Approaches
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the strengths of the Behiourist approach?
Uses lab studies with controlled variables to clearly define a cause and effect relationship
Success of Systematic Desenitisation Therapy (60-90%)
Support from Bandura’s study and Fox and Bailenson study
What is the therapy linked with the Behaviourist Approach?
Systematic Desensitisation Therapy - Progressive stages of exposure to fear inducing stimuli paired with calming techniques to re-establish the association to neutral
What are the weaknesses of the Behaviourist Approach?
Issues with Bandura’s study
Uses animals which are less complex than humans
Research ignores the complexity of the multitude of differetn stimuli in everyday life
Failure’s of SDT (10-40%)
Describe Bandura’s bobo doll study (1961)
3 groups of 12 girls and and 12 boys, sorted using aggression ratings to limit participant variables. Groups 1 and 2 observed an adult role model acting towards a bobo doll.
Condition 1 - Agressive action towards the doll.
Condition 2 - Gentle action towards the bobo doll
Condition 3 - No model (control)
After 10 minutes the child was given mild aggression arousal (you can’t play with these toys they’re for special kids), and bought back into bobo doll room.
Conditon 1 - Aggressive behaviour from children
Condition 2 & 3 - Little to no aggressive behaviour
Describe Bandura’s bobo doll study (1963)
4 groups of 12 girls and 12 boys, observed different things similar set up to first study. Used aggression ratings/matched ‘pairs’.
Condition 1 - Aggressive behaviour from model in the same room
Conditon 2 - Aggressive behaviour of an adult on a film
Condition 3 - Aggressive behaviour from a cartoon cat
Condition 4 - No model (control)
Mild aggression arousal.
Conditon 1,2 & 3 - All similar levels of aggression displayed by kids
Condition 4 - Little to no aggressive behaviour.
What is a schema?
A mental framework that is used to organise and link the information in our memory.
What are the strengths of Bandura’s bobo doll study?
Highly controlled variable lab study (high internal validity)
Matched pairs design
What are the weaknesses of Bandura’s bobo doll study?
Unnatural enviroment (no interaction between child and adult model)
Most children had not seen a bobo doll before (Cumberbatch follow up study 5X less aggressive to bobo doll)
Issues with sampling (all taken from Stanford nursery WEIRD)
What are the strengths of the Social Learning Theory?
Support from Bandura’s and Fox and Bailenson’s study
Application into crime prevention (role models and vicarious reinforcement)
Application into health campaigns (BAME)
What are the weaknesses of Social Learning theory?
Issues with Bandura’s study
Ignores the complexities of human emotion and daily interactions
What are the key ideas of the behaviourist approach?
We learn behaviour from our enviroment and consequences
Humans are no more complex than animals so we can use animals fro research
Experiments should be lab scientific controlled lab studies
What are the key ideas of Social Learning Theory?
We learn behaviour from other people by imitating their behaviour
We imitate behaviours from a model (some-one we identify with: same-sex, older, attractive, successful)
There are mental process that happen in order to imitate behaviour
What therapy is linked with the behaviourist approach?
Systematic desensitisation therapy - Using the principles of classical conditioning to pair increasing exposure to a phobia with calming techniques to re associate. (60-90%)
What mental processes are involved in imitation?
Attention
Retention
Motor reproduction
Motivation
What are the key ideas of the cognitive appraoch?
Behaviour is controlled by complex internal mental processes
These mental process can be studied by making inferrences from observed behaviour
Brain processes can be explained using theoretical and computer models
What is the multistore model of memory?
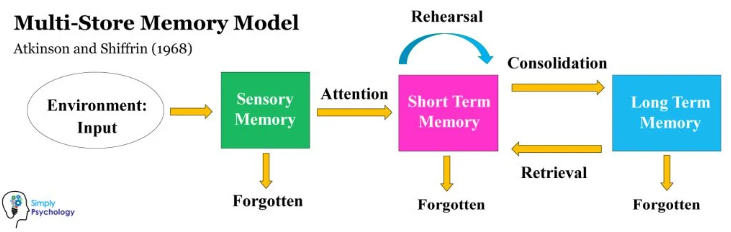
Describe Pavlov’s research.
Salivation of a dog was measued with test tubes surgically attatched to dogs cheeks.
Paired a bell (neutral stimulus) that had no response with dog food (unconditioned stimulus) which caused salivation (unconditioned response).
After repeated pairings the bell on its own caused same volume of salivation as food (now a conditioned response). The bell was now associated with receiving food and became a conditioned stimulus.
Describe Skinner’s research.
Rats in a box with two levers. One released food (reinforcement), the other released an electric shock (punishment).
The lever that released food was pressed more often, and the lever that released the elctric shock was pressed very little.
Therefore, actions that have beneficial consequences are more likely to be repeated and actions that have harmful consequences are less likely to be repeated.
What are the different types of consequences according to Skinner’s research?
Negative Punishment - Taking away a good thing
Positive Punishment - Adding a bad thing
Negative Reinforcement - Taking away a bad thing
Positive Reinforcement - Adding a good thing
What is the computer model in the cognitivie approach?
Compares the human mind to a computer, input is the sensors, hard drive is memory, RAM is memory retreival, output is behaviour.
What are the strengths of the cognitive approach?
Success of cognitive behavioural therapy (90% with depression)
Scientific controlled experiments (high internal validity)
Application in police interviews
What are the weaknesses of the cognitive approach?
Over simplifies brain activity (human minds are more complex than computers)
Failure of CBT (10%)
Ignored human emotions and free will
Studies have low external validity
What therapy is linked with the cogntiive approach?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy - Replacing irrational thoughts with rational thoughts