Physics Unit 1 AOS 3 😁
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
what is AC
alternating current, electrons oscillate backwards (-) and forwards (+) in a circuit.
what is dc
direct current. electrons travel directly from one terminal of the battery to the other in one direction only. batteries provide DC
rms
root mean squared. a maths term, it averages the sine wave. Because households are supplied with AC voltage, we have to be careful about labelling the voltage: 240rms means this AC voltage has the same effect as 240V voltage
delete this shit
is a measure of frequency. this means it oscillates 50 times every second
Household energy is AC (-340V to +340V, which gives an equivalent amount, root-mean-square, of potential as 240V at 50 Hz)
Why do powerpoints have 3 pins?
brown/red for active, blue or black for neutral, green/yellow for earth
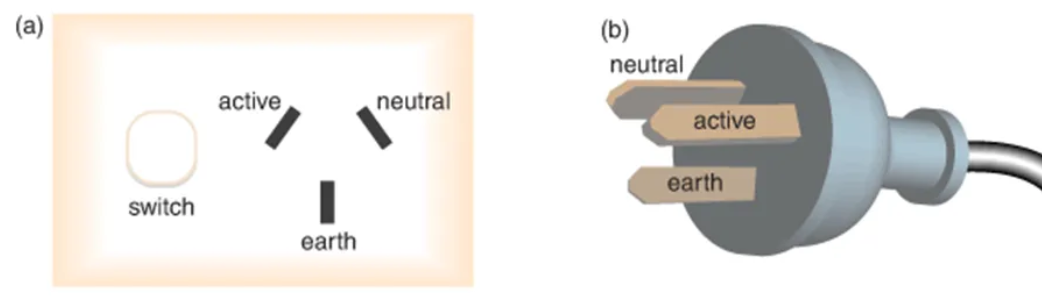
How do we connect to mains power? Recall the different sockets
a 3 point socket. The top left point is active, right is neutral, and the bottom one is the earth connection. The switch is connected in the active wire. Pins and circuits correspond to each other
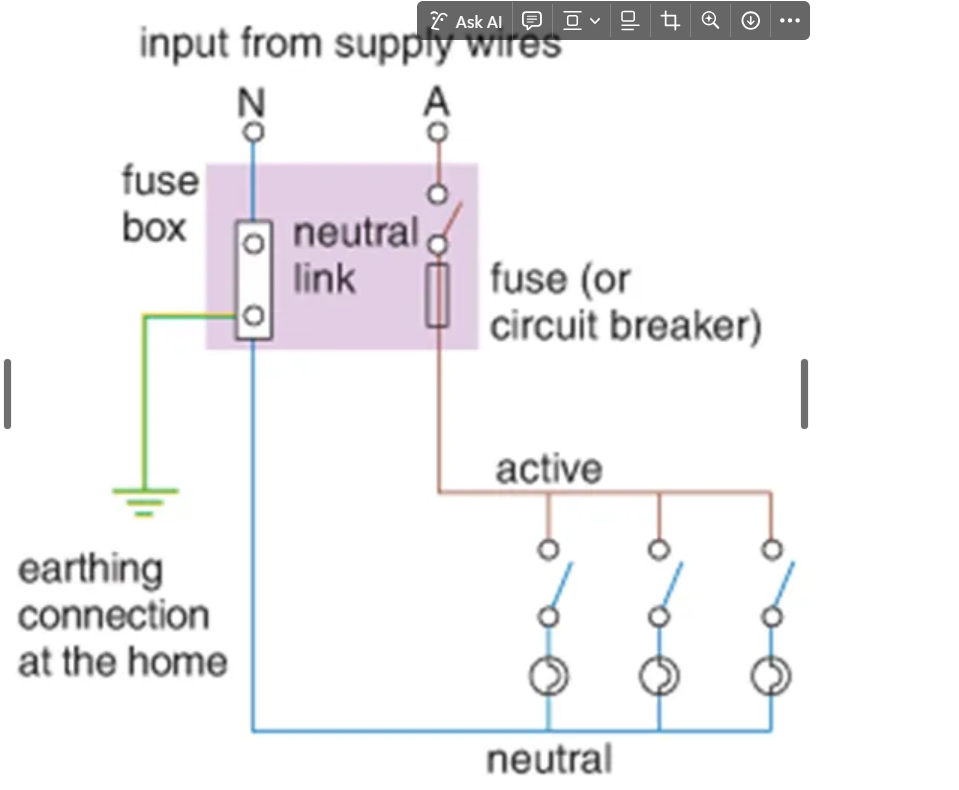
How does a circuit work if it doesn’t have a + and – end?
when an appliance is connected, current flows back and forth between the active and neutral wires through the device, supplying it with energy.
What does active wire do
it is connected to 240V whose voltage oscillates periodically between +340V and -340V (giving a root-mean-square equivalent voltage of 240V) relative to a reference voltage called ‘earth’, considered to be 0V.
What does the neutral wire do?
it ****is connected to the neutral link at the switchboard (to complete the circuit), which is also connected to the *earth* via a rod driven into the ground at the switchboard. The neutral wire is always at 0 V.
Remember what unit shows up on the electricity bill?
Kilowatt hours (kWh) (convert 1 J to kWh), because this gives a convenient number, without scientific notation, that is easy to write.
Before being _to various parts of the house, the active wires pass through _that _the amount of _ _ supplied to the household
distributed, active wires, measure, electrical energy
Every domestic circuit contains?
a fuse or circuit breaker to interrupt the flow of current if it exceeds a certain value. They are safety devices that prevent wires from getting overloaded.
Why is there a limit to how much current the wires in a house or building can safely carry?
wires heat up when current passes through them
How to prevent overload of circuits?
put appliances that draw a lot of current such as ovens, hot water systems, and air-conditioners on separate circuits to lights and power points. don’t overuse power boards
What happens if too many high-current appliances, such as heaters, kettles and irons, are plugged into a power board?
it can overheat. This may cause the insulation around the wires to melt, causing a short circuit or even a fire.
What are short circuits, and why do they happen?
they occur when an electric circuit contains a near “0” resistance conductor in parallel with another household appliance or load. Current will want to take the path of least resistance (if there is near “0” resistance”) so it will completely pass through the “short circuit” and not pass any current though the other element.
Large amounts of current means?
that wires will heat up, causing insulation to melt or catch alight.
What is another way that short circuits can occur?
occur in an electrical appliance when insulation between active and neutral wires becomes damaged and they come in direct contact.
What happens if the active wire inside an appliance with a metal case becomes loose and touches the case? How can this be prevented?
the whole case becomes electrically live. If anyone touches the case, zzzzzaaaappp the current will flow through their body, with possibly fatal consequences. To prevent this, an earth wire is permanently connected to the metal case of the appliance, which is connected via the household wiring system to the earth (recall the third prong in a power point).
What happens if the active wire touches the case?
a short circuit (very large current) ****will be created and current will immediately flow directly to *earth* and should trip the fuse or circuit breaker, alerting users of the appliance to the problem.
Is Earth wire a part of the conducting circuit?
no, it’s just in place in case of fault – it provides a low resistance path to trip the circuit breaker/ blow the fuse
What is double insulation
involves using two insulating barriers to protect users. e.g. A plastic case and plastic insulation surrounding the active wire inside the appliance. Double insulated appliances do not need an earth wire, so their electric plugs have only two pins. this is indicated by a double square idk why tho
RESIDUAL CURRENT DEVICES (RCDs)
Also known as earth leakage systems, they detect any difference between the current in the active wire and the current in the neutral wire. In a property operating circuit, these two currents should be exactly the same. The most likely reason is that some current is going to earth through a fault or through a person. If this happens, the RCD is able to switch off the supply in about 20 milliseconds, hopefully preventing any serious harm.
How can an electrical fault cause a fire?
Wires get hot & melt their insulation due to…. overload, short circuit, or a faulty device.
What is overload?
parallel circuits therefore (too many appliances on a single power circuit = current adds large current in wires)
What is a short circuit?
current flows from one wire to the next with little or no resistance. Current increases rapidly.
How does a faulty device cause a fire?
it short circuits
What do the effects of electric shock depend on?
the amount of current passing through the body, the amount of it, and the path it takes through the body, and the amount of current that will flow through the body. If the current is in good contact with a 240 V source, it is well above the level that will cause death. Anything that improves the contact, like wet hands or bare feet, lowers the resistance and increases the current, potentially to life-threatening levels.
What is electric shock
the amount of current passing through the body
Since our bodies are _ _ _, _ _ passing through our bodies is quickly _into _ and can cause terrible _ and _ _.
relatively poor conductors, electrical energy, converted, heat, internal, external, burns.
Why is external current dangerous to the body?
because our bodies use electrical impulses to control vital functions, so external current can interfere
What can external current do to breathing?
cause chest muscles to contract and breathing to stop
What happens if current flows from one arm to the other?
it can pass through the chest and interfere with breathing
What happens if current passes through the heart region?
it may disrupt heart coordination and cause the heart to stop
How much current can cause fibrillation?
about 80 mA if it flows directly through the heart
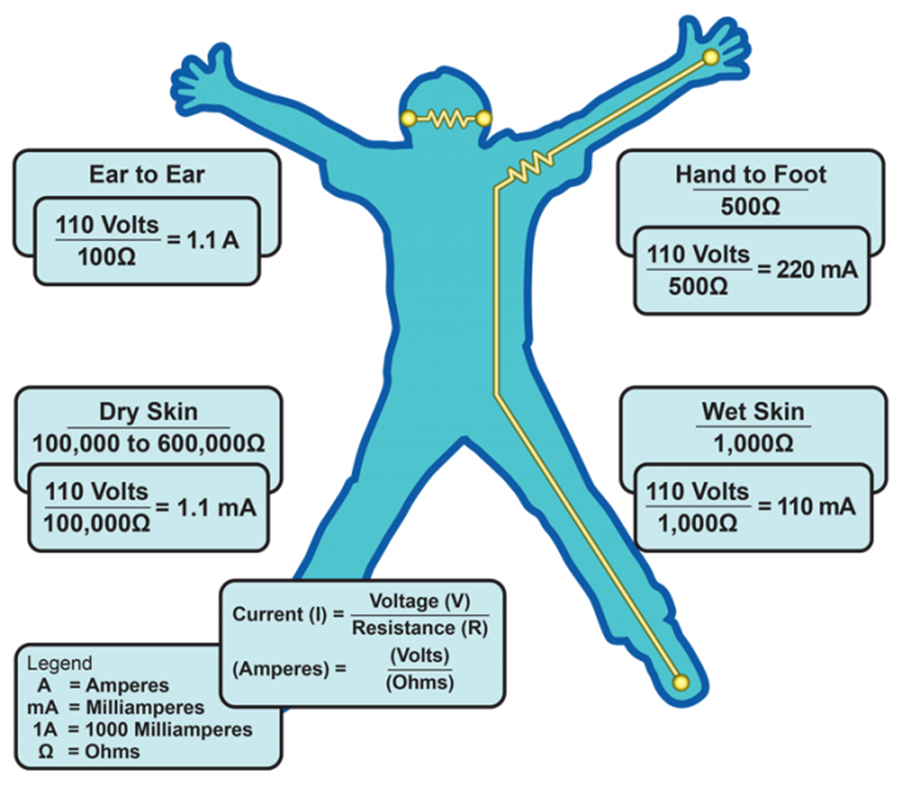
What causes most electrical fatalities?
current flowing through the heart causing fibrillation
total resistance in parallel
decreases when resistors are added in a parallel circuit
series circuit
a circuit that contains more than one electrical component connected one after another in a continuous loop
current in series circuit
the current is the same in every part of the circuit
series circuit pros
easy to construct and learn from
series circuit cons
if one component breaks or is removed, the circuit won’t work as it’s no longer a closed loop
energy in vs out
energy put into a circuit equals the energy that comes out
voltage in a loop
the sum of voltage drops in a closed loop must equal the emf (voltage) from the battery
potential gain vs drop
energy gained by charges equals energy lost by charges
energy loss in series
in a series circuit, energy loss is shared across components
independent loops
each loop in a parallel circuit acts like an independent circuit with its own current
resistance and current
current flows more to branches with less resistance
total current in parallel
splits across branches and recombines afterward
voltage in parallel
the voltage is the same across all branches
parallel circuit advantage
components can operate independently of one another
Kirchhoff's Junction Rule
the total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving the junction
friction
resistance to motion
ohm
the unit used to measure resistance
resistance (R)
the measure of how hard it is for current to flow through a material, measured in ohms
electron speed
electrons move very slowly through a wire because they are so tiny
effect of resistance on current
as resistance increases, the flow of electrons (current) decreases
current
the flow of electric charge
wire length and resistance
as the length of a wire increases, resistance increases
short circuit
occurs when there is zero resistance or no load in a circuit, causing a large current
resistors
components used to control the current and voltage drop across parts of a circuit
ohmic
describes a straight-line relationship between voltage and current
ohmic conductors
used to control the amount of current in a circuit, obey Ohm’s Law
non-ohmic conductors
do not show a straight-line relationship between voltage and current
rate
measuring a quantity over time
current
the flow of electric charge from positive to negative (conventional current)
actual electron flow
from negative to positive
current direction memory aid
"Longer is positive, shorter is negative" – conventional current flows from positive to negative, electron flow is the opposite
battery
converts conventional energy into potential energy and stores a difference in electric charge
work
energy changes from one form to another (an energy conversion)