omol
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
what is a radioactive isotope
One in which the nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy. Can decay to a different element
what is a cation
A positively charged atom
what is an anion
A negatively charged atom
what is estradiol
A steroid hormone that stimulates the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics; the major estrogen in mammals
what is testosterone
Asteroid hormone required for development of the male reproductive system, spermatogenesis, and male secondary sex characteristics; the major androgen in mammals
what is a hydroxyl group
group consisting of an oxygen atom joined to a hydrogen atom. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols
what is an ester group
A chemical group consisting of a carbon double bonded to oxygen and single bonded to another oxygen (must be in middle of chain)
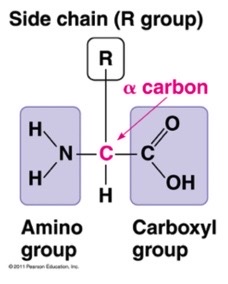
what is a carboxyl group
A chemical group consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group
what is an ionized carboxyl group
A chemical group consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a negatively charged oxygen
what is an amino group
A chemical group consisting of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms can act as a base in solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of 1⁺
what is a sulfhydryl group
A chemical group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
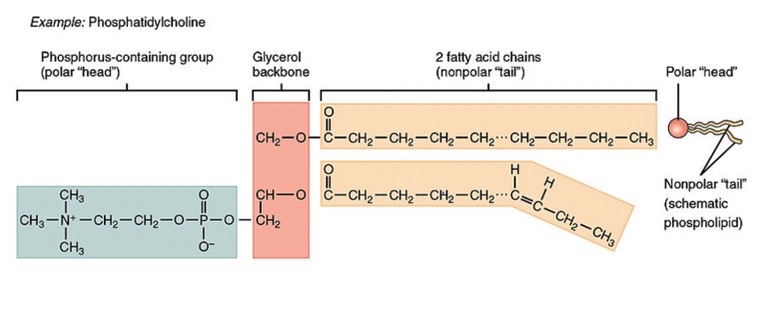
what is a phosphate group
A chemical group consisting of a phosphate atom bonded to four oxygen atoms; important in energy transfer
what is metabolism
All the chemical conversions that occur within a cell
Metabolism = anabolism + catabolism
what is catabolism
Conversion of complex organic molecules into smaller molecules by breaking chemical bonds
what is anabolism
Conversion of small organic molecules by forming chemical bonds between smaller molecules
what is a methyl group
a group where a carbon atom bound to 3 hydrogen atoms
what is a amine group
when 2 nitrogen valence electrons don’t have bonds and the others are bonded with hydrogens or an R group
what is HDL and LDL
HDL is good cholesterol and LDL is bad cholesterol
what are some examples of steriods
cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone, vitamin D, progesterone, cortisol, and aldosterone
what is a peptide bond
covalent bond between amino acids
what do protein hormones do
they function in structure, messaging, and homeostasis.
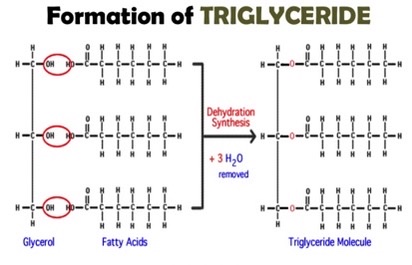
what is an ester bond
bond that happens triglyceride is formed when 1 glycerol molecule links with 3 fatty acid molecule
what is a monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
•can form 4 covalent bonds with atoms
•can form single, double, and triple covalent
• Can form large molecules which will differ based on bonds, shape, and structure
• Can form large molecules which will differ based on bonds, shape, and structure
• can form isomers (things with the same molecular formula but different atomic structure)
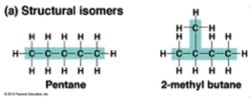
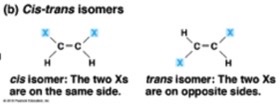
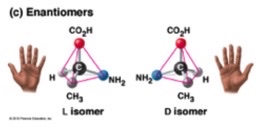
what are the 6 carbon monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, and galactose
what are some examples of polysaccharides
cellulose (plants), starch (plants), glycogen (animals), and chitin (plants/insects)
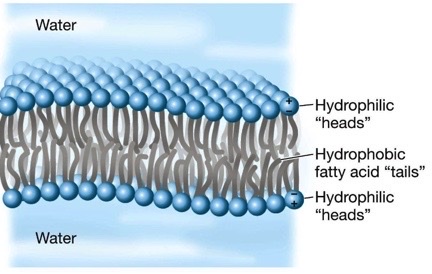
what is the N terminus
it is the start of a protein and the part that leaves the ribosome first during protein synthesis
what is the c terminus
the end of a protein that has C O O H