Dental Anatomy and Terminology Flashcards
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from a dental anatomy lecture, focusing on dentitions, tooth types, numbering systems, terminology, and clinical considerations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is a dentition?
The natural teeth in the jaws.
What are the two dentitions a person has during a lifetime?
Primary and permanent.
What is the goal of every dental professional regarding dentition?
To assist in keeping each dentition healthy, functional, and esthetic mainly by preserving the existing teeth within it.
What is a dental prosthesis?
An intraoral replacement used to restore intraoral defects within each dentition; examples include dental veneers, crowns, dental bridges, dentures, and dental implants.
What is prosthodontics?
The dental specialty that focuses on therapy using dental prostheses.
What is the deciduous dentition?
Another term for the primary dentition, referring to the fact that the primary teeth are shed and replaced by permanent teeth.
What is another name that patients call the permanent teeth?
The adult teeth.
What tooth types are included in both arches within the primary dentition?
8 incisors, 4 canines, and 8 molars, for a total of 20 teeth.
What tooth types are included in both arches within the permanent dentition?
8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, and 12 molars, for a total of 32 teeth.
What is the Universal Numbering System (UNS)?
A system used in the United States for the designation of both dentitions, using capital letters for primary teeth and digits for permanent teeth.
In the UNS, how are the primary teeth designated in a consecutive arrangement?
Starting with the maxillary right second molar, moving clockwise and ending with the mandibular right second molar.
What is the International Numbering System (INS)?
A system that can be used internationally as well as by electronic data transfer, designating teeth using a two-digit code.
How are teeth designated from each other using the two-digit code in the INS?
The first digit indicates the quadrant (1-4 for permanent, 5-8 for primary) and the second digit indicates the tooth's position in the quadrant.
What is the Palmer Notation Method?
A system that uses a right-angle symbol indicating the quadrants and arch, with the tooth number placed inside, allowing immediate discussion of teeth needing treatment.
What are the three dentition periods throughout a person's lifetime?
Primary, mixed, and permanent.
When does the primary dentition period begin and end?
Begins with the eruption of the primary mandibular central incisors and occurs between approximately 6 months and 6 years of age.
When does the mixed dentition period begin and end?
Occurs between approximately 6 and 12 years of age, with both primary and permanent teeth present.
When does the permanent dentition period begin?
Begins with shedding of the last primary tooth and occurs approximately after 12 years of age.
What are some characteristics of the child to adolescent patient's smile during the mixed dentition period?
Temporary edentulous areas and dentition crowding.
What is the alveolus?
The bone of the tooth socket.
What is the alveolar process?
The tooth-bearing part of each jaw.
What is occlusion?
Contact between the teeth of the mandibular arch and the maxillary arch; also describes the anatomic alignment of the teeth.
What teeth are considered anterior teeth?
Incisors and canines.
What teeth are considered posterior teeth?
Molars (and premolars, if present).
What are the four quadrants of the oral cavity?
Maxillary right, maxillary left, mandibular right, and mandibular left.
What is the correct sequence of words when describing an individual tooth using a D-A-Q-T System?
Dentition, arch, quadrant, and tooth type.
What the sextants of the mouth?
Right posterior sextant, anterior sextant, and left posterior sextant.
What covers the dentin of both the crown and root of teeth?
Enamel covers dentin in the crown, and cementum covers dentin in the root.
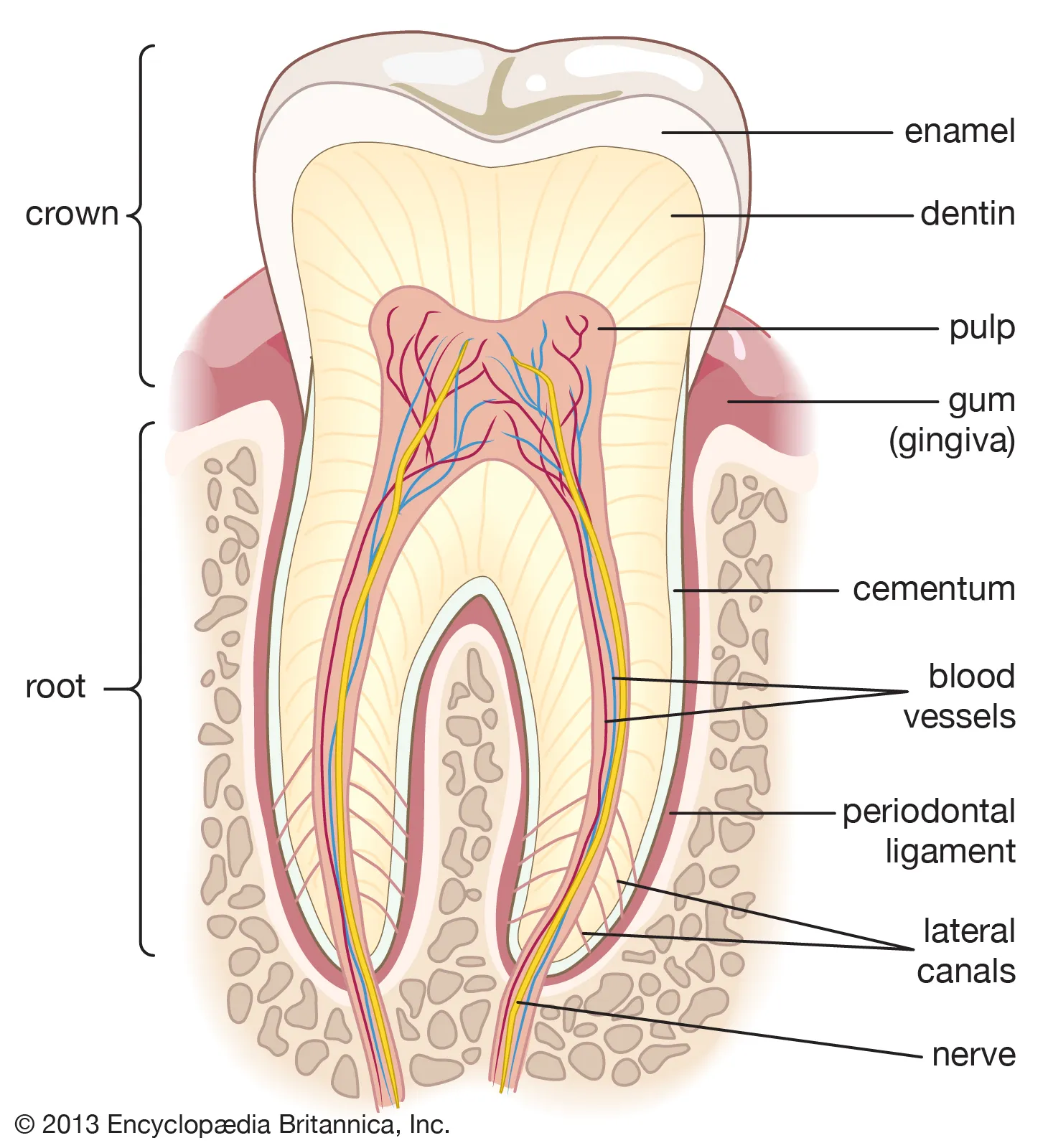
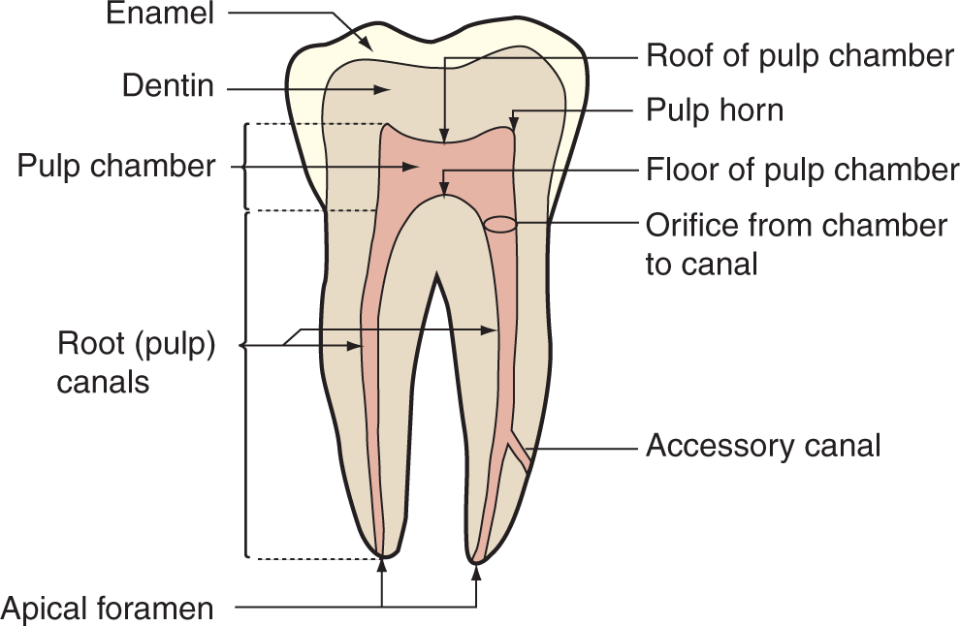
What are the components of the pulp cavity?
Pulp chamber, pulp canal (or canals) with an apical foramen (or foramina), and may have pulp horn (or horns).
What is the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
An external junction noted at the neck or cervix of the tooth where the enamel of the crown and cementum of the root meet.
What is the anatomic crown?
That part of the crown covered by enamel; it remains mostly constant throughout life, except for attrition and other physical wear.
What is the clinical crown?
That part of the crown that is observable and not covered by the gingiva; it is only a part of the anatomic crown.
What is the root axis line (RAL)?
A reference line representing the long axis of the tooth drawn in the center of the root.
What are the three basic shapes to the roots on cervical cross section?
Triangular, oval, and elliptical.
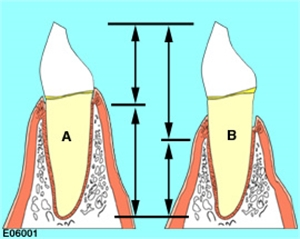
What is the crown-to-root ratio?
The ratio of the length of the part of the tooth that appears superior to the alveolar process versus what is inferior to it.
What is the facial tooth surface?
The tooth surface closest to the facial surface (labial on anteriors, buccal on posteriors).
What is the lingual tooth surface?
The tooth surface closest to the tongue (sometimes also considered palatal on the maxillary arch).
What is the masticatory tooth surface?
The chewing surface on the most superior surface of the crown (incisal for anteriors, occlusal for posteriors).
What are the mesial and distal tooth surfaces?
The surface closest or more anterior to the midline, and the surface farthest or more posterior from the midline.
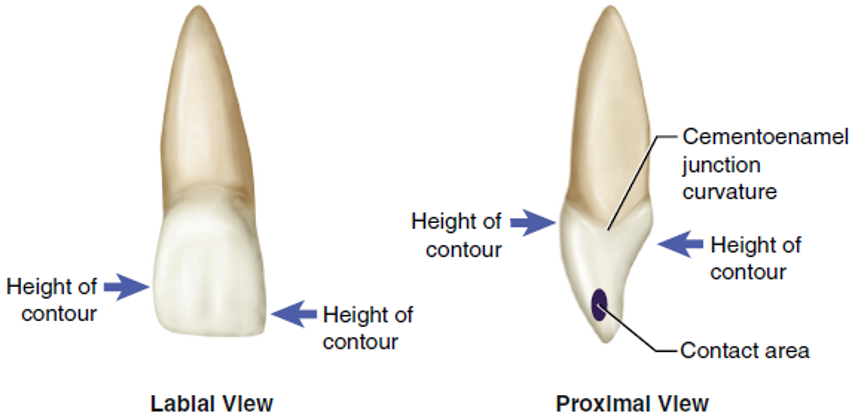
What is the contact area?
The area where the crowns of adjacent teeth in the same arch physically touch each adjacent proximal surface when in an ideal alignment.
What is the height of contour?
the greatest bulge or elevation on the crown.
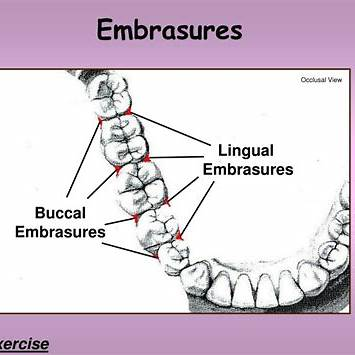
What are embrasures?
Triangular-shaped spaces between two teeth, caused by the sloping away of both the mesial and distal surfaces, that diverge facially, lingually, occlusally, and apically.
How is the size of facial embrasures related to lingual embrasures?
Facial embrasures are generally narrower than lingual embrasures. The curvature of teeth are typically more pronounced on the lingual side, allowing for a larger embrasure.
What is a line angle?
The junction of two crown surfaces, named by combining the names of the two surfaces.
What is a point angle?
The junction of three crown surfaces, named after the three surfaces.
Where is the facial height of contour located?
Located in the cervical third when viewed from the proximal surfaces.
What is Digital Smile Design (DSD)?
A technical tool to design and modify a patient's smile digitally, allowing patients to visualize the smile before treatment.
What is the function of incisors?
Biting and cutting food.
What is the function of canines?
Seizing, piercing, and tearing food.
What is the function of premolars?
Assist canines in piercing and tearing food and assist molars in grinding food.
What is the function of molars?
Grinding food.
What is Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)?
A variation of conventional computed tomography (CT) that rotates around the patient, capturing data with a cone-shaped radiation beam to reconstruct a 3D image.