Protozoan Biology: Morphology, Life Cycle, and Diagnosis
1/281
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
282 Terms
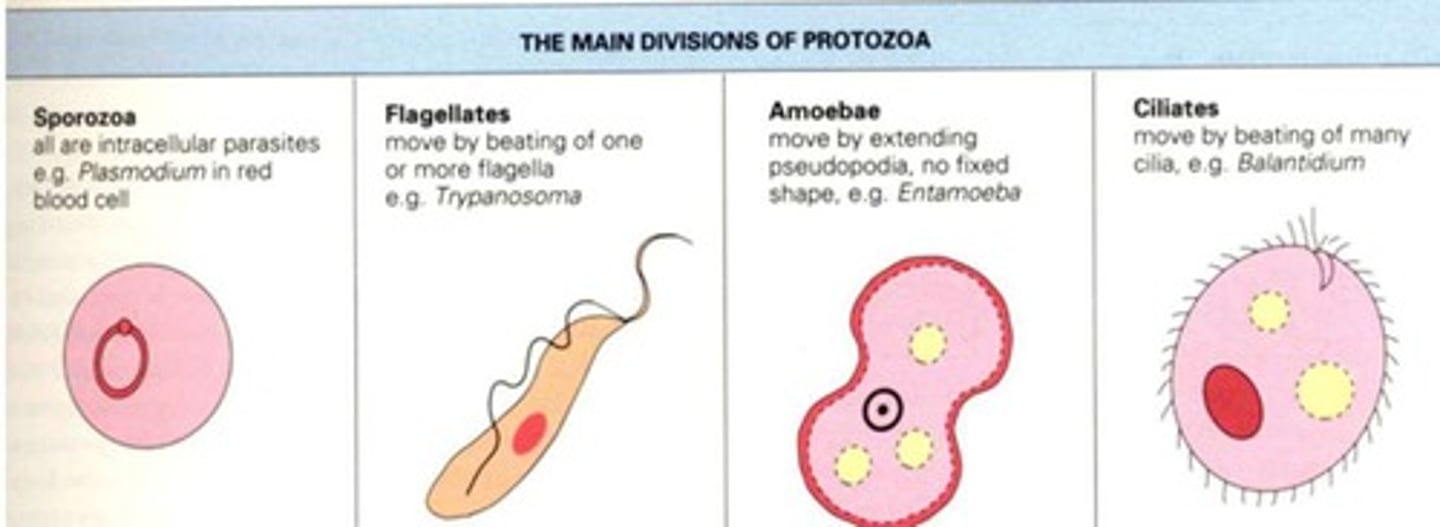
Protozoan
Unicellular organisms that can infect humans.
Amoebas
Protozoa characterized by pseudopodia for movement.
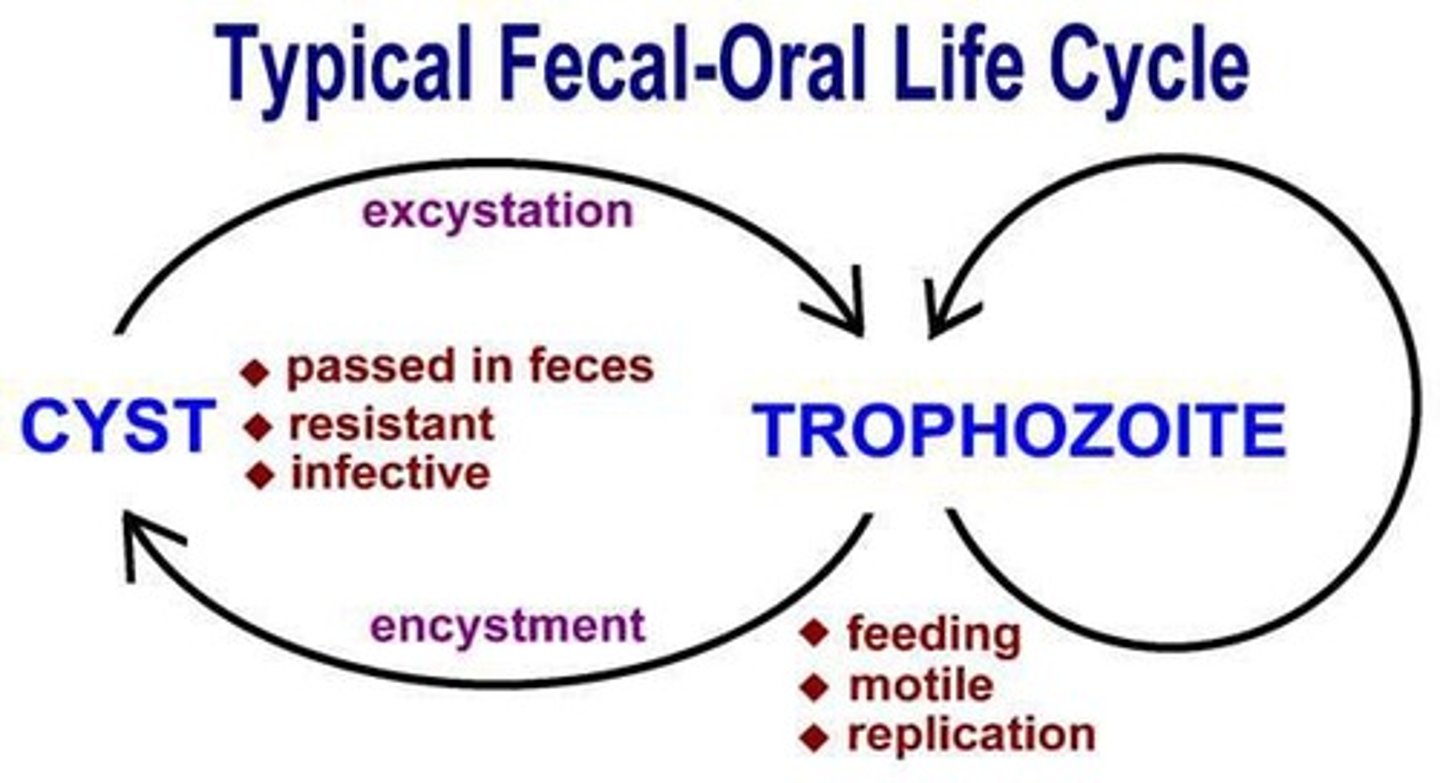
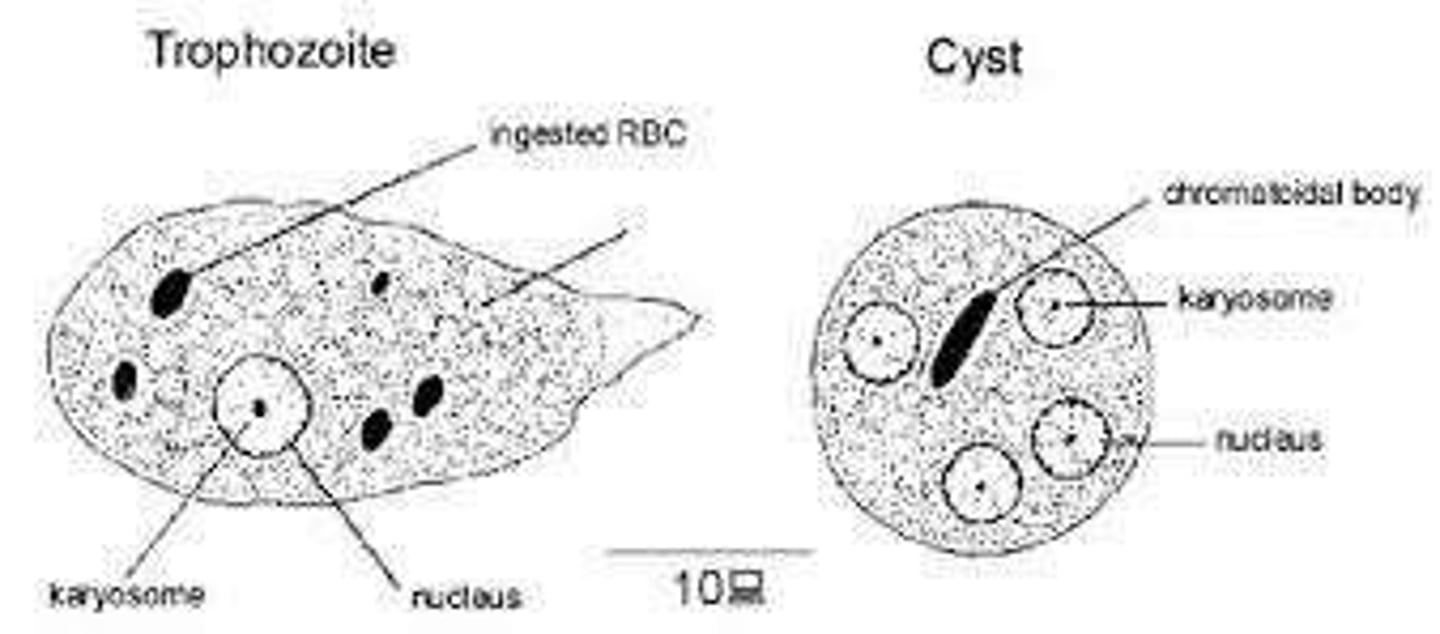
Trophozoite
Feeding, growing stage of protozoa; fragile.
Cyst
Non-feeding stage; allows survival outside host.
Excystation
Conversion from cyst to trophozoite in intestine.
Encystation
Conversion from trophozoite to cyst in adverse conditions.
Macrocnucleus
Vegetative nucleus in protozoan morphology.
Micronucleus
Reproductive nucleus in protozoan morphology.
Karyosome
Nucleolus used to distinguish Entamoeba species.
Endoplasm
Site of metabolism and organelles in protozoa.
Ectoplasm
Region where locomotion organelles arise.
Saline Wet Preparation
Method to observe motility of amoebic trophozoite.
Iodine Wet Preparation
Enhances visibility of internal structures in protozoa.
Permanent Smears
Used to confirm identification of parasites.
Ciliates
Protozoa that move using hair-like cilia.
Sporozoa
Intestinal and tissue-dwelling protozoan parasites.
Blastocystis hominis
Sole member of class Blastocystea.
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Formerly Pneumocystis carinii; a unique protozoan.
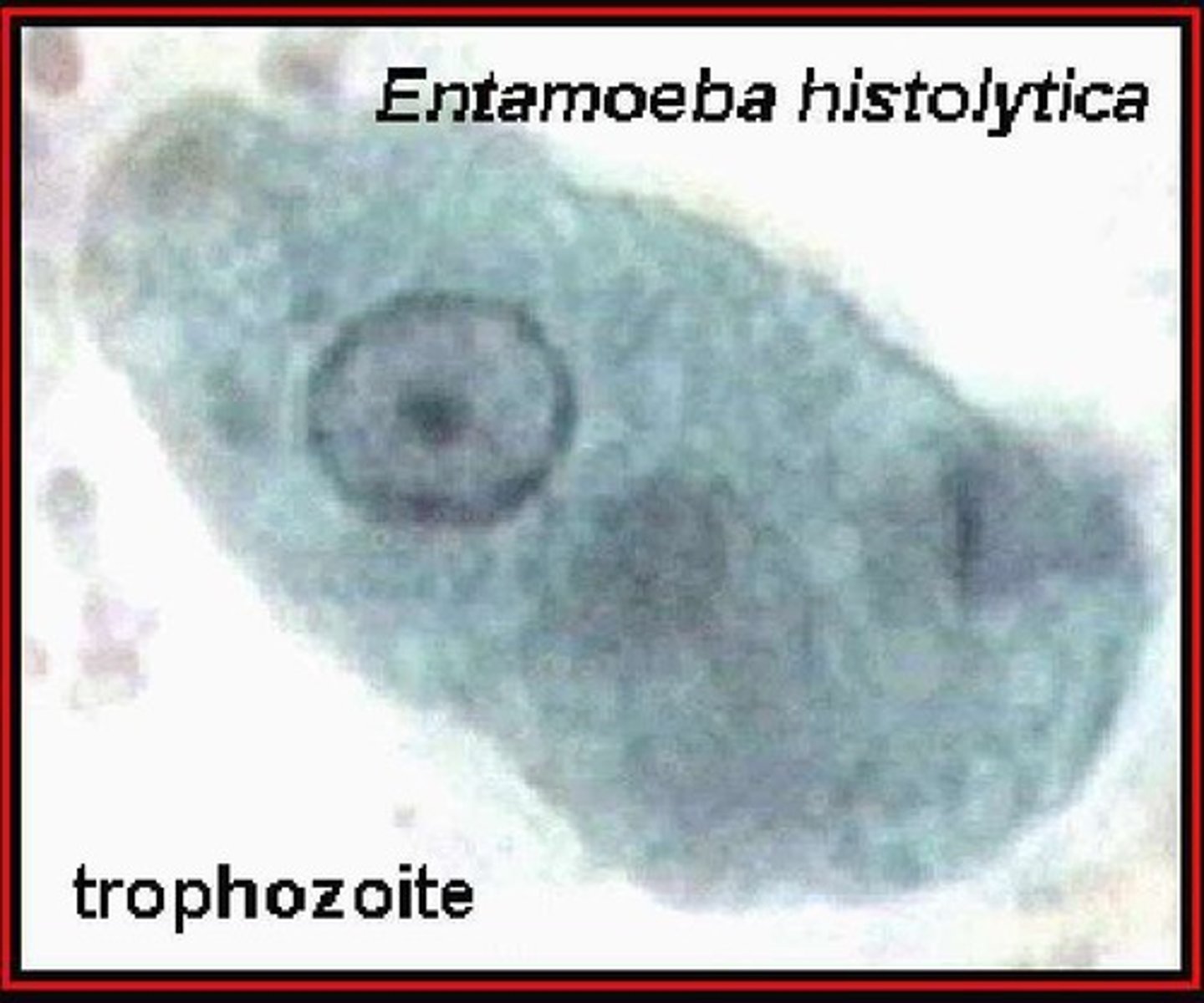
Entamoeba histolytica
Causes intestinal amoebiasis; identified in 1903.
Amoebic Dysentery
Severe intestinal infection caused by E. histolytica.
Entamoeba dispar
Morphologically similar to E. histolytica; non-pathogenic.
Entamoeba coli
Commensal amoeba; not typically pathogenic.
Entamoeba hartmanni
Smaller form of E. histolytica; non-pathogenic.
Endolimax nana
Non-pathogenic amoeba; small size.
Iodamoeba bütschlii
Non-pathogenic amoeba with distinctive morphology.
Entamoeba polecki
Amoeba found in pigs and humans.
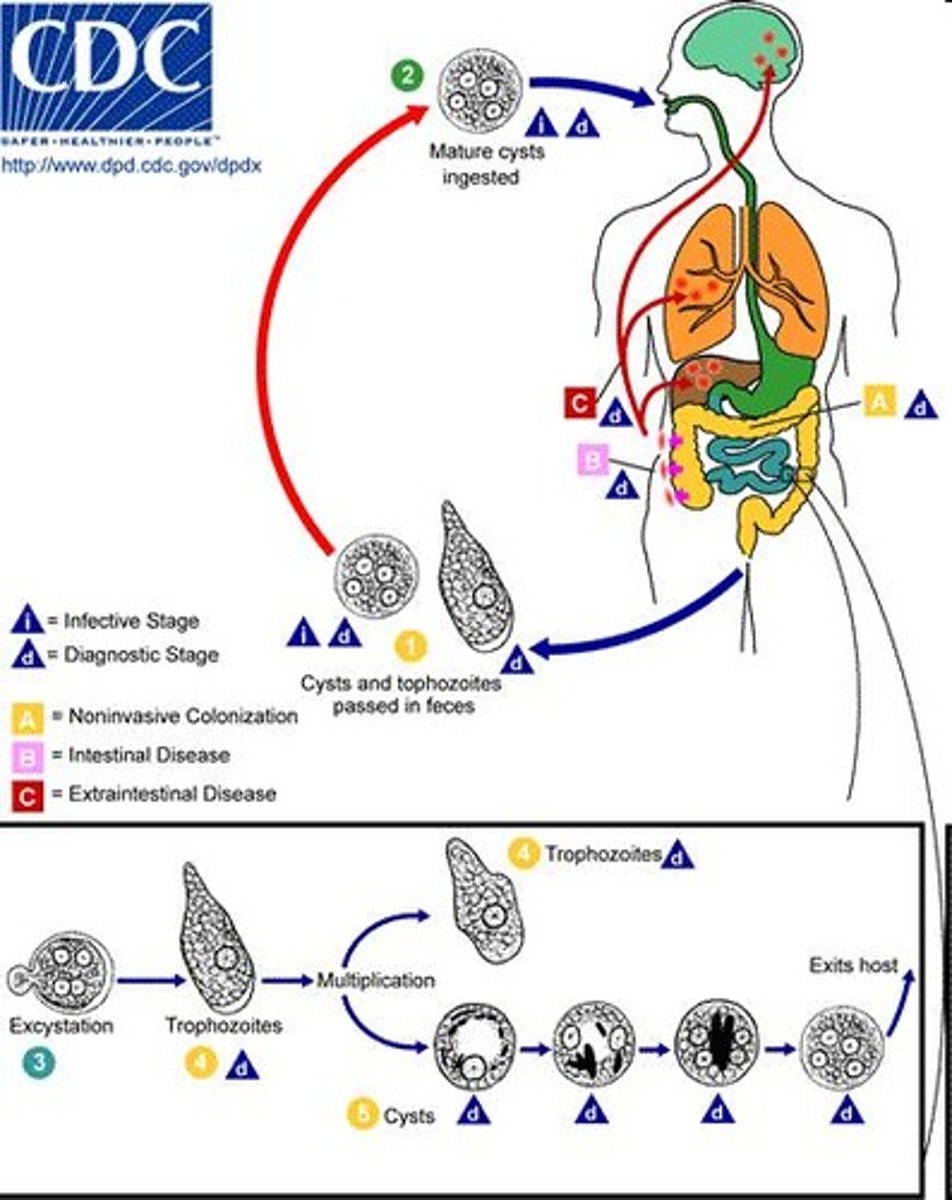
Intestinal Amoebiasis
Infection caused by pathogenic amoebae in intestines.
Amoebic Colitis
Inflammation of colon due to amoebic infection.
Amoebic Dysentery
Severe diarrhea with blood and mucus from amoebae.
Extraintestinal Amoebiasis
Amoebic infection outside the intestines, like liver.
E. histolytica
Pathogenic amoeba causing intestinal and extraintestinal disease.
E. dispar
Non-pathogenic amoeba, often misidentified as E. histolytica.
Trophozoite
Active, vegetative stage of amoeba, motile and feeding.
Precyst
Unripe cyst formed from undigested food and cells.
Cyst
Mature infectious stage with four nuclei.
Metacyst
Stage following cyst, leading to metacystic trophozoite.
Metacystic Trophozoite
Stage after metacyst, ready to invade host.
Pseudopodium
Extension of amoeba for locomotion and feeding.
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction method in amoebae.
Encystation
Process of forming cysts in intestinal lumen.
Glycogen Vacuoles
Inclusions in amoeba, storage for energy.
Chromatoidal Bars
Sausage-shaped bodies in cysts, indicate maturity.
Active Progression
Movement direction of trophozoites during locomotion.
Asymptomatic Cyst Passers
Individuals carrying cysts without showing symptoms.
Amebic Liver Abscess (ALA)
Common extraintestinal complication, causing liver abscess.
Virulence Factors
Molecules aiding pathogen adherence and tissue damage.
Gal/Gal Nac Lectin
Adhesion factor for E. histolytica to host cells.
Amebapores
Pore-forming proteins damaging host cell membranes.
Cysteine Proteinases
Enzymes causing tissue damage in host during infection.
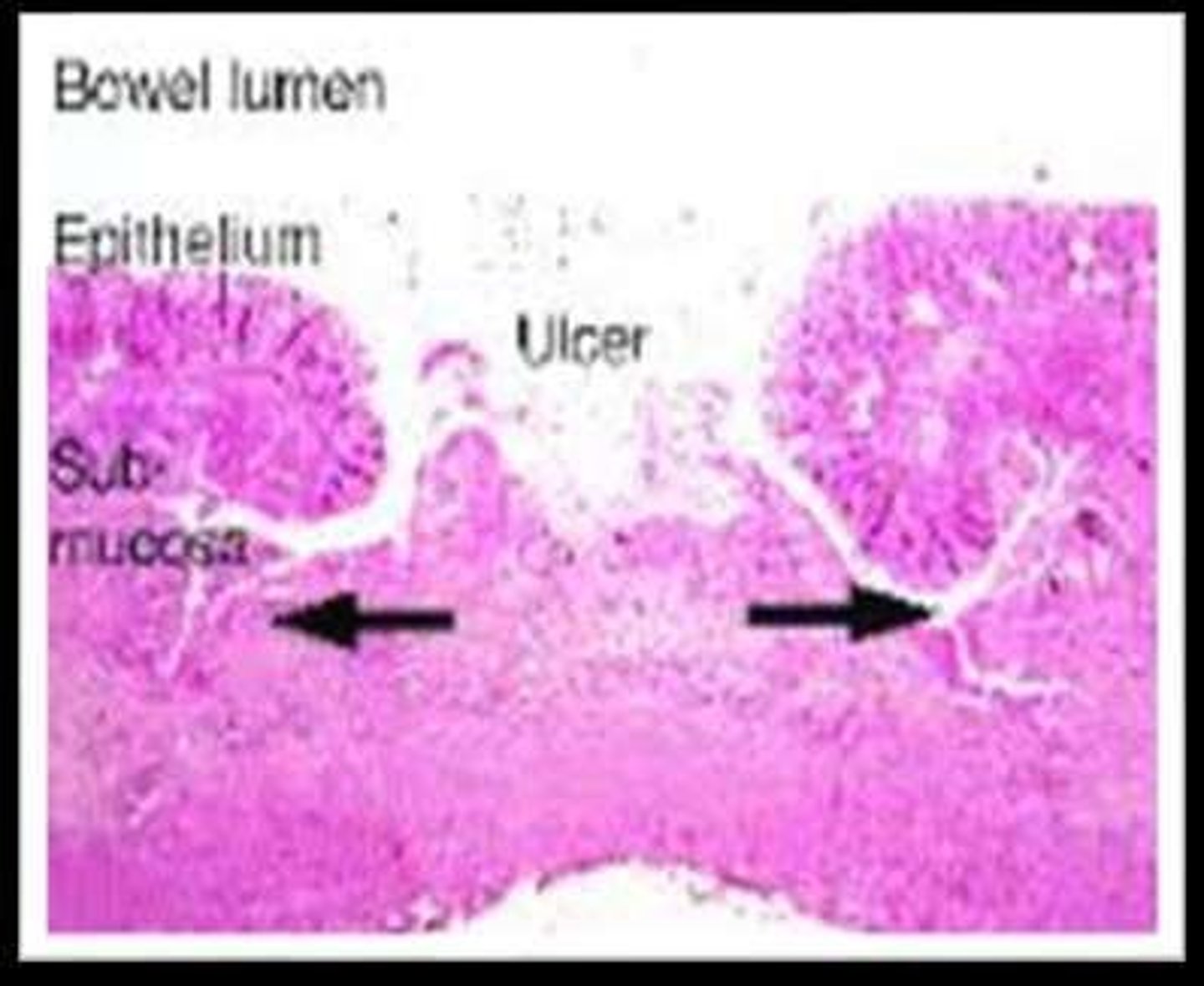
Flask-Shaped Ulcers
Characteristic ulcers formed by trophozoite invasion.
Common Ulcer Sites
Cecum, ascending colon, and sigmoid are affected.
Entamoeba histolytica
Pathogenic amoeba causing intestinal and liver infections.
Trophozoite
Active form of Entamoeba histolytica in tissues.
Portal vein
Vein transporting blood from intestines to liver.
Periportal inflammation
Inflammation around the portal vein in the liver.
Anchovy sauce-like aspirate
Necrotic debris in liver abscess, odorless.
Amoebic ulcer
Ulcer caused by Entamoeba histolytica in intestines.
Incubation period
Time before symptoms appear, varies from days to months.
Chronic intestinal amoebiasis
Long-term infection with intermittent diarrhea and discomfort.
Acute amoebic dysentery
Severe form resembling bacillary dysentery.
Differential diagnosis
Distinguishing between bacillary and amebic dysentery.
Microscopy
Examination method for identifying pathogens in stool.
Charcot-Leyden crystals
Crystals indicating eosinophilic response, found in stool.
Gold standard diagnosis
Microscopic examination of stool specimens.
Concentration methods
Techniques enhancing detection sensitivity of amoebic cysts.
Stool culture
Culturing stool to identify pathogens, more sensitive than microscopy.
PCR
Molecular method for species identification of amoeba.
Serology
Antibody detection methods for diagnosing amoebic infections.
Metronidazole
First-line treatment for amoebic colitis, 800 mg thrice daily.
Tinidazole
Alternative treatment for amoebic infections, effective like metronidazole.
Luminal amoebicide
Drug to clear intestinal parasites after invasive treatment.
Prevention of amoebiasis
Improved hygiene and clean water access to reduce infection.
Commensal amoeba
Non-pathogenic amoeba that can be mistaken for E. histolytica.
Cysts
Infective form of amoeba, resistant to environmental conditions.
Epidemic potential
Amebic dysentery is seldom epidemic compared to bacillary dysentery.
Fecal Contamination
Contamination of food or water by feces.
Non-Pathogenic Amoebae
Amoebae that do not cause disease.
Entamoeba dispar
Non-invasive, non-pathogenic amoeba similar to E. histolytica.
Entamoeba hartmanni
Smaller strain of E. histolytica, non-pathogenic.
Entamoeba coli
Harmless inhabitant of the human colon.
Entamoeba polecki
Non-pathogenic amoeba found in pigs and humans.
Entamoeba gingivalis
Found in the human mouth, lacks cyst stage.
Endolimax nana
Small, non-pathogenic amoeba in the intestines.
Iodamoeba beutschlii
Non-pathogenic amoeba with large karyosome.
Entamoeba genus
Amoebae with spherical nucleus and chromatin granules.
Endolimax genus
Amoebae with vesicular nucleus and irregular karyosome.
Iodamoeba genus
Amoebae with chromatin-rich karyosome and globules.
Trophozoite
Active feeding stage of amoebae.
Precyst
Stage before cyst formation in amoebae.
Cyst
Dormant stage of amoebae, resistant to environment.
Metacystic
Stage following cyst, before returning to trophozoite.
E. histolytica
Pathogenic amoeba causing dysentery.
Cyst differentiation
Cysts of E. histolytica and E. dispar indistinguishable.
Trophozoite size
E. hartmanni trophozoites are 4-12µm.
Cyst size
E. hartmanni cysts measure 5-10µm.
Sluggish movement
Characteristic movement of E. coli trophozoites.
Differential Diagnosis
Comparison of E. histolytica and E. coli characteristics.
Cytoplasmic Inclusions
Bacteria and debris found in E. coli trophozoites.
Entamoeba polecki
Parasite of pigs and monkeys; rare in humans.
Cyst
Uninucleated structure in Entamoeba polecki.