Biological - Brain scans
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the different types of scans we need to know?
- CAT/CT
- PET
- fMRI
Why is taking brain scans useful?
Allows researchers to examine what is happening in live patients
What are the scans which show brain structure?
- fMRI
- CAT/CT
What are the brain scans which show brain functioning?
- PET
What does CAT scan stand for?
Computerized Axial Tomography
What does PET scan stand for?
Positron Emission Tomography
What does fMRI scan stand for?
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
How do CAT scans work?
Uses multiple X-ray beams passed through the head, creating cross-sectional images of the brain. Sometimes dyes such as iodine are used
What images can CAT scans give us?
3D images or the slides can be looked at individually
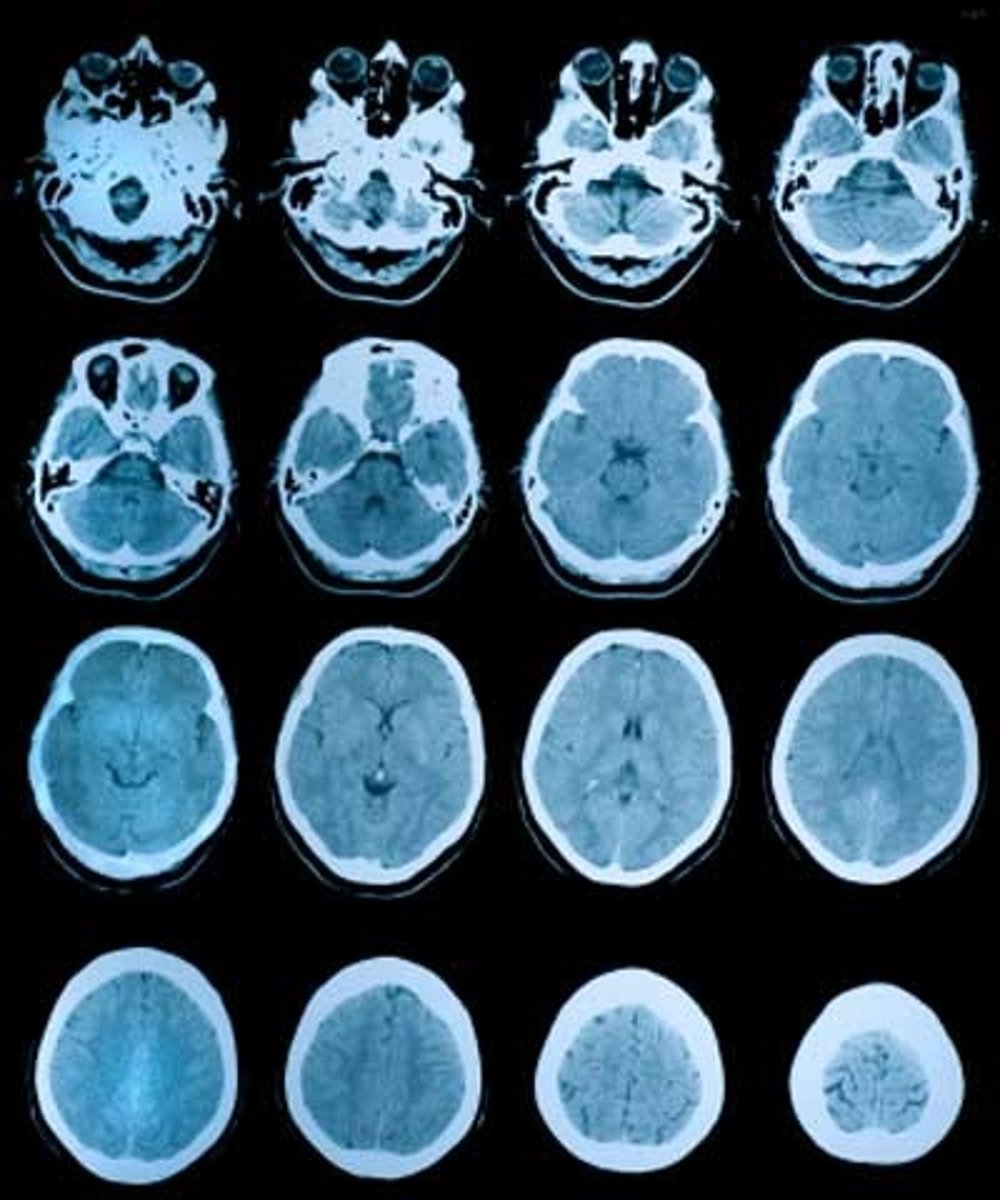
What are CAT scans often used for?
To identify if brain damage is present
Why are dyes used in CAT scans?
To highlight the blood vessels in the brain and produce more detailed images
Describe the process of getting a CAT scan.
1. Remove all metal
(1.5. An injection of dye may be given)
2. Lie still on the scanning table for 20-30 mins
3. The table moves through the scanner and rotates around pts head
Give advantages of CAT scans.
- Quick
- Provide useful image of brain structure to help determine treatment plans
- Reduce pt risk as they can identify problems and potential solutions
- Detect physical changes in the brain
- Have medical and research uses
- Non-painful and non-invasive
Give disadvantages of CAT scans.
- X-rays are a harmful form of radiation (cost/benefit argument)
- CAT scans give lower quality images than alternatives
- CAT scans can only tell us about physical damage, not about activity or infection etc
- Cannot be routinely used for research due to the radiation causing cancer
How do PET scans work?
A radioactive material which is injected. Glucose in the brain causes this material to break down and form positrons which collide with electrons, form gamma rays which are detected by the scanner
What images do PET scans give us?
They give us colourful images of cross-sections of the brain
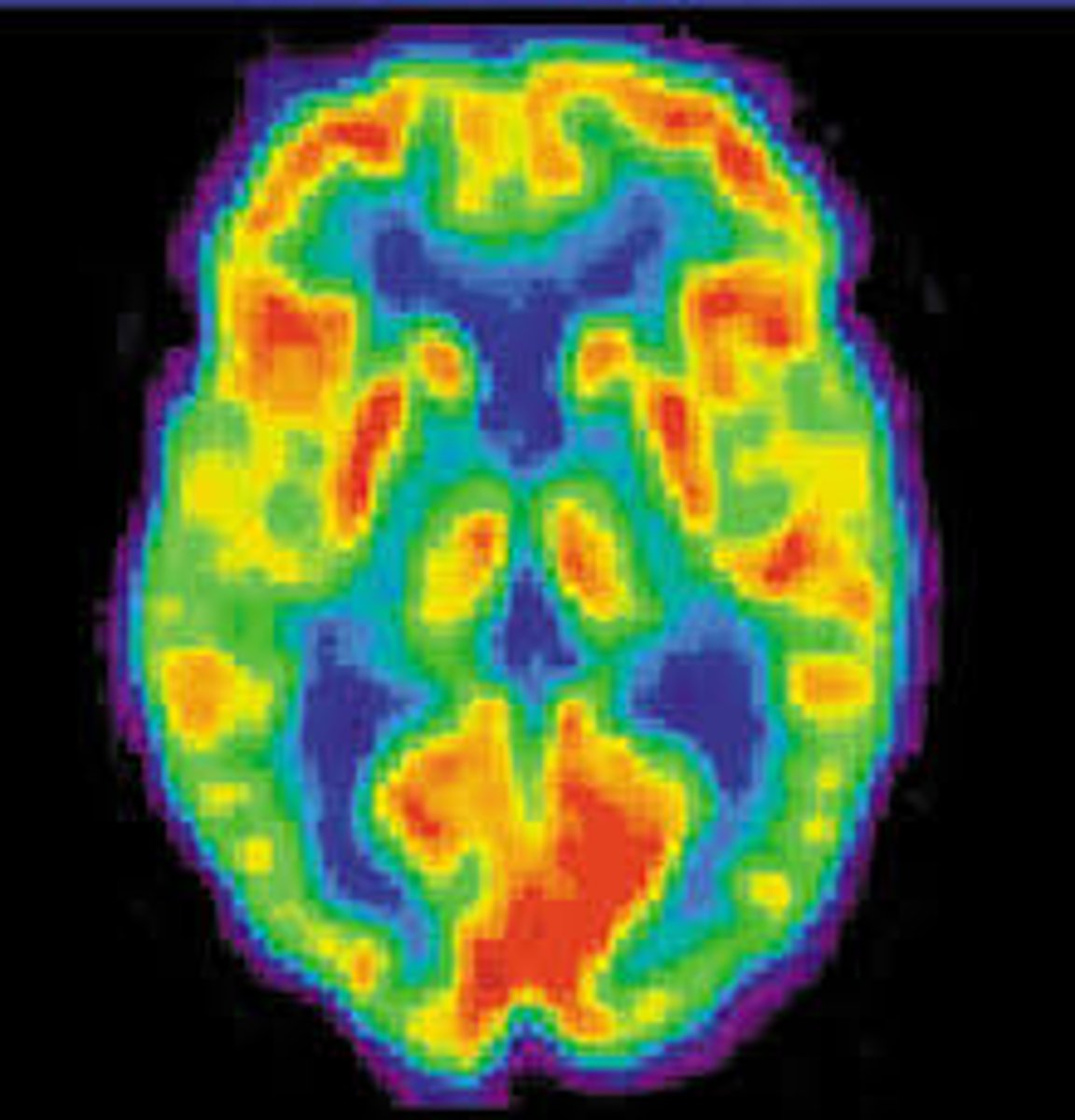
What do PET scans show us?
As the radioactive material breaks down with glucose, areas of the brain which are more high activity show up as this on the scanner, with red being high activity and blue being low
What are PET scans used for?
Medical purposes such as checking damage caused by a stroke as well as for research
What are advantages of PET scans?
- Mostly non-invasive and non-painful
- Valid method to measure brain activity
- Reliable - can be repeated and give the same results
- Reduce pt risk as they can identify problems and potential solutions
Give some disadvantages of PET scans.
- Radioactive tracer is invasive
- Scan is claustrophobic so could be risk to pt
- Difficult to isolate different brain functioning precisely
- Can take long time
How do fMRI's work?
Head is placed inside an
electromagnet which detects the changes in O2 demand and haemoglobin oxygenation
What images do fMRIs provide us?
Images of brain activity (activation maps in certain mental processes). These can be 3D or slides
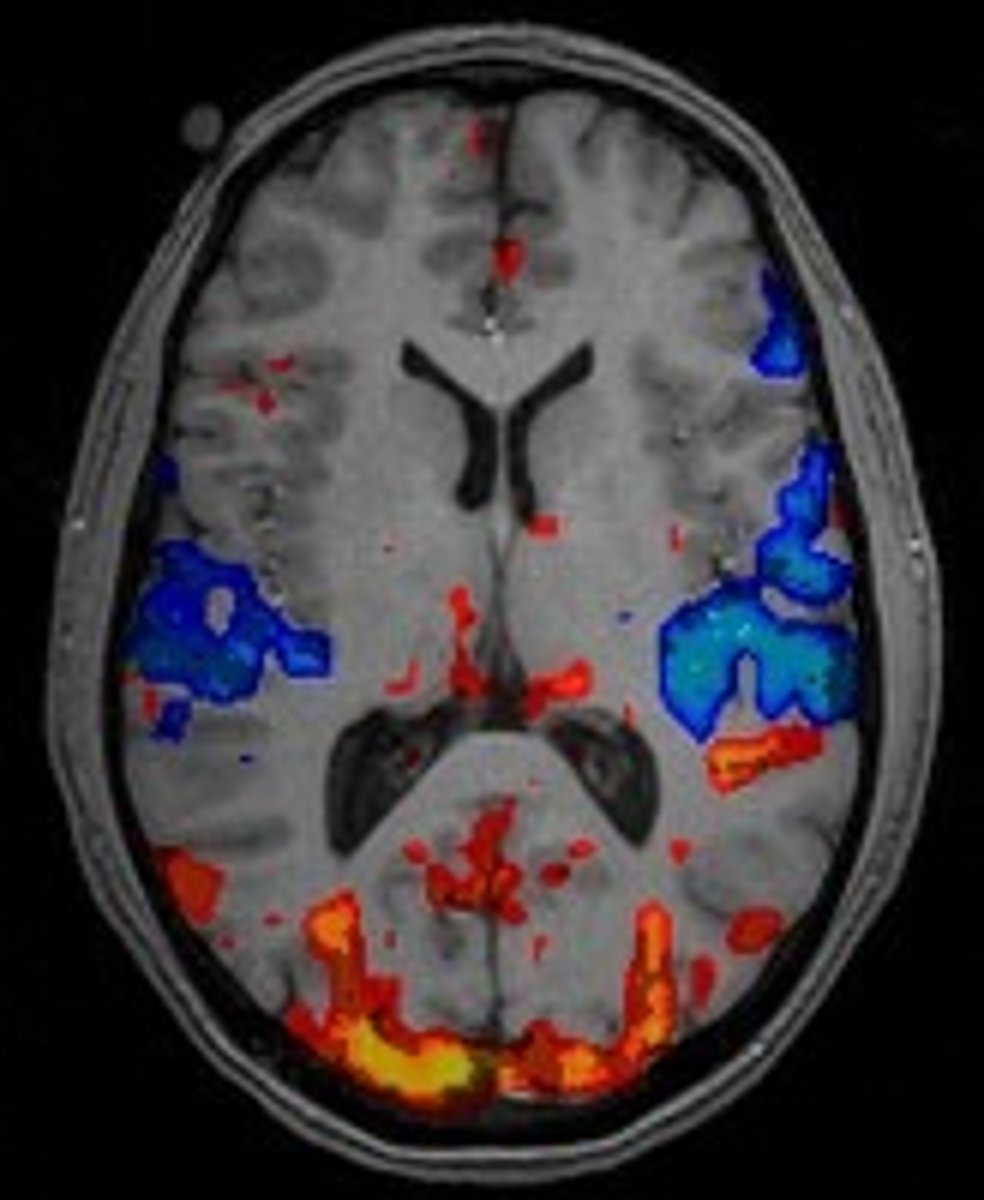
Describe getting an fMRI scan.
1. Head is placed in a brace to hold it still
2. Goggles and earphones may be given to wear
3. Table moves into the machine and scans
Describe some strengths of fMRIs.
- Safe for pregnant women and children (no radiation)
- Show structure and activity
- Research and medical benefits
Describe some weaknesses of fMRIs.
- Claustrophobic
- Not super precise areas of activity
- Poorish resolution
- Expensive