Bonding
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does ionic bonding occur between?
Metal and non-metal
What is transferred in ionic bonding?
Metal atoms transfer electrons to non-metals
What is the structure of ionic compounds referred to as?
Lattice structure
What is the strength of ionic bonds affected by?
The size of the ions
Charge of the ions
How does size of ions affect ionic bonds?
The smaller the ion they stronger the attraction to the electrons
What state are ionic compounds at room temperature? and why?
Solid
They have a giant structure therefore a high melting temperature as the forces require a lot of energy to overcome
In what states do ionic compounds conduct electricity? and why?
Molten and aqueous
Ions that carry the current are free to move in the liquid state
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
They form a lattice of alternating positive and negative ions, a blow may move the ions and produce a contact between like charges
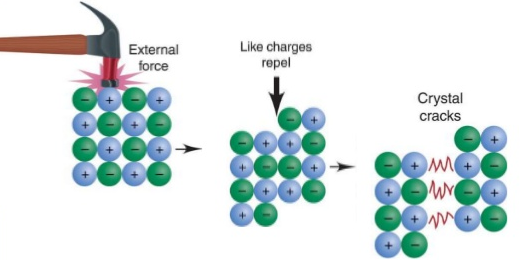
What are molecules?
When two or more atoms bond together
What are the forces like in simple covalent compounds?
Atoms are held together by covalent bonds
Molecules are held together by weak intermolecular forces
What is the structure of graphite?
Carbon atoms are arranged in sheets of flat hexagons covalently bonded with 3 other atoms
The fourth electron is delocalised
The sheets are held together by a weak van der Waals force
What are the properties of graphite?
Weak bonds between the layers mean that it is slippery and can slide over each other
Delocalised electrons in graphite are free to move along the sheets
Layers are quite far apart compared to its length of the bond so it has a low density
High melting point
Insoluble in any solvent
What is the structure of diamond?
Each carbon atom has 4 bonds
They arrange themselves in a tetrahedral shape
What are the properties of diamonds?
High melting point
Hard
Good thermal conductor as particles allow vibrations to pass through
Can’t conduct electricity
Won’t dissolve in any solvent
What is dative bonding?
This is where one of the atoms provides both of the shared electrons
This occurs when an atom has a lone pair of electrons and the other has none to share
What is valence shell electron pair repulsion theory?
Electron pairs repel each other
This results in each pair of electrons being at positions at the greatest possible distance from each other
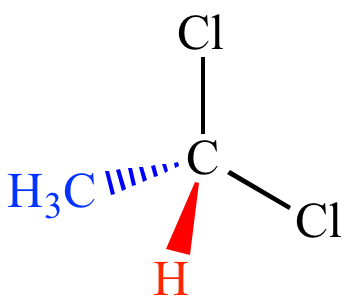
What does each line represent?
Full line represents bond in no direction
Wedge represents bond pointing towards you
Many lines represents bond pointing away from you
How do you find the number of electron pairs?
Find the central atom
Work out how many electrons are in the outer shell
Add 1 electron for every atom that the central atom is bonded to (take ions into account)
Add up the electrons, Divide by 2
Compare the number of electron pairs to the number of bonds to find lone pairs
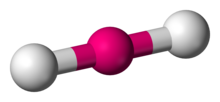
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Linear
2 electron pairs
2 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
180 bond angle
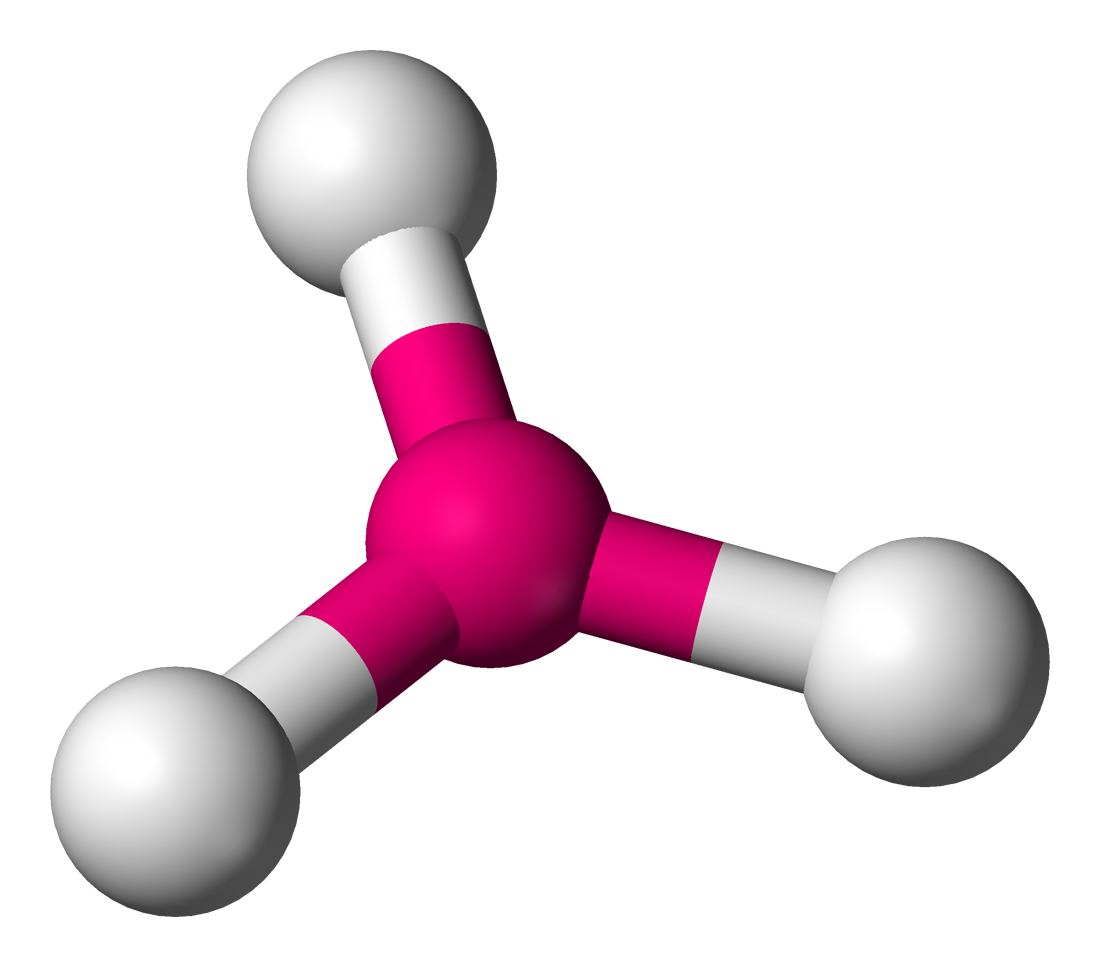
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Trigonal planar
3 electron pairs
3 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
120 bond angle
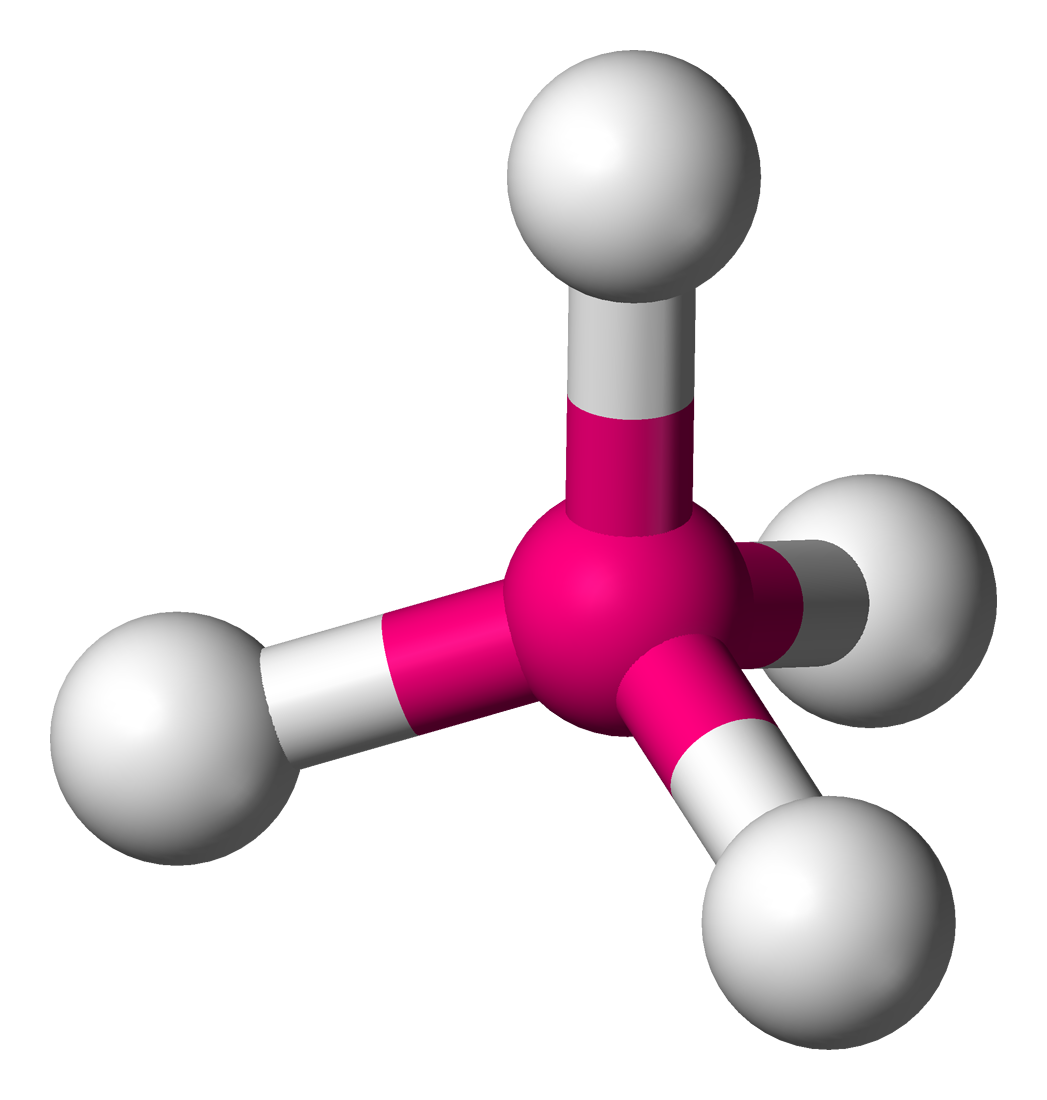
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Tetrahedral
4 electron pairs
4 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
109.5 bond angle
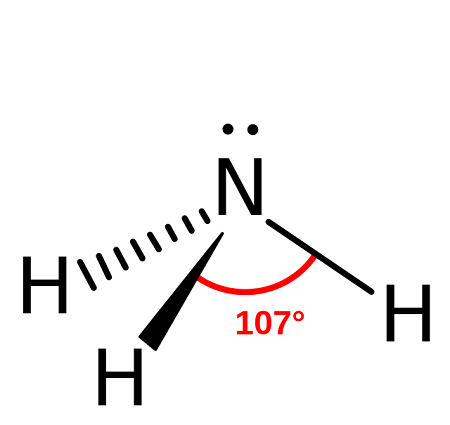
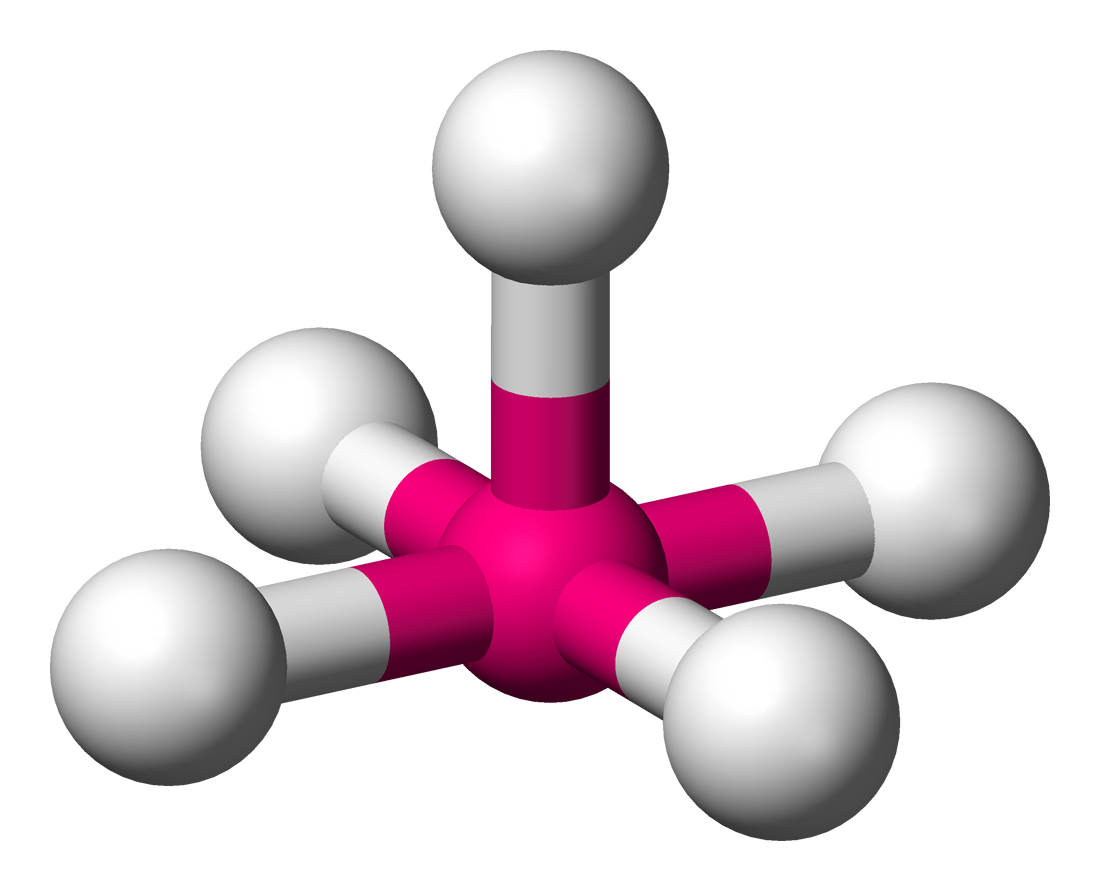
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Trigonal pyramidal
4 electron pairs
3 bond pairs
1 lone pair
107 bond angle
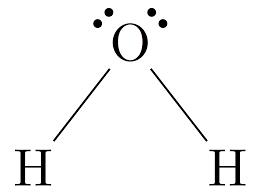
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Bent (V-shape)
4 electron pairs
2 bond pairs
2 lone pairs
104.5 bond angle
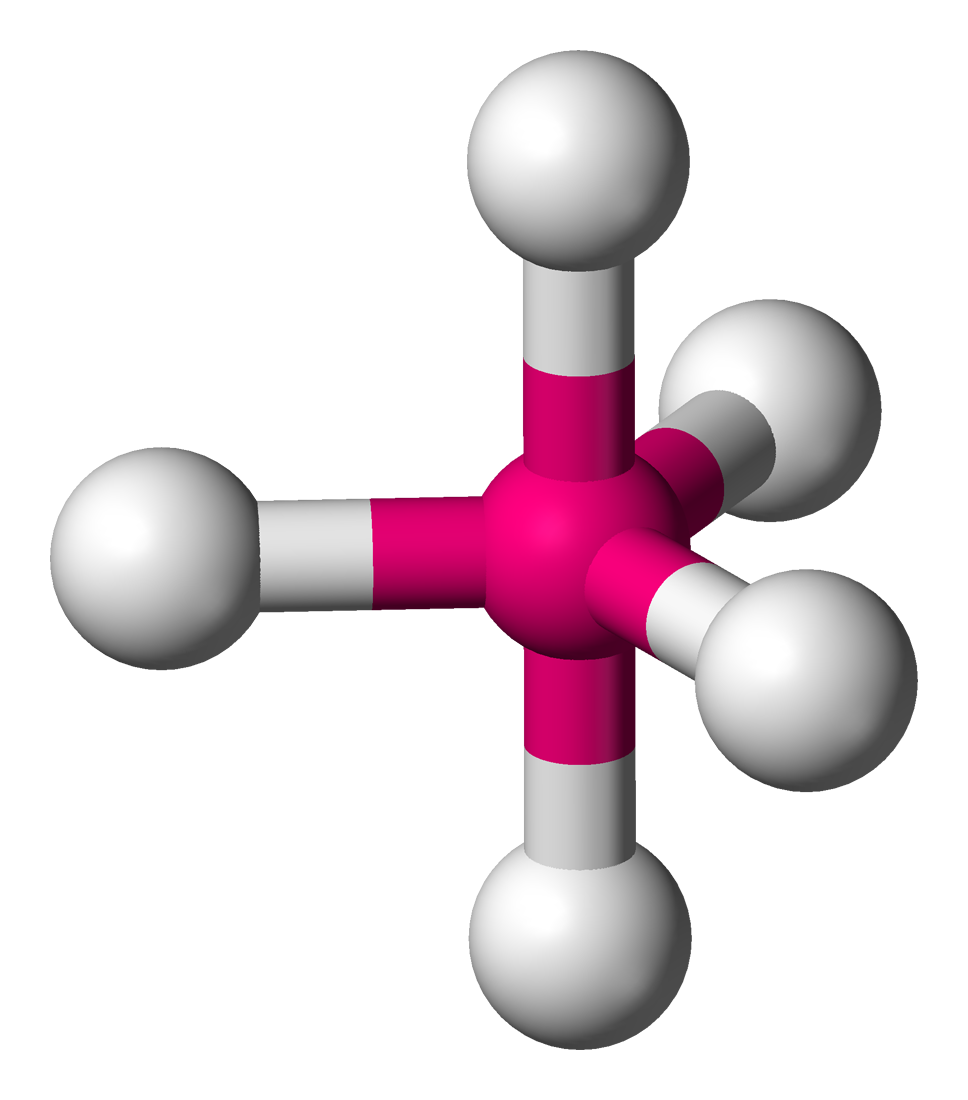
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Trigonal Bipyramidal
5 electron pairs
5 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
120/90 bond angles
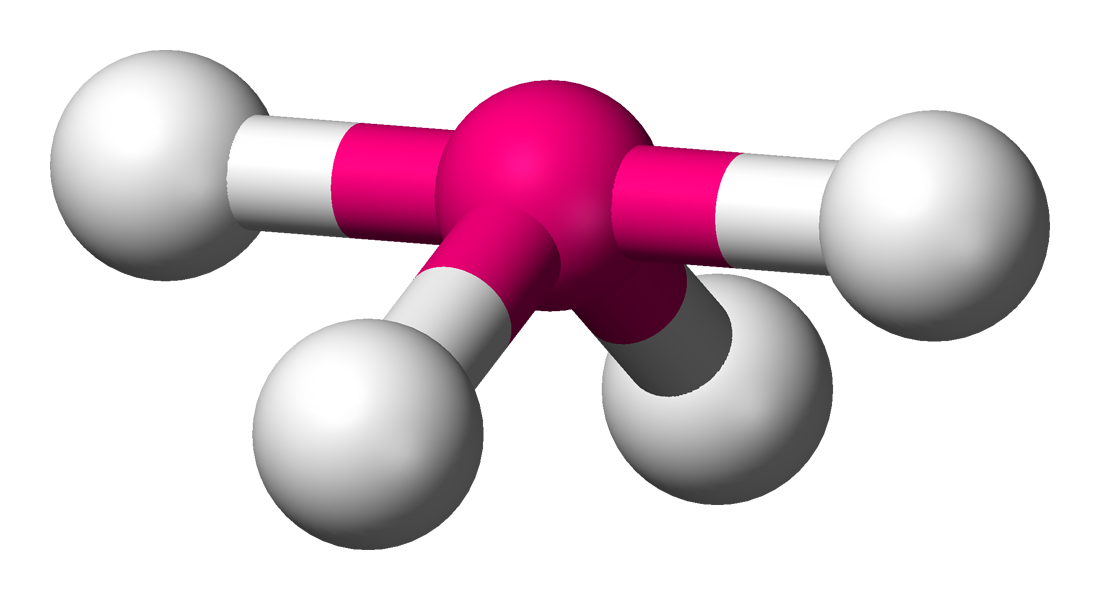
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Seesaw
5 electron pairs
4 bond pairs
1 lone pair
86/102 bond angles
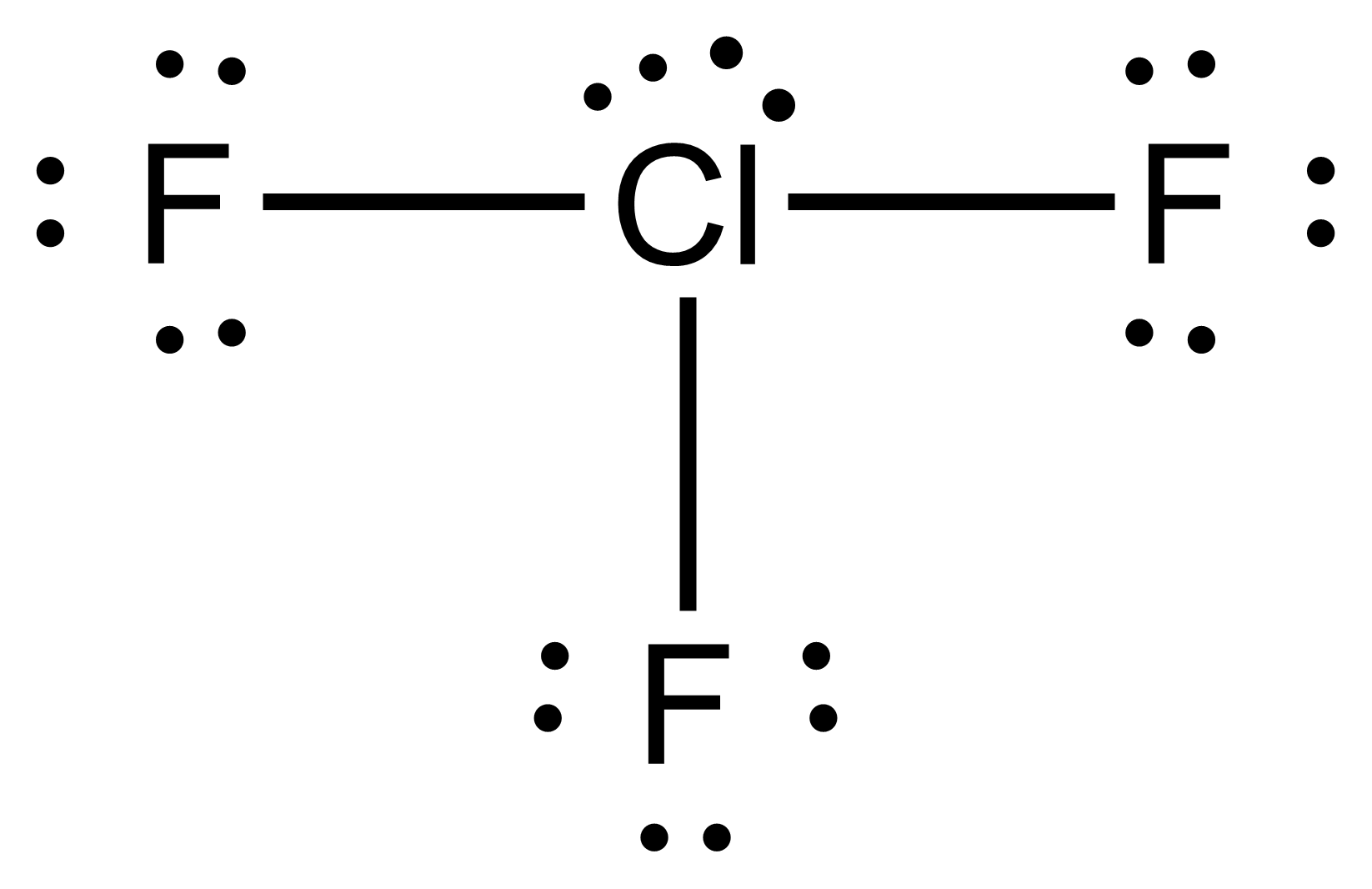
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
T-shape
5 electron pairs
3 bond pairs
2 lone pairs
90 bond angles
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
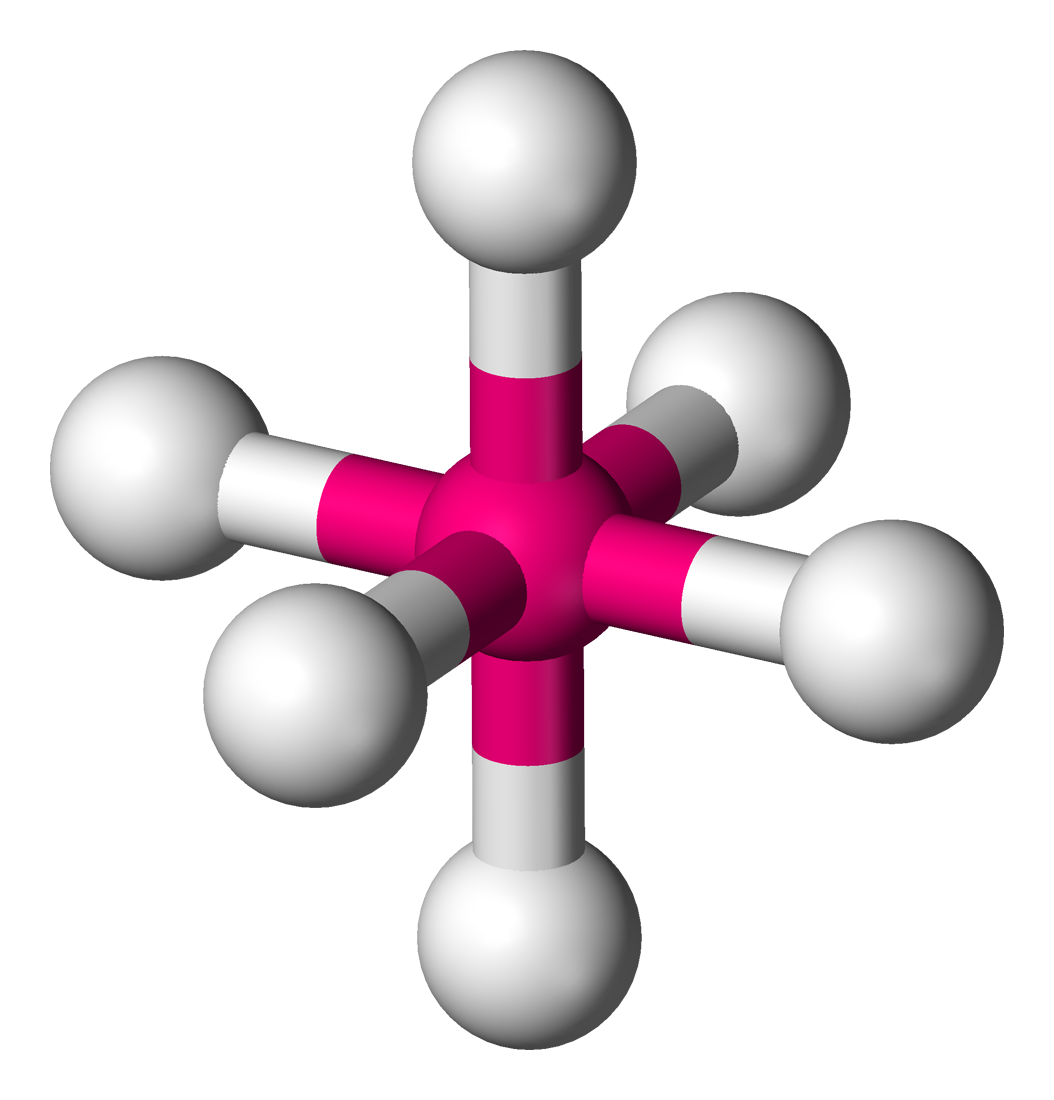
Octahedral
6 electron pairs
6 bond pairs
0 lone pairs
90 bond angles
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Square pyramidal
6 electron pairs
5 bond pairs
1 lone pair
90 bond angles
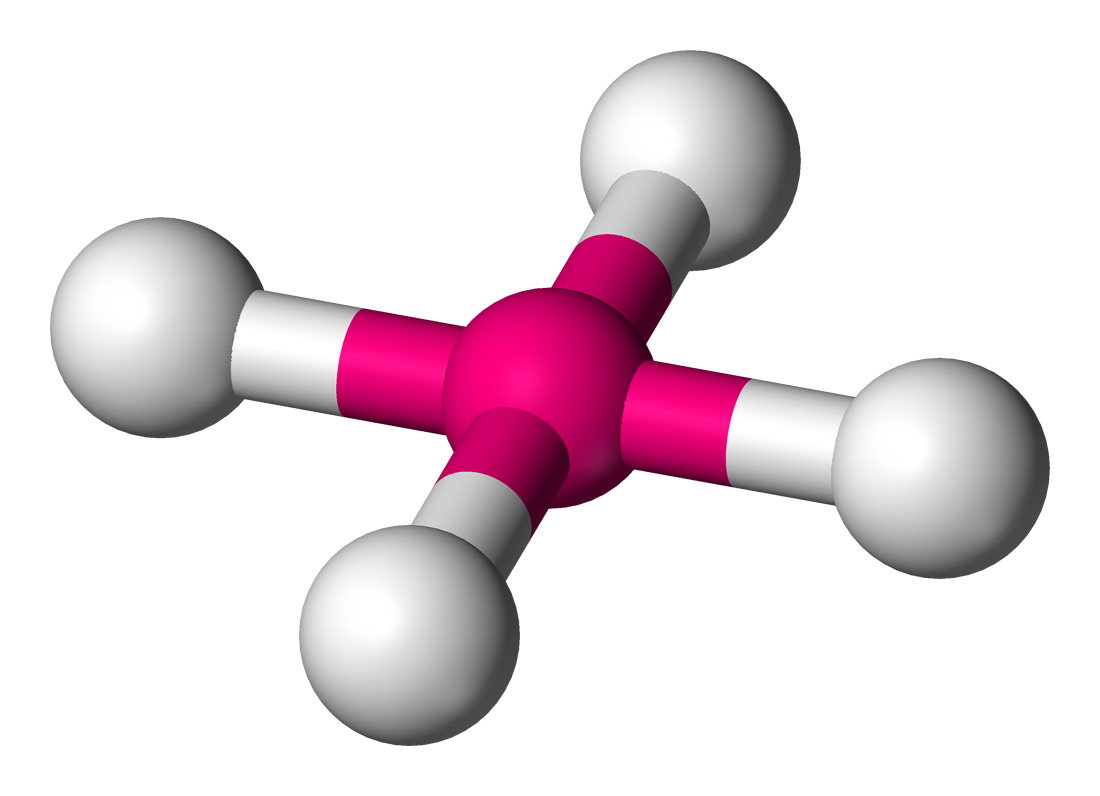
Name the structure, how many electron pairs it has, how many bond pairs ,lone pairs it has and its bond angle
Square planar
6 electron pairs
4 bond pairs
2 lone pairs
90 bond angles
What is electronegativity?
The power of an atom to attract the electrons in a covalent bond
What are the most electronegative elements?
F, O, N, Cl
What is the pauling scale?
A higher number means an element is better able to attract bonding electrons
When do non-polar covalent bonds form and what does this mean about the shared electrons?
When atoms have equal number of electronegativity
Or when both aren’t very electronegative
This means that the electrons are shared equally
An example is F2
When do polar covalent bonds form and what does this mean about the shared electrons?
When one atom is more electronegative than another
Electrons shared will be closer to the more electronegative one
An example is H2O
What is a dipole?
It is a difference in charge between two atoms caused by a shift in electrons density in the bond
What is a polar molecule?
If charge is distributed unevenly over a whole molecule then the molecule will have a permanent dipole
Non-polar molecules | Non-polar molecules | Polar molecules | |
|---|---|---|---|
Description | No polar bonds | Contains polar bonds but all dipoles cancel out | Contains polar bonds but all the dipole moments do not cancel out |
Example | CH4 | CO2 | H2O |
What is a van der Waals’ force?
Causes all atoms and molecules to be attracted to each other
Electrons in charge clouds are always moving quickly
These move and and cause temporary dipoles
These are attracted to each other
Dipoles destroy and create themselves all the time, but the overall effect is the same
larger molecules have larger electrons clouds which mean they have stronger van de Waals
Branched molecules are weaker
What are permanent dipole-dipole forces?
In molecules that have permanent dipoles, there will be weak electrostatic forces of attraction between the δ+ and δ- charges on neighbouring molecules
What is hydrogen bonding?
Strongest intermolecular forces
It only happens when hydrogen is covalently bonded to F, N or O
The bond is polarised, and hydrogen has such a high chance density that the hydrogen atoms form weak bonds with lone pairs of electrons
What is the behaviour of simple covalent compounds?
They don’t conduct electricity
Low melting points
Can dissolve in water depending on low polarised they are
What are the trends in melting and boiling points?
As you go down group 7 hydrides, two factors complete
Polarity of the molecule
Number of electrons
General trend is that it increases
What is metallic bonding?
The outermost electrons of a metal atom becomes delocalised
This leaves a positive metal ion surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons
These exist as giant metallic lattice structures
What are the properties of metallic compounds?
Metals have high melting points
They are malleable
They are ductile
They can conduct electricity
They are mostly insoluble