Cell Structure and Function Chapter 9
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Metabolism
All the chemical reacts in a cell
Anabolic Pathways
Synthesize cellular components, often polymers such as starch and glycogen
Increase in order and a decrease in entropy
Endergonic
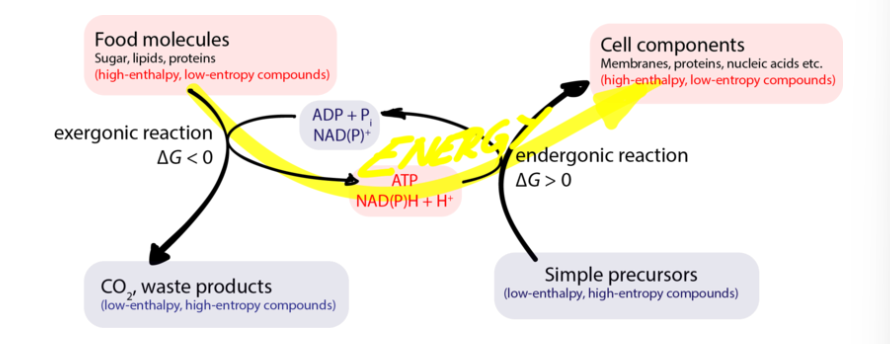
Catabolic Pathways
Breakdown of cellular constituents such as the hydrolysis of glucose
Decrease in order and increase in entropy
Exergonic
Release free energy
Can be aerobic or anaerobic
3 Important Chemical Players
ATP
NAD+/NADH
Glucose
What is the role of ATP?
Primary energy currency
Power cell movement, transport of molecules/ions, and enzyme catalyzed reactions.
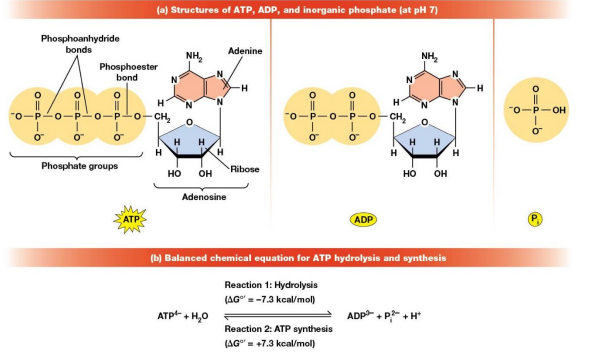
Phosphoanhydride Bonds
Energy Rich Bonds
Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi is exergonic because?
Charged Repulsion between the adjacent negatively charged phosphate groups
Resonance Stabilization of both products of hydrolysis
Increases entropy and solubility of the products of hydrolysis
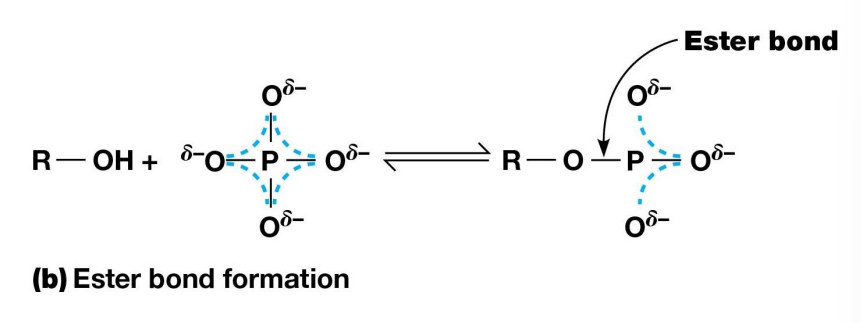
Resonance Stabilization
When a Phosphoester bond is formed between a phosphate and alcohol group, the extra electrons are delocalized over only three oxygen atoms instead of four
Less resonance stabilized and more energy
Increase in Entropy
Once the phosphate group gets removed from ATP it is no longer in a fixed position. The spatial randomization of ADP and Pi after hydrolysis decreases their free energy and makes the reaction more exergonic.
This in turn makes them become more soluble and their increased interactions with water molecules decreases their free energy
Summary: Phosphate group removed - more entropy. Randomization/entropy decreases free energy and makes them exergonic. More exergonic means more soluble.
Catabolic Fuels
Highly reduced compounds like lipids and sugars
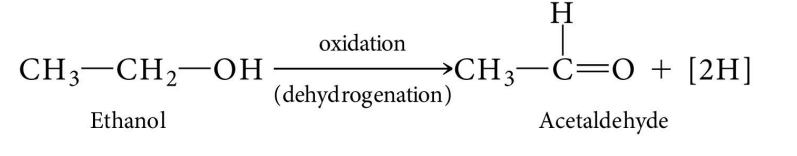
Oxidation
Removal of electrons
Dehydrogenation
Removal of a proton and an electron (i.e. hydrogen)
Cellular reacts involving organic molecules are almost always dehydrogenation reactions
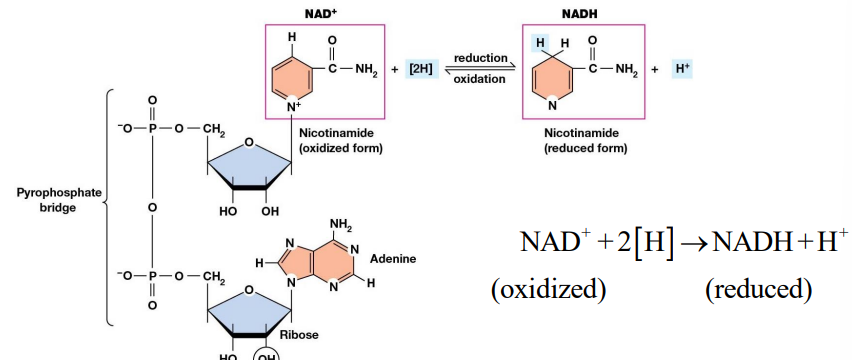
Coenzymes
Function along with enzymes, serving as carriers of electrons or small functional groups
Electrons or Hydrogens removed during biological oxidation are transferred to them
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
Most common coenzyme serving as an electron acceptor.
Adds 2 electrons and a proton to its aromatic ring, generating NADH plus a proton
Glucose
its oxidation is a highly exergonic process
Oxidized to CO2 and Oxygen reduced to Water
Aerobic Respiration
Oxidation of glucose in the presence of oxygen
Yields 36 ATP/glucose
Anaerobic Respiration
Yields 2 ATP/glucose
Via glycolysis
Fermentation
Electrons removed during glucose oxidation are returned to an organic molecule later in the same pathway
Obligate aerobes
absolute requirement for oxygen
Obligate anaerobes
cannot use oxygen as an electron acceptor; oxygen is toxic to these organisms.
Facultative organisms
can function under aerobic or anaerobic conditions.
Glycolysis
Ten step reaction sequence that converts one glucose molecule into 2 molecules of pyruvate
glucose goes to 2 three-carbon pyruvates
ATP and NADH produced
Occurs in cytosol
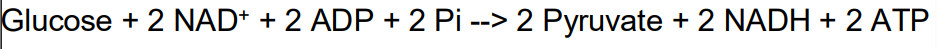
Important Features of the Glycolytic Pathway
Initial input of 2 ATP
Sugar splitting reaction in which glucose is split into 2 three carbon molecules
Oxidative event that generated NADH
2 Steps at which the reaction sequence is coupled to ATP generation
Glycolysis Mechanism