DH 390: Exam #2
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Describe the health stage
Firm and resilient tissue, minimal sulcus depth
Coral pink
Variations in color may depend on race
Evidence of previous disease may be present
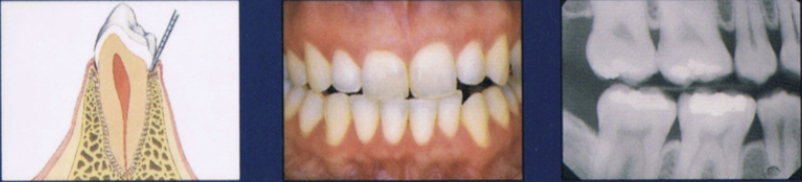
Describe gingivitis
Inflammation of the gingiva
Clinically: change in color, gingival form, position, surface appearance, presence of bleeding/exudate
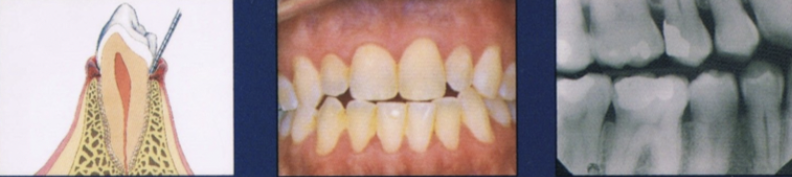
Describe early stage of periodontitis
Progression of gingival inflammation into deeper periodontal structures and alveolar bone crest
Slight bone loss
Slight loss of CT attachment + alveolar bone
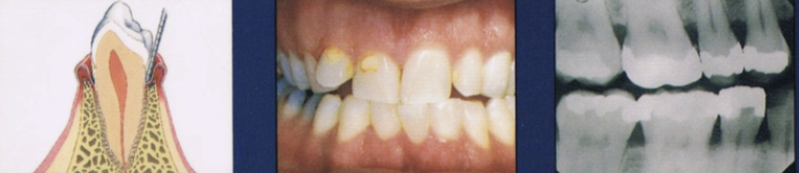
Describe moderate stage of periodontal disease
More advanced stage of previous condition
Increased destruction of periodontal structures
Noticeable bone loss, support, and increase in mobility
Furcation involvement
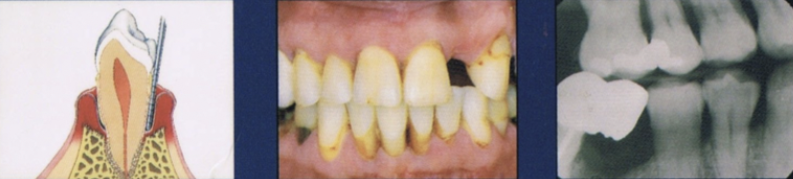
Describe advanced stage of periodontal disease
Major loss of alveolar bone support
increased tooth mobility
Furcation involvement
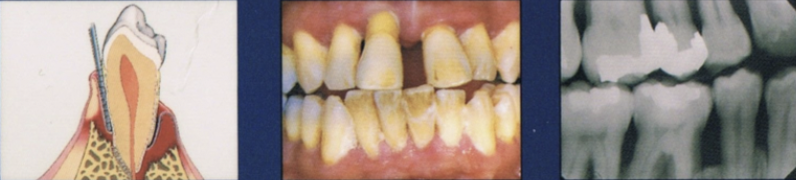
What are the three subcategories that periodontal health, gingival diseases, and conditions are divided into?
Periodontal health and gingival health
Gingivitis: dental biofilm-induced
Gingival diseases: nondental biofilm-induced
Describe periodontal health and gingival health subcategoy
Clinical gingival health on an intact periodontium
Clinical gingival health on a reduced periodontium
Stable periodontitis patient
Non-periodontitis patient
Describe gingivitis - dental biofilm induced subcategory
Associated with DENTAL BIOFILM alone
Mediated by systemic or local risk factors
Drug-influenced gingival enlargement
Describe gingival diseases - nondental biofilm induced subcategoy
Genetic/developmental disorders
Specific infections
Inflammatory and immune conditions
Reactive processes
Neoplasms
Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases
Traumatic lesions
Gingival pigmentation
What are the three forms that periodontitis is divided into?
Necrotizing periodontal diseases
Periodontitis
Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease
What are the other five categories that periodontitis is subdivided into?
Systemic diseases or conditions affecting the periodontal supporting tissues
Periodontal abscesses and endodontic periodontal lesions
Mucogingival deformities and conditions
Traumatic occlusal forces
Tooth and prosthesis related factors
Describe mucogingival deformities and conditions around teeth
Gingival pheotype
Gingival/soft tissue recession
Lack of gingiva
Decreases vestibular depth
Aberrant frenum/muscle position
Gingival excess
Abnormal color
Condition of the exposed root surface
What are the subdivisions of Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions?
Peri-implant health
Peri-implant mucositis
Peri-implantitis
Peri-implant soft and hard tissue deficiencies
What are characteristics of periodontal health?
Absence of:
Bleeding on probing
Erythema
Edema
Attachment loss
Bone loss
Gingival tissue = uniform pink color
Gingival margin tightly encircles tooth’s cervical region (contour)
What is intact periodontium?
No loss of periodontal tissue
No signs of inflammation
No loss in bone level
What is reduced periodontium?
Preexisting loss of periodontal tissue but not currently undergoing loss of CT/alveolar bone
Describe periodontial health on reduced periodontium in non-periodontitis patient?
No inflammation
Recession
No bone loss
Features of dental biofilm-induced gingivitis
Most common form of periodontal disease
Does NOT directly cause tooth loss, must be managed as active disease
Inflammatory response of gingival tissues by periodontal pathogens
Prevalent in all age groups
Describe tissue contour in gingivitis
Edema causes enlargement of gingival tissues
EX: Bulbous papilla
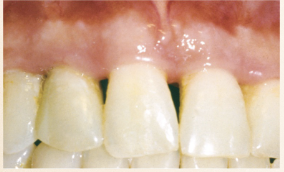
Describe the tissue contour in this image?
Blunted papilla
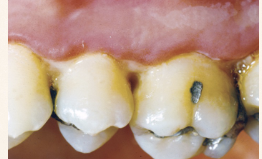
Describe the tissue contour in this image?
Cratered papilla
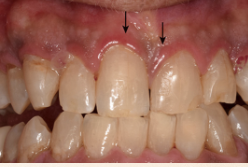
Describe the tissue contour in this image?
Rolled - thickened gingival margin
What is the tissue consistency in gingivitis?
Inflamed free gingiva loses firm consistency
Tissue spongy with light pressure
Compressed air readily deflects gingival margin and papillae away from neck of tooth
Can appear smooth and very shiny
Almost has “stretched” appearance
May lose gingival
What is the position margin of gingivitis
More coronal
B/c tissue swelling and enlargement
What is presence of bleeding like in gingivitis?
Occurs with gentle probing before color changes
Epithelial lining of sulcus becomes ulcerated and blood vessels engorge
Heavier bleeding as inflammation increases
Where can distribution of inflammation affect?
Only interdental papilla (papillary gingivitis)
Gingival margin and papilla (marginal gingivitis0
Gingival margin, papilla, and attached gingiva (diffuse gingivitis)
What are the subcategories of dental biofilm induced gingivitis?
Dental biofilm induced gingivitis on intact periodontium
Dental biofilm induced gingivitis on reduced periodontium in non-periodontitis patient
Gingival inflammation on reduced periodontium in a successfully treated stable periodontitis patient
What are the treatment objectives for dental biofilm induced gingivitis on reduced periodontium in a non periodontitis patient?
Remove etiologic factors
Reinforce oral hygiene
Avoid further loss of periodontal tissues
Minimize risk of gingivitis converting into periodontitis
What are some potential modifying factors of biofilm-induced gingivitis?
Systemic condiitons
Oral factors enhancing plaque biofilm accumulation
Drug influenced gingival enlargements
Describe systemic conditions as modifying factors?
Sex and steroid hormones
Puberty
Menstrual cycle
Pregnancy
Oral contraceptives
Describe gingivitis associated with puberty?
TEMPORARY increase in gingival inflammation b/c of increased steroid hormone levels
Exaggerated response to little plaque biofilm
Describe gingivitis associated with menstrual cycle?
Only MODEST observable inflammatory changes during ovulation
Few women extremely sensitive to hormonal changes in gingiva
No clinically evident inflammatory changes in gingiva in most women
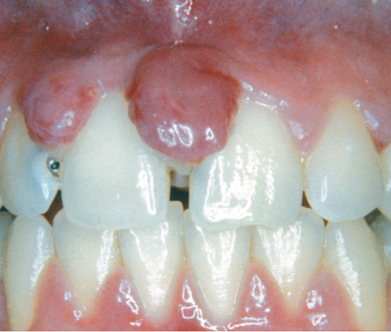
Describe gingivitis associated with pregnancy?
Increased hormones = more gingival crevicular fluid flow
High inflammation w/ little plaque biofilm
Can spontaneously resolve postpartum
Pregnancy associated pyogenic granuloma
What is hyperglycemia?
Presence of abnormally high concentration of glucose in circulating blood
Occurs with DM
Inflammation exacerbated by high blood glucose levels
Describe gingivitis associated with leukemia?
Bleeding and tissue enlargement
Gingival tissues appear swollen, spongy, red
Tissues = friable = bleed with slight provocation
You do not need biofilm to have gingivitis for pts w/ leukemia
Describe gingivitis associated with smoking?
Gingival fibrosis = abnormal amount of fibrous tissue
Smokers have fewer clinical signs
Describe gingivitis associated with malnutrition>
Not fully understood
Similar to biofilm-induced gingivitis
Vitamin C important for:
Collagen and fibrous tissue for normal intercellular matrices
Structural integrity of capillary walls
Deficiency = scurvy, delayed healing
What are some oral factors that enhance plaque biofilm accumulation?
Prominent subgingival restoration margins
Increase plaque accumulation
Hyposalivation can cause:
Progressive caries, taste disorders, halitosis, inflammation
Worsen gingival inflammation
What medications cause gingival enlargements?
Anticonvulsants (Phenytoin/dilantin, methsuximide, divalproex sodium)
Calcium channel blockers (Amlodipine, nifedipine, verapamil)
Immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine)
Enlargements occur within 3 months of use
Characteristics of drug influenced gingival enlargements?
More in younger age groups
Tissues in anterior sextants most commonly affected
Irregular pattern of enlargement
Increased flow of crevicular fluid from sulcus
BOP with no attachment loss
What is hereditary gingival fibromatosis?
Rare benign oral condition involving slow, progressive enlargement of maxillary and mandibular attached gingiva
Causes: specific bacterium not typically found
Oral ulcerations, chancres, mucous patches
Describe hypersensitivity reactions: intraoral allergic reactions
Often caused by flavoring agents
Most common in pts with allergic conditions
Diffuse fiery red gingivitis
May have ulcerations
What is erythema multiforme?
Uncommon acute inflammatory disorder
Causes large symmetrical erythematous papules resembling target in circular pattern
Cause: unknown
What is oral lichen planus?
Purplish, itchy, flat-topped bumps on skin
Lacy white patches, sometimes w/ painful sores in mouth
Usually chronic
Increases risk for oral cancer
6 clinical manifestations
Papular, reticular, plaque type, erythematous, ulcerative, bulbous lesions
What are some signs and symptoms of periodontitis?
Accumulation of plaque biofilm and calculus
Erythema, edema
Gingival bleeding
Suppuration (pus)
Periodontal pockets
CAL, mobility
Pain
Odor
What is loss of attachment characterized by?
Apical migration of junctional epithelium
Destruction of gingival and periodontal ligament fibers
Loss of alveolar bone support around tooth
What are some contributing factors of periodontitis?
Environmental - smoking
Systemic - diabetes, HIV
Genetic
Local intra oral factors such as tooth crowding and or overhanging restorative margin
What are some symptoms of periodontitis?
Usually painless
Gingival bleeding while brushing
Spaced between teeth
Mobility
Food impaction, sensitive to temp, dull pain radiating into jaw
Onset of periodontitis?
Dental biofilm induced gingivitis:
Always precedes onset of periodontitis
May remain stable for years
Manifests days or weeks after biofilm accumulation
Can occur ANY AGE, most common in adults
Localized vs. Generalized periodontitis: LESS than 30% of teeth exhibit attachment loss and or bone loss?
Localized periodontitis
Localized vs. Generalized periodontitis: 30% or MORE of teeth exhibit attachment loss and or bone loss
Generalized periodontitis
What are the types of progressions of periodontal disease?
Continuous disease
Random burst
Asynchronous burst
Describe recurrent form of periodontitis?
Return of destructive periodontitis that had been previously arrested by conventional therapy
Risk for anyone with history of periodontitis
Recurrence common
Describe refractory form of periodontitis?
PTs that do not respond well despite treatment
Receiving appropriate perio therapy
Practicing self care
Following recall schedule
Etiology unknown
Treatment for refractory form of periodontitis?
PT education and behavior modification
Periodontal instrumentation
Use of systemic and or local antibiotics
Removal of hopeless teeth
Correction of restorations that cause plaque retention
Surgical therapy
Strict adherence to perio maintenance regimen
Describe the structure of bacterial cell envelope
Complex multilayered structure
Protects microorganism from unpredictable and inhospitable external environment
Gram staining
Classifies bacteria based on structure
Gram positive or gram negative
What is gram staining?
Depends on permeability of strain through cell envelope when viewed under light/microscope
Gram positive: purple
Gram negative: pink
What is biofilm?
Complex, dynamic microbial community embedded within matrix adhered to living or nonliving surface
May be responsible for 65% of diseases
Describe timeline for biofilm formation
Minutes
Free floating microbes attach to surface
2-4 hours
Form strongly attached microcolonies
6-12 hours
Produce initial ECM
2-4 days
Biofilm evolves into fully mature biofilm
How does mature biofilm protect bacteria?
Blocking
Preventing large molecules from penetrating matrix
Mutual protection
Hibernation (quiescence)
Laying dormant until conditions become more favorable
Define oral biofilm
Polymicrobial
3D community embedded in protective matrix
Consists of microbial metabolic products and or host components
What does commensal bacteria contribute to the oral cavity?
Normal flora in mouth
Prevent colonization by opportunistic pathogenic bacteria
Symbiotic relationship w/ host
Host nutrition, maintain robust immune system, provide cover for mucous membranes
Host provides nutrients, stable environment for survival
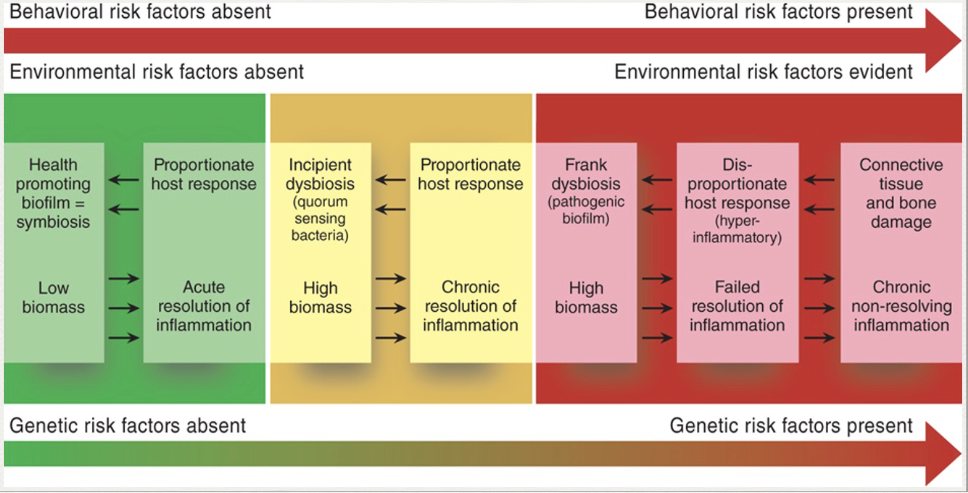
What is dysbiosis?
Microbial imbalance on or inside body
Occurs when oral biofilm not disrupted frequently
Leads to gingival inflammation (initial dysbiosis or incipient dysbiosis)
What is established dysbiosis?
Symbiotic host = microbe becomes pathogenic
Triggers inappropriate, excessive host response = irreversible periodontal tissue damage
Model of Host-microbe interactions
Why is physical removal of dental plaque biofilms important?
Breaks up biofilm = forces bacteria to start over
Periodontal instrumentation needed for subgingival plaque
TRUE OR FALSE: Biofilm bacteria is resistant to antibiotics and antimicrobial agents
TRUE
Describe transmission of biofilm bacteria
Transmissible via DIRECT or INDIRECT contact
Most common route: vertical transmission
Sharing saliva between caregiver + child
Less common route: horizontal transmission
Same generation kissing
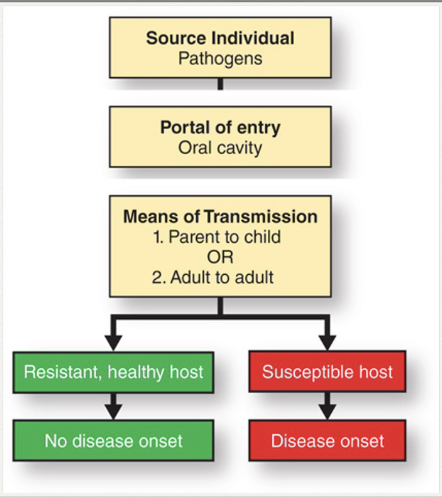
TRUE OR FALSE: Periodontal pathogens are transmissible, but periodontal disease is not an infectious disease
TRUE
What are the 5 stages of biofilm formation?
Initial attachment
Permanent attachment
Maturation I
Maturation II
Dispersion
Describe stage 1: initial attachment
Acquired salivary pellicle immediately forms over clean tooth surface
Free-floating microbes attach using fimbriae
Initial attachment dynamic and reversible
Describe stage 2: permanent attachment
Attained by microbes that can weather hydrodynamic forces and maintain steadfast grip on tooth surface
Microbes begin producing substances that attract other free floating bacteria to community
Process = coaggregation
Describe stage 3: Maturation phase I - Self protective matrix formation
Attached bacteria secrete extracellular protective matrix = protects against host immune defenses
Consists of: proteins, glycolipids, bacterial DNA
Describe stage 4: Maturation Phase II - Mushroom shaped microcolonies
Microcolony formation
Combination of cell division and recruitment
Microbes cluster, form mushroom shaped microcolonies = exchange and share nutrients + genetic info
Diverse population
Internal organization of mature biofilm
Layers of microbes
Fluid channels form = penetrate ECM = direct fluids around biofilm
Cell to cell communication using chemical signals
Quorum sensing = bacteria communicates by releasing small proteins
Describe stage 5: Dispersion - Escape from the matrix
Essential stage of biofilm life cycle
Dispersal enables:
Spread
Colonize new tooth surfaces
Describe sequence of bacterial colonization
Early bacterial colonizers = release chemical signals = indicate conditions favorable for joining biofilm
Favorable conditions necessary for microbes to join
Mature biofilm collection of multiple microbial species
What are the bacterial attachment zones?
Tooth surface
Epithelial lining of periodontal pocket
😄 HI
What are some more specific bacterial attachment zones?
Tooth associated plaque biofilms
Attached to tooth surface = invade dentinal tubules
Tissue associated plaque biofilms
Adhere to epithelium = invade gingival tissue
Unattached bacteria
Free floating = not part of biofilm
What are the 5 hypotheses that explain role in periodontal disease?
Nonspecific plaque
Specific plaque
Ecological plaque
Microbial homeostasis-host response
Keystone pathogen-host response
What is the nonspecific plaque hypothesis?
Accumulation of plaque biofilm at gingival margin = gingival inflammation + tissue destruction
Limitations:
Too simple, superficial
Fails to explain why most gingivitis never become periodontitis
What is the specific plaque/microbial shift hypothesis?
Oral microbiota shifts from primarily beneficial to primarily pathogenic as periodontitis develops
Increase in specific pathogens causes periodontitis
Bacteria change from mainly gram+ aerobic community to gram- anaerobes
Socranksy:
Assigned colors for each microbes
Orange + red = periodontal disease
Yellow, blue, green and purple = gingival HEALTH
What is the current perspective of ecological plaque hypothesis?
Accumulation of nonspecific bacteria triggers host inflammatory response, altering local environment
Environment becomes more conducive to growth of pathogenic bacteria
Support for hypothesis:
Sites with BOP + deeper probing depths strongly associated with higher GCF flow = alters microbial ecology = favors pathogens
What is microbial homeostasis-host response hypothesis?
Plaque biofilms cause initial inflammatory response = gingivitis
But pathogenic bacteria is NOT direct cause of tissue destruction in periodontitis
Pathogenic biofilm community → triggers uncontrolled host response → damage to periodontal tissues
What is the keystone pathogen-host response hypothesis?
Specific bacterial species is key in creating shift from symbiotic microbes to dysbiotic microbes
Dysbiotic biofilm community triggers uncontrolled host response = damage to periodontal tissues
Difference of immune status of periodontal tissue between healthy vs. diseased patients?
Healthy tissue: mild subclinical inflammation
Diseased tissue: disordered severe inflammation
Shift from beneficial pathogenic community = triggers potent host inflammatory response = contributes to tissue destruction + alveolar bone loss
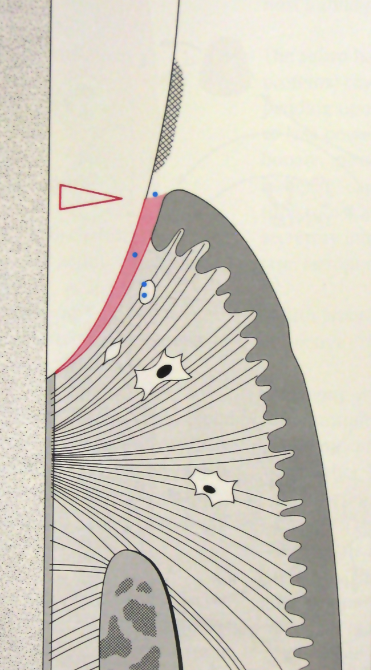
Describe heathy gingiva structure
Few mainly G+ aerobic bacteria
Normal junctional epithelium
A few PMNs (WBCs) with very little crevicular exudate
Connective tissue WNL
Alveolar bone WNL
Describe early gingivitis structure
Build up of G+ aerobic bacteria
Alteration of junctional epithelium
Vasculitis, increase in crevicular fluid outflow, increase PMNs, inflammatory cell migration
Attention fibroblasts, collagen changes
Attention bone WNL
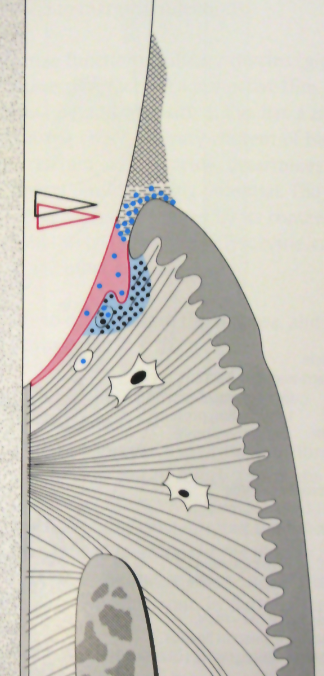
Describe progressing or Est. Gingivitis structure
Build up of G+ AND G- anaerobic bacteria
JE migrates both laterally + apically
Acute inflammatory alterations, further increase of crevicular fluid flow, increase in PMNs, formation of wall PMNs
Severe fibroblast damage, further collagen loss with exudate
Alveolar bone WNL
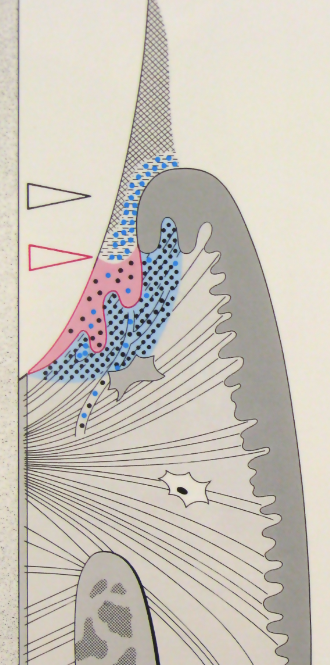
Describe periodontitis structure
Mostly G- anaerobic bacteria, subepithelial
Further migration of JE, ulcerations, and true pocket formation
Acute inflammatory alterations with gingivitis, massive PMN migration, expansion of inflammatory cells
Further collagen loss and fibrosis in surrounding CT
Resorption of alveolar bone loss, attachment loss
Define immune system
A network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases
Detects and response to pathogens, viruses, cancer, and foreign objects
Distinguishes from organism’s own healthy tissue
What are the two major subsystems of the immune system?
Innate immune system
Adaptive immune system
What is the function of the innate immune system?
Provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli
What is the function of the adaptive immune system?
Provides a tailored response to each stimulus by recognizing molecules it has previously encountered
When does innate immunity develop?
Present at birth
Is innate immunity antigen specific or nonspecific?
NON SPECIFIC
Exposure results in NO immunologic memory
TRUE OR FALSE: Innate immunity is always present
TRUE
Responds quickly to infection
Programmed to respond to many pathogens
What are the cells of innate immunity?
Neutrophils
Monocytes
Macrophages
Eosinophils
Basophils
Mast cells
NKT lymphocytes
NOTE: Physical barriers such as skin and mucosal membranes help protect
When does adaptive immunity develop?
Develops throughout life after initial exposure to antigen
Learns how to counterattack pathogen
Is adaptive immunity antigen specific or non specific?
ANTIGEN SPECIFIC
Repeated exposure = immunologic memory
TRUE OR FALSE: Adaptive immunity is alway present
FALSE
Responds slowly the 1st time