Option G: Urban Environments
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Urban area
A built up area that forms part of a city or town.
Characterized by
1. population size
2. employment
3. facilities and functions
4. government legislation
Rural area
an area of small towns or farms, usually an undeveloped land or a settlement of fewer than 2500 people
Characteristic of Urban areas
- population size
- specic features, such as a CBD and residential zones
- predominant economic activities, such as manufacturing and services
- an administrative function.
Site
Actual land on which a settlement is built
Situation/Position
Refers to its relationship with its surrounding area
Reason of Location
- readily available water
- freedom from flooding
- level sites to build on (but less easy to defend)
- local timber for construction and fuel
- sunny, south-facing slopes
- proximity to rich soils for cultivation and lush pasture for grazing
- the potential for trade and commerce, such as proximity to bridges or weirs, a confluence site, the head of an estuary, a point of navigation and upland gaps.
Land Use in Urban Areas
- residential: where people live
- industrial: manufacturing industries that process raw materials
- for services: education, health care, retail, entertainment
- open space: parks, gardens, sports facilities, rivers
- for recreation: including open space, sports centers, playgrounds, sports stadium
- transport routes
Vertical Zoning
Where the same building is used for one function on one floor and another function on another floor
- retailing on the ground floor where offices or apartments on the upper floors
Urban Land use: New York
Land is divided into different settlements
Range
the maximum distance that customers are prepared to travel to access a good or service
Sphere of Influence
an area served by a settlement which can also be called its hinterland
High order goods
more luxurious or goods that are purchased on an infrequent basis and generally more costly such as tablet devices or cars
Low order goods
convenience goods brought on a daily basis and include items such as bread, milk, or rice
Threshold
the absolute minimum number of people required to support a service and keep it in business
Megalopolis
conurbations have joined together to become one large urban area
10 million+
Conurbation
group of large cities that have strong links connecting them to each other
3-10 million
Metropolis
city and surrounding towns that are in close proximity and started to merge
1-3 million
Large city
city with large population and many services
300,000 - 1 million
City
city would have wide range of services but not as many as a large city
100,000 - 300,000
Large town
varied range of shops available when compared to villages
20,000 - 100,000
Town
increase in services
A built-up area with a name, defined boundaries, and local government, that is larger than a village and generally smaller than a city.
1,000 - 20,000
Village
some basic services (petrol stations, village shops)
100 - 1,000
Hamlet
very tiny populations and few services
<100
Isolated dwelling
often in rural areas, tend to be farm houses or holiday houses
Few buildings
Retail Land Use
Shops, located within the CBD. Now, many shops are being set up in the rural-urban fringe.
Central shopping areas/high streets
Characterized by department stores, chain stores, specialized shops and by pedestrianized malls.
Shopping parades
Cluster of shops, usually include a small supermarket, an off-licence, a newsagent and other non-order outlets
Superstores
Large outlets close to residential areas with >2500 square meters of shopping space, ample parting and good road access
Retail park
Cluster of electrical and furniture superstores
Out-of-town shopping precincts
Shopping malls located outside the main central shopping area of a town
Burgess Model
Based on the idea that land values are highest in the center of a town or city.
High-rise, high-density buildings being found near the central business district (CBD)
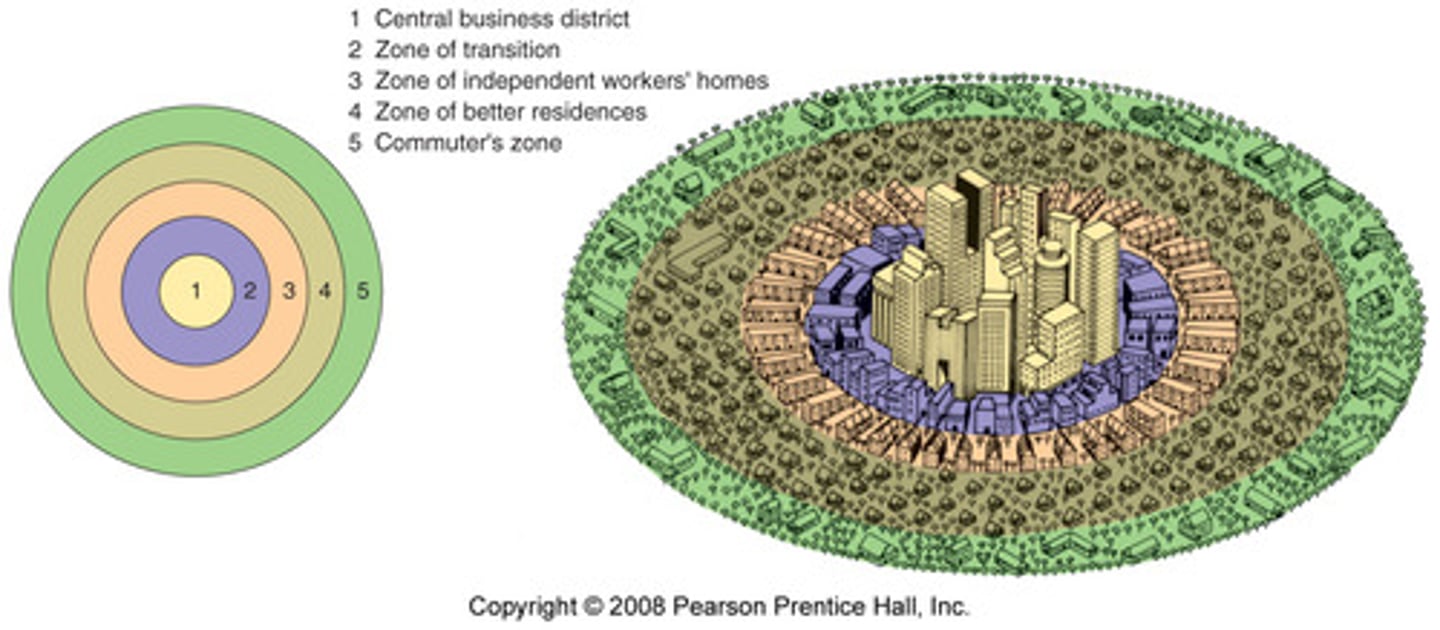
Central Business District (CBD)
The downtown or nucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated; building densities are usually quite high; and transportation systems converge.
Factories/Industries
Outside the CBD
Places include:
- inner-sity areas close to railways and/or canals
- brownfield suburban sites close to airports
Working class housing
Zone of transition - often high numbers of immigrants live
- Blue collar workers (industries)
- White collar workers (offices)
- Suburban ring (high class homes)
Middle class housing
Contains many apartments and HDB's as well as average residential housing. There is access to many schools and leisure locations, however is rather crowded with not much independent space
Commuter zone
the outer most zone of the model that represents people who choose to live in residential suburbia and take a daily commute in the CBD to work.
Inner city
The older, central part of a city with crowded neighborhoods in which low-income families live. (usually minority groups living)
- factory workers and ethnic ghettos
- social deprivation
- high-density housing
Suburbs
Residential areas surrounding a city.
- independent housing
- medium population density
- middle class housing
Rural-urban fringe
A zone of transition between the built-up area and the countryside, where there is often competition for land use.
- boundary zone between rural and urban
- private, high quality housing
- land may be used for agriculture, recreation, or residential
Positive segregation
Ethnic groups gain advantages by being located in the place by choice, as there is enough support
Negative Segregation
Groups excluded from particular areas
- cost or "red-lining" in illegal processes whereby people and authorities prevent particular groups from locating in an area
e.g. Gate of Communities
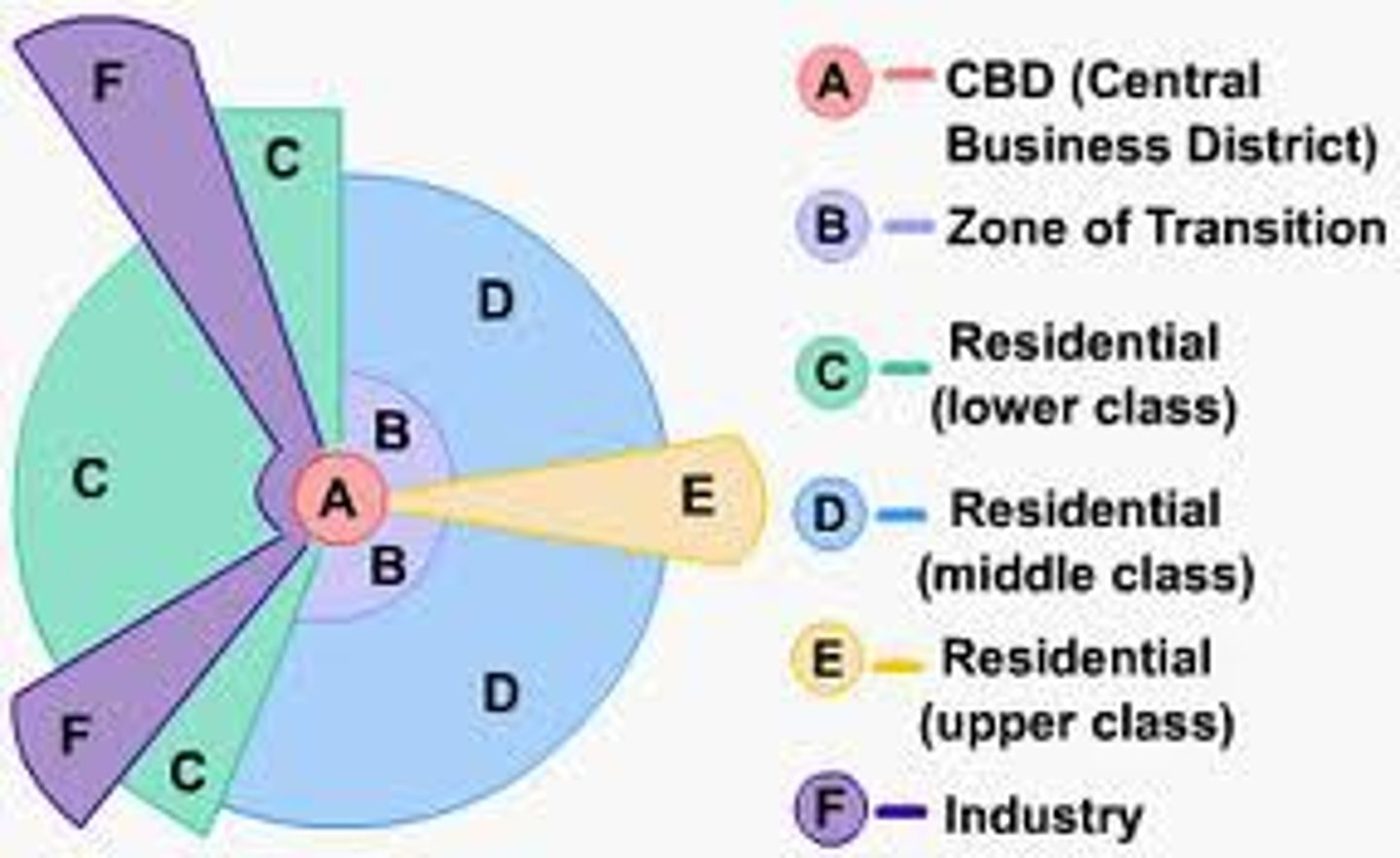
Hoyt Model
An urban land use model showing wedges (sectors), based on main transport routes and social groupings.
Favelas: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
drug guards and peace creators living
→ no zoning, no public service, no presence of government. Being neglected from public services
Cause of Growth: slavery, rural Brazilians migrating to urban cities
Challenges
- Environmental: pollution due to industrialization and urban sprawl
- Health: very poor health care services, as there are not enough local clinics
- Social: inequalities within the city and rapid migration pressuring services
- Education: disparities in education due to the shortage of schools and lack of money
- Energy: blackouts due to power cuts, and lack of safe energy
- Water: leaking pipeline and water shortages
Deprivation
the state of lacking or doing without something; loss
Factors to measure Deprivation
Physical
- quality of housing
- levels of pollution
- vandalism and graffiti
Social
- standards of education
- reported and fear of crime
- levels of health/access to health care
- proportion of lone-parent familes
- unemployment, disability, free school meals
Economic
- access to employment
- unemployment and underemployment
- levels of income
Political
- opportunities to vote
- take part in community organization
Deprivation: Barcelona, Spain
Greatest deprivation in two main areas:
- Inner city areas: coincides with old and standard housing built during the industrial revolution to house factory workers
- Towards the city edge: in estates of social housing built by the city to house large numbers of migrants from other parts of Spain who moved looking for jobs
Inequalities in Health
- higher life expectancy in wealthier areas
- impacts to education - students suffering malnutrition
Deprivation: Nairobi, Kenya
Distribution of poverty spread equally
- slum settlements found all over Nairobi, except the city center
Deprivation in Nairobi
- not as many sources of water
- inequalities in healthcare, more focused on the metropolitan area
- lower life expectancy in the poor areas
Formal Economy
The legal economy that is taxed and monitored by a government and is included in a government's Gross National Product; as opposed to an informal economy
- made up of offices, factories, and commercial buildings
- produces goods and services for an elite population
Informal Economy
Economic activity that is neither taxed nor monitored by a government; and is not included in that government's Gross National Product; as opposed to a formal economy
- consists of servants, gardeners, maids, cleaners, taxi drivers and a variety of other occupations
- small scale, and often locally owned and labor intensive
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
- Proportion of people living in built environments such as towns and cities.
Natural Increase
When the birth rate is higher than the death rate
Rural to Urban migration
To the long-term movement of people away from the countryside to towns and systems
Push factors
Negative features that cause people to move away from rural areas
Pull factors
Attractions (real or imagined) of urban areas
e.g. better wages, more jobs, and good schools
Centripetal movement
Inward movement of population into an area
- rural-to-urban migration
- rapid urbanization
Centrifugal movement
Outward movement of population away from an area
- counter urbanization
- suburbanization
Urban Migration: China
160 million people (about 12% of the population) left rural areas to seek for jobs in urban areas.
- Average income of rural was less than 40% of the urban population, as factories focused in coastal towns
Plan, moving farms into the city, has been called warehousing
If farmers start life in urban systems, their lifestyle will stoke the Chinese economy
If the plan succeeds, farmers will be relocated to newly built apartment buildings
- lot of people move to urban areas for the high wage jobs, but they may have a hard time readjusting to the new challenges in the city.
- The Hukou registration system of Chinese citizens is a problem because it does not allow children from rural areas to get free education in the city. Some rely on NGOs for tuition.
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.
Re-urbanization
The development of activities to increase residential population densities within the existing built-up area of a city. This may include the redevelopment of vacant land, the refurbishment of housing and the development of new business enterprises.
Urban Renewal
Rehabilitation of city areas that have fallen into decline
- clearing out of blighted areas in inner cities to clear out slums and create opportunities for higher class housing, businesses, and more.
Sub Urbanization
Outward growth of urban development which may engulf surrounding villages and towns into a larger urban cluster. Suburbs are the outlying areas of a city which are close enough to the city center to be accessible by commuters.
Counter Urbanization
When large numbers of people move from urban areas into surrounding countryside or rural areas.
- net decline of the cities
- net growth of the more accessible rural areas beyond the city limits
through migration
It is both a demographic (population driven) and social process, but has to a lesser extent also involved the movement of some businesses and economic activities.
Rapid Urbanization
When people flooded into cities to live. Tremendously crowded situations are born.
Urban infrastructure growth may be occurring due to this process.
Issues:
- poor sanitation
- rise in crime rates
Urban Infrastructure Growth: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
National capital of Ethiopia in East Africa
Ethiopia has made development gains in education, health, food security, and economic growth. Addition if health extension has helped reduce the under-five child mortality rate by more than 6% a year since 2000.
- Greater social stability
- Youthful potential
Changes in infrastructure:
- Transport
- Sanitation
- Water
- Waste Disposal
- Telecommunications
Change in Infrastructure (Addis Ababa): Water and Sanitation
Flooding → mismanagement of waste and the poor condition of sanitation spreading the disease related to poor water
- 60% of the food consumed is irrigated with untreated wastewater, therefore food poisoning is common
- Epidemics caused by pathogenic agents in the water imply a medical treatment cost of around $700,000 per year
Lack of infrastructure → relatively high rainfall is not being stored. Downpours cause an abundant runoff in which little water can be saved due to the lack of storage infrastructures.
- only 7% of the population used a safely managed sanitation service (variations in the water accessibility in the country - great disparities in the accessibility to safe water systems)
Changes in Infrastructure (Addis Ababa): Transport
Congested roads of Addis Ababa, commissioning a new urban metro largely funded, constructed, and run by Chinese institutions:
- Railroad system implemented in 2009, improved the transportation systems to reach out to other parts of Ethiopia.
Positive/Negative
- Quality and effectiveness of the railroad system is quite low
- Lot of refugees → the quality of car roads have improved
Changes in Infrastructure (Addis Ababa): Waste Disposal
Waste of 550t/day being collected
- Open dumpsite where all the collected waste is disposed, located 13 km away from the city center
Problems:
- Site is getting full
- Surrounded by housing areas and institutions
- Nuisance and health hazard for people living nearby
- Poor qualities of waste collection and disposal services
What has been done to solve the issues:
- Community participation (sanitation activities, supply of dust bins, cleaning initiative)
- Developing transfer stations and new sanitary land fil
Has been enhancing environmental protections through waste management:
- Dump site (only dump site in Addis Ababa - Koshe dumpsite) into a new waste-to-energy plant
- 80% of rubbish is converted into energy, supplying 25% of the household electricity in the capital
- However, policies have not been effective in preventing illegal dumping of waste as well as contamination of water, soil, and air resources
Changes in Infrastructure (Addis Ababa): Telecommunications
Launches 4G mobile service in the capital
- state-run telecoms launched a 4G mobile service aiming to catch up with the high-speed communications available in some East African neighborhoods (Kenya and Uganda)
- telecoms industry is booming
- vast parts still suffer from occasionally patchy mobile reception
Significant growth in the percentage of individuals using the internet since 2010
- 0.75% in 2010 to 18.6% in 2017
Deindustrialization
Reduction of industrial activity or capacity in a region or economy. Process of social and economic change caused by the removal, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry.
Caused by Globalization:
- automations
- easy transportation of goods
- factories moved to countries with cheaper land prices i.e. MIC/LIC
Deindustrialization in Detroit, US
Previously: a city where the city's economy was heavily dependent on car industry.
Currently:
- neighborhoods abandoned as high paying jobs vanished
- racial strife and loss of good-paying assembly line jobs worked as a push factor: population has declined
- high unemployment and crime rates, as well as corruption
Deindustrialization in London Docklands, UK
Previously, the city was functioning as a trade harbor.
However, as shipping became usual and large cargo ships were used for imports and exports, economic activity in the area declined.
Large ships could not enter the harbor.
This lead to deindustrialization in the city, however, gave an opportunity for redevelopment.
Redevelopment in London Docklands, UK
Redevelopment of the city by local governments (LDDC)
- more green space
- improved transportation links (roads and trains)
- improved housing and safety (new low costing houses and luxury houses built. Increase in the number of public services available)
This resulted the city to grow back
- more employment
- more offices settled
- more vertical zoning
Inner city decline
Cause of centrifugal movement
- urban stress (noise pollution, air pollution, congestion)
- lack of green space
- higher danger risks
Deliberately wealthy people and married couples moving towards suburbs causing the population in inner cities to decline