Chapter 56 Placenta
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Permits the exchange of oxygenated maternal blood with deoxygenated fetal blood
placenta
The placenta can be see as early as what week
week 7
What are the two components of the placenta
Chorion frondosum
Decidua basalis
fetal portion of the placenta
chorion frondosum
maternal portion of the placenta
decidua basalis
What is the major functioning unit of the placenta
chorionic villis
What are within the chorionic villus
intervillous spaces
What is the maternal surface
basal plate
How does fetal umbillical circulation originate
With deoxygenated blood from the heart through the ductus arterious into the aorta
What arteries does the fetal blood circulate
hypogastric arteries to the umbillical arteries to the umbillical cord
where is 40% of fetal cardiac output directed through
umbilical circulation
Umbilical arteries divide within the placenta into
multiple tiny capillaries that branch into the tertiary villi
Where is oxygenated blood brought to the placenta by
80-100 branches of the uterine arteries spiral arteries
Maternal blood returns through a network of
basilar, subchorial, interloblar, and marginal veins
How is the fetal placenta attached to the maternal placenta
cytotrophoblastic shell and anchoring villi
insertion at the placental margin
battledore
insertion into the membrane
may cause hemorrhage if the vessel is postioned over the internal os
velamentous
responsible for the transfer of nutrients to the embryo until the plaenta takes over
yolk sac
condition when the placenta implants too close to the internal os
placenta previa
What day does the amnion develop and attaches to the embyronic disk
day 28
originates from trophoblastic cells and remains in contact with the trophoblasts throughout the pregnancy
chorion
expansion of the amniotic cavity occurs with increase in
amniotic fluid
By what week do the amnion and chorion fuse and are no longer seen
week 16
If the chorion and amnion are not fused by 16 weeks what should you evaluate for
abnormal amount of fluid
When does the umbilical cord form
first 5 weeks
what surrounds the umbilical cord
whartons jelly
bowel herniates into the umbilical cord (gastroschisis) from what week
week 7-10
What is the largest vessel in the umbilical cord
the vein
One umbilical artery is found in waht percent of single ton births
1%
What can be confused with normal placenta
braxton hicks contractions
very common
large vessels that appear cystic behind the chronic plate and between the chorionic plate and between the chorion and amnion filled with maternal blood
venous lakes
occurs when the placenta lies on both the anterior and posterior walls and does not communicate
succenturiate placenta
grade of placenta that is uninterrupted chorionic plate and homogenous placental substance
grade 0
grade of placenta with subtle indentations in the chorionic plate and some small calcification
grade 1
grade of placenta with moderate indentations in the chorionic plate with comma like calcifications
grade 2
grade of placenta with prominent indentation in the chorionic plate that extends to the basal layer and echogenic and anechoic areas within the placenta
grade 3
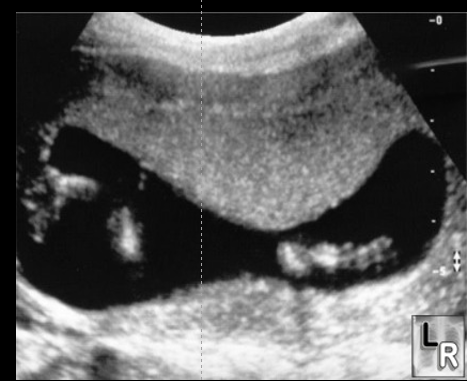
grade 0
what grade placenta is seen late 1st- early 2nd
grade 0
what grade placenta is seen mid 2nd-early 3rd
grade1
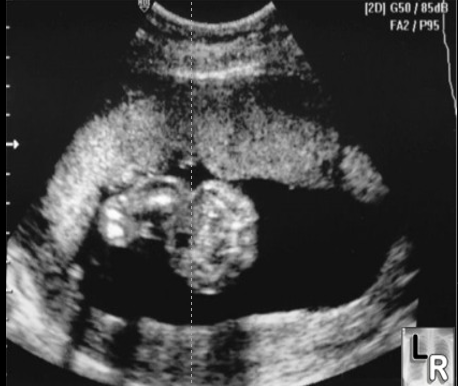
grade 1
what grade placenta is seen late 3rd
grade 2
what grade placenta is seen 39- post due date
grade 3
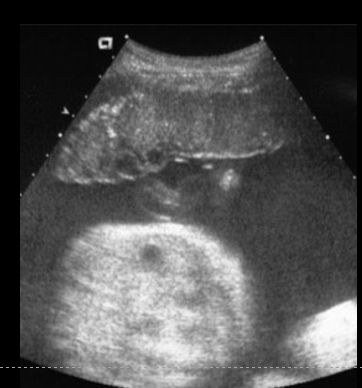
grade 2
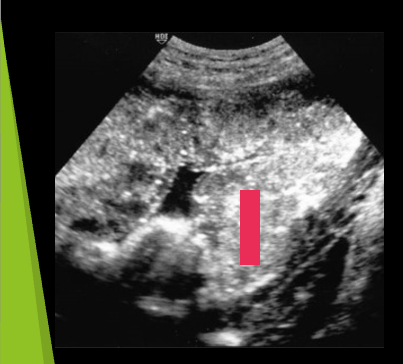
grade 3
type of arteries that are low resistant on doppler
trophoblastic spiral arteries
are variable with gestational age and location
uterine arteries
flow measurements will decrease with
gestational age
Normal diameter of the placenta
15-20 cm
normal thicken of placenta
4 cm
approx weight of placenta
600g
protein derived from fibrogen
found throughout the placenta and septa
fibrin deposition
appears as hypoechoic area beneath the chorionic plate of the placenta
fibrin deposition