Subsection of Unit 4 - The Skeletal System
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers slides 1-50 on the Unit 4 Skeletal System slides posted on Google Classroom
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Wht are the FIVE functions of the skeletal system?
Support (bear the weight of the body)
Storage (bones store Ca ions)
Protection (EX: ribcage protects heart)
Movement (EX: point of muscle attachment, joints)
Manufacturing of blood cells (called hematopoiesis)
What is hematopoiesis?
The production of red blood cells in RED bone marrow.
What are the different bones (give examples too)?
Flat Bones (scapula)
Irregular Bones (vertebrae)
Long Bones (femur)
Short Bonse (wrist)
Sesamoid Bones (patella [knee cap])
What are the two major sections of the skeleton?
Axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton.
What is the axial skeleton? What bones does it contain?
It is the central axis of the body and contains the skull, rib cage, vertebrae, and 80 other bones.
What is the appendicular skeleton? What bones does it contain?
It is the bones of the appendages and contains the pectoral, pelvic girdles, bones of the arms, legs, pelvis, shoulders (126 bones).
How many bones does the skull have (be specific in the types)…
8 CRANIAL bones, 14 FACIAL bones.
What is the hyoid bone’s function?
Serves as a moveable base for the tongue, aids in swallowing and speech, and is the only bone that does not connect with another bone.
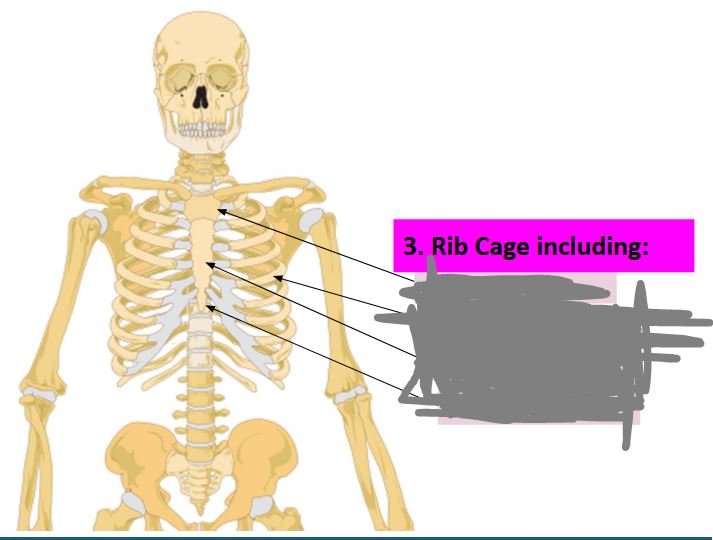
Label this image… (top to bottom)
manubrium, ribs, sternum, xiphoid process.
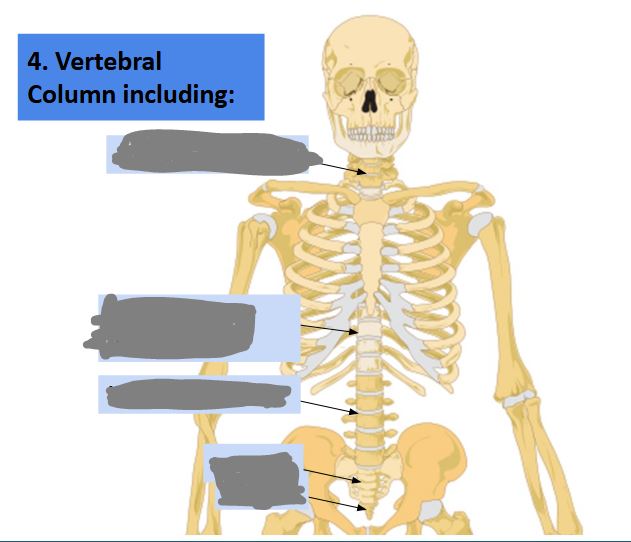
Label this image… (top to bottom)
Cervical vertebrae, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx.
What is the function of the vertebral column?
It provides suport and protects the spinal cord that runs through it.
What is the function of intervertebral discs?
They separate the vertebrae and provide cushioning and absorb shock.
What happens if your vertebrae discs begin to degenerate?
It causes extreme pain.
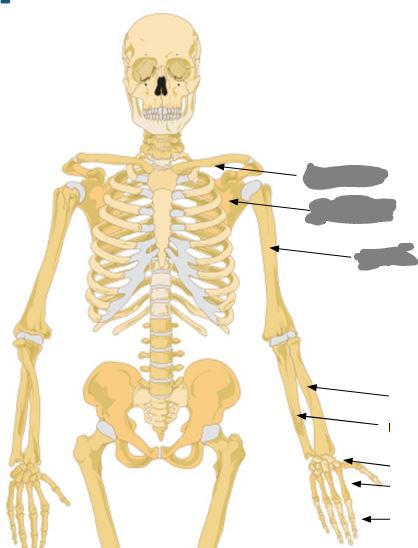
Label this image from top to bottom…
clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges.
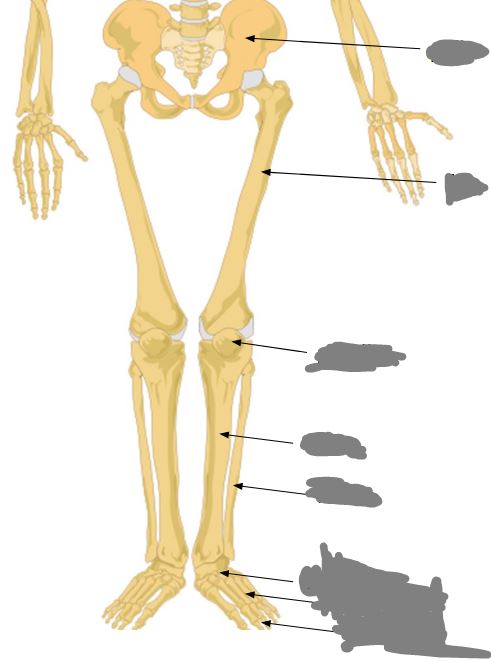
Label this image from top to bottom…
Pelvic girdle (pelvis), femus, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
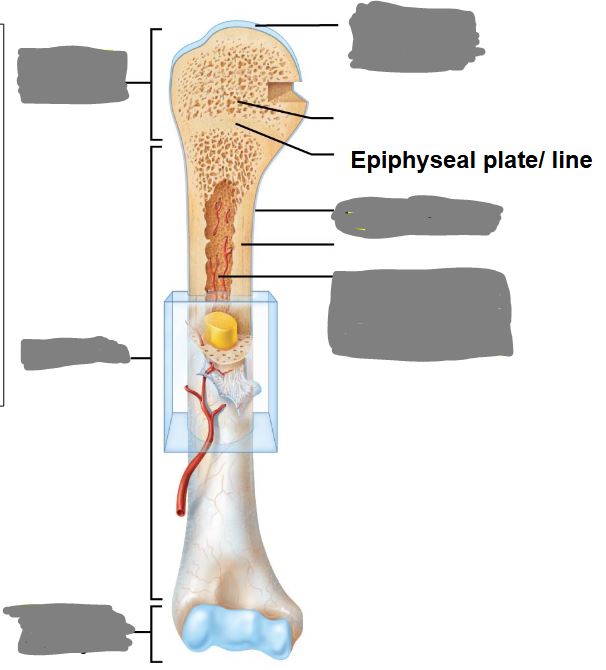
Label this image from top to bottom…
Articular cartilage, proximal epiphysis, periosteum, medullary cavity (lined by endosteum), diaphysis, distal epiphysis.
What is the diaphysis?
The shaft or long part of a long bone.
What is the epiphyses?
The ends of a long bone.
What is located between the epiphysis and diaphysis?
An epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
What is articular cartilage (function) and where is it? WHAT IS IT MADE OUT OF???
It provides smooth movement of joints and cushion from shock. It is located at the ends of the epiphyses.
Made from Hyaline cartilage.
Where is the medullary cavity found?
It is the hollow cavity in a long bone.
What fills the medullary cavity in young people? What about older people?
Younger people have it filled with red bone marrow, older people have it filled with yellow bone marrow.
What does yellow bone marrow maintain?
It maintains cartilage, bone, and fat cells.
What is the periosteum?
It surrounds the perimeter of a long bone AND is the site of muscle attachment/bone repair.
What is the endosteum?
It surrounds the medullary cavity (inside of the bone).
What is the articular cartilage?
It surrounds each epiphysis and provides smooth motion.
What are ligaments?
They connect bone to bone.
What is a tendon?
It connects muscle to bone.
What are the three structural types of joints?
Fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints.
Describe fibrous joints…
They are immoveable or slightly movable and are held together by fibrous connective tissue.
Describe cartilaginous joints…
They are immovable/slightly movable and are held together by cartilage.
Describe synovial joints…
They are very movable, contain capsules of synovial fluid, lined with synovial membrane which secretes fluid.
What is the function of synovial fluid?
It decreases friction between bones.
Which joint is the move movable? (test question)
The ball and socket joint
I am skipping over joints because they seem like common sense. Here’s the difficult to know ones:
Where is the condylar joint? Where is the plan joint? Where is the saddle joint?
Condylar: Wrist and moves in tons of directions.
Plan: Ankle
Saddle: Wrist and moves in many directions
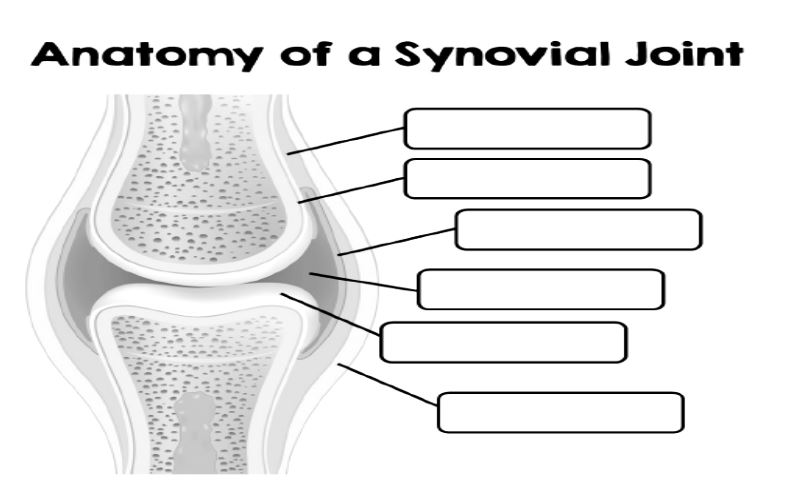
Label this image from top to bottom…
Fibrous layer, periosteum, synovial membrane, joint cavity/synovial fluid, articular cartilage, and ligament.
What is the composition of bone (two types)? List information about each type
Organic
35% Osteoid (made of ground substance)
Provides flexibilty and strength to sustain bones
Lack of collagen causes Brittle Bone Disease.
Inorganic
65% Mineral Salts
Provides bone strength + Hardness
Lack of hydroxyapatite (crystalline salts) causes Rickets.
What are two types of bone?
Spongy and compact.
What is the function of spongy bone?
They reduce bone density and spaces are filled with bone marrow. It is compressable but sturdy to maximize stability. Used for growth.
What are the small, needle like pieces called in spongy bone?
Trabeculae.
Describe what compact bone is…
It is dense, smooth. The tissues are arranged in osteons (called corticol bone). Very sturdy and hard. NOT compressable.
Flat and Short bones contain mostly _______ bone with a thin layer of ______ bone surround it.
spongy; compact
Long bones contain mostly _____ bone with small sections of ______ bone.
compact; spongy