GEL 12 Final Exam
1/344
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
345 Terms
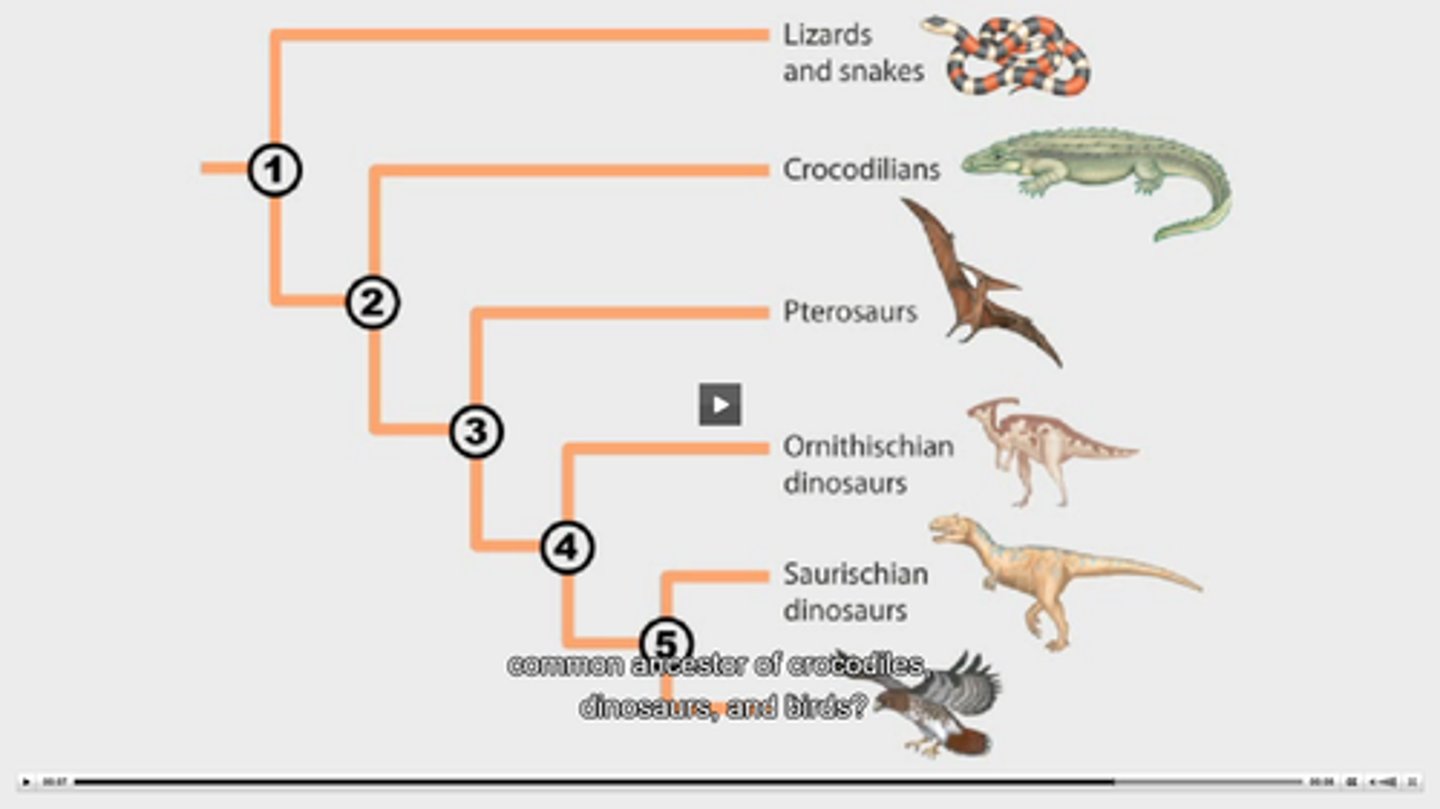
Which dinosaurs are birds related to?
Theropods
Similar to theropods, birds are also ________________. (What kind of hips?)
Saurischians
Maniraptora
a group that includes birds and their closest relatives within the theropod dinosaurs
semilunate carpal
half-moon shaped wrist bone that allows wing folding in birds
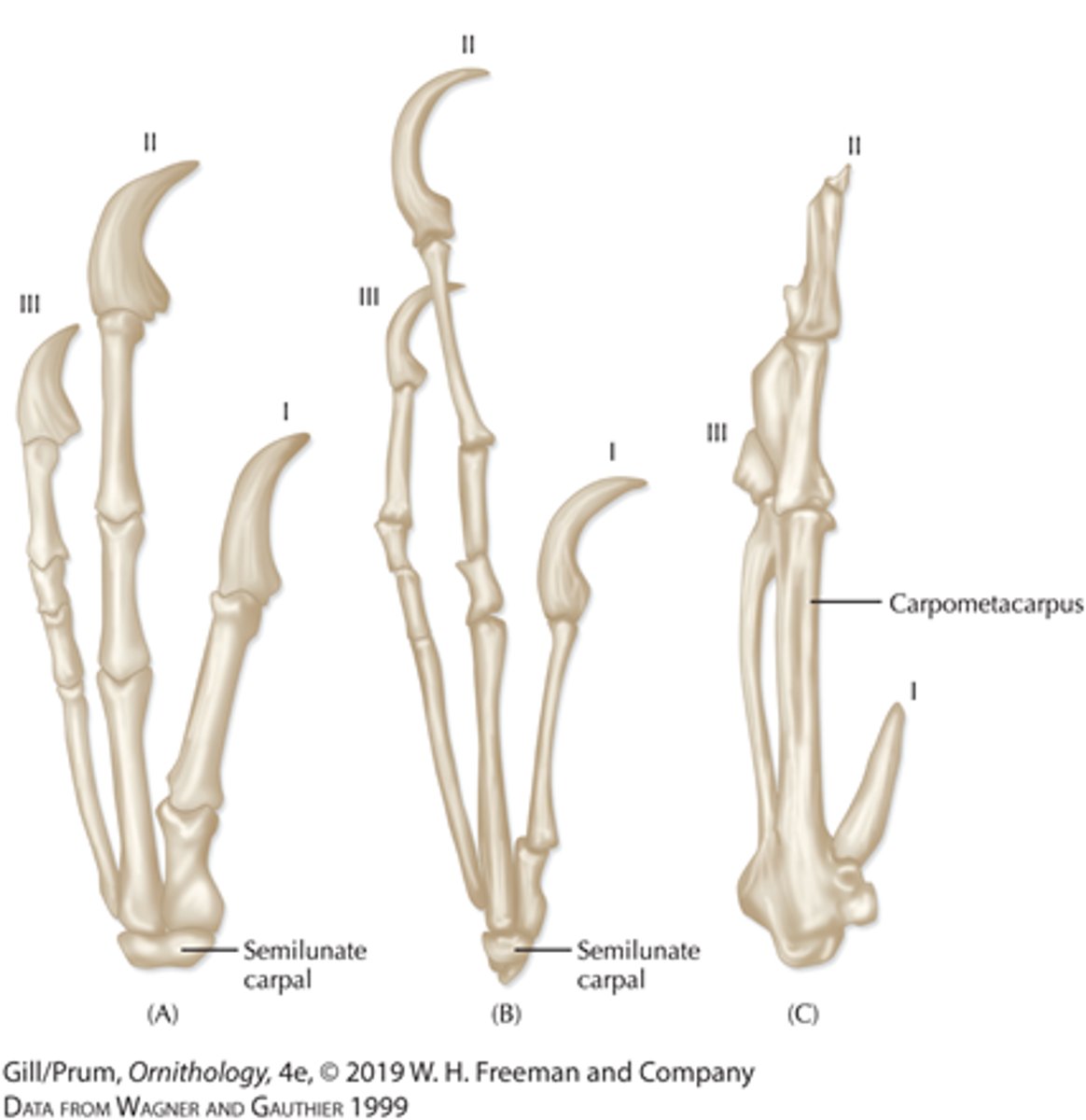
What key anatomical feature of the hands allows birds to fly?
The semilunate carpal allows the hands to be folded back all the way.
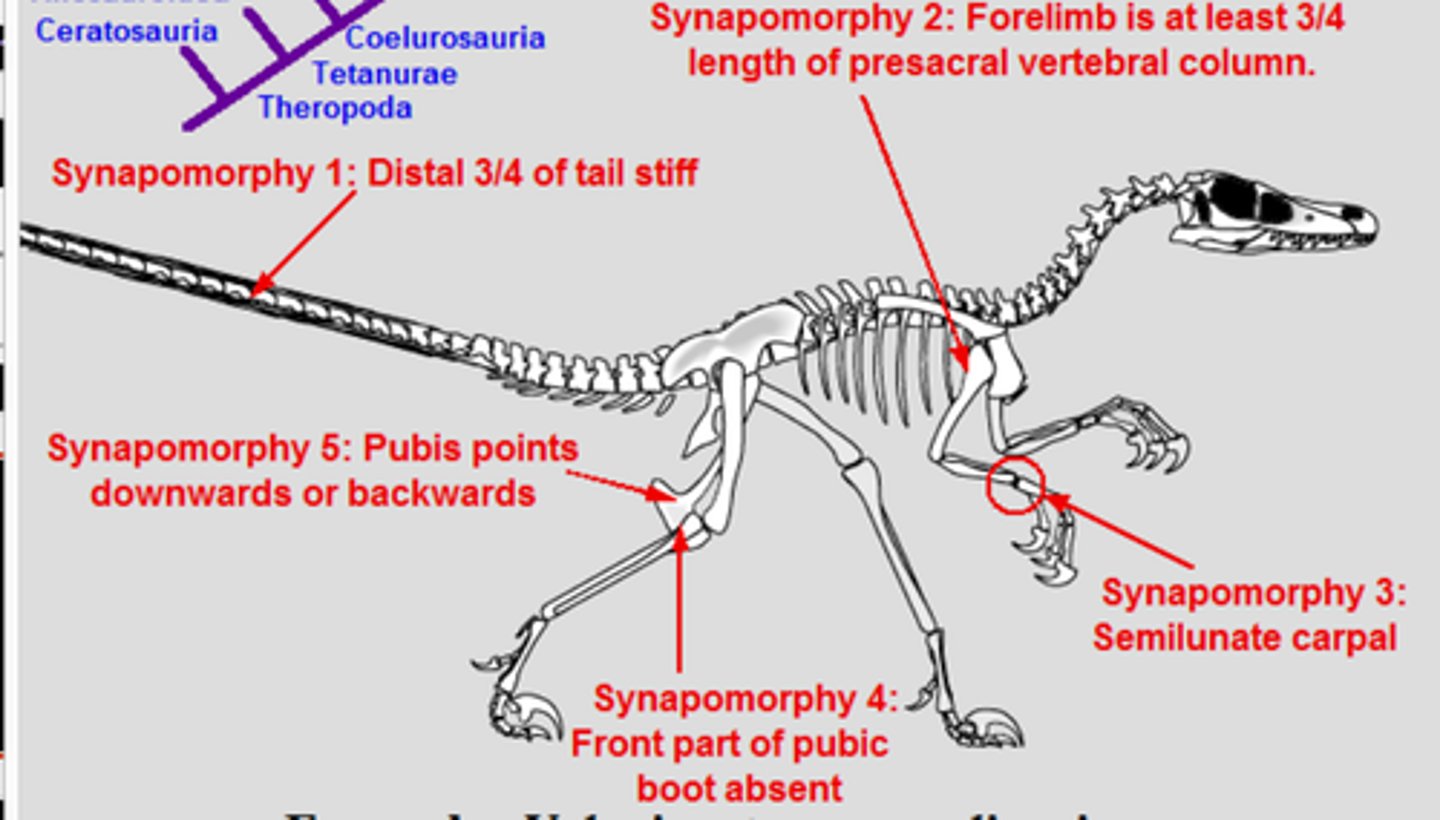
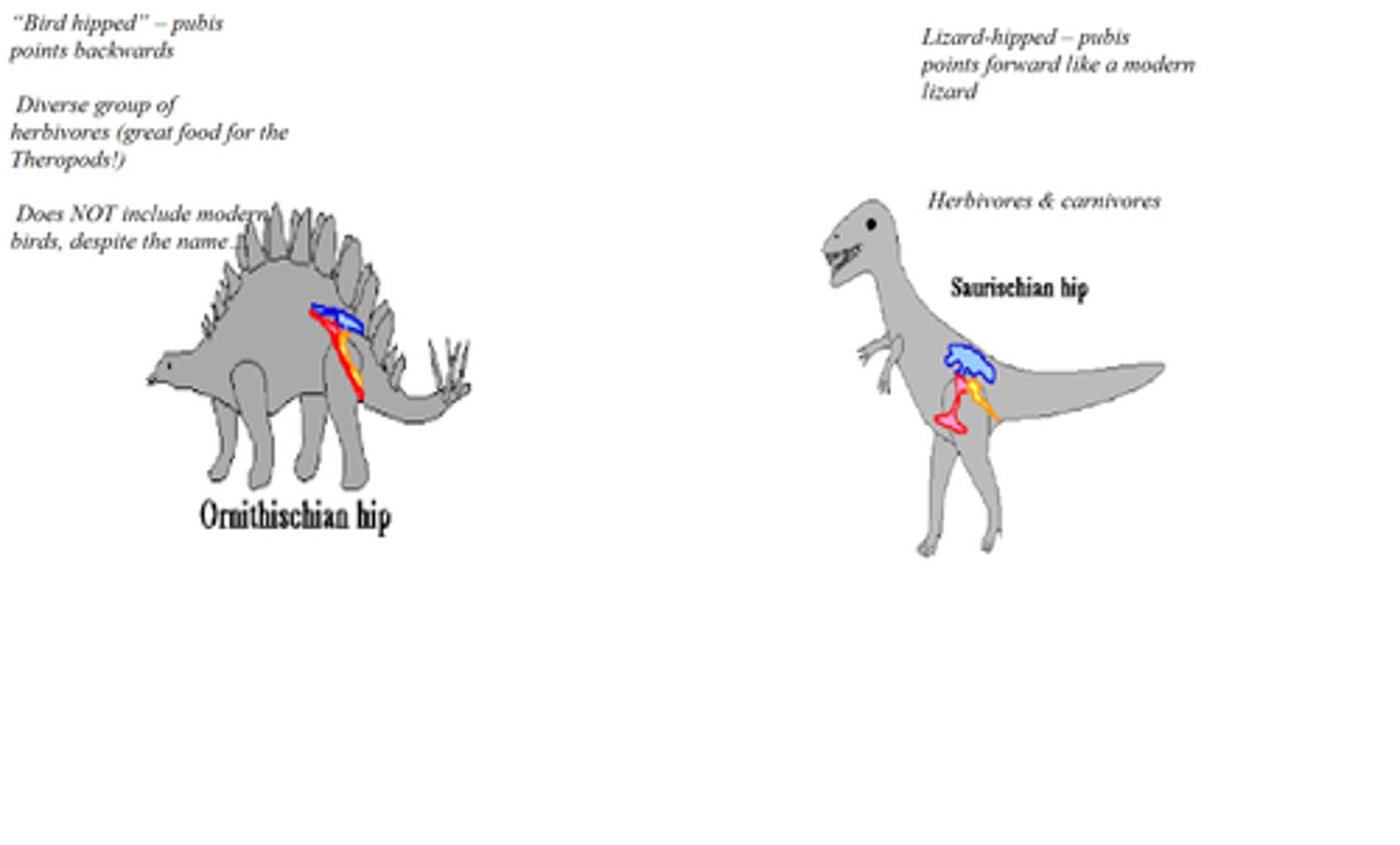
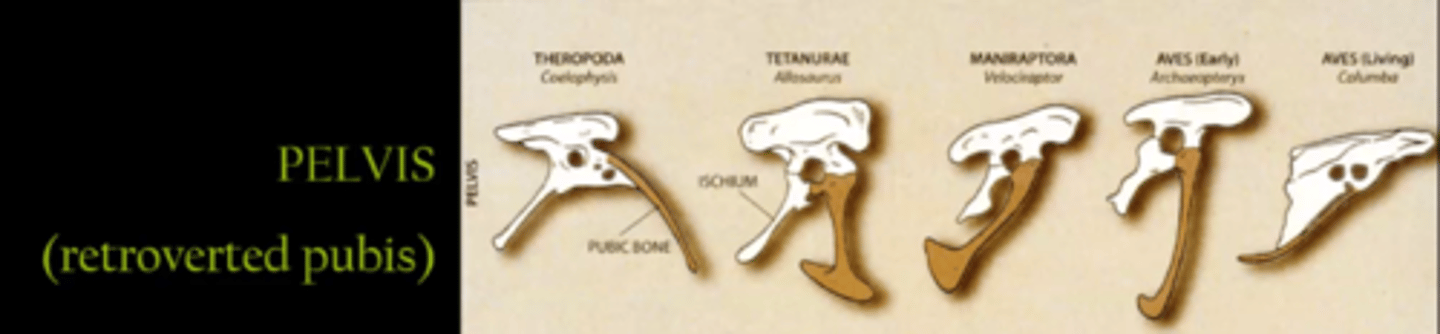
Retroverted pubis
One of the features that evolved from theropods to birds of flight
Furcula
wishbone, the fused clavicles of birds
What are 3 anatomical evolutionary changes from dinosaurs to birds?
1) retroverted pelvis
2) Semilunate carpal
3) Furcula
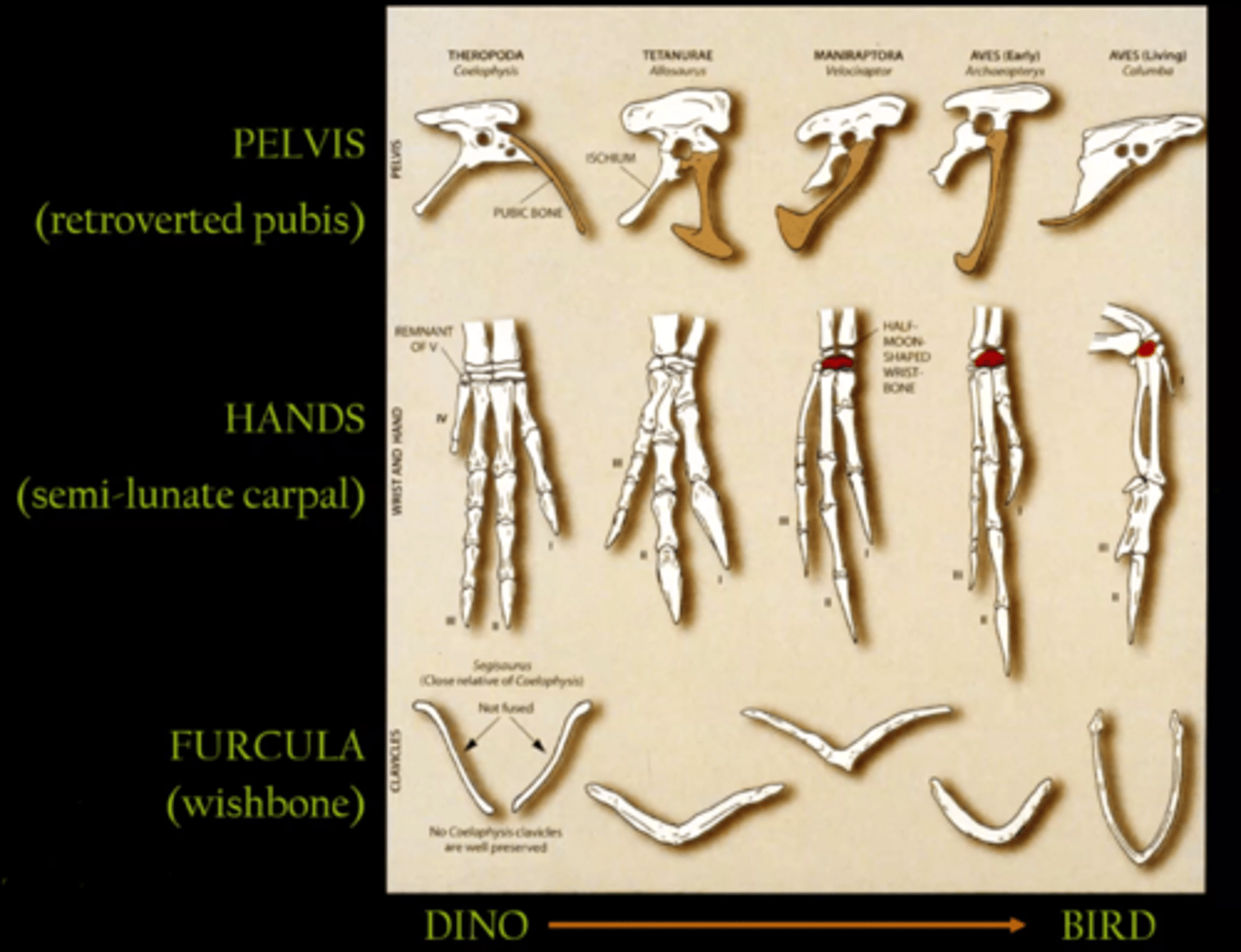
What anatomical feature is only found in theropods and birds?
The furcula, the wish bone
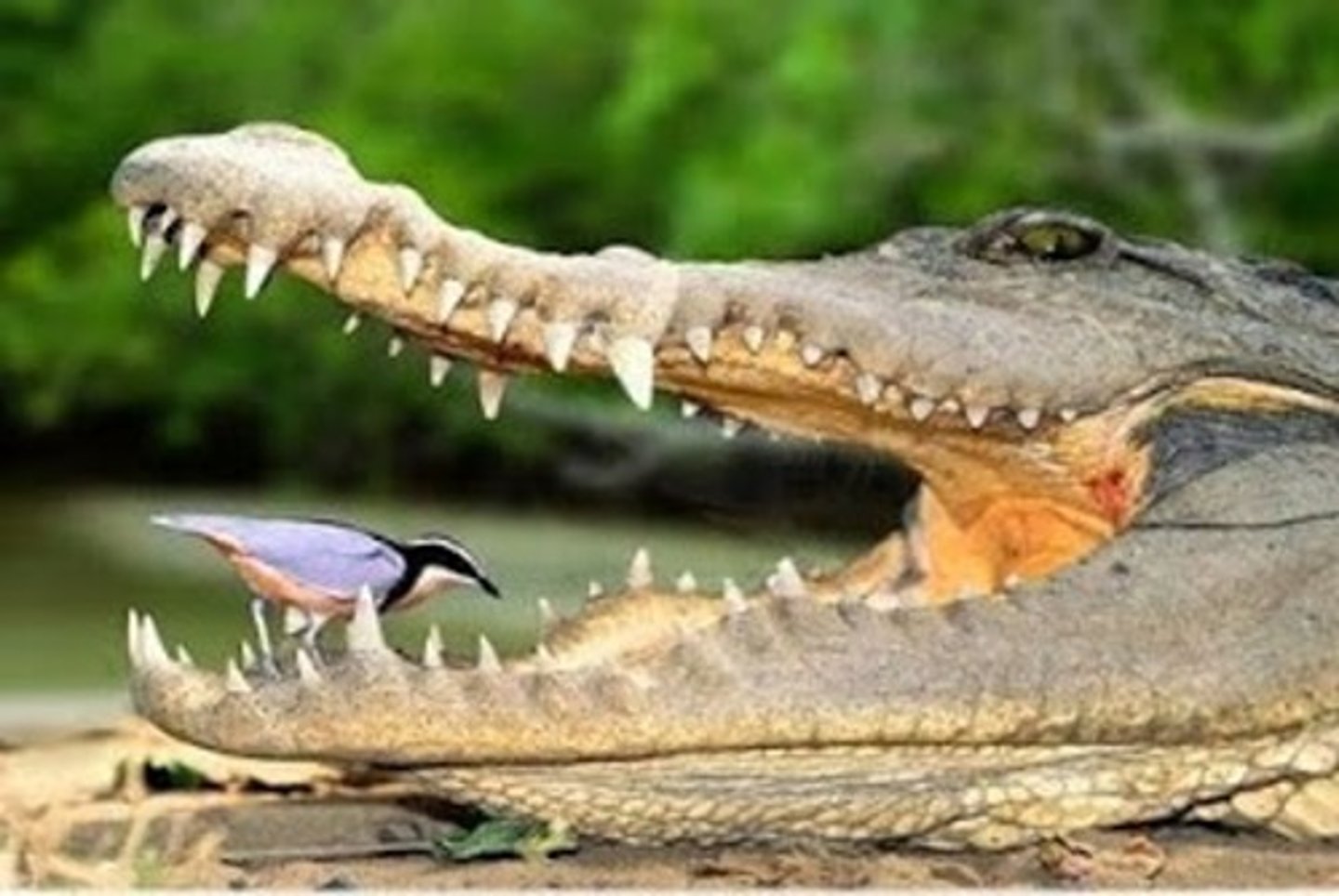
What two animals are studied to understand dinosaurs?
Birds and crocodiles

T/F: In 1859, Darwin published the Origin of Species; some used birds as a counter-example against evolution, as there were apparently no transitional forms between birds and other vertebrates.
True, we now know that Darwin was correct because we now have more fossil records than before

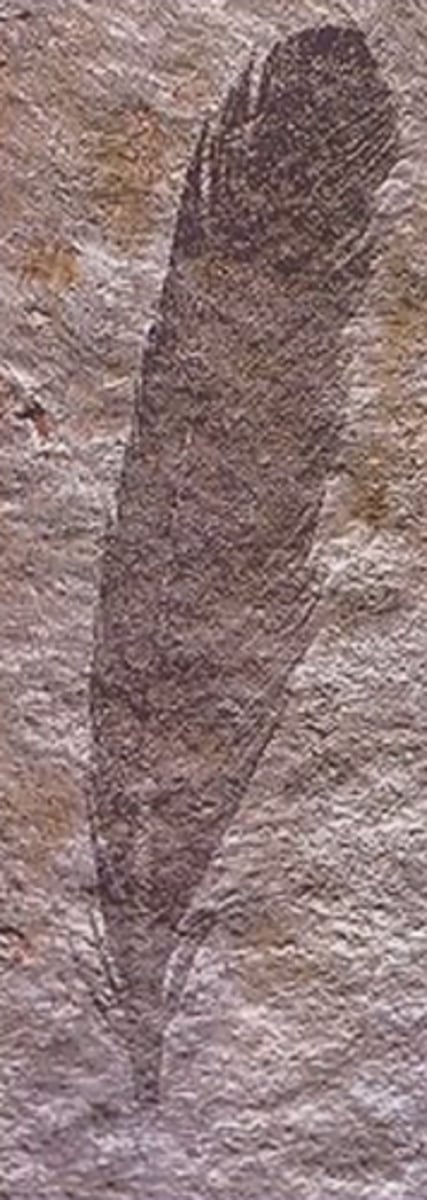
How did we know that birds lived amongst dinosaurs?
A feather fossil was found that dated back to the late Jurassic

Archaeopteryx
extinct primitive toothed bird of the Jurassic period having a long feathered tail and hollow bones
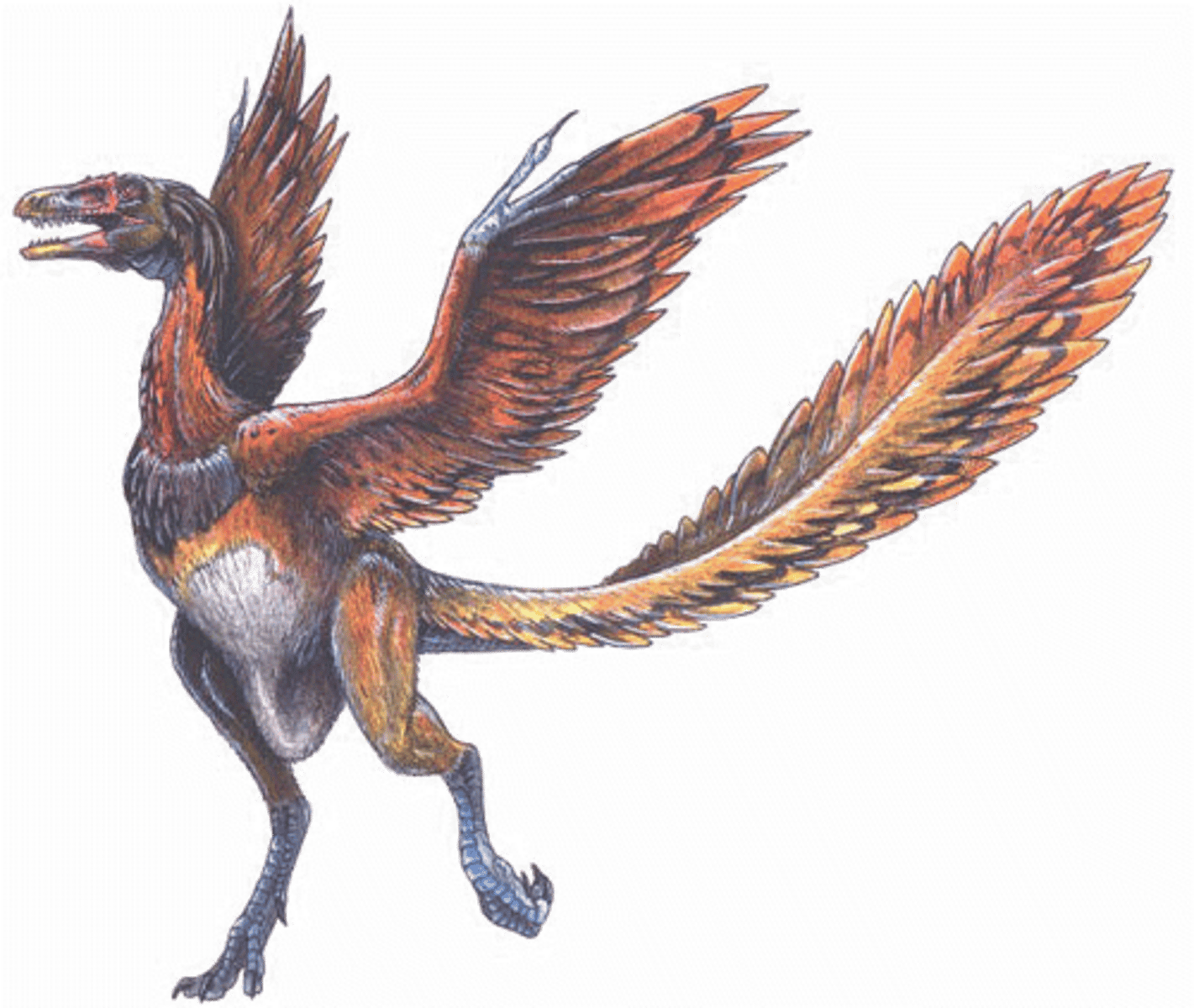
How is archaeopteryx different from birds today? (3 ways)
1) had hand claws
2) had teeth
3) infused tail that be move
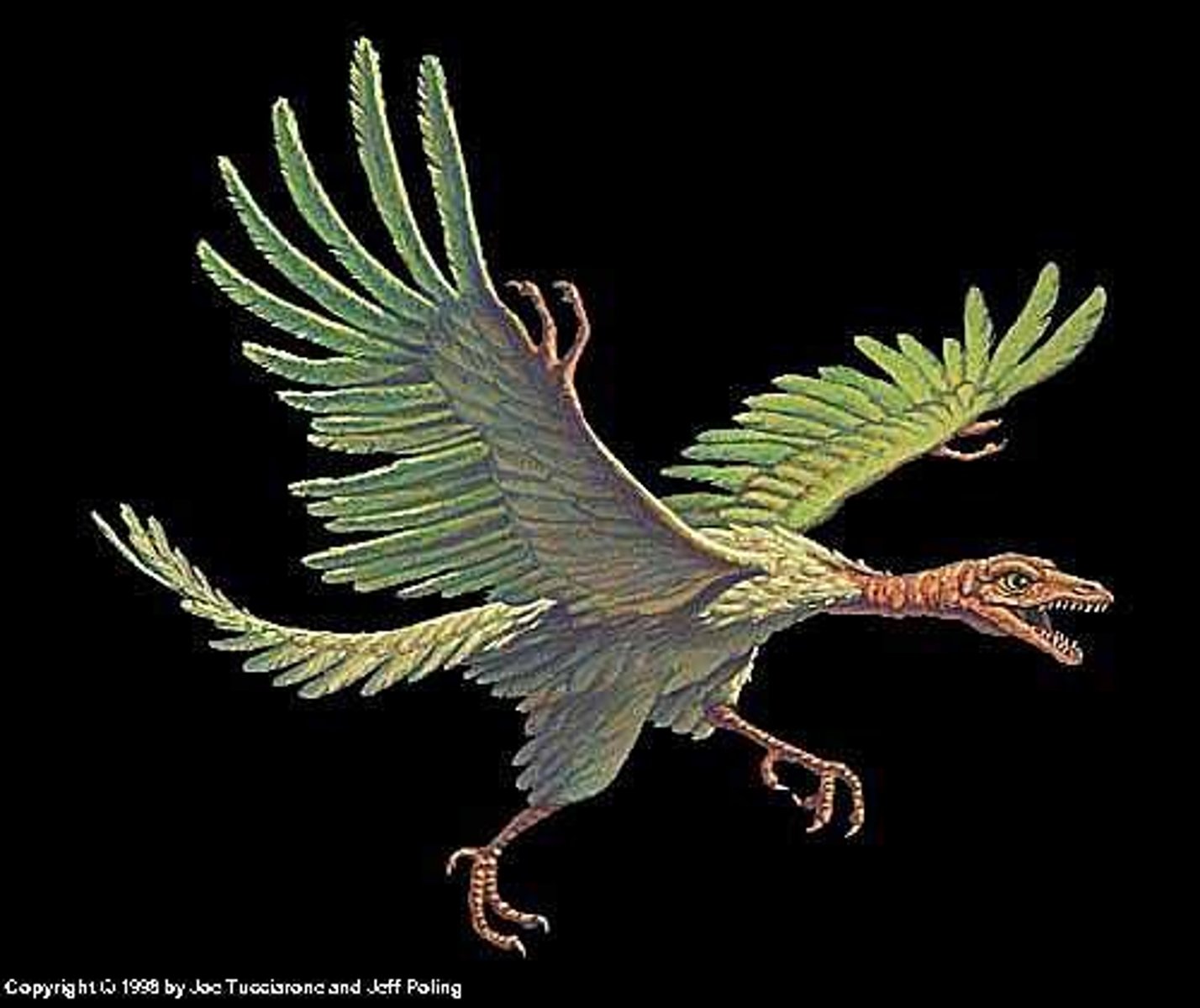

How is Archaeopteryx similar to modern birds?
1) Feathered wings and tail
2) Backwards-pointing pubis
3)Backwards-pointing pedal digit, to help hold on to branches and such

Confuciusornis
Earliest known bird with true beak, toothless, clawed fingers, mix of primitive and modern bird features

T/F: Archaeopteryx could fly like a normal bird today.
False, it most likely couldn't. If it did, then it probably fluttered around like a chicken does. It also had a big tail which is not optimal for flying because it creates drag

Name 3 other functions of feathers, besides flight.
1) Thermoregulation
2) Coloration/mating/display
3) Sensory

T/F: It was common for infant/junior theropods to have Dino fuzz for thermoregulation.
True, it helped keep them warm

How do birds use feathers for sensory?
They can only see so close to themselves so they can rely on their feathers to help them feel for what they are doing.
ex. Cats have whiskers since they can't see something if it get too close to them, so they feel their surroundings with their whiskers
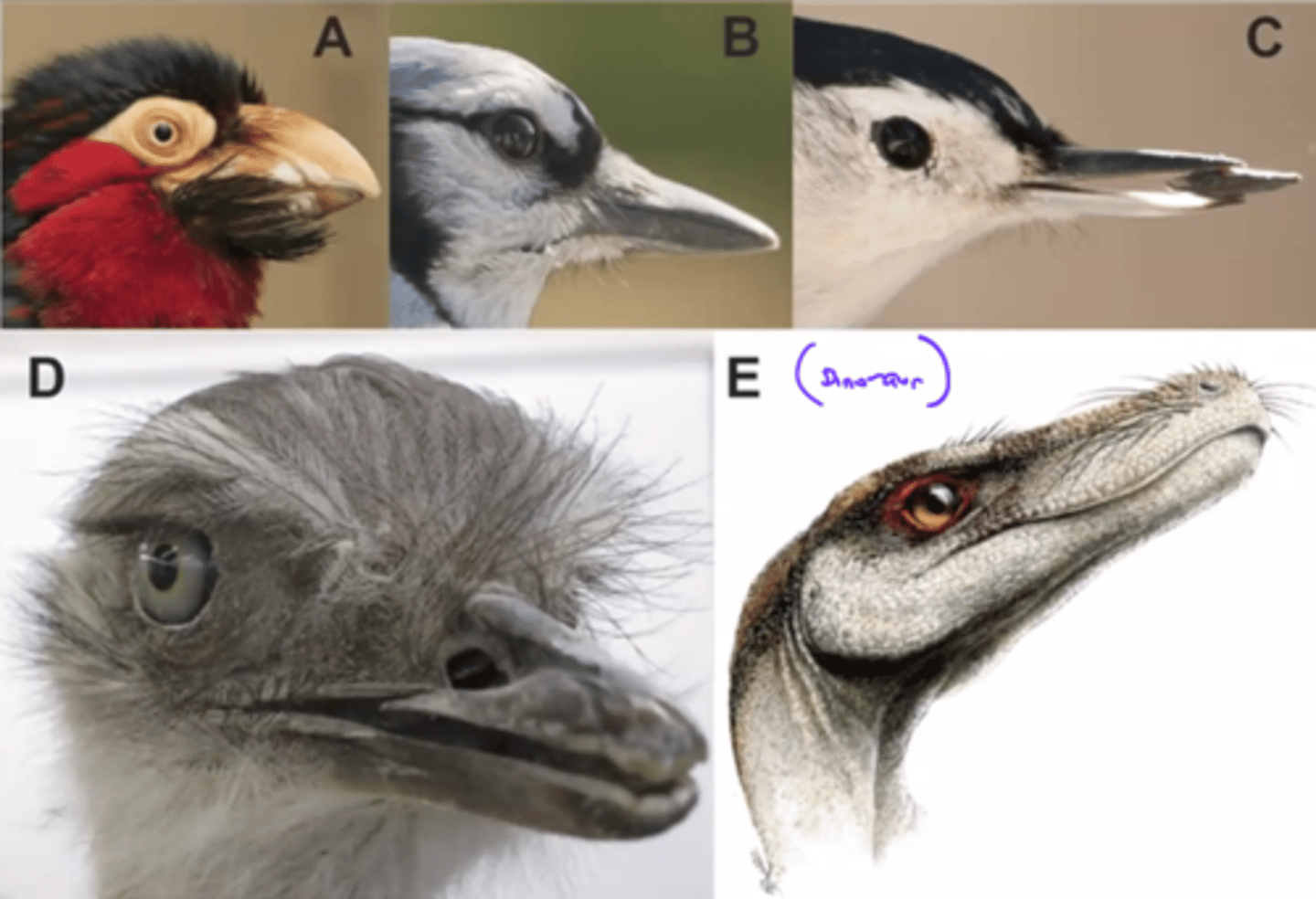

Is archaeopteryx a bird?
It depends on how a bird is defined. There is an on going debate on this.
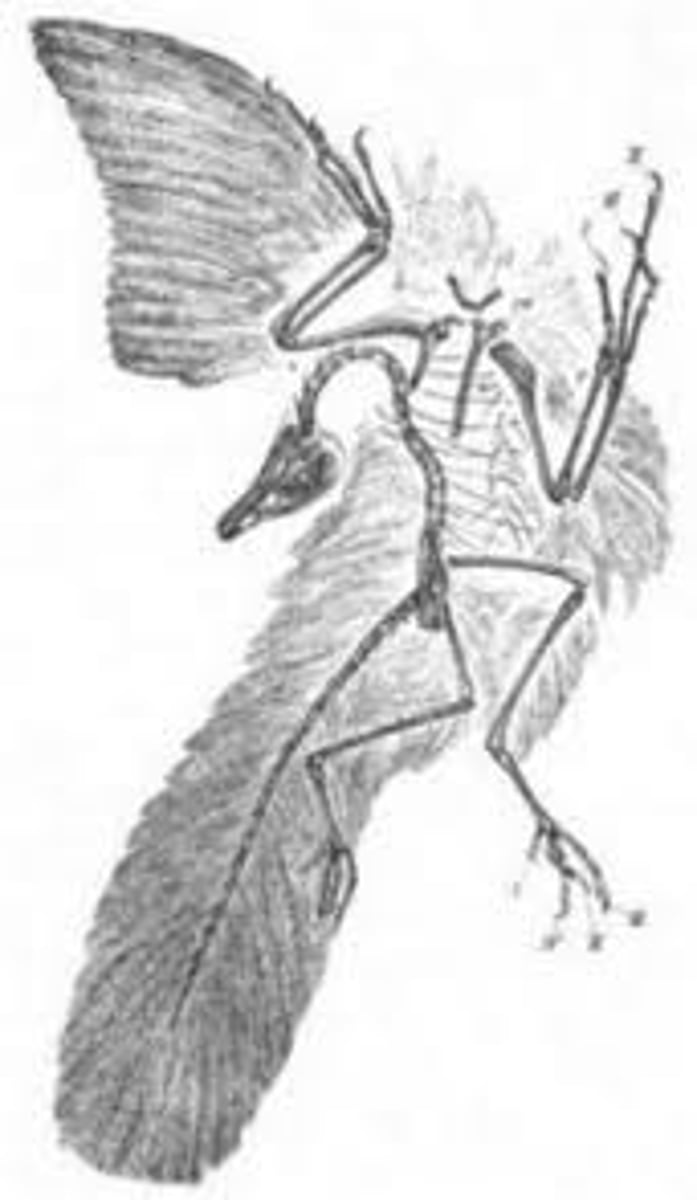

What are the 3 hypothesis for the origin of birds?
1) Birds are not related to dinosaurs and that they evolved from something else
2) Birds came off of the crocodilians linage (no much evidence here)
3) Birds are related to theropods and have come from them (most accepted)

What are some hypothesis as to why wings evolved for flying?
1) To help escape from predators
2) To help catch flying or speedy prey
3) To help move from place to place faster
4) To free the hind legs for use as weapons
5) To gain access to new food sources
6) To gain access to an unoccupied niche

What are the 3 origin of flight hypothesis?
1) The tree-down model
2) The ground-up model
3) The compromise model (mix of the 2 above)

Protofeathers
The hypothetical precursors of bird feathers, believed to have been grown by certain dinosaurs.

T/F: Through out their life times, all birds go through stages 1-5 of feathers, where as dinosaurs Went through a transition among different species. (Ex. Some had state 1 feathers and later a different species had stage 2 feather, etc)
True

How was dinosaur behavior thought to be before and after?
Past: They were initially thought to be lazy and dumb lizards that sat around and did nothing all day long
Current: We now know that dinosaurs were highly active and some of them were incredibly intelligent as a result of their large brain to body size ratios.

What is the correlation between brain size and body size ratio?
The larger the brain is compared to the size of the body, the more intelligent the animals tent to be.
ex. Sauropods had tiny brains compared to the body size so they were not very smart
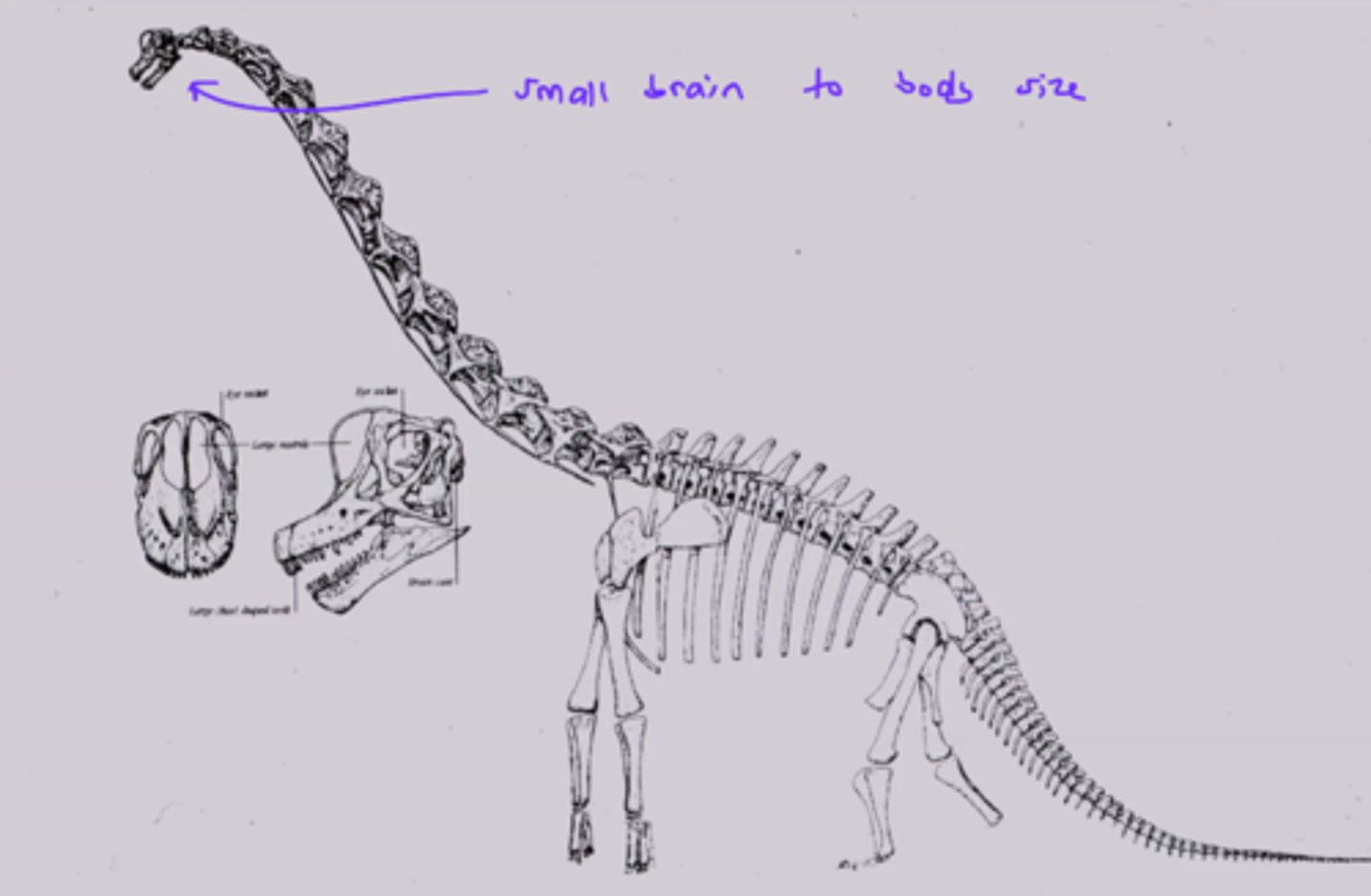
What dinosaur is not so smart?
The sauropods because relative to their body size, their brains were very small.
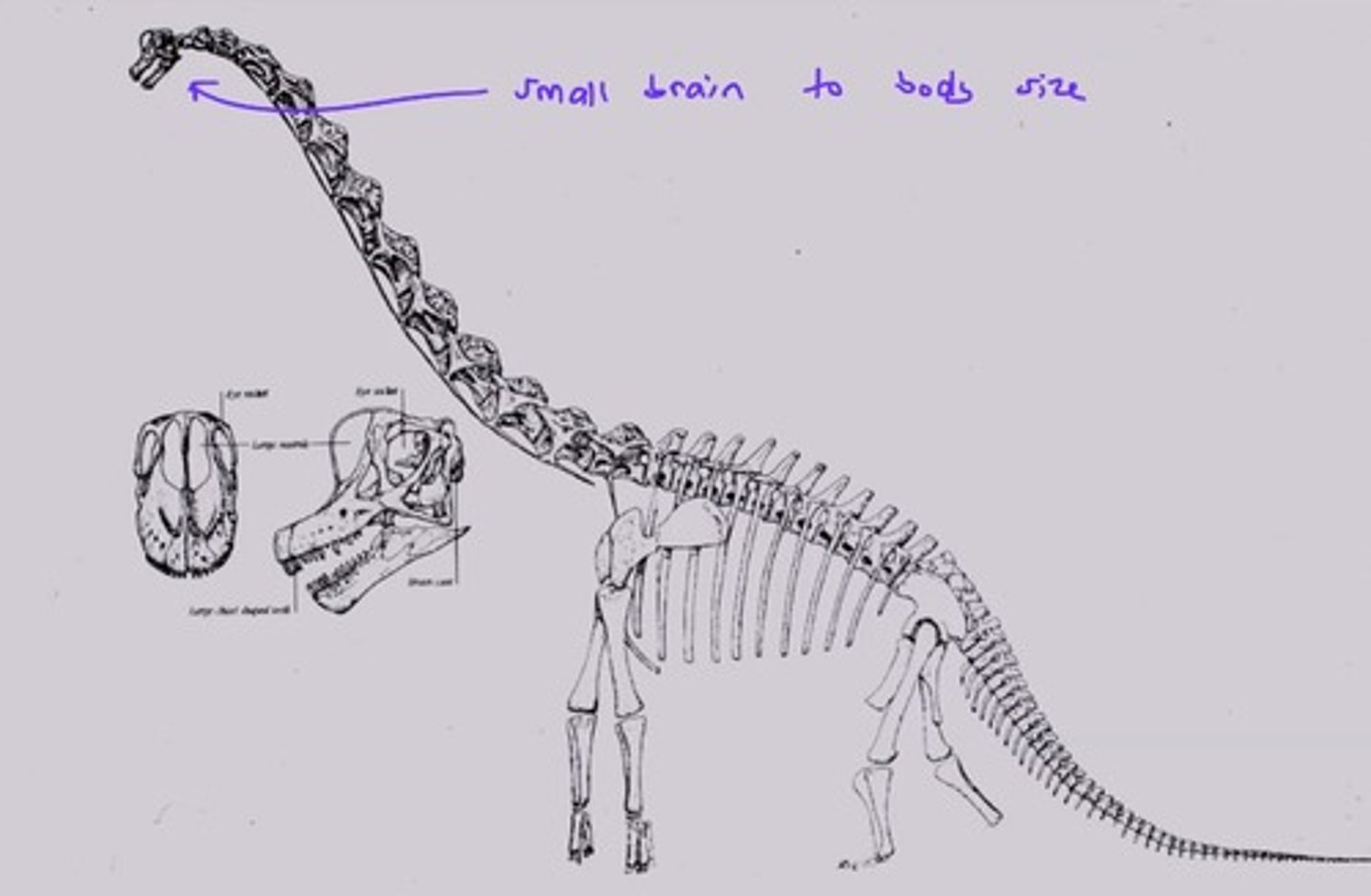
Who proposed that dinosaurs were not actually lazy, but actually active organisms?
Charles Knight in 1897
What are some things that prey animals did to fend off predators?
Wacky them with their tails such as the stegosaurus and ankylosaurus
What are some ways that prey animals fended off predators?
Wacky them with their tails such as the stegosaurus and ankylosaurus or use their thumb spikes like with the iguanodon. Sometimes the actual size of the dinosaur was enough to fend off prey such as with the sauropods
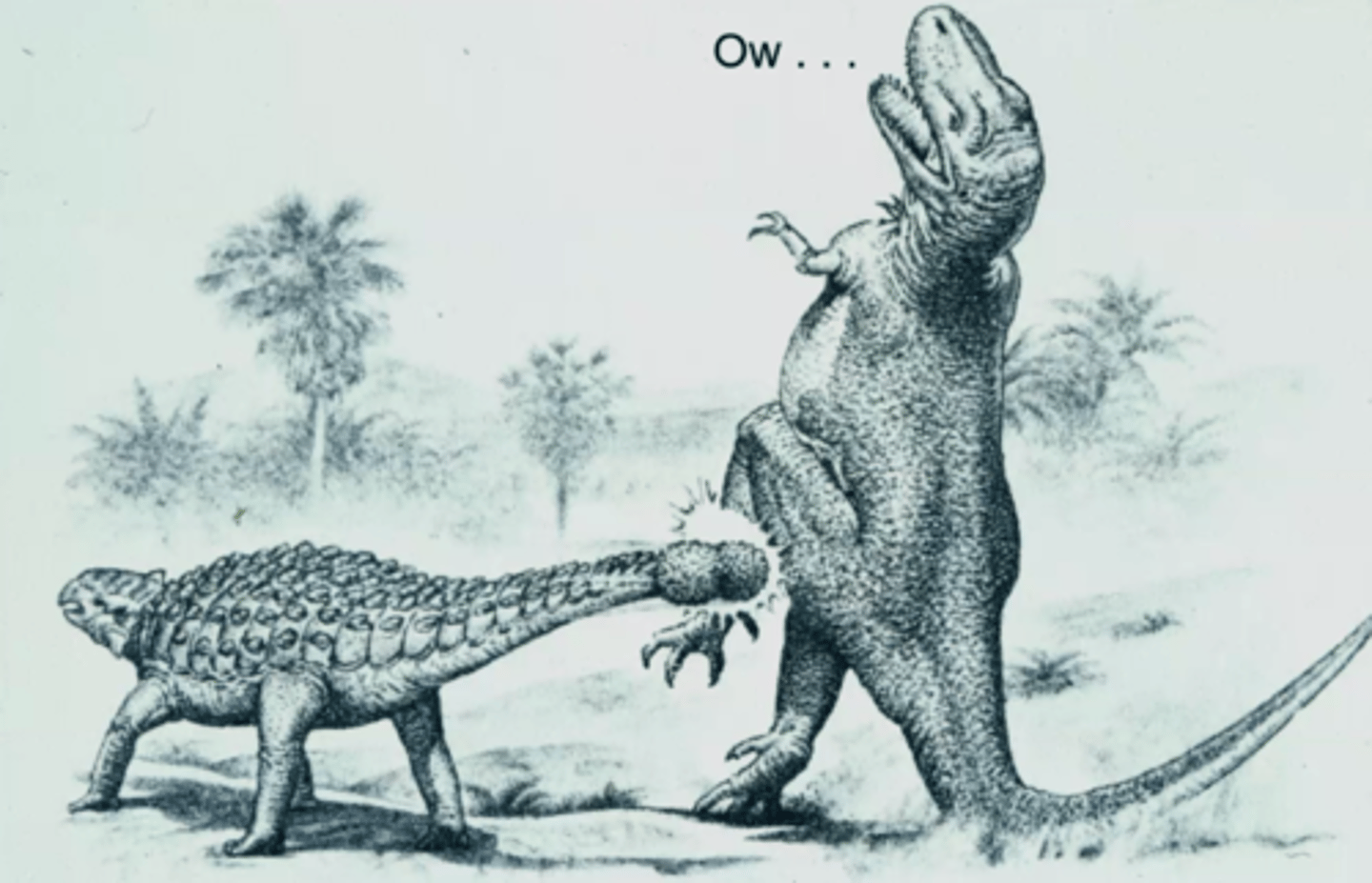

T/F: Sauropods were rarely hunted because of their vast size and how easily they could injure a predator.
True, think how a lion rarely hunts an elephant unless it is desperate

What is thought to be the primiary function of the ceratopsian frills?
For display because there is so much variation among species of ceratopsians that if it was for heat release or even defense, why would there be so much variation among them.
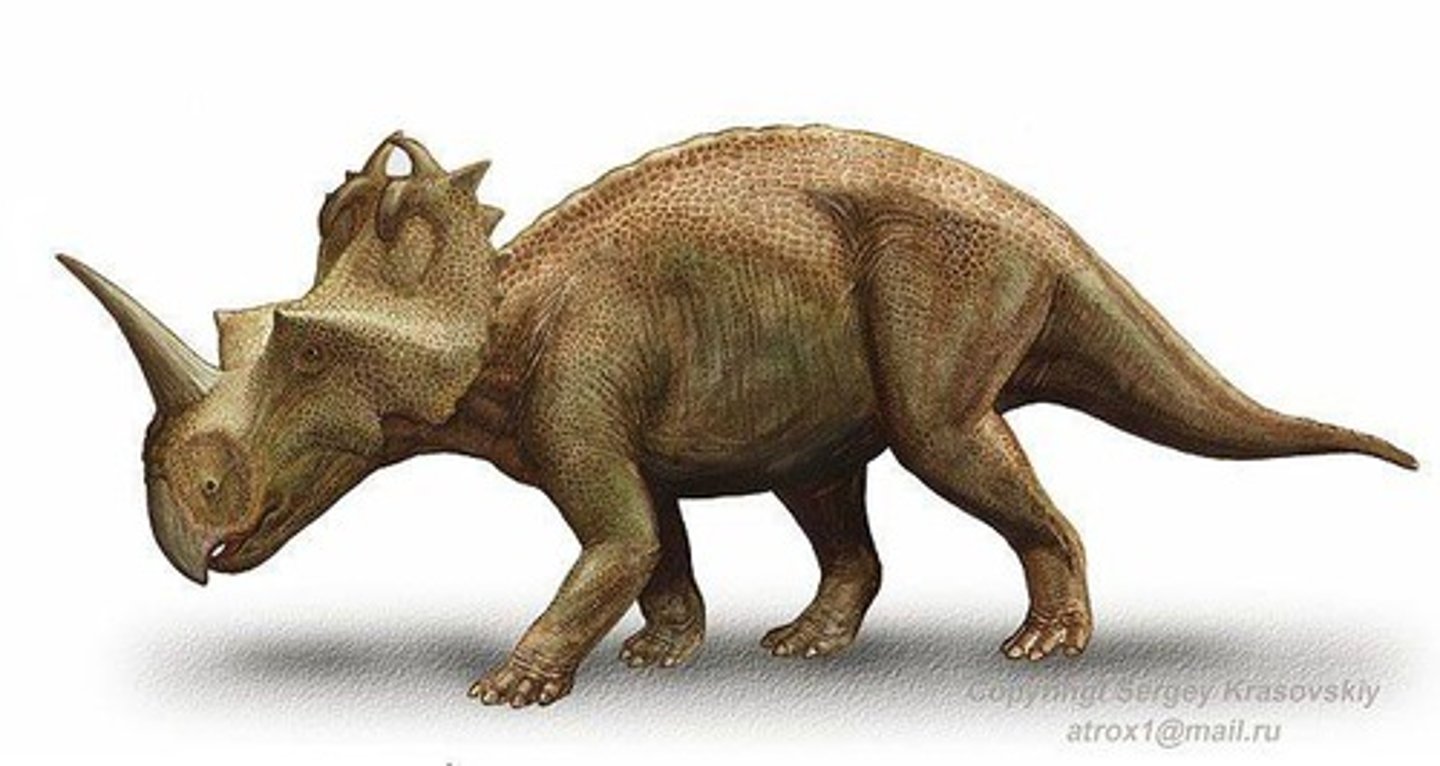
What is the primary reason for Hadrosaur crests?
Likely for sexual display and recognizition of it's own species by the sounds they make as a result of different head shapes.
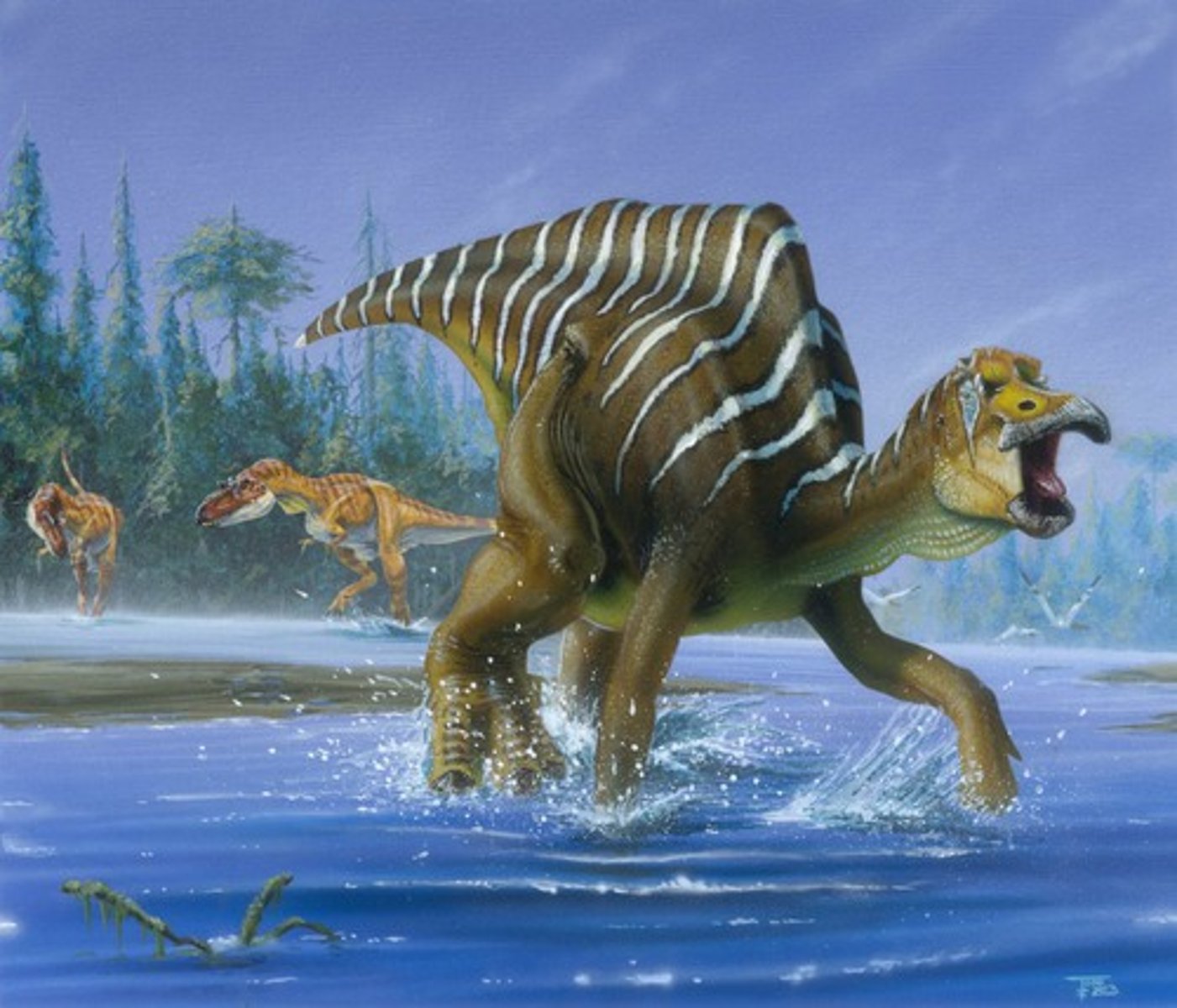

T/F: All hadrosaurs have the same body and only differ when it comes to the head crests.
True, and each different crest creates a unique sound
T/F: The hadrosaurs used their long heads to snorkel?
Nope, it was for display and species recognition
think: Birds in the forest with their unique calling
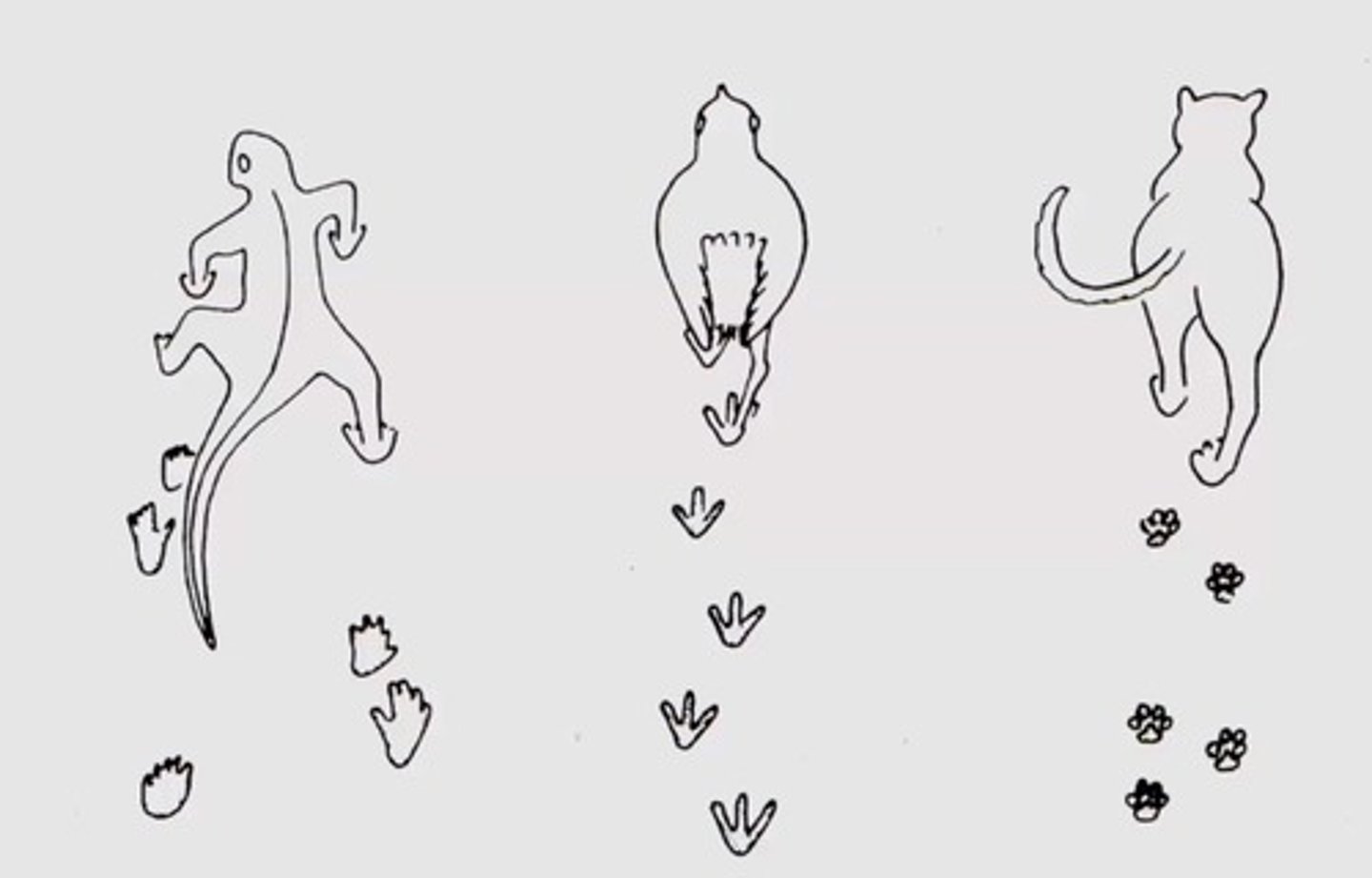
From the footprint trace fossils, what can be determined?
Posture, speed, and direction of travel of the animal

T/F: Different dinosaurs leave behind different foodprints.
True
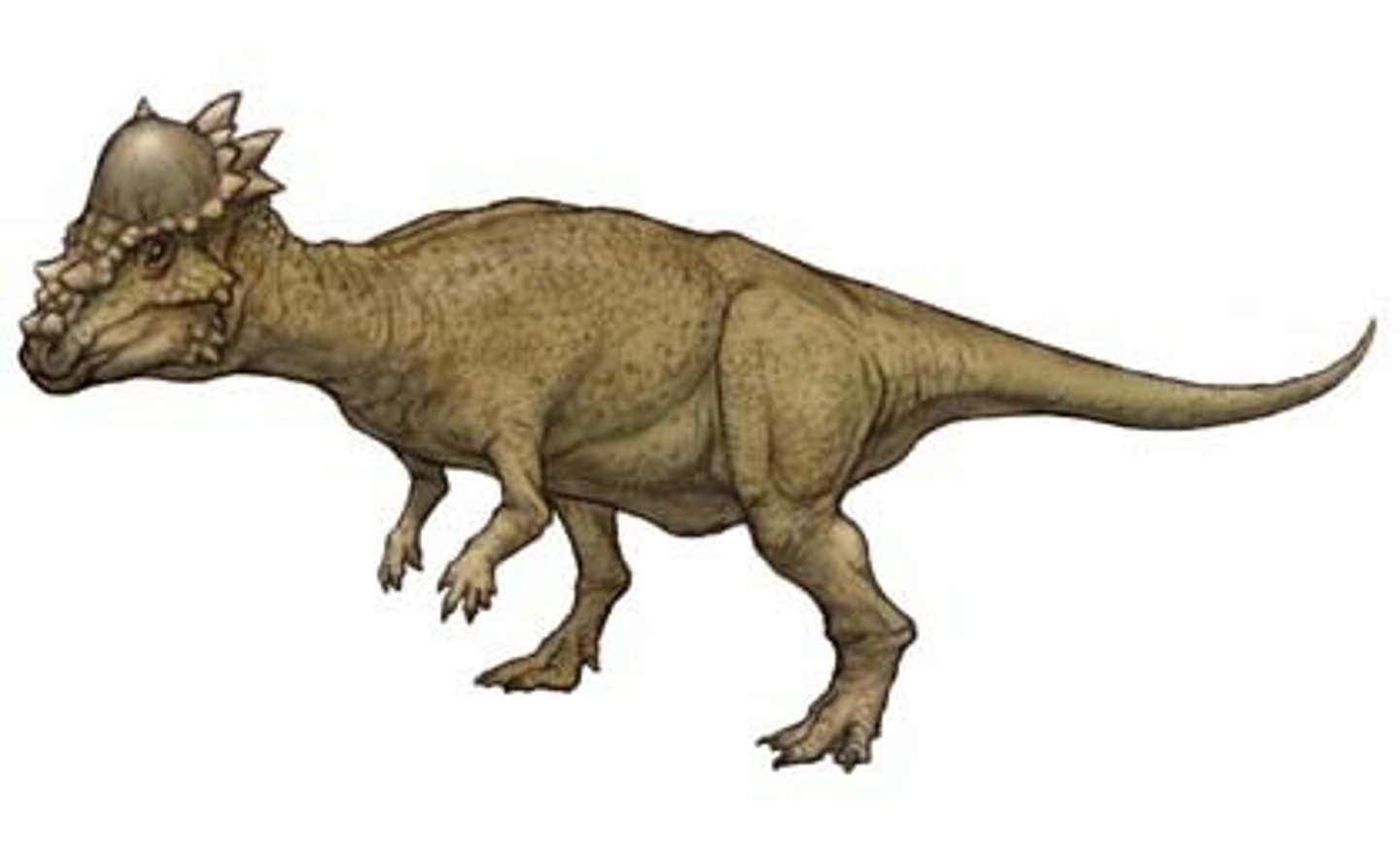
T/F: Pachycephalosaurs head butted like sheep do.
False, their heads are dome shaped and not flat like that of sheep. Sheep can head butt because they have curved horns and flat heads that once they hit each other, they turn their heads and lock their horns with each other so that they don't mess up their necks. Sheep also have spongey bones around their brains to help it stay protected. The pachycephalosaurs lacked all these features.
By studying what 2 species can help us understand more about dinosaur behaviors?
Crocodiles and birds. If they both do something, it is likely that their dinosaur ancestors also did the same.

What are the 5 crocodilians nesting behaviors?
1) Lay lots of eggs at a time (> a dozen)
2) Nest on ground
3) Eggs piled in the nest without order
4) Lined with vegetation for heat
5) no incubation from the body
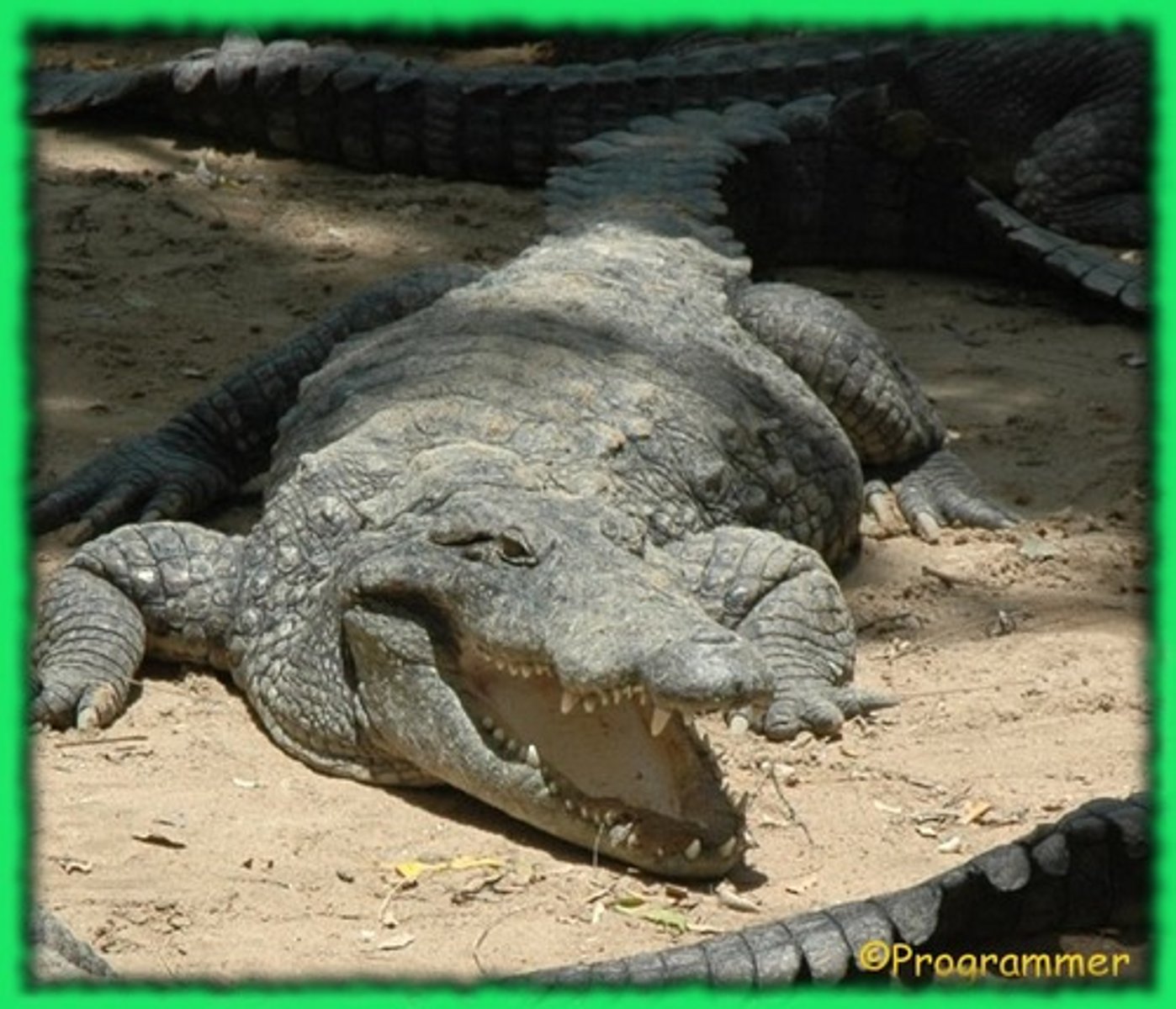

T/F: Crocodiles and birds both incubate their nests with their bodies.
False, crocodiles do not incubate with their bodies

By studying what 2 species can help us understand more about dinosaur behaviors?
Crocodiles and birds. The ideas is that if they both have common behaviors then it is likely that dinosaurs did the same.

Precocial
Babies that are fairly self-sufficient meaning that they need little to no parental care or help
ex. Crocodile babies

Altricial young
babies that are helpless at birth or hatching so they need parental care
ex. Some birds

What are 5 ways that birds take care of their nestlings?
1) Lay few eggs (

T/F: Dinosaurs payed eggs.
True, there is a lot of egg fossils found

Who was the first person to find fossilized dinosaur eggs?
Roy Chapman Andrews (the same guy that led expeditions in Mongolia and that motivation behind Indiana jones)

T/F: All dinosaurs incubates their nets with their bodies.
False, some did and some didn't. A sauropod did not it on it's eggs. Lol
How many ovaries are dinosaurs thought to have?
2 ovaries since they lay pairs of eggs next to each other in their nests.
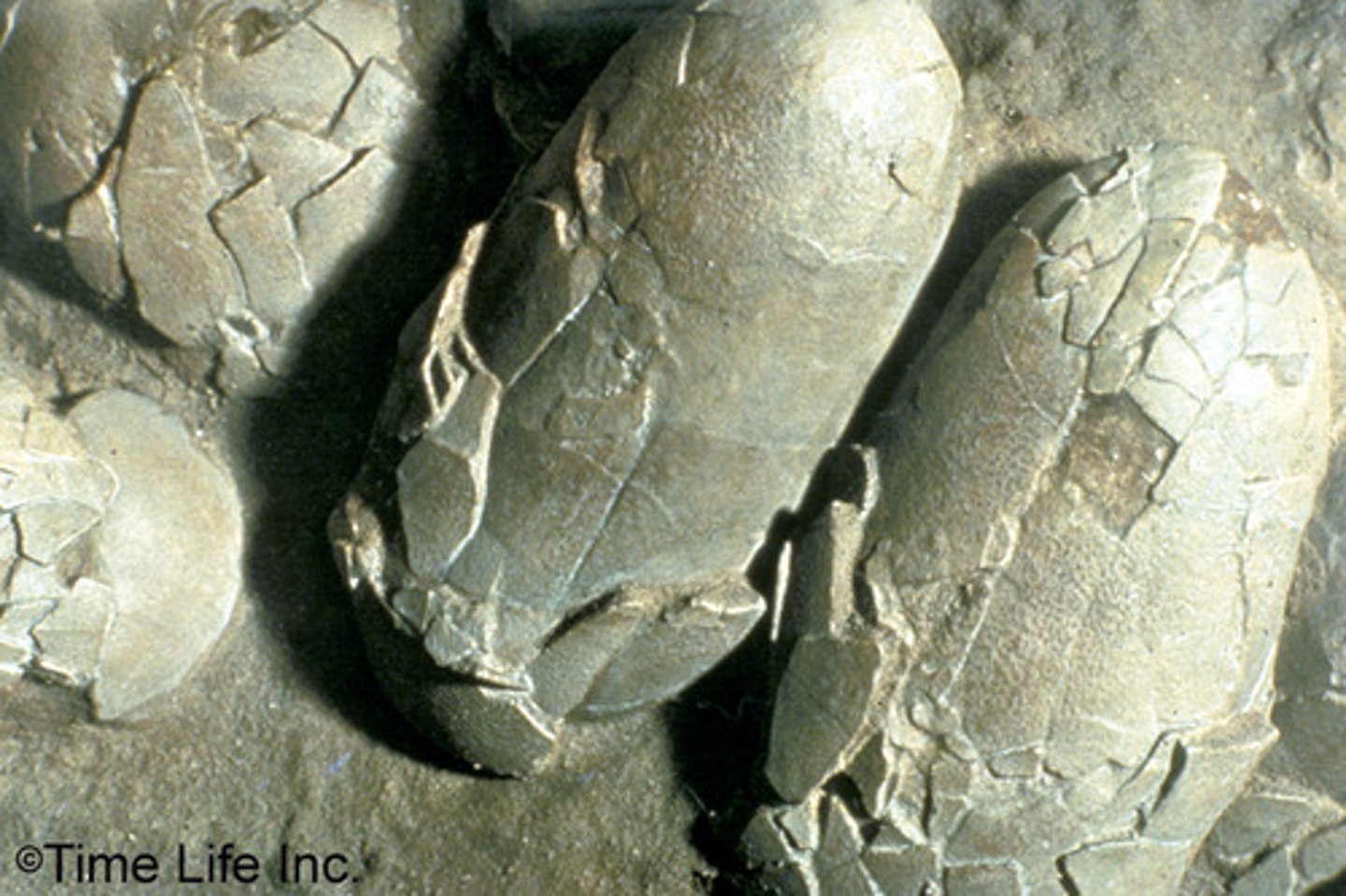
T/F: Most dinosaur infants were precocial.
True, think about how a sauropod is huge compared to its babies and it will not be able to keep up with the parents because they would be moving too fast compared to the infants.

What is one evidence that some dinosaurs took care of their young?
The bones of juices ranging from 1 to 5 ft have been preserved in the nests along with broken eggshells which indicates that the infants must have moved around their nests and crushed them.
Communal parental care
Coming back as a herd to the same area each year to nest their young
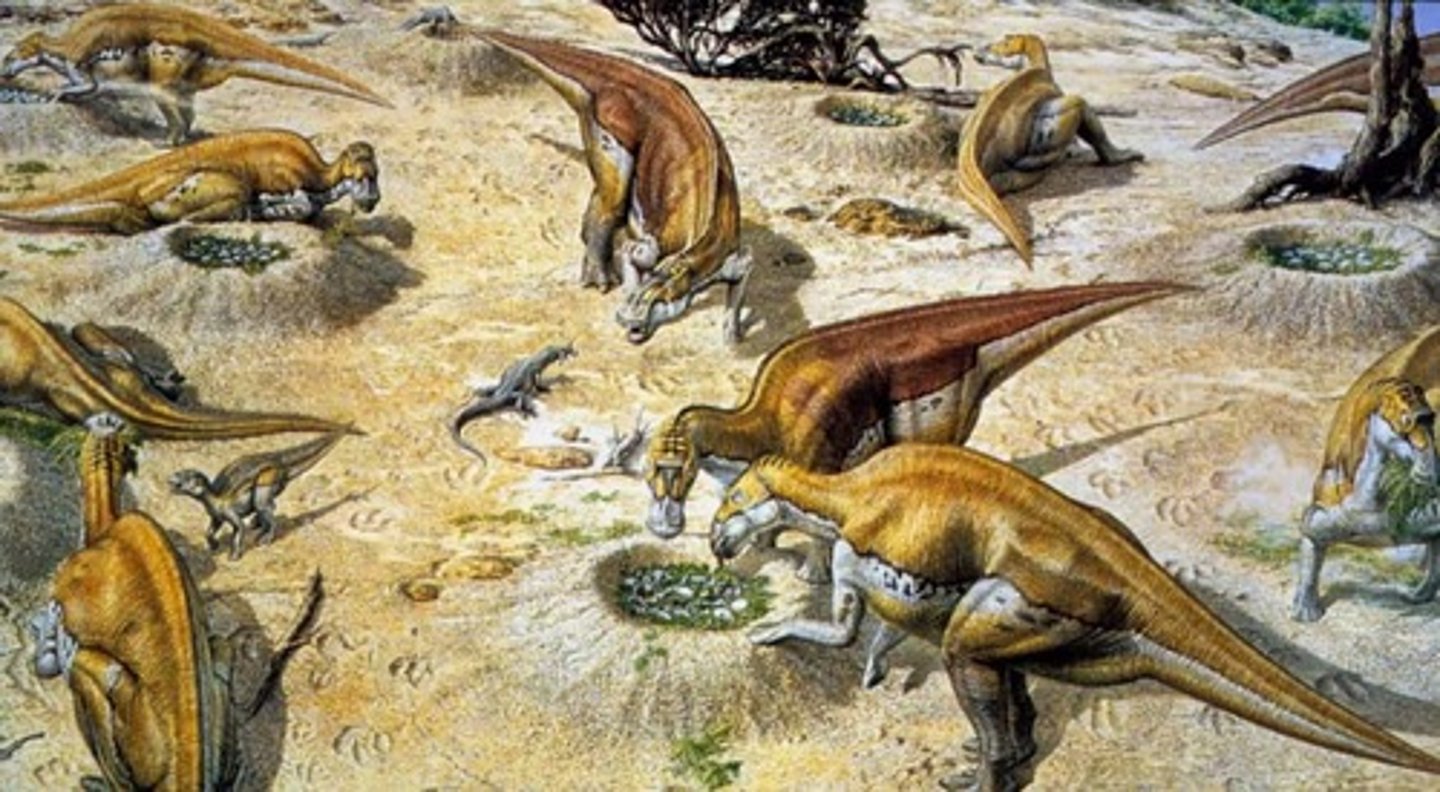

Maiasaura
good mother lizard which nourished their young
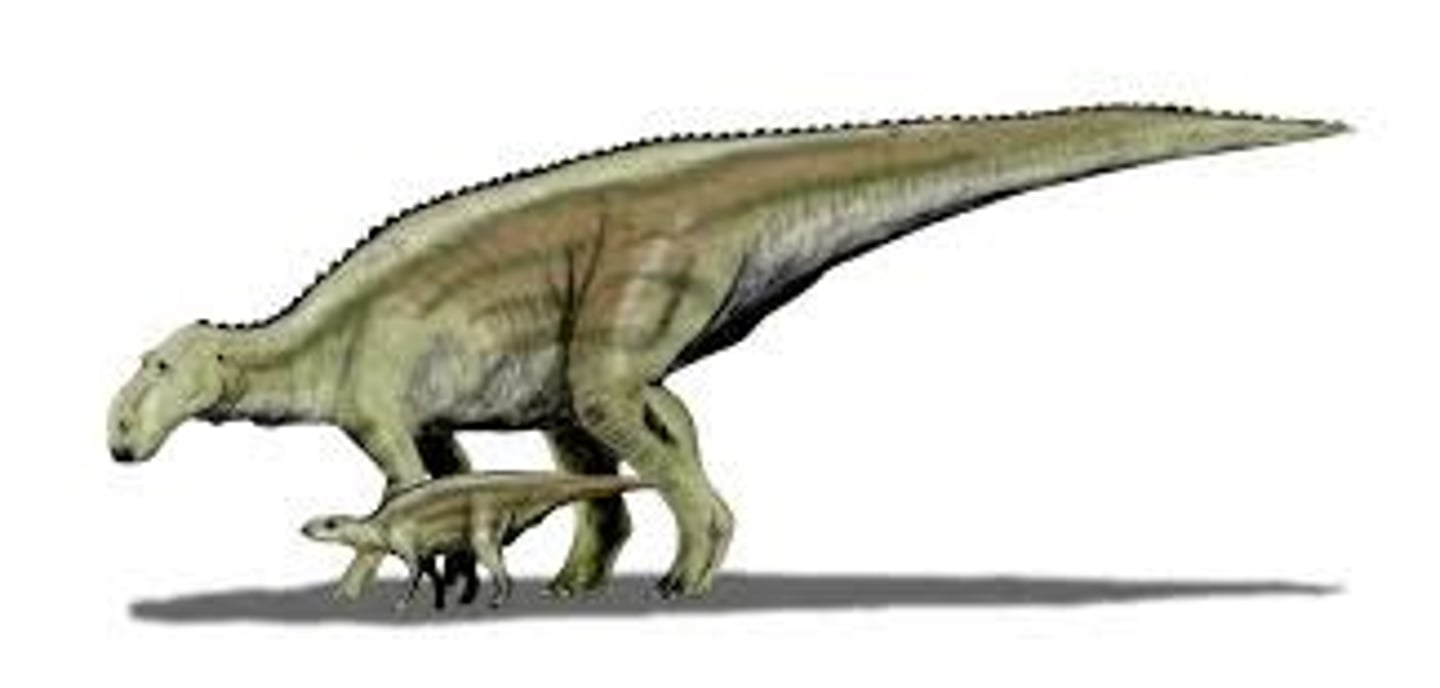
T/F: Sauropods took care of their hatchlings.
False, they laid the eggs and left. The baby sauropods would eventually get large enough and join a heard and be protected. Until then, they are on their own.
Ex. This is similar to how turtles do except that the turtles do not care for their young at all

How did the sauropods create their nests?
They used their back legs to big a hole, deposited their eggs into it, and covered it with dirt.

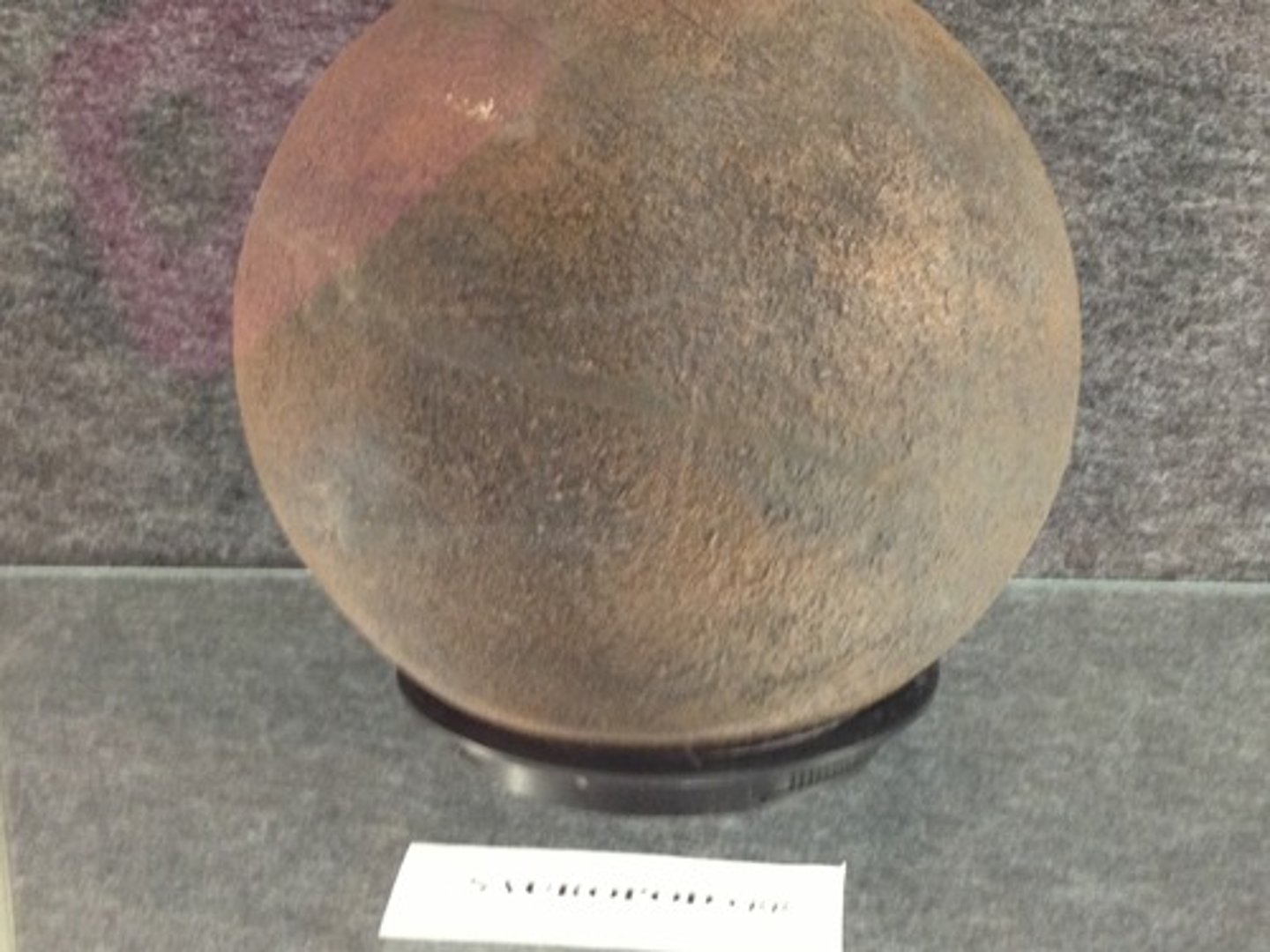
T/F: Dinosaurs did not lay eggs.
False, they did lay eggs
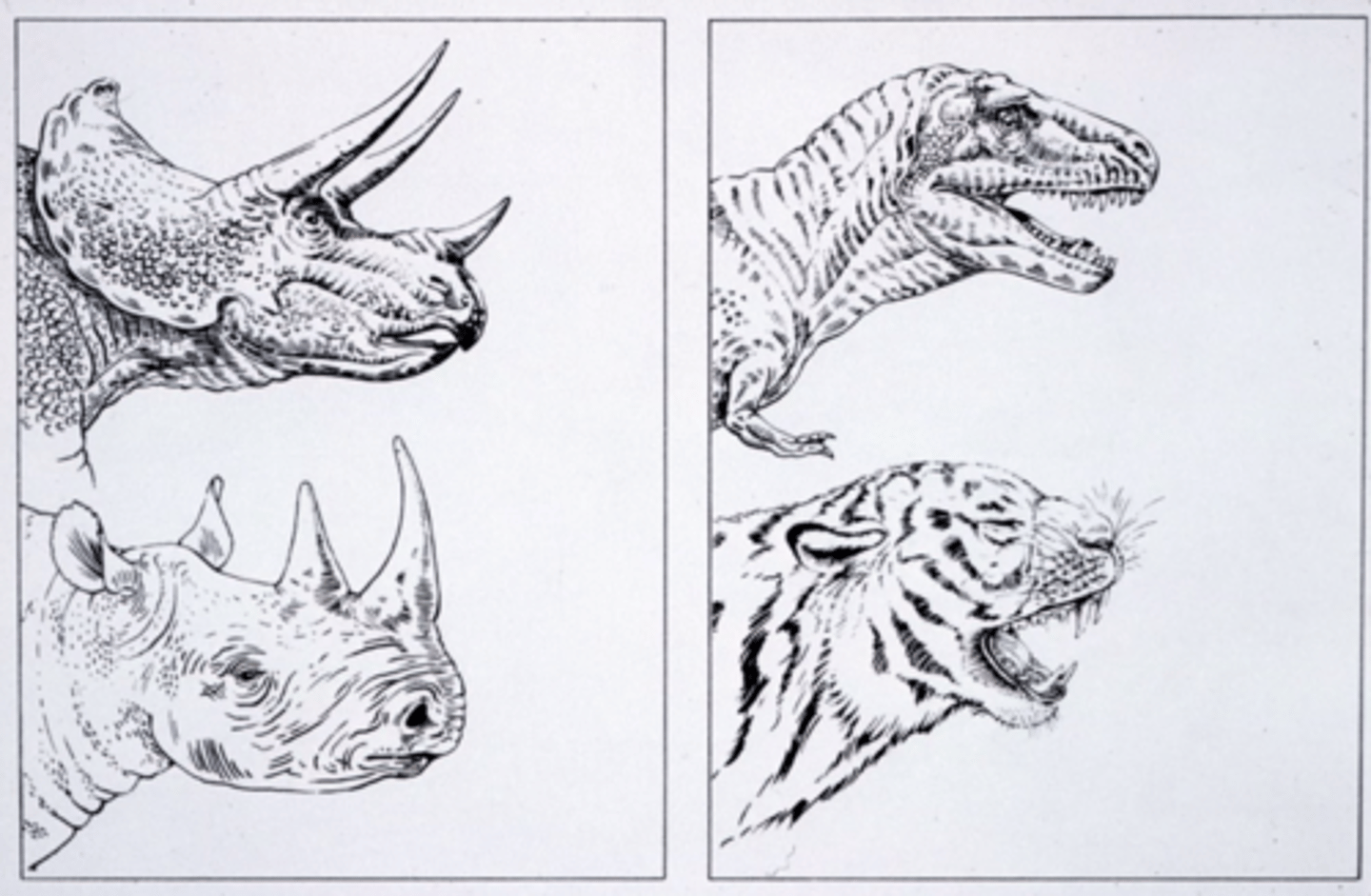
How do paleontologists study extinct dinosaurs?
By using modern analogues
-using the alive animals as comparisons to the extinct
T/F: Our goal in science is not to gather as much supporting evidence as possible. It is to reject as many implausible hypotheses as possible.
True

Ectotherm
An animal whose body does not produce much internal heat

What is another name for ectotherm?
Cold blooded
ex. Snakes

Endotherm
An organism that is internally warmed by a heat-generating metabolic process

What is another term for endotherm?
warm blooded

Are mammals endothermic or ectothermic?
endothermic

How do ectotherms regulate their body temperature?
By using the environment around them such as a cold rock or being directly under the sun

In general, the body temperatures of endotherms tend to be _____________.
Constant

What are the 5 benefits of endotherms?
1) Don't need to warm up in the morning
2) Avoid predation more easily
3) Can move more quickly
4) Can love in colder climates
5) Can digest food more quickly

What are a drawback of endotherms?
It's energetically expensive meaning that we have to eat and breathe a lot more than ectotherms
ex. Humans eat about 5 times a day as apposed to a snake that only needs to eat once every week or two weeks

T/F: The body temperatures of endotherms varies.
True, for example, birds have a regular temperature of 104

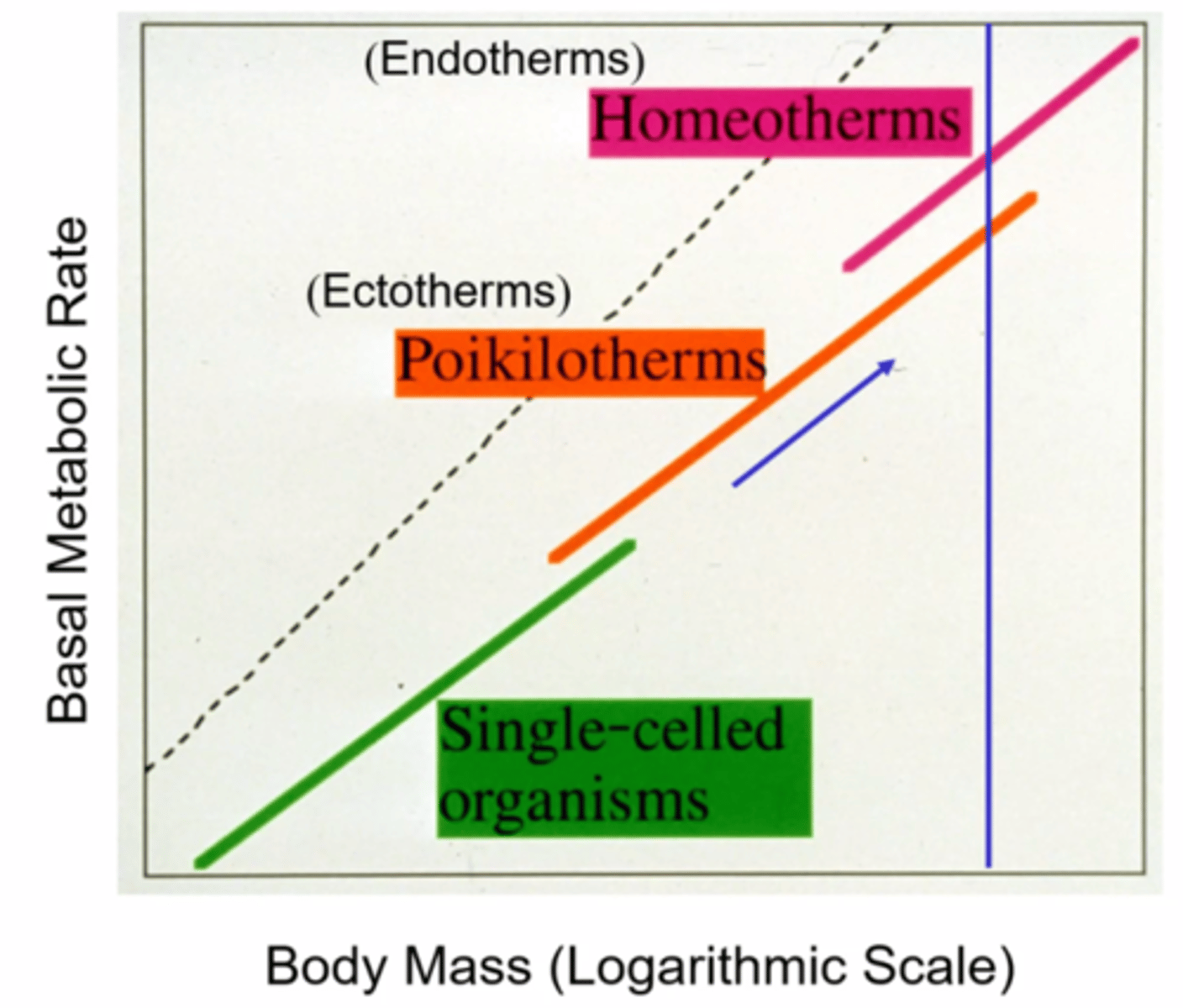
What is the relationship between body mass and BMR?
Species with larger body masses tend to have higher BMRs and are often endotherms.
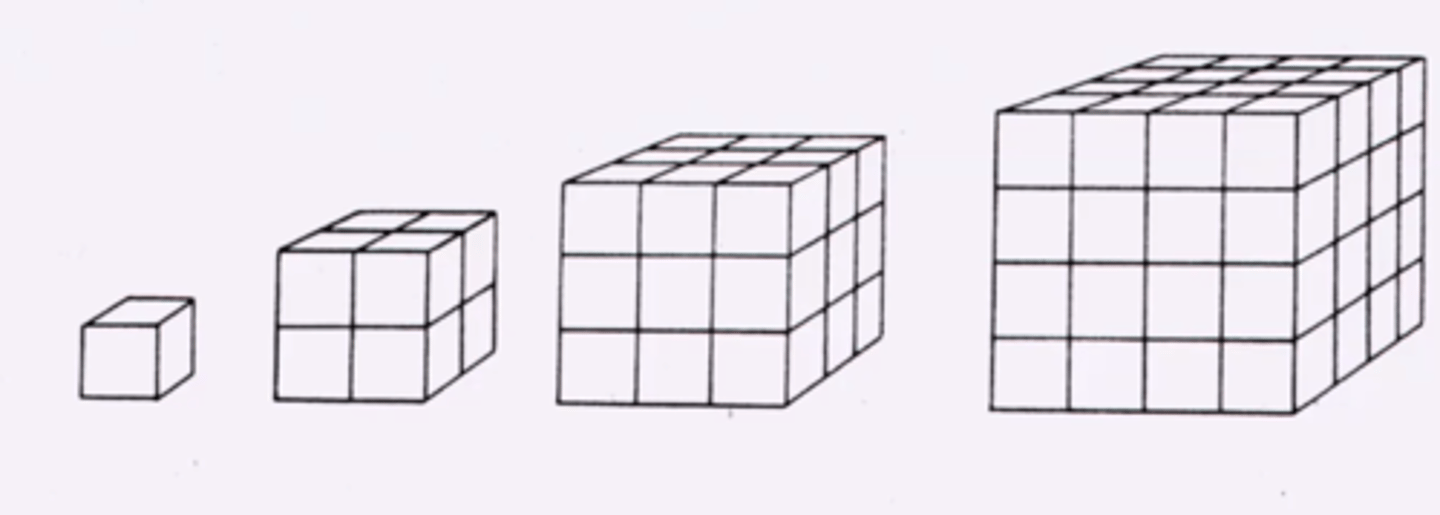
Isometry
as size increases, shape stays the same
What is the correlation between BMR and energy requirements?
As BMR increases, the more the energy requirement increases

If you have two 20-lb animals, one is an endotherm and the other is an ectotherm. Which one requires more food?
The endotherm because it has a higher BMR

What is the correlation between body size and energy requirements?
As body size increases, energy requirements scale down because of the increased surface area

If you have a one 20-lb cat and twenty 1-lb kittens, who needs more food?
The kittens because

How do we measure metabolic rate in terrestrial dinosaurs?
Posture, and biomechanics (locomotion)

What is the relationship between posture (and locomotion) to respiration (and circulation)?
Animals with a sprawling posture can't breath easily while they run.
Ex. A lizard
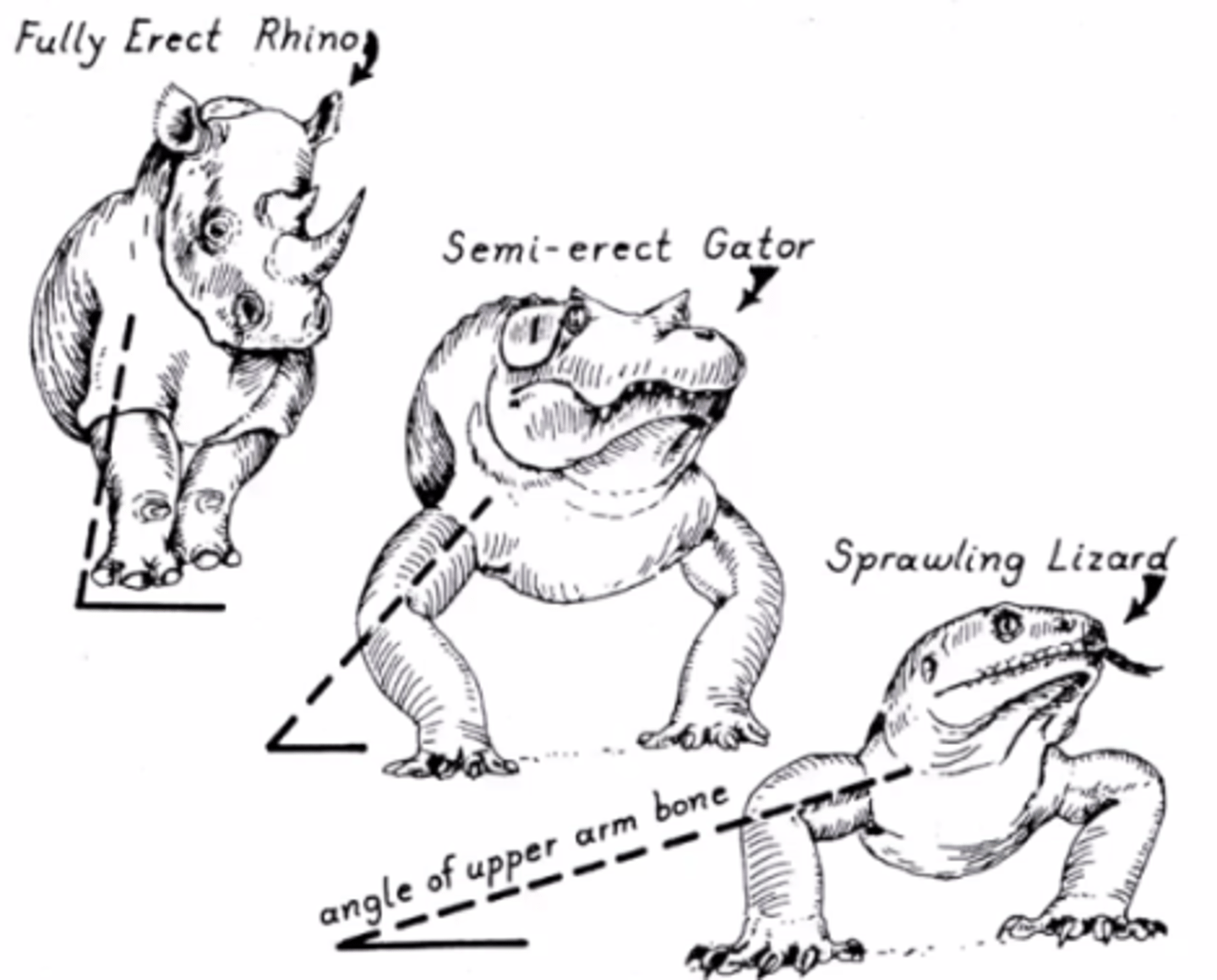
T/F: Almost all endotherms have an upright posture and can breathe and run at the same time.
True

T/F: endotherms with an upright posture can also run very fast for longer periods of time.
True

What posture were dinosaurs?
Upright and erect
All living animals with _________ posture today have _____________ physiology.
Erect, endothermic

How many heart chambers do lizards and snakes have?
3 chambers because they aren't as active and are ectotherms
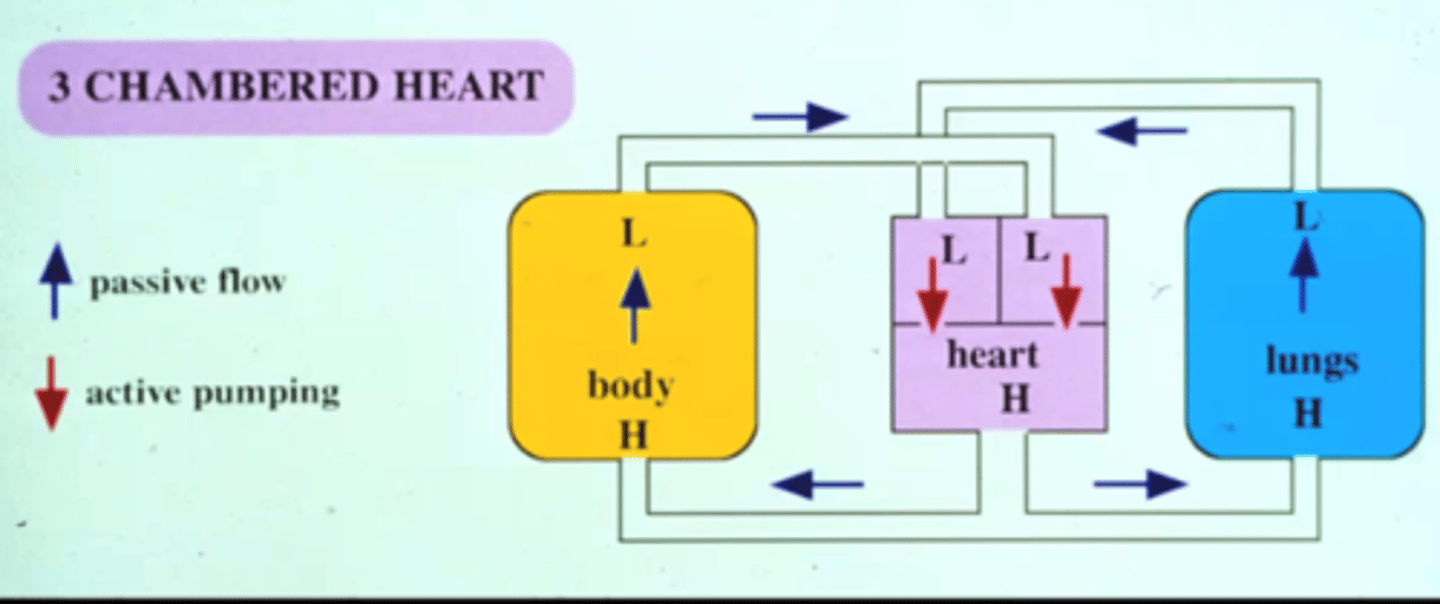
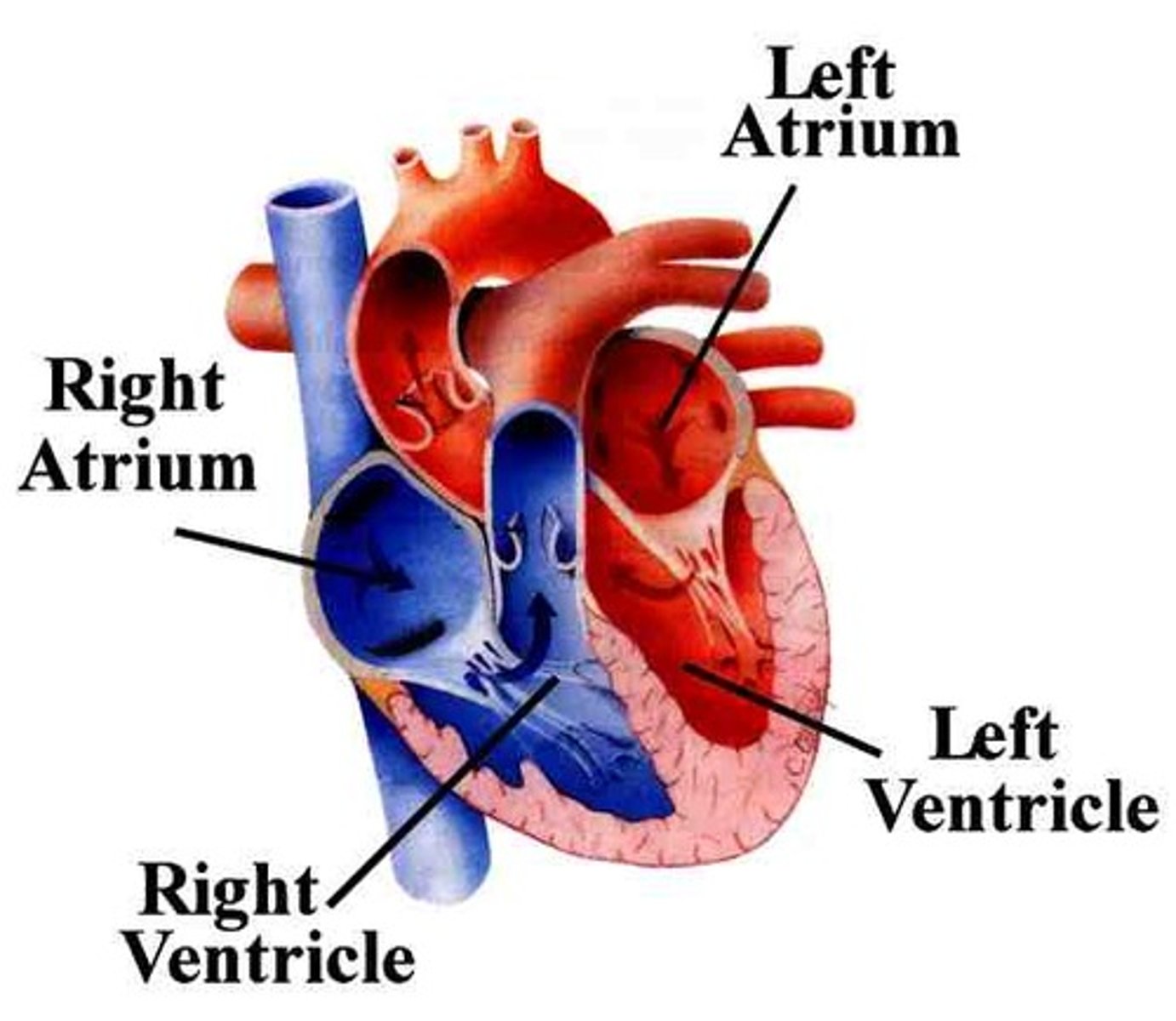
How many heart chambers do mammals and birds have?
4 chambers because they need their hearts to be more efficient at delivering blood because having a 4 chambered heart keeps the oxygenate and the unoxigenated blood separate unlike the heart of lizards and snakes
What are some characteristics of animals with a sprawling posture?
1) inhibited respiration
2) Locomotion in short bursts
3) Lower activity levels
4) 3-chambered hearts

T/F: Dinosaurs are endotherms?
Can't say because it is a working hypothesis

In the 1970s, who proposed that dinosaurs are endothermic?
Robert Bakker

Haversian canal
Channels in bone that contain blood vessels and nerves
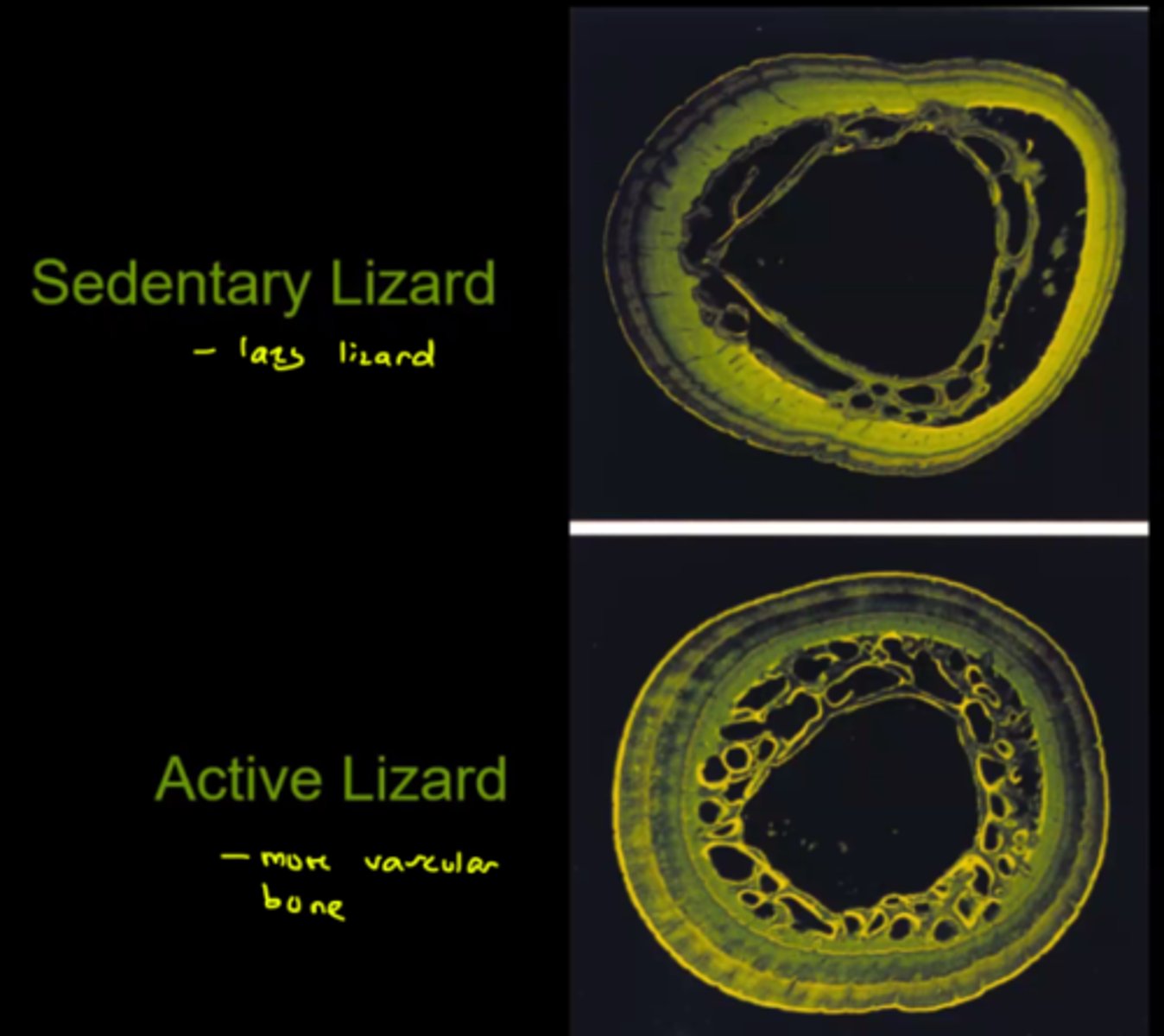
note: these are the black parts in the image
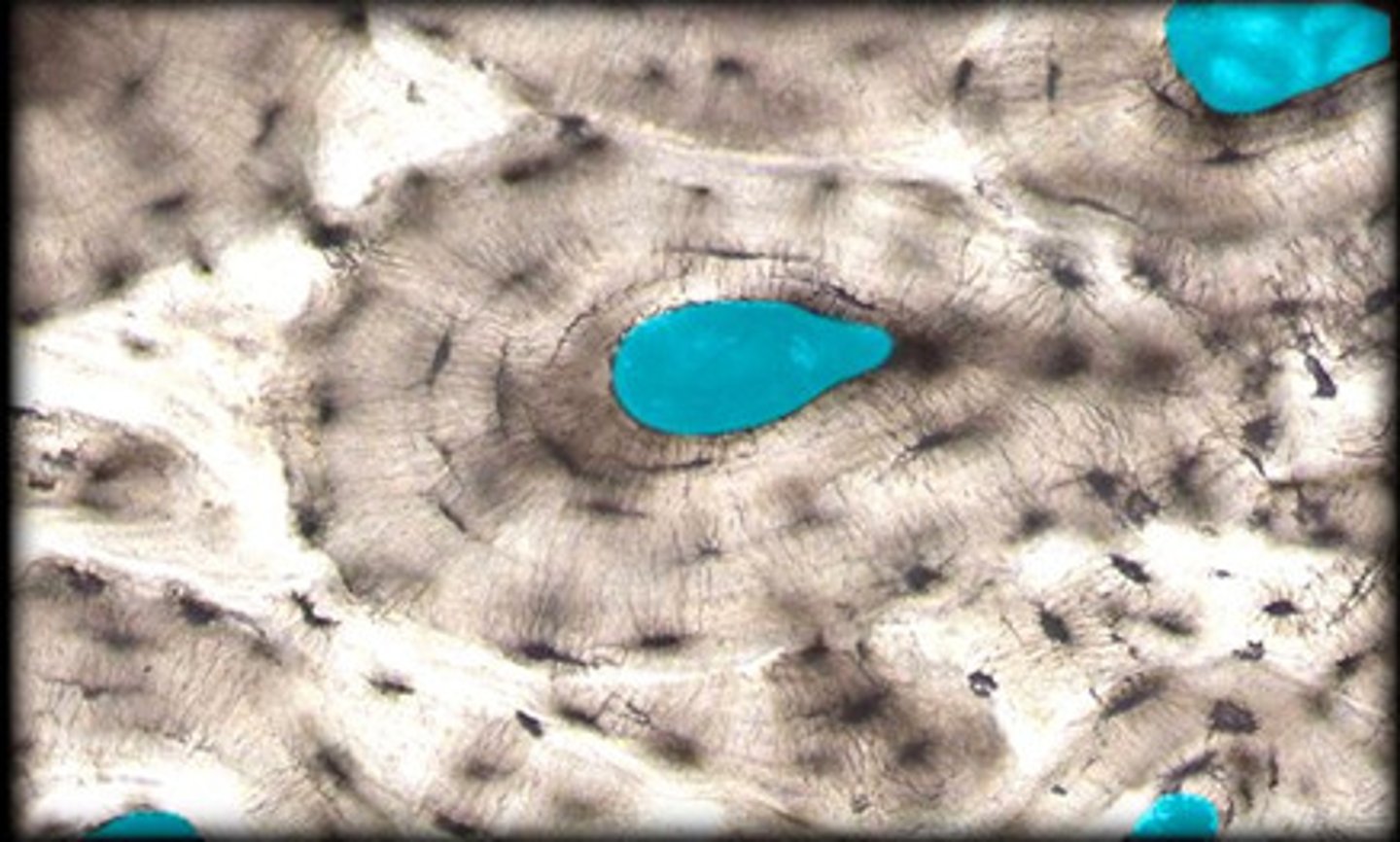
T/F: Dinosaurs bones contain many Haversian canals.
True
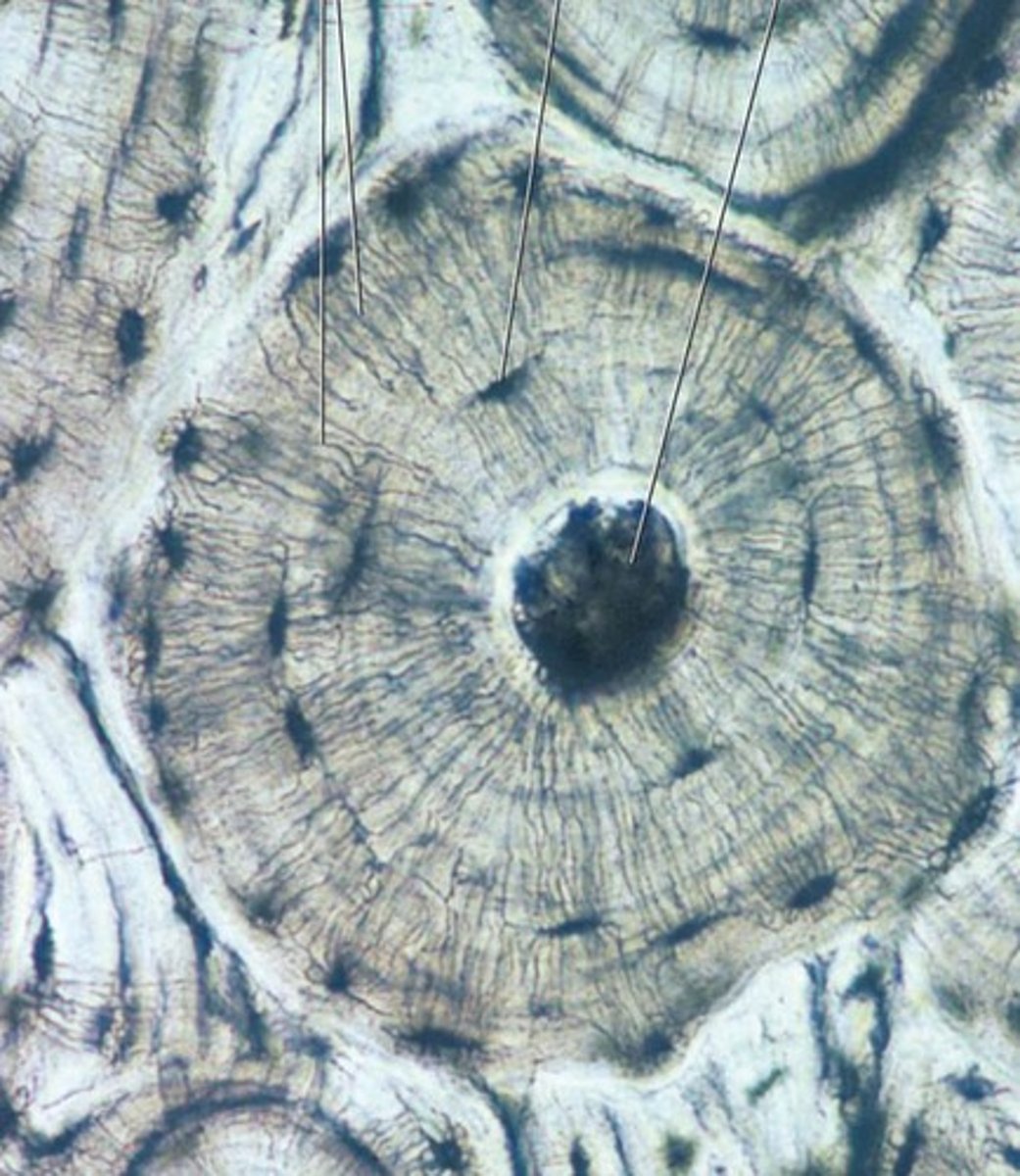
Is highly vascularized bone specifically associated with endotherms?
No, activity also plays a role. The more active the individual is, the more vascularity the bone will have
T/F: Using predator/prey ratios are strong evidence For endothermy.
False, because some area contain fossils that have been found to have more predators than herbivores which would hint to dinosaurs being ectotherms and not endomorphs
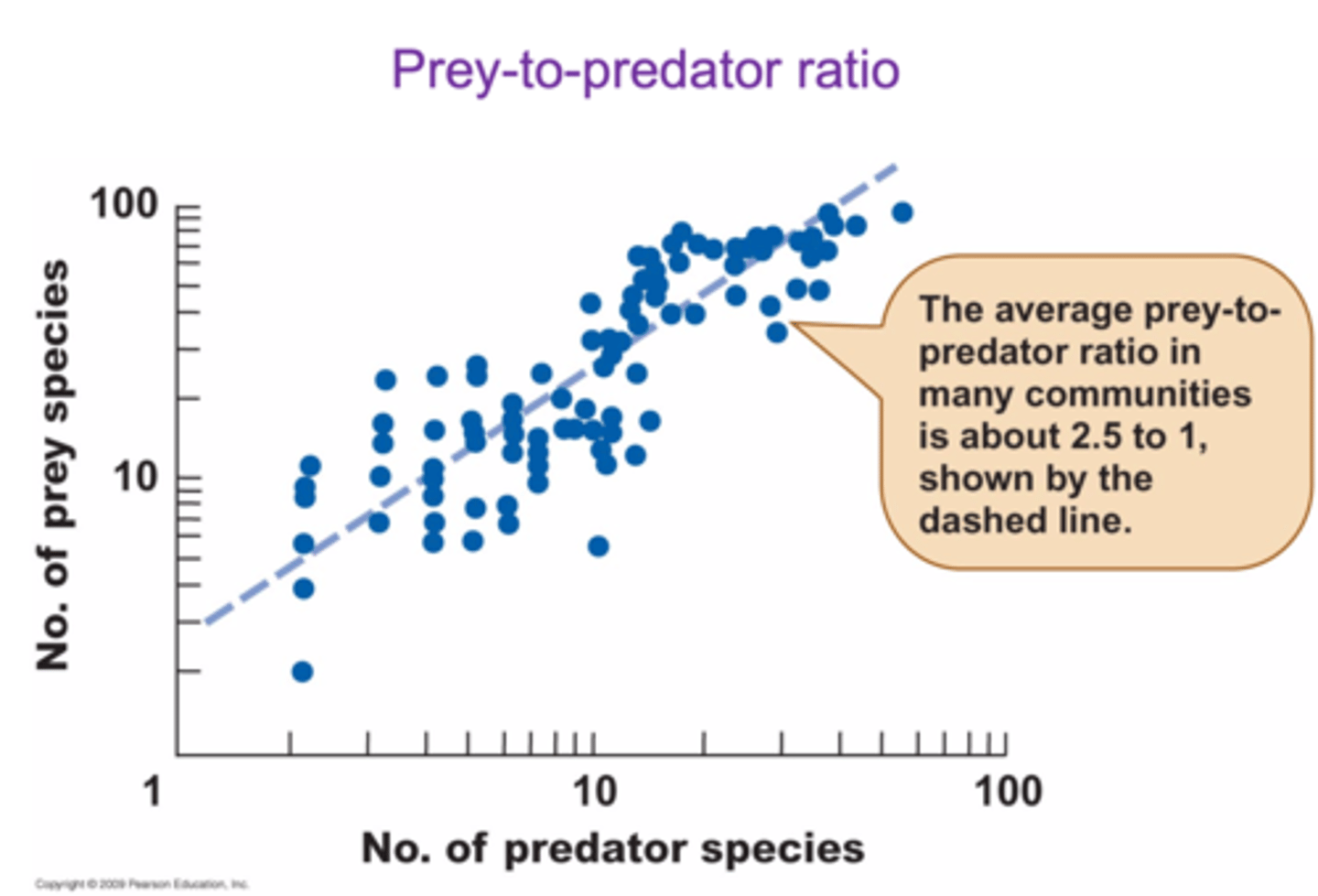
If dinosaurs where ectomorphs, the number of prey animals needed to sustain the carnivores would be ________.
Lower because they would not be as active so they won’t need to eat as much food
In general, more __________ animal are required per endothermic predator.
Prey

What is the evidence against dinosaurs being endotherms?
Gigantothermy - the idea that something is so large that it can sustain it's own body temperature without needing to be an endotherm

Gigantothermy
the ability of an extremely large animal to maintain a constant and relatively high body temperature due to its low surface/volume ratio
nasal turbinates
scroll-like cartilages covered with highly vascular mucous membranes
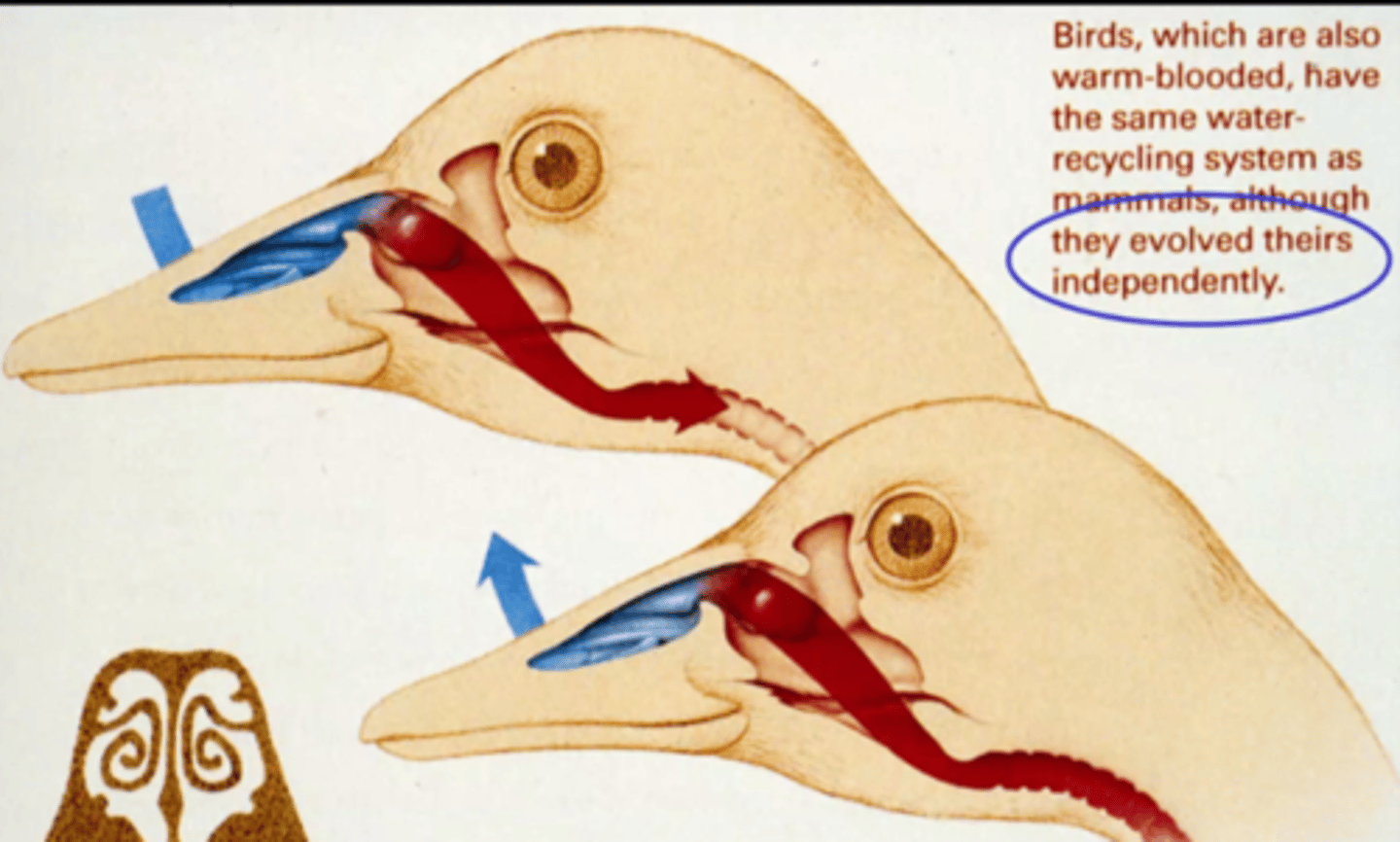
T/F: Nasal turbinates are found in 99% of living endotherms.
True
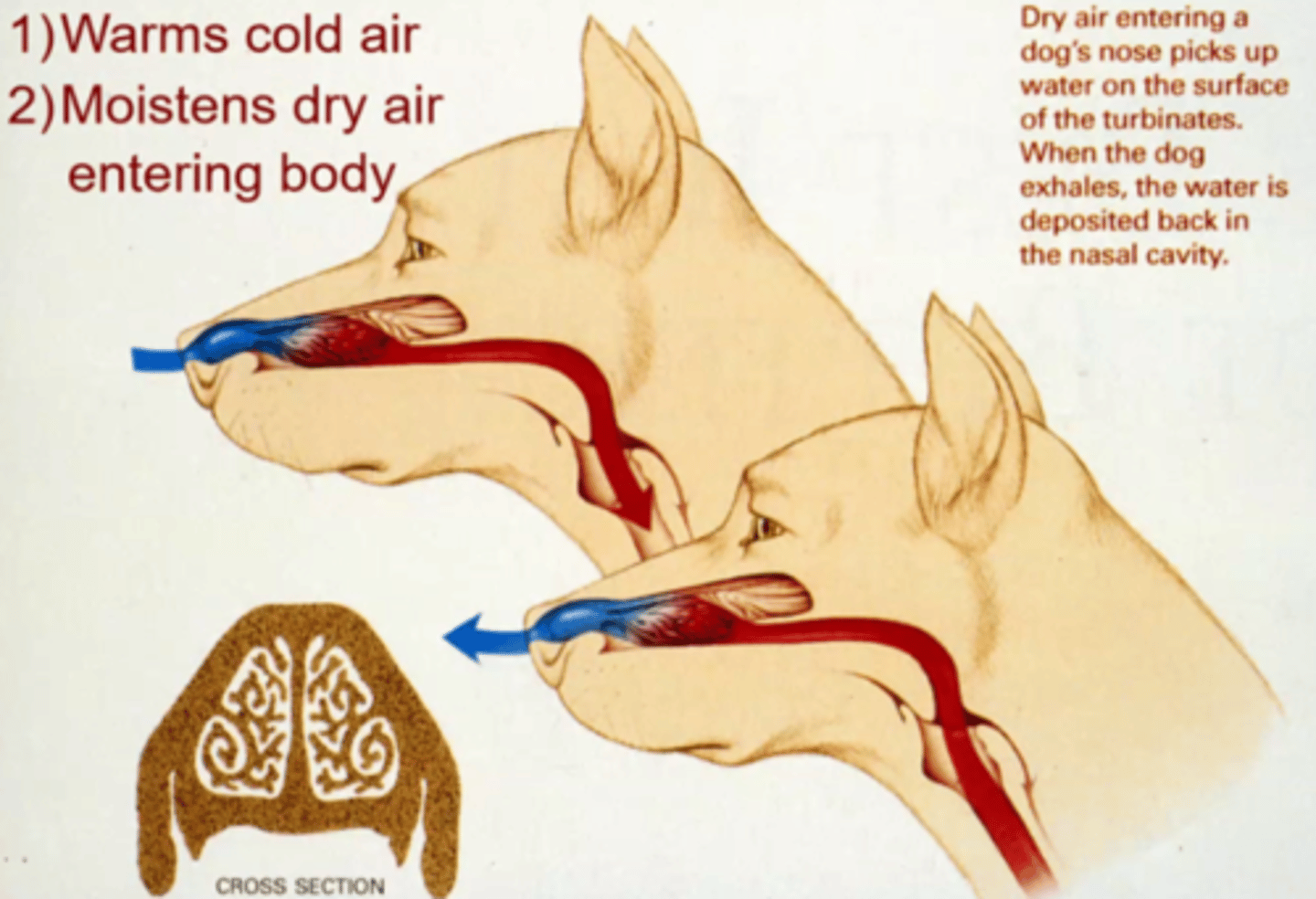
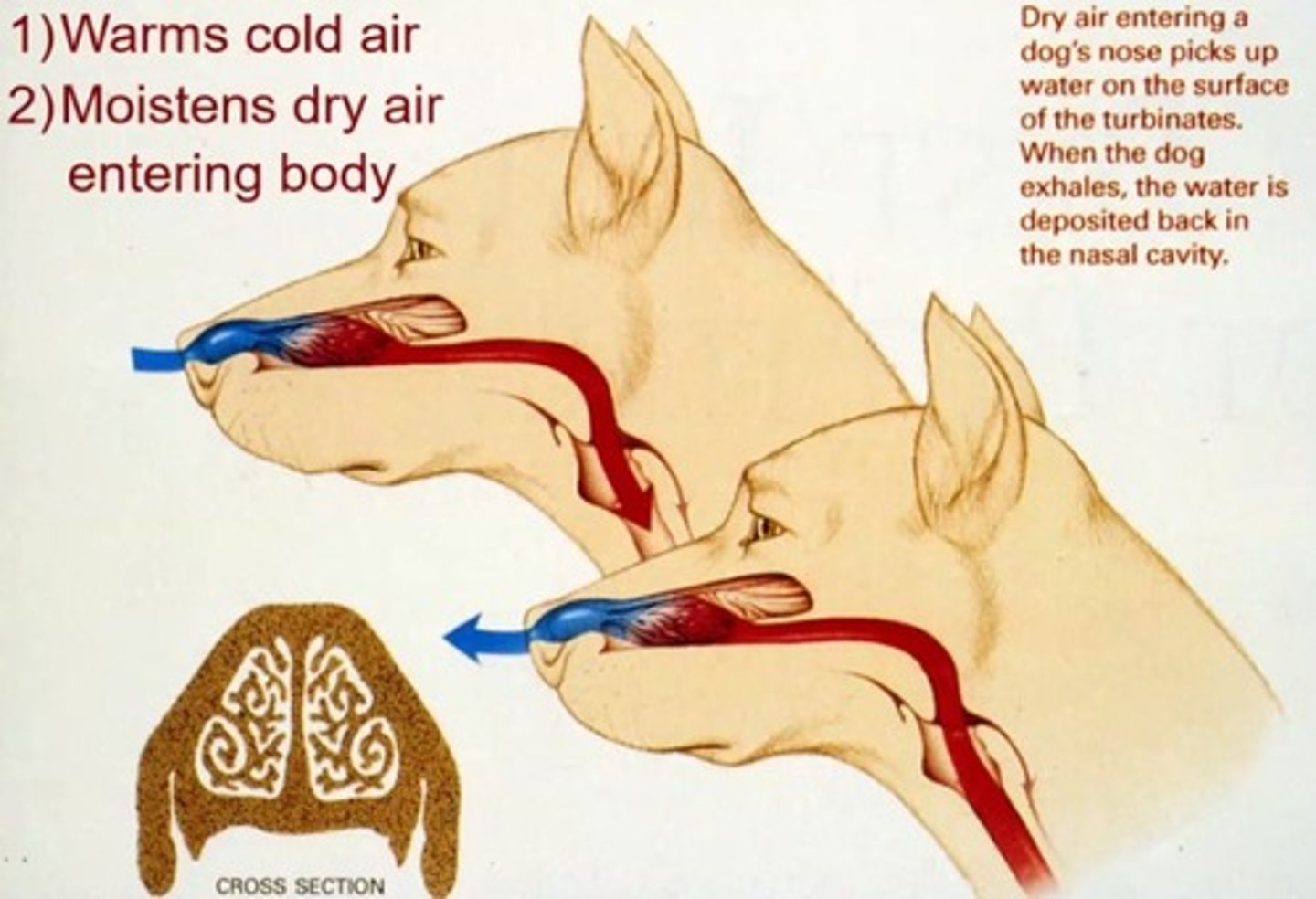
What are the 2 purposes of nasal turbinates?
1) Warms cold air
2) Moistens dry air entering the body
T/F: Dinosaurs had nasal turbinates.
False, they most likely didn't because none of the fossils contain them, even the well preserved ones.
Evolution
Change over time