Muscle Tissue: Types, Structure, and Function 1/2
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
contractility
Muscle tissue is specialized for
Types of muscle tissue
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Cell lengthening
&
Synthesis of myofibrillar proteins actin and mysoin
Differentiation of muscle tissue entails
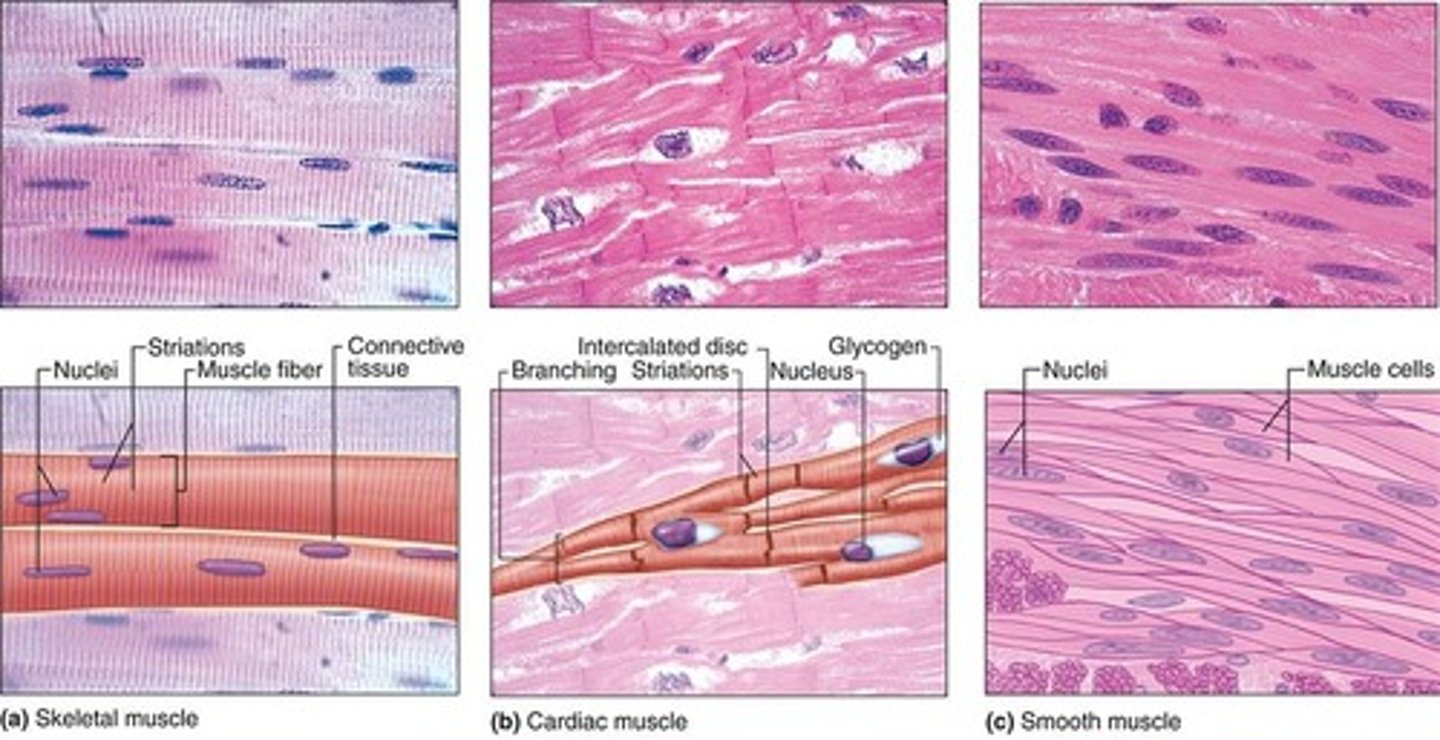
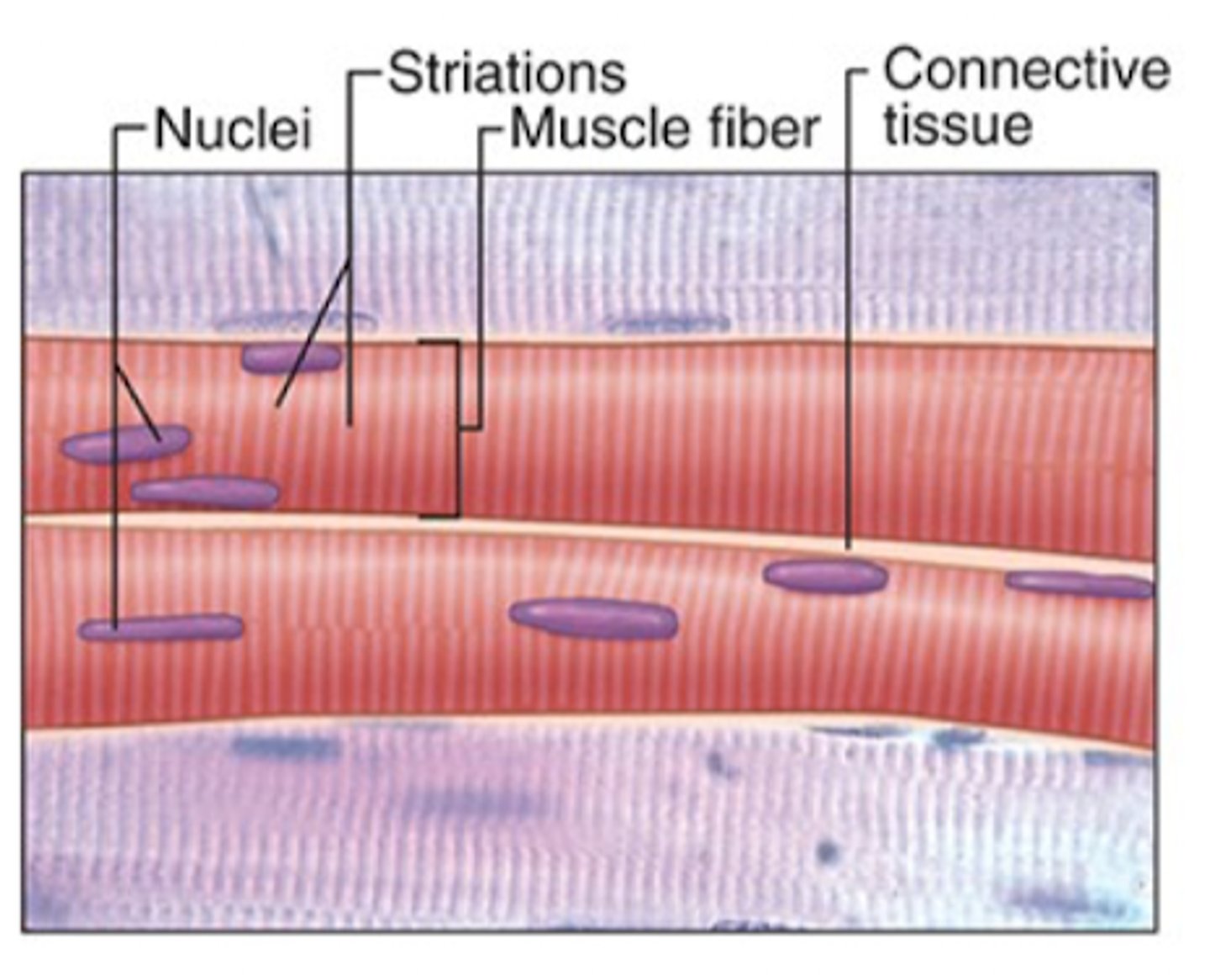
Verly long fibers (cells)
Multinucleated cells
Cross-striations
Skeletal muscle has what features?
Fast and strong, voluntary control
How are the contractions of skeletal muscle?
Cardiac muscle
What muscle tissue has branched cells with intercalated discs & cross-striations
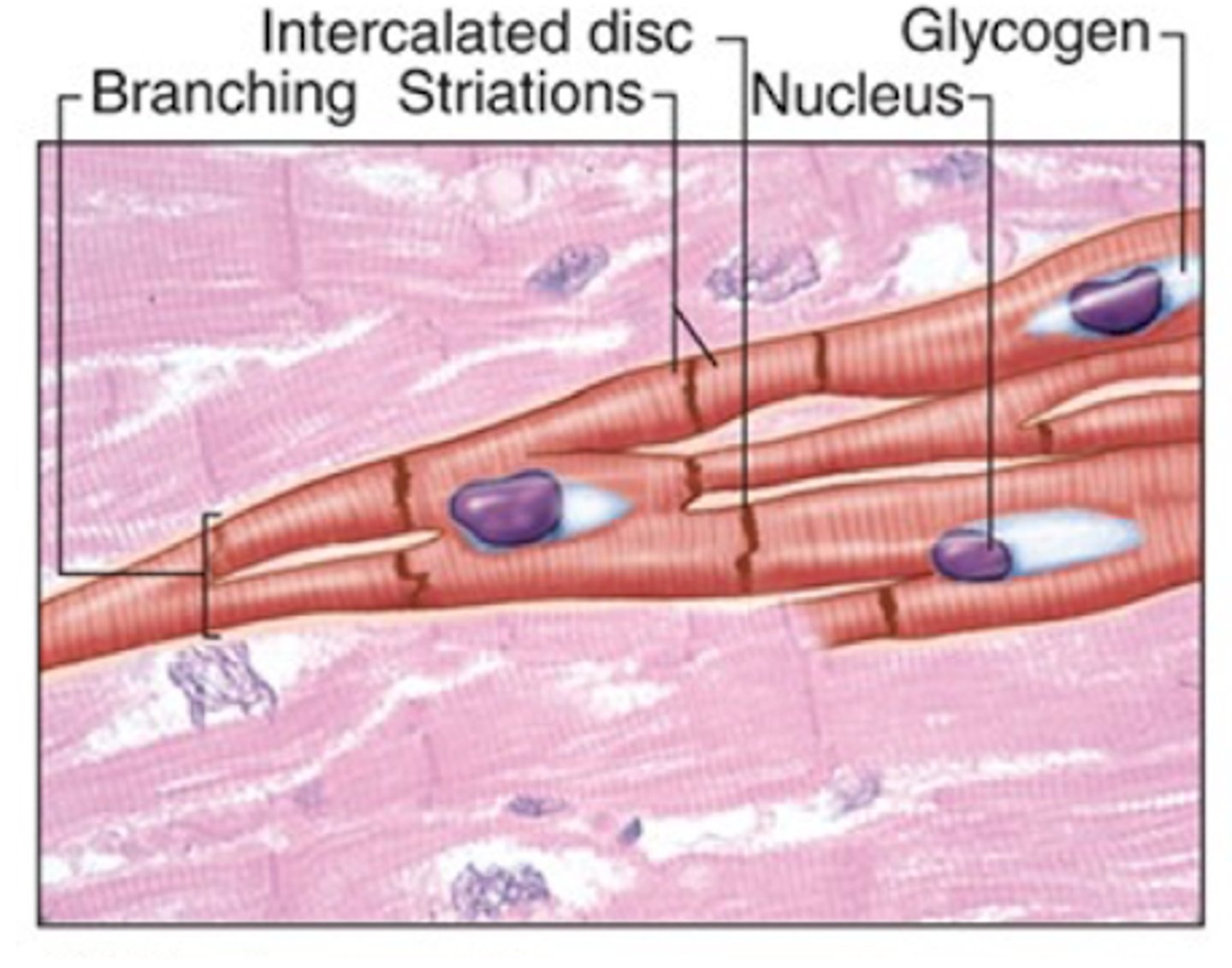
Vigorous, rhythmic, and involuntary
Describe the contractions of the cardiac muscle tissue
Spindle-shaped (fusiform) cells, involuntary, no striations.
What are the features of smooth muscle tissue?
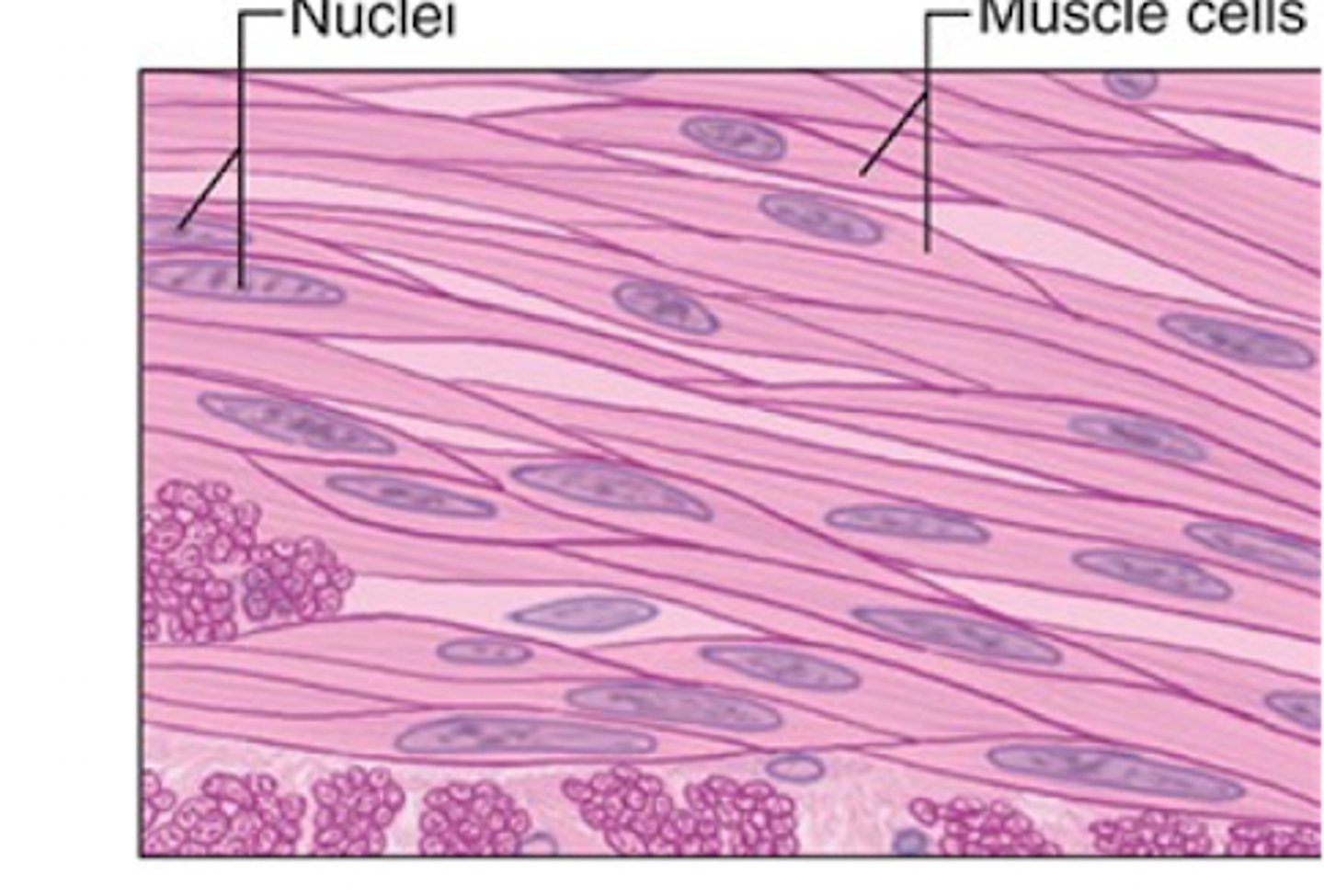
SM contractions are slow and involuntary
Are smooth muscle contractions fast or slow?
Wall of hollow, internal organs (except the heart)
Smooth muscle tissue lines the walls of what
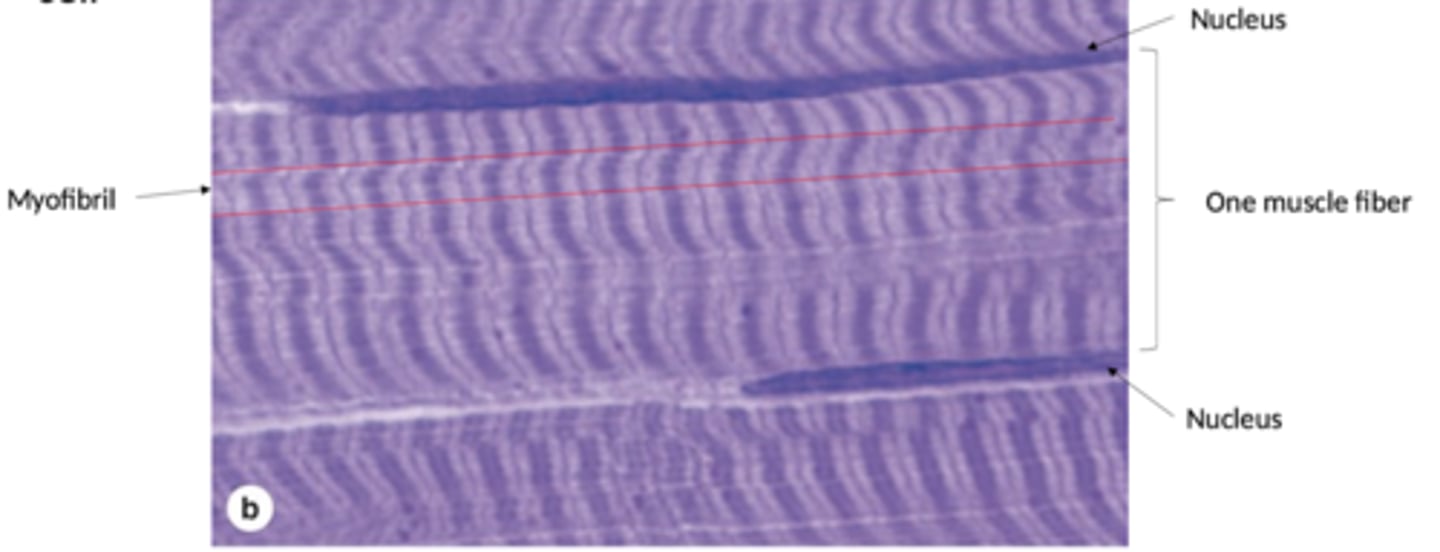
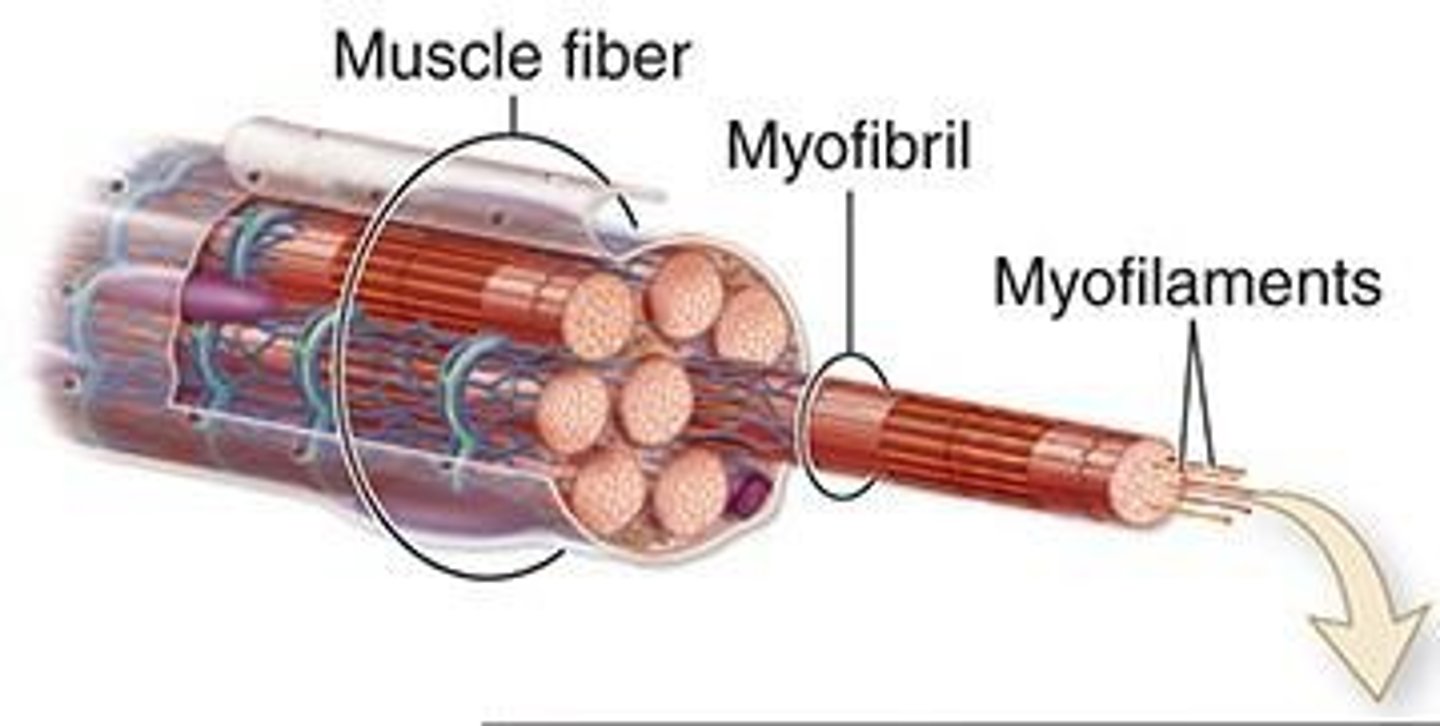
muscle fiber
muscle cell =
sarcolemma
cytoplasmic membrane =
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm =
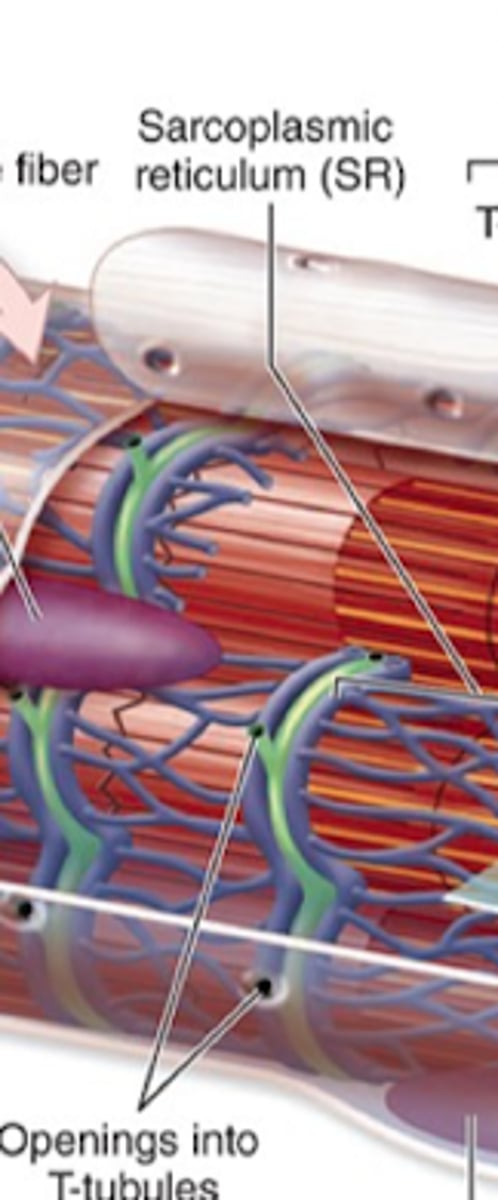
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER =
Surrounds myofibrils and creates proteins for sequestration
Location and function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
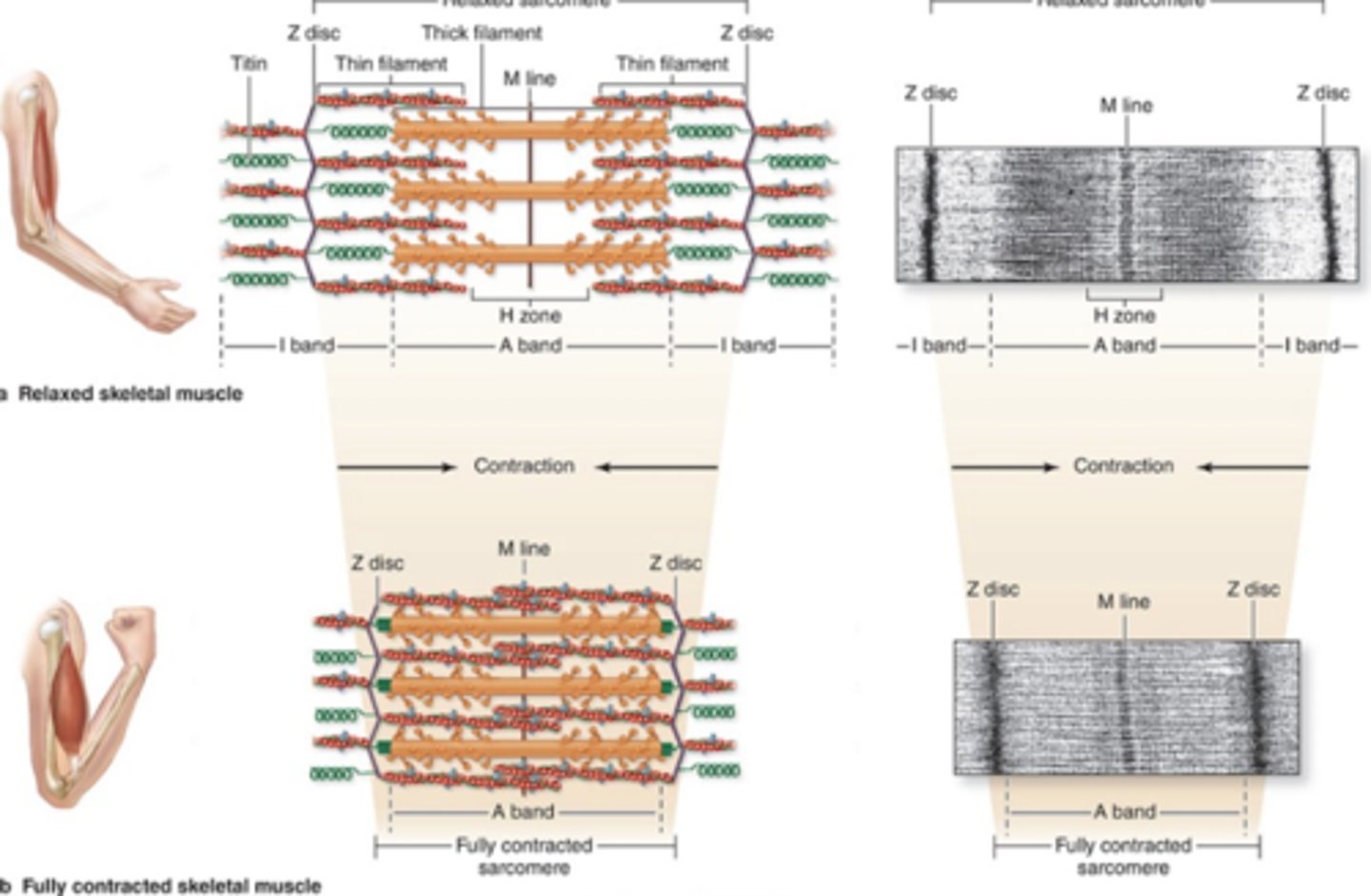
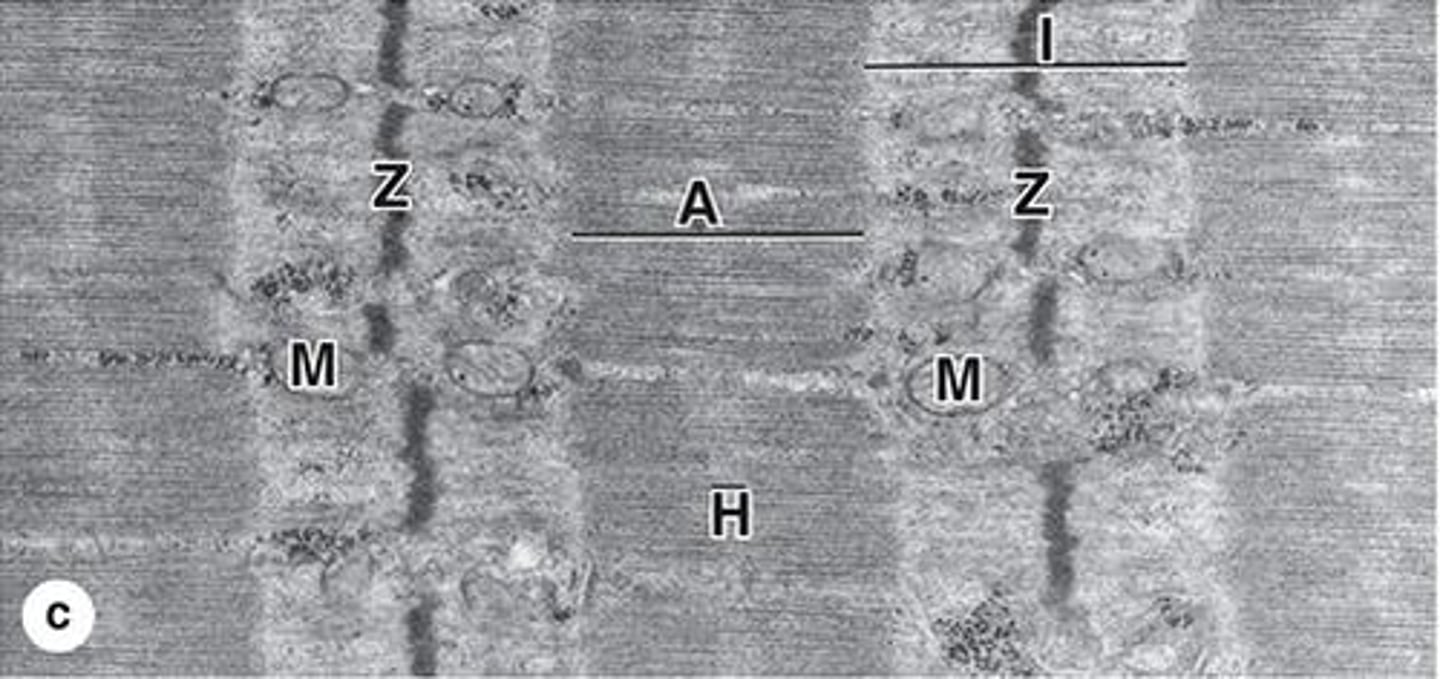
Sarcomere
Functional unit of contraction between Z discs.
Myoblasts -> form myotubes -> muscle fiber
How does skeletal muscle develop?
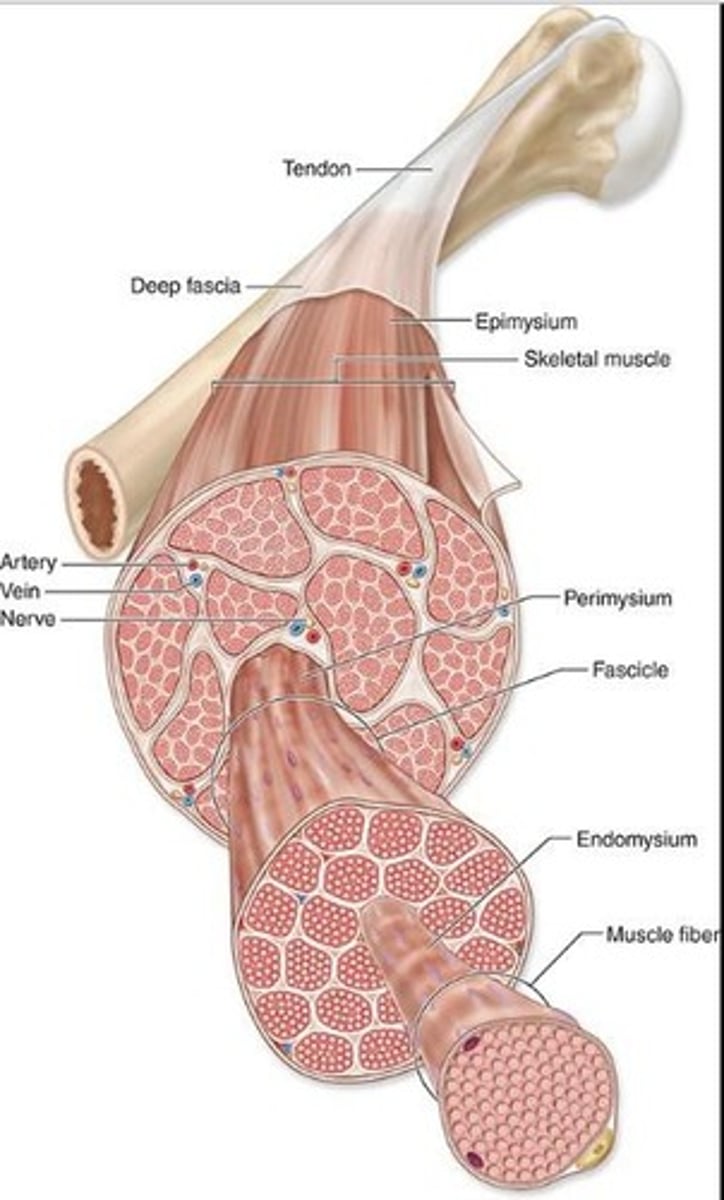
Epimysium
What is the dense connective tissue surrounding the ENTIRE muscle?
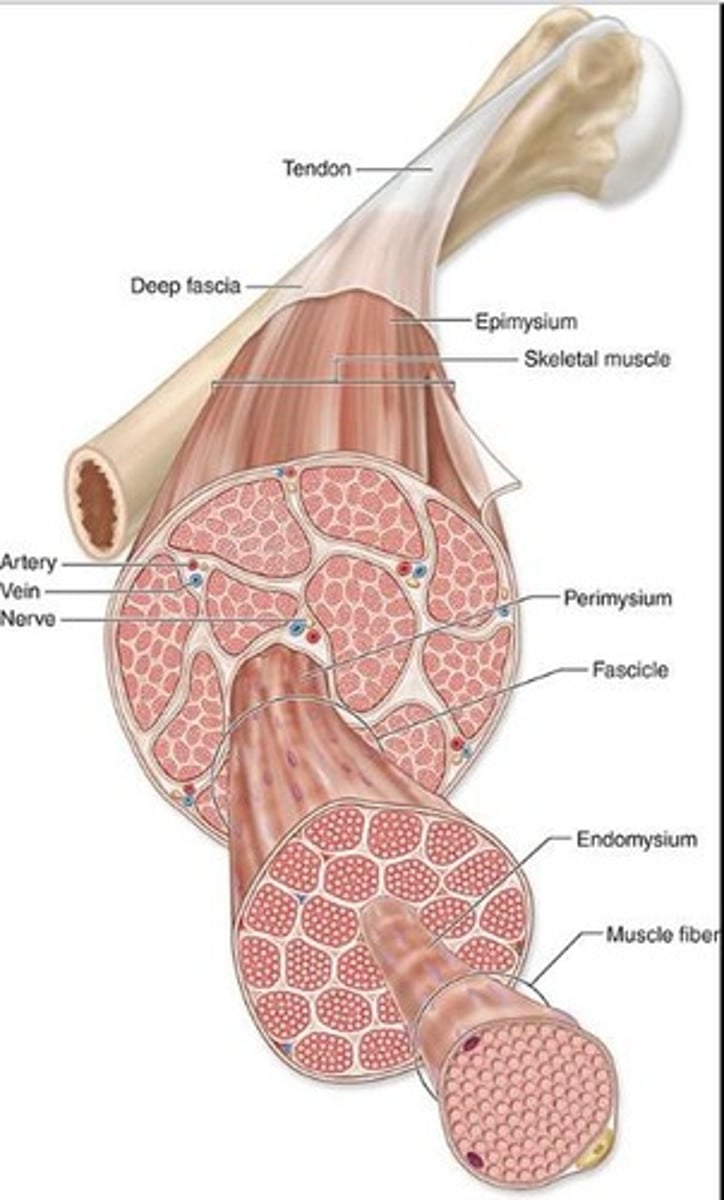
Perimysium
What is the thin tissue surrounding muscle fascicles.
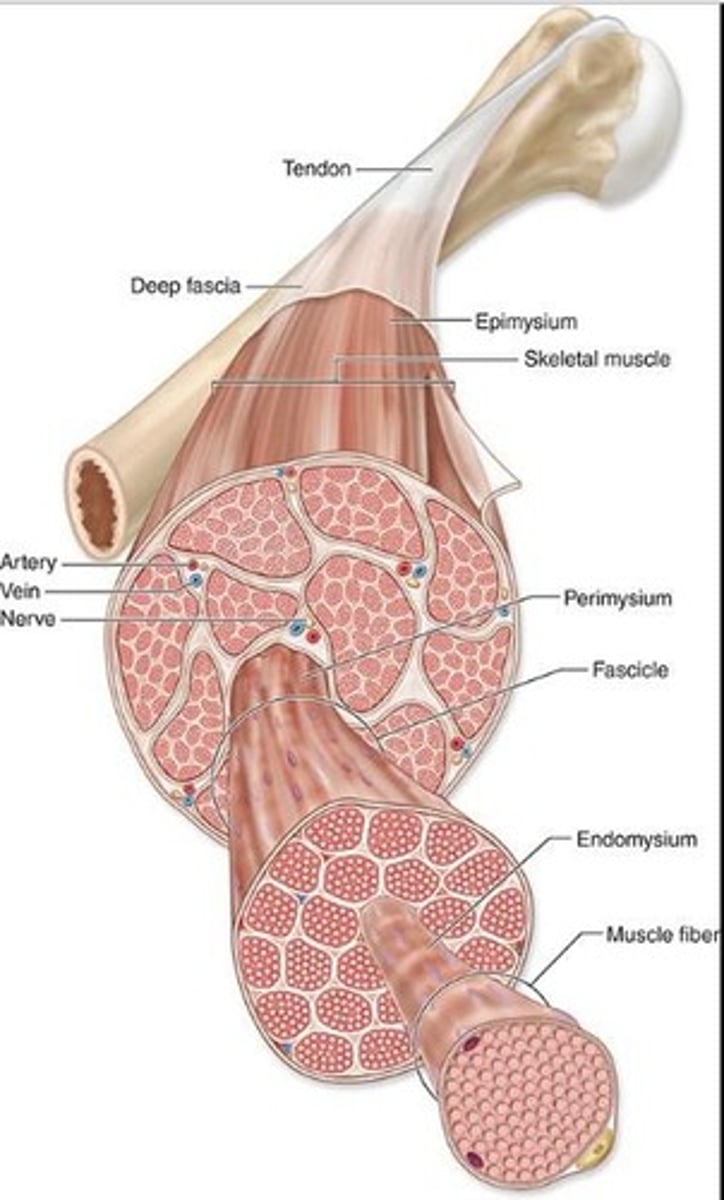
Endomysium
What are the reticular fibers and fibroblasts that surround INDIVIDUAL muscle fibers?
P = perimysium
En = endomysium
E = epimysium
Identify the parts of the skeletal muscle
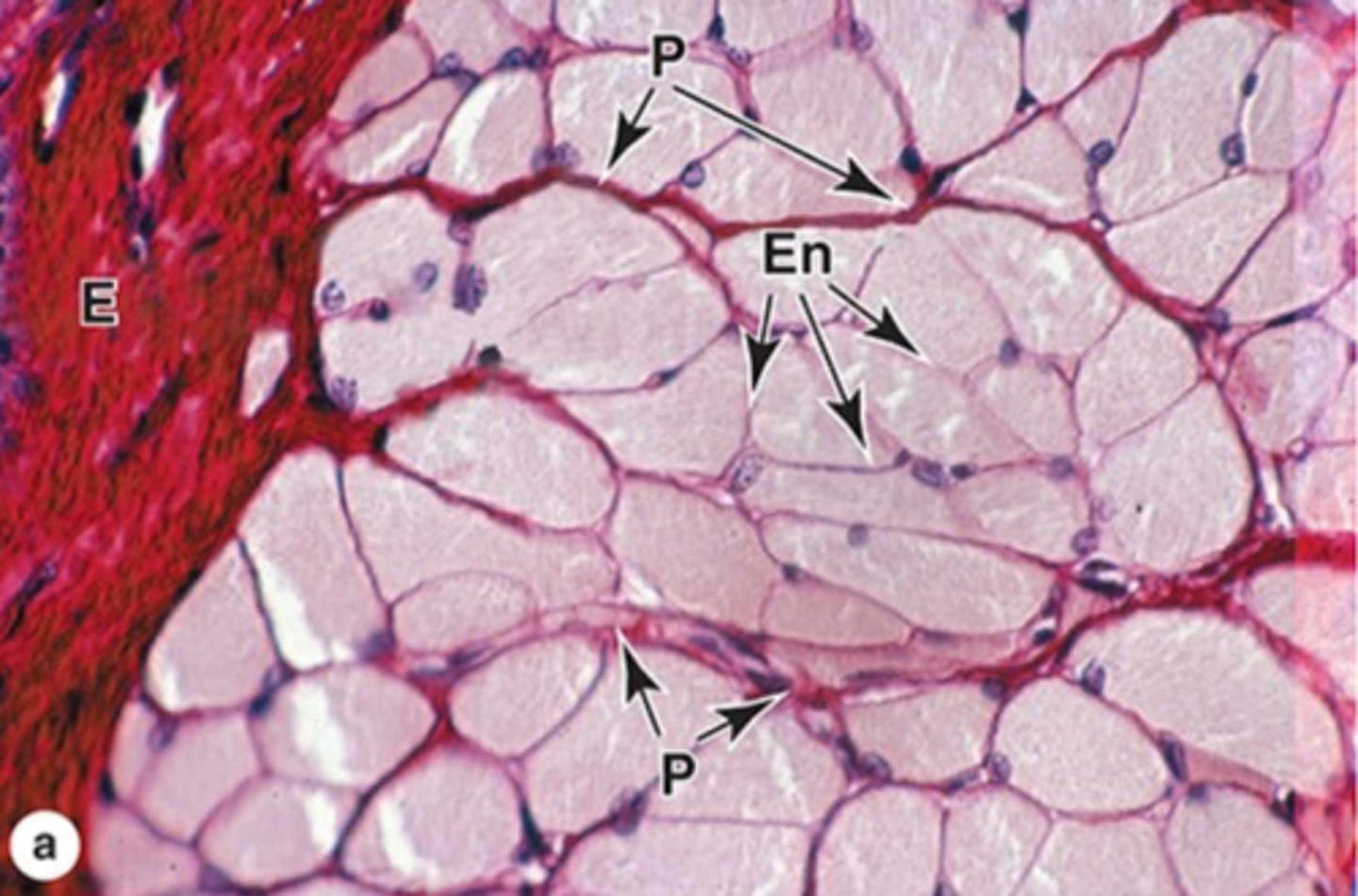
It carries a rich vascular network that surrounds each muscle fiber
What's an important trait of the endomysium?
Striations
Alternating dark and light bands
Myofirbrils run parallel to long axis of the cell. Consists of repetitive sarcomeres.
How are myofibrils organized?
Mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum
What cell structures are found in between myofibrils?
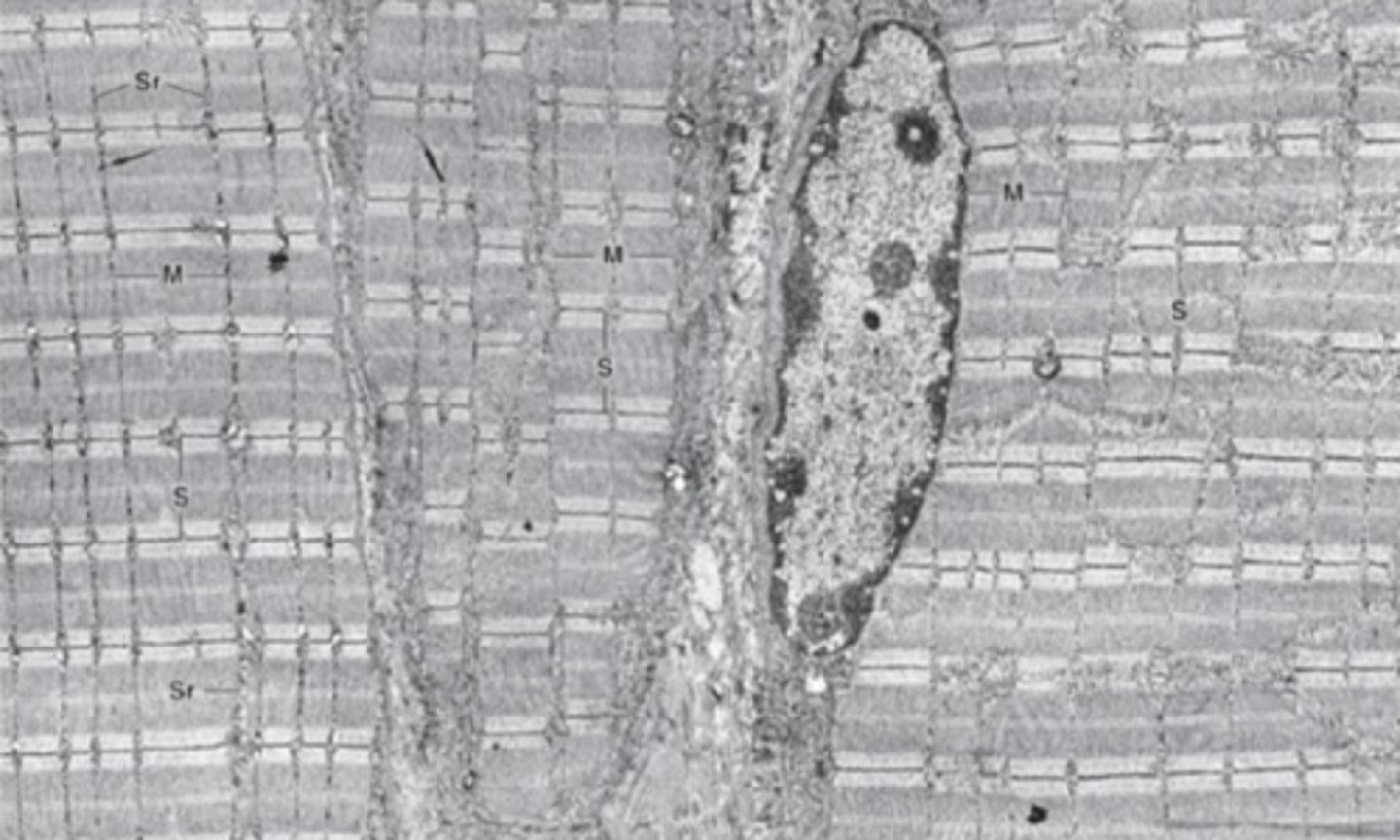
from z disc to z disc
What are the boundaries of one sarcomere?
A bands (anisotropic)
Dark bands in muscle fibers containing myosin.
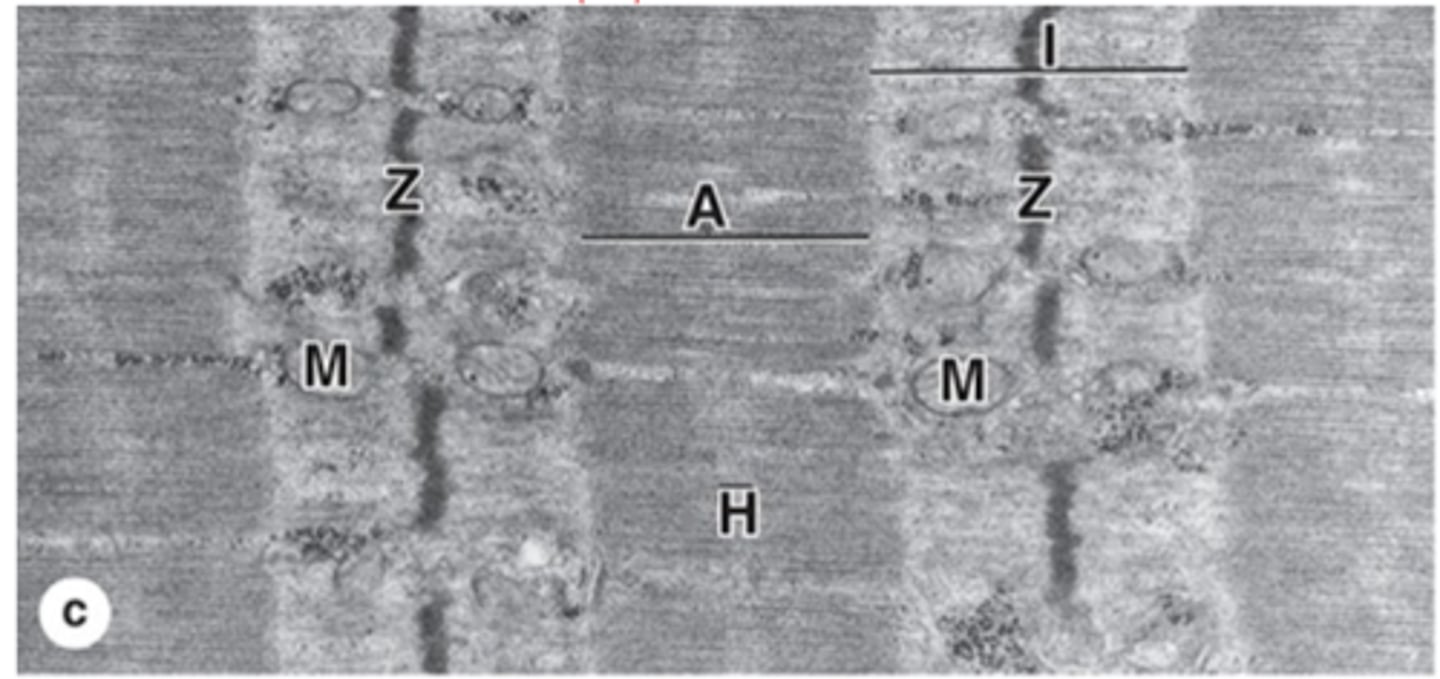
I bands (isotropic)
Light bands in muscle fibers containing actin.
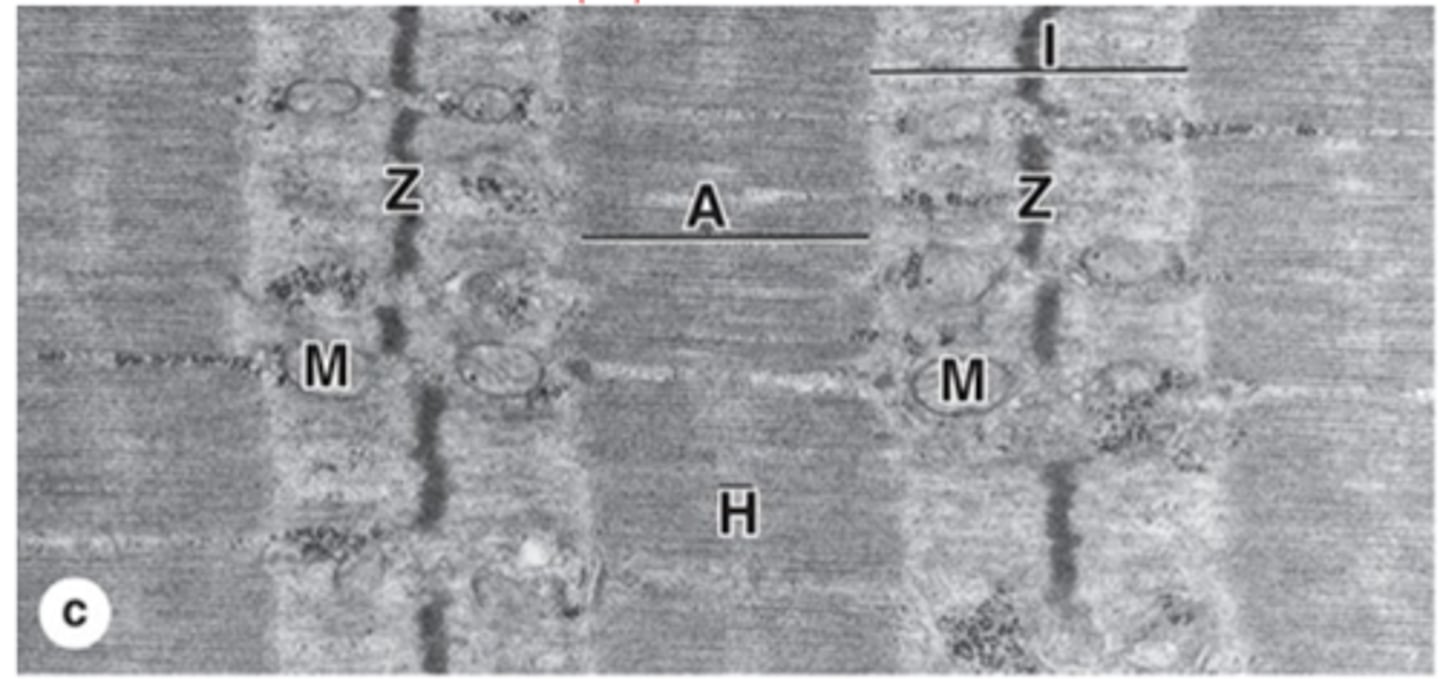
Z disc
What is the dissection of the I band?
H zone
Central lighter zone in A band, no actin.
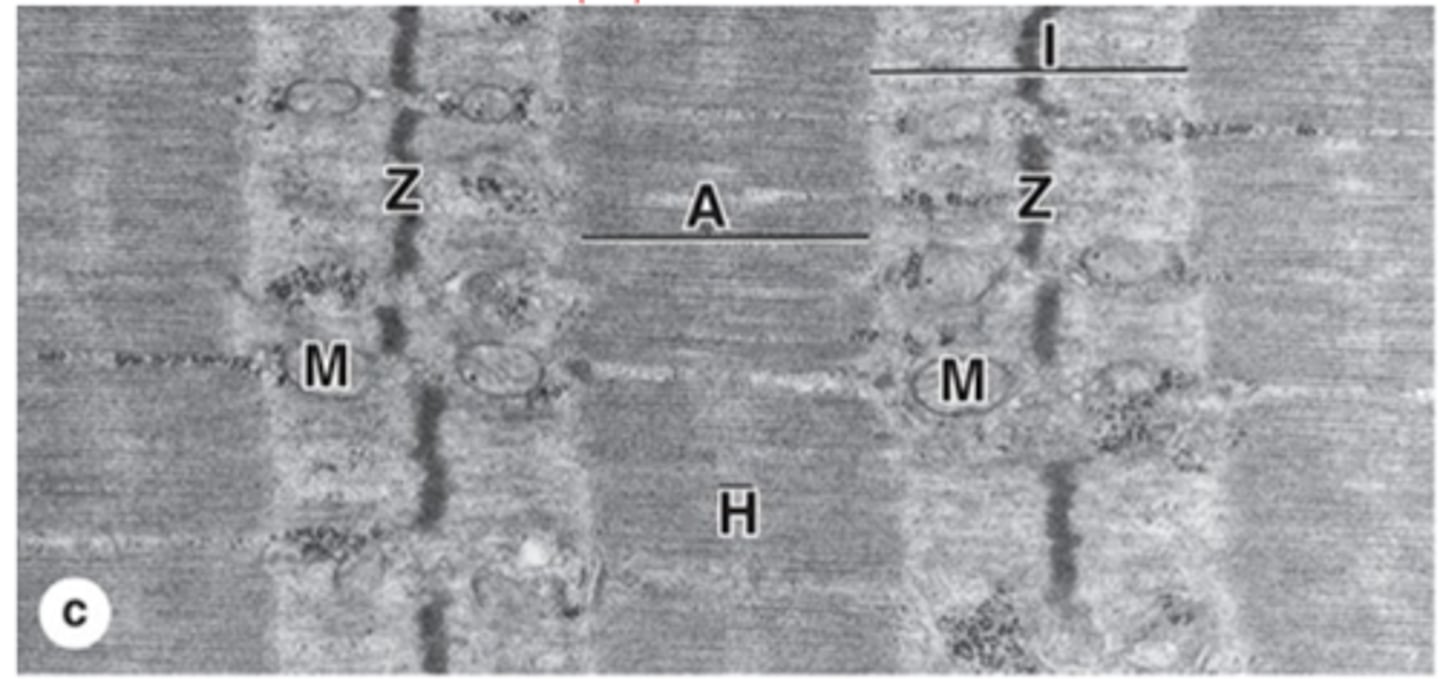
Sarcomere
What is the functional unit of contractile apparatus between two Z discs?
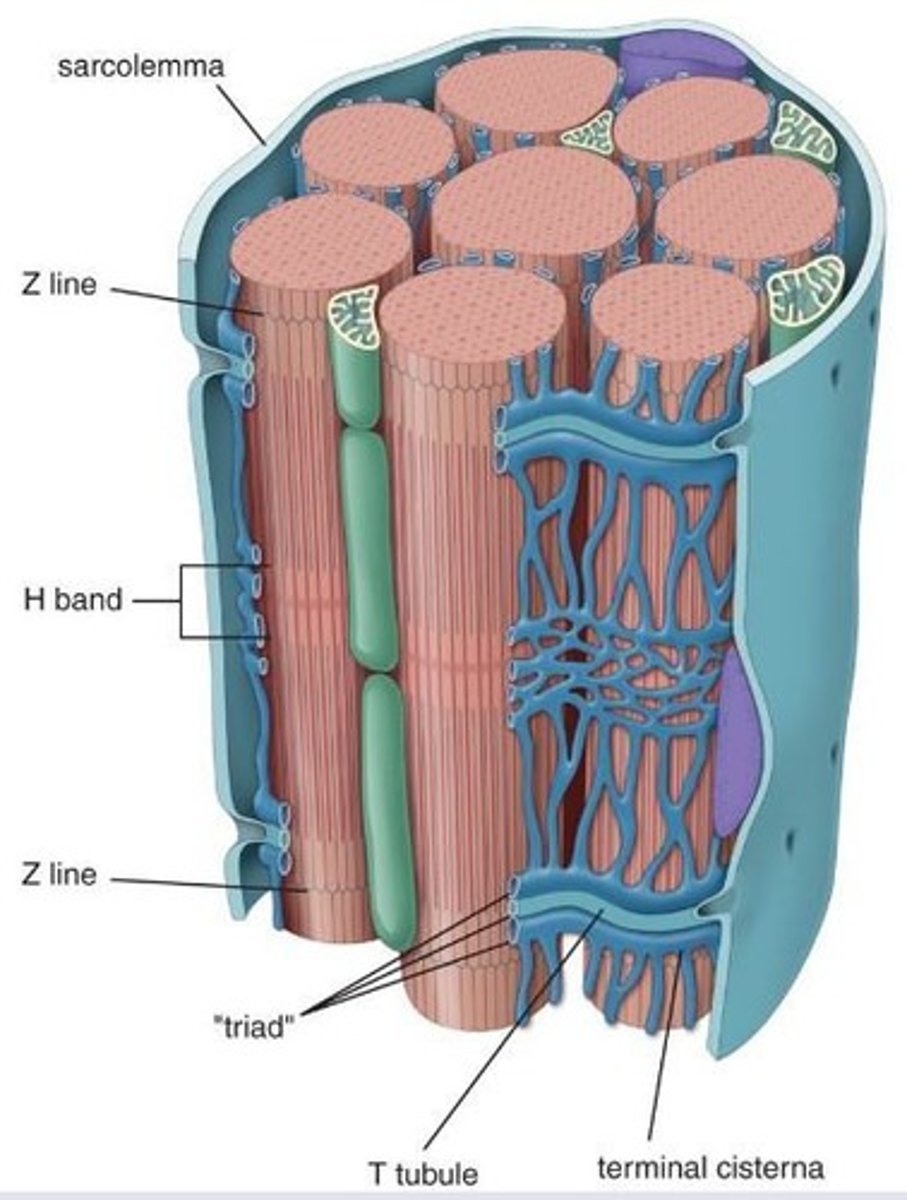
T tubules (transverse tubules)
Extensions of that sarcolemma (plasma membrane) that penetrate muscle fibers.
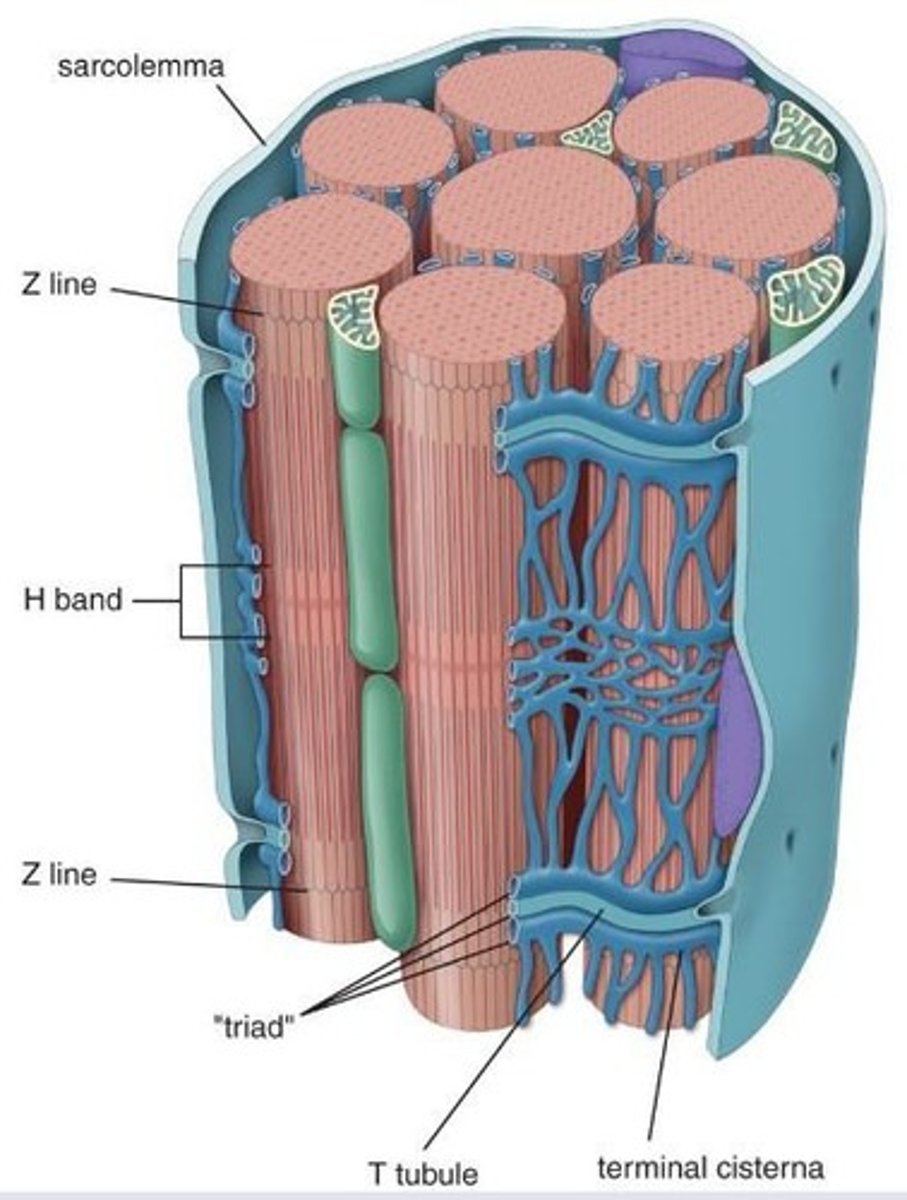
T tubules encircle each myofibril close A- and I- band boundaries of sarcomeres
What structure is surrounded by t-tubules?
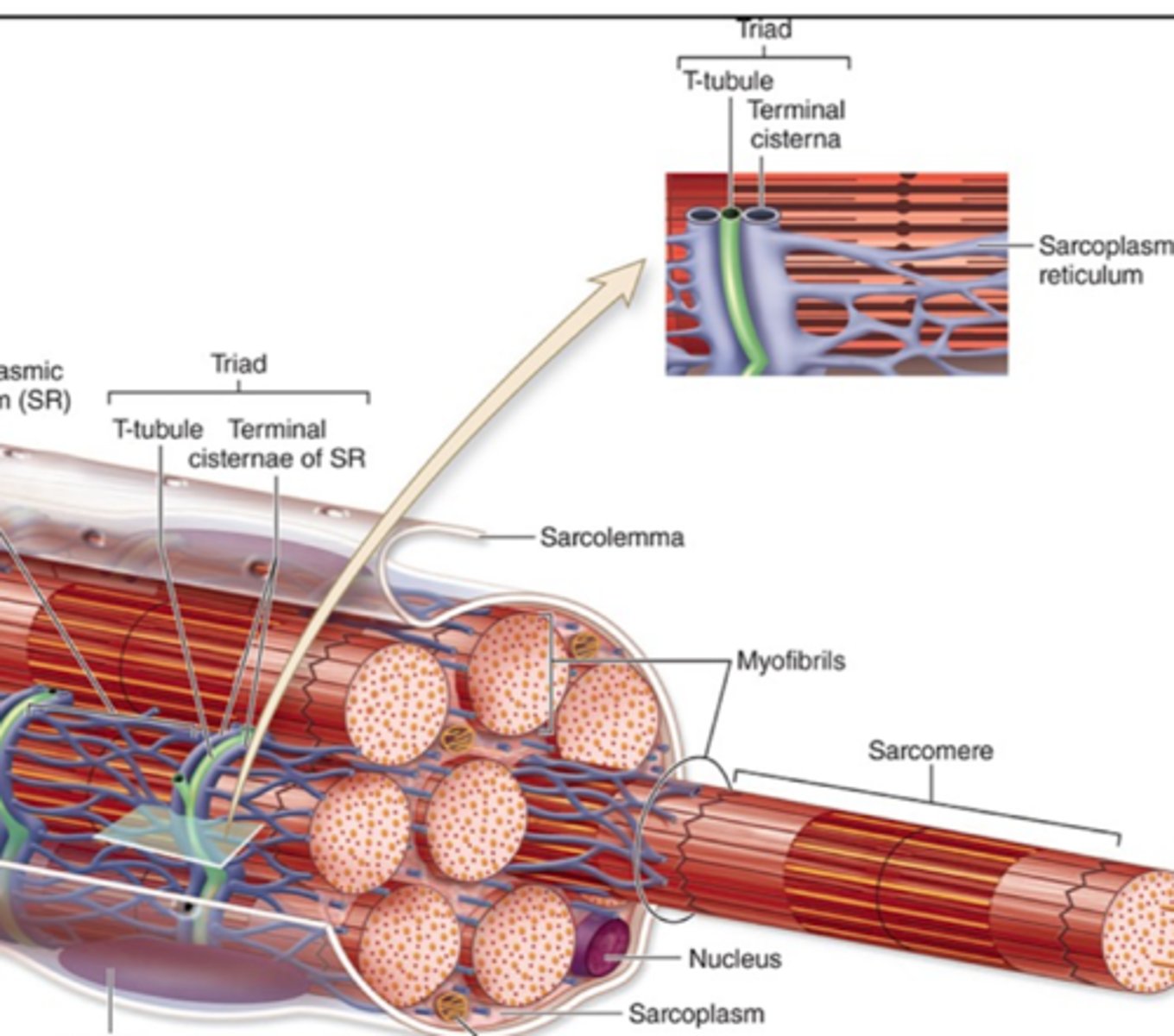
Triad
One T-tubule and two terminal cisternae.
Depolarization triggers Ca2+ release by the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm
How does depolarization of t-tubules affect sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Initiates contraction of sarcomeres
Presences of Ca2+ in the sarcoplasm causes what?
Thick and thin (myosin and actin)
What two myofilaments make up myofibrils?
Two identical heavy chains, two pairs of light chains
What do thick filaments (myosin) consist of?
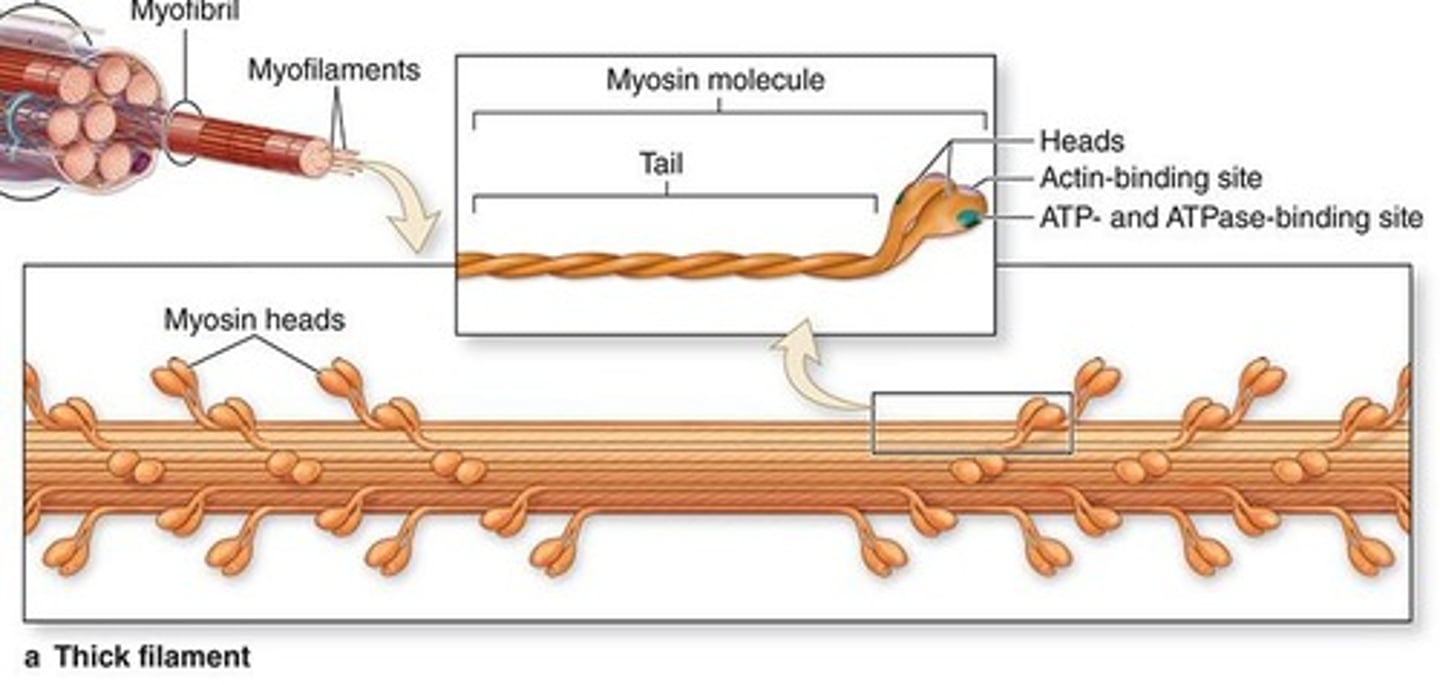
They are twisted as myosin tails b/c they have thin, rod-like motor proteins.
How do the heavy chains of myosin function?
End in globular projections, formed at the head of each heavy chain.
Describe the structure of the 2 pairs of light chains.
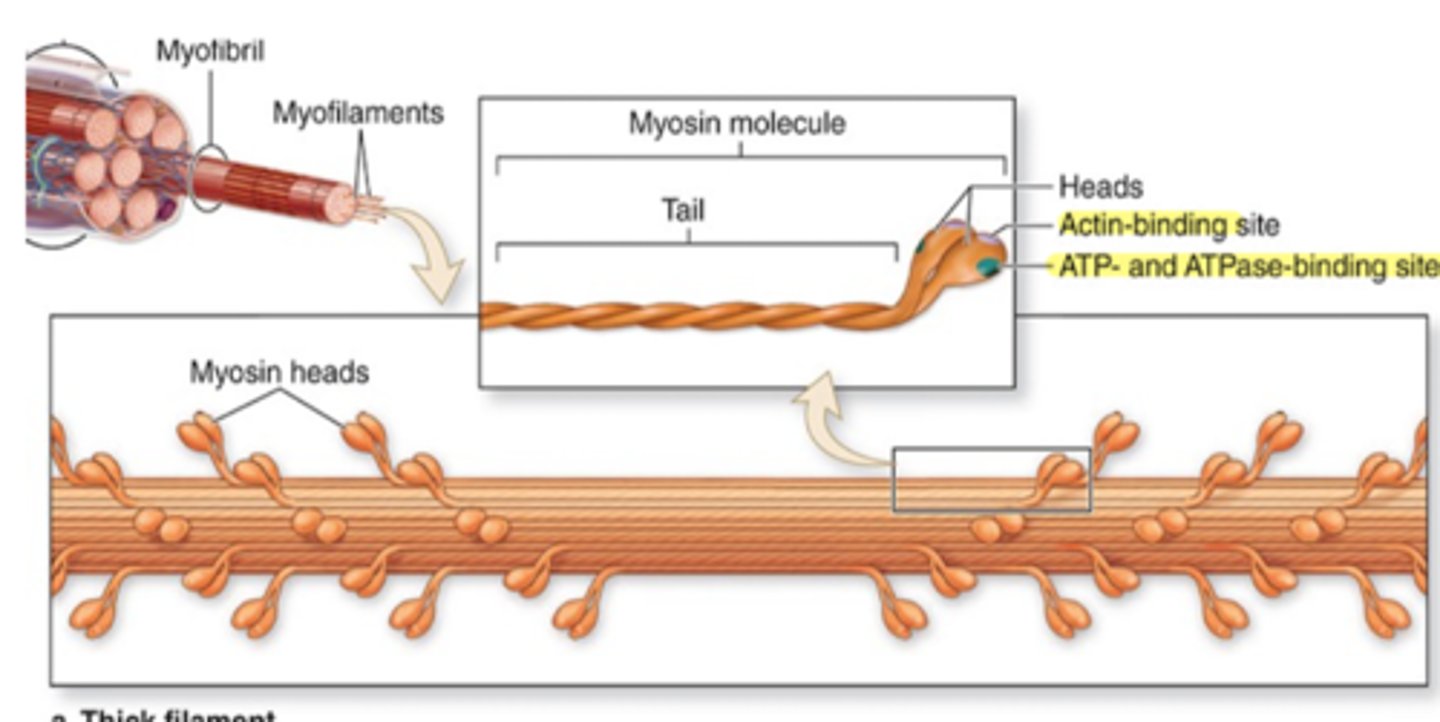
Bind to actin (forming cross-bridges) and ATP (actomyosin ATPase activity).
What do the light chains bind?
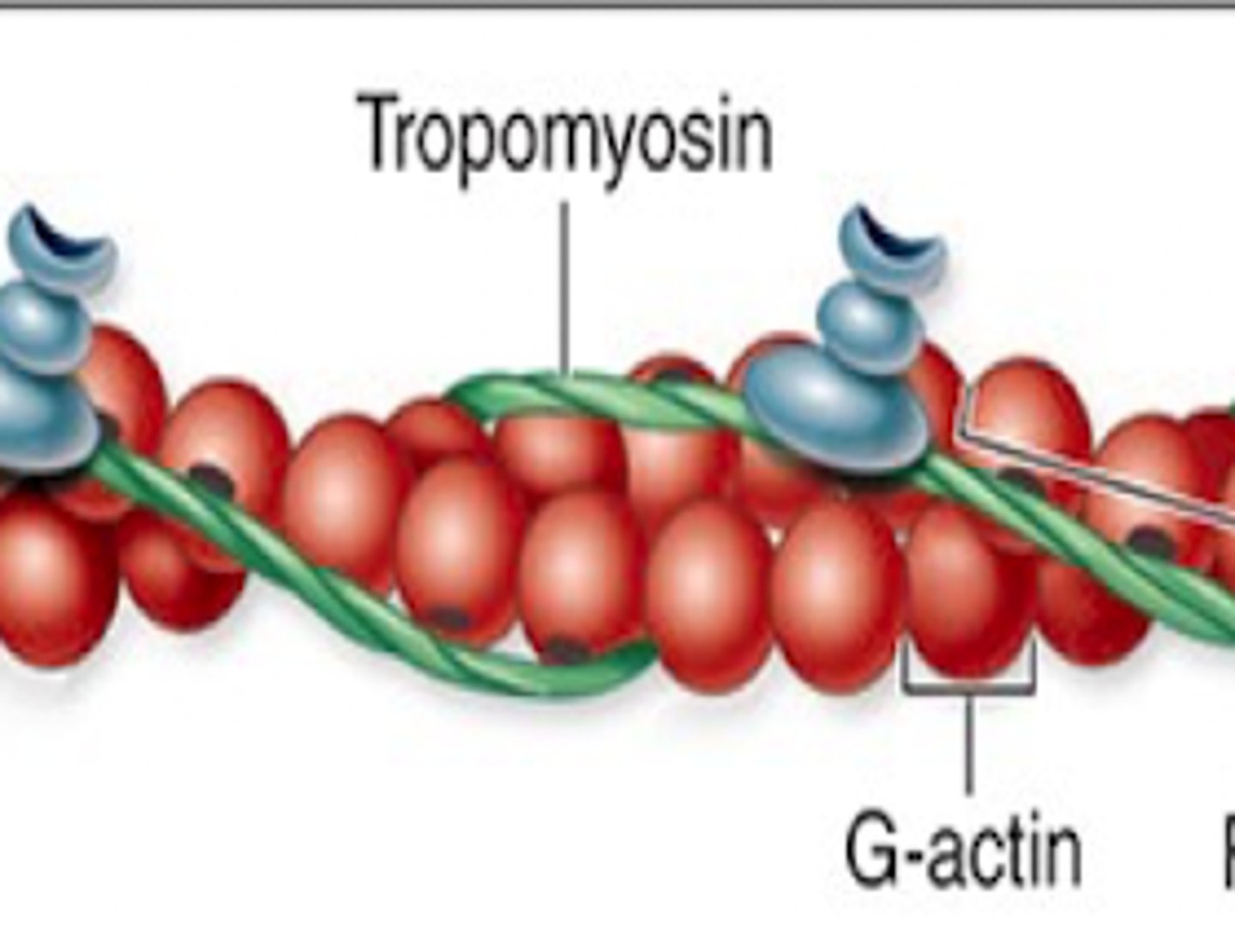
Thin filaments: F-actin
This type of filament is composed of monomers of G-actin and are located between thick filaments
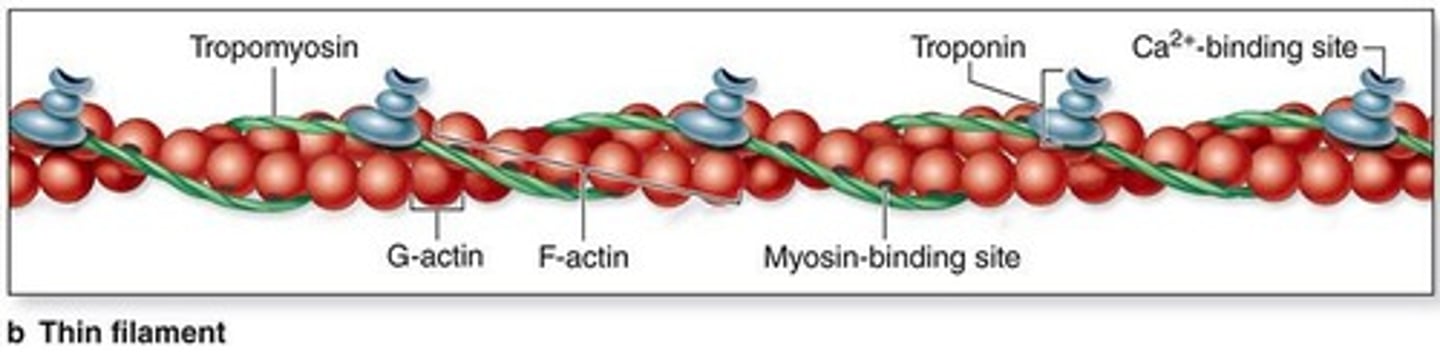
Each monomer has a binding site for myosin
Each monomer of thin filaments contain a what?
Tropomysoin and Troponin
What two regulary proteins are associated with thin filaments?
Tropomyosin
Protein that blocks actin binding sites. Located in the grove of actin strands.
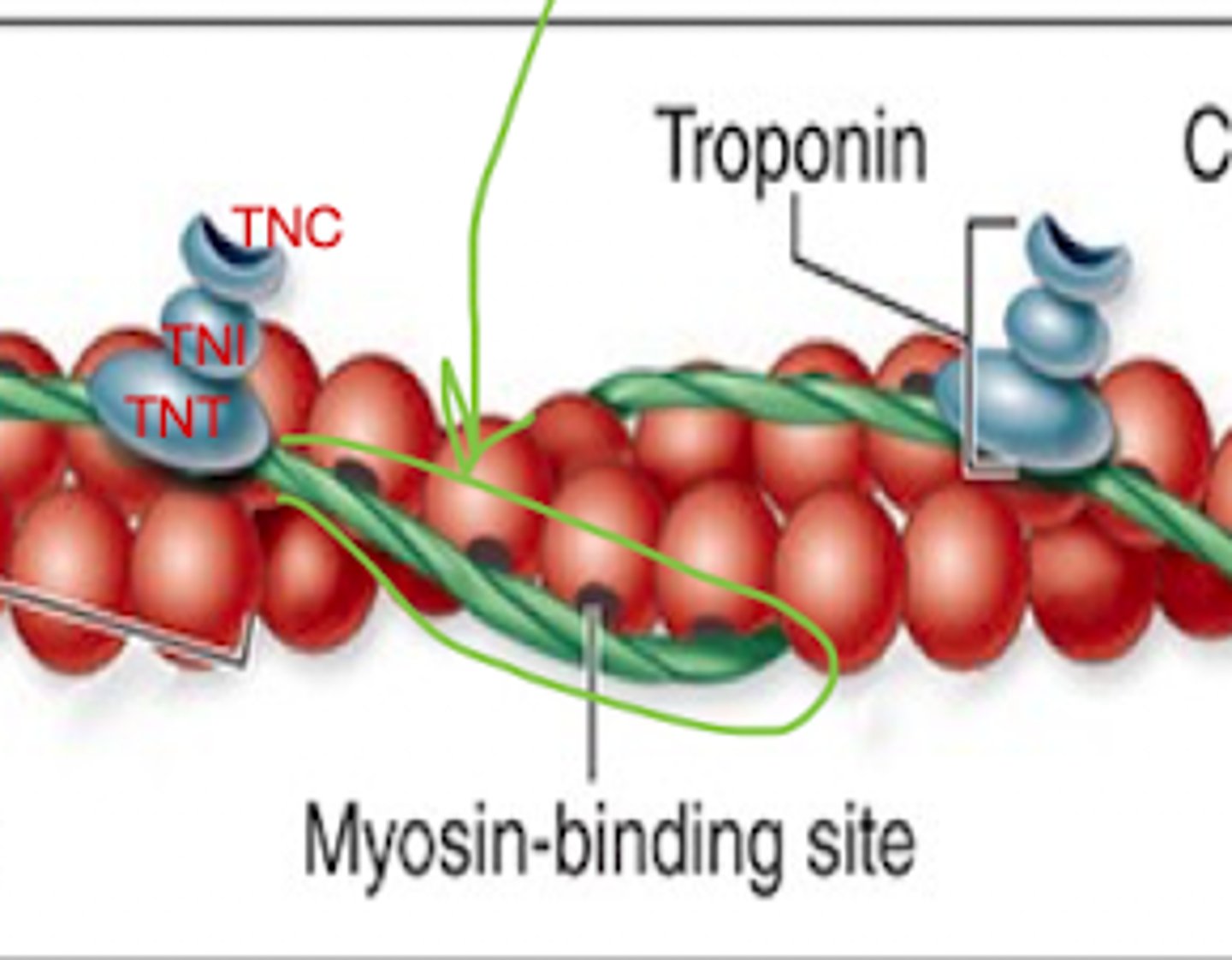
TnT
TnC
TnI
What are the 3 subunits that make up troponin?
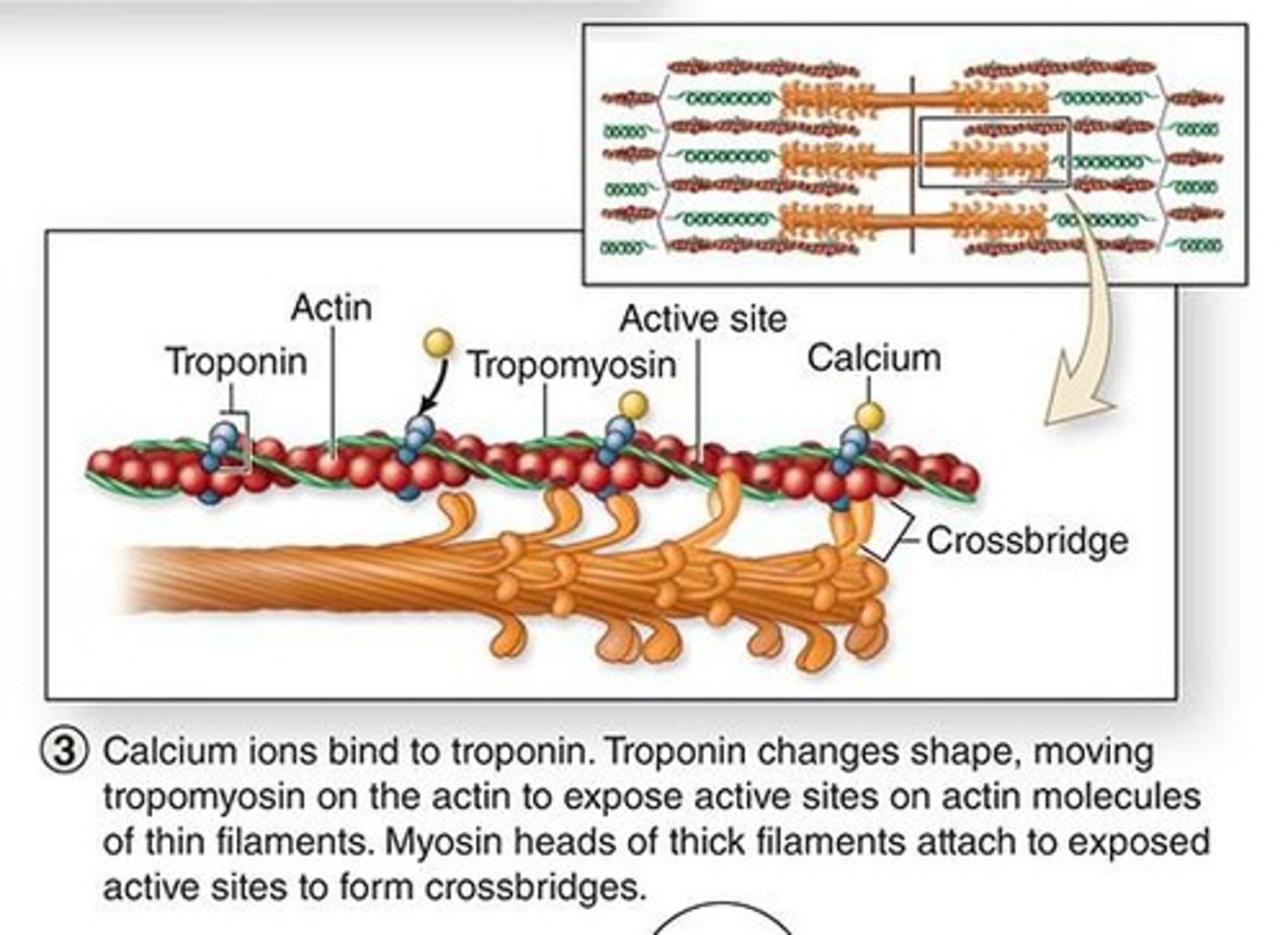
TnT: attaches to tropomyosin
TnC: binds Ca2+
TnI: regulates actin-myosin interaction
List the functions of the 3 subunits
Causes a change in confirmation of troponin
Which causes a movement of tropomyosin from the site
Exposing the active site of globular actin so myosin can bind
Describe what happens when Ca binds to a subunt:
Thin filaments not overlapping thick filaments, contains Titin
Describe the structure of the I band
Titin anchors myosin to Z disc
Titin is the largest protein of the body and has what function in the I band?
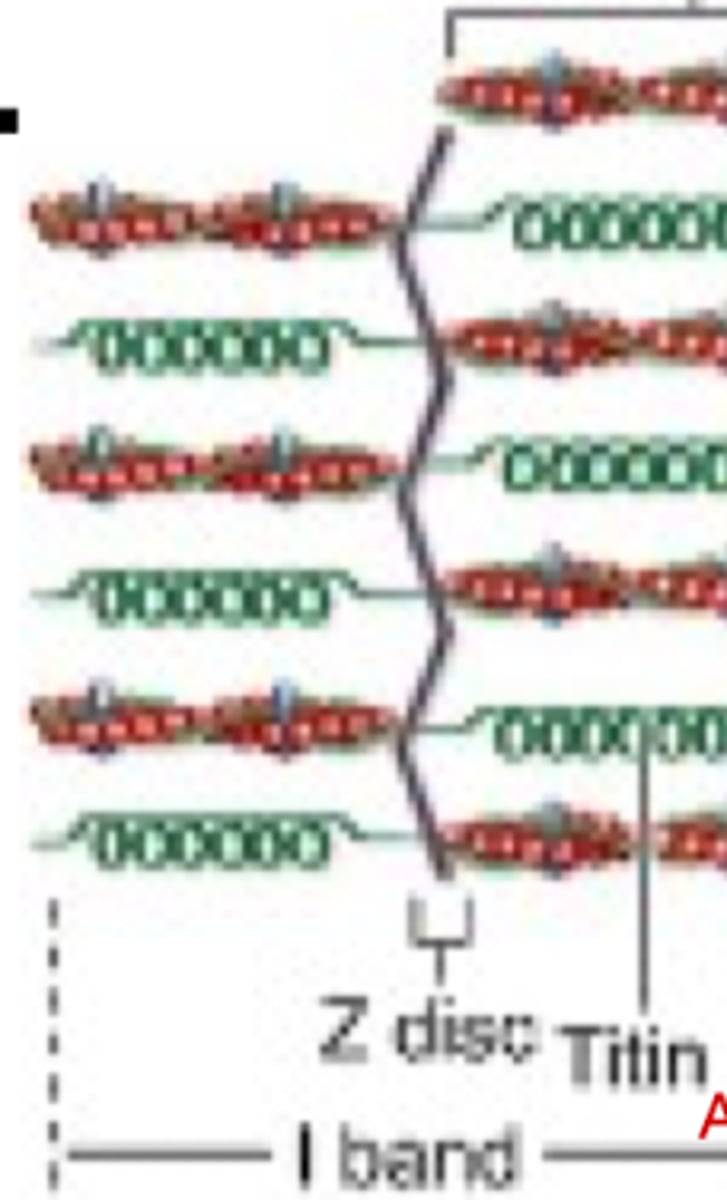
alpha actin
What protein anchors actin filaments to Z discs?
Thick filaments that have overlapping portion of thin filaments and an H zone in the center
How is the A band organized?
NO, the H zone has no thin filaments; it is just the lighter central zone
Does the H zone contain thn filamets?
the -M line-—containing myomesin and creatine kinase
What bisects the A band?
Actomyosin ATPase
Enzymatic activity of myosin during contraction.
ACh is released from the synaptic lobe into the synaptic cleft. 2 molecules of Ach binds to the motor end plate.
During the 1st step of a contraction, describe the path of ACh?
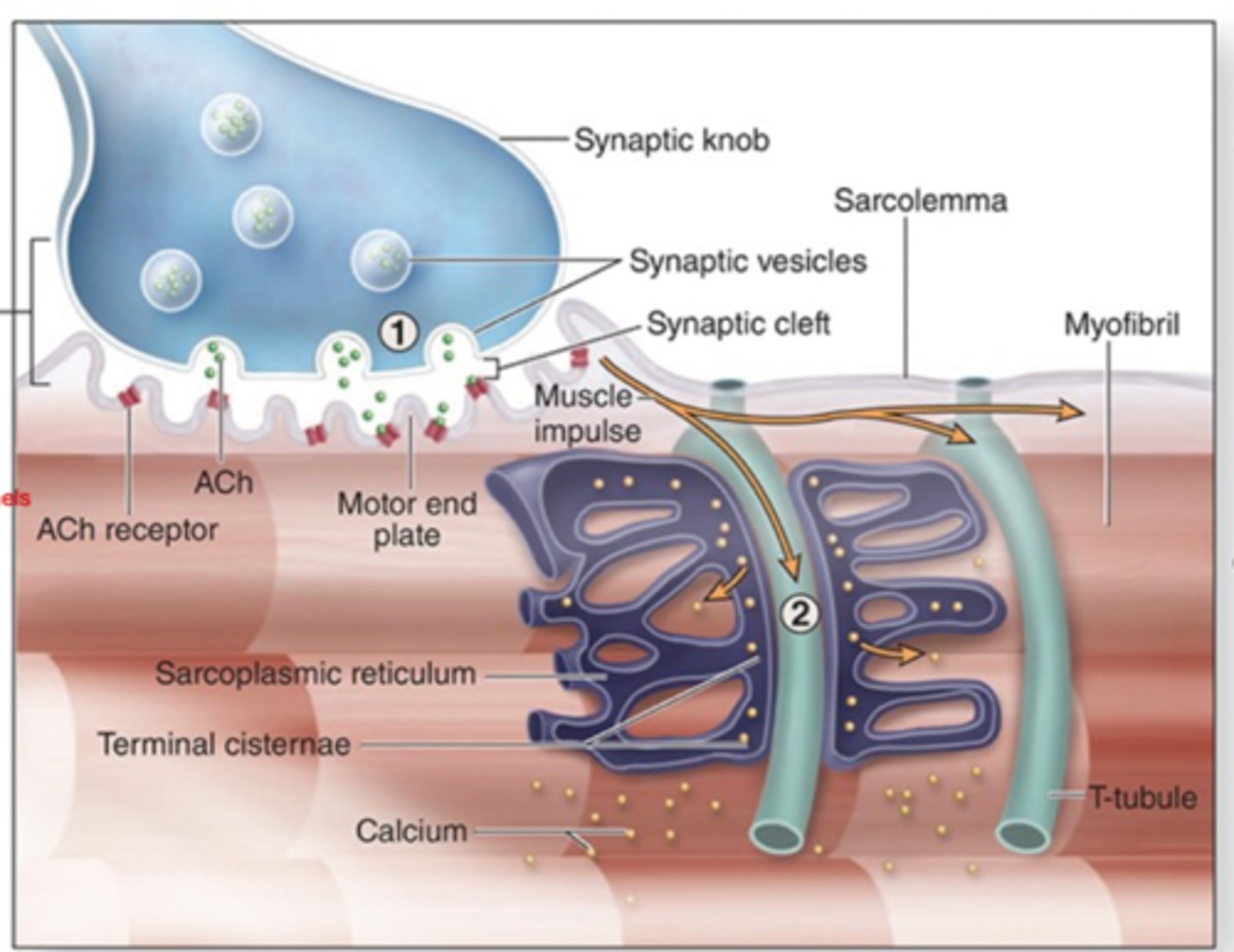
Binding of AcH initiates a muscle impulse in the sarcolemma of the muscle fiber.
What gets initiated when ACh binds at the motor end plate?
in the neuromuscular junction
the motor end plate is found where?
Muscle impulse spreads quickly from the sarcolemma along T tubules.
How does the muscle impulse spread after the binding of ACh? (step 2)
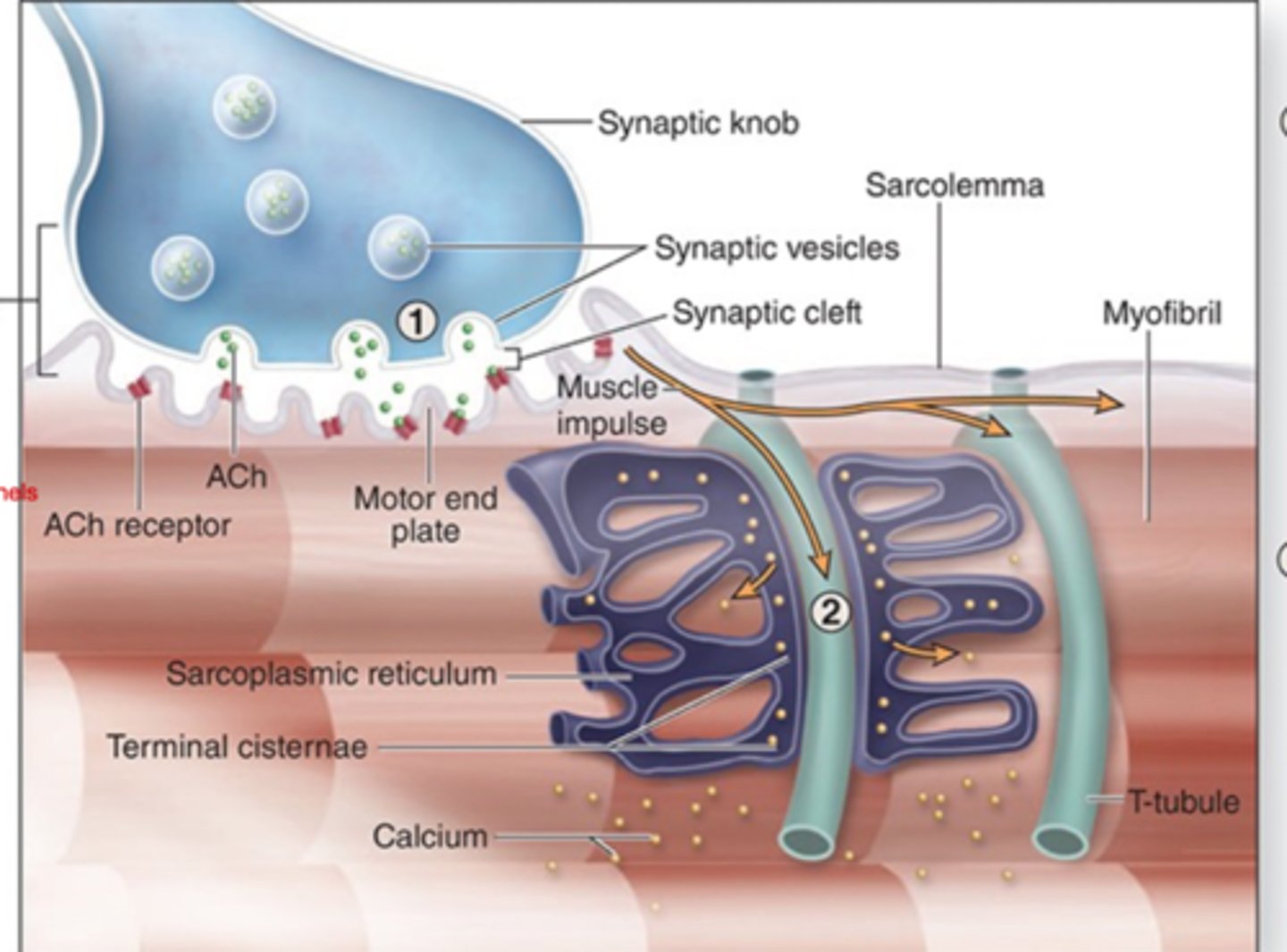
calcium ions are released from terminal cisternae into the sarcoplasm.
During the spreading of the muscle impulse, calcium ions are released from?
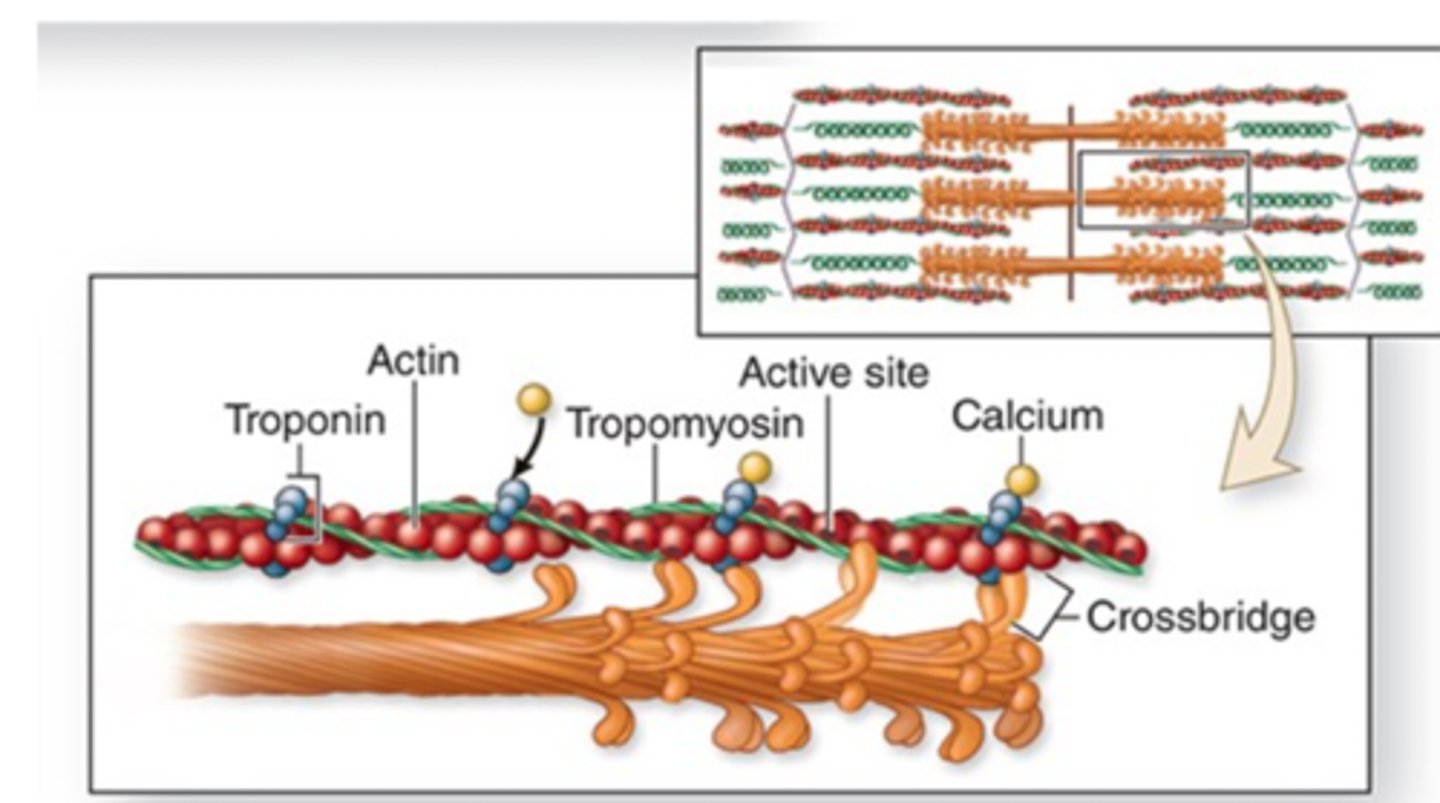
Calcium ions bind to troponin.
where do calcium ions bind after being released into the sarcoplasm? (step 3)
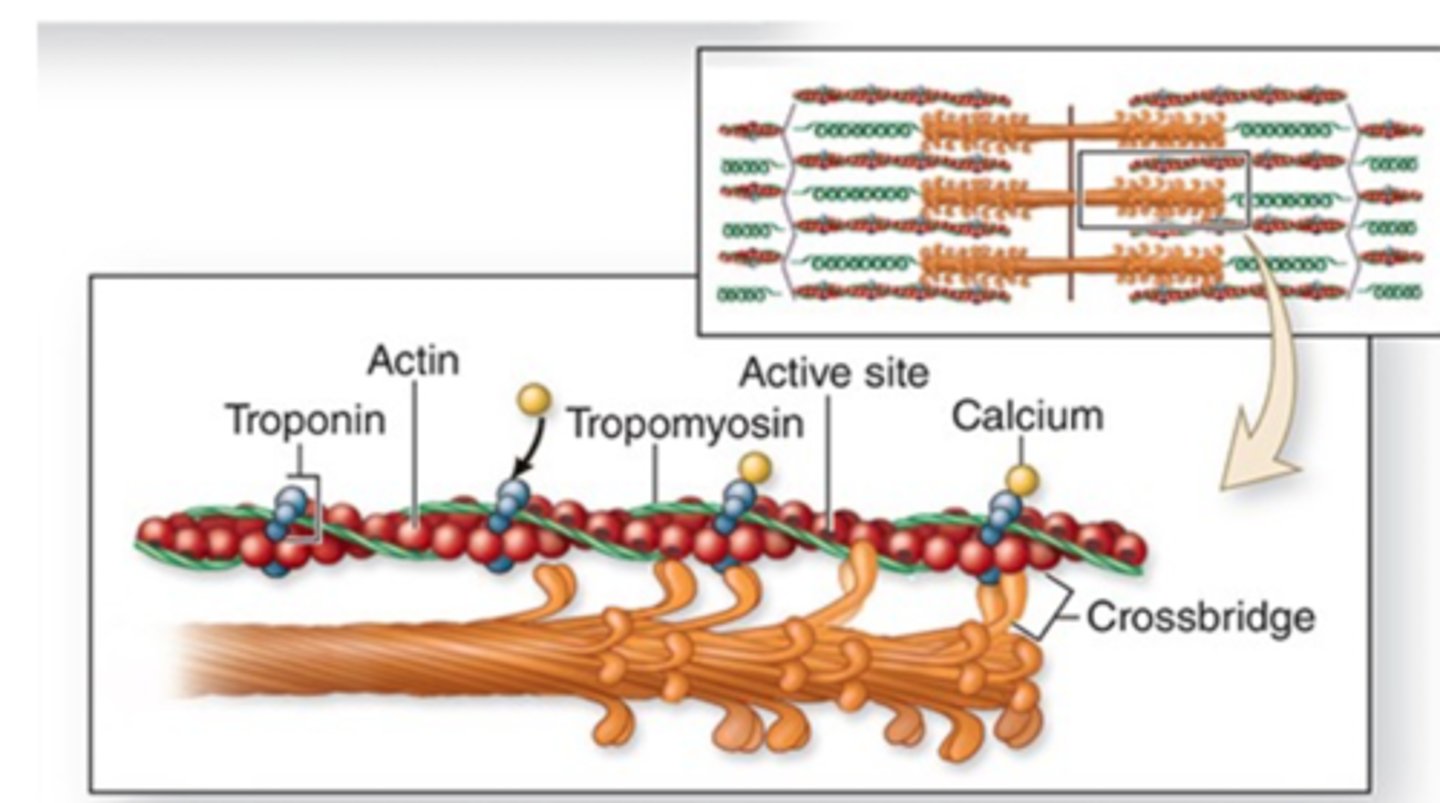
troponin will change shape and ultimately the active site on actin is exposed (thin filaments)
Describe the conformational change that calcium ions cause
myosin heads of thick filaments attach to form crossbridges
when the active site of actin is exposed, what attaches to it? (step 3)
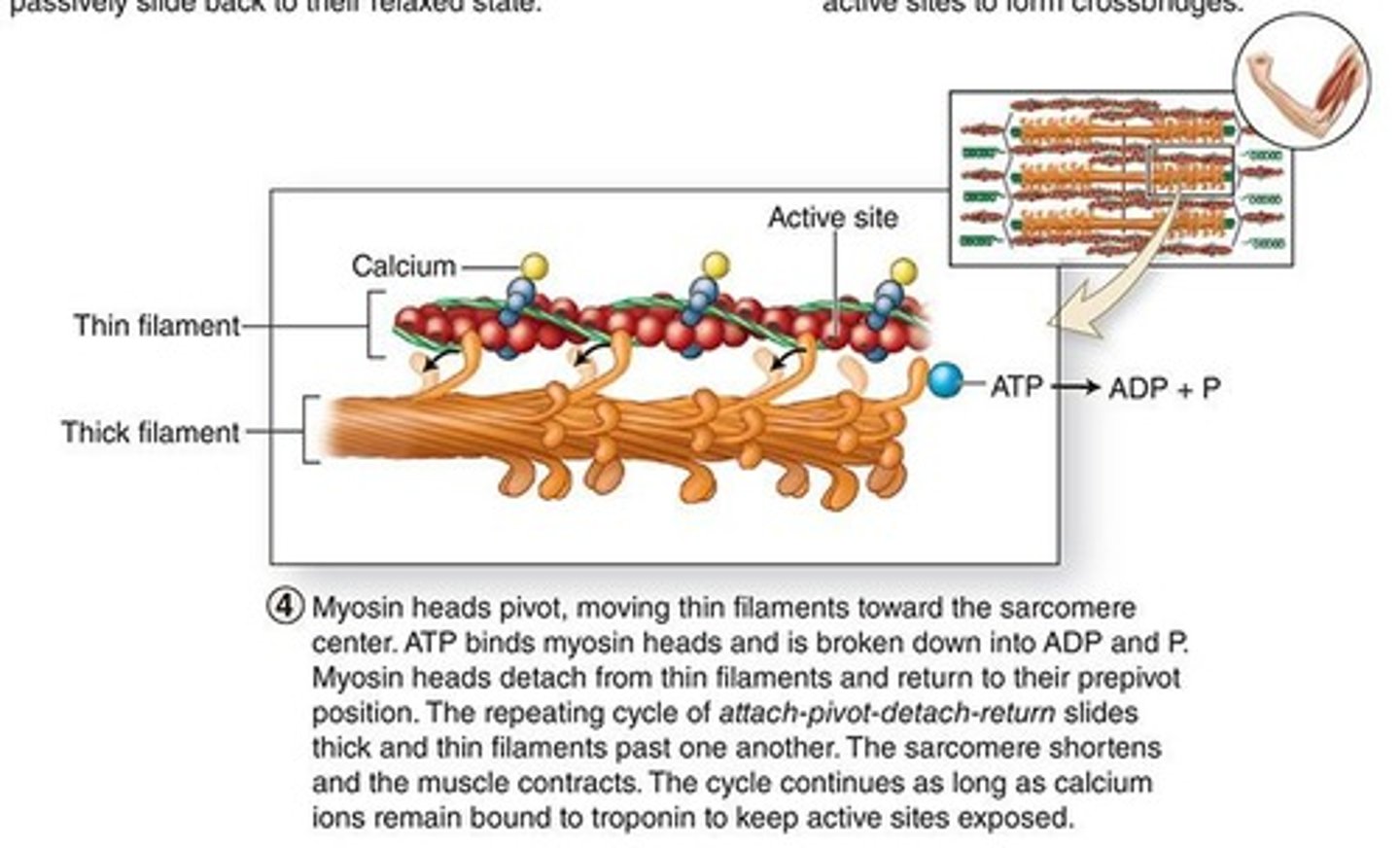
the repeating cycle of attatch-pivot-detach-return slides thick and thn filaments past each other
How do myosin heads cause the shortening of sarcomeres? (step 4)
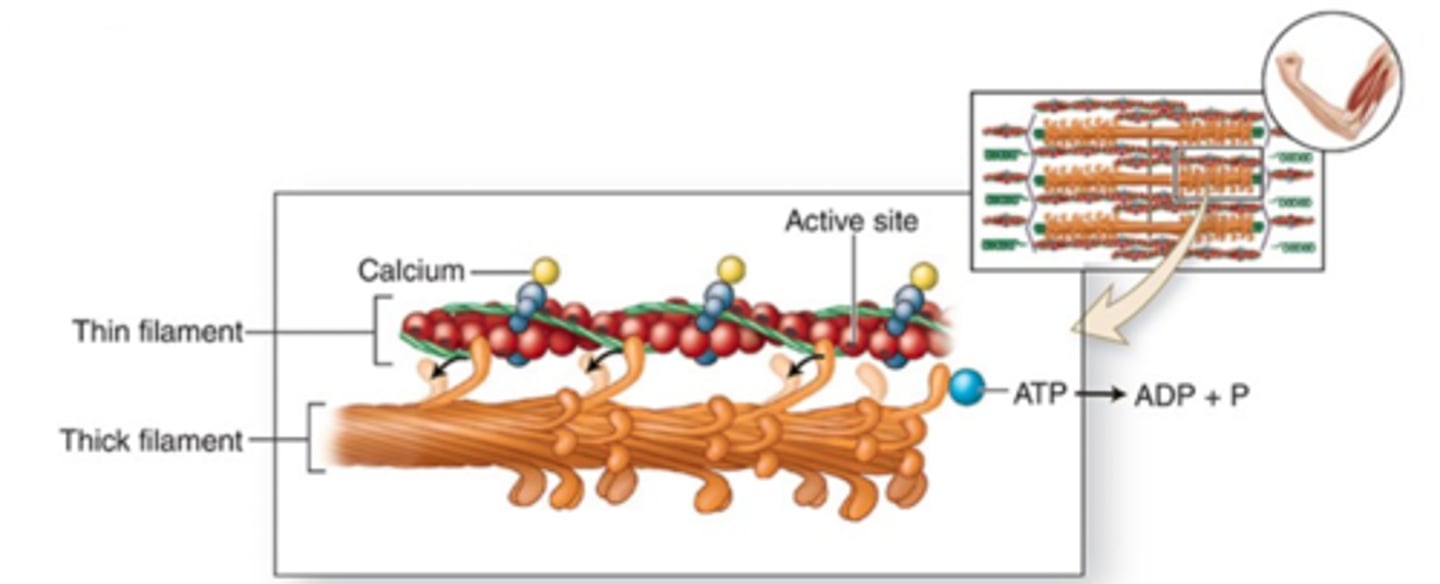
ATP
ATP binds myosin heads = ADP +Pi
what high energy molecule is involved in the pivoting of myosin heads?
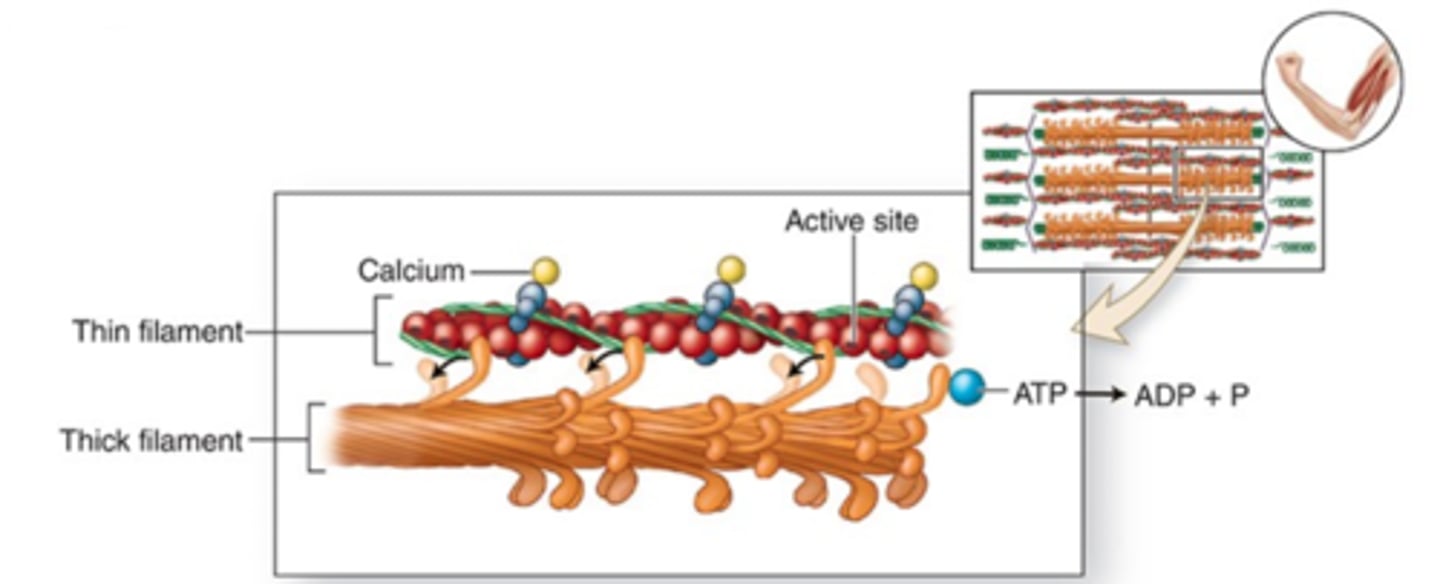
1. calcium ions ACTIVELY transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
2. active sites no longer exposed
3. filaments relax
what happens once the muscle impulse stops? (step 5)
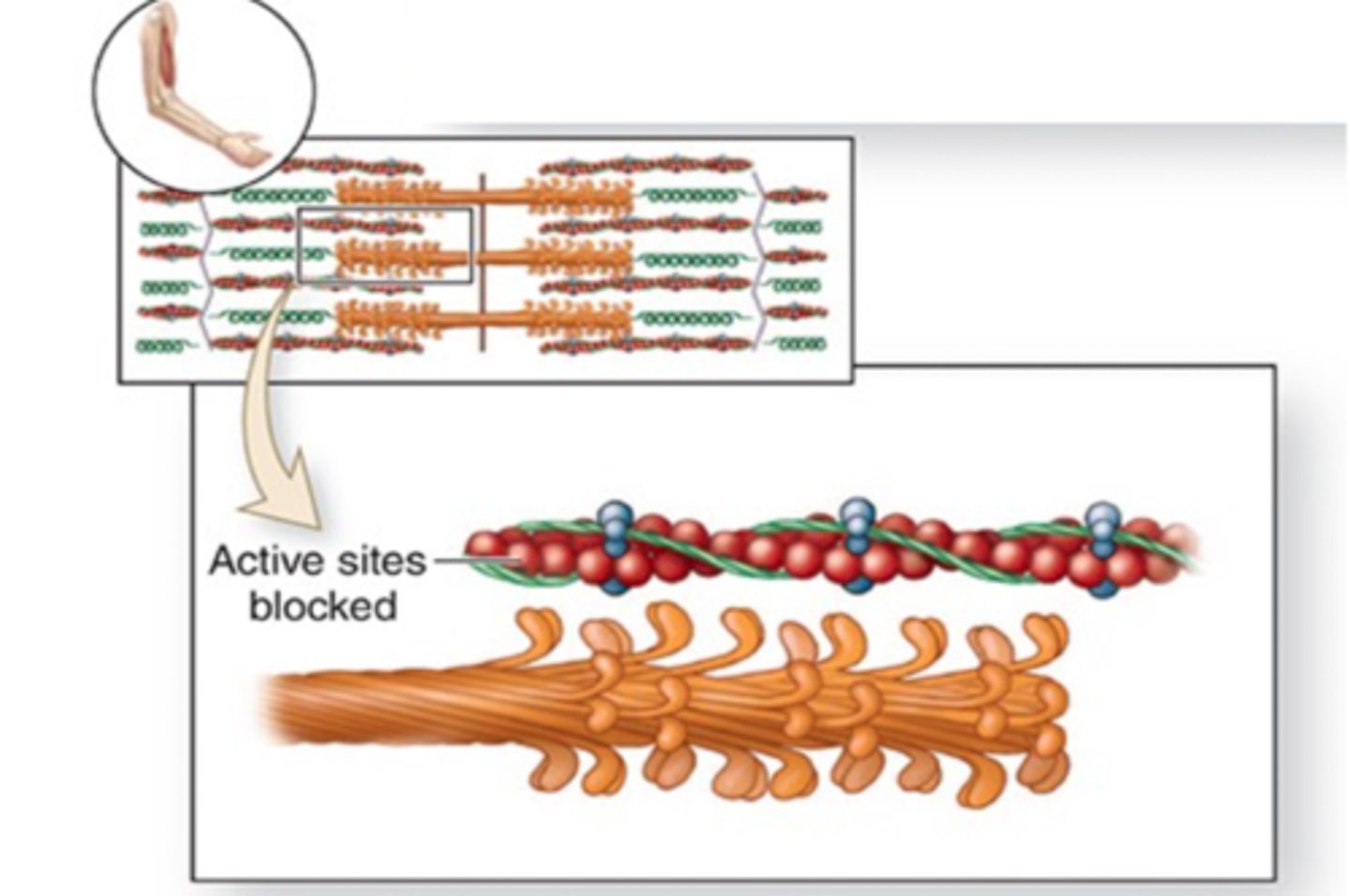
A band same length
During sarcomere shortening/muscle contractions, what band stays the same length?
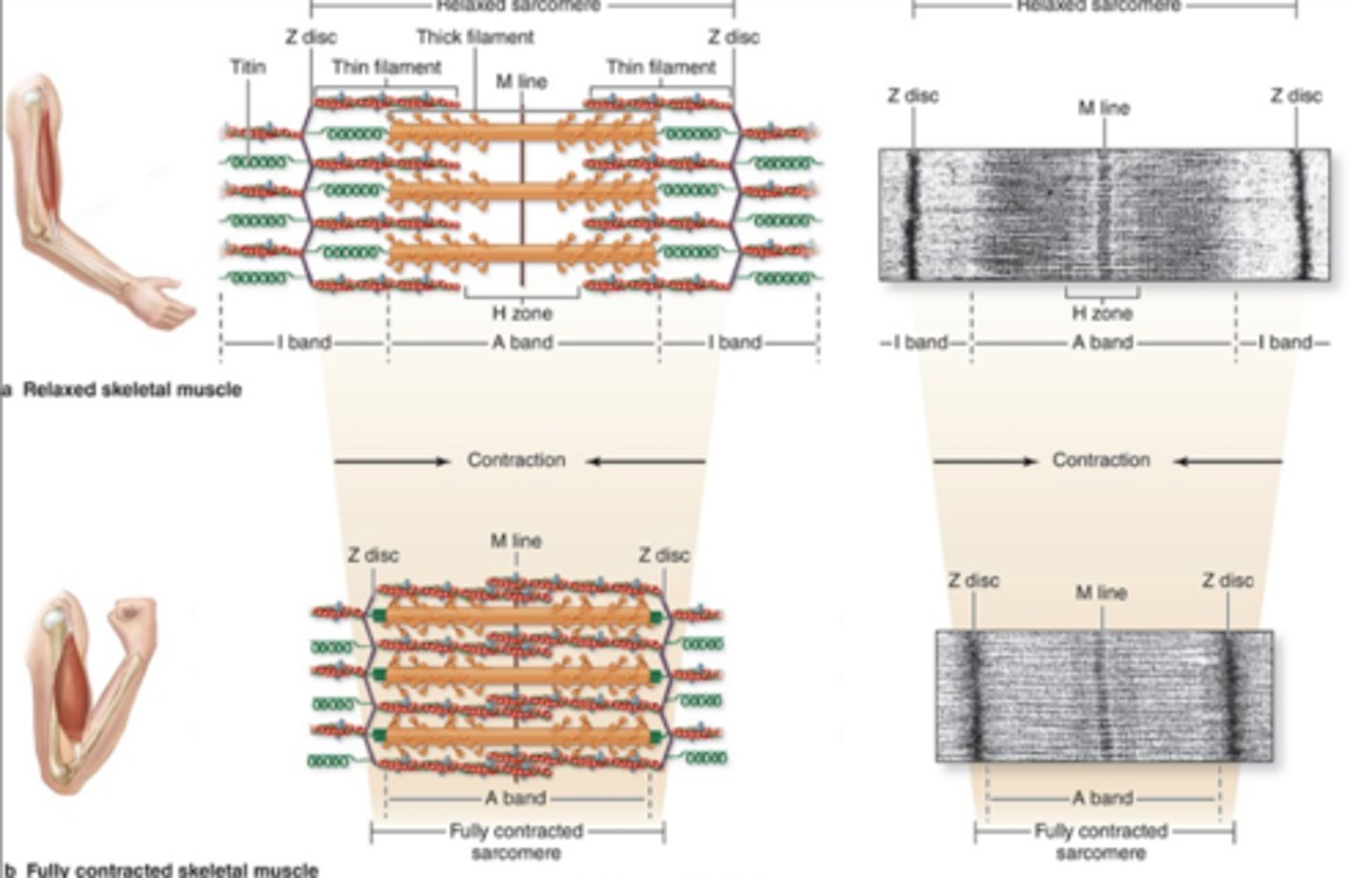
I band is reduced, and overlapping zones increase in size
Which band is reduced in size during contraction?