Chap 9B - Acid-base equilibria B
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Describe Kw + equation
Aka autoionisation of water
Pure water ionises to a very slight extent:
H2O (I) + H2O (I) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + OH- (aq), Kw = [H3O+][OH-]
Amount of water dissociated is negligible so [H2O] is constant -> omitted from Kw expression
Kw: ionic product of water
Units: mol^2 dm^-6
Constant at constant temperature
At 25 degrees, Kw = 10^-14 for all aqueous solutions
![<ul><li><p><span>Aka autoionisation of water </span></p></li><li><p><span>Pure water ionises to a very slight extent: </span></p><ul><li><p><span>H2O (I) + H2O (I) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + OH- (aq), Kw = [H3O+][OH-]</span></p></li></ul></li><li><p><span>Amount of water dissociated is negligible so [H2O] is constant -> omitted from Kw expression</span></p></li><li><p><span>Kw: ionic product of water</span></p><ul><li><p><span>Units: mol^2 dm^-6 </span></p></li><li><p><span>Constant at constant temperature </span></p></li><li><p><span>At 25 degrees, Kw = 10^-14 for all aqueous solutions </span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7c1f0194-51fc-4590-844a-e4ea95a738cb.png)
Calculate pH of water at 25 degrees

Describe conditions for acid, basic and neutral solutions
Solution | Condition | At 25 degrees | ||
Acidic | [H+] > [OH-] | [H+] > 10^7 | [OH-] > 10^7 | pH < 7 |
Neutral | [H+] = [OH-] | [H+] = 10^7 | [OH-] = 10^7 | pH = 7 |
Basic | [H+] < [OH-] | [H+] < 10^7 | [OH-] < 10^7 | pH > 7 |
Describe relationship between Kw and temp
Dissociation of water is endothermic
By Le Chatelier's Principle, as temperature increases, the position of equilibrium shifts right to favour the endothermic reaction by absorbing the added heat -> [H*], [OH] and Kw will increase
NOTE: At 50°C, pH of water is 6.63 -> water is NOT acidic -> at a higher temperature (above 25°C), the pH for neutrality is not 7 but at a lower pH. At higher temperatures, water still remains neutral, since [H+] is still equal to [OH-]
Describe relationship between Kw, Ka and Kb

Describe calculations for strong acids
Commonly encountered strong acids include the monobasic acids (HCI04, HC/ and HNO3) (single dissociable proton) and a dibasic acid (H2SO4) (2 dissociable protons)
[H+] in solution = initial [HCI]
If concentration of acid > 1.0 x 10-7 mol dm^-3 -> H+ (aq) ions from acid will suppress self-ionisation of water according to Le Chatelier's Principle -> assume H+ (aq) comes from acid ONLY
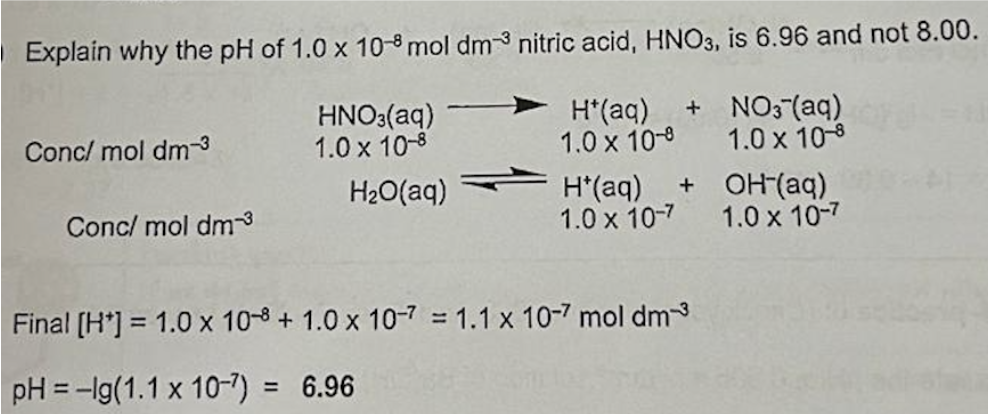
If the concentration of acid < 1.0 x 10^-7 mol dm^-3 -> include H+ (aq) from water too!
To show acid is strong: Using pH, find [H+], in strong acid [H+] = [HA]
Explain why the pH of 1.0 x 10-8 mol dm-3 nitric acid, HNO3, is 6.96 and not 8.00.
Describe calculation for weak acid
HA (aq) + H2O (I) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq): At equilibrium, there is some H3O+, A- and some undissociated HA
NOTE: In reality, before any weak acid dissociates, [H+] = 10^-7 due to autoionisation of water. But weak acid is still stronger and dissociates to a larger extent -> H+ from weak acid suppress autoionisation of water according to Le Chatelier’s Principle -> assume H+ come from acid only
Calculate the pH of 1 mol dm-3 aqueous ethanoic acid, CH3CO2H, given that its Ka = 1.8 × 10-5 mol dm-3

Explain when a salt undergoes hydrolysis
A salt will undergo hydrolysis (reaction with water) if:
Anion is a conjugate base of the weak acid (Eg. CH3CO2-)
Cation that is a conjugate acid of the weak base (Eg. NH4+)
Cation has high charge density (Eg. Ai3+, Cr3+)
Describe salts formed from strong acid and base (Eg. NaCI)
Form neutral salt solutions
Eg. NaCI (pH = 7)
Na+ has a low charge density -> not polarising enough to undergo hydrolysis
CI- is a conjugate base -> does not undergo hydrolysis
Describe salts formed from strong acid and weak base (Eg. NH4CI)
Produce H3O+ in water
Eg. NH4CI (pH < 7)
NH4+ is a conjugate acid of weak base NH3 -> NH4+ will undergo hydrolysis in water producing H3O+
NH4+ + H2O ⇌ NH3 + H3O+
Resulting solution is acidic as there is more H3O+ than OH-
Describe salts formed from weak acid and strong base (Eg. CH3CO2Na)
Produce OH- ions in water
Eg. CH3CO2Na
CH3CO2- is a conjugate base of weak acid CH3CO2H -> CH3CO2- will undergo hydrolysis in water producing OH-
CH3CO2- + H2O ⇌ CH3CO2H + OH-
Resulting solution is basic because there is more OH- than H3O+
Describe salts that contain small, highly charged cations (Eg. AICI3)
Salts that contain small, highly charged cations form acidic solutions because these cations hydrolyse to produce excess H3O+ ions
All metal ions exist in aqueous solution as hydrated cations but the acidity depends on charge density unhydrated metal ion
Eg. Cr3+, Fe3+
Eg. AICi3
A/Cl completely ionises in solution: A/CI(s) + 6H20(I) → [A/(H2O)6]3+ (aq) + 3C/ (aq)
As AI3+ ion has a high charge density (high charge and small radius), [Al(H2O)6] undergoes hydrolysis to form H3O+
AI3+ draws electrons from O-H bond in the water molecule towards itself, weakening the O-H bond to transfer the H+ ion to H2O to form H3O+ -> acidic solution