Chapter 7: Experimental Designs
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Experimental research design
seeks to determine if a specific treatment influences an outcome.
The researcher assesses this by providing specific treatment to one group and withholding it from another and then determining how both groups scored on an outcome.
True experiments
Experiments include _____ , with the random assignment of subjects to treatment conditions, and quasi-experiments that use nonrandomized assignments (Keppel, 1991).
Quasi-experiments
Experiments include true experiments, with the random assignment of subjects to treatment conditions, and _____ that use nonrandomized assignments (Keppel, 1991).
Method of Difference
To translate the _____ into an experiment, we need to formulate a specific, testable question or hypothesis, such as, ‘Does stress impair memory for events?’
Constant
To translate the Method of Difference into an experiment, we need to formulate a specific, testable question or hypothesis, such as, ‘Does stress impair memory for events?’
To answer it, we manipulate one variable (the independent variable, or IV), and measure the effects of these manipulations on another variable (the dependent variable, or DV), while keeping all other variables as _____as possible.
Confounding variables
In designing an experiment, the tricky bit is to ensure that the independent variable is the only thing that varies systematically between the groups.
Variables that have unwanted influences on our experimental results are called
Between-groups design or between-subjects design
is an experimental design in which each condition in the experiment is performed by a different group of participants.
Within-subjects designs or repeated measures designs
is an experimental design in which each participant takes part in more than one condition of the study.
Matched-pairs design
is an experimental design in which participants are carefully matched on variables that might be relevant to the research (such as age, socioeconomic status, intelligence, etc.)
Post-test only/control group design
is an experimental design in which participants are allocated randomly to different conditions and given different treatments.
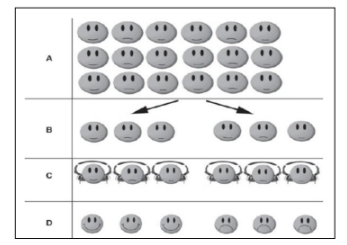
Pre-test/post-test control group design
the subjects are allocated to groups and are measured both before some manipulation and after the manipulation.
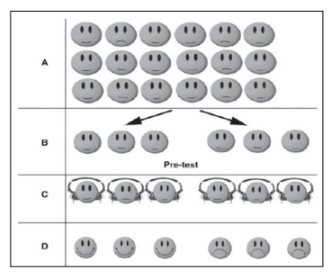
Solomon four-group design
is an experimental design in which participants are allocated randomly to different groups, given different treatments (different levels of an independent variable), and then tested in some way, in the expectation that the different treatments will have affected their behavior in some way.
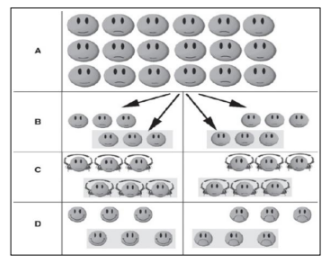
Longitudinal design
is a repeated-measures design that is often used in developmental research. A group of participants is tested repeatedly over time (e.g. at different ages).
Cross-sectional design
is a between-groups design that involves using different groups of participants to represent different points in development (e.g. different ages).
Multifactorial design
is an experimental design in which the effects of more than one independent variable are investigated within the same study. It permit investigators to study how variables might interact with each other.
Mixed design
an experimental design that combines within-subjects and between subjects (e.g. the effects of sex and alcohol on memory performance could be investigated with a mixed design.
Participants
Readers need to know about the selection, assignment, and the number of participants who will take part in the experiment.
Often investigators aim to recruit a study sample that shares certain characteristics by formally stating specific inclusion and exclusion study criteria when designing their study.
Variables
Identify the independent variables in the experiment and how they will be manipulated in the study.
Include a manipulation check measure that evaluates whether your study successfully manipulated the independent variable(s) of interest. A manipulation check measure is defined as a measure of the intended manipulated variable of interest.
Identify the dependent variable or variables (i.e., the outcomes) in the experiment. Identify other variables to be measured in the study.
Three categories of variables are worth mentioning.
Manipulation check measure
Include a _____ that evaluates whether your study successfully manipulated the independent variable(s) of interest.
A _____ is defined as a measure of the intended manipulated variable of interest.
Instrumentation and Materials
The experimental study plan calls for a thorough discussion about the instruments used - their development, their items, their scales, and reports of reliability and validity of scores on past uses.
Thoroughly discuss the materials used for the manipulated variable(s) of interest.
Often the researcher does not want participants to know what variables are being manipulated or the condition they have been assigned to (and sometimes what the primary outcome measures of interest are).
Experimental Procedures
also need to be identified.
Identify the type of experimental design to be used in the proposed study.
Identify what is being compared in the experiment.
Provide a diagram or a figure to illustrate the specific research design to be used.
Threats to validity
Experimental researchers need to identify potential ______ of their experiments and design them so that these threats will not likely arise or are minimized.
Internal validity threats
are experimental procedures, treatments, or experiences of the participants that threaten the researcher’s ability to draw correct inferences from the data about the population in an experiment. For example, history, maturation, testing, instrumentation, etc.).
External validity threats
arise when experimenters draw incorrect inferences from the sample data to other persons, other settings, and past or future situations.
For instance, interaction of selection and treatment, interaction of setting and treatment and interaction of history and treatment.
Step 1
Administer measures of the dependent variable or a variable closely correlated with the dependent variable to the research participants.
The Procedure
Step 2
Assign participants to matched pairs based on their scores on the measures described in Step 1.
The Procedure
Step 3
Randomly assign one member of each pair to the experimental group and the other member to the control group.
The Procedure
Step 4
Expose the experimental group to the experimental treatment and administer no treatment or alternative treatment to the control group.
The Procedure
Step 5
Administer measures of the dependent variables to the experimental and control groups.
The Procedure
Step 6
Compare the performance of the experimental and control groups on the post-test(s) using tests of statistical significance.
Data Analysis
Report the descriptive statistics.
Indicate the inferential statistical tests used to examine the hypotheses in the study.
For single-subject research designs, use line graphs for baseline and treatment observations for abscissa (horizontal axis) units of time and the ordinate (vertical axis) target behavior.
Abscissa
For single-subject research designs, use line graphs for baseline and treatment observations for ____ (horizontal axis) units of time and the ordinate (vertical axis) target behavior.
Ordinate
For single-subject research designs, use line graphs for baseline and treatment observations for abscissa (horizontal axis) units of time and the ____(vertical axis) target behavior.
Interpreting Results and Writing a Discussion Section
Interpret the findings in light of the hypotheses or research questions and to draft a discussion section. In this interpretation, address whether the hypotheses or questions were supported or whether they were refuted.
Address whether the results might have been influenced by unique strengths of the approach, or weaknesses (e.g., threats to internal validity), and indicate how the results might be generalized to certain people, settings, and times.
Finally, indicate the implications of the results, including implications for future research on the topic.