Final Exam Intro to business CH 10-16 kms
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Human Resource Management
determining the organization's needs for Human Resources and acquiring, maintaining, and developing an organization's human resources
Job Analysis
procedure through observation and the study that determines the pertinent information about the job
job description
a written description of the basic tasks, duties, and responsibilities required of an employee holding a particular job
job specification
a description of the qualifications necessary for a specific job, in terms of education, experience, and personal and physical characteristics
what is not performed by the human resources managers?
selling
what is a reason internal recruiting has advantages over external sources?
1. improved employee morale
2.cultural understanding
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
1. prohibits discrimination (equal employment opportunity commission (EEOC) )
what can not be asked on an employment application?
1. race, sex, age, religion
(FSLA) Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
1. established minimum wage
turnover
replacement of employees (quit, fired)
to avoid legal problems, before firing an employees, companies should ensure what?
have documented all problems and warnings in the employees work records.
who investigates sexual harassment in the workplace?
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
What is having a diverse work force have on a company?
1.a greater ability to serve the needs of a diverse customer base.
2.increased innovation and creativity
3. better decisions on complex problems
To achieve its objectives, labor may not use what type of activity? and why?
Lockout- management version of a strike where employees cannot work
what is the first step in developing a marketing strategy?
selecting a target market
what is the goal of the marketing concept?
customer satisfaction
what is the most flexible element of the marketing miz and can be changed ?
price
now that someone had identified their target market, what must be done next?
develop an appropriate marketing mix
distribution
making products available to customers in the quantities desired.. also referred as place.
in the context of the marketing concept. what is the first step that a business must take?
find out what consumers desire
what is the central focus of the marketing mix. It includes the size,color, features, branding, packing , quality
product
target market
refers to a specific group of consumers on whose needs and wants a company focuses it marketing efforts.
promotion
a persuasive form of communication that attempts to expedite a marketing exchange by influencing individuals, groups, and organizations to accept goods, services, and ideas
Marking strategy
a plan of action that consists of selecting a target market and developing a marketing mix to satisfy it.
Marketing
the process by which companies try to satisfy customers' need through activities.
Marketing Orientation
considers the needs of customers when developing a marketing mix
Market Segmentation
the process of dividing a market into meaningful, relatively similar, and identifiable segments or groups
what are the 4ps in marketing mix and what do they mean?
1. Product- good or service
2. price- the value placed on the product
3. place (distribution)- making products available
4. Promotion- informing customers
Marketing Research
collect info about potential customers
primary data vs. secondary data
1. primary- directly from respondents (surveys)
2. secondary- infor compiled inside or outside organization (U>S Census Bureau)
what are the various types of market segmentation?
1. demographic- (people based differences) age, sex, family size, income, race
2. Behavioral- habits, loyalty, benefits looking for
3. Geographic- location. climate
4. Phychographic- motives, lifestyles, personality
marketing statement
description of the target market,and sales and profit goals
consumer products
products intended for household or family use
convenience products
items bought frequently with no planning
shopping products
purchased after consumers have "shopped around"
speciality products
items that the consumer makes a special effort to search out and buy (cars, designer purse)
business products
Used directly or indirectly in the operation or manufacturing processes of businesses
product line
a group of closely related products that are treated as a unit because of similar marketing strategy, production, or end-use considerations.. (toothpaste, mouth wash)
product mix
all the products offered by an organization
Product Life Cycle and differences.
1. introduction- make customers aware
2. growth- strengthen its market position
3. Maturity- severe competition and heavy costs
4. Decline- firms eliminate models, cut costs, and phase out products
manufacture products
owned by the manufacturer (kelloggs's)
generic products
products that have no brand aname and come in simple packages and carry only their generic name (peanut butter, tomato juice)
Phychological pricing
based on emotional rather than rational responses (2 cans for 1$)
fixed costs
the cost incurred no matter how many units are produced or sold. (rental lease, property tax)
marketing channel
organizations that moves products from their producer to customers
Different Channels of Distribution
In Channel A, the product moves from the producer directly to the consumer. (fruits on side road)
In Channel B, the product goes from producer to retailer to consumer. (college textbooks)
In Channel C, the product is handled by a wholesaler and a retailer before it reaches the consumer. (tv, watches)
In Channel D, the product goes to an agent, a wholesaler, and a retailer before going to the consumer. (candy)
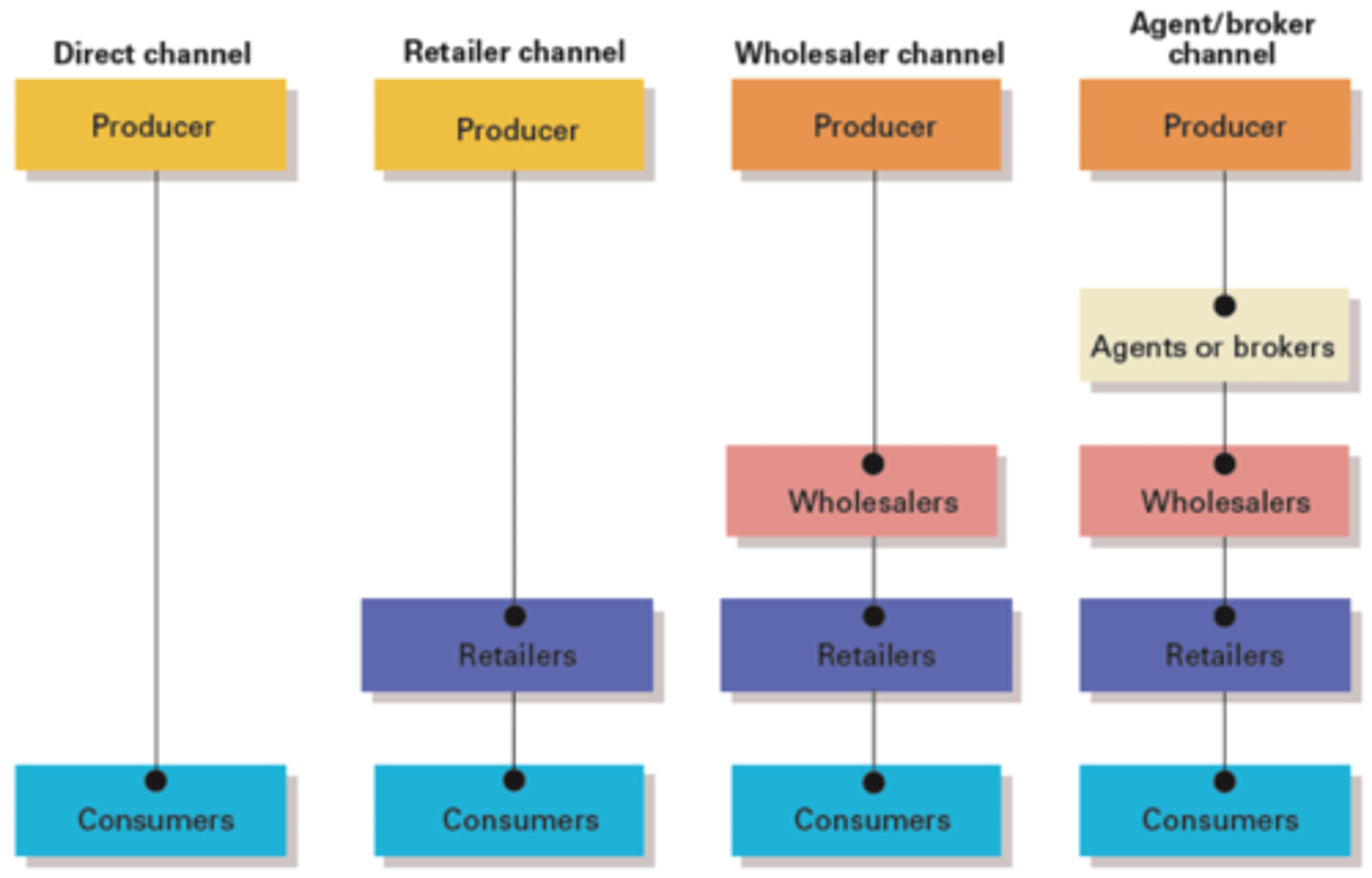
retailer
intermediaries who buy products from manufacturers and sell them to consumers for household use
wholesalers
intermediaries who buy from producers or from other wholesalers and sell to retailers (large quantities)
what kind of form can promotion take?
advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, publicity, social networking
Advertising
paid form of non-personal communication through mass media
advertising campaign
a series of related advertisements focusing on a common theme, slogan, and set of advertising appeals
personal selling
direct two-way communication with buyer
publicity
non-personal communication, and is presented as a news story, and not from originator
sales promotion
Short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or service
(CPA) certified public accountant
an individual who has been state certified to provide accounting services ranging from the preparation of financial records and the filing of tax returns to complex audits of corporate financial records
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
A law passed by Congress that requires the CEO and CFO to certify that their firm's financial statements are accurate. It required firms to be more rigorous in their accounting and reporting practices
bookkeeping
the recording of business transactions..day to day
cash flow
The movement of money through a business on a daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly basis.
annuel report
summary of a firm's financial information, products, and growth plans for owners and potential investors.
liability
debts a firm owes to others
assets
A firm's economic resources, or items of value that it owns, such as cash, inventory, land, equipment, buildings, and other tangible and intangible things.
Owner's Equity
doesnt have to be paid back.
O'E=assets-liabilities
double-entry bookkeeping
a system of recording and classifying business transactions that maintain the balance of the accounting equation
Accounting Cycle
the process by which companies produce their financial statements for a specific period
what is the four step procedure for the accounting cycle?
1. examining source documents (receipts)
2. recording transactions in journal (dated)
3. "posting" transactions into ledger
4. preparing financial statements
what are the three financial statements?
1. Income Statement
2. Balance Sheet
3. Statement of Cash Flows
Income Statement
"The bottom line" profitability over a period of time. profit or loss statement
Revenue (Sales)
The total amount of money received from the sale of goods or services, as well as from related business activities.
Cost of Goods Sold
the amount of money a firm spent to buy or produce the products it sold during the period to which the income statement applies
what consist of the income statement?
for company
1. revenue (sales)
2. costs of goods
3. profit
4. expenses
5. net income (net earnings)
Gross Income (profit / earnings)
earnings before interest and taxes...
profit= revenue - the cost of goods sold
expenses
The cost of assets consumed or services used in the process of generating revenues.
Net Income (earnings)
total profit after all expenses and taxes.
Balance Sheet
A "snapshot" of a company's financial position at a given moment.. ability to meet financial obligations
what consist of the balance sheet?
1. current assets
2.fixed assets
3.intangible assets
4.current liabilities
5. long-term liabilities
6. owners equity
assets
A firm's economic resources, or items of value that it owns, such as cash, inventory, land, equipment, buildings, and other tangible and intangible things.
order of assets and what they consist of
1. current assets- year or less (cash)
2. fixed assets- longer than one year (building)
3. intangible assets- value based on rights (patents)
Accounts Receivable (current assets)
money owed to company by clients promising to pay later
Liabilities
debts that you owe
Current Liabilities
a firm's financial obligations to short-term creditors, which must be repaid within one year.
Accounts Payable
A short-term liability that will be paid in the future and arise as a result of making credit purchases
long-term liabilities
liabilities owed for more than a year. (mortgages)
accrued expenses
all unpaid financial obligations incurred by an organization.
Depreciation
The process of spreading the costs of long-lived assets such as buildings and equipment over the total number of accounting periods in which they are expected to be used.
Statement of Cash Flows
the financial statement that identifies a firm's sources and uses of cash in a given accounting period. "cash in/out"
ratio analysis
measures financial health of organization
Profitability Ratios
Measures of the operating success of a company for a given period of time.
Financial Ratios
relationships determined from a firm's financial information and used for comparison purposes
profit margin
net income/net sales
Return on Assets (ROA)
Net Income/Total Assets
Return on Equity (investment) (ROI)
net income/ owners equity
Receivable Turnover
revenue / receivables
collect credit sales in year
Inventory Turnover
sales/ inventory
sells and replaces inventory
total assets turnover
sales/total assets
uses assets in creating sales
asset utilization ratios
ratios that measure how well a firm uses its assets to generate each $1 of sales
Liquidity Ratios
measure speed turn its assets into cash to meet short-term debt
current ratios
current assets/current liabilities
quick ratio (acid test)
(Current Assets - Inventory) / Current Liabilities
debt utilization ratios
ratios that measure how much debt an organization is using relative to other sources of capital, such as owners' equity
debt to total assets ratio
total liabilities/total assets