Chapter 2 The Leadership Equation The Art of Leadership Manning & Curtis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Sir Francis Galton.
is credited with being one of the earliest leadership theorists, mentioning the trait approach to leadership for the first time in his book Hereditary
Genius, published in 1869.
The trait theory of leadership?
(1) basic intelligence,
(2) clear and strong values, and
(3) high level of personal energy.
One of the most widely reported studies of leadership traits was conducted by
_______________ who evaluated over 300 managers from 90 different businesses in the
United States.
Edwin Ghiselli
Ghiselli identified six traits as being important for effective leadership:
1. Need for achievement—seeking responsibility; working hard to succeed.
2. Intelligence—using good judgment; having good reasoning and thinking capacity.
3. Decisiveness—making difficult decisions without undue hesitation.
4. Self-confidence—having a positive self-image as a capable and effective person.
5. Initiative—being a self-starter; getting jobs done with minimal supervision.
6. Supervisory ability—getting the job done through others.
4
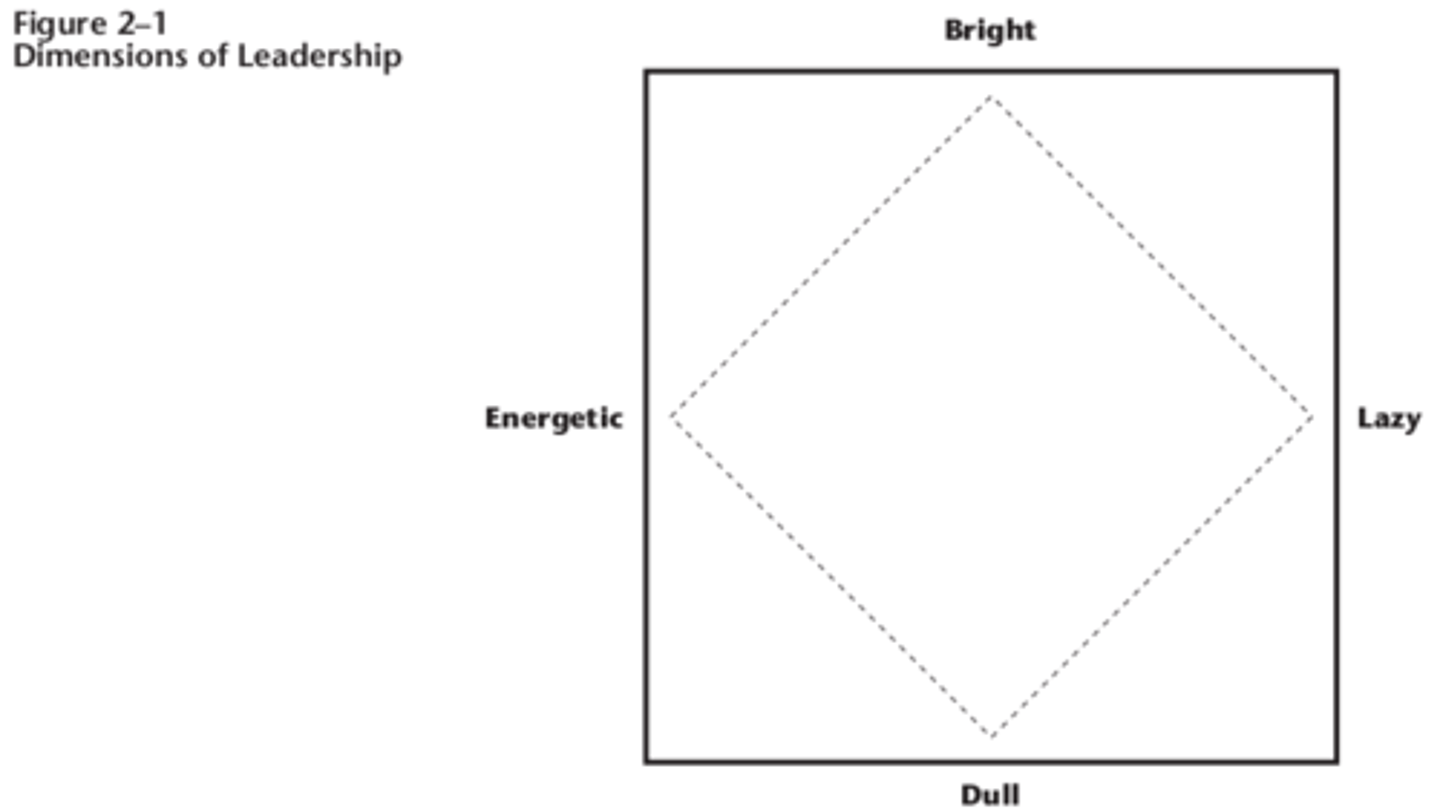
An interesting application of trait theory was practiced by _________________________ war
hero and second president of post-World War I Germany. _______________ used a
form of trait theory for selecting and developing leaders. He believed that leadership
ability was determined by two primary qualities—intelligence (bright versus dull)
and vitality (energetic versus lazy). He used a box (see Figure 2-1) to evaluate
potential military leaders on these two dimensions.
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul von Hindenburg, model
Who is this model attributed to?
During the 1930s, a growing emphasis on behaviorism in psychology moved leadership
researchers in the direction of the study of leadership behavior versus leadership traits. A
classic study of leadership behavior was conducted at the University of Iowa by ___________________ and his associates in 1939. These researchers trained graduate assistants in behaviors indicative of three leadership styles: autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire.
Kurt
Lewin
These researchers trained graduate assistants in behaviors indicative of three leadership styles: autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. Who is associated with this?
Kurt
Lewin
In 1945 _____________and others at Ohio State University developed an assessment instrument known as the Leader Behavior
Description Questionnaire (LBDQ).
Ralph Stogdill
Leader Behavior
Description Questionnaire (LBDQ). Ralph Stogdill
9 Respondents to the questionnaire described
their leaders' behaviors toward them in terms of two dimensions:.
1.Initiating structure—the extent to which leaders take action to define the
relationship between themselves and their staff, as well as the role that they expect
each staff member to assume. Leaders who score high on initiating structure
establish well-defined channels of communication and ways of getting the job
done. Five assessment items measuring initiating structure are as follows:
a. Try out your own new ideas in the work group.
b. Encourage the slow-working people in the group to work harder.
c. Emphasize meeting deadlines.
d. Meet with the group at regularly scheduled times.
e. See to it that people in the group are working up to capacity.
2. Showing consideration—the extent to which leaders take action to develop trust,
respect, support, and friendship with subordinates. Leaders who score high on
showing consideration typically are helpful, trusting, and respectful, and have
warm relationships with staff members. Five questionnaire items that measure
showing consideration are as follows:
a. Be helpful to people in the work group.
b. Treat all people in the group as your equals.
c. Be willing to make changes.
d. Back up what people under you do.
e. Do little things to make it pleasant to be a member of the group.
At about the same time the Ohio State studies were being conducted, the University
of Michigan's Survey Research Center started leadership studies under the direction
of Rensis Likert, who gave special attention to the impact of leaders' behaviors on
worker motivation and the performance of groups.
10
The Michigan studies identified
two similar dimensions of leadership behavior?
1. Job-centered—same as initiating structure.
2. Employee-centered—same as showing consideration.
1964 Robert Blake and Jane Mouton The Managerial (Leadership)
Grid for Leadership
Effectiveness
The Managerial (Leadership)
Grid for Leadership
Effectiveness
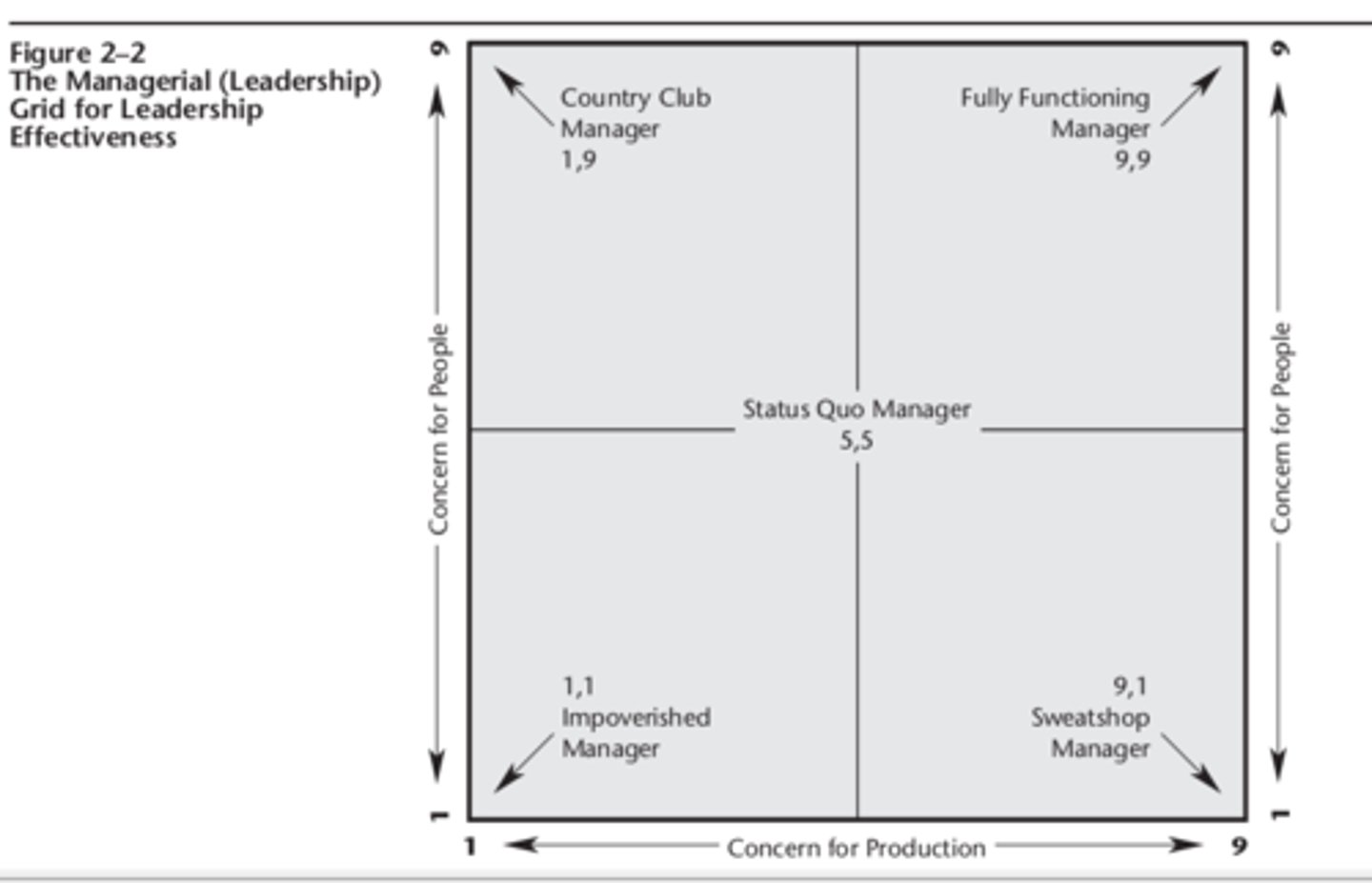
In recent years, two additional styles have been seen with such frequency that they
are now listed as major styles:
1. The Paternalistic Manager—uses high concern for production (9,1) combined
with use of rewards (1,9) in exchange for compliance and loyalty.
2. The Opportunistic Manager—uses whichever style will best promote his or her
advancement (1,9 to please subordinates; 5,5 in interactions with peers; and 9,1 to
gain favor with bottom-line-focused bosses).
Ernest Shackleton's Endurance expedition.
The four cornerstones of Shackleton's leadership behavior are _____, _____,_____, and ______.
leading by example
communicating a vision
keeping up morale
maintaining a positive attitude
transformational leadership
can be used to describe the leadership of
individuals such as Vince Lombardi. These leaders use optimism, charm, intelligence, and a myriad of other personal qualities to raise aspirations and transform
individuals and organizations into new levels of high performance.
Although ____________________ was first discussed by J. V. Downton in
1973, its emergence as an important theory of leadership can be traced to ___________, who
distinguished two kinds of leadership: transformational and transactional. Transactional leaders focus on exchanges between leaders and followers. An example would
be a manager who exchanges pay and promotion for work performed. In contrast,
transformational leaders focus on the potentialities of the relationship between the
leader and followers. This leader taps the motives of followers to better reach the
goals of both.
transformational leadership
James MacGregor Burns
Transactional leaders focus on exchanges between leaders and followers. An example would
be a manager who exchanges pay and promotion for work performed. In contrast,
transformational leaders focus on the potentialities of the relationship between the
leader and followers. This leader taps the motives of followers to better reach the
goals of both.
James MacGregor Burns his book Leadership, political sociologist James MacGregor Burns