Block 5 - Manufacture of Modern Firearms
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What is one of the more common methods used in firearms manufacturing?
Broaching
In which machining process is the barrel held in place and rotated at the desired twist rate while a broach passes through it?
Broaching
Parallel lines on lands/grooves can be indicative of which machining process?
Broaching
What are some advantages of broaching?
Fast
Less stress on barrel
What are some disadvantages of broaching?
Broaches are expensive
New configurations require new broaches
Broached barrels must be lapped
Increased potential for subclass carryover
In which machining process is a button bearing a negative form of the finished lands and grooves pushed/pulled through a smooth bore of slightly smaller diameter?
Button rifling
What are some advantages of button rifling?
Fast and economical
Doesn’t require lapping
Barrel easier to clean and maintain due to smooth surfaces
Consistent and accurate
What are some disadvantages of button rifling?
Buttons are expensive to make
Different groove/twist configurations require a new button
Barrels must be stress relieved after rifling
Button rifling is a _____ working process.
Cold forming
Button rifling typically creates _____ marks that are often removed from the grooves but remain on the lands.
Perpendicular
In which machining process is a drilled and reamed barrel compressed onto a mandrel which bears the negative shape of the finishing rifling?
Hammer forging
What are some advantages of hammer forging?
More durable barrels
More consistent barrels
What are some disadvantages of hammer forging?
Machinery and mandrels are expensive
Can introduce stress into the barrel
Leaves few individual characteristics
Hammer forging can leave what type of marks on the outside of the barrel?
Peening
Hammer forging can also form the _____ and _____ if desired.
Chamber; throat
True or false: Hammer forging can produce both polygonal and traditional rifling.
True
In which machining process is a single point hook shaped cutter pulled through a barrel, cutting one groove at a time?
Hook cutting
What are some advantages of hook cutting?
Groove characteristics can be changed easily
Consistent twist
Little stress on barrel
What are some disadvantages of hook cutting?
Slow method
More expensive
Increased potential for subclass carryover
_____ is one of the oldest barrel rifling machining methods.
Hook cutting
In which machining method is a multi-point cutter pushed/pulled into a barrel to cut/scrape two opposed grooves simultaneously?
Scrape cutting
What is the main disadvantage of scrape cutting?
Increased potential for subclass carryover
In which machining method are the barrel and electrode placed in electrolyte, followed by the electrode travelling down the barrel at the desired rate of twist, removing the metal using electrolysis?
ECM
What are some advantages of ECM machining?
Short timeframe
No tool wear
More consistent/accurate
Can cut any metal
What are some disadvantages of ECM machining?
High equipment costs
Requires strong acids and neutralizers
What company uses ECM machining for rifling revolver barrels?
Smith & Wesson
True or False: In ECM machining, the barrel and electrode come into contact.
False
What type of machining can leave randomized pock marks/voids in grooves, creating a lower potential for subclass carryover?
ECM
In which machining method are both the workpiece and tool electrode immersed in dielectric fluid and moved close together, generating sparks that vaporize tiny pieces of both electrodes?
EDM
What are some advantages of EDM machining?
Precise
Useful for hard material
What are some disadvantages of EDM machining?
Slow
High electricity consumption
Expensive machinery
EDM machining is also known as _____.
Spark machining
EDM machining is more likely to be used to create dies for other manufacturers, such as _____.
Bunter tools
What type of machining can leave a pitted/granular appearance, resulting in a lower potential for subclass carryover?
EDM
In which machining process is wax injected into a die forming a wax pattern, which is then attached to a tree that is coated in a ceramic slurry that creates a mold?
Investment casting
What are some advantages of investment casting?
Potentially good surface finish
Material versatility
What are some disadvantages of investment casting?
Poorly defined rifling
Presence of deformities
No distinctive directional twist
Some potential for subclass
What manufacturer uses investment casting for some parts?
Ruger
The reaming out of a chamber in the end of a barrel blank
Chambering
Any of various forms of muzzle treatment meant primarily to protect rifling.
Crown
Beveling a sharp external edge
Chamfering
The smoothing of the tops of the lands of a rifled barrel by the forced passage of a hardened steel ball of appropriate diameter
Ball Burnishing/Ballizing
The process of driving a piece of lead through the bore of a rifled barrel to determine the minimum bore and groove diameters
Bore Slugging
_____ is a multi-step manufacturing process that combines metal powders with a plastic binder into a solid metal part through molding, debinding, and sintering.
Metal injection molding
What are some advantages of MIM?
Form small, complex shapes
Significant cost savings
Comparable hardness to traditional molds
What are some disadvantages of MIM?
Expensive equipment
Long manufacturing times
Dedicated, single part molds
What are some parts commonly manufacturing using MIM?
Trigger
Hammer
Sear
Extractor
In MIM, a ____ is the initial molded form created by injecting a mixture of metal powder and binder into a mold?
Green part
In MIM, a _____ is porous, fragile part left behind after the debinding process.
Brown part
_____ carries an increased potential for subclass carryover due to reusing the same mold.
MIM
What are the two categories of metal forming?
Gross
Fine
_____ reduces raw metal stock to a rough form that is intermediate to the required shape.
Gross forming
_____ renders the intermediate form to its final dimensions, with the exception of parts requiring hand fitting.
Fine forming
What are the two main types of gross forming?
Casting
Forging
_____ is a subcategory of forging.
Stamping
What are the different types of casting used in the manufacture of firearms?
Sand
Wax
Investment
Die
What are the two different types of machine forging used in the manufacture of firearms?
Hammer
Press
In _____, force is applied via a ram or drop hammer in one or two sharp blows
Hammer forging
In _____, force is applied slowly, providing greater control of the material
Press forging
What are some benefits of machine forging?
Better strength/durability
Minimal variations in grain structure
List five types of fine forming operations.
Drilling
Turning
Grinding
Milling
Broaching
List the 8 basic steps of manufacturing a barrel from a steel blank.
Cut to length
Deep hole drilling
Reaming
Rifling
Lapping
Straightening
Contouring/Profiling
Chambering/Throating
List four types of common cosmetic finishing applications on firearm parts.
Bluing
Electroplating
Anodizing
Parkerization
_____ is used as protective anti-corrosive on steel parts and imparts a blue-black appearance.
Bluing
_____ adds a protective coating and bright finish.
Electroplating
_____ provides a protective coating for aluminum/titanium by using an electrical current.
Anodizing
_____ converts iron on the surface of metal by using phosphoric acid and imparts a gray/black matte coloring.
Parkerization
_____ refers to helical grooves cut or impressed into the bore of a firearm barrel to impart rotary motion to a projectile when fired.
Rifling
What is rifling twist rate?
The rate at which the rifling of the firearm turns within the bore
What is rifling pitch?
The angle at which the rifling is cut in relation to the axis of the bore
A higher rifling pitch will create _____ angled rifling on the projectile.
More
_____ is the typical type of rifling found in many barrels and has sharp, defined lands and grooves.
Conventional
_____ refers to rifling in which the lands and grooves have a more rounded profile than in conventional rifling.
Polygonal
Name three common manufacturers that manufacture polygonally rifled barrels.
Glock
HK
Walther
What are the five major contributors to the workpiece surface?
BUE
Shearing
Plowing
Sideflow
Tool wear
_____ is the source of individual characteristics.
Surface roughness
_____ is when a piece of BUE is displaced into the workpiece rather than forming a chip, creating an uneven surface.
Plowing
_____ is the plastic deformation of workpiece material displaced to the side of the area being cut by the tool.
Sideflow
_____ involves the complete removal of metal being cut and extracted from the surface.
Shearing
_____ occurs when there is vibration either in the workpiece, tool, or both during machining.
Chatter
List three different types of tool wear.
Abrasive
Adhesive
Diffusive
_____ tool wear involves material loss due to rubbing/friction when a harder material contacts a softer one.
Abrasive
In _____ tool wear, the substrate being cut bonds to the cutting tool with enough strength to supersede the adherence of the cutting tool material to itself.
Adhesive
_____ tool wear is the progressive loss of material from one surface to another.
Diffusive
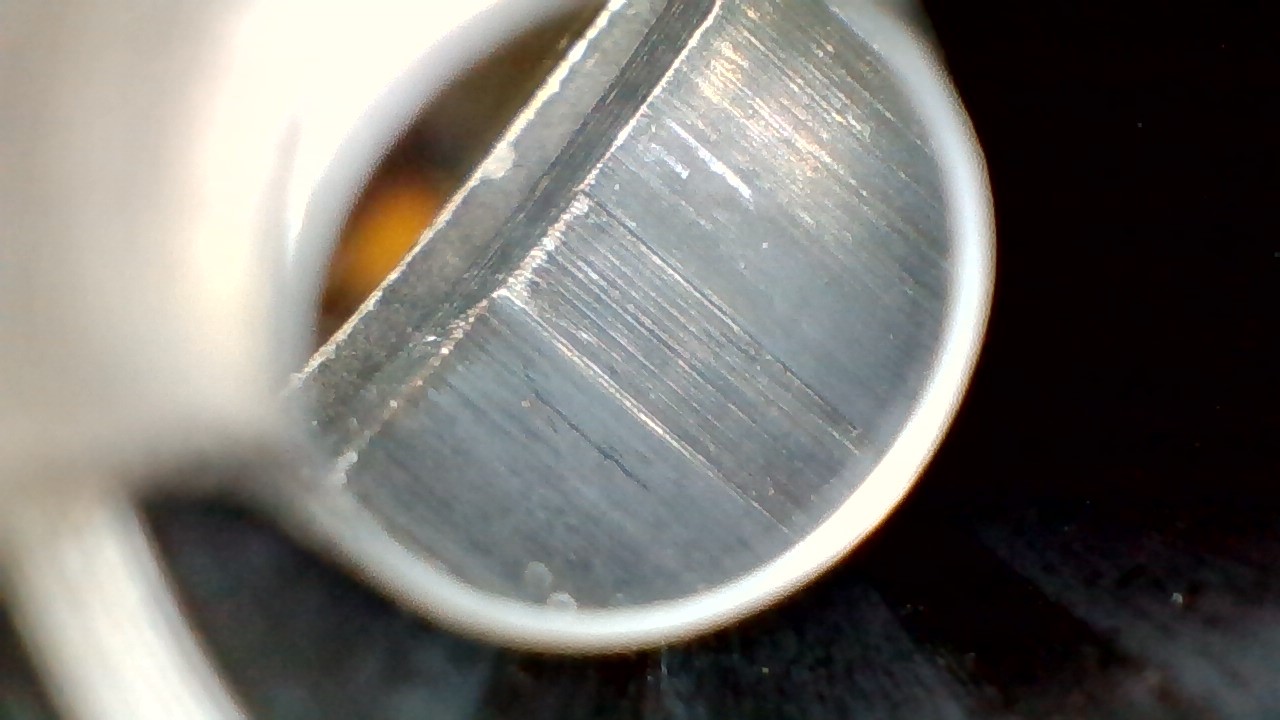

What type of machining likely created the continuous lines running parallel to the rifling (mostly on the lands) seen in this barrel?
Broaching
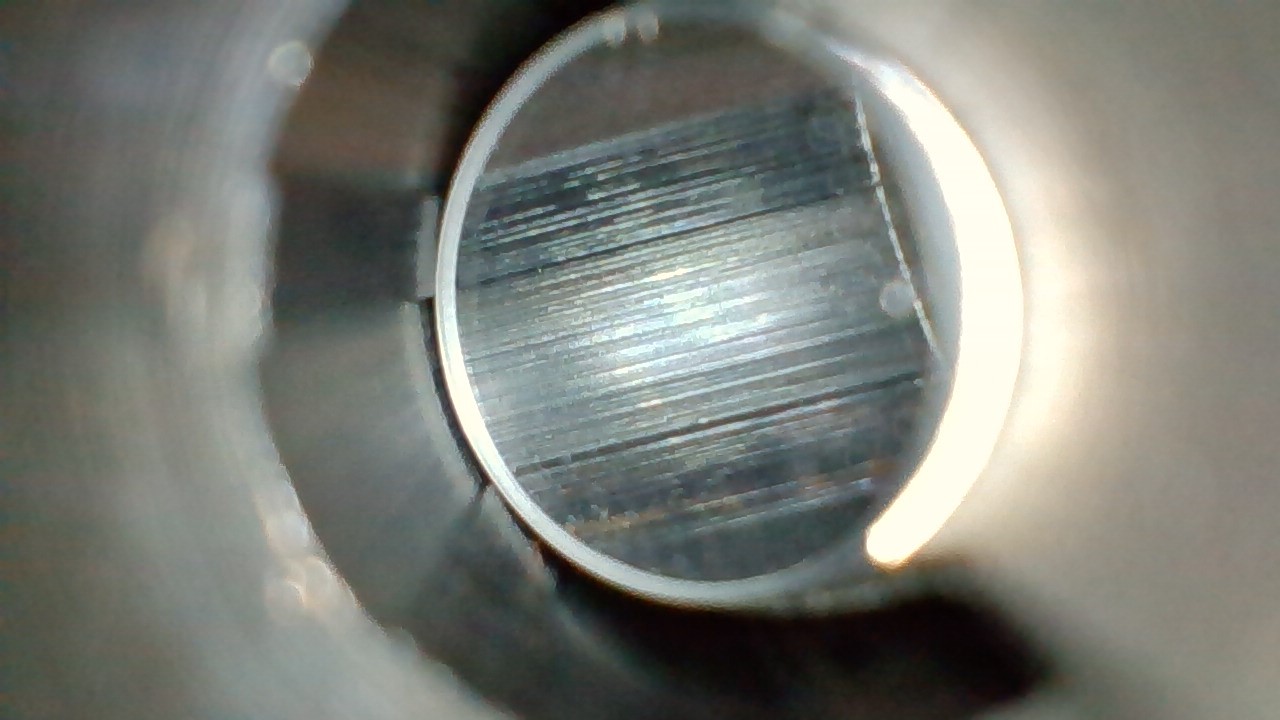
What type of machining likely created the continuous lines running parallel to the rifling (in the lands and grooves) seen in this barrel?
Double broaching
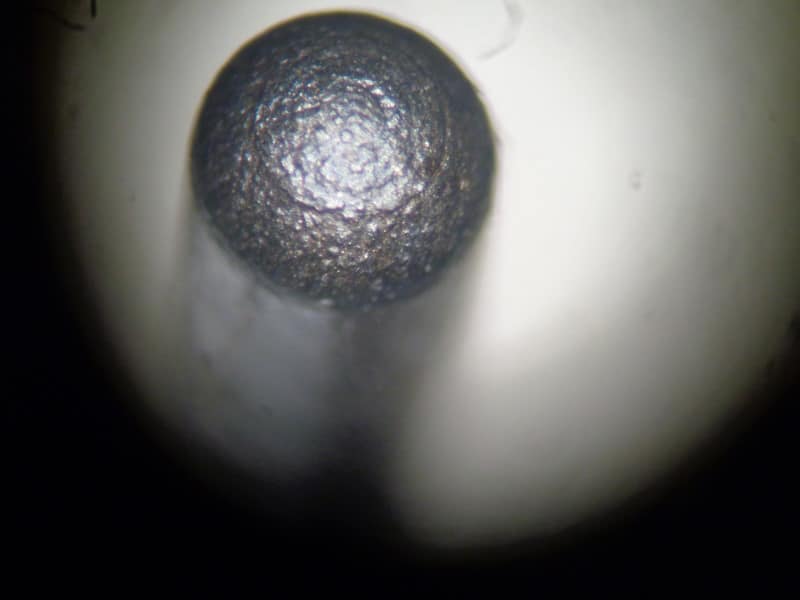
What type of machining likely created the granular pattern seen on this firing pin?
EDM
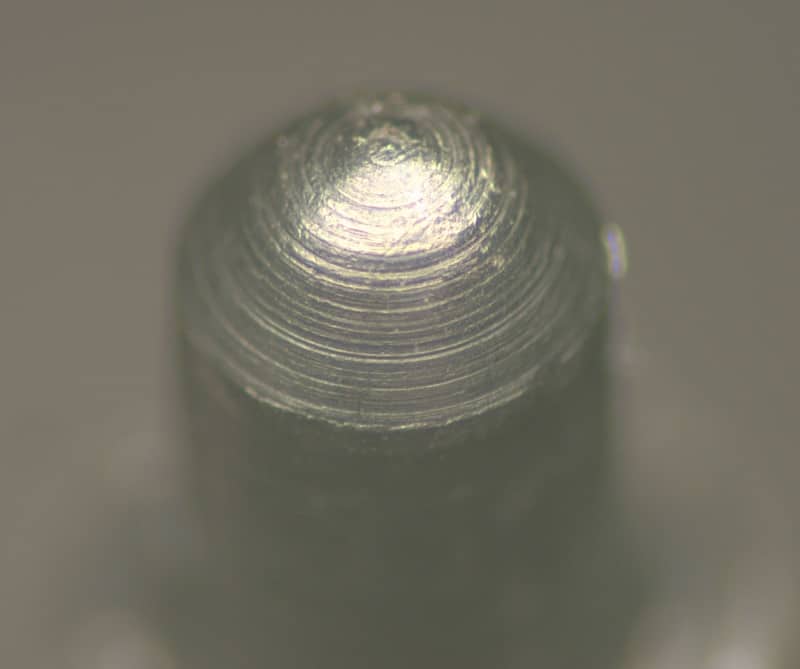

What type of machining likely created the concentric rings seen on this firing pin?
Lathe turning
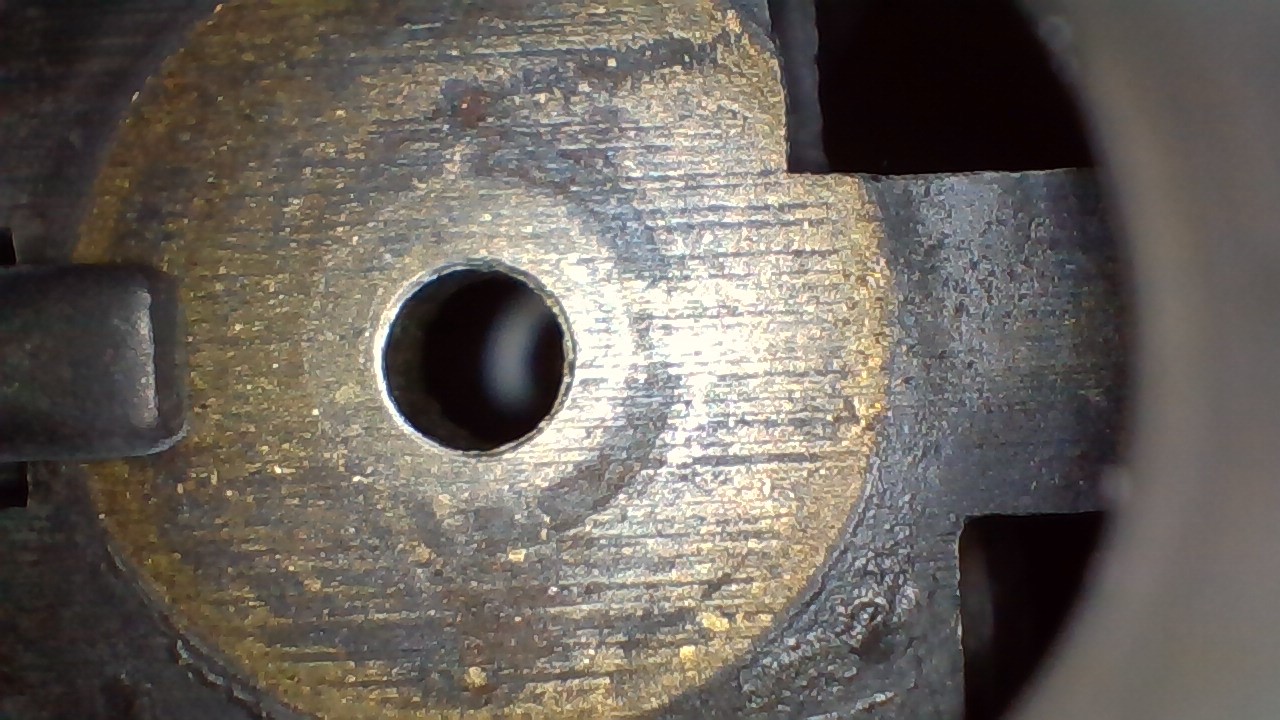

What type of machining likely created the continuous parallel lines seen on this breechface?
Gang broaching
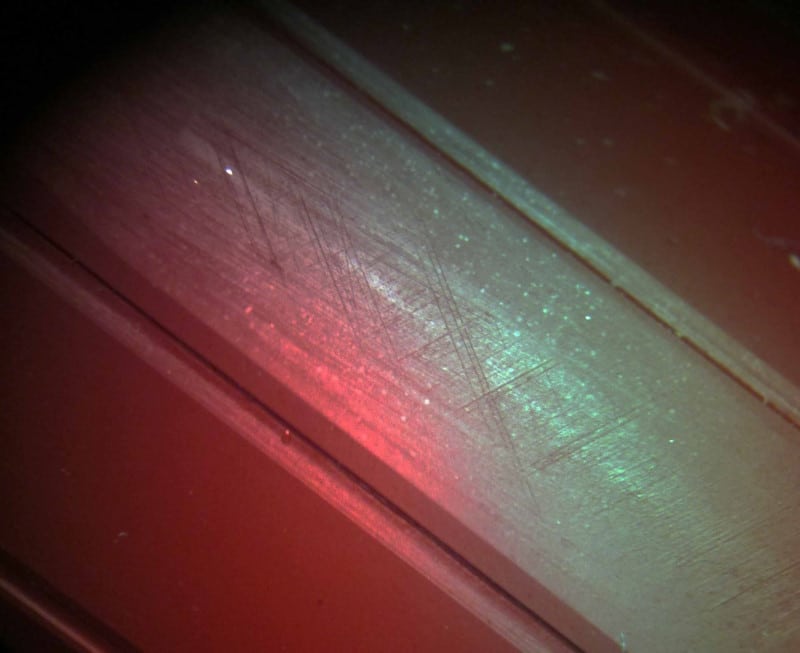

What type of machining likely created the crosshatch marks seen in this barrel?
Honing
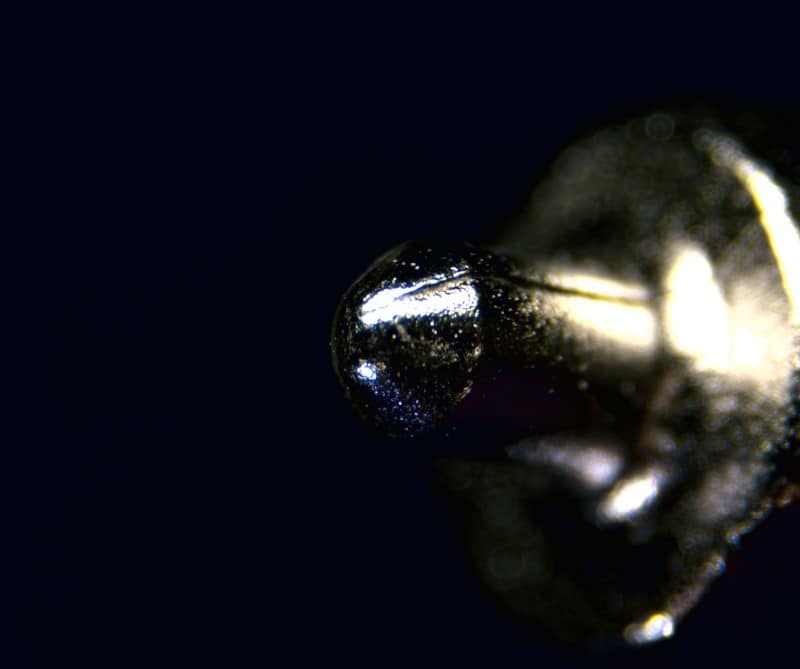
What type of machining often creates seams in metal, as seen on this firing pin?
MIM
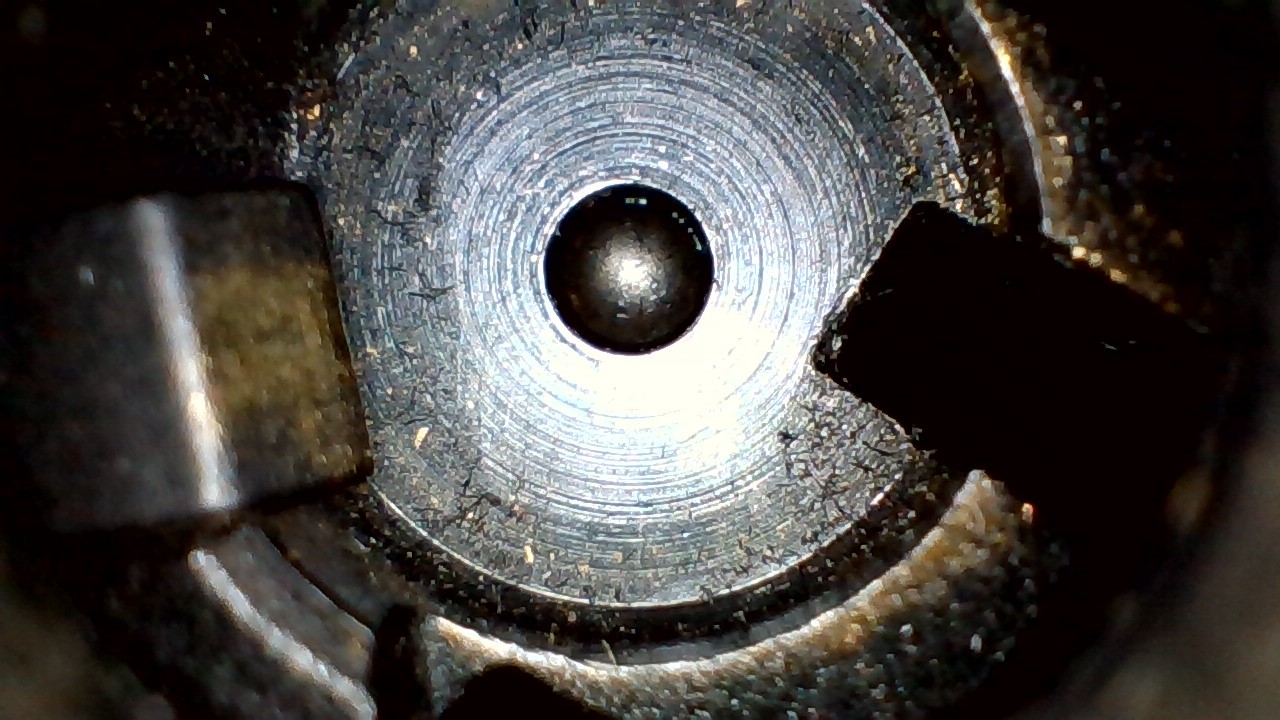

What type of machining likely left these concentric rings on this bolt breechface?
Plunge milling
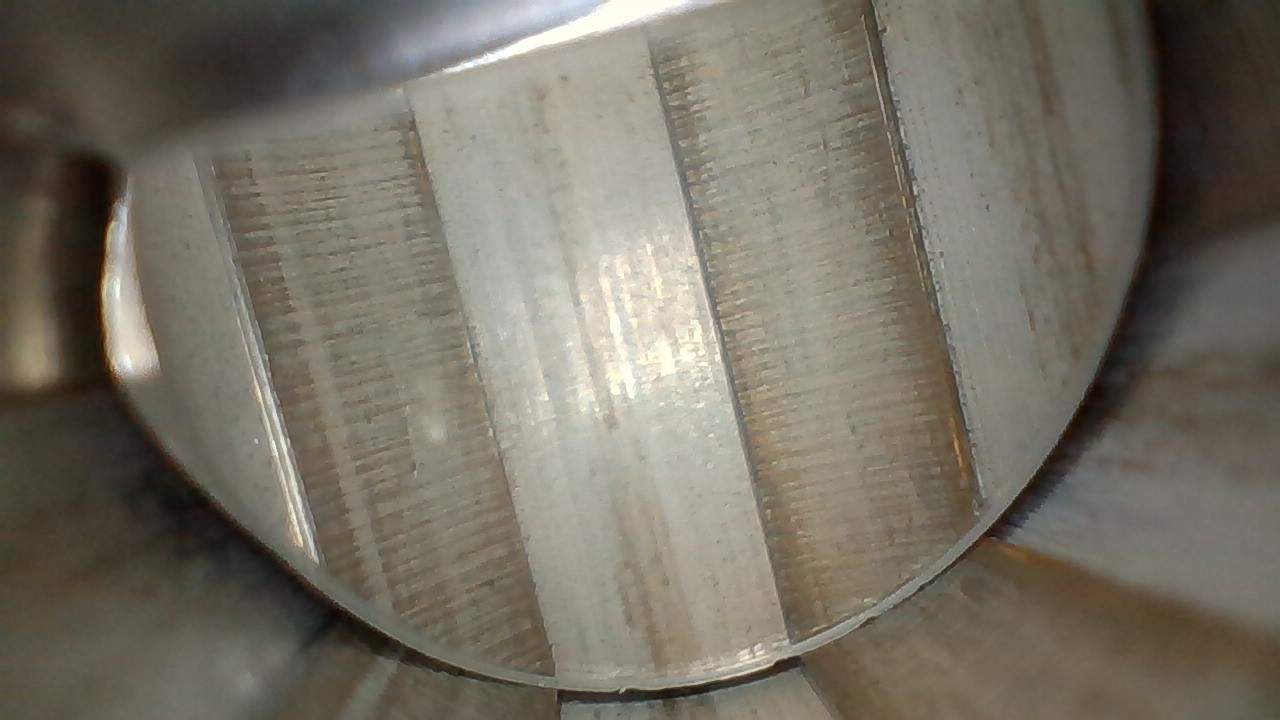

What type of machining likely left these perpendicular markings in the grooves of this barrel?
Reaming
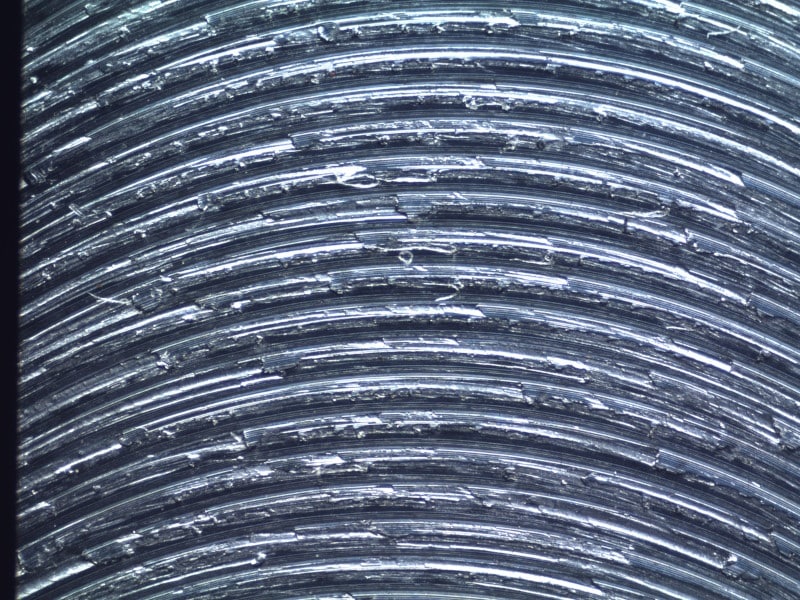

What type of machining likely created these jagged, spaced apart arches?
Face milling (slow)
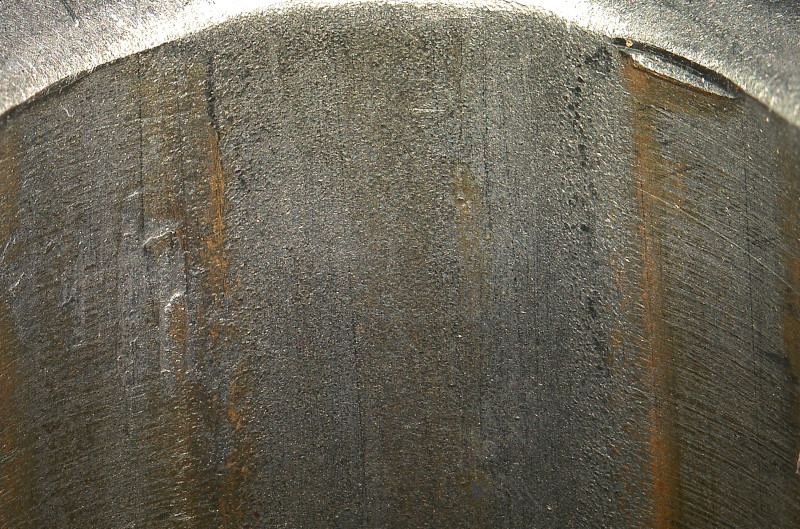

What type of machining likely left this pock marked finish on the rifling of this barrel?
ECM