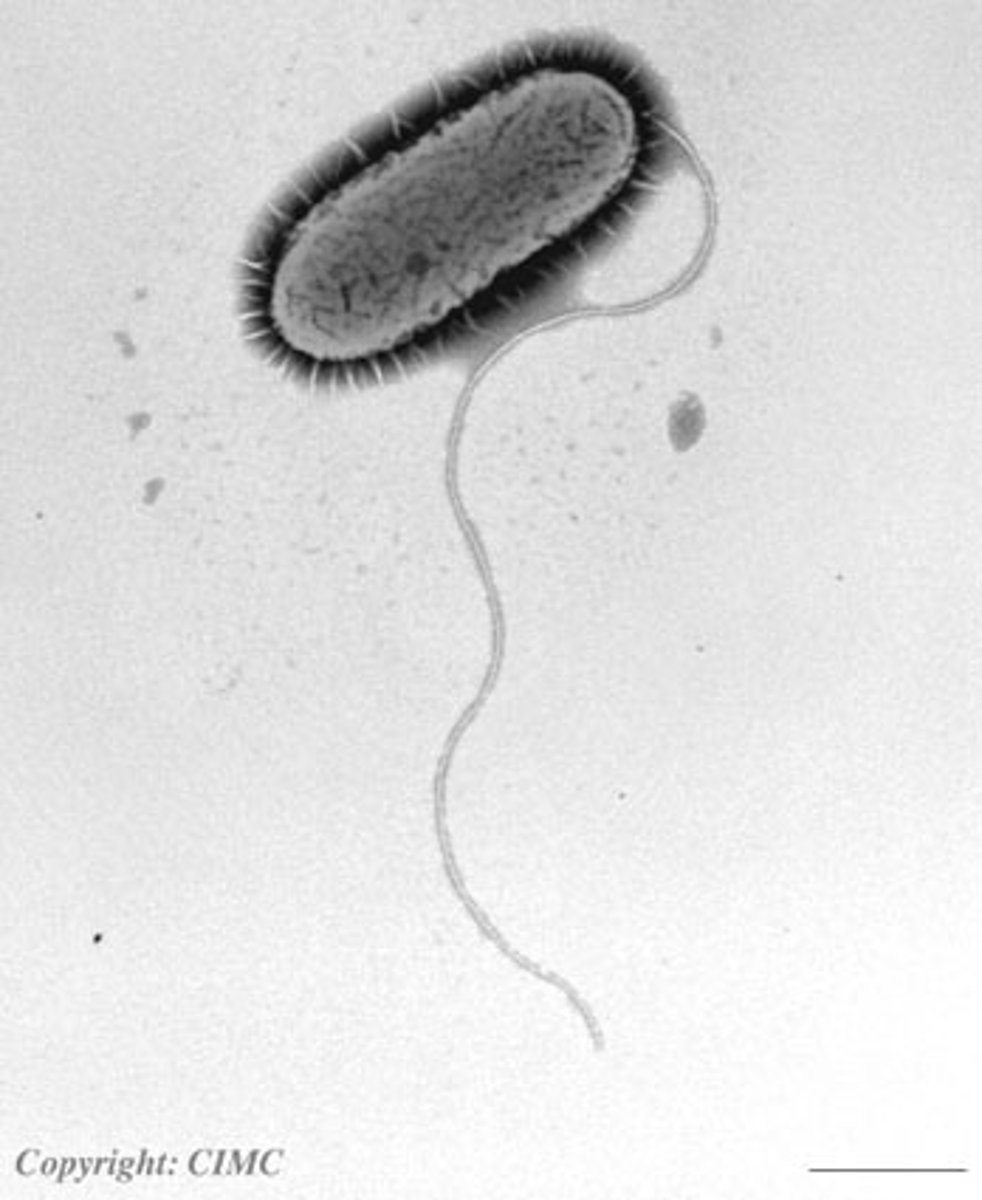
Microbiology Chapter 3 Bio-Rad
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
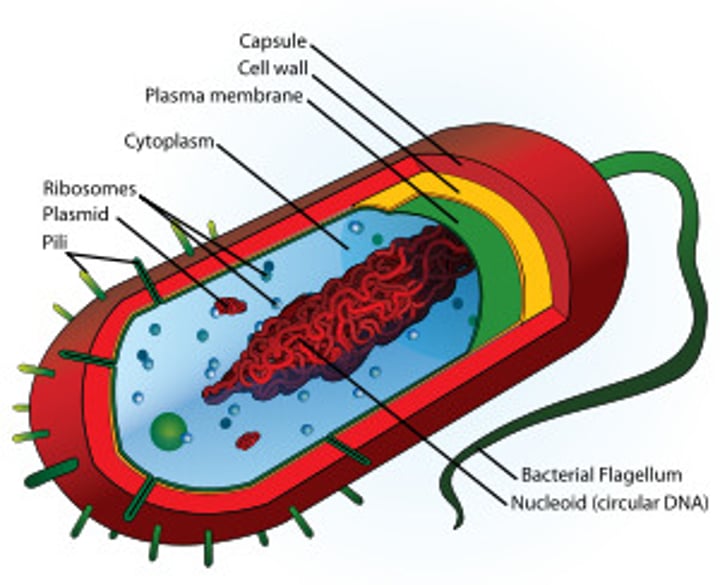
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
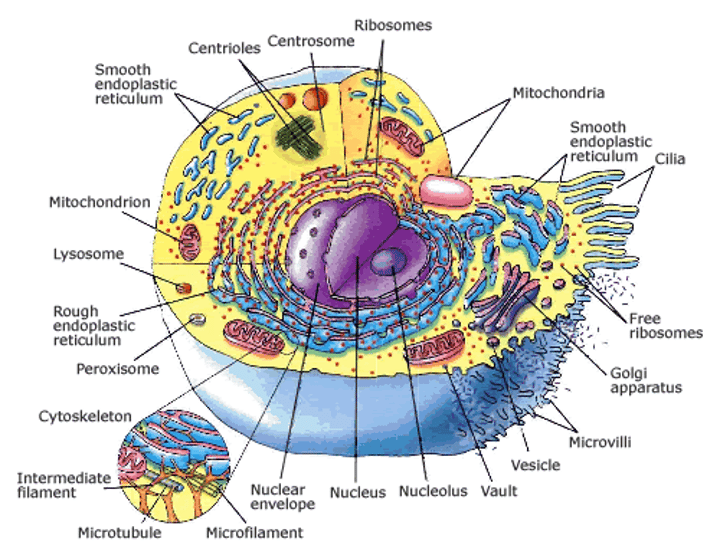
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
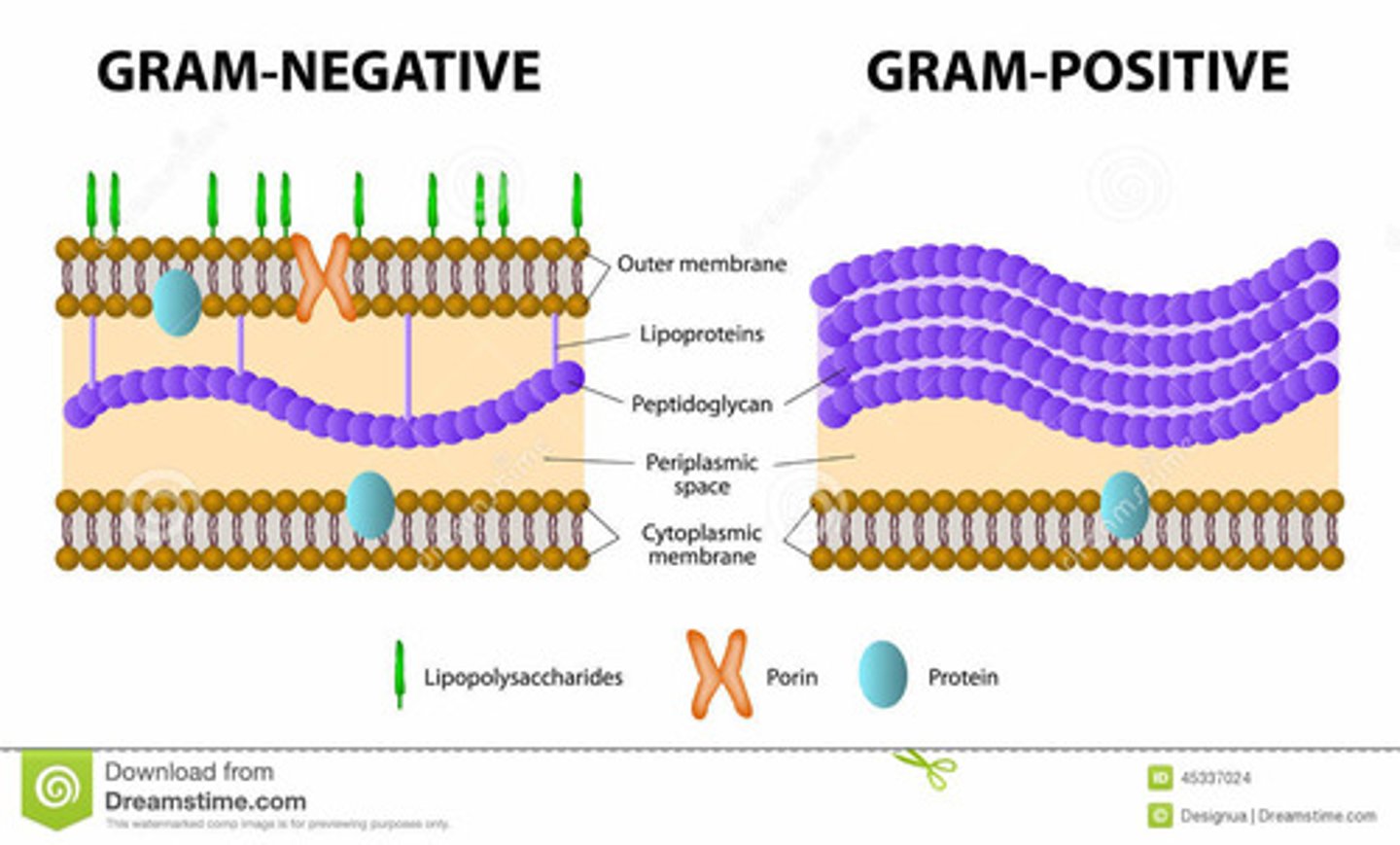
gram positive
purple
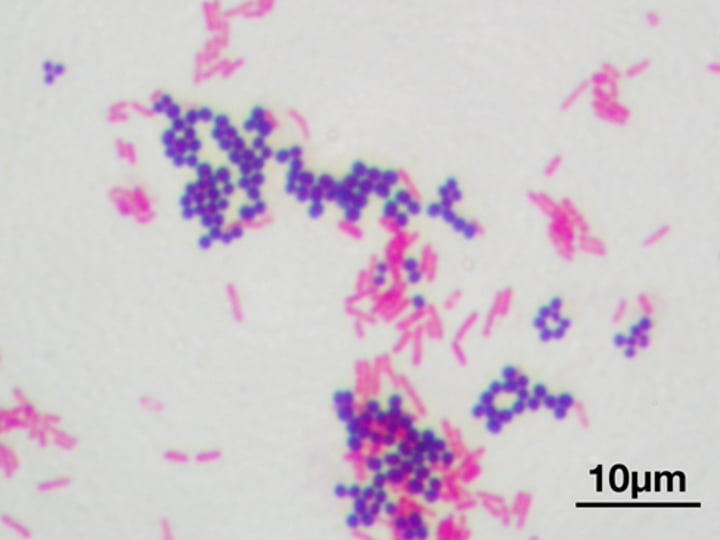
gram negative
pink
Alexander Fleming
Discovered penicillin in 1928

Kirby-Bauer Test
The test to determine the efficacy of antibiotics or the antibiotic resistance of bacteria. Zone of Inhibition
Pencillin
antibiotic
petri dish
a shallow dish used to culture bacteria

aseptic
preventing infection; having a cleansing effect

Pathogen
a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease.

Black Plague/Bubonic Plague
the disease that killed a large part of the European population in the Medieval times

Archeabacteria
ancient bacteria; live in extreme conditions

Eubacteria
A kingdom that contains all prokaryotes except archaebacteria
Bacillis
rod shaped
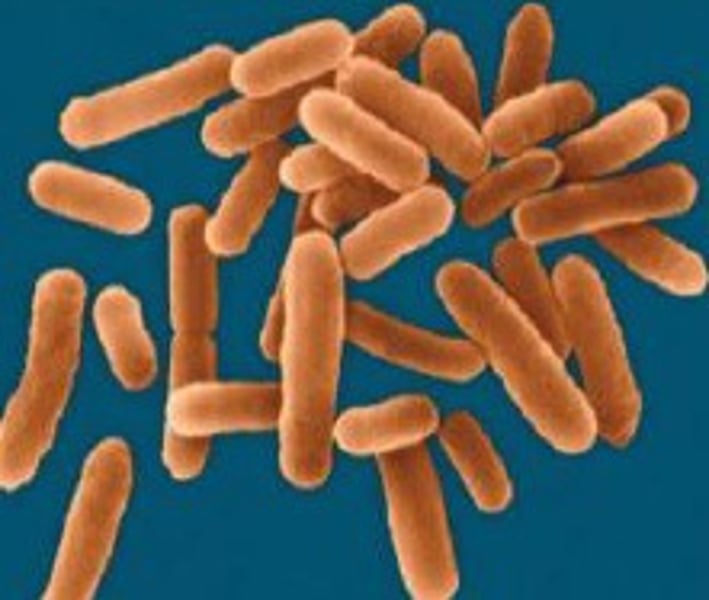
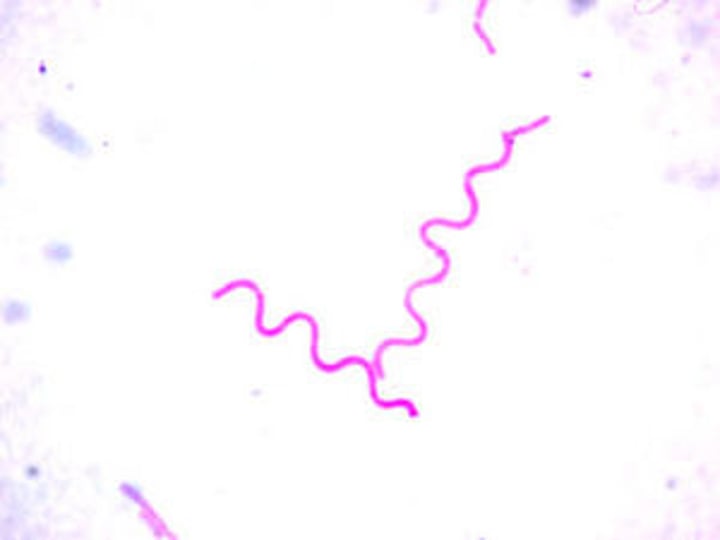
Spirrilum
spiral shaped bacteria
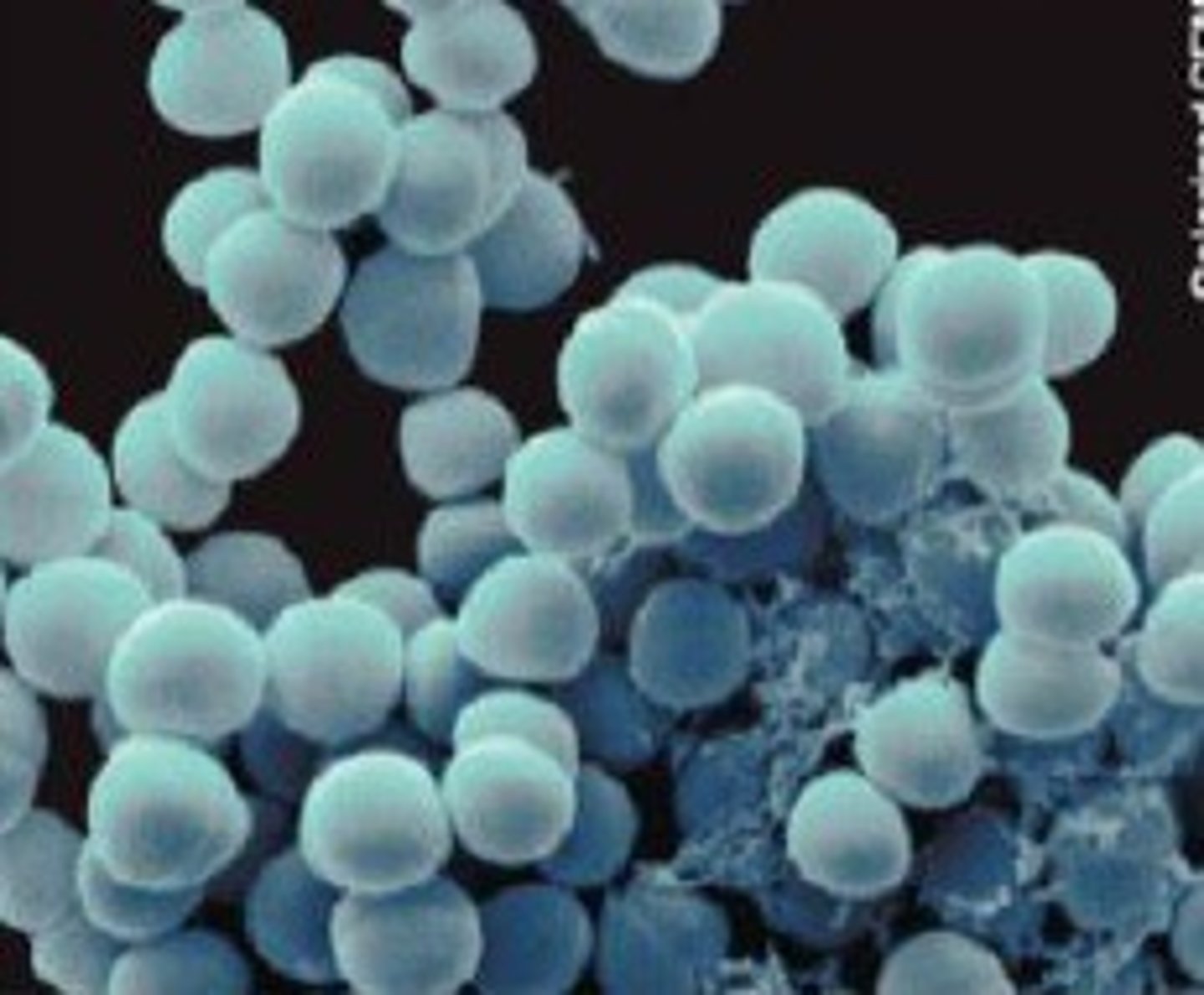
Cocci
sphere shaped bacteria
Inoculation Loop
a metal rod with a small wire loop at the end, used as a swab

centrifuge tube
glass or plastic tube that holds samples within a centrifuge

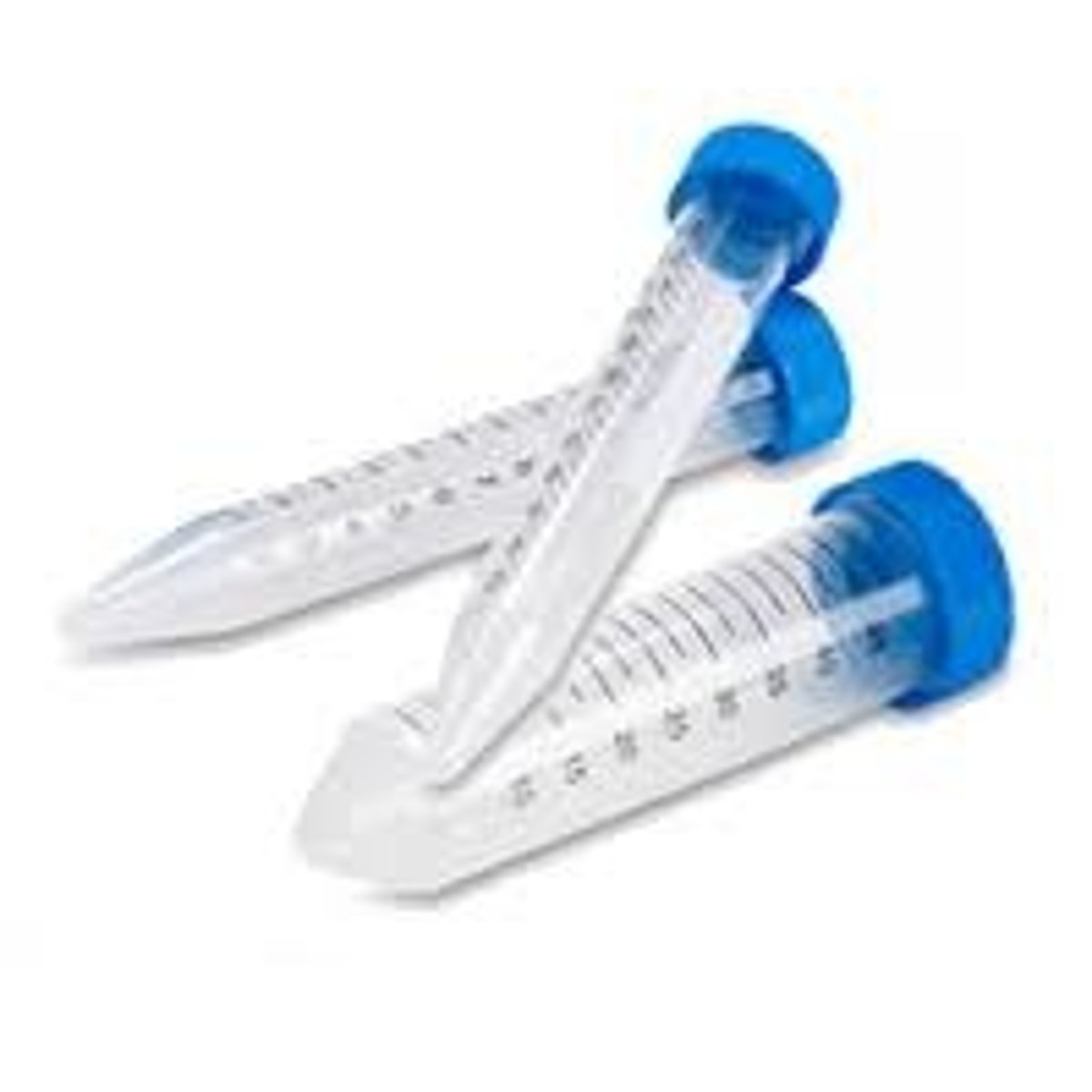
conical tube
Tubes ideal for cell centrifugation.
Bunsen burner
used to heat substances

spectrophotometer
An instrument that measures the proportions of light of different wavelengths absorbed and transmitted by a pigment solution.

CFU
colony forming unit
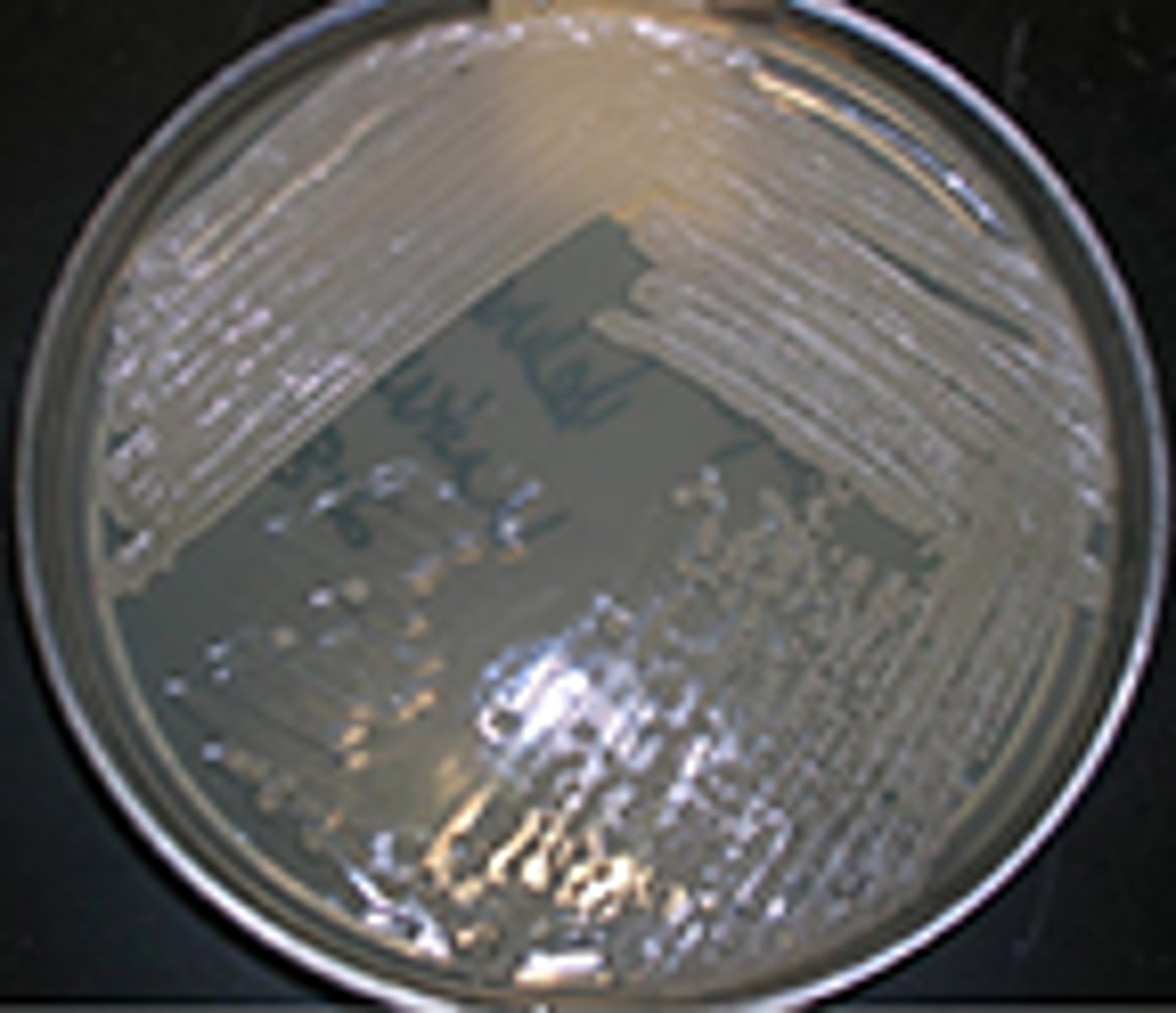
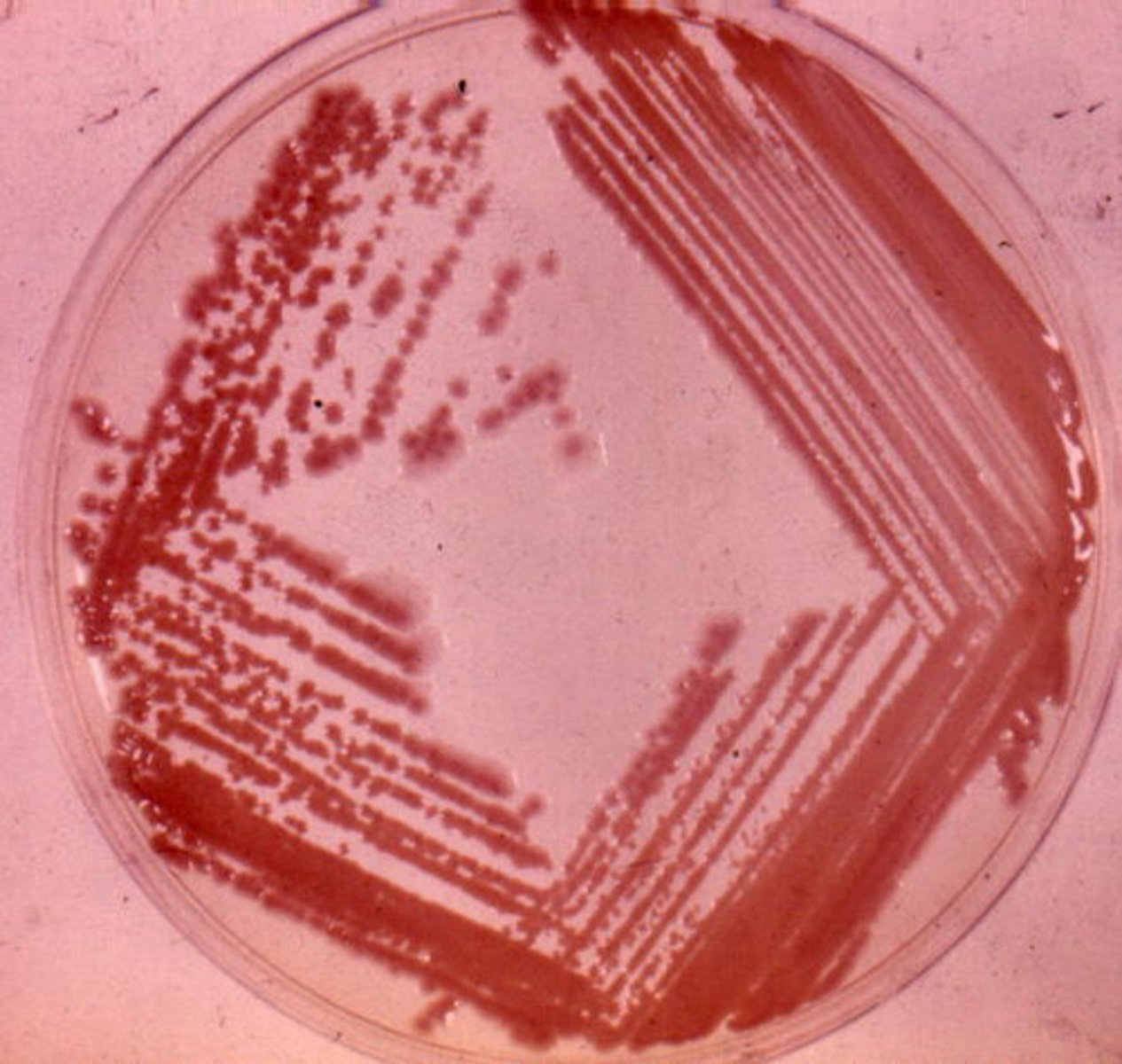
streaking for isolation
the purpose of this procedure was to obtain isolated colonies
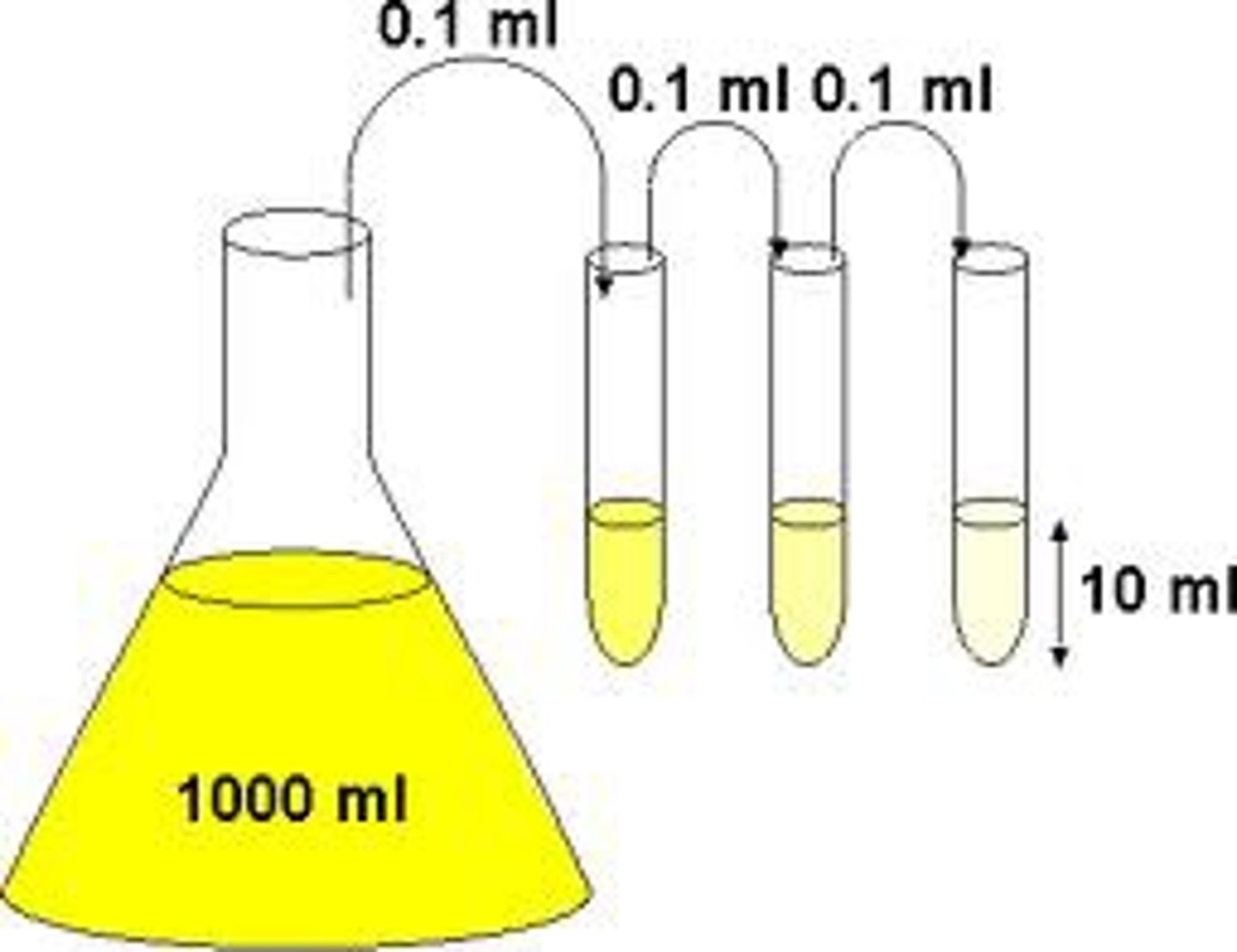
serial dilution
the process of diluting a sample several times
Optical Density (OD)
A numerical representation of the film's ability to transmit light. Measure how cloudy a concentration is. Determine cell concentration.

Transmitance
Amount of light sent through the sample
Absorbance
The amount of light absorbed by a sample
Koch's Postulates
series of guidelines used to identify the microorganism that causes a specific disease
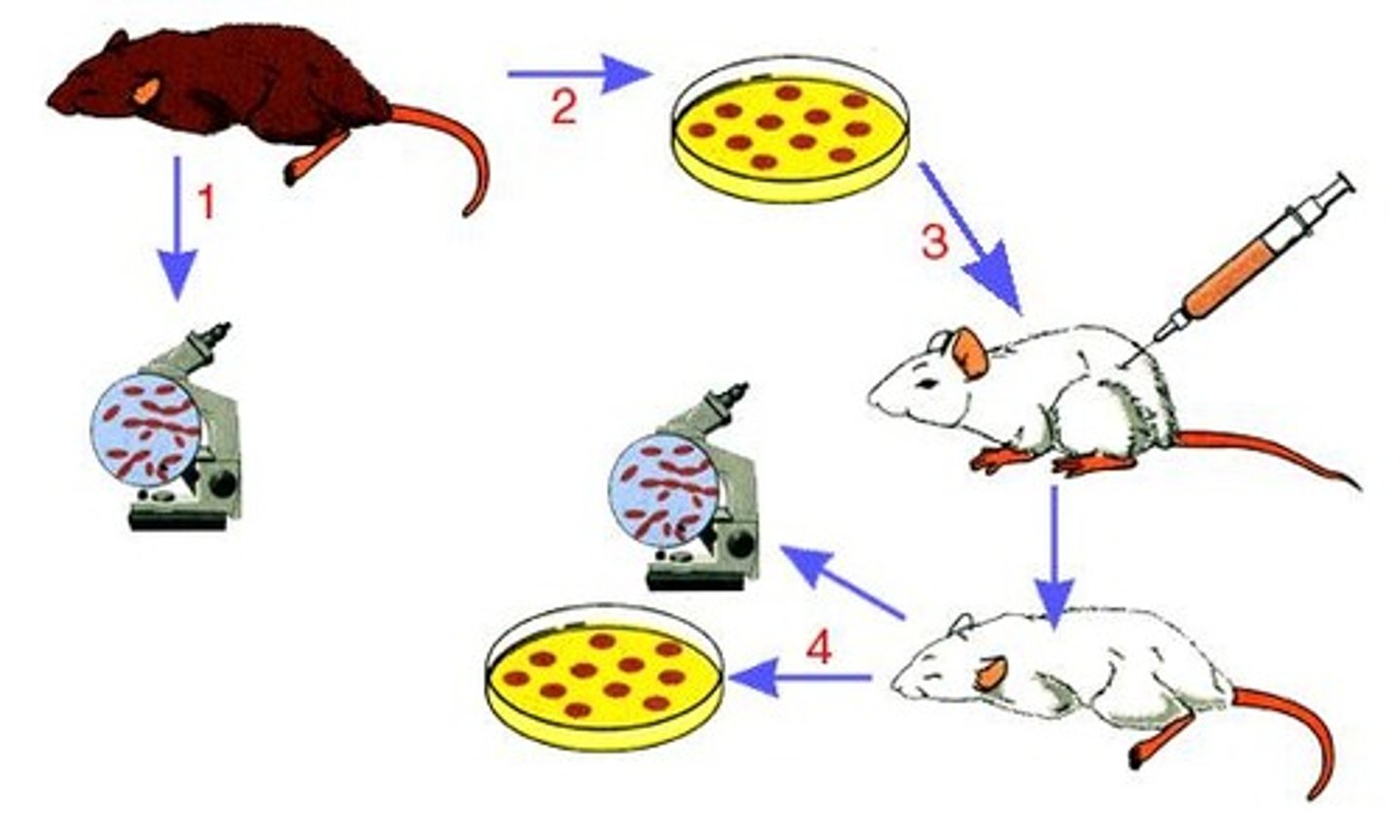
Koch's second postulate
The suspected pathogen must be grown in pure culture
Koch's first postulate
The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease
Koch's third postulate
The same disease must result when the isolated microorganism is inoculated into a healthy host
Koch's fourth postulate
The organism should be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original
Agar
Gelatin-type material derived from seaweed

Luria Broth (LB)
a nutritionally rich medium, is primarily used for the growth of bacteria
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)
Developed a vaccine for rabies & anthrax.

microorganism
an organism that is microscopic in size, may exist as single cells or colony of cells (aka microbe)

Koch's Postulates
determine if microorganisms cause disease
Peptidoglycan
the compounds that build cell walls in gram positive and negative cell walls.
anaerobic
without oxygen
aerobic
occurring only in the presence of oxygen.
Microbiology
the study of microbes

Biosafety cabinet
Enclosed, ventilated lab workspace

Thermophiles
Type of bacteria found at Yellowstone National Park

Insulin
A medicine created using genetically modified bacteria.
Conjunction
Bacteria sexual reproduction
Eubacteria
true bacteria
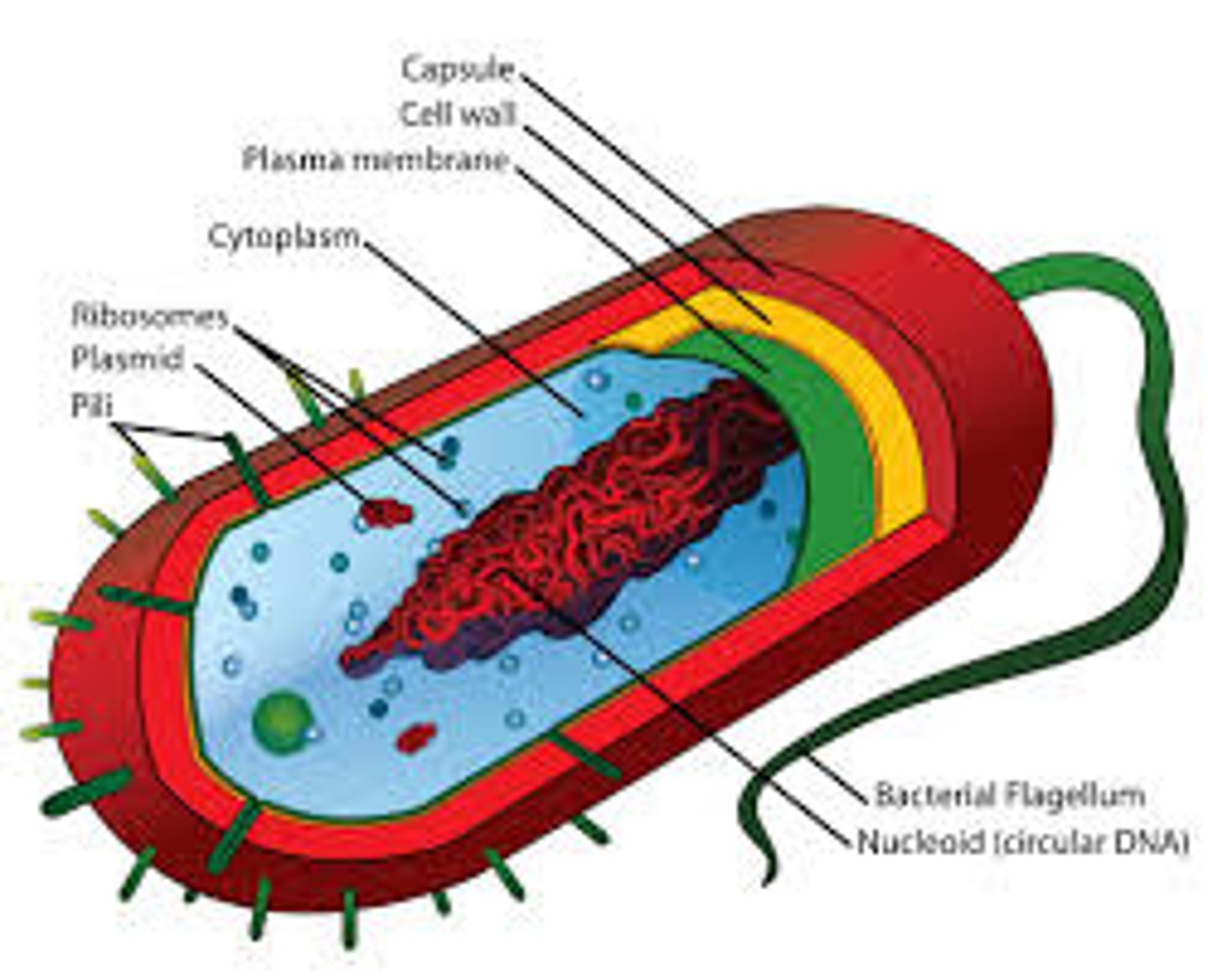
Archaebacteria
considered ancient life forms that evolved separately from bacteria and blue-green algae

Ribosomes
Makes proteins
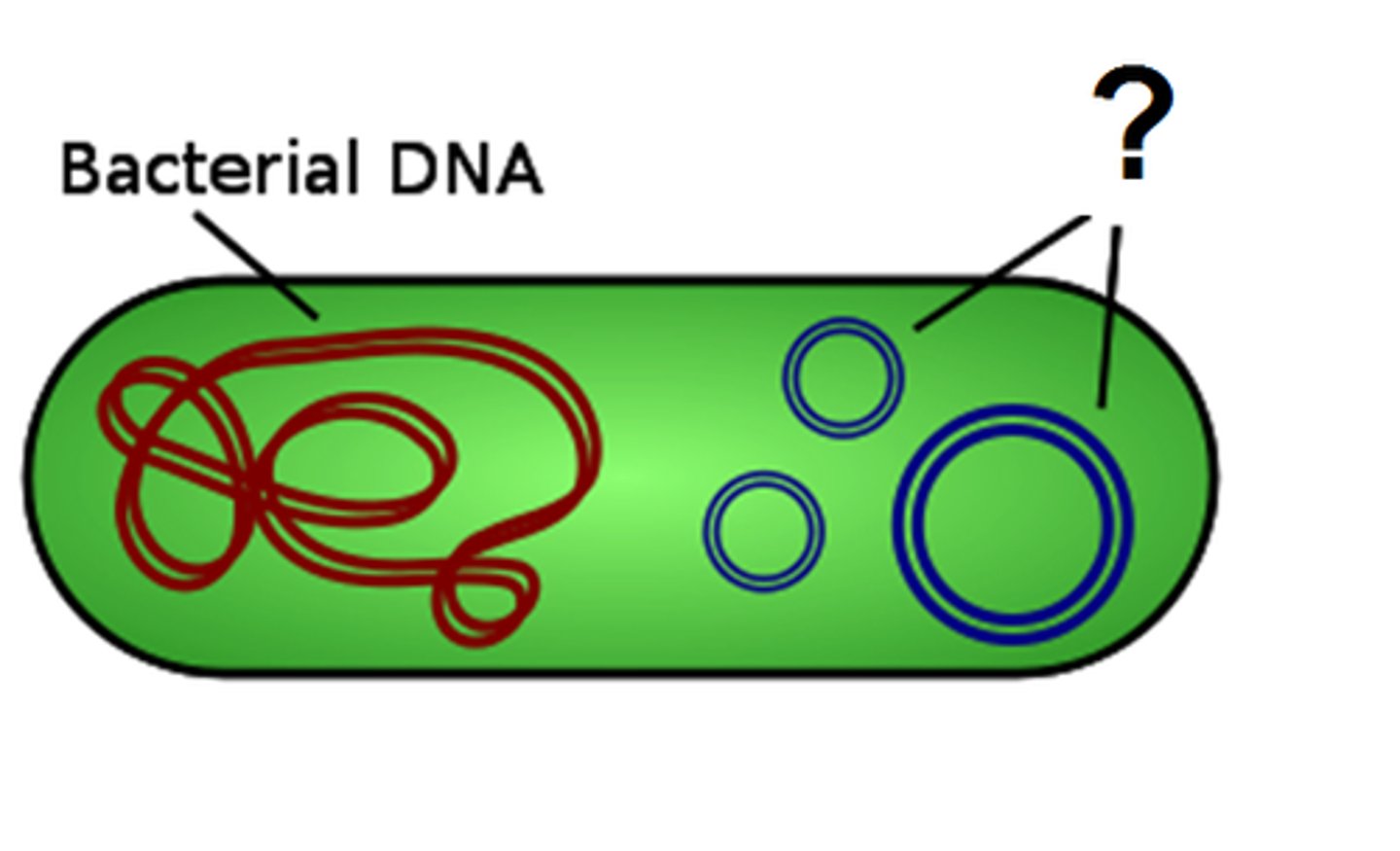
Plasmid
small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
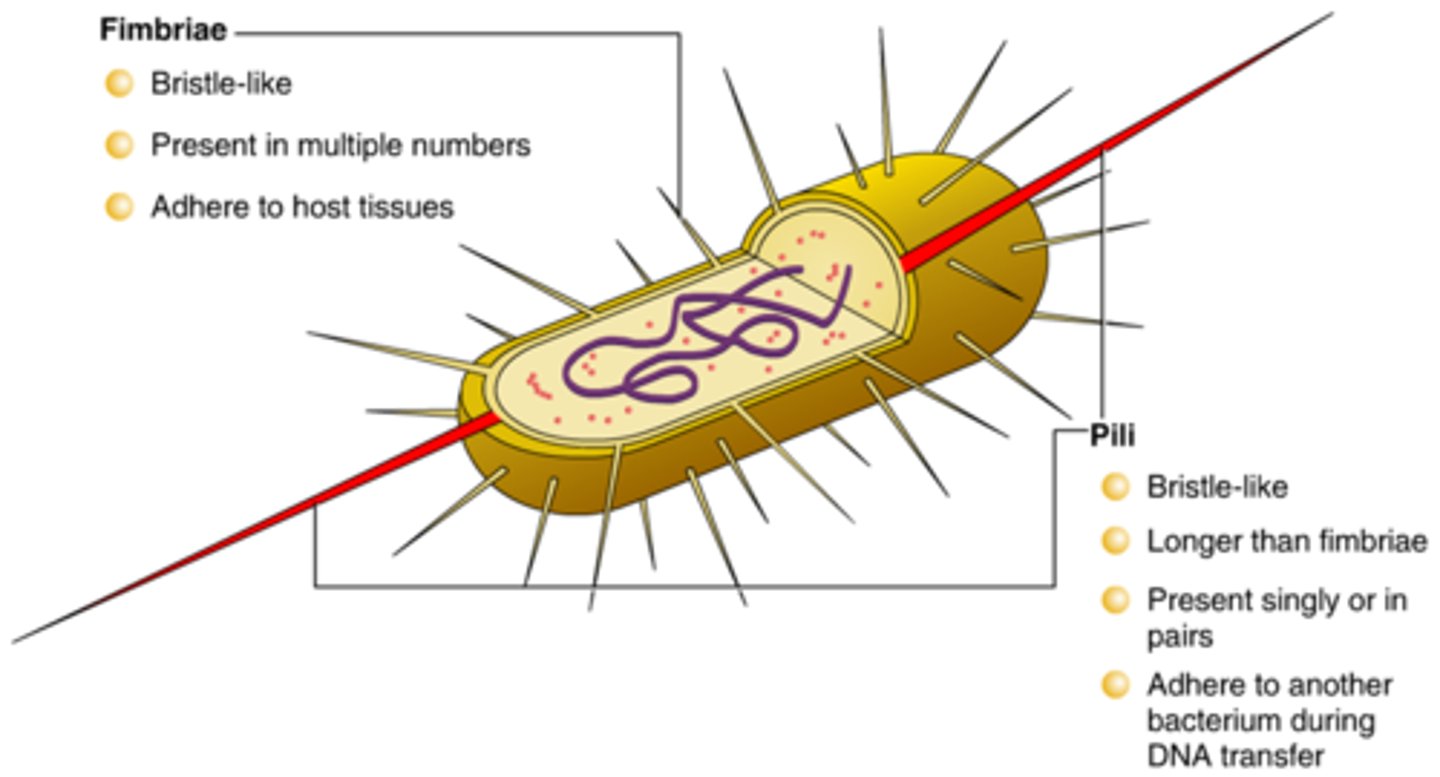
Pili
short, hairlike protein structures on the surface of some bacteria
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.