transport in humans (chap 6) -olevel pure bio
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
function of plasma
contains mainly water
transports blood cells around the body
transports excretory products to excretory organs for removal
transports substances such as glucose, proteins, fats, salts, vitamins
transports nutrients from small intestines to other parts of the body
transports hormones from endocrine glands to target organs
functions and adaptations of red blood cells
to transport oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body
contains haemogoblin which can combine with oxygen to form oxyhaemogoblin to transport oxygen around the body
has a biconcave shape to increase surface area-to-volume ratio which increases the rate of diffusion of oxygen into and out of the cell
has no nucleus to make more space available for more haemogoblin
flexible and can change into a bell-shaped structure so they can move easily through narrow capillaries
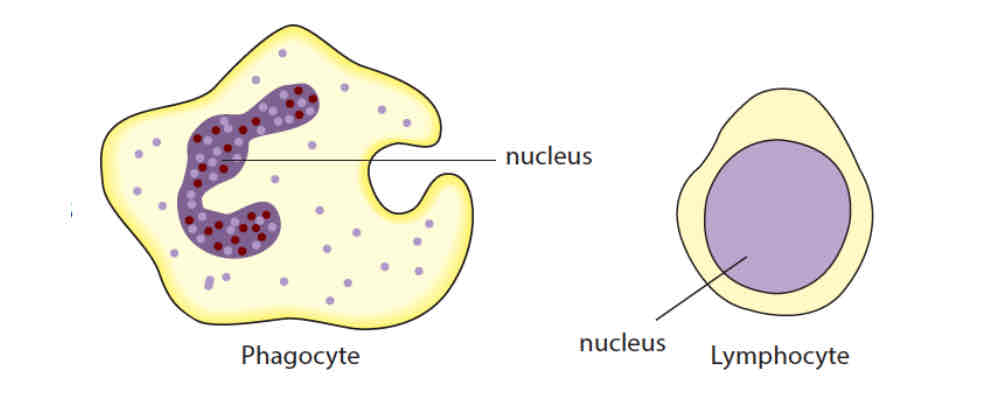
white blood cells
phagocytes
engulfs and destroys pathogens such as bacteria -phagocytosis
lymphocytes
produces antibodies that can
recognise and destroy pathogens
cause pathogens to clump together for easy ingestion by phagocytes
neutralise toxins produced by bacteria
platelets
cytoplasm fragments
contains an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin threads
fibrin threads form a network that entangles red blood cells to form blood clots that seals wound
prevents entry of microorganisms and excessive loss of blood
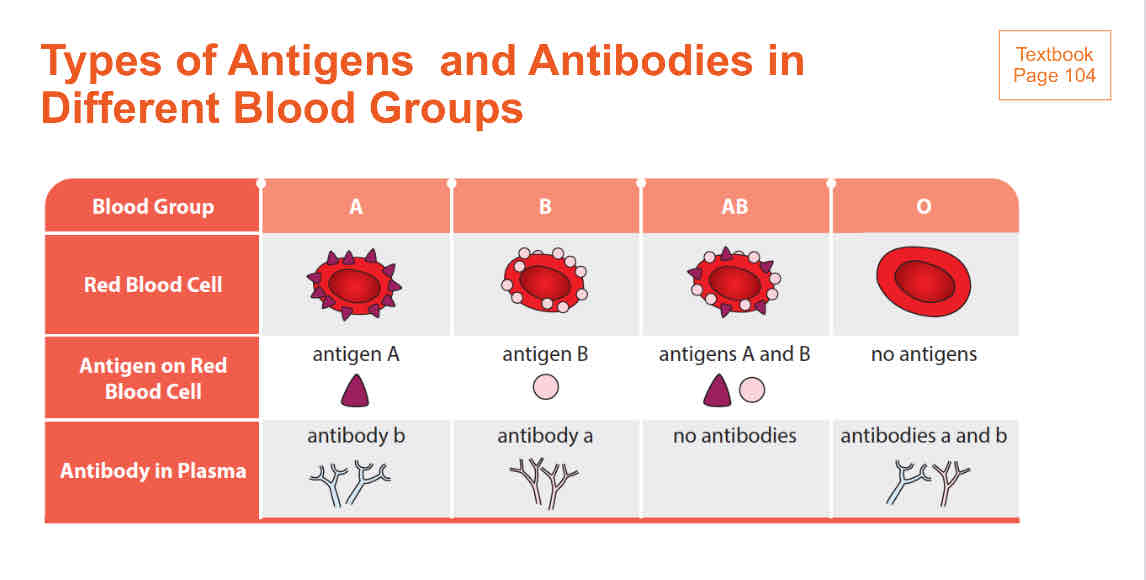
types of antigens and antibodies in different blood groups
certain types of antibodies react with certain types of antigens. this can cause blood agglutination which is fatal
adaptations of arteries
thick muscular and elastic walls to withstand the high pressure of blood flowing within
elasticity helps the artery wall to stretch and recoil
contraction and relaxation of muscles in the arterial wall brings about constriction and dilation of the artery. when the artery constricts, its lumen becomes narrower and less blood flows through it. when an artery dilates, its lumen becomes wider and more blood flows through. (eg dilation of arterioles of skin to divert blood to skin capillaries during thermoregulation)
adaptations of veins
transport blood back to the heart
blood pressure in veins is much lower than blood pressure in arteries.
blood flows more slowly and smoothly in the veins, so the walls of veins do not need to be as thick and muscular as those of arteries.
since blood in the vein has lower pressure and speed, it has a tendency to backflow, so veins have valves to prevent backflow of blood.
adaptations of capillaries
numerous branches of capillaries to provide a large surface area for the exchange of substances between blood and tissue cells
wall of capillaries are made up a single layer of flattened cells to provide a short diffusion distance for exchange of substances
there is continuous blood flow through the capillaries to provide a steep concentration gradient
when an arteriole branches into many capillaries, the total cross sectional region of the blood vessels increases, lowering blood pressure in the capillaries. the flow of blood is slowed down, giving more time for exchange of substances
label
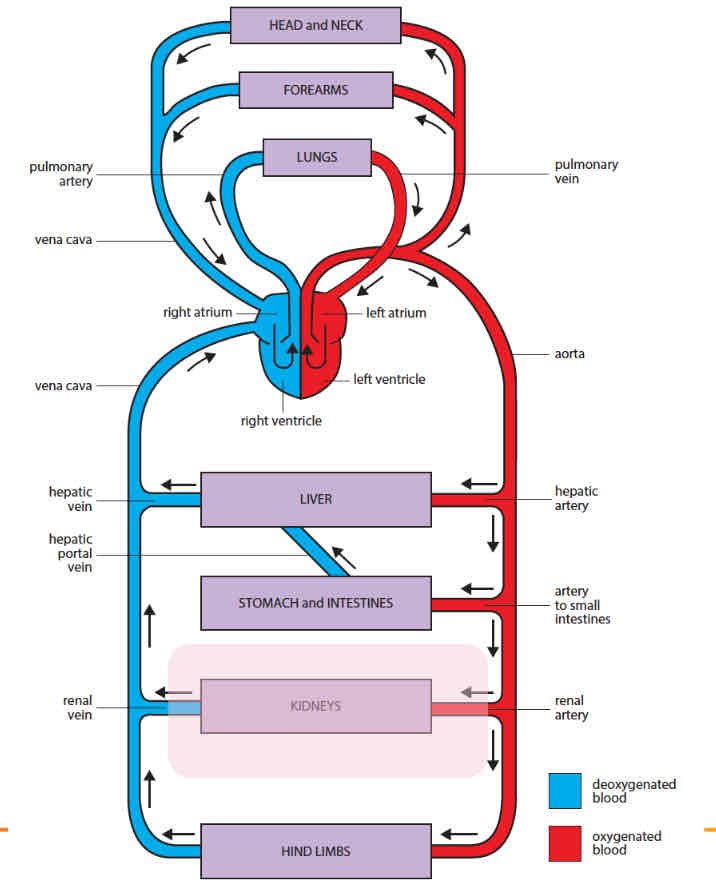
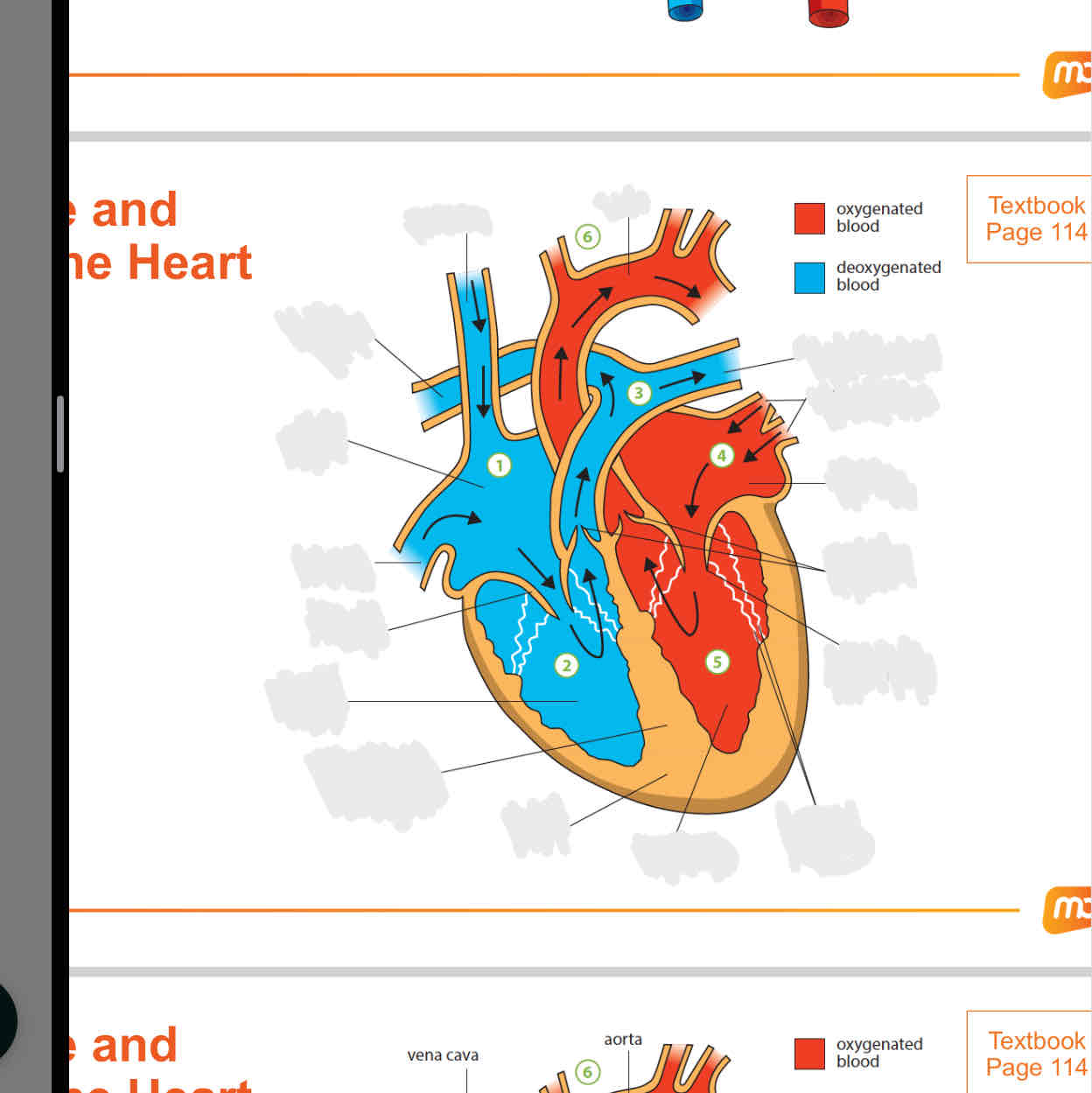
Label
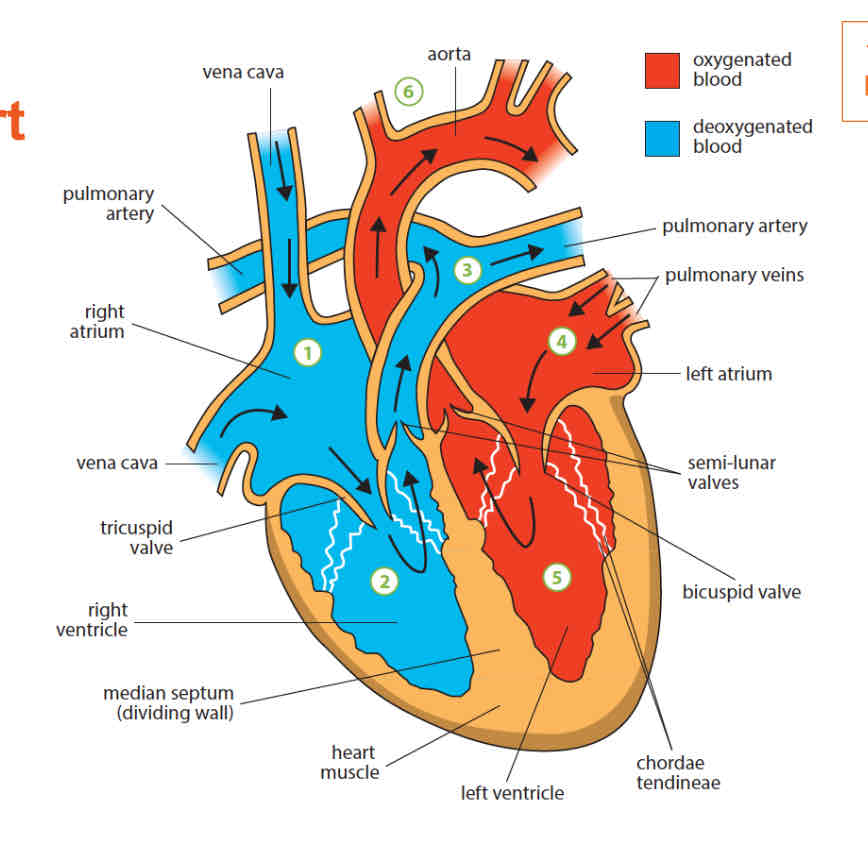
why do the ventricles have thicker walls than the atriums
the atria receive blood from the veins.
they have comparatively thin muscular walls as they only need to force blood into the ventricles that lie directly below them. this does not need high pressure
ventricles have thicker muscular walls. the left and right ventricles pump blood to the rest of teh body and lungs respectively. this requires high pressure
why is the left ventricle thicker than the right ventricle
the left ventricle pumps blood around the whole body and this requires high pressure
the right ventricle has thinner walls as it pumps blood to the lungs, which is close to the heart.
purpose of the median septum
a muscular walls that separates the right and left side of the heart
prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood will reduce the amount of oxygen carried to the rest of the body
what are the valves located in the heart
tricuspid valve: prevents blood from the right ventricle from backflowing into the right atrium
bicuspid valve: prevents blood from the left ventricle from backflowing into the left atrium
aortic valve (semi-lunar valve): prevents blood from the aorta from backflowing into the left ventricle
pulmonary valve (semi lunar valve): prevents blood from the pulmonary artery from backflowing into the right ventricle
what happens when there is a hole in the heart
mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood
causes less oxygen to be transported to the body cells for respiration
causes shortness of breath as not enough oxygen being transported fast enough for cellular activies
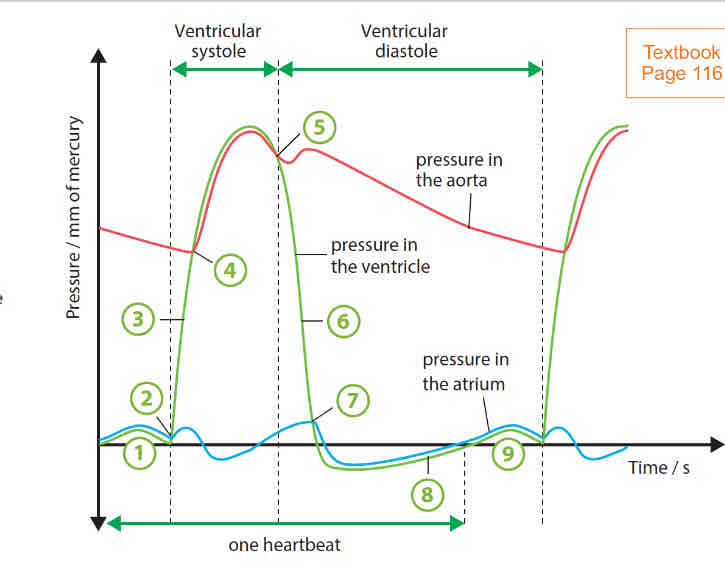
what is systole and diastole
systole - ventricular or atrial muscles contract
diastole - ventricular or atrial muscles relax
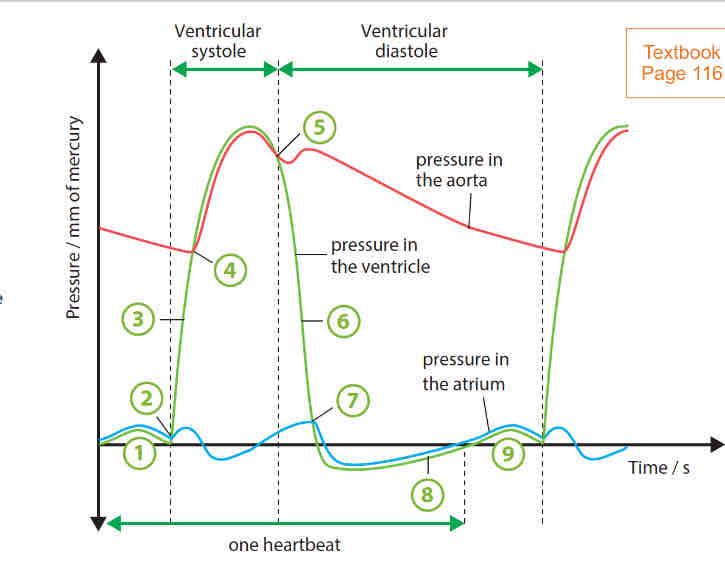
cardiac cycle
the atrial muscles contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. a slight increase in ventricular pressure is due to the contraction of the left atrial muscles, forcing blood into the ventricle.
ventricular muscles begin to contract. bicuspid valve closes
ventricular muscles continue to contract without change in volume of blood. pressure continues to rise
pressure in ventricles becomes higher than that in aorta. aortic valve opens and volume of blood into ventricle decreases as blood is forced out of the aorta
ventricular muscles begin to relax. drop in pressure causes aortic valve to close to prevent backflow of blood into ventricle
ventricular muscles continue to relax without change in volume of blood
bicuspid valve opens when pressure in ventricle becomes lower than that in atrium
pressure in ventricle rises as blood continues to enter the ventricle from the atrium.
what happens during a heart attack
blood flow to a particular part of the heart may be completely blocked. due to the blocked blood flow, that part of the heart does not receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients. that region of the heart muscle dies.
what are the causes of coronary heart disease
fatty substances such as cholesterol and saturated fats may be deposited on the inner surface of the coronary arteries.
this narrows the lumen of these arteries and increases blood pressure.
affected artery develops rough inner surface which increases the risk of a blood clot being formed in the artery.
if it occurs in the coronary arteries, the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart muscles may be completely cut off.
without oxygen, aerobic respiration cannot occur to release energy for the activities of the muscle cells and the heart muscles may be damaged, causing a heart attack.
risk factors of heart disease
unhealthy diet rich in cholesterol, saturated fats and salt content
age
lack of exercise and being active
genetic factors
smoking
how to prevent coronary heart diseases
healthy diet that is low in saturated fats
avoid smoking
regular physical exercise