The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, Reflexes, & the Autonomic Nervous System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Protection of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is part of the CNS that is protected by the meninges and enclosed inside the vertebral column.
Meninges include three layers:
Dura Mater- thick outer layer (tough structure, protects brain)
Arachnoid Mater- middle layer
Pia Mater- inner layer attached to the spinal cord and brain
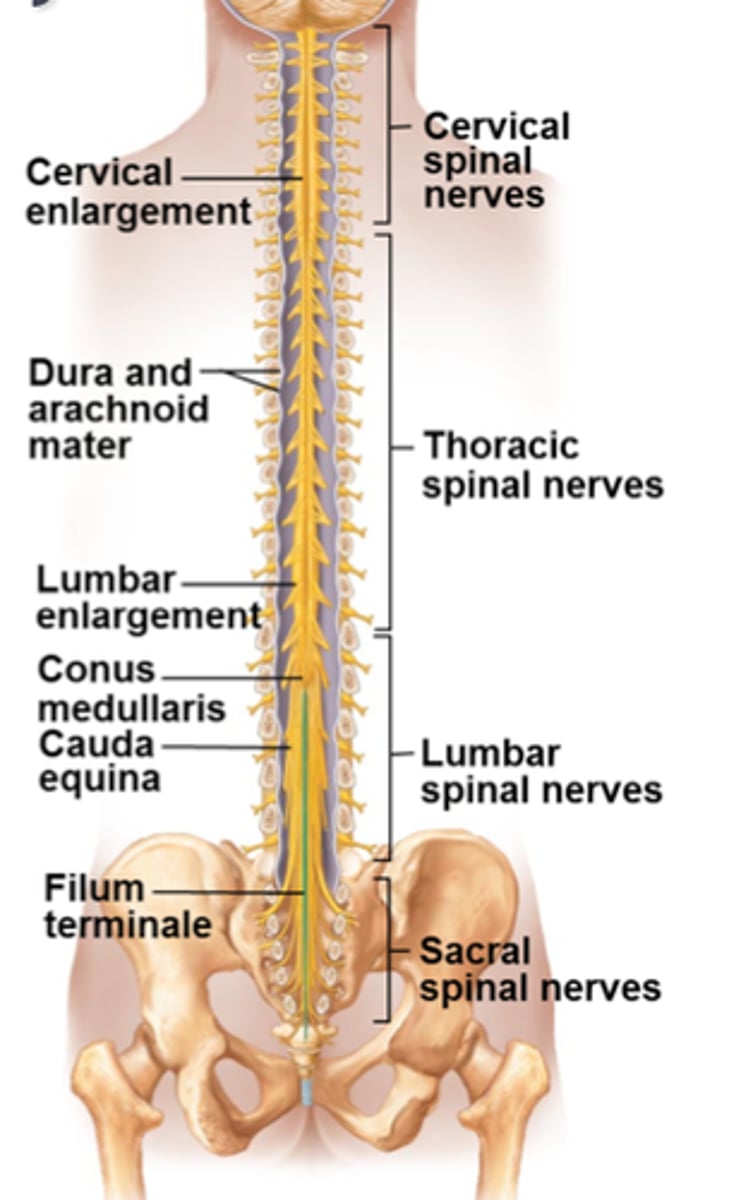
External Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
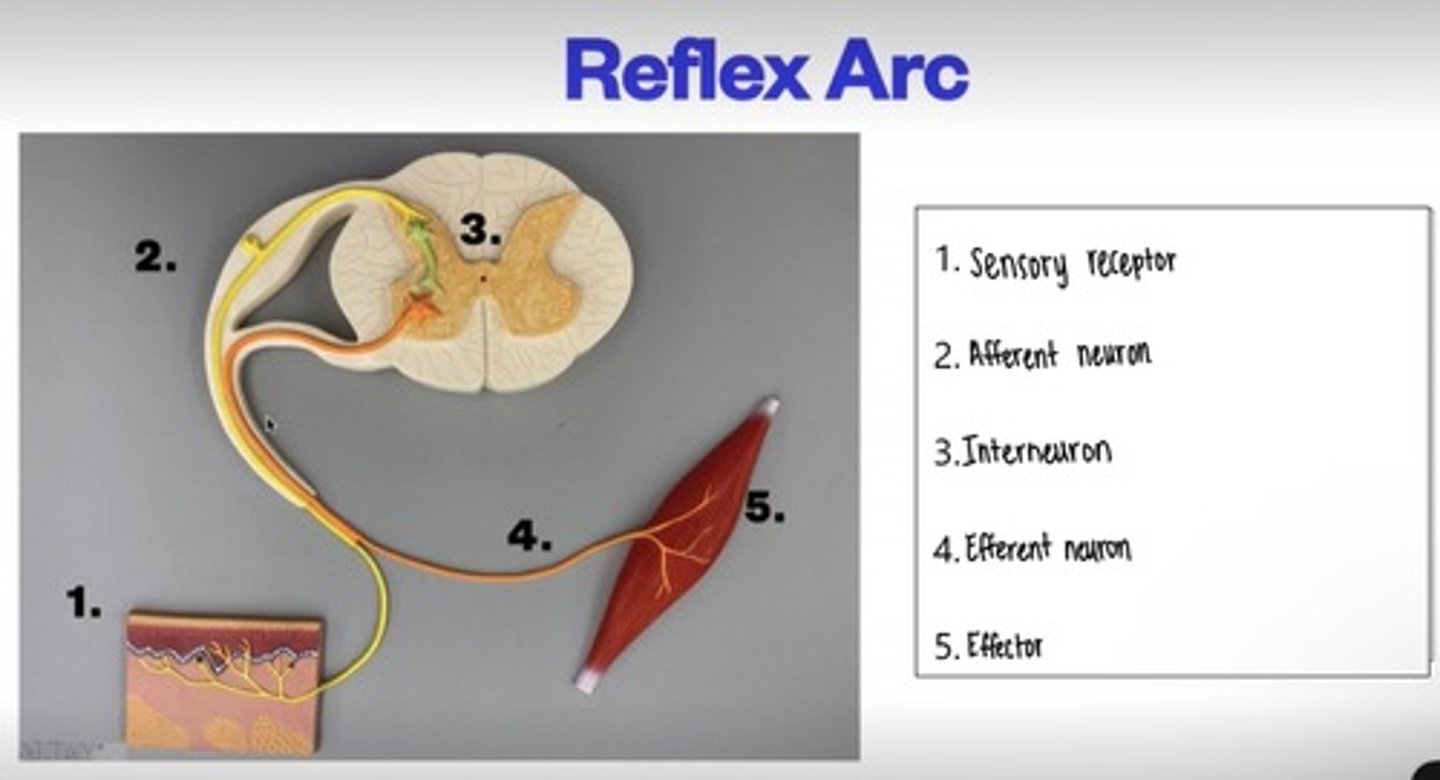
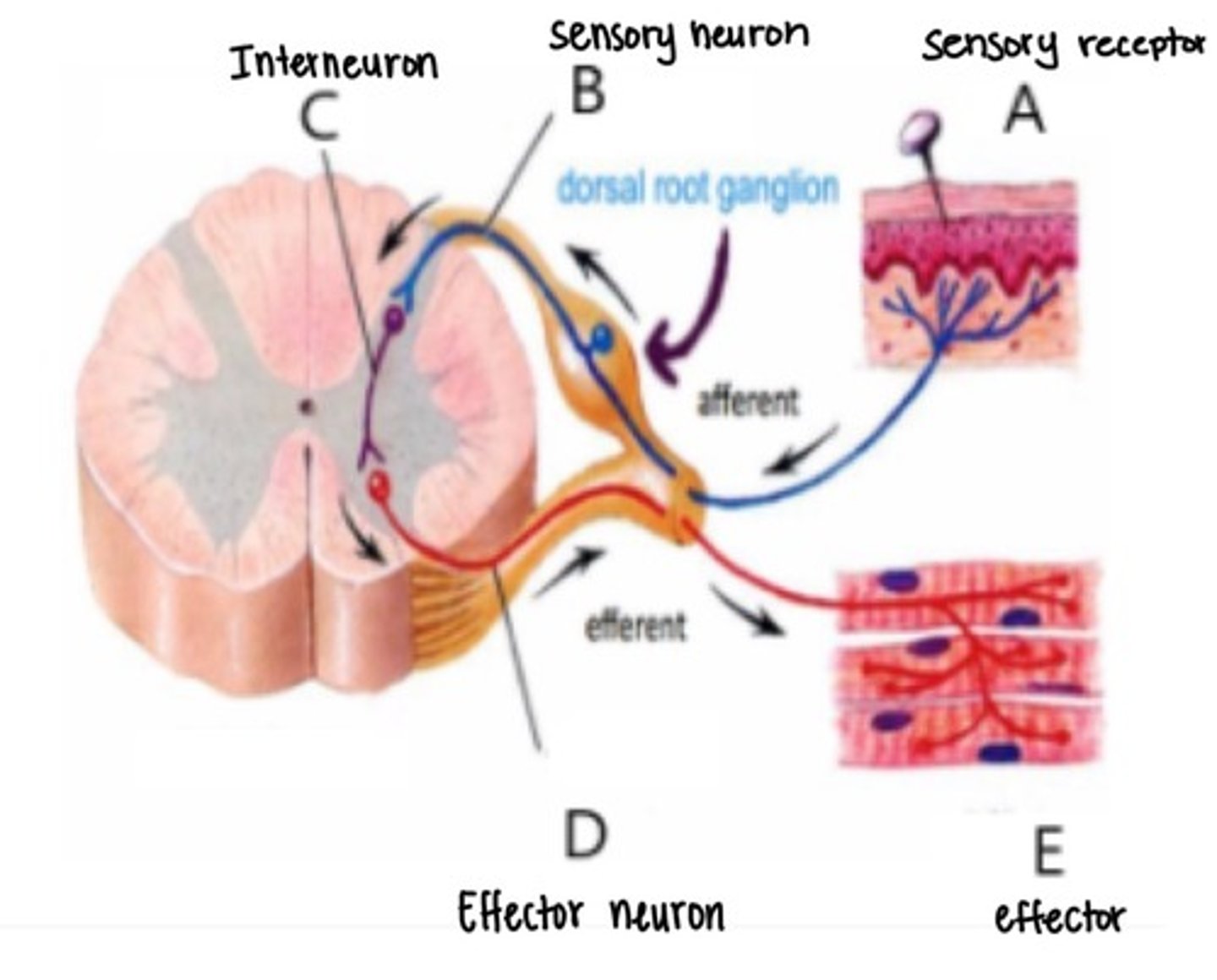
Sensory signals are passed into the spinal cord through the dorsal root of each spinal nerve. Sensory (afferent) spinal nerve cell bodies are clustered together in the dorsal root ganglion
Motor (efferent) signals from the spinal cord pass through the ventral root of each spinal nerve to trigger an action of either a skeletal muscle contraction or a gland secretion
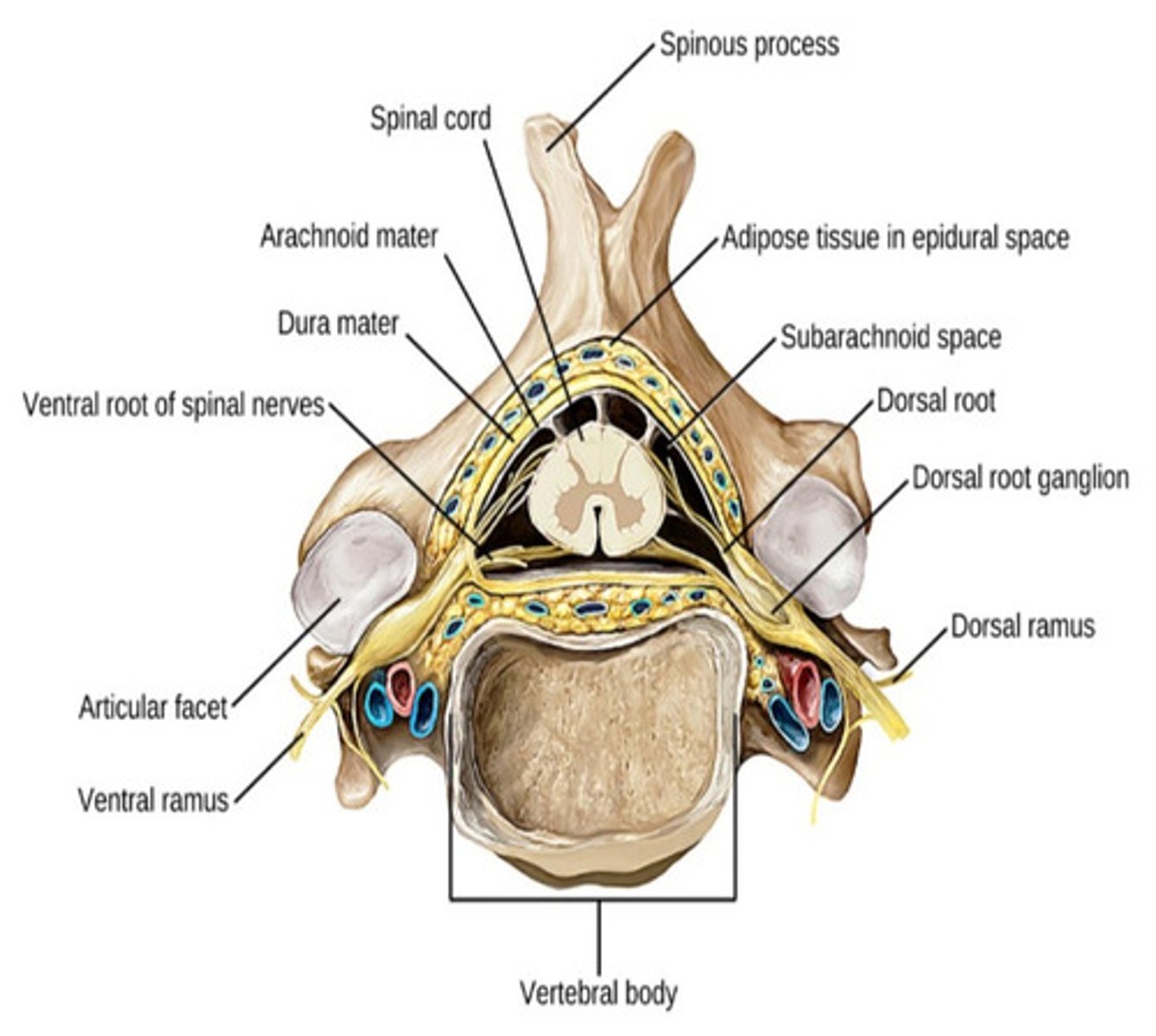
Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord pt.2
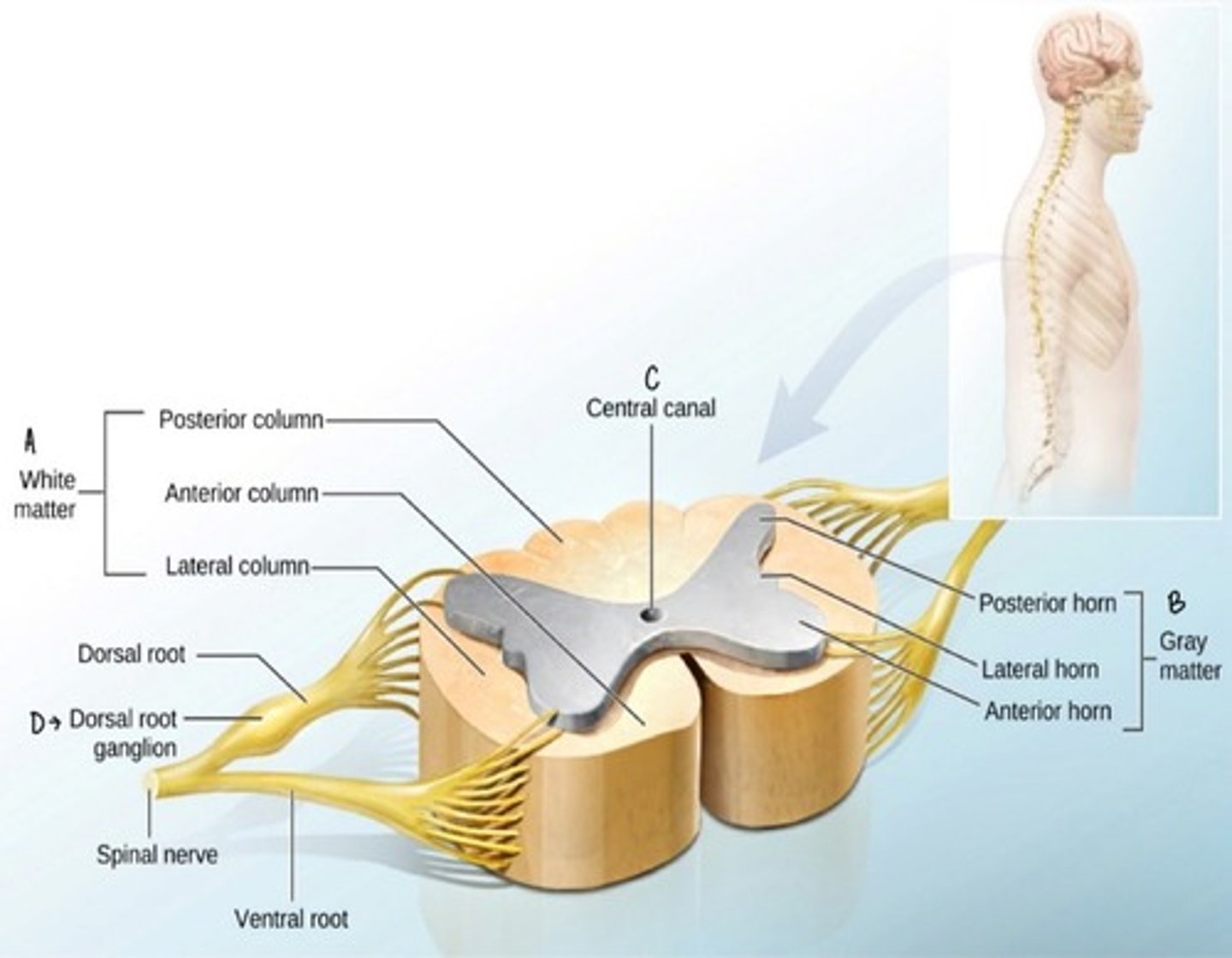
Gray Matter
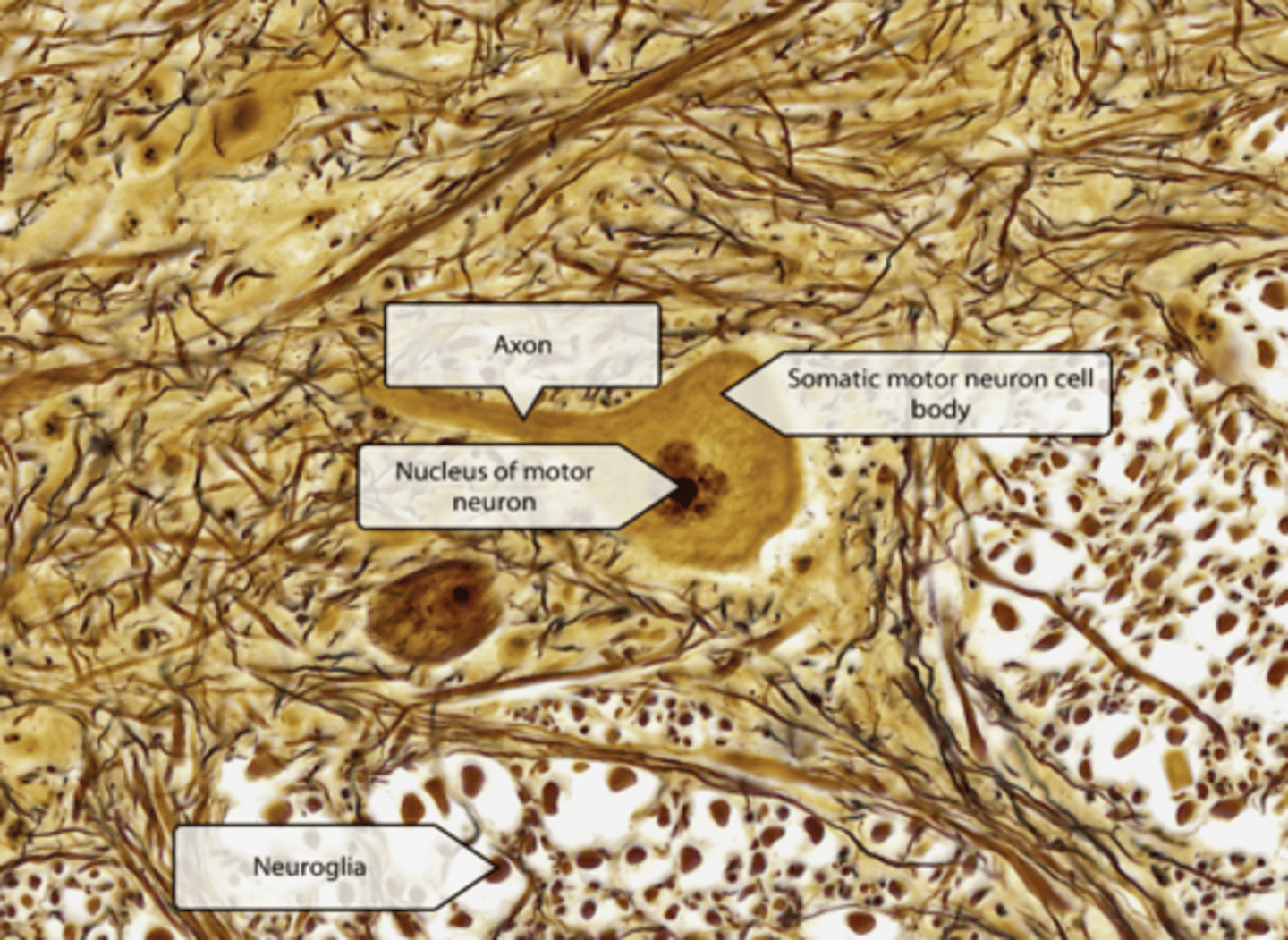
Histology of gray matter: anterior horn
Gray matter horns composed of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, and neuroglia: form a centrally located H-shaped area in spinal cord.
Posterior horns contain interneurons and sensory relay neurons that receive sensory input from axons conveying touch, temp, pain, and proprioceptive info from body.
Anterior horns contain somatic motor neuron cell bodies that facilitate movement.
gray commissure connects these regions and surrounds the central canal: the (CFS) cerebrospinal fluid-filled space that runs down the center of the spinal cord.
Lateral horns are present ONLY in thoracic and superior lumbar spinal cord segments and contain autonomic motor neuron cell bodies that intervene in the visceral organs
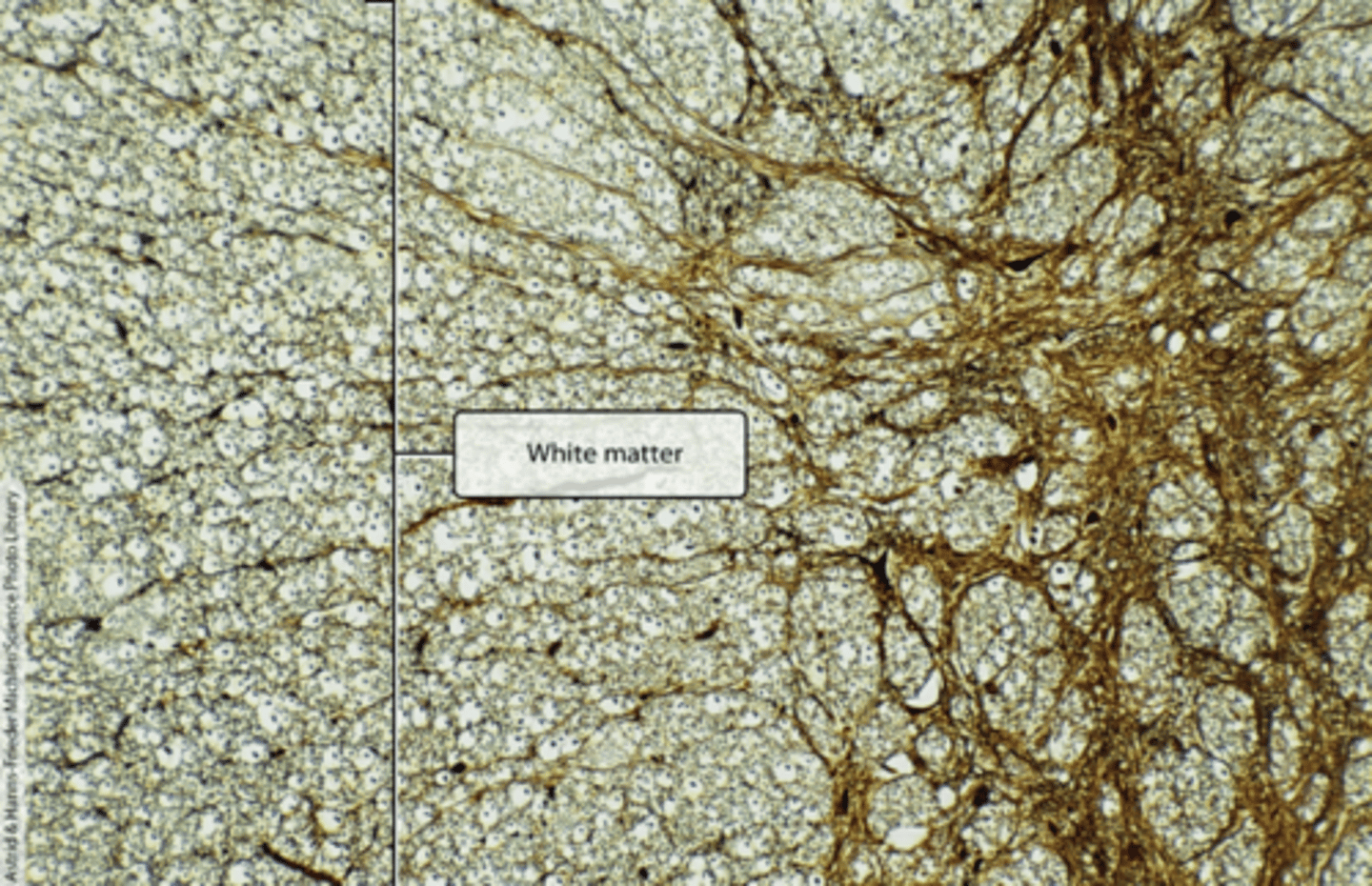
White Matter
Histology of white matter
forms the superficial part of the spinal cord and is composed of both myelinated and unmyelinated axons that travel in ascending and descending fiber tracts.
Appears white because of the abundance of lipid-rich myelin that surrounds and insulates most axons, facilitating rapid signal conduction
Ascending axons carry sensory signals up the spinal cord toward the brain. Descending axons carry motor signals down the spinal cord toward the periphery.
Commissural fibers: axons that cross the spinal cord.
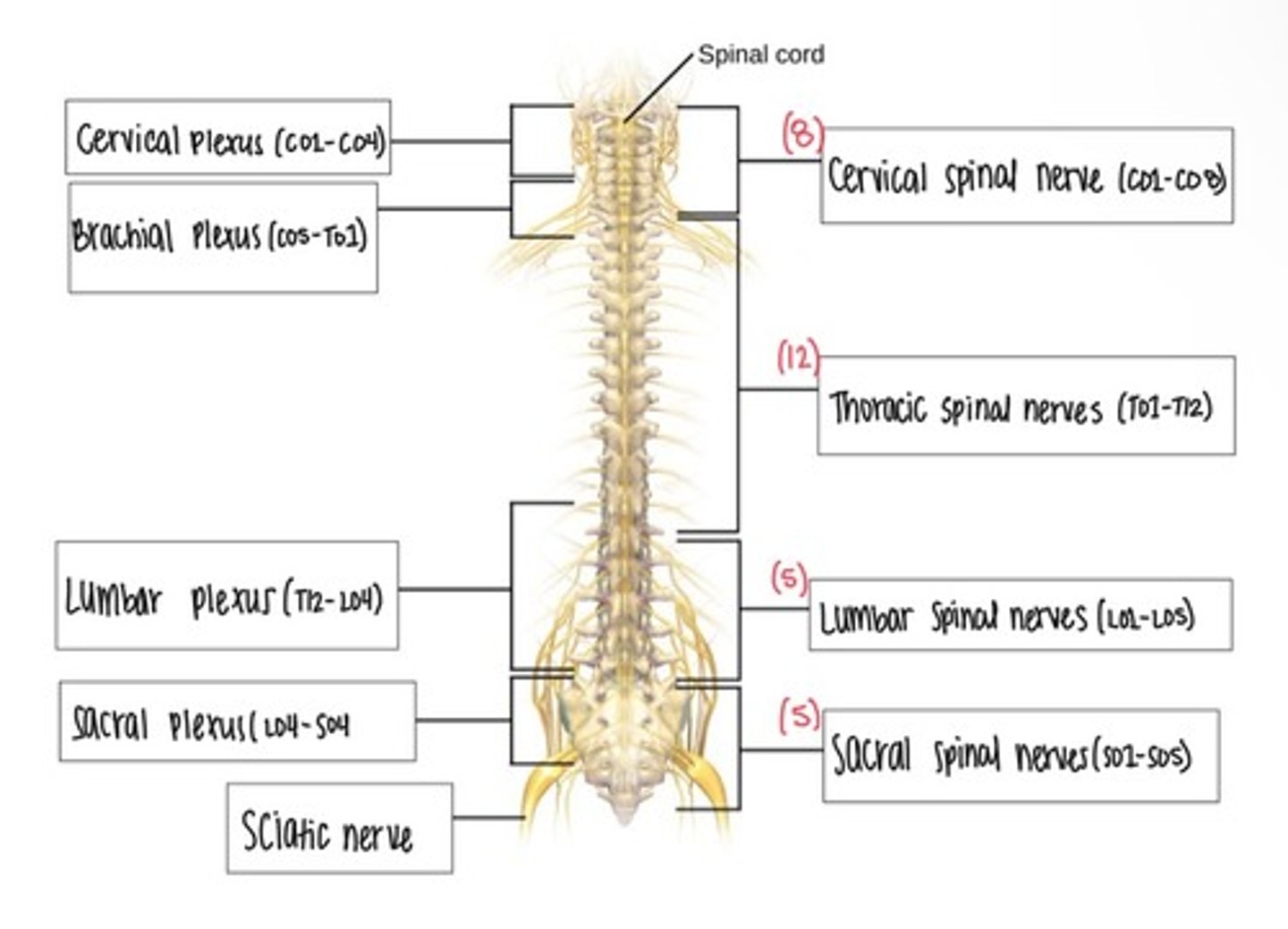
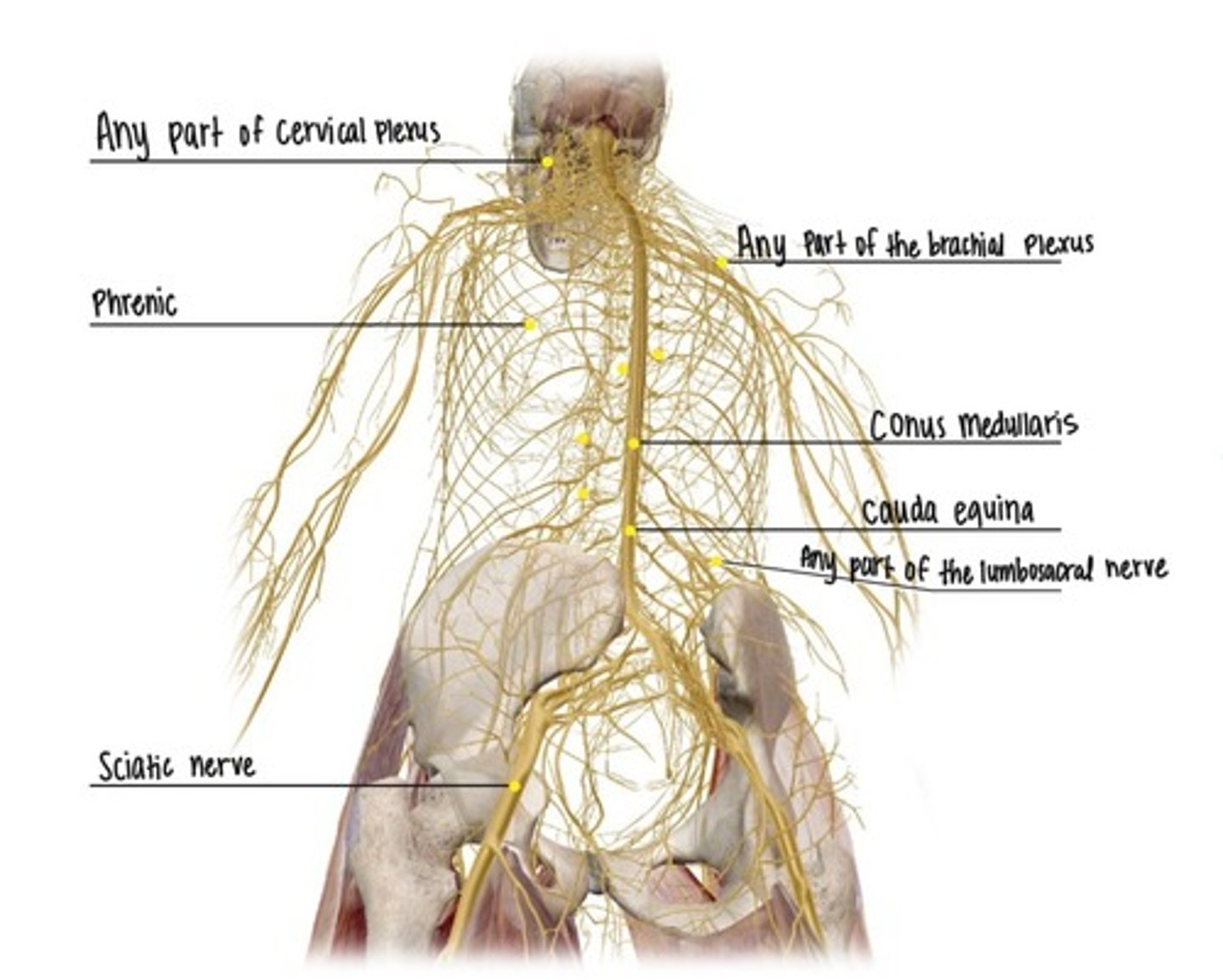
Spinal Nerves
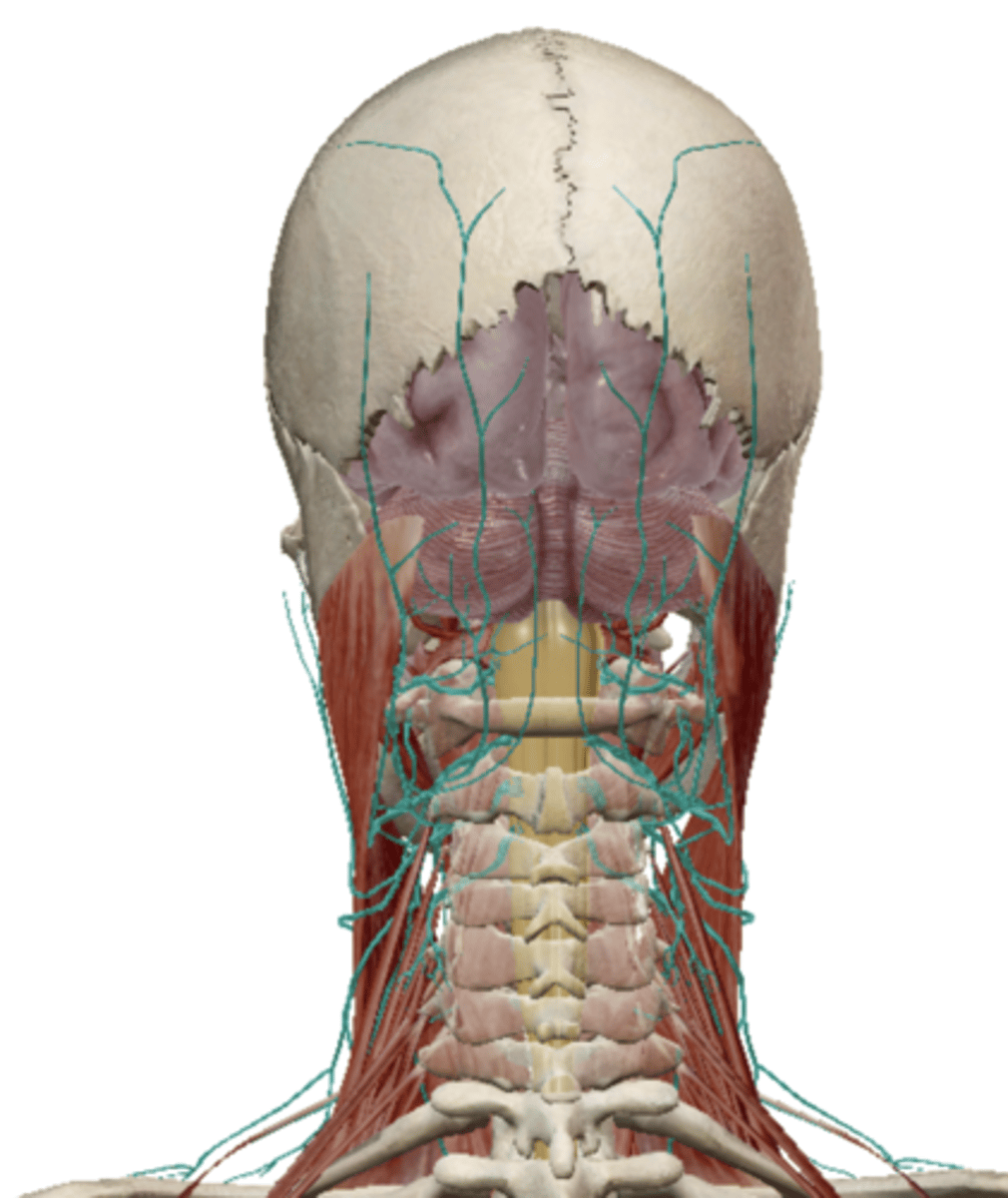
Cervical Plexus
Supraclavicular Nerve (Cervical Plexus)
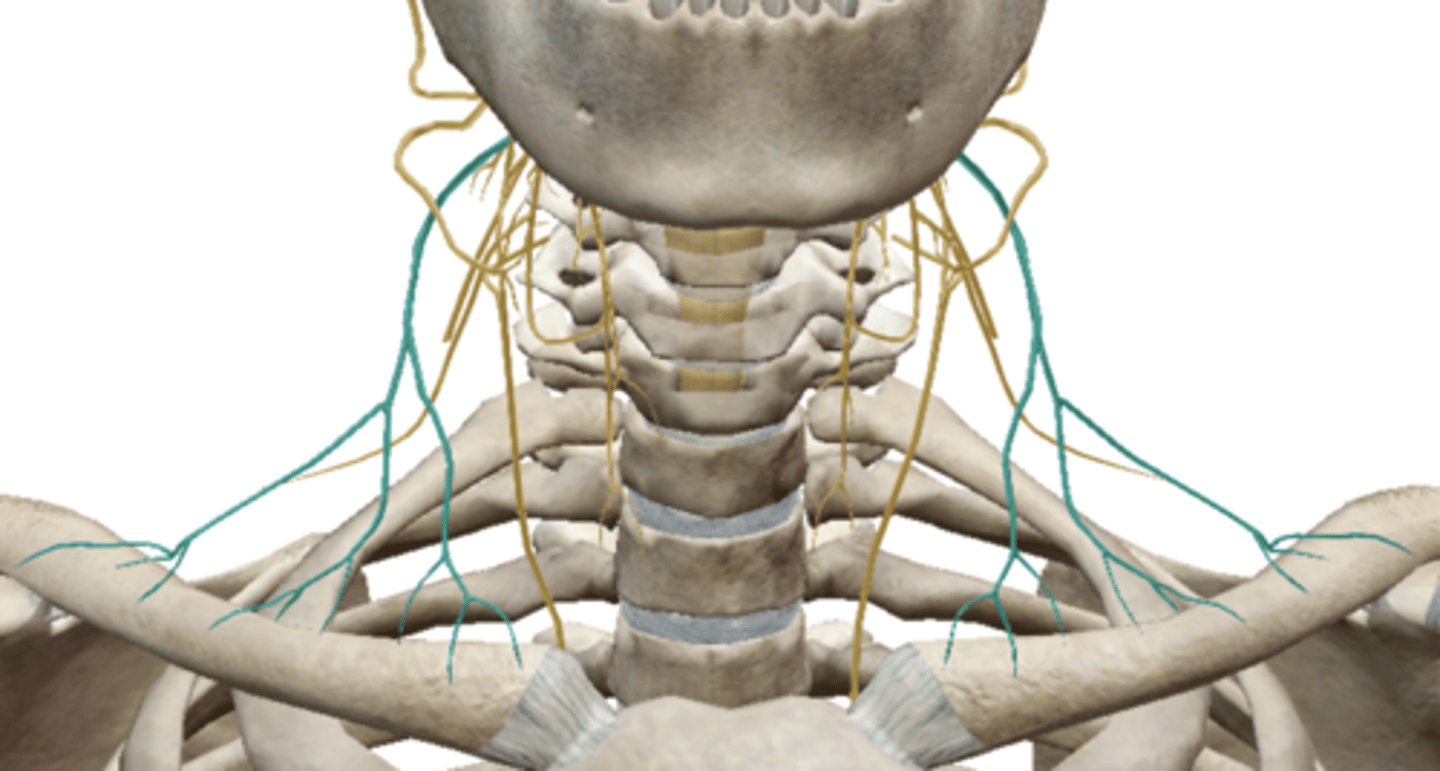
Phrenic Nerve (Cervical Plexus)
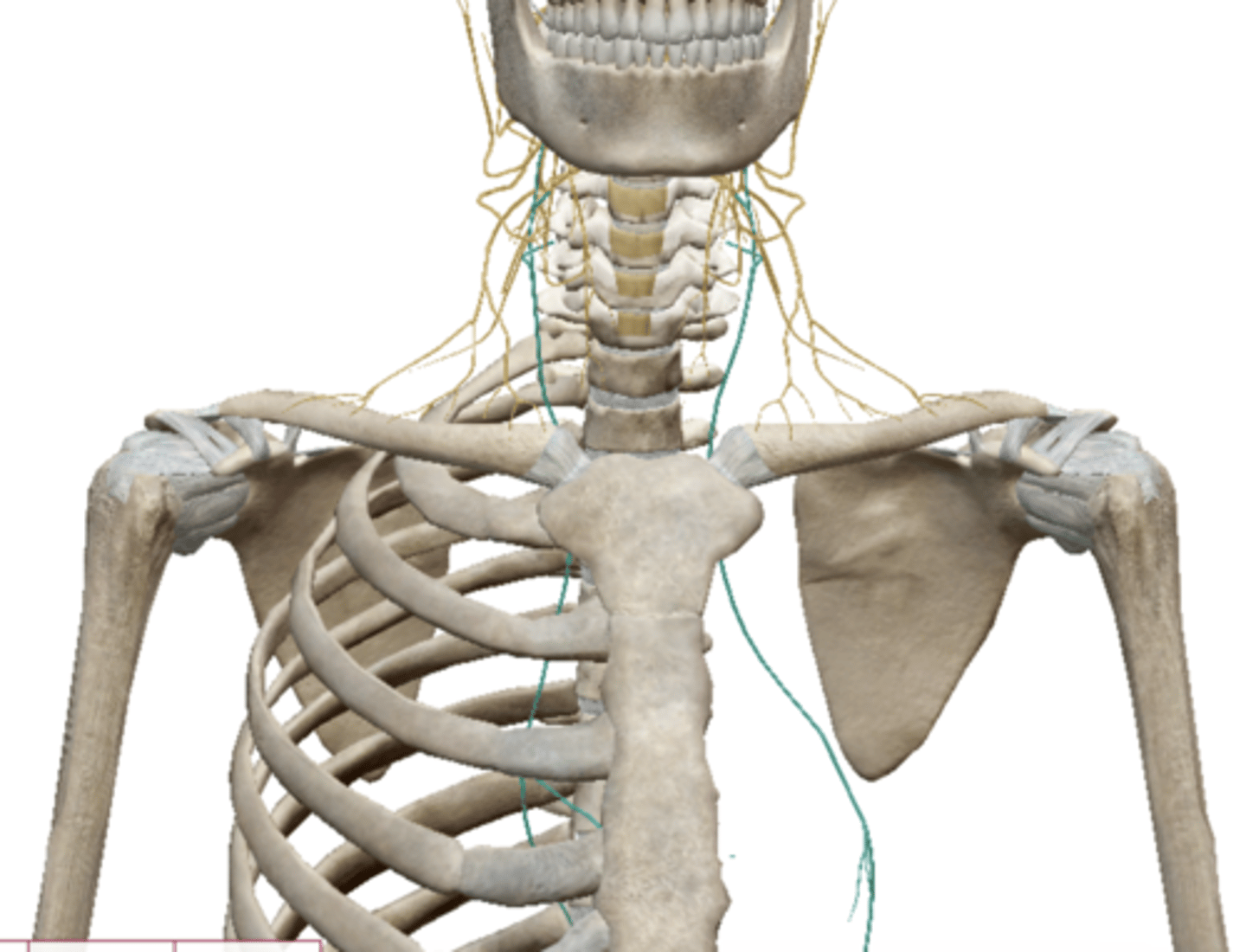
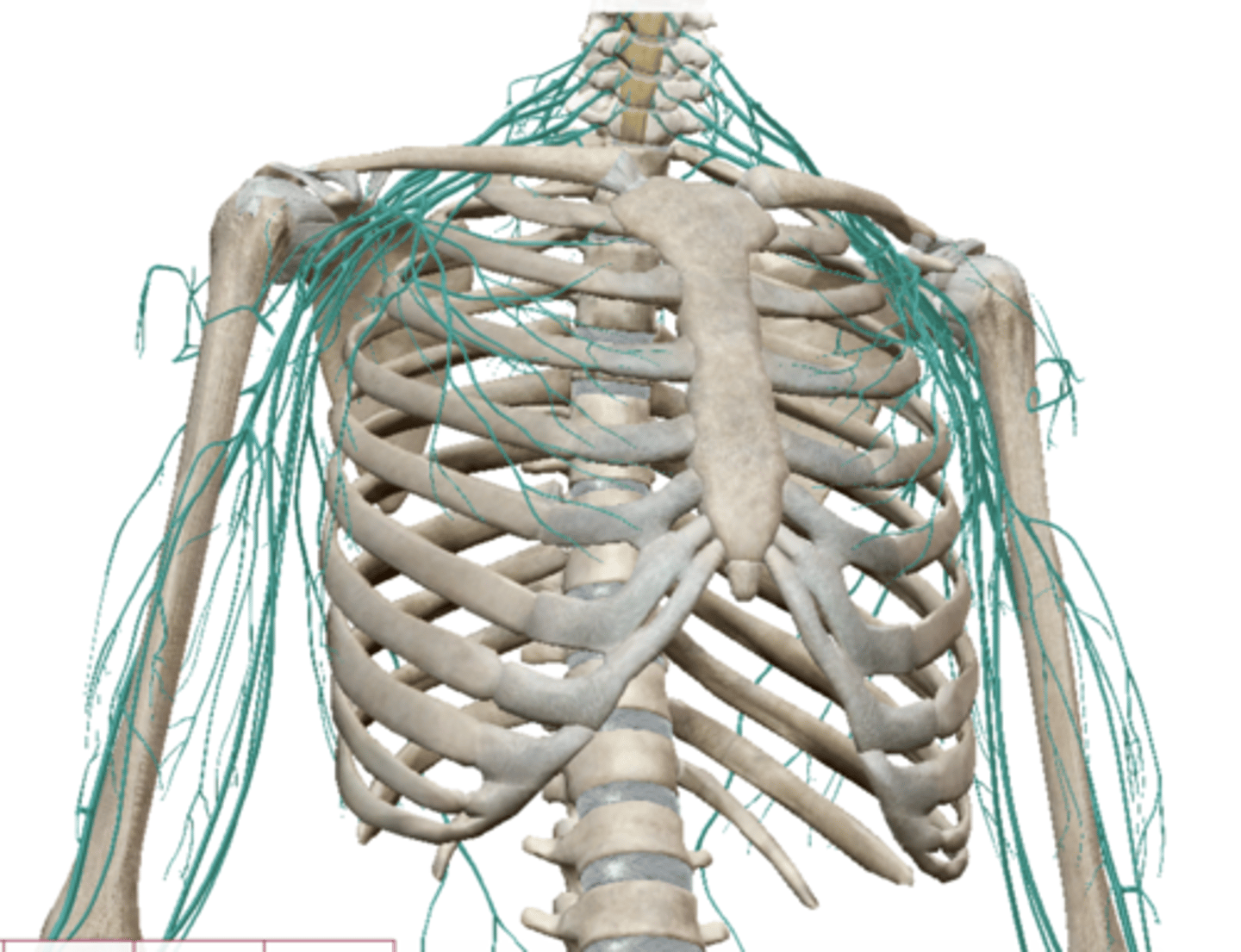
Brachial Plexus
Axillary Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
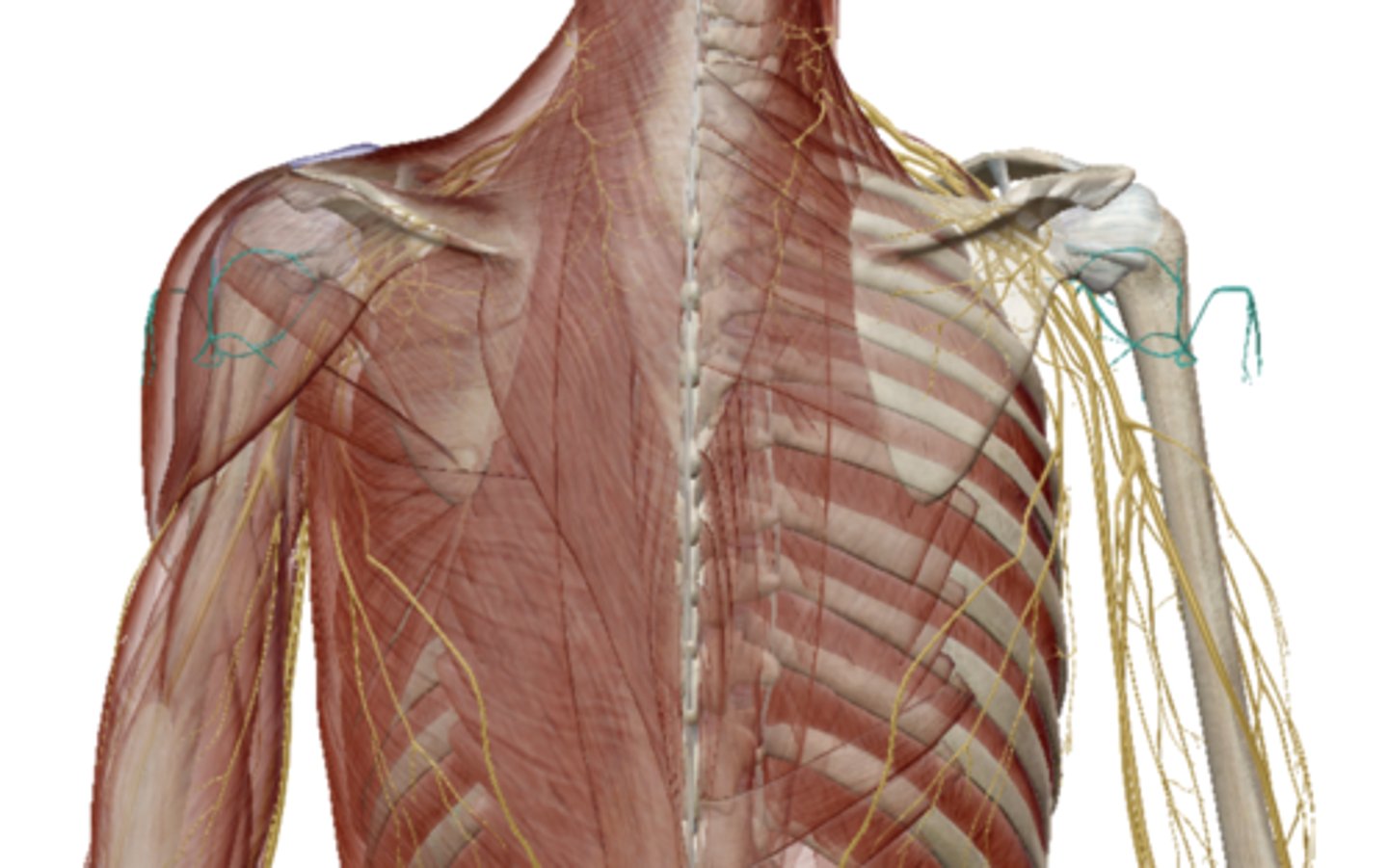
Radial Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Median Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
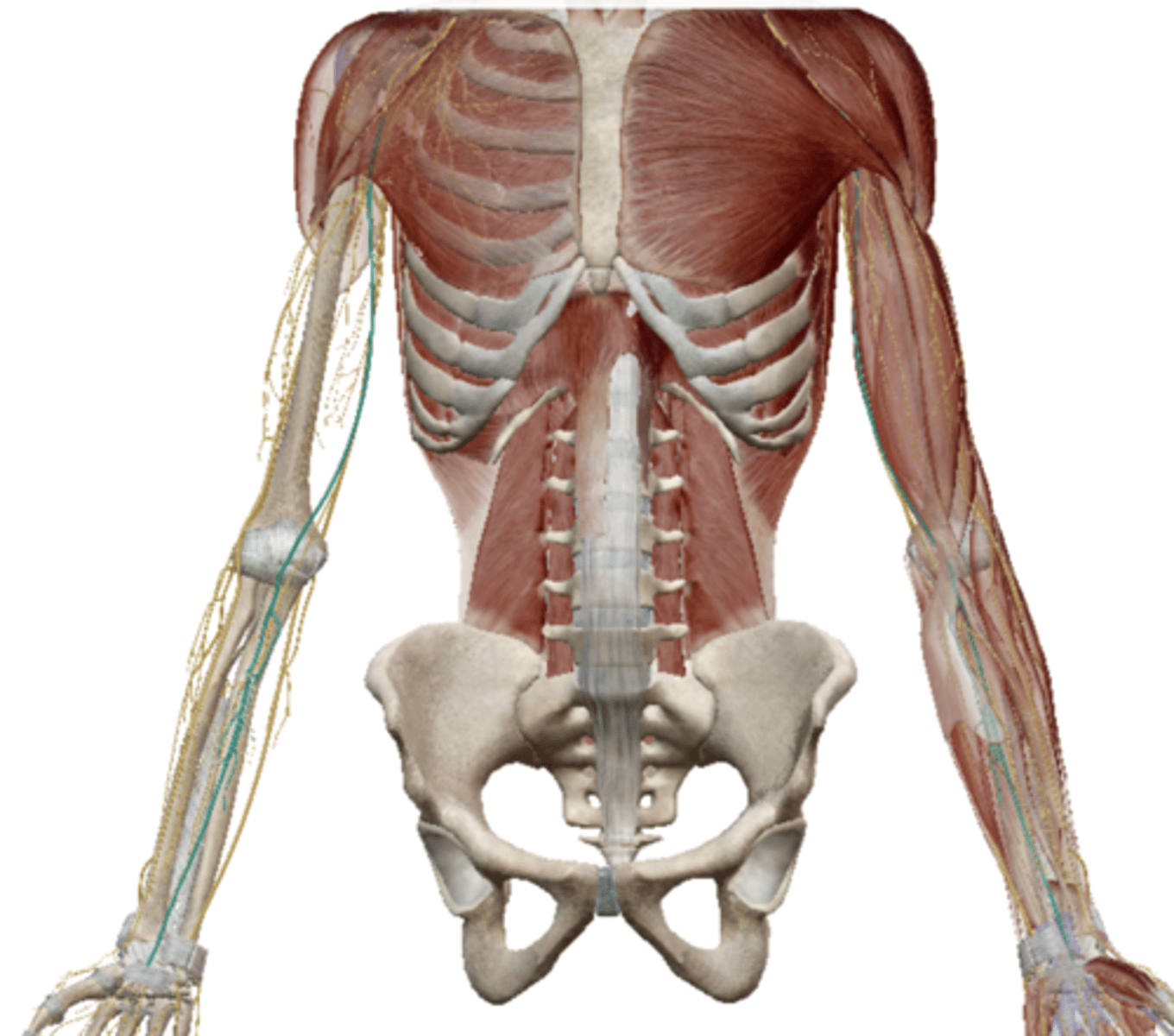
Musculocutaneus Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
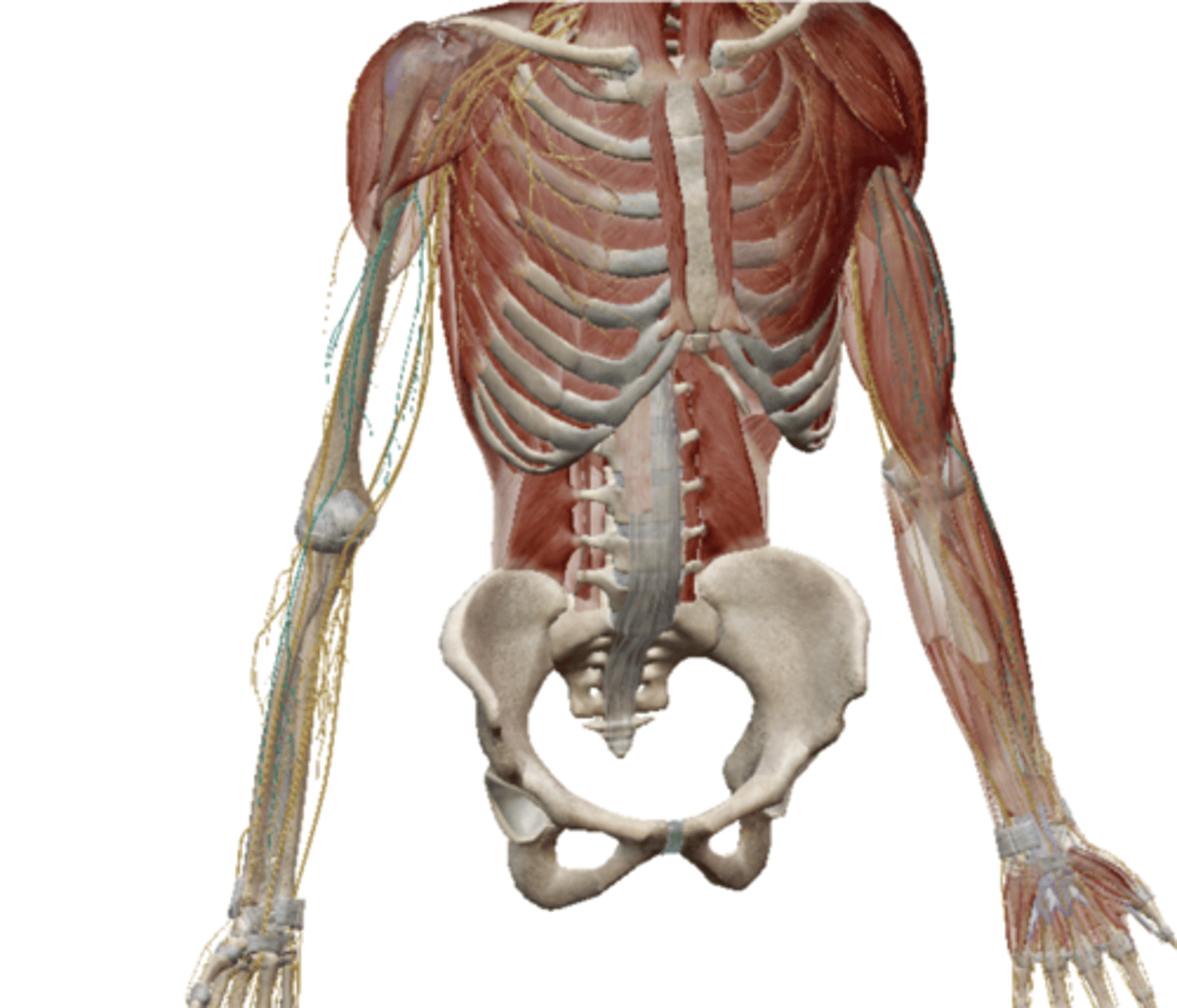
Ulnar Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
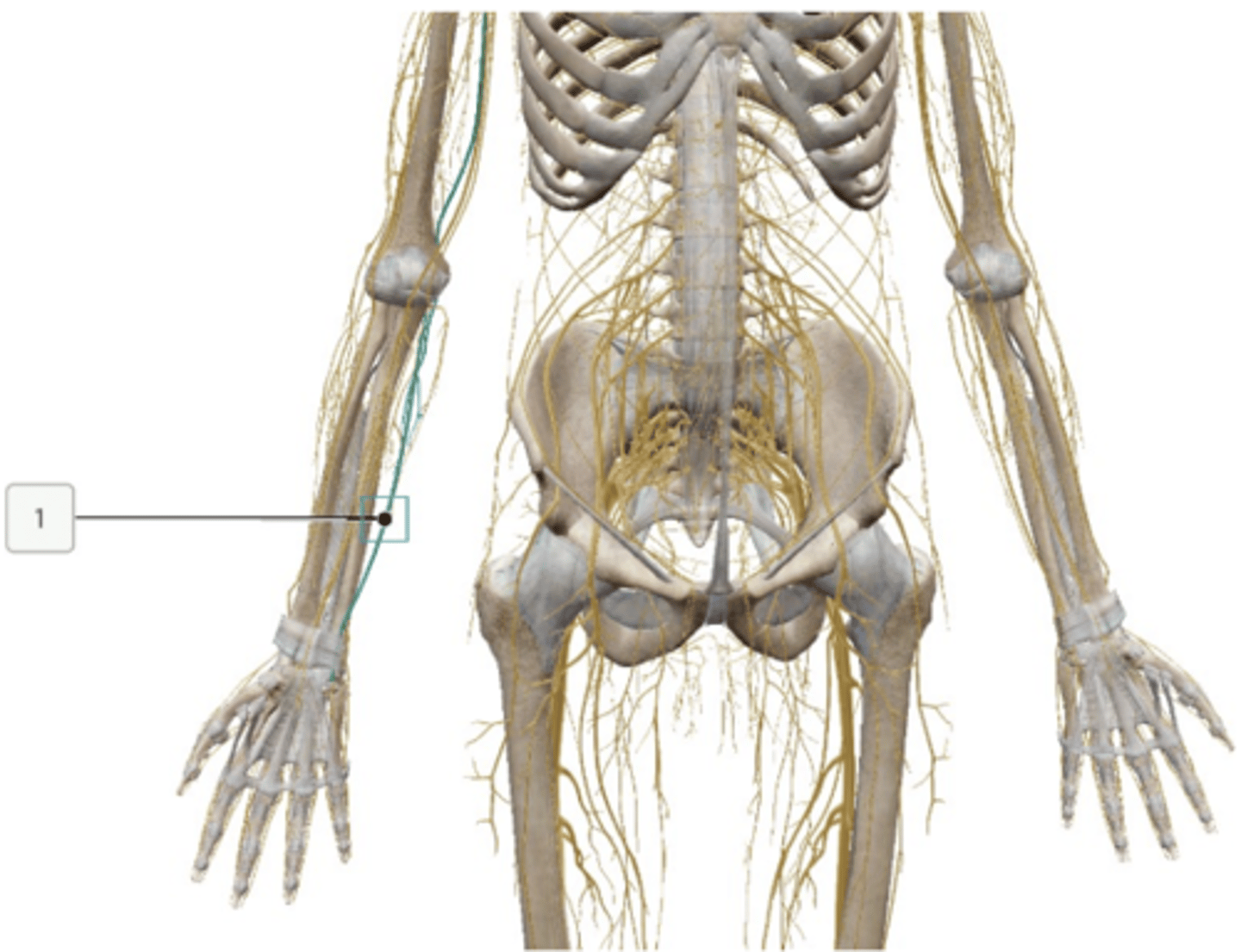
Lumbosacral Plexus
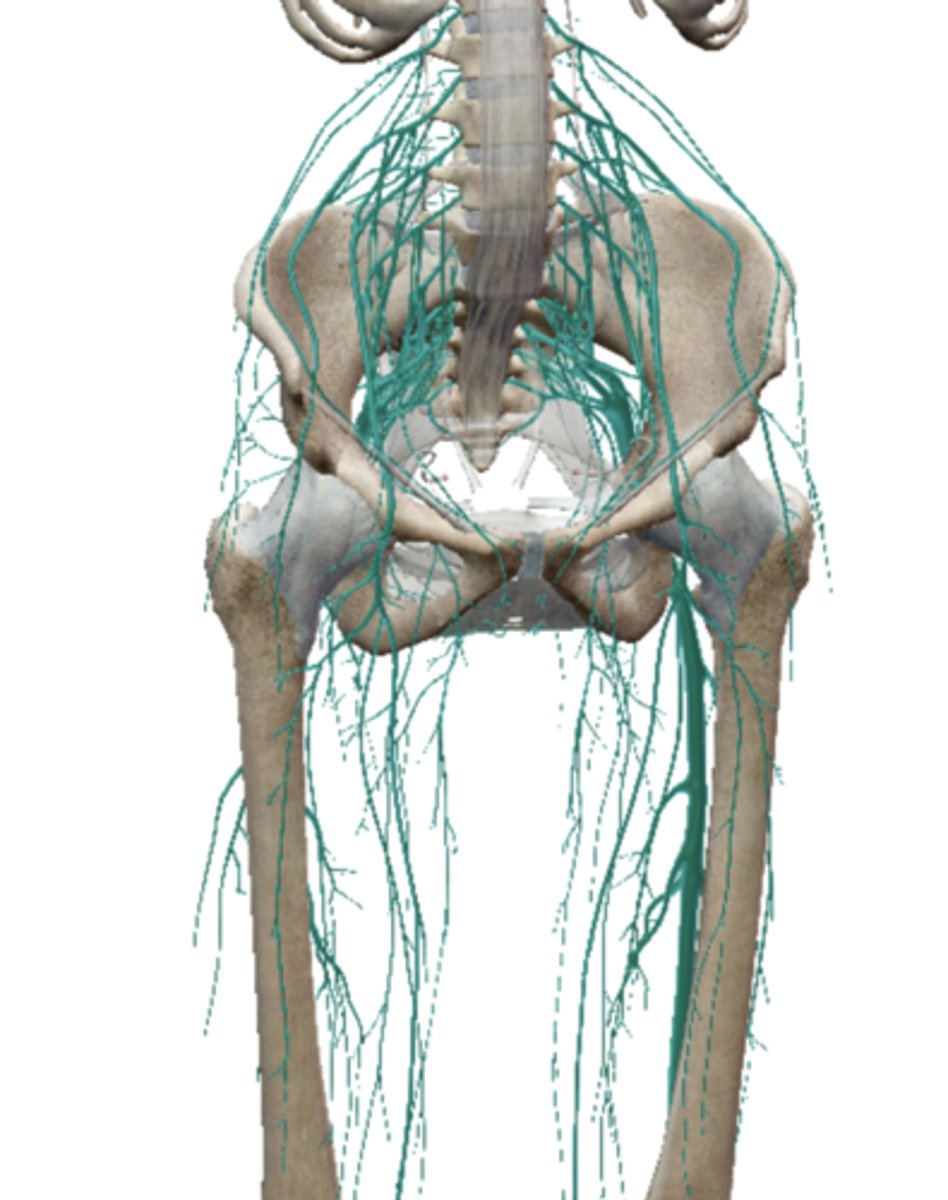
Femoral Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
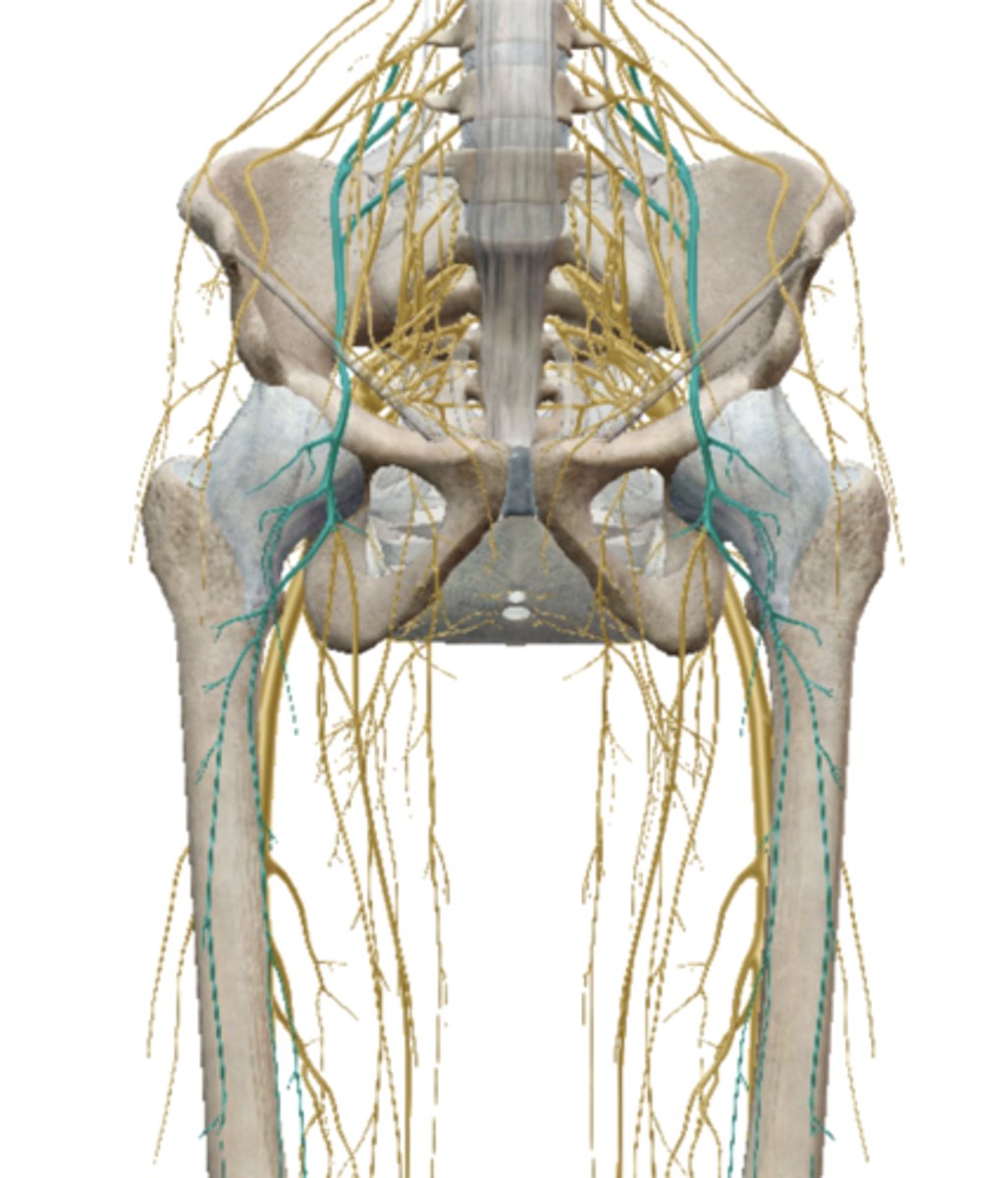
Obturator Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
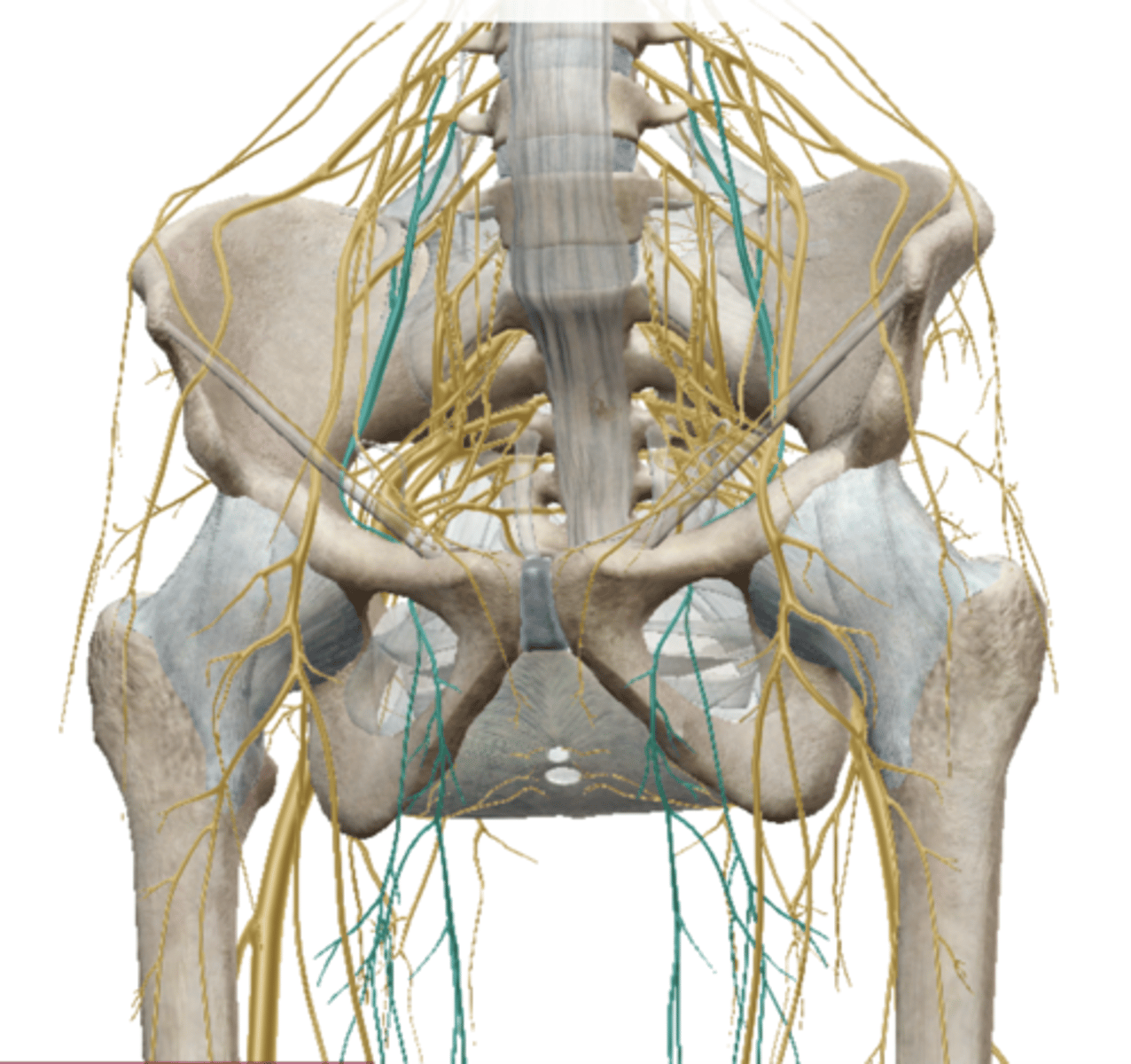
Sciatic Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
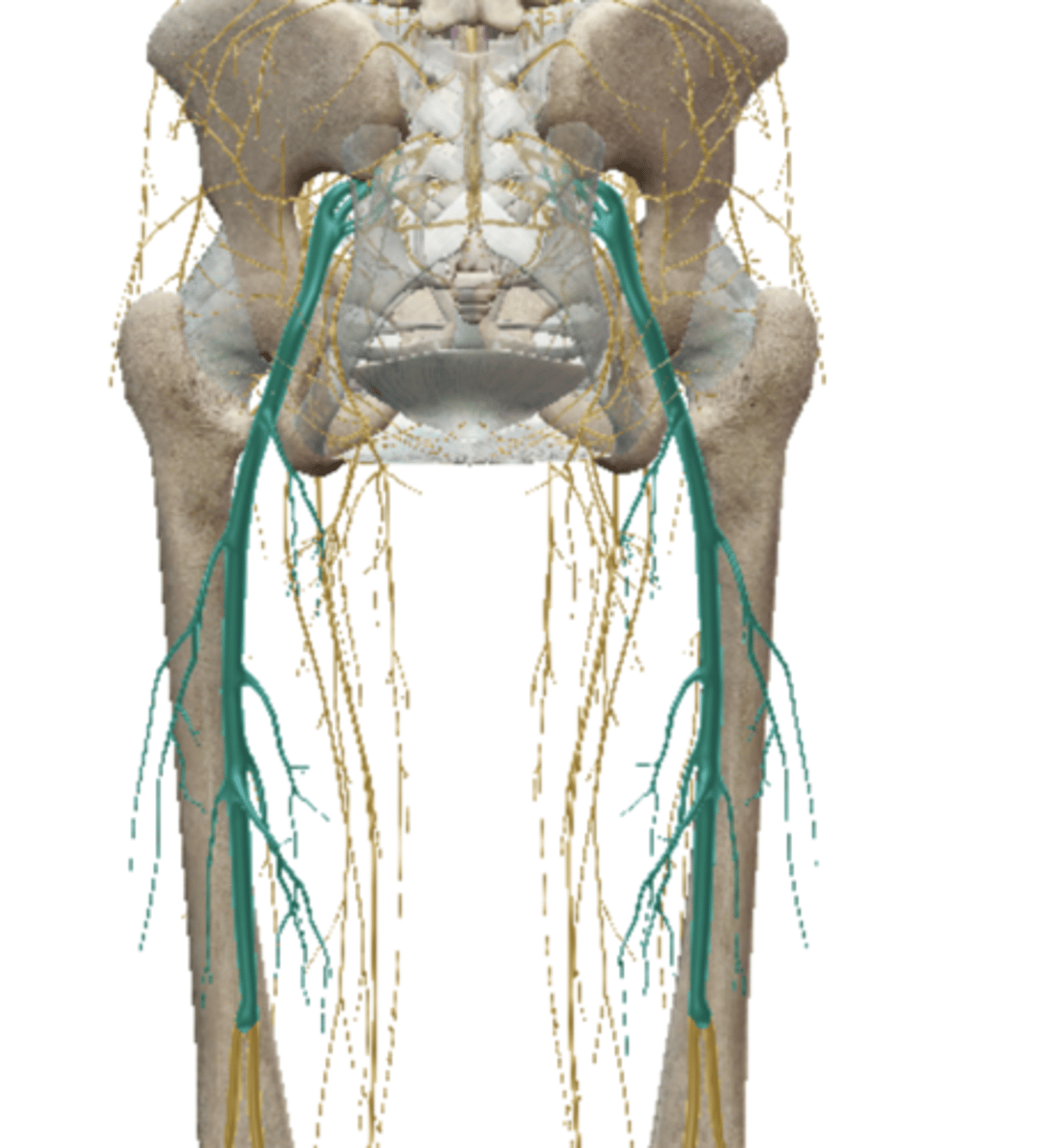
Gluteal Nerves (Sacral Plexus)
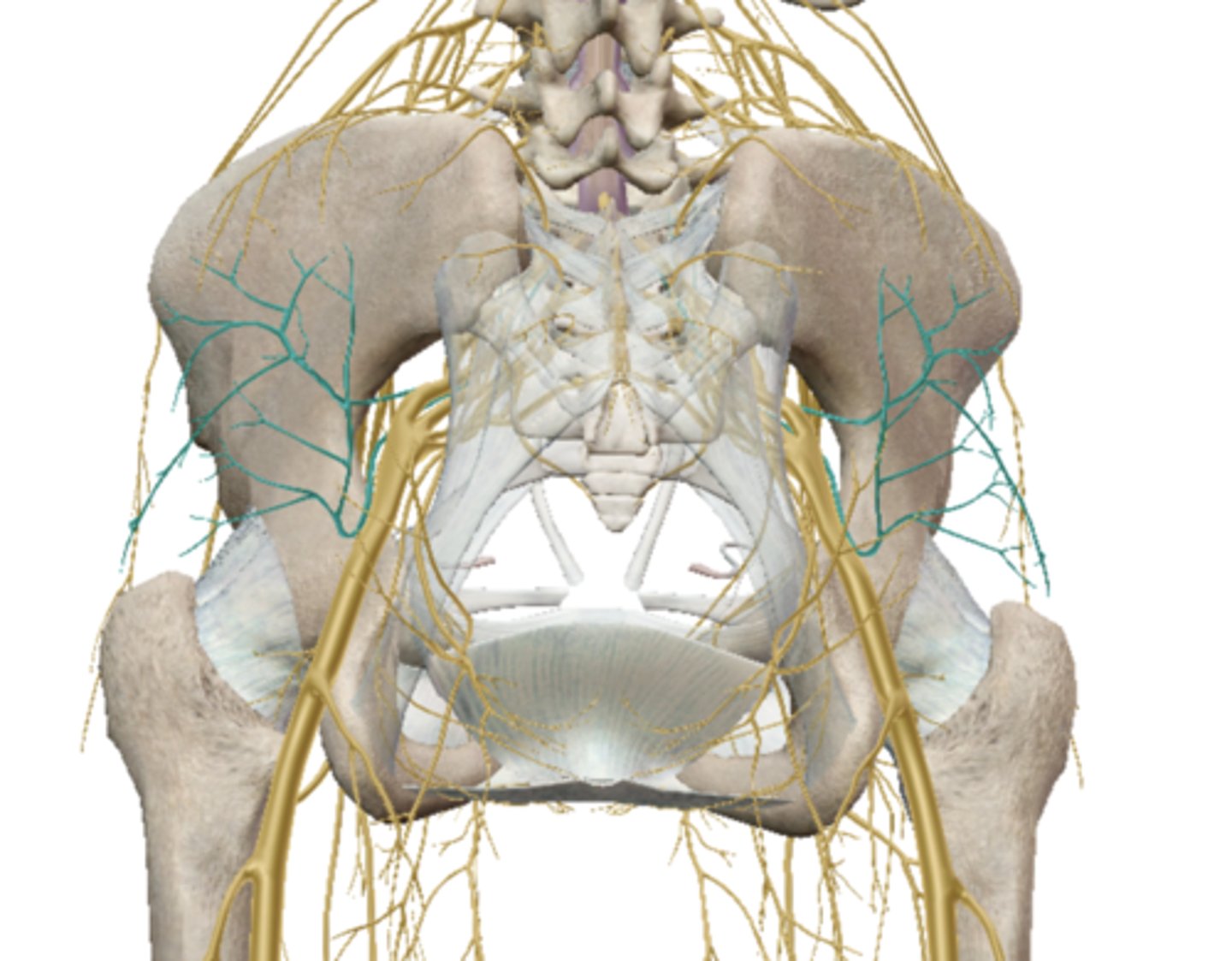
Common Fibular (peroneal) Nerve - Lab Activity
Superficial Fibular (peroneal) - VB
(Sacral Plexus)
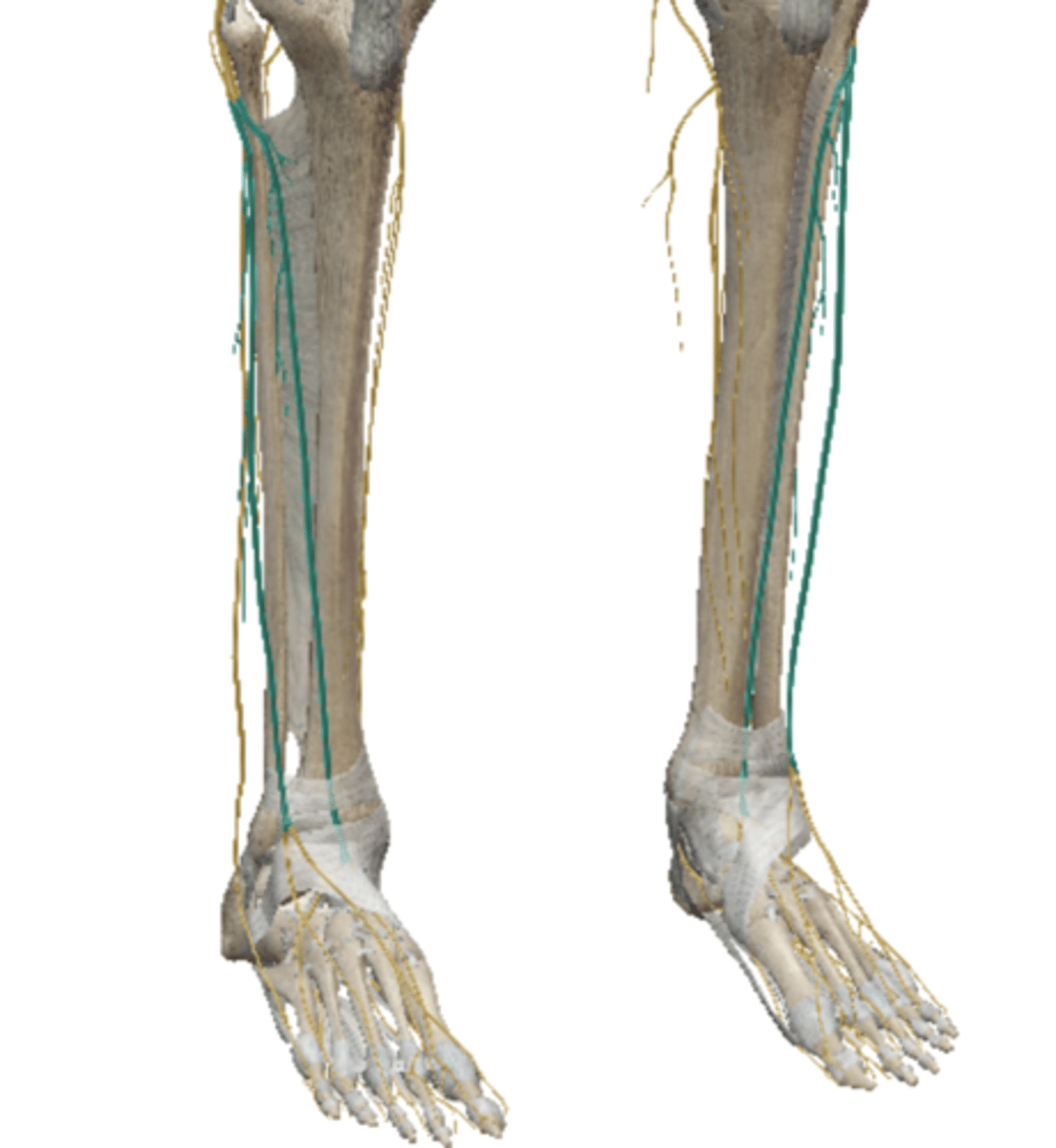
Tibial Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
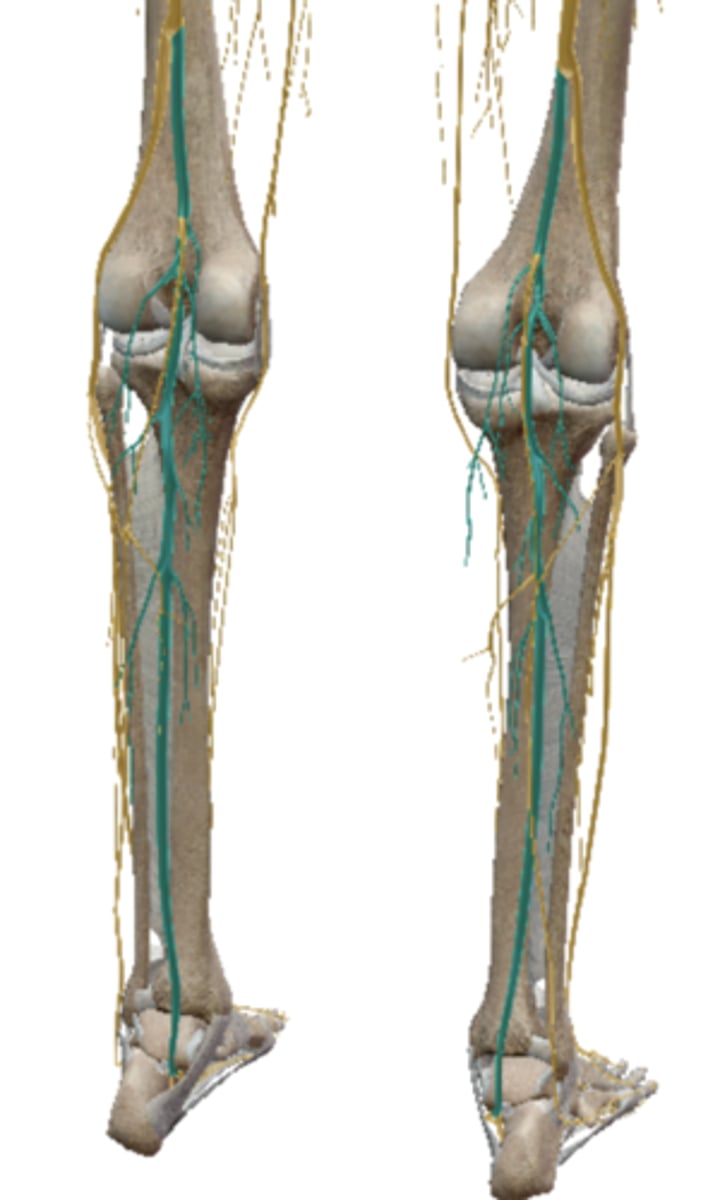
Gross Anatomy of Spinal Nerves
??
Major Branches of Spinal Plexus
??
SOMATIC REFLEXES
Reflex Arc
Reflex Arc pt.2
Somatic Reflex Testing
Biceps Reflex: Biceps tendon - C5, C6 nerve group
Triceps Reflex: Tricep Tendon - Arm will extend- involves the radial nerve (C7 & C8)
Brachioradialis Reflex: Brachioradialis muscle until it becomes a tendon (C6)
Patellar Reflex: Patella tendon- Small jump (L4) femoral nerve
Achilles Reflex: tapping the Achilles tendon - Tibial nerve- test for S1 nerve root
Plantar Reflex: response of the toes, particularly the big toe, to certain stimuli, such as stroking the sole.- toes crawl
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Gross Anatomy of the ANS
??
Fucntions of the ANS
senses internal conditions and regulates the involuntary activity of visceral organs
controls involuntary visceral activities like heart rate, respiration, digestion, glandular, secretions, and reproduction.
The hypothalamus and brain stem are the main centers of control for these functions
All autonomic functions are managed by nerves that activate daily processes (eating, breathing, etc.) or nerves that manage the need for increased activity
Testing Autonomic Reflexed
Pupillary Light Reflex: controls the constriction of the pupil in response to light. This reflex helps regulate the amount of light entering the eye, thereby maintaining optimal visual acuity and protecting the retina from excessive light exposure.
Crossed Extensor Reflex: occurs in response to a painful stimulus, typically in the lower limbs. It involves a coordinated movement pattern where one limb withdraws from the painful stimulus while the opposite limb simultaneously extends to provide support and balance.
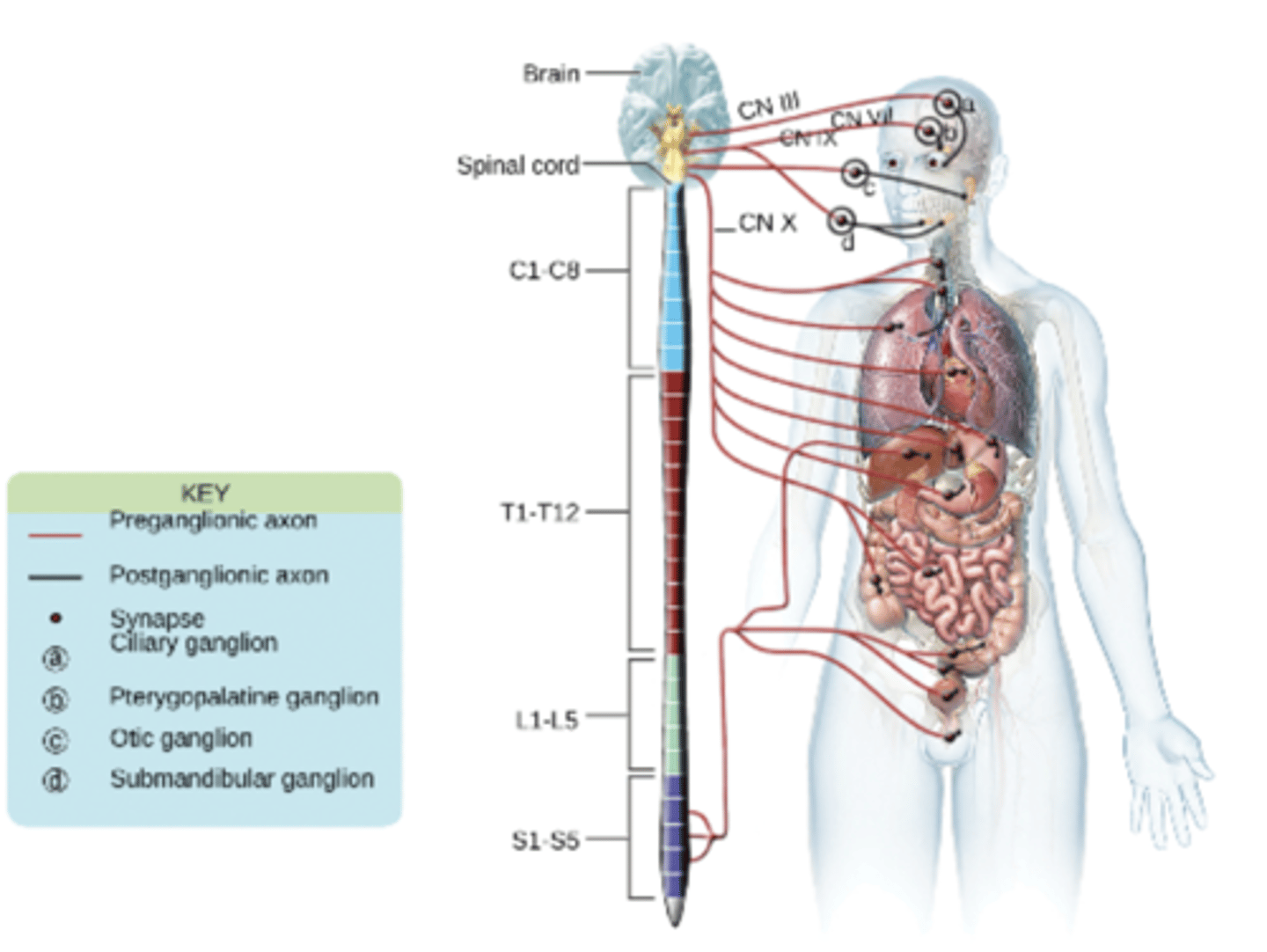
Parasympathetic Nervous System
the parasympathetic division will NOT cause the heart rate to increase
(the heart rate decreases)
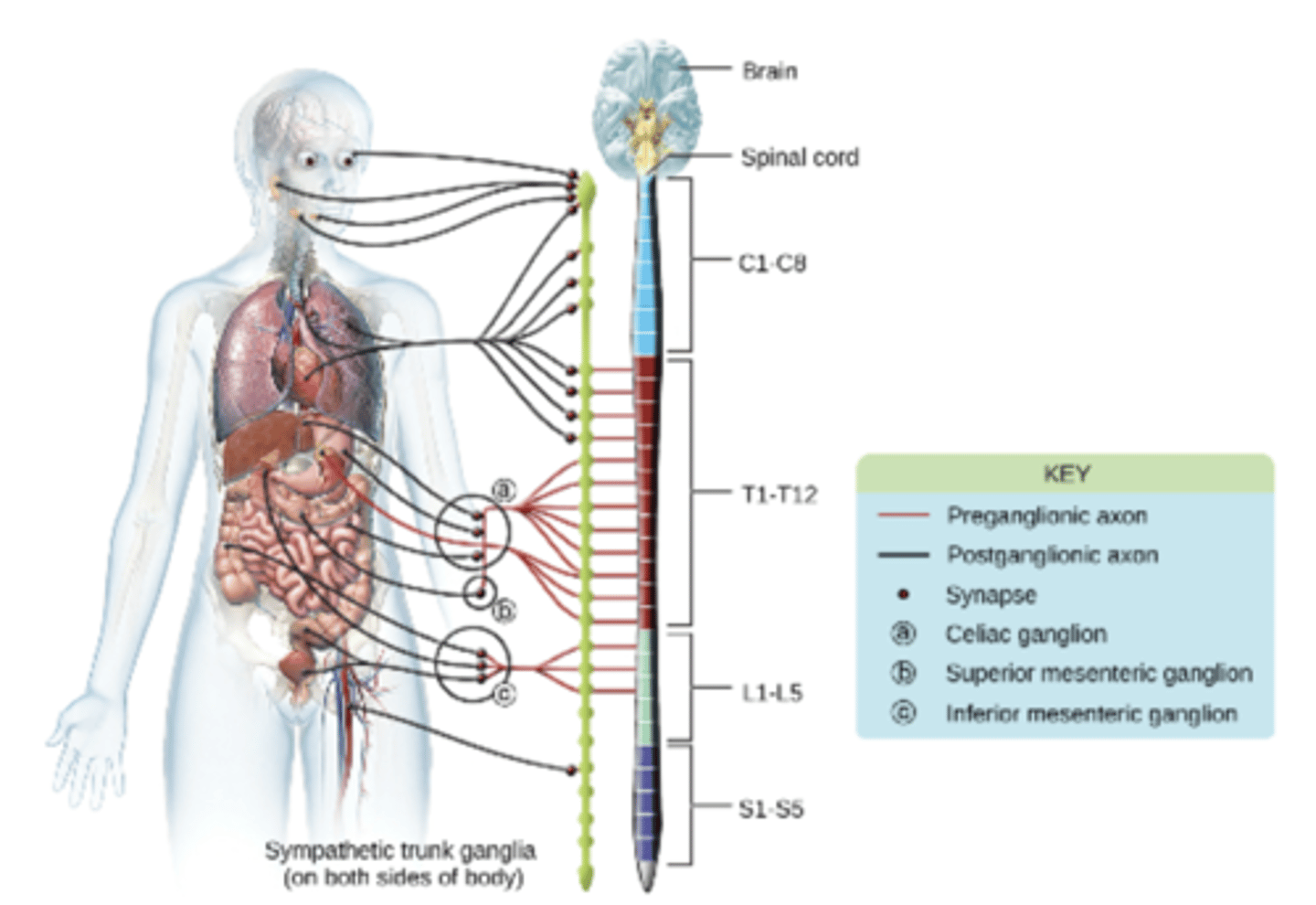
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic Nervous System stimulates the fight or flight responses
Subarachnoid Space
the area/space around the spinal cord that contains CSF.
Myelin Sheath
the lipoprotein covering around some portions of the axons.