space physics
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
satellite
any object that orbits a celestial body i.e star or planet
natural satellite
have formed naturally
i.e moon, earth and comets
artificial satellites
man made
i.e orbiting telescopes, rockets, communication
what is the central star
sun
planets
mercury
venus
earth
mars
jupiter
saturn
uranus
neptune
what do the 8 planets do
orbit the sun- natural satellites
asteroids
made of rock and metal found on asteroid belt
comet
ice an dust
more elliptical orbits
elliptical shape
galaxy
collections of billions of stars that have their own solar systems
i.e Milky Way
what force hold stars together
gravity
universe
scattered with galaxies and mostly empt space
what is the asteroid belt
a region of our solar system that contains millions of asteroids
it is in between mars and Jupiter
nebula
a large cloud of dust and gaswha
what pulls the gas and dust in a nebula together to form a protostar
attraction of gravity
what happens when a protostar grows in size
attracts more particles from he surrounding nebula
becomes more dense
temp increases
nuclear fusion could initiate
once nuclear fusion starts in a protostar, what does it become
a main sequence star
explain why the forces are balanced acting on the sun
The energy released from nuclear fusion creates an outward pressure that balances against the inward pressure from gravity.
what stage of stars life is the sun currently in
mai sequence star
what could a main sequence star become
red giant
red super giant
what does main sequence star make when it fuses together hydrogen
helium
up to which element can red giants/super giants form with nuclear fusion
iron
what are elements heavier than iron formed by
supernovasw
what occurs next after small/medium stars swell then cool
red giants form
what occurs next after really big stars swell
become red supergiants
what does red giant form when it becomes unstable and expels outer layers
white dwarf
white dwarf
hot dense solid core
what forms after white dwarf gets cooler and emits all of its energy
forms black dwarf- no longer has enough energy to emit life
what happens when a red super giant has more nuclear fusion and expands
explodes into supernovae
elements in supernova
forms elements heavier than iron and these are ejected across universe
what occurs if the star was just very big after supernova explosion
condenses into very dense core called neutron star
what occurs if the star was absolutely massive after supernova explosion
star collapses in on itself and becomes a black hole
gravity is able to pull in any light that passes nearby- no light
life cycle of star
dust and gas
protostar
main sequence star
red giant-white dwarf-black dwarf
red supergiant-supernova-neutron star-black hole
orbit
the curved path of one celestial object or spacecraft around another celestial object
what can be said about the speed for circular orbits
stays the same but force of gravity pulls in constantly meaning direction is changing constantly so constantly changing velocity
therefore it is accelerating wha
what is the force that keeps an object moving in a circle
centripetal force
smaller objects orbit means
faster the object is travelling in order to keep a stable orbit
what law is this "An object travelling at a certain velocity will continue to travel at that velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force."
newtons first law
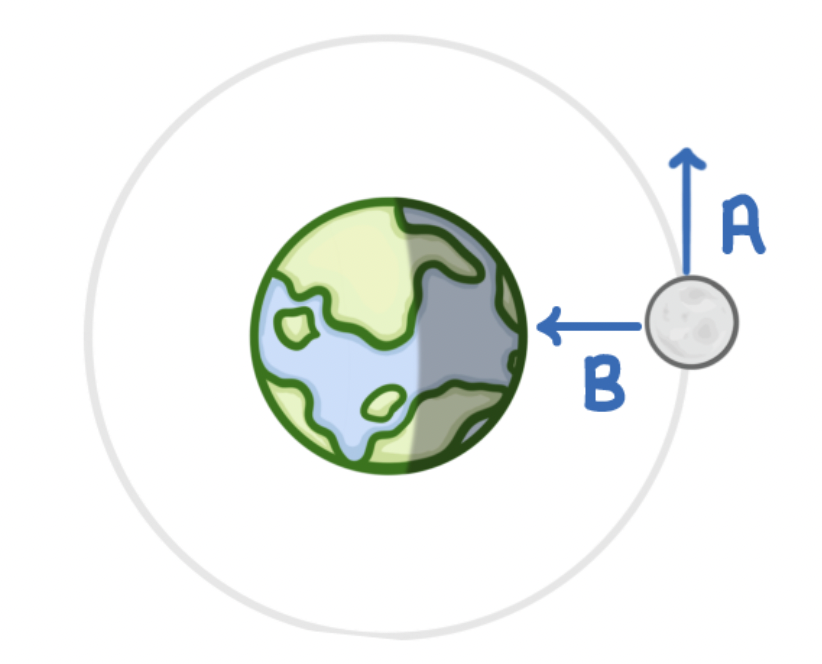
what arrow shows direction of instantaneous velocity
A- as it is the direction that the moon will be travelling
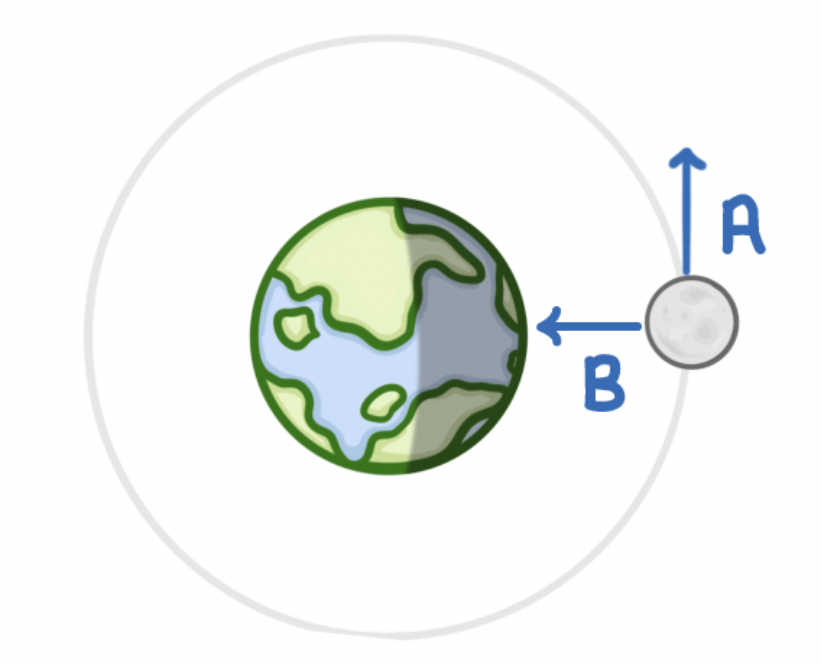
what arrow shows force of gravity
B-as it shows the moons weight
What is required for the object to stay in orbit?
The magnitude of the velocity must increase
speed of light in vacuum
3×10^8
absorption spectra
sun emits light at all wavelengths
elements in sounds atmosphere absorb wavelengths of light spectra to that element
removes those wavelength from spectra so appear as black lines
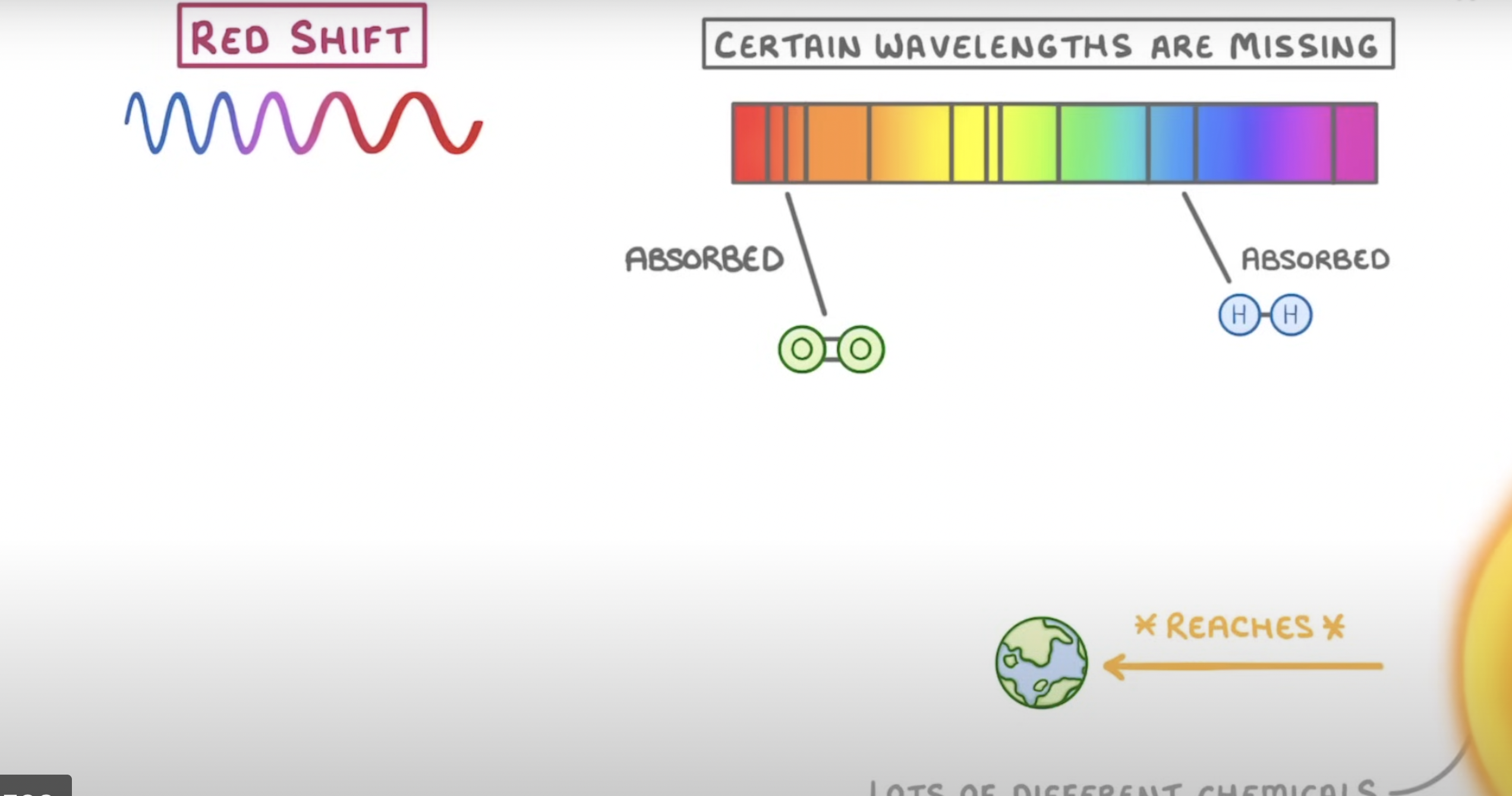
blue light open absorption spectra has
shorter wavelength
higher frequency
red light on absorption spectra has
longer wavelength
lower frequency
blue shift
when star moves towards us, wavelength of light decreases and shifts towards blue end of spectrum
red shift
Red-shift occurs because the light emitted by an object moving away from us will be stretched.
The stretching causes the light's wavelength to increase.
The faster an object moves away from us, the larger the red shift.
what is wavelength measured in
nano metres wh
which galaxies appear to be moving away fastest- greater red shift
furthest away galaxies
big band theory
universe was initially an infinitely small, dense point which exploded and expanded
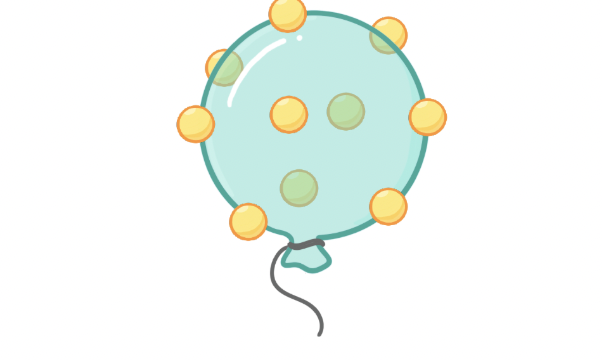
give one strength and weakness of this model representing idea of expanding universe
strength-as balloon expands, dots get further apart which represents galaxies moving apart
weakness-dots are only on surface of balloon, whereas galaxies are throughout universe