ANSC 2060 Exam 3 Ritchie
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
DAMNIT
degenerative, developmental, anomalies, allergies, metabolic, miscellaneous, nutritional, neoplastic, infectious, inflammatory, immune-mediated, toxic, traumatic
canine TPR
temp: 100-102.5°F
pulse: 60-160 / minute
respiratory: 10-30 / minute
feline TPR
temp: 100-102.5°F
pulse: 160-240 / minute
respiratory: 20-30 / minute
vaccines
a weakened biological agent meant to stimulate an immune response
how are vaccines delivered in animals?
subq
under the skin instead of intramuscular
role of vaccination
expose the naive immune system to viral and bacterial antigens
immune system will be able to recognize illness in future
killed vaccines
immunizations that are manufactured from dead versions of pathogens
ex: rabies
MLV (modified live vaccine)
weakened pathogen replicates in host
not capable of producing disease
stimulate a strong active immunity response
intranasal
short duration of immunity (6 months)
local immunity by IgA response
ex: kennel cough
MDA
maternally derived antibody
core vaccines
considered vital to all dogs based on risk of exposure, severity of disease or transmissibility to humans
non-core vaccines
given depending on the dog's exposure risk-dogs lifestyle and geographic distribution of disease
normal reactions to vaccines
soreness, fever, and/or decreased appetite
mild reactions to vaccines
hives, rash and/or swelling
severe reactions to vaccines
anaphylaxis
vaccine failure
failure to induce protective immunity
maternal antibody persistence, vaccine mishandling, expired, ill or immunocompromised animals
abscesses
opened or closed localized area of infection, lump containing pus
area is generally warm and painful
common hair loss and/or redness
causes: bites, fights
kennel cough
Bordetella bronchiseptica
infectious tracheobronchitis
highly contagious upper respiratory infection
prevention: vaccine
lyme disease
ixodes tick transmits
humans get rashes but rare in dogs
cat scratch disease
bacterial infection of the species bartonella
causes infections in people
fleas involved
leptospirosis
spiral shaped bacteria called leptospires
zoonotic - number one disease worldwide
spread through urine
pyoderma
staphylococcus pseudintermedius
not contagious or zoonotic
mild to severe
localized hot spots
treatments: antibiotics, shampoos
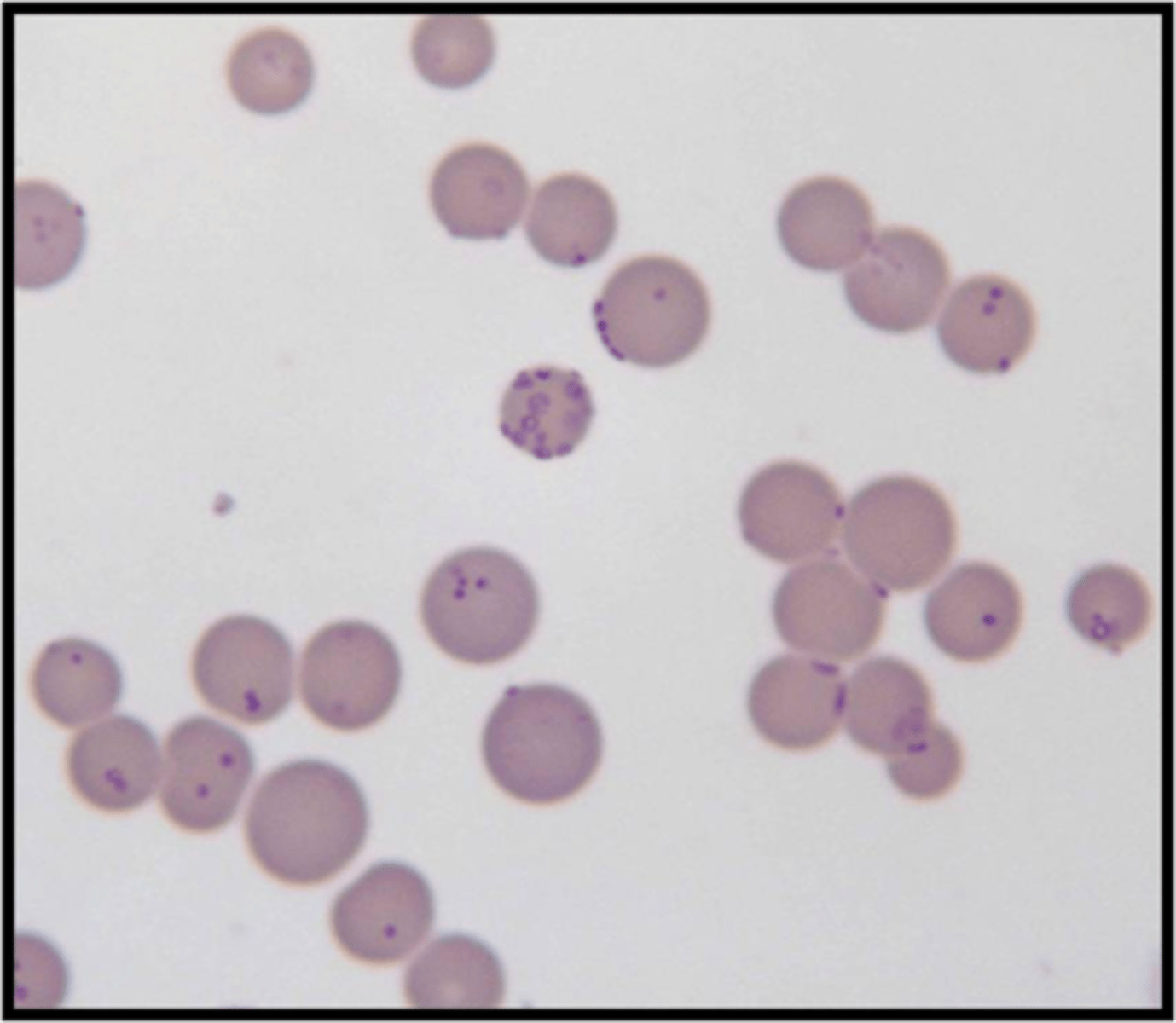
mycoplasmas
bacteria that naturally lack a cell wall
mycoplasma hemofelis
infect RBCs of cats
causes feline infectious anemia
transfusions
tetracyclines treat
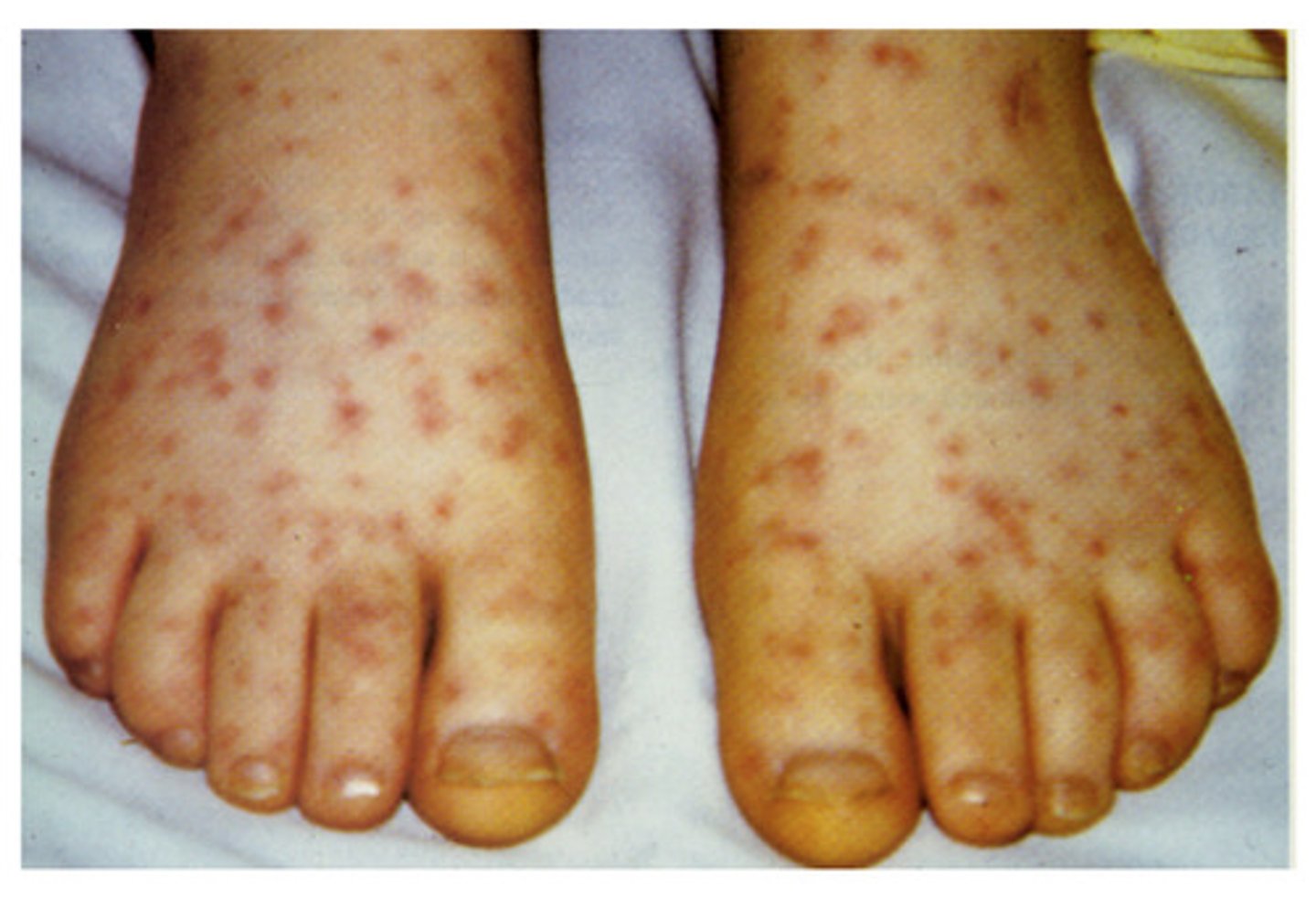
ehrlichiosis
transmitted by ticks
rocky mountain spotted fever
Rickettsia rickettsii
transmitted by dermacentor ticks
signs: fever, bruising/bleeding, lymphadenopathy
not a true zoonotic disease but can catch it if bitten
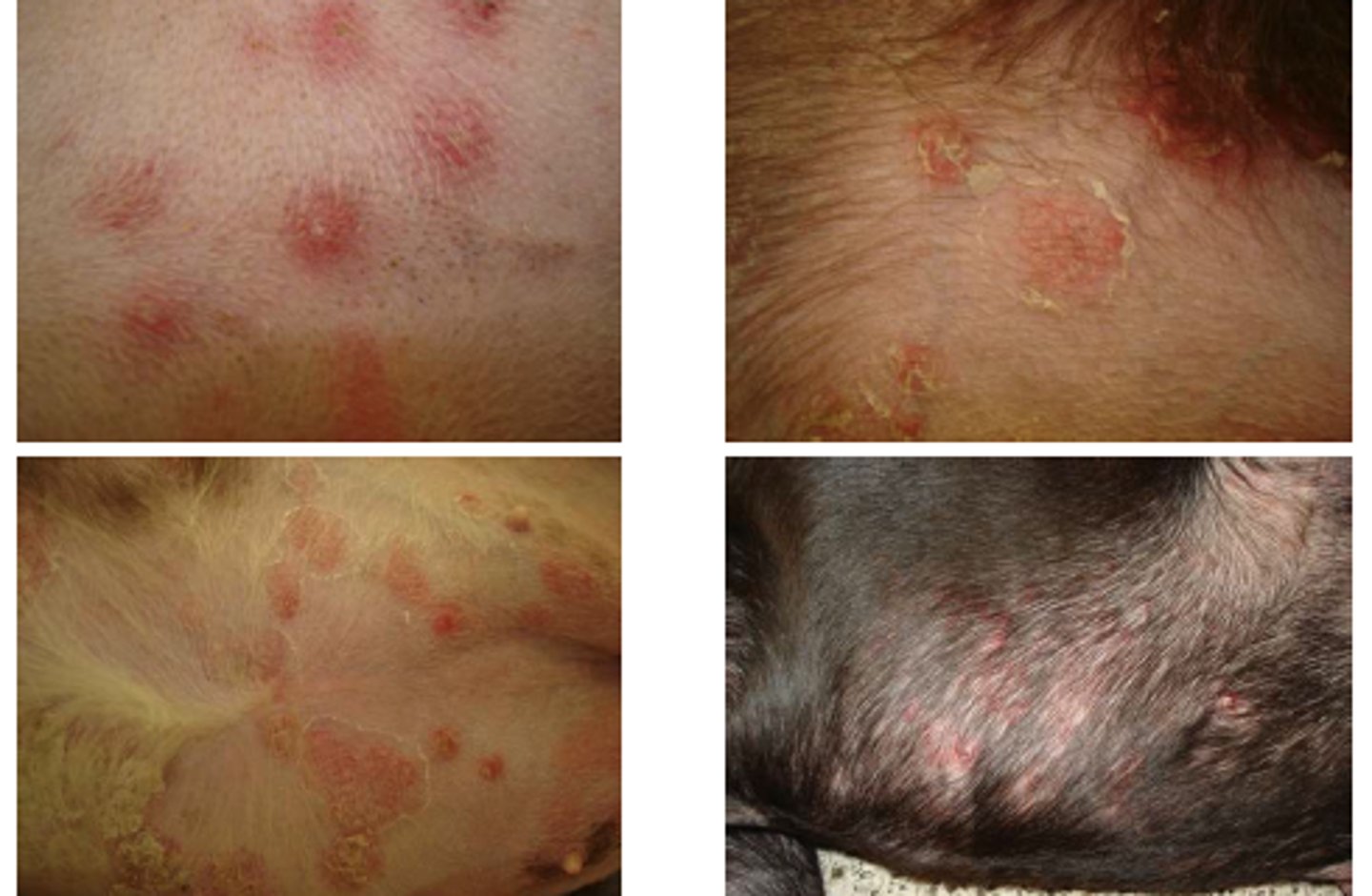
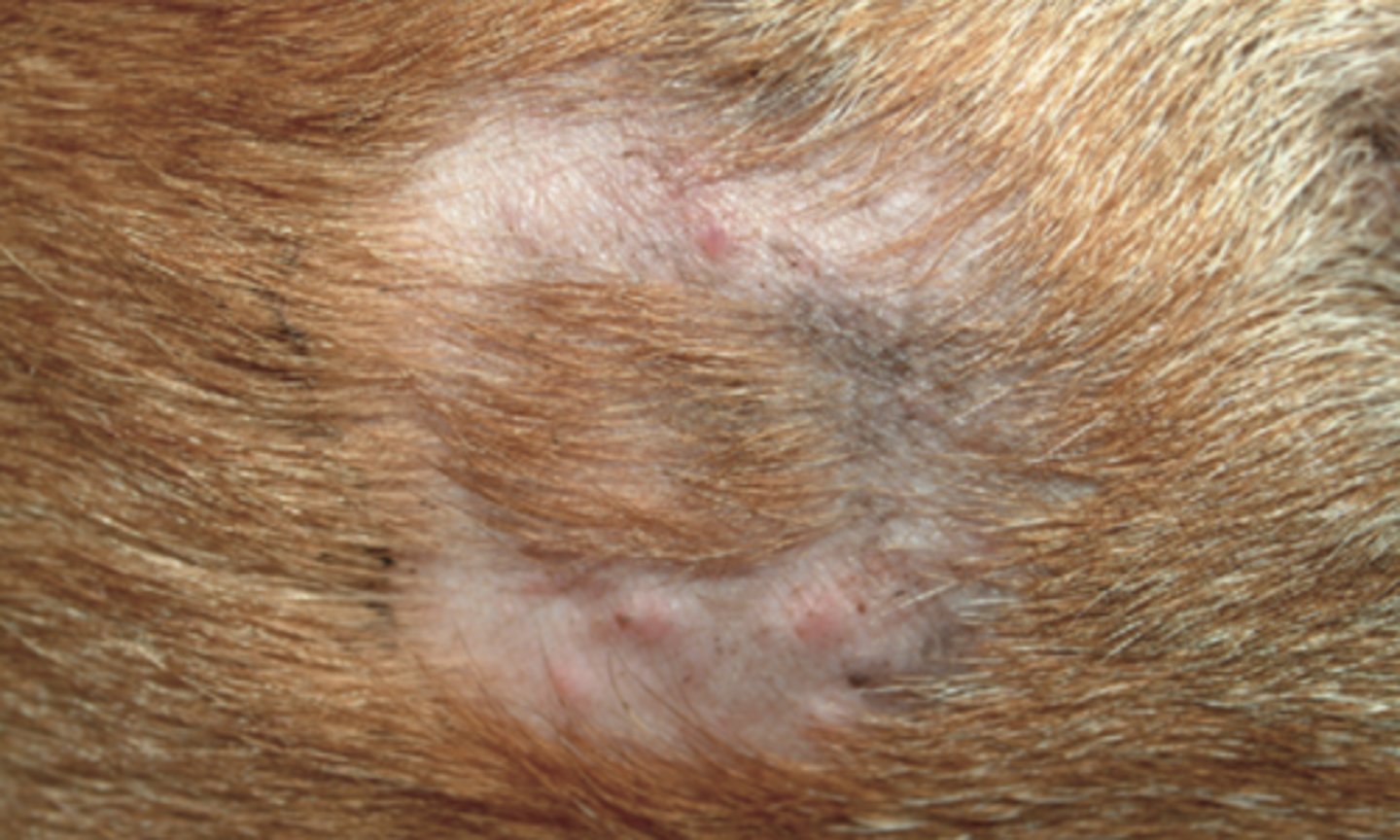
dermatophytosis
ringworm (zoonotic)
malassezia
yeast dermatitis
normal flora
ear canal, between toes, rectum
signs: hair loss, recurrent ear, skin infections
blastomycosis
Blastomyces dermatitidis
soil fungus
spores inhaled
young male large breed most at risk
signs: coughing, pneumonia, weight loss, skin lesions
histoplasmosis
Histoplasma capsulatum
contaminated soil with bird or bat poop
signs: coughing, fungal pneumonia, fever, diarrhea, weight loss
sporothrix
worldwide in soils rich in decaying organic matter
considered to be an emerging zoonotic disease
anatomy
form and structure of an animal
physiology
discipline that studies the way a body operates
integumentary system
skin and hair coat
many diseases manifest in skin-largest organ
functions of skin: vitamin D psychosis, metabolism, protection
2 layers to integumentary system
epidermis and dermis
epidermis
epithelial cells with keratin
avascular
dermis
deeper than epidermis
connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, specialized muscles
appendages-sweat and sebaceous glands, hair follicles
hair
project caudally and ventrally to shed water
compound hair follicles - multiple hairs in one opening
growth occurs in cycles
influenced by: genetics, photoperiod, ambient temps, hormones, overall health
skeletal system
functions: minerals movement, circulating calcium
felines:
- short jaw to hold prey
- large eye sockets (visual hunter)
canines:
- dolichocephalic
- mesaticephalic
- brachycephalic
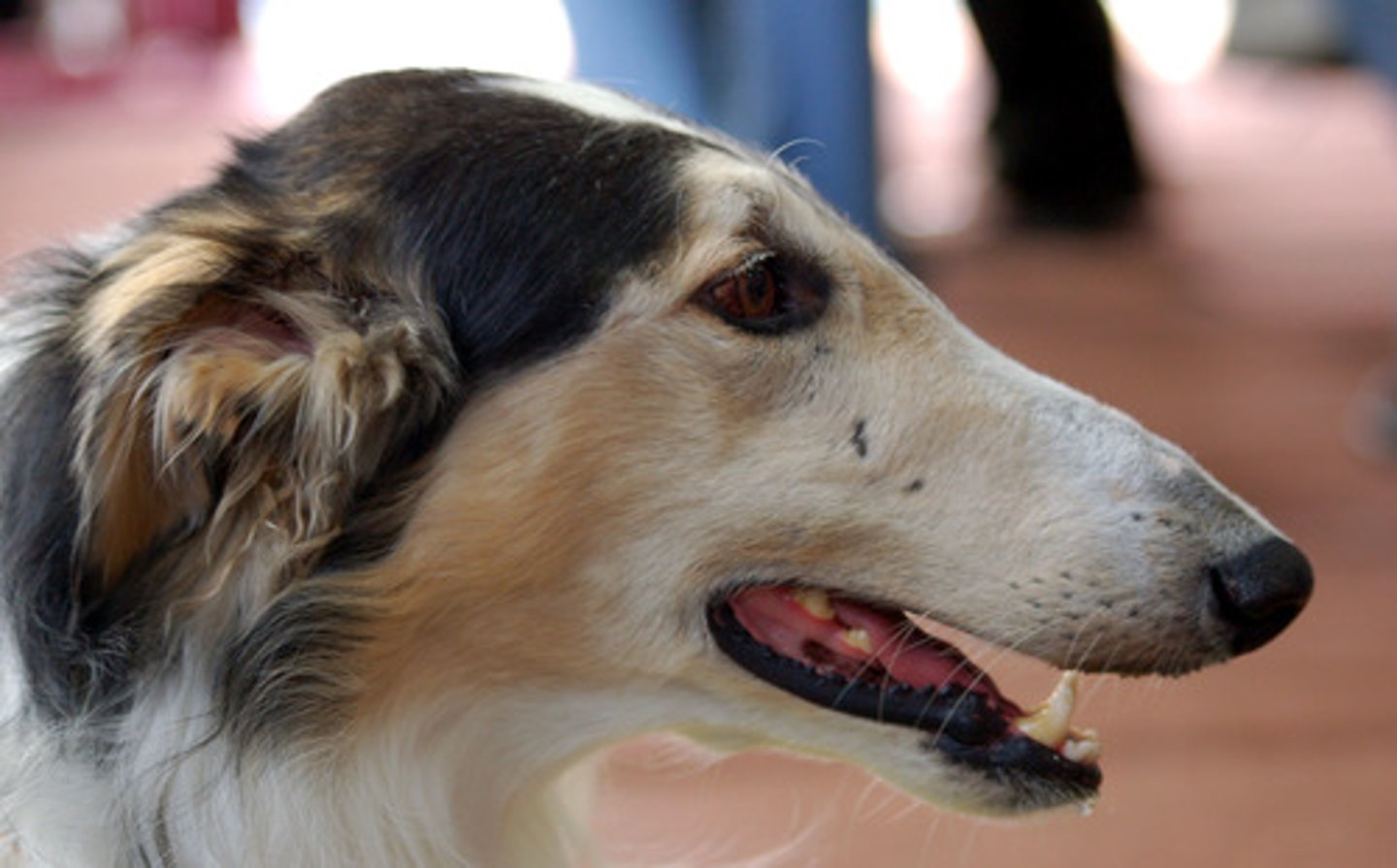
dolichocephalic skull
a long, narrow skull (Greyhound)

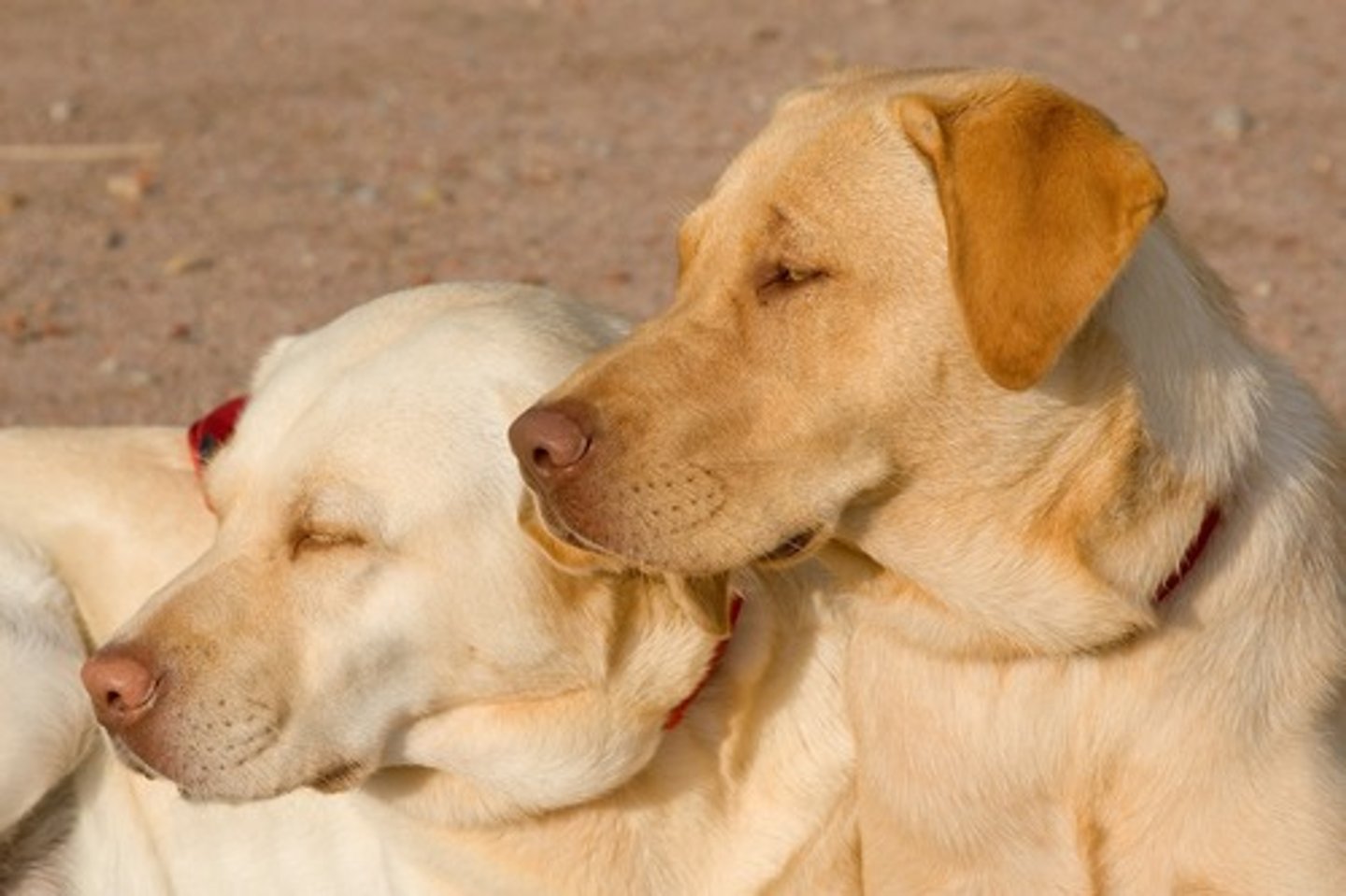
mesaticephalic skull
medium skull (Labrador)

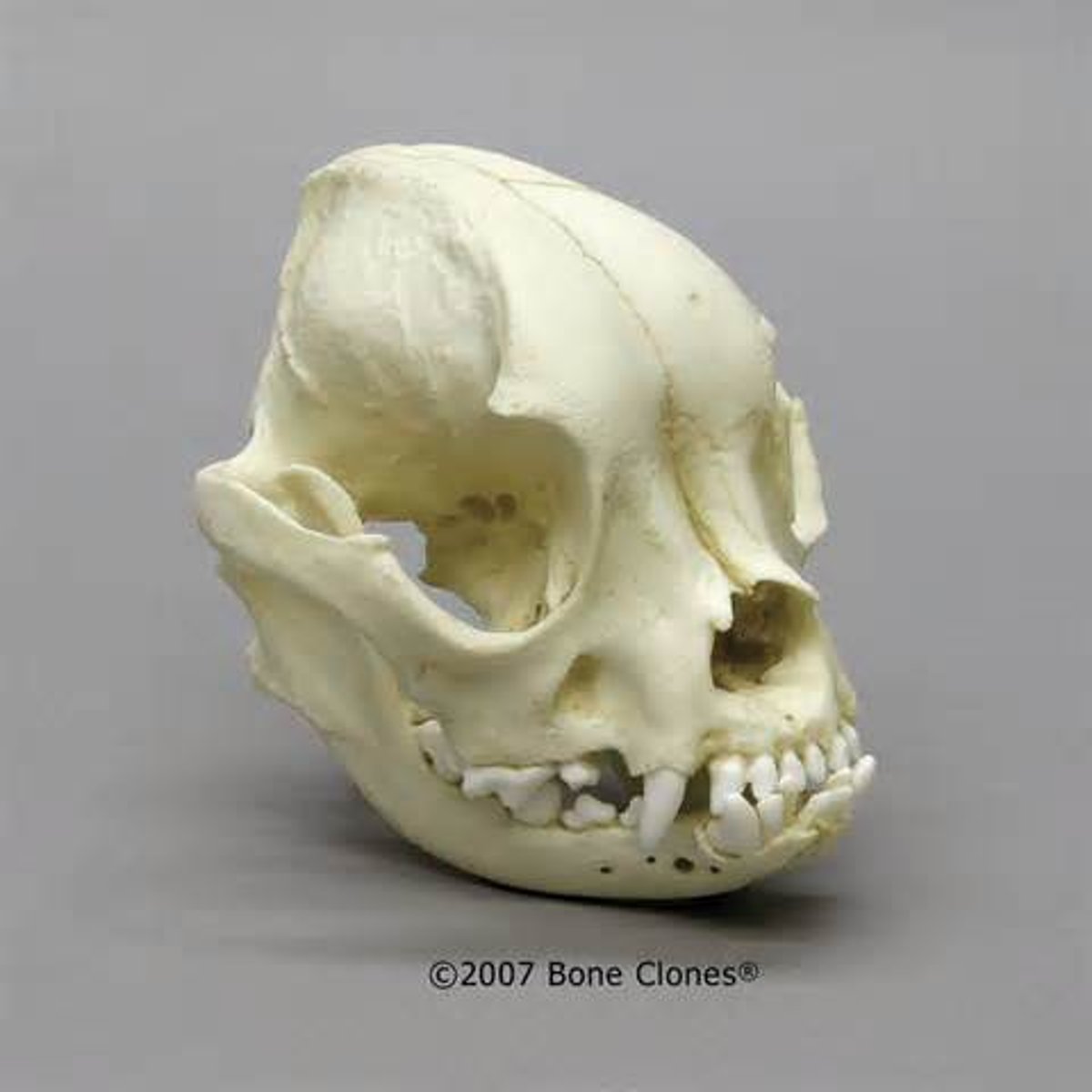
brachycephalic skull
broad skull base and short length (e.g., Pug, Pekingese).

teeth
incisors, canines, premolars, molars
dogs are omnivorous - pointed and flat teeth
cats are carnivores - pointed teeth
vertebrate
locomotion, protection of spinal cord
all mammals have 7 cervical
c1: atlas
c2: axis
which two vertebrates allow the movement of yes and no
c1 and c2
forequarters
stride and movement
shoulder blade, scapula, humerus, radius and ulna
hindquarters
pelvis-sacrum, femur, pubis, tibia and fibula, feet
coxofemeral joint
hip joint, ball and socket
synovial
knee
stifle joint
patella
cat claw
muscular system
functions: circulation, breathing
voluntary: skeletal
involuntary: smooth and cardiac
smooth muscles
hollow organs, blood vessels, respiratory tract, uterus, stomach, intestine
involuntary
nonstriated
controlled by ANS and hormones
cardiac muscle
heart
involuntary, striated
arranged in networks to provide controlled pumping action of heart
controlled by ANS and hormones
skeletal muscle
many attached to bones to coordinate movement
voluntary, striated (orderly arrangement of fibers)
circulatory system
heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, lymphatic vessels
bone marrow: creates red blood cells
spleen: filters waste
lymph nodes: filters, important for immune function
systemic circulation
supplies tissues
pulmonary circulation
vessels that go to the lungs (deoxygenated from lungs)
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
veins
carry blood to the heart
mammalian heart
4 chambers
located in ventral thorax (chest cavity)
SA node: pacemaker for heart
lymphatic system
circulate immune cells throughout body and remove antigens
filter foreign substances and produce lymphocytes
solid portion of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
liquid portion of blood
plasma
central palure
middle thinness at maturity
RBC do not have a nucleus but filled with hemoglobin
3 functions of the respiratory system
1. deliver oxygen to tissues in lungs
2. breathing, smelling
3. removes waste gases
nares
nasal turbinates-cililated
pharynx
throat
epiglottis
flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering
larynx
passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
trachea
windpipe
c-shaped cartilaginous rings for protection
where does gas exchange occur
alveoli
depth of lungs
Two parts of the nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
nerve cells
neurons
purpose of pns
integration
receives info and makes sense of it
ex: collecting scent molecules and sending to brain
parts of cns
cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, spinal cord
cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory.
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination, sense of space
cerebellar hypoplasia
underdeveloped cerebellum
brain stem
pons and medulla oblongata
life sustaining functions: heart rate, swallowing
can integrate info like brain
can the brain stem sustain trauma like the brain?
no
meninges
covers CNS
epidural space - between meninges and CNS
parts of PNS
somatic and autonomic
somatic nervous system
supply muscles
brachial plexus, radial nerve, sciatic nerve
autonomic nervous system
supply glands, blood vessels, heart, smooth muscle movement
sympathetic and parasympathetic branches
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
urinary system
2 kidneys and ureters, 1 bladder and urethra
kidneys
paired, ventral to lumbar vertebrae
millions of nephrons that produce urine
maintain proper hydration
ureters
The tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
bladder
stores urine
micturition: brain tells muscles to relax and urine is expelled
lined with smooth muscle
urethra
urine exits body here
cornea
clear window in front, captures light
sclera
white, thick tissue
medial and lateral canthus
upper and lower eyelids meet
naslacrimal duct
near medial
drains tears
Palpebrae
upper and lower eyelids
lined with cilia
nictitating membrane
third eyelid
protection, tear production
taste
gustation