hspts exam 1
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
what is 3 showing
epimysium
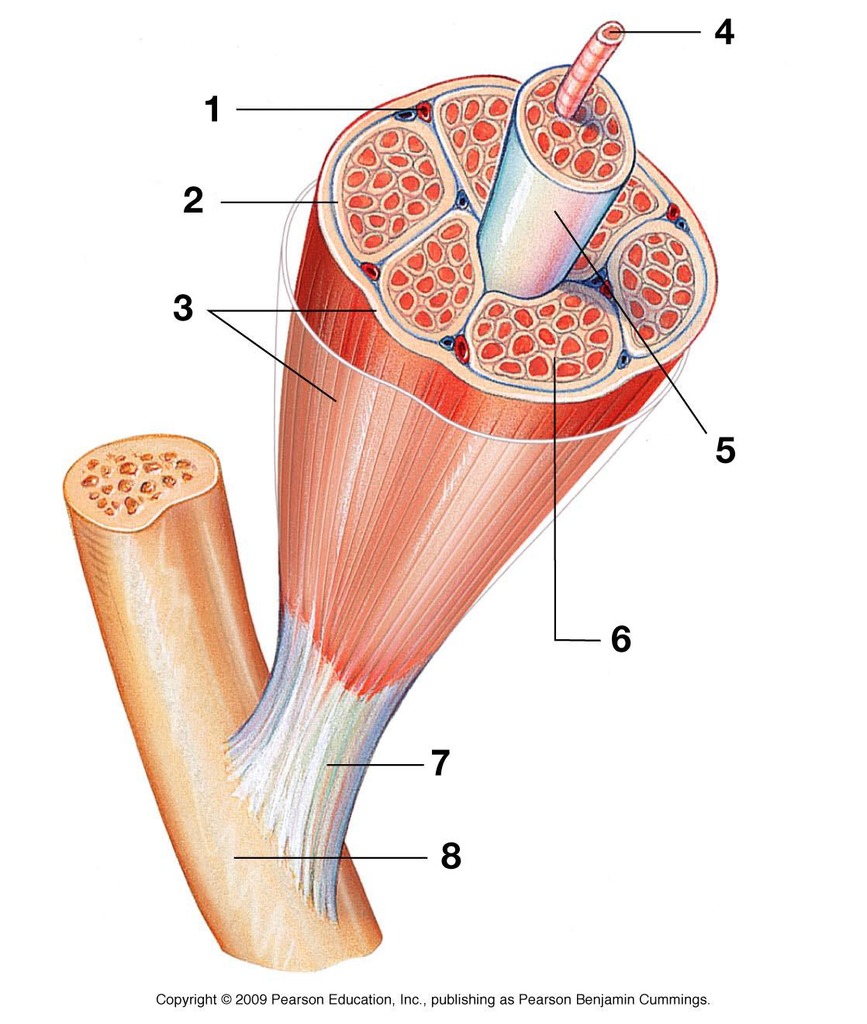
what is 2 showing
perimysium
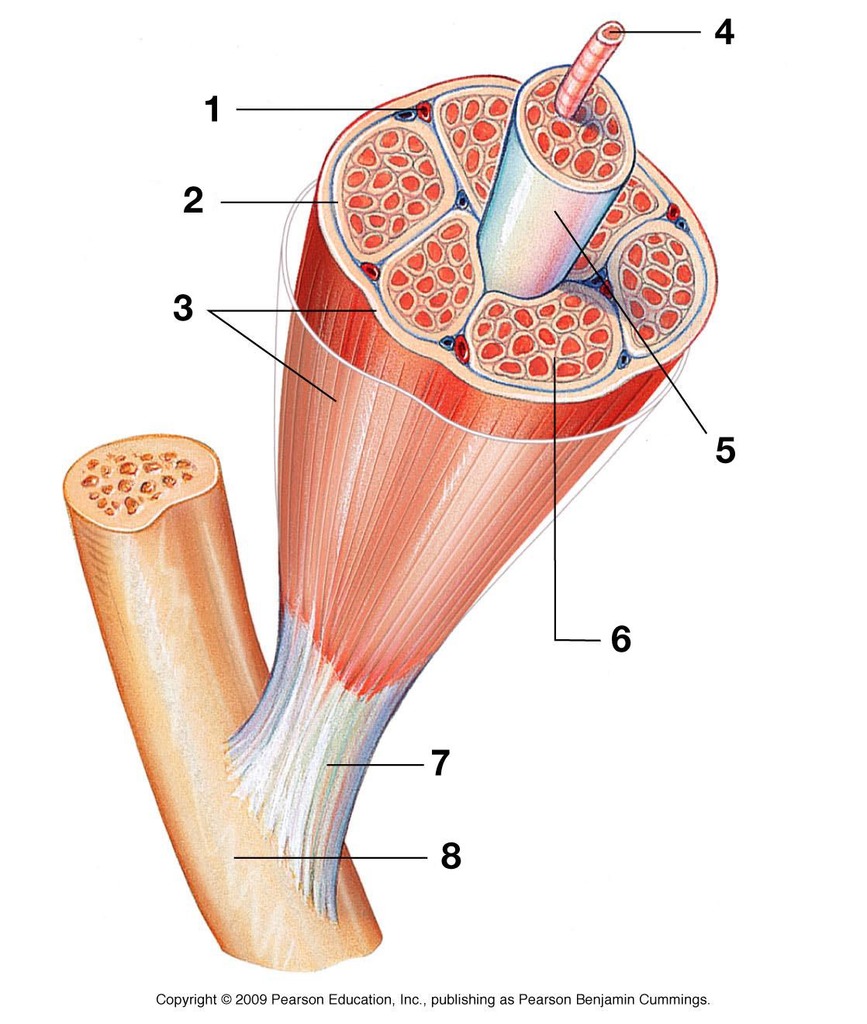
what is 5 showing
fasiculus
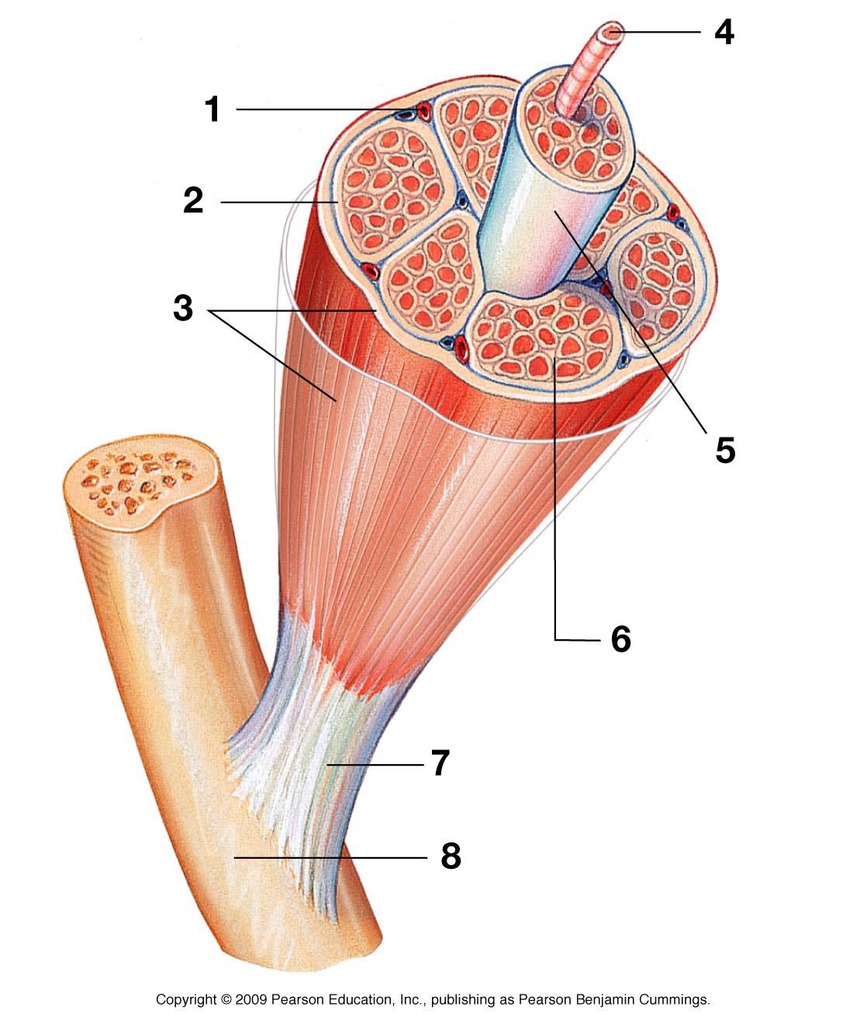
how many muscles fibers are in a fasiculus
150
what is 4 showing
muscle fiber

what is 6 showing
epimysium
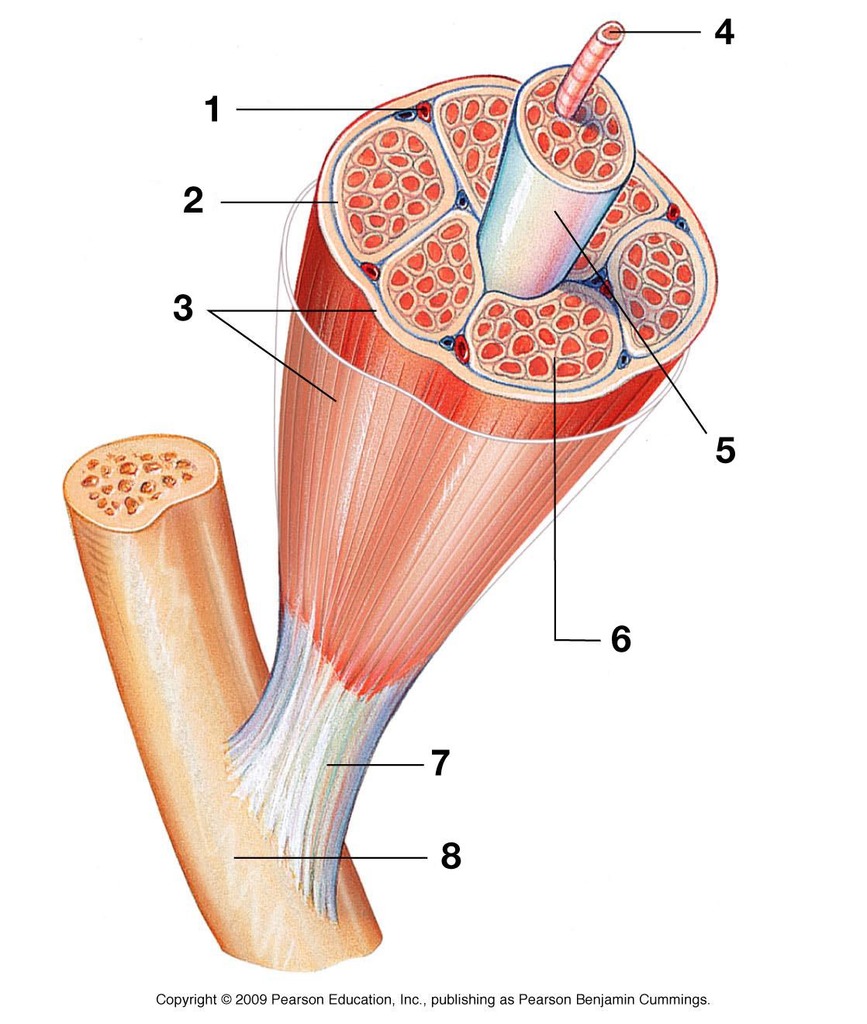
when muscle fibers contract, what direction do they contract in
together in the same direction because the force is applied in one direction
what is tropomyosin made of
thin filament
what is troponin made of
thick filament
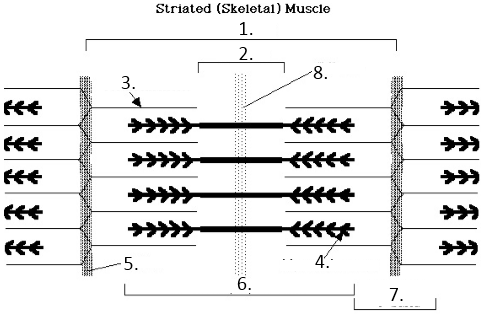
what is number 8
midline
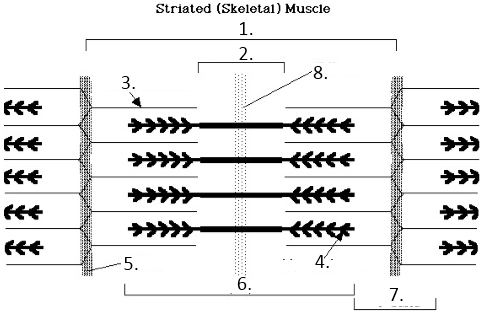
what is 6 showing
h zone
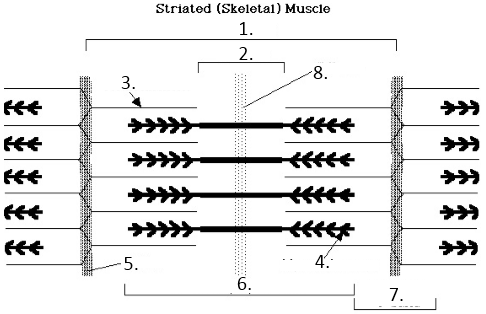
what is 2 showing
a band
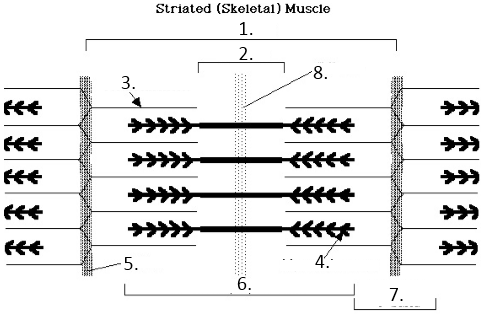
what is 7 showing
I band
what occurs in the resting phase
no muscle tension
what occurs in excitation-coupling
Motor neuron is excited
Ca2+ is released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Troponin moves to reveal binding site
Cross bridges are formed
what occurs during contraction
ATP energy is released for cross bridges flexion
myosin heads pull & shorten muscle fiber
what occurs during recharge
cross bridges repeat flexion with Ca2+ and ATP presence
what occurs during relaxation
motor nerve stimulation ends
Ca2+ returns to sarcoplasmic reticulum
Troponin hides binding sites again
what is type I muscle fiber
slow twitch, long term usage
what classification is type 1
oxidative and fatigue resistant
what levels of mitochondira, aerobic enzyme, and capillary density does type 1 have
high mitochondria, aeorbic enzyme, capillary density
what is type 2a muscle fiber
fast twitch
what classification is type 2a
oxidative & glycolytic and has resistant qualities
what levels of mitochondira, aerobic enzyme, and capillary density does type 2a have
medium
what is muscle type 2b
fast twitch, fast contractions
what classification is type 2b
glycolytic and easily fatigued
what levels of mitochondira, aerobic enzyme, and capillary density does type 2b have
low
what is the relationship between concentric muscle actions
total tension > resistance, muscle shortens
what is the relationship between eccentric muscle actions
total tension < resistance, muscle lengthens
what is the relationship between isometric muscle actions
total tension = resistance, muscle is unchanged
what is motor recruitment
muscle type does not matter when recruited, more number of fibers = more F produced
what type of fiber produces more force in one motor unit
type 2
what is all or none
all fibers contract and develop F
stronger action potential does not equal stronger contraction
what is preloading
when a load is lifted, there must be enough F to overcome the inertia
what is proprioception
awareness of the body in space with gravity
function of muscle spindles
tells muscle to contract and prevents muscle tear from excess stretching
where are muscle spindles located
inside the muscles
function of golgi tendon organs
senses tension and force exerted from muscle, inhibits contraction to prevent injury
where is the golgi tendon organ located
outside the muscle, innervates the ends of the muscle
what is bio energetics
flow of energy in biological system such as macronutrients converted to usable forms for energy
what is catabolism
breakdown of large molecules and releases energy from broken bonds
what is anabolism
synthesis of large molecules which use energy from catabolic reactions
what is exergonic rxns
energy releasing, catabolic
what is endergonic rxns
needs energy, anabolic
what is metabolism
total reactions in a system
what are the products of hydrolyzed ATP
energy + Pi + ADP + H+
what are the products of hydrolyzed ADP
energy + Pi + AMP + H+
what is the phosphagen (ATP-PCr) rxn used for
baseline ATP usage in the body
what does the ATP-PCr rxn use
creatine kinase
what is the process of ATP-PCr rxn
creatine kinase binds to phosphate group of ADP
create ATP for body usage
replenishes quickly
anaerobic
what is law of ass actin
concentration of reactants/products drive the production
what are the products of glycolysis
2 ATP/3 ATP, 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH
what are the two pathways that pyruvate can take
becoming lactate or going into the mitochondria for the Kreb’s cycle
what is the differences between pyruvate’s pathways
lactate is used for short term energy and limited
kreb’s cycle produces more atp and for long term
what stimulates glycolysis to start
hi concentration of ADP, Pi, and ammonia
what stops glycolysis
low concentration of pH and ATP
what is lactate threshold in individuals
the increasing reliance on anaerobic mechanisms to produce energy
what s onset of blood lactate (OBLA)
the secondary increase of lactate accumulation in blood
what are oxidative systems used for
primary source of ATP during low intensity activities
what do oxidative systems use for their rxns
carbs / fats
what are the products of the krebs cycle (2 rotations)
2 ATP + 2 FADH + 6 NADH + 4 CO2
how much ATP is made in the electron transport chain
30-32 ATP
what is fat oxidation
break down of triglycerides into free fatty acids by lipase
how does fat oxidation make energy
free fatty acids entire mitochondria and broken into Acetyl-CoA for Kreb’s cycle & e- transport chain
400 ATP
what is protein oxidation
proteins are broken into amino acids and converted into glucose/pyruvate/any Kreb’s cycle intermediate to make ATP
when is the Kreb’s cycle reduced
low concentration of NAD + and FAD+
what is the e- transport chain inhibited and stimulated by
stimulated by ADP and inhibited by ATP
when are anaerobic energy systems used
short, hi-intensity exercise
when are glycolytic energys systems used
medium-high intensity workouts
when are oxidative energy systems used
low intensity, long duration exercise
how is each system important during energy usage
each system is used to some degree, never just one system supplying energy
how are phosphagens depleted
creatine phosphate is depleted quickly in early stages of exercise (seconds)
how are phosphagens replenished
ATP is replenished in short amount of time (minutes)
how is glycogen delepted
depleted in relation to exercise intensity
how is glycogen replenished
replenished through carb ingestion
what is the function of the hypothalamus
body temperature, heart rate, and hunger
what is the function of the pituitary gland
growth, metabolism
what is the function of the thyroid gland
metabolic activity
what is the function of the parathyroid gland
calcium levels in the blood
what is the function of the adrenal gland
body response to stress and blood pressure
what is the function of the pancreas
blood sugar levels
how do steroid hormones affect the body
long term effects, attach directly to cell
how do polypeptide hormones affect the body
short term effects, attach to receptors on cell and are secondary messangers
how does force produced in a muscle lead to muscle growth
can activate anabolic factors (ie. hormones)
what mechanisms can change the concentration of hormones in the blood
venous blood pooling/shifting, binding proteins, hormonal degradation
how does testosterone affect muscles
interacts with skeletal muscles and protein synthesis to increase strength and size
what time of day do men get better results
later in day due to testosterone levels
what is free hormone hypothesis
only free hormones interact with target tissues
what does growth hormone respond to
stress (ie. resistance exercise)
how is growth hormone affected with training
little changes in trained individuals and typically when induced with exercise stress
what do insulin-like growth factors do in exercise
involved in protein synthesis and muscle growth
what does cortisol do in exercise
inhibits protein synthesis through catabolic effects
how does cortisol respond with exercise
increases with resistance exercise and additional training may reduce negative effects through increasing cortisol
what do training protocols need to be aware of with hormonal changes
must allow adrenal gland to recover otherwise an increase of cortisol will give negative effects
what is the agonist
muscle most directly involved in bringing about a movement
what is the antagonist
muscle that slows down/stops movement
what is the synergist
muscle that assists the agonist with movement, fine tuning
how does a lever apply force
applies force on object equal in magnitude but opposite direction from resisting force
what is mechanical advantage
ratio of arm movement where applied force is greater than resistance force
what does a mechanical advantage of over 1 mean
applied force is less than resistive force and produces equal torque