Chemistry - Reactivity series: Redox + Rust
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What does the reactivity series sort the elements into?
The order of reactivity is determined through their reactions with water and acids.
Which metals will only react with dilute acids?
Metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series.
What is a displacement reaction?
a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from it’s compound.
What is a redox reaction?
a reaction which both reduction and oxidation are occuring
What is oxidation involving oxygen?
The gain of oxygen
What is reduction, involving oxygen?
The loss of oxygen
What is oxidation, involving electrons?
The loss of electron
What is reduction, involving electron?
The gain of electrons
What does OIL RIG stand for?
Oxidation is loss, reduction is gain (of electrons)
What is a reducing agent?
A substance that reduces something. (It is already oxidised/being oxidised)
What is an oxidising agent?
A substance that oxidises something. (It is already reduced/being reduced)
When does rusting occur?
when iron reacts with oxygen and water
What is produced when iron reacts with oxygen and water?
rust (obviously) AKA Hydrated iron (III) oxide
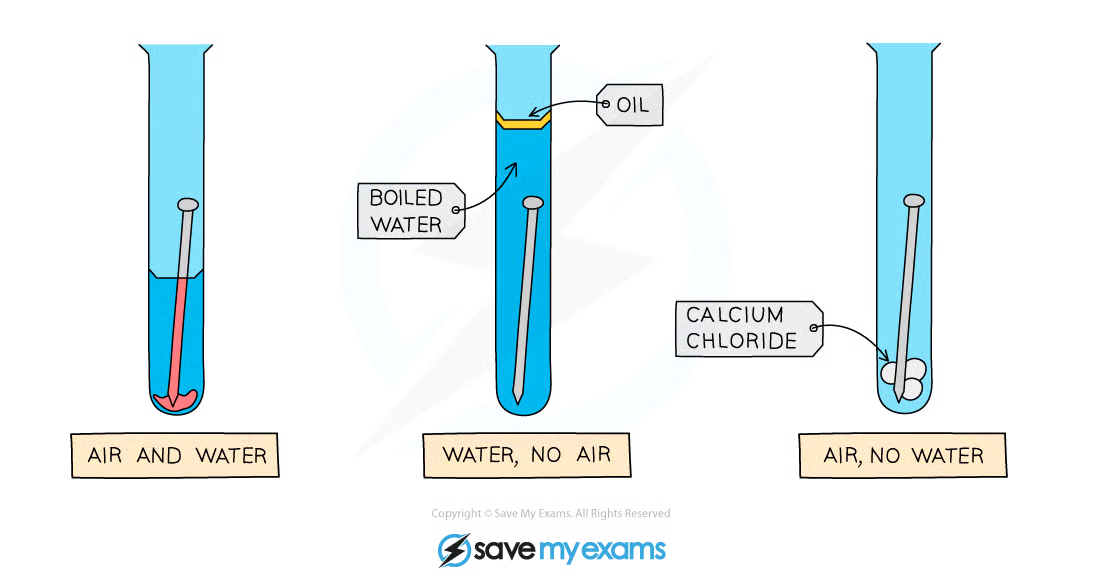
What is the experiment to test for rusting?
A test tube with a nail and water and air
A test tube with a nail and water, but no air as there is a layer of oil on top and boiled water.
A test tube with a nail and air, but no water
What is the rust prevention method of barrier methods and examples?
coating iron with barriers that prevent the iron from coming into contact with water and oxygen
examples incude: paint, oil, grease, and electroplating
What is the rust prevention method of sacrificial protection and examples?
using the reactivity series
A more reactive metal can be attached to a less reactive metal
The more reactive metal will oxidise and therefore corrode first, protecting the less reactive metal from corrosion
eg: Zinc is more reactive than iron therefore will lose its electrons more easily than iron and is oxidised more easily
What is the rust prevention method of galvanising and examples?
iron to be protected is coated with a layer of zinc by electroplating or dipping it into molten zinc
zinc reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air to form ZnCO3 and protects the iron by the barrier method
If the coating is damaged or scratched, the iron is still protected from rusting by sacrificial protection