AP Bio Unit 1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
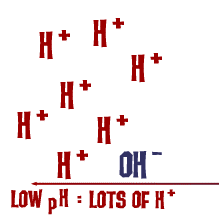
Acid
A substance that increases the number of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Acids have a pH less than 7.
Adenine
A nitrogen base in DNA and RNA that pairs with thymine (in DNA) or uracil (in RNA).
Adhesion
When water molecules stick to other substances (like glass). Helps water move up plant stems.
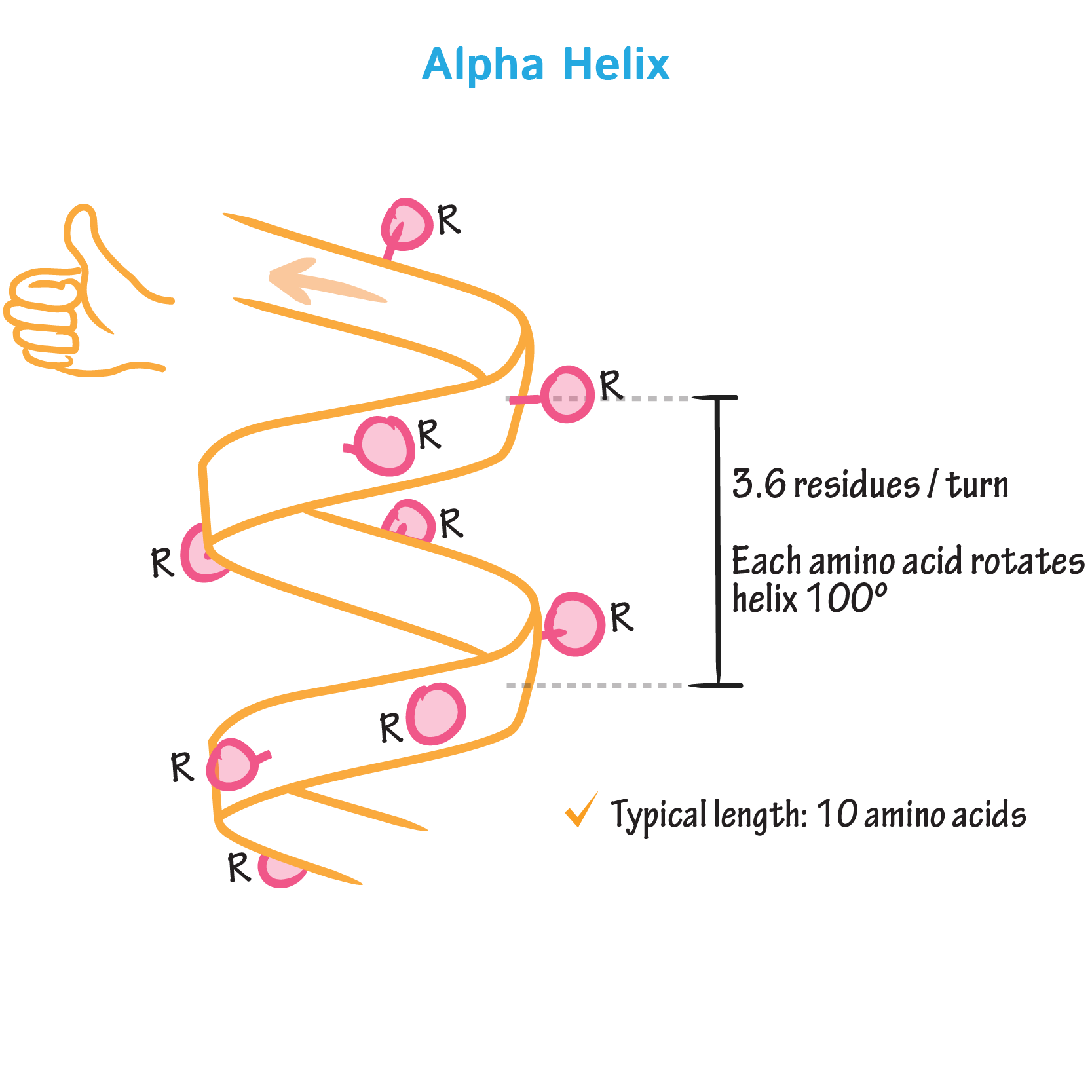
Alpha helix
A coiled structure in proteins, like a spring, formed by hydrogen bonding.
Amine group
A part of an amino acid that contains nitrogen (–NH2). It helps amino acids join together.
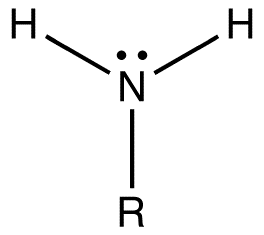
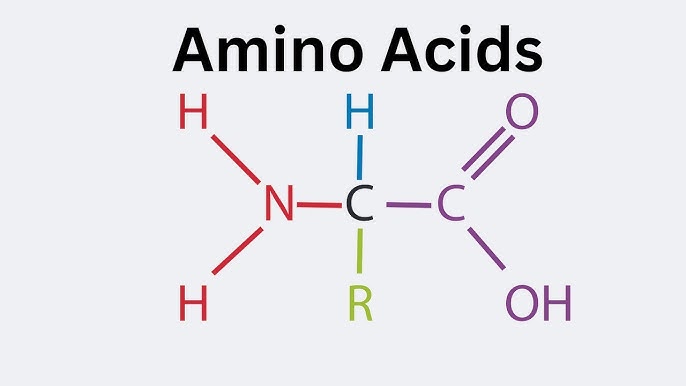
Amino acid
The building blocks of proteins. Each has a central carbon, an amine group, a carboxyl group, and an R group
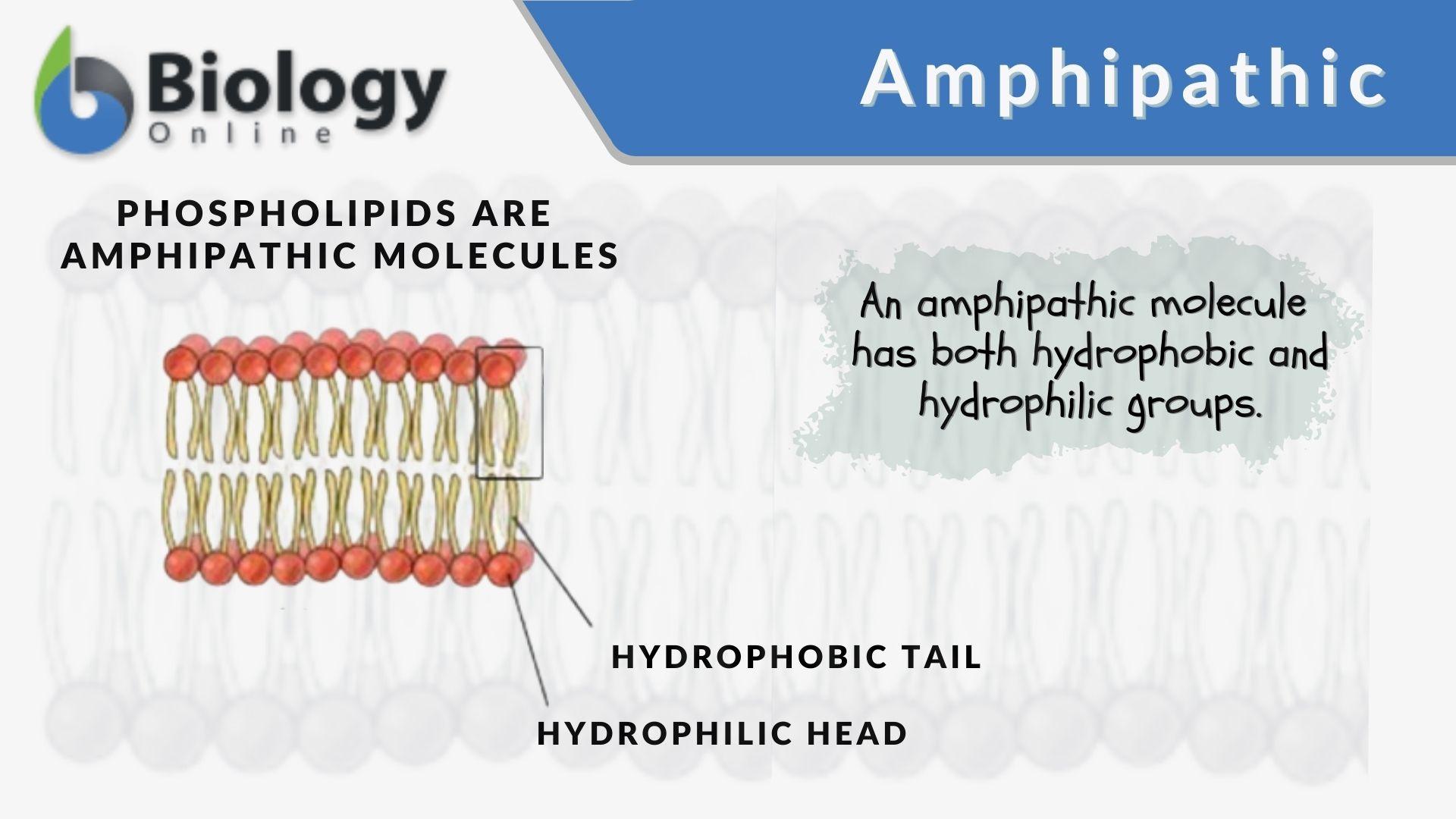
Amphipathic
chemical compounds that have both polar and nonpolar regions, giving them both hydrophilic (water-loving) and lipophilic (fat-loving) properties
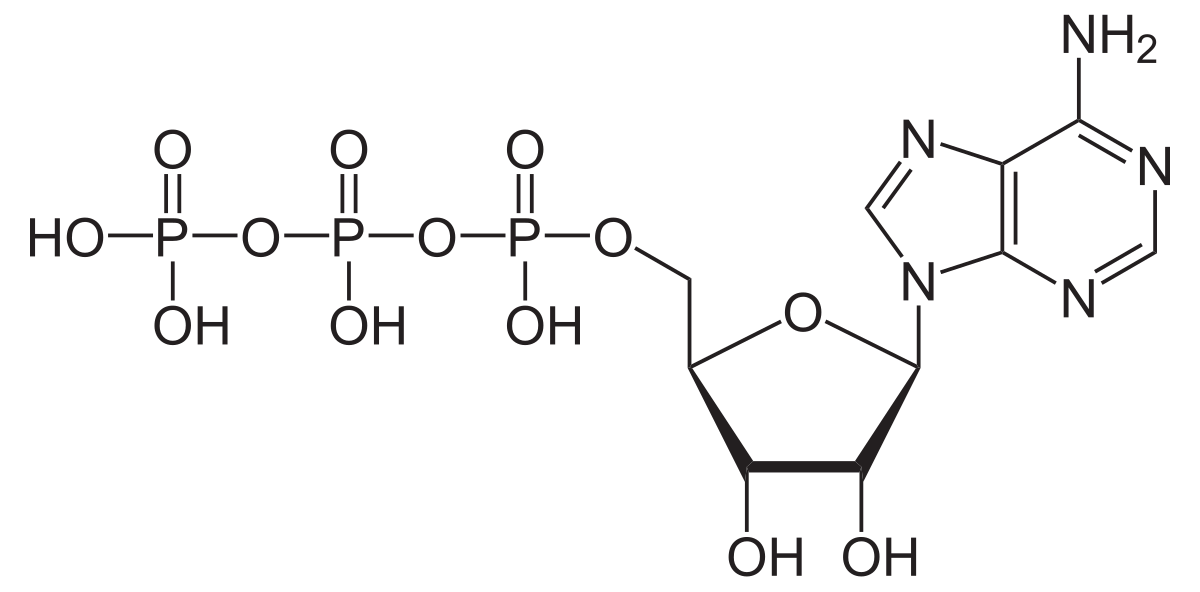
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate; the main energy source for cells
Base
A substance that decreases hydrogen ions (H+) or adds hydroxide ions (OH–). Bases have a pH above 7.

Pair rule
In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine (A–T and G–C).
Beta sheet
A folded, sheet like shape that is one type of protein secondary structure.
Biochemistry
The study of the chemicals and reactions that happen in living things.
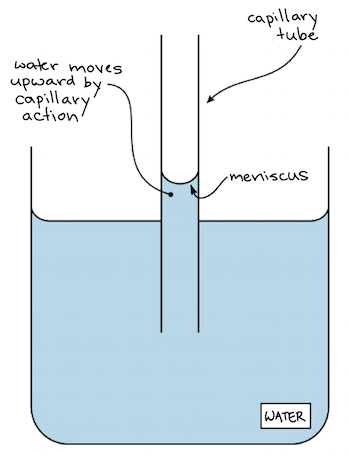
Capillary action
When water moves upward through narrow tubes (like plant stems) due to adhesion and cohesion.
Carbohydrate .
A macromolecule made of sugars and Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen. Provides energy. Examples: glucose, starch
Carboxyl group
A functional group (–COOH) found in amino acids and fatty acids. Acts like an acid.
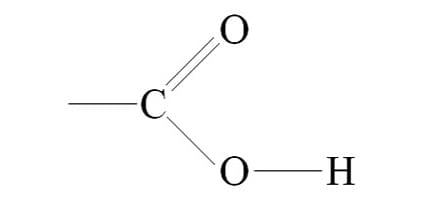
Cholesterol
A lipid found in cell membranes and used to make hormones.
Cohesion
When water molecules stick to each other due to hydrogen bonding.
Cytosine
A nitrogen base in DNA and RNA that pairs with guanine.
Covalent bond
A strong bond formed when two atoms share electrons.
Defensive proteins
Proteins like antibodies that help protect the body from disease.
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction where two molecules are joined by removing water.
Denaturation
When a protein loses its shape (and function) due to heat, pH, or other changes.
Density of water
Water is less dense as a solid (ice floats on water), which helps aquatic life survive in winter.
Deoxyribose sugar
The sugar found in DNA. It's a 5 carbon sugar with one less oxygen than ribose.
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate made of two sugars joined together. Example: sucrose (table sugar).
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid; stores genetic information in cells.
Electronegativity
How strongly an atom pulls electrons toward itself. Oxygen has high electronegativity.
Enzyme proteins
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
Fatty acid
A long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. Part of lipids like triglycerides.
Glycerol
A 3 carbon molecule that joins with fatty acids to make fats and oils.
Glycosidic bond
A bond that links sugar molecules together in carbohydrates.
Guanine
A nitrogen base that pairs with cytosine in DNA and RNA.
Hormonal proteins
Proteins that act as chemical messengers (like insulin).
Hydrogen bond
A weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another electronegative atom (like oxygen).
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks bonds using water.
Hydrophilic
“Water loving”; molecules that dissolve easily in water.
Hydrophobic
“Water fearing”; molecules that do not dissolve in water (like fats).
Hydroxyl group
A functional group (–OH) found in alcohols and sugars.
Ion
An atom with a charge because it gained or lost electrons
Ionic bond
A bond between oppositely charged ions (like Na⁺ and Cl⁻).
Lipid
A macromolecule made mostly of carbon and hydrogen. Includes fats, oils, and steroids.
Macromolecule
A very large molecule made of smaller units. The four types are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Methyl group
A nonpolar functional group (–CH3) that affects molecular interactions and gene expression.
Monomer
A small molecule that can join with others to form a polymer.
Monosaccharide
The simplest sugar. A single sugar unit. Example: glucose. Also the monomer of carbohydrates
Motor proteins
Proteins that help move parts inside the cell or move the cell itself.
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogen containing molecule found in DNA and RNA. Examples: A, T, C, G, U.
Non polar molecule
A molecule with no charge separation; does not mix with water.
Nucleic acid
A macromolecule made of nucleotides. Includes DNA and RNA.
Nucleotide
The building block of nucleic acids. Made of a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base.
Organic molecule
A molecule that contains carbon and is found in living things.
Peptide bond
A bond that links amino acids together in a protein.
pH
A scale that measures how acidic or basic a solution is, from 0 to 14.
Phosphate group
A functional group (–PO4) found in DNA, RNA, and ATP.
Phospholipid
A lipid with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails; makes up cell membranes.
Polar molecule
A molecule with partial positive and negative charges; water is polar.
Polymer
A large molecule made of many monomers joined together.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids. Folds into a functional protein.
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate made of many sugar units. Example: starch, cellulose.
Primary structure
The sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Protein
A macromolecule made of amino acids; does most work in cells (structure, transport, enzymes, etc.).
Proton (H+)
A hydrogen ion; determines acidity. More H+ = more acidic.
Purines
A type of nitrogen base with two rings. Includes adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines
A type of nitrogen base with one ring. Includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Quaternary structure
The level of protein structure formed when multiple polypeptides join together.
R group
The side chain in an amino acid that determines its properties.
Receptor proteins
Proteins that receive signals from outside the cell.
Ribose sugar
The sugar in RNA. It has one more oxygen than deoxyribose.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid; helps make proteins from DNA instructions.
Saturated fat
A fat with no double bonds between carbon atoms; solid at room temp.
Secondary structure
The folding of a protein into alpha helices or beta sheets.
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solution
A liquid mixture where a solute is evenly dissolved in a solvent.
Solvent
The substance (usually liquid) that dissolves the solute. Water is the most common.
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. Water has a high specific heat.
Storage proteins
Proteins that store nutrients. Example: casein in milk.
Structural proteins
Proteins that provide support. Example: collagen in skin.
Surface tension
The tight surface layer of water due to cohesion. Allows insects to walk on water.
Tertiary structure
The overall 3D shape of a protein caused by interactions between R groups.
Thymine
A nitrogen base in DNA that pairs with adenine.
Transport proteins
Proteins that move substances across cell membranes.
Triglyceride
A fat made of glycerol and three fatty acids. Stores energy.
Unsaturated fat
A fat with at least one double bond; liquid at room temperature.
Uracil
A nitrogen base in RNA that pairs with adenine.
Water
A polar molecule essential for life. Has high cohesion, adhesion, and heat capacity.
Xray crystallography
A method used to determine the 3D structure of molecules like DNA and proteins.