conjugation in bacteria, Recombinants formed, Temperate phage (P22) – moves genes
speacalized transduction
Only specific genes can be transferred
Donor: leu+ thr+ aziR
Recipient: leu thr azis
what are the transductants?
selected for any trait (leu+); checked for
unslected markers (thr+ aziR)
co-tramsduction way 1
near each other on chromosome (packaged
together)
co-transduxtion way 2
carried by 2 different phages (simultaneous infection)
Co-transduction
degree of linkage between genes
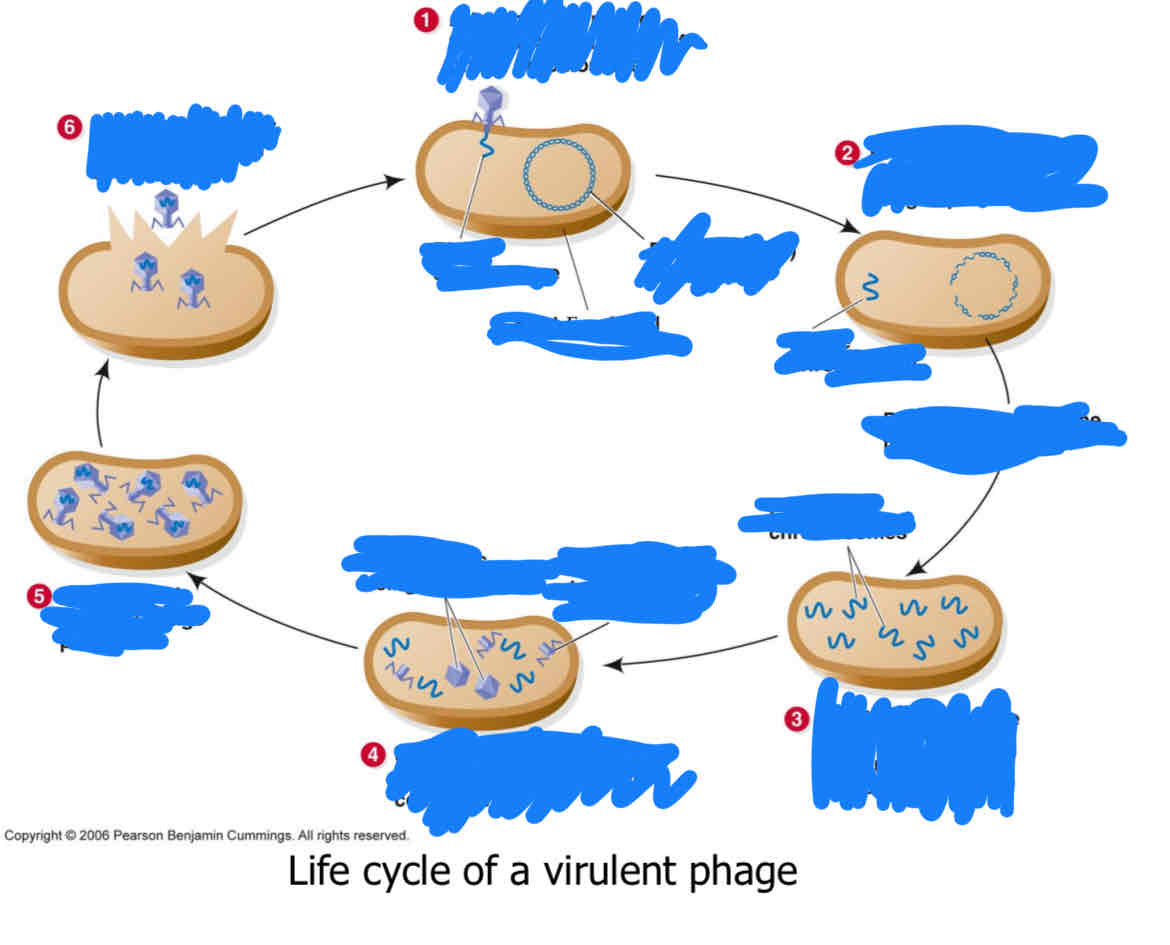
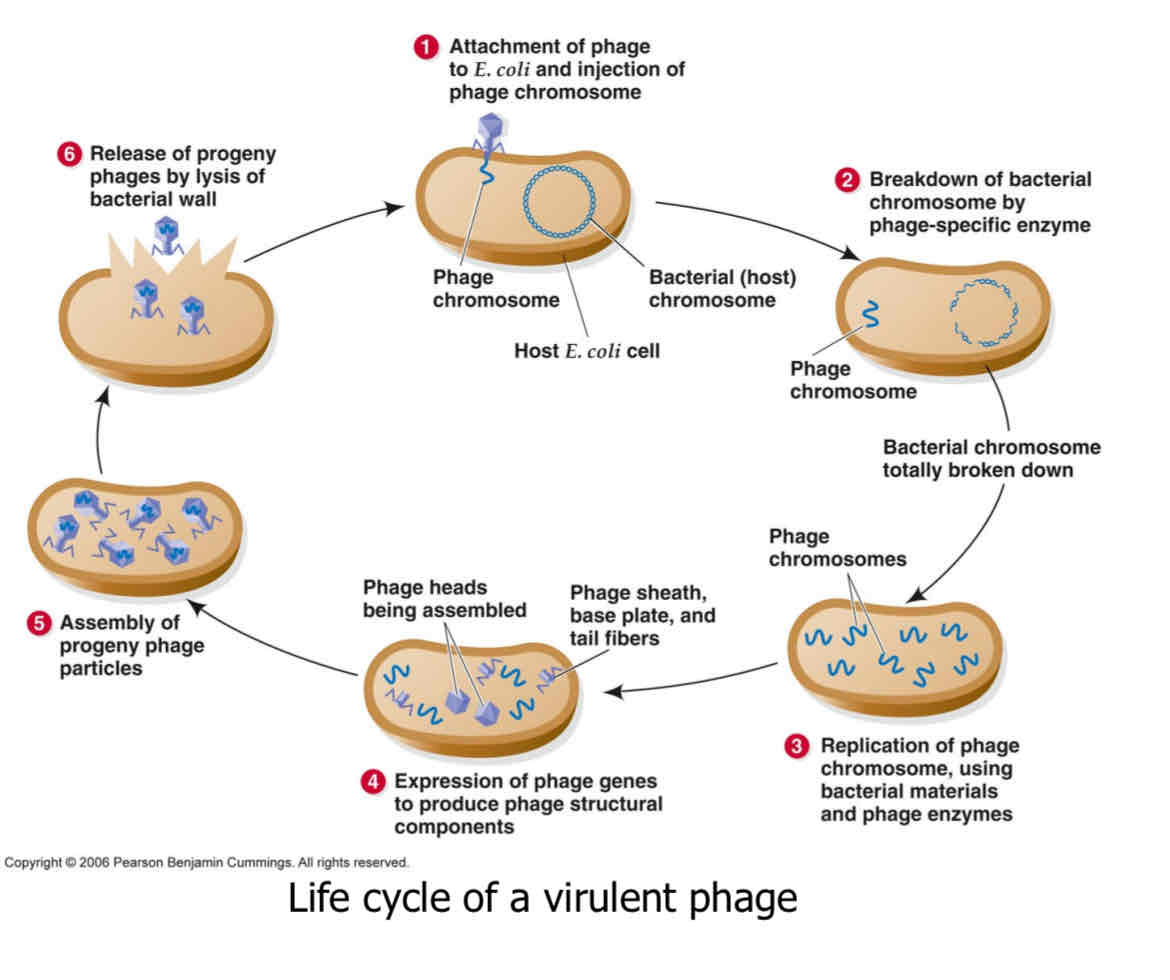
fill this out for the virulent phages
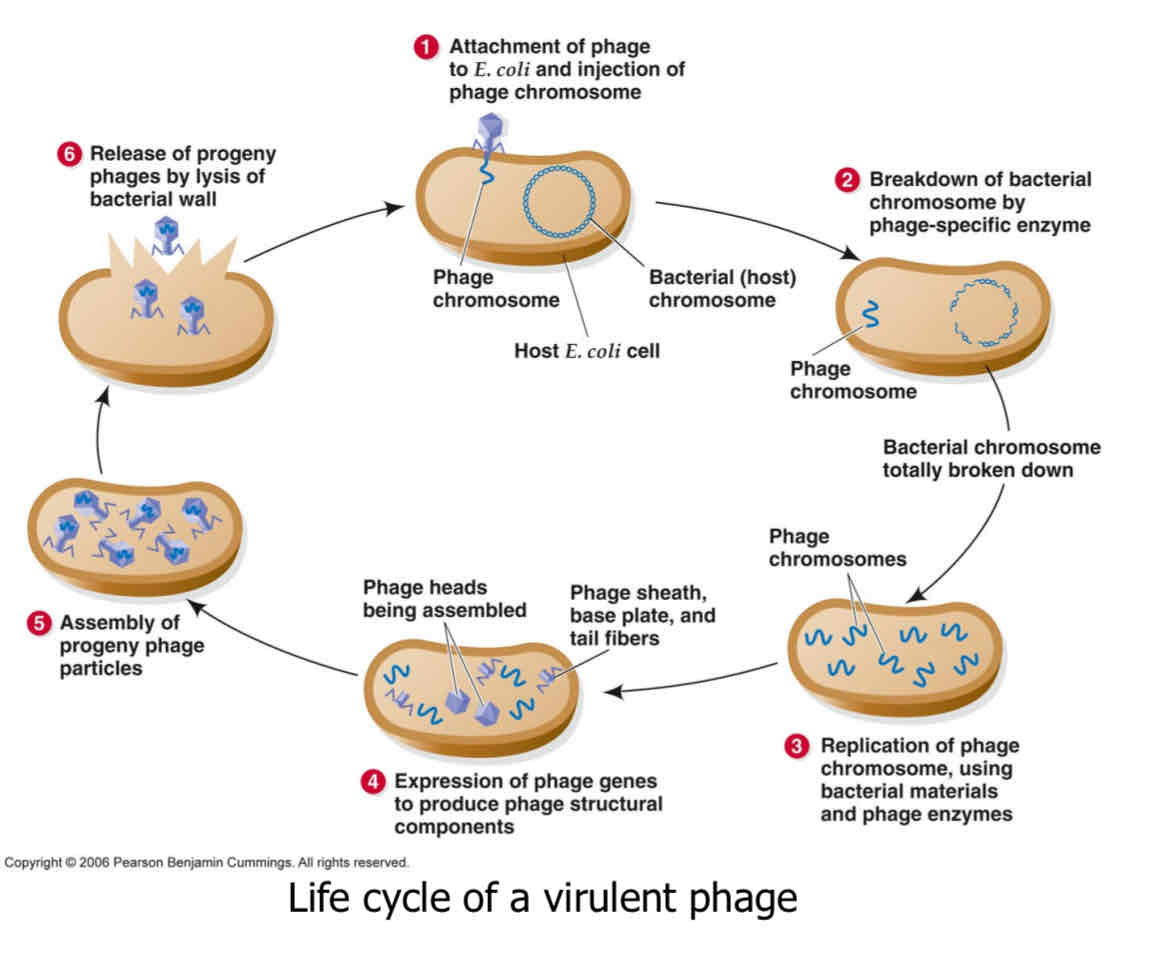
fill this out for temperate phage
what distinguishes virulent ans temperate
virulent only has lytic phase
map distances
Use co-transduction frequency of gene pairs Only for genes – very close! Transduction (a+ b+) donor to (a b) recipient # of single-gene transductions ÷ #total transductions X 100 (a+ b) / ((a b+) + (a+ b+)) X 100%
Specialized Transduction
Some temperate bacteriophages can transduce only certain sections of the bacterial chromosome, e.g. specialized transducing phage l
attlamda
attachment site for lambda): the site on the E. coli chromosome where the lambda genome integrates into the bacterial chromosome
LFT
low-frequency transducing lysate
HFT
high frequency transducing lysate
Principles of performing a genetic cross with bacteriophages
h +: able to lyse the B strain (the permissive host), but Not the B/2 strain
r: produce large plaques with distinct borders
r+ : produce small plaques with fuzzy borders
Plaques produced by progeny of a cross of T2 strains h r+ X h +r
h +: able to lyse the B strain (the permissive host), but Not the B/2 strain
r: produce large plaques with distinct borders
r+ : produce small plaques with fuzzy borders
Complementation tests
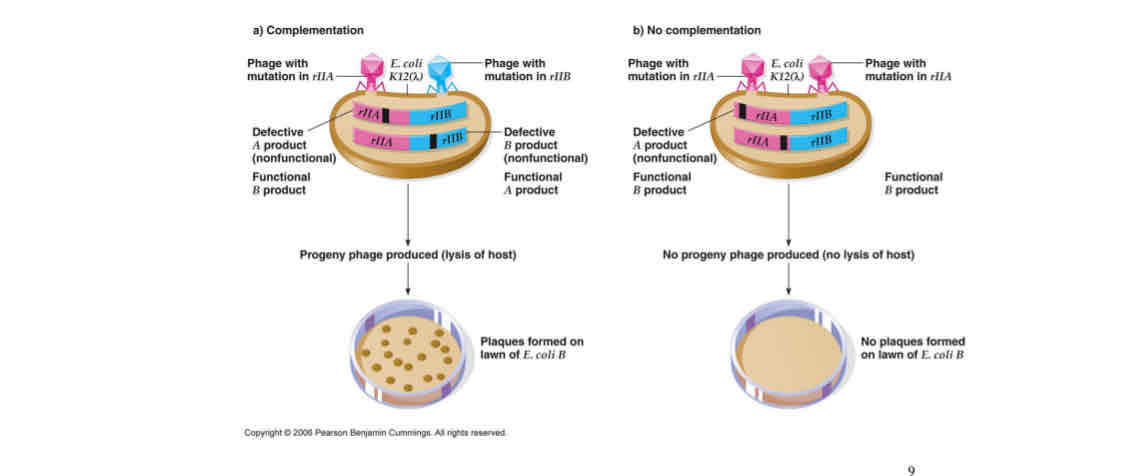
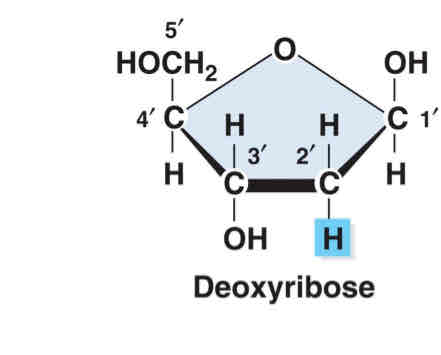
write the structure of deoxyribose
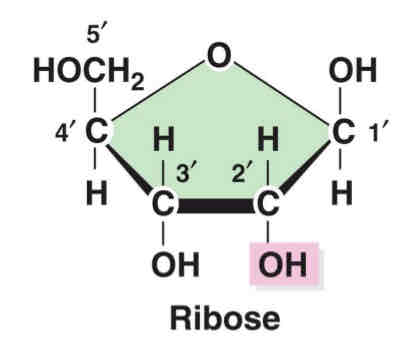
draw Ribose
do herbivorse contain DNA and RNA
debatable prions
know the structure of bases
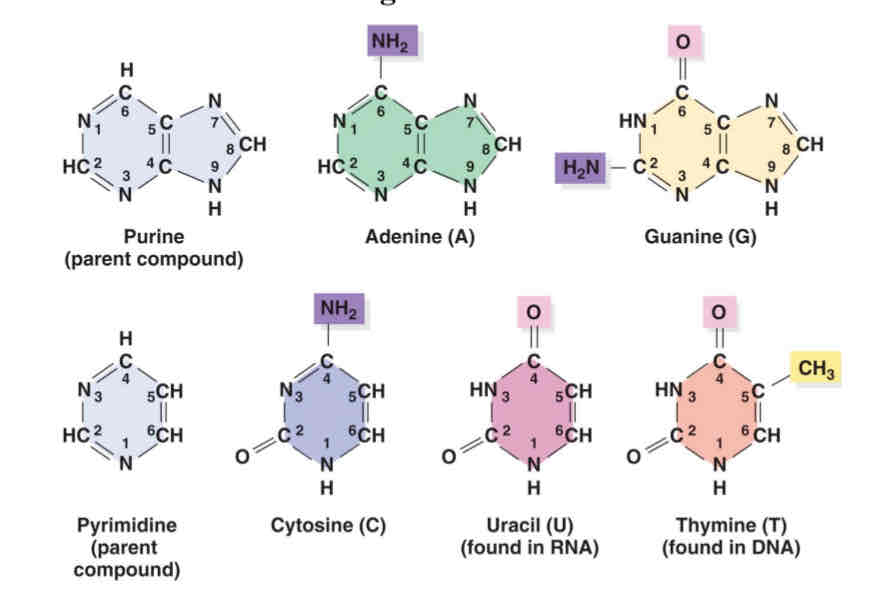
what are the chemical constiuents pf DNA
phosphate group, sugar, base
chemical componenets
phosphate group ribose, base
what base can change both in humans and bacteria
cytosine can become methylcytosine
Base composition studies by
Erwin Chargaff hydrolyzed the DNA from a number of organisms and had quantified the purines and pyrimidines releasedPurines : pyrimidines = 1:1 (A + G = T + C), A : T = 1; G : C = 1, (A+ T) : (G+C) ratio varies
X-ray diffraction analysis of DNA by
rosalind franklin and maurice Wilikins
X-Ray Crystallography
The X-ray beam is diffracted (broken up) by the atoms in a pattern that is characteristic of the atomic weight and the spatial arrangement of the molecules.DNA is a helical structure with two distinctive regularities of 0.34 nm and 3.4 nm along the axis of the molecule
A-T and G-C base pairs have favorable what kind of bond reactions?
hydrogen