Chapter 1: Rocks and mineral extraction
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Igneous rocks
Rocks that are formed by the solidification of molten magma or lava.
Intrusive ignenous rock
Magma cools beneath the surface
Extrusive igneous rock
Magma comes out as lava and cools on the surface
Give two examples of igneous rocks.
Granite and Obsidian
Give two properties of igneous rocks.
Contains crystals
High density
Sedimentary rock
Rocks that are formed from sediments
Give two examples of sedimentary rock.
Limestone and Sandstone
Give two properties of sedimentary rock.
Soft and break apart easily
May contain remains of living organisms
Metamorphic rocks
Rocks that are formed from high pressures or temperatures
Give two examples of metamorphic rocks.
Gneiss and Quartzite
Weathering
The breaking down of minerals or dissolving of rocks in the Earth’s surface
Erosion
The process of wearing away and moving of rocks, soil, or other materials on the Earth's surface by natural forces like wind, water, or ice.
Mineral
A solid, hard natural substance
Ore
A rock containing high amounts of minerals
Give two methods of mining.
Subsurface and surface mining
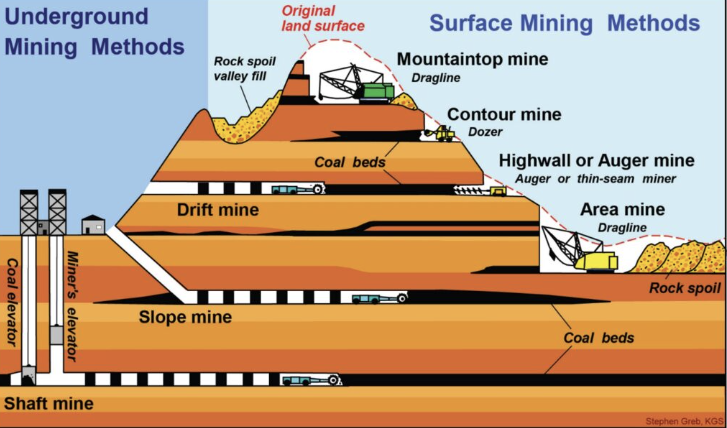
Subsurface mining
Mining involves sinking a vertical shaft underground to the rocks containing minerals and building a horizontal tunnel down to the mineral layers and loose rock from the mines is transported to the surface where the minerals get transported away. This type of mining is used when the ore deposits are below the Earth’s surface.
Surface mining
Mining that involves the removal of vegetation, and explosion of rocks, where the machines are used to remove loose rocks, and the rock being transported by trucks or railway wagons
Give three types of surface mining.
Open pit mining
Quarrying
Strip mining
Identify some uses of different rocks.
Sand → Makes glass
Chalk→ Manufacturing cement
Gravel → Makes concrete
Granite → Used for construction
Identify an advantage of subsurface mining
Lesser pollution
Identify the disadvantages of subsurface mining.
More expensive
More dangerous to miners
Tunnel collapses
Identify an advantage of surface mining
Less expensive
Identify the disadvantages of surface mining
Visual pollution
Noise pollution
Destruction of habitats
People have higher risks of getting infectious diseases
Identify three ways of conserving the environment damaged by mining.
Landfilling
Landscaping
Reclamation
Landfilling
The dumping of waste in an area.
Identify the impacts of landfilling.
Cheap and easy way to dispose waste
Causes pollution
Affects nearby communities with polluted water and higher risks to diseases such as cholera
Landscaping
Land is made to look like a natural landscape to make it look as if the land was not disturbed by mining
Reclamation
The land can be reclaimed by from mining to be used for farming