Biological Molecules, Human nutrition and digestion
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
TERM
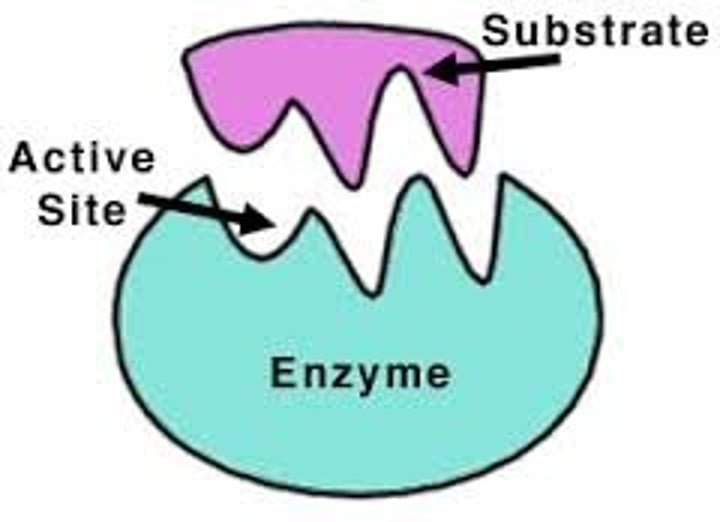
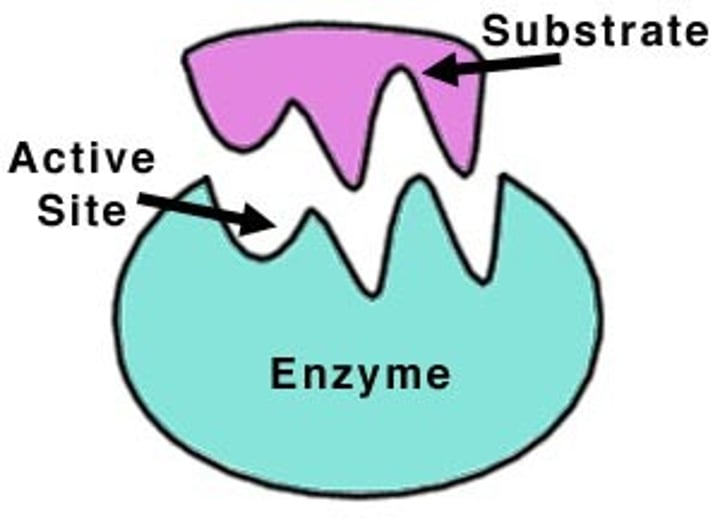
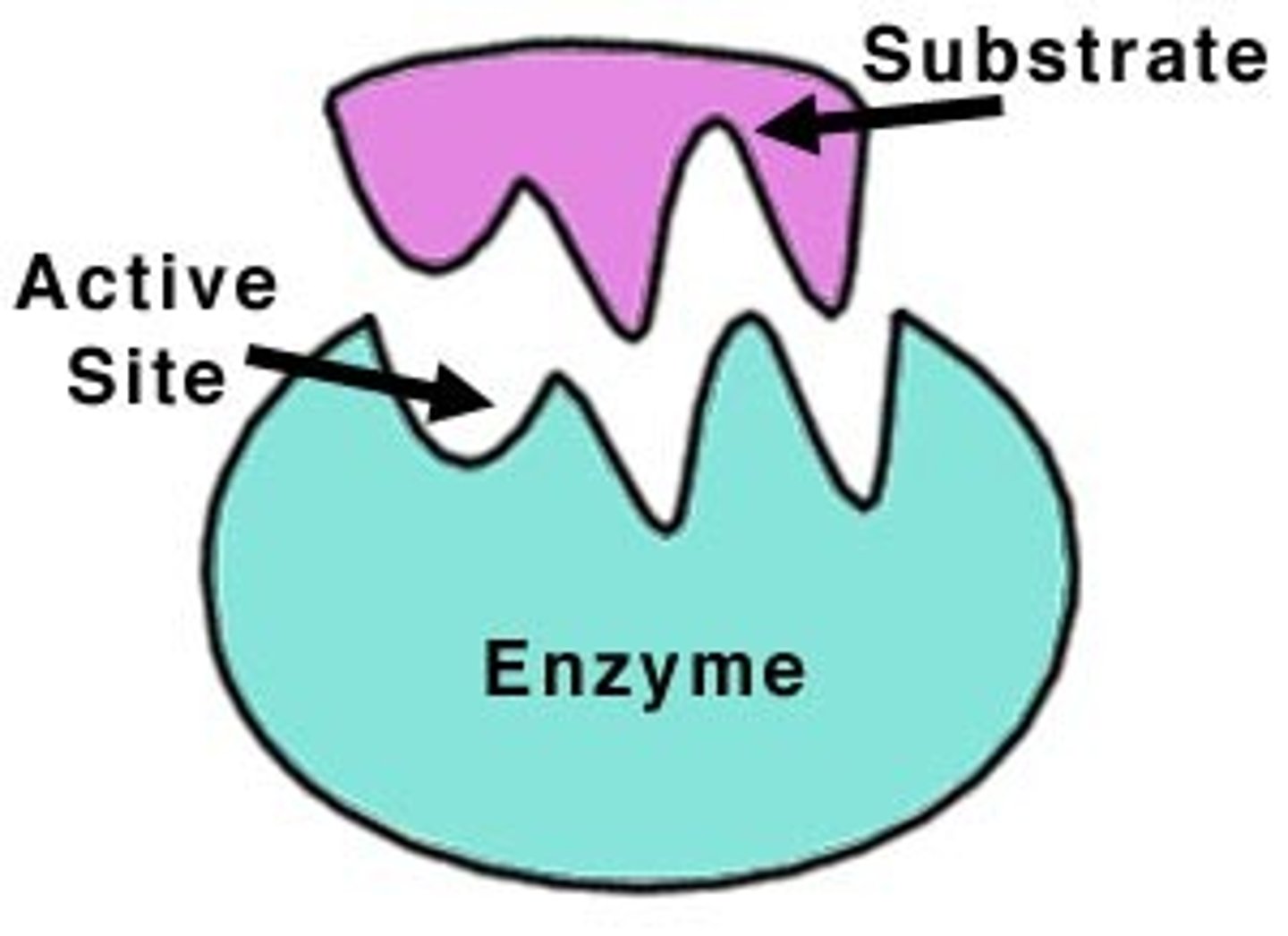
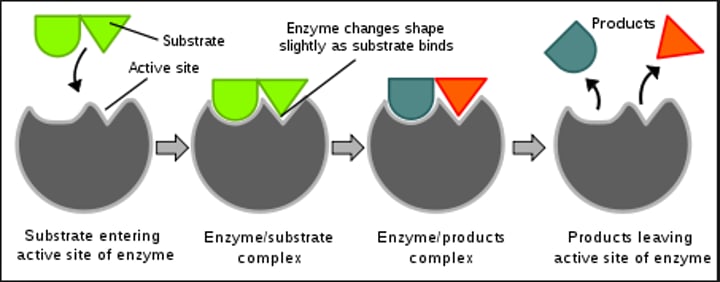
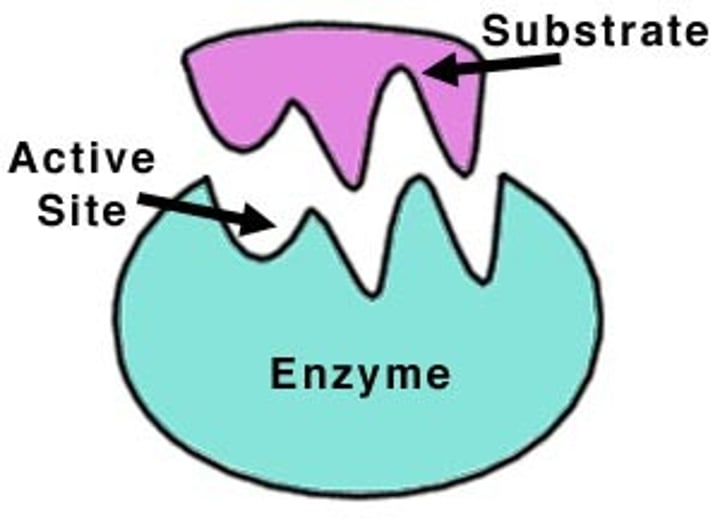
active site
DEFINITION
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
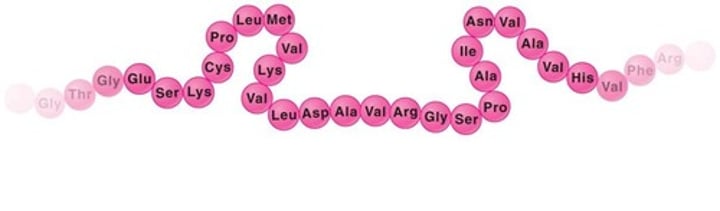
amino acid
The building blocks that make up a protein molecule.
carbohydrate
Food belonging to the food group consisting of sugars, starch and cellulose.

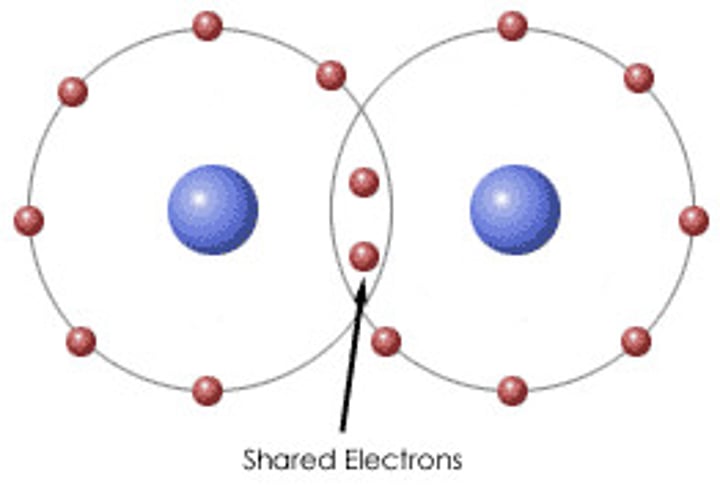
covalent bond
A bond between atoms formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of electrons.
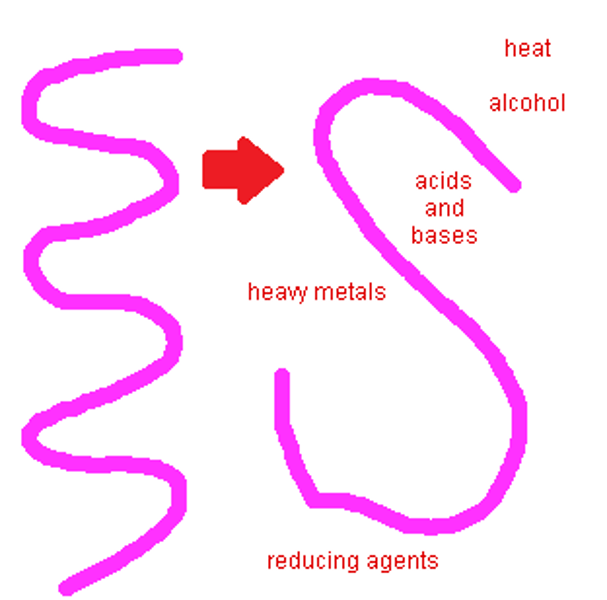
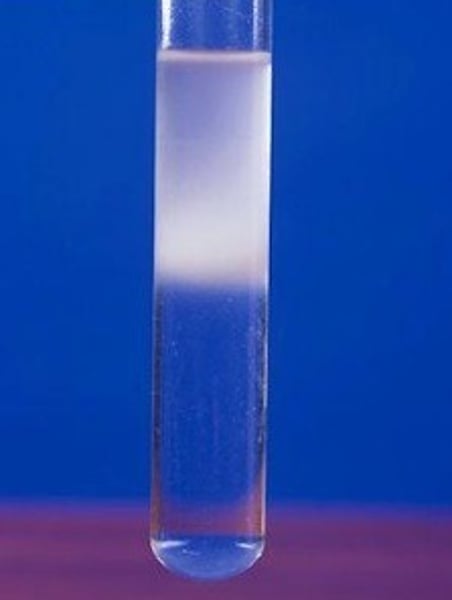
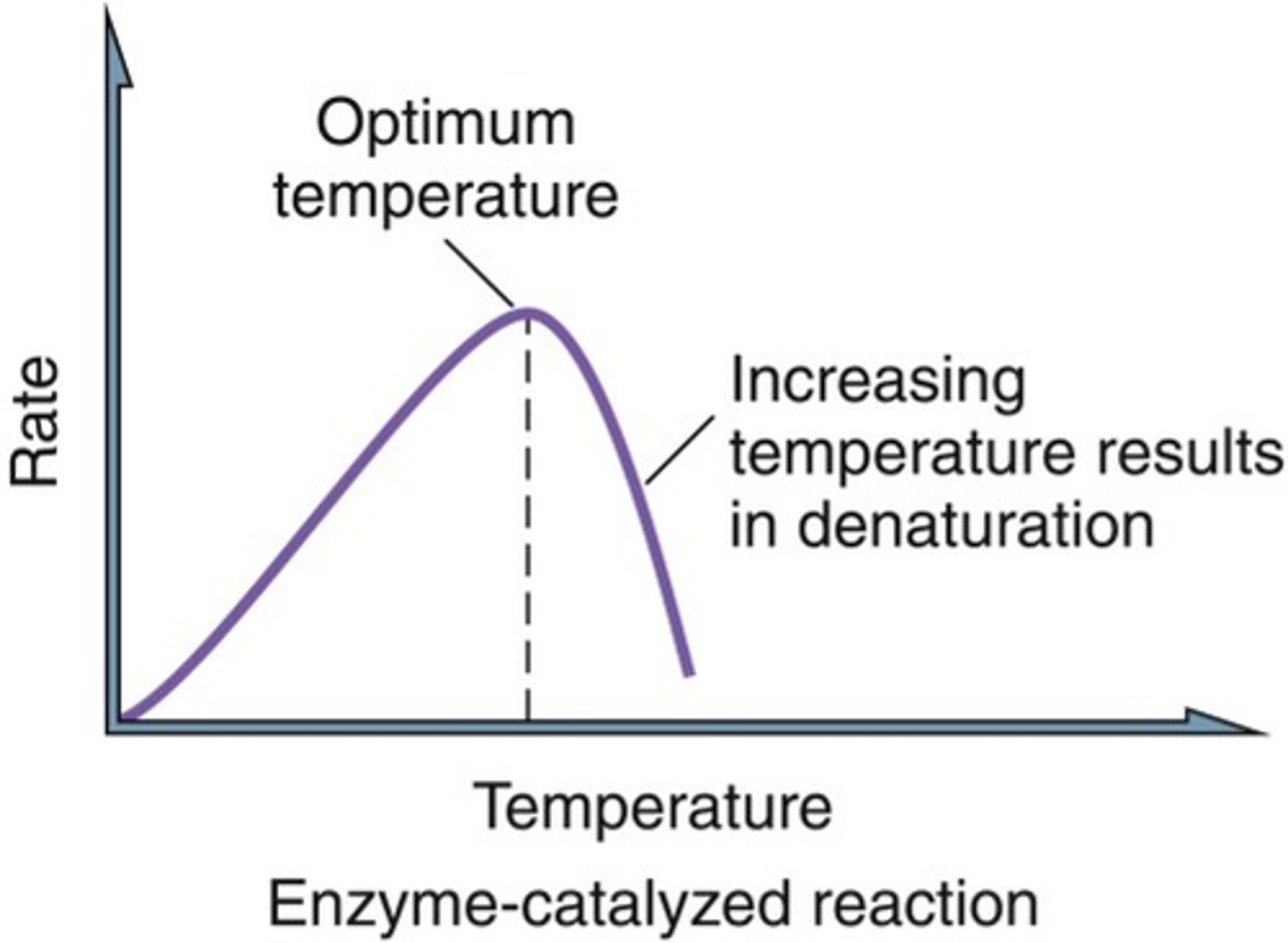
denatured
The structure and function is altered. This can be caused by heat, altered pH or by chemical agents.
emulsion
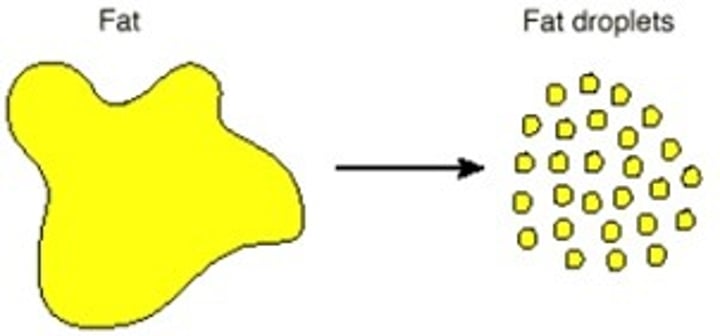
Cloudy mixture formed between a lipid and water.

TERM
enzyme
DEFINITION
A protein which catalyses or speeds up a chemical reaction.

fats
Naturally occurring compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They are esters made from fatty acids and glycerol.
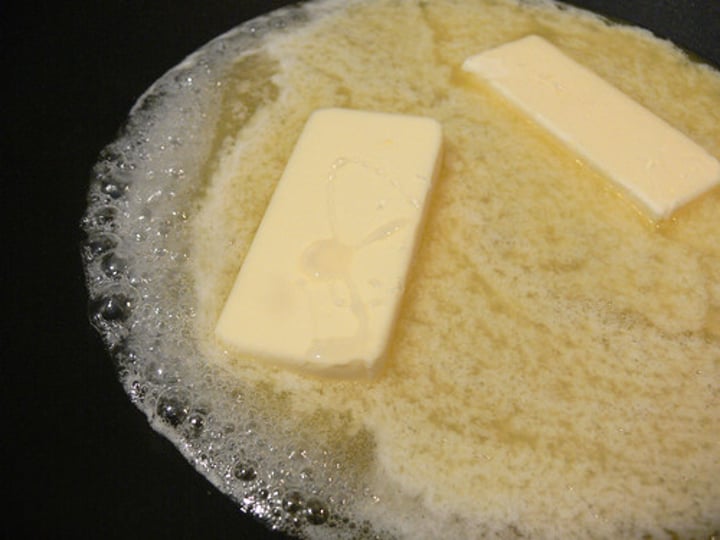

lipid
Fat or oils, composed of fatty acids and glycerol.
metabolism
All the chemical reactions in the cells of an organism, including respiration.
molecule
A collection of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
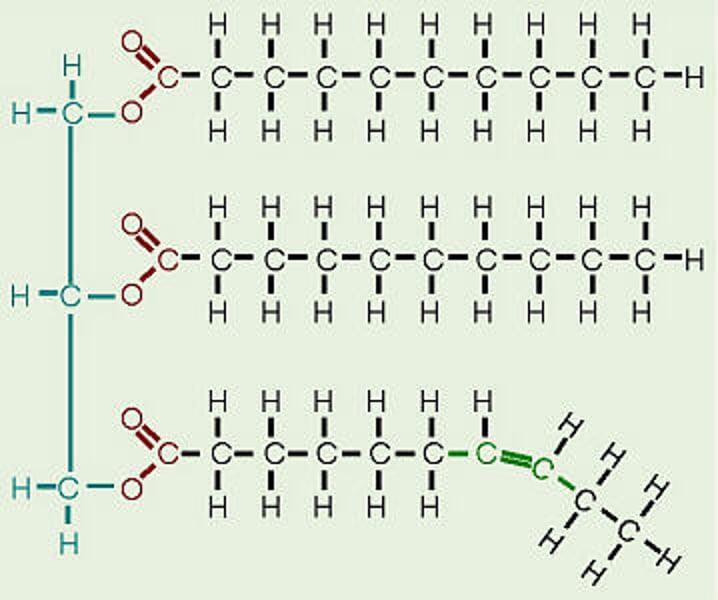
oils
Natural substances produced from the reaction of glycerol with fatty acids.
pH
power of hydrogen. Scale of acidity or alkalinity. Below 7 is acidic, above 7 is alkaline.
protein
Organic compound made up of amino acid molecules. One of the three main food groups, they are needed by the body for cell growth and repair.

TERM
substrate
DEFINITION
A substance on which enzymes act.
optimum temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme is most active
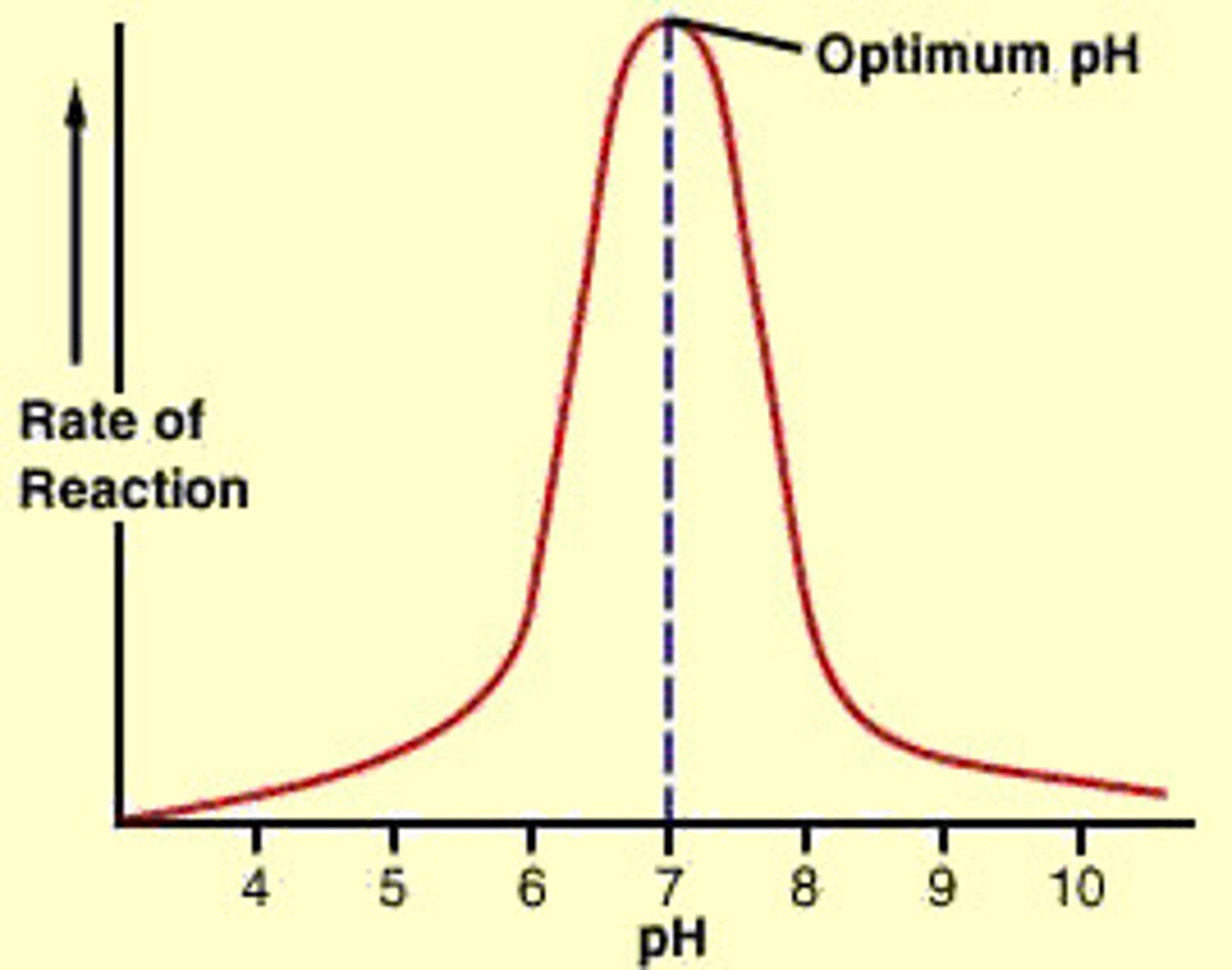
optimum pH
the pH at which an enzyme is most active
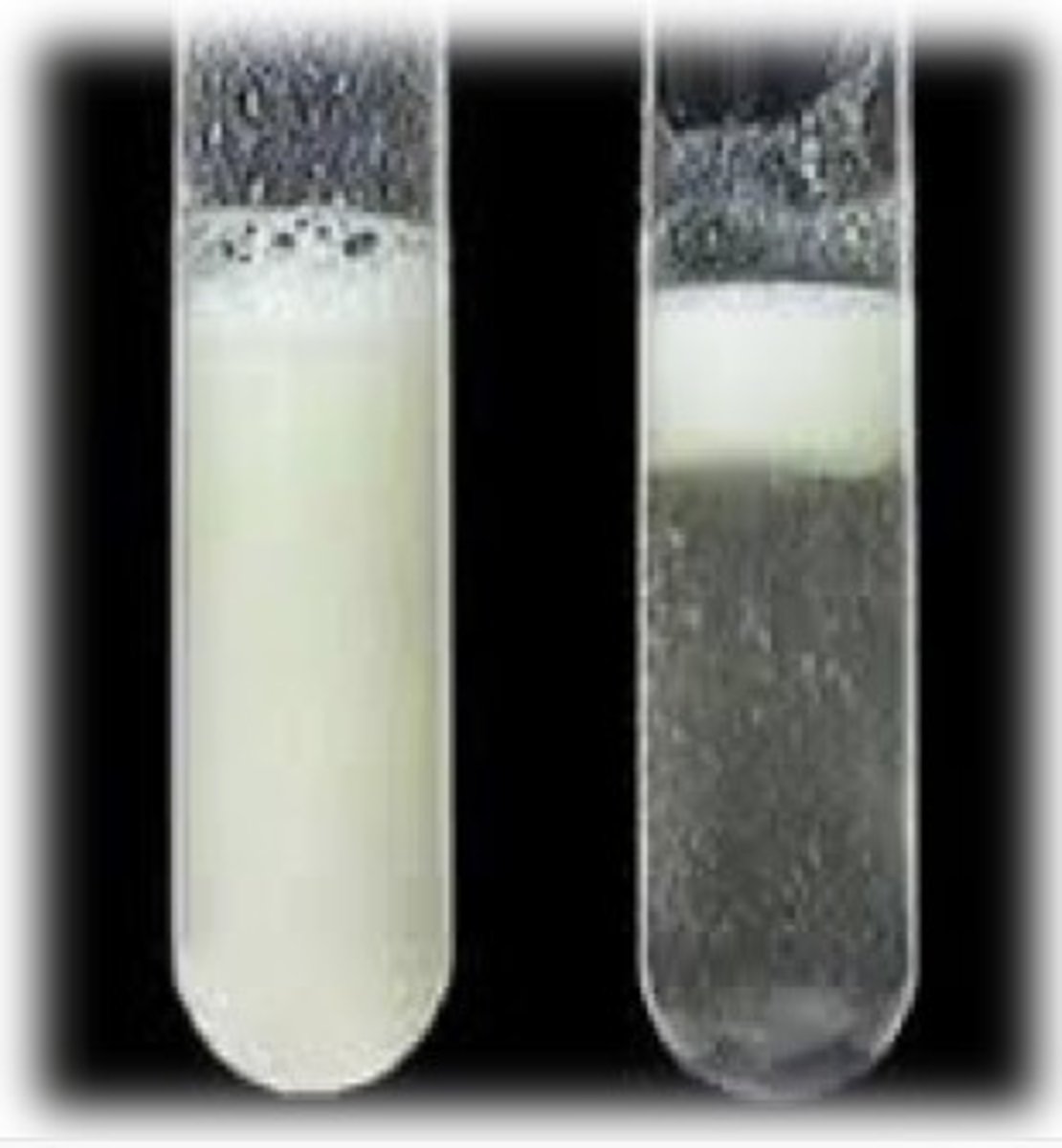
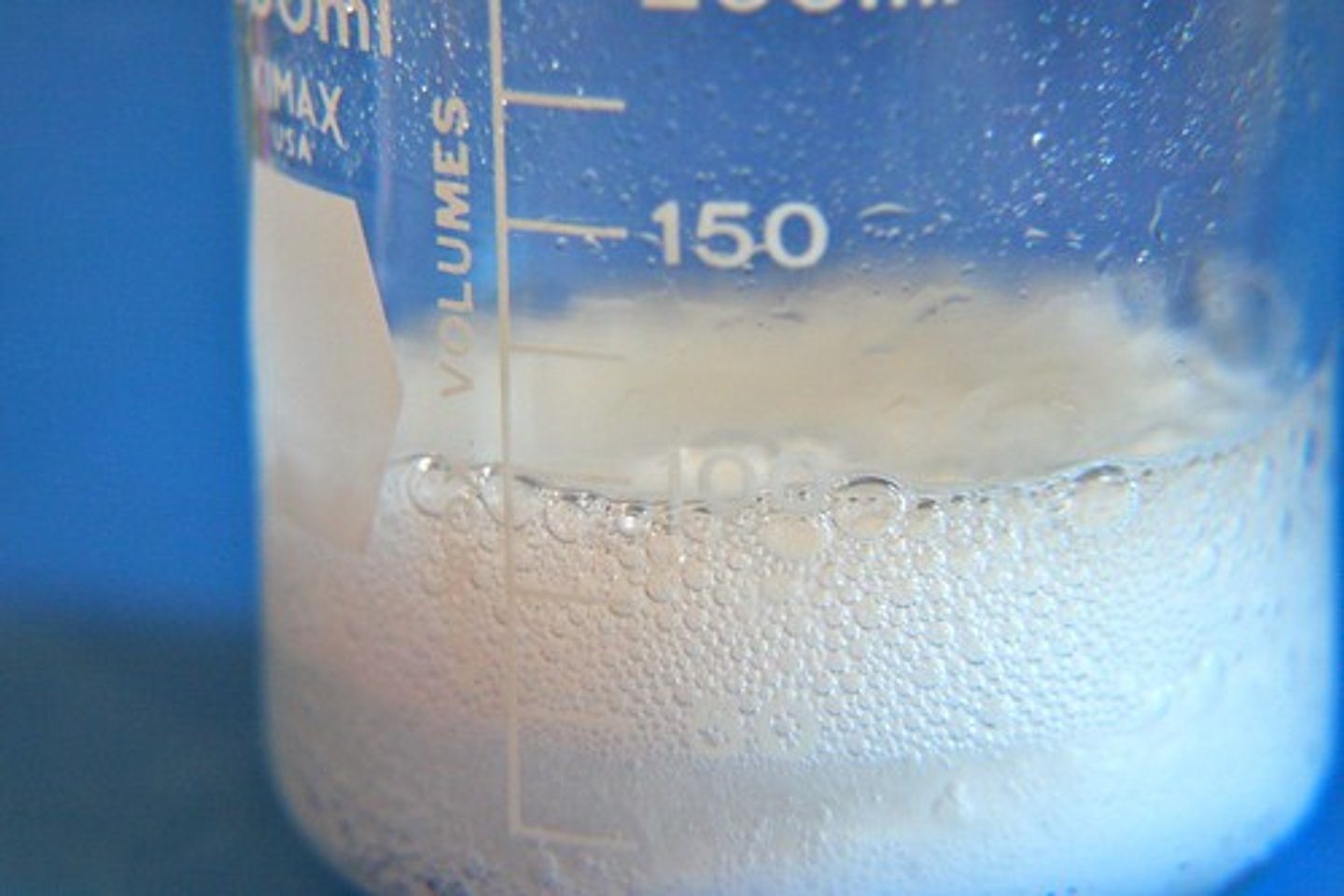
Emulsion test
laboratory test for lipids using ethanol; a white emulsion indicates the presence of a lipid.
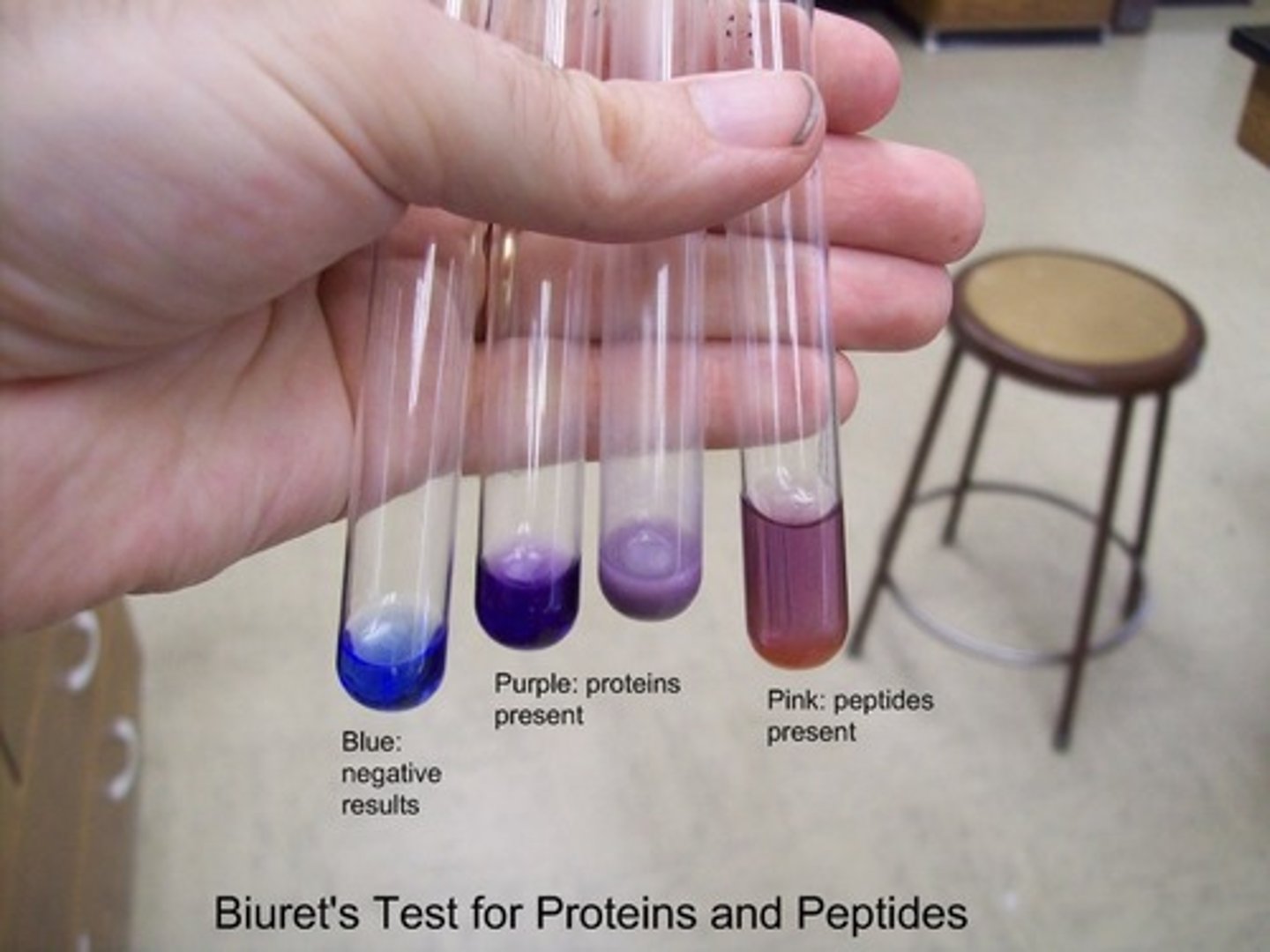
Biuret test
Test for the presence of proteins. Turns from blue to purple.
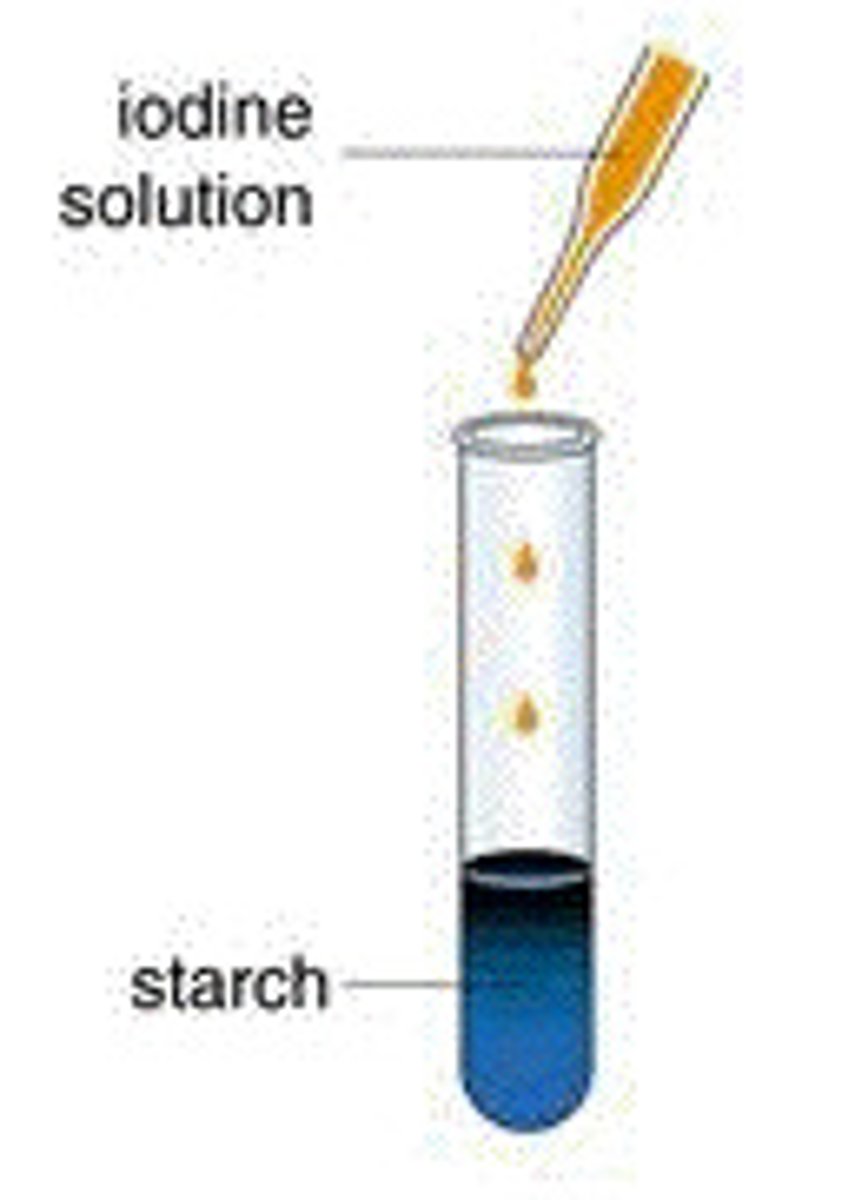
Iodine test
Test for starch - turns from brown to blue/black
Benedict's test
A test for sugars. Must be heated. Turns from blue to orange/red.

biological catalysts
Enzymes- a biological molecule that speeds up a chemical reaction
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction

nucleic acids
DNA and RNA, made up of nucleotides
TERM
Product
DEFINITION
What is made by the reaction
TERM
Enzyme-substrate complex
DEFINITION
Enzyme and substrate locked together

Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods

Protein
makes up muscle, can be broken down into amino acids

Lipids
fats and oils

vitamin A
allows good vision, healthy skin and strong immunity against infection. Found in carrots, milk and oily fish.

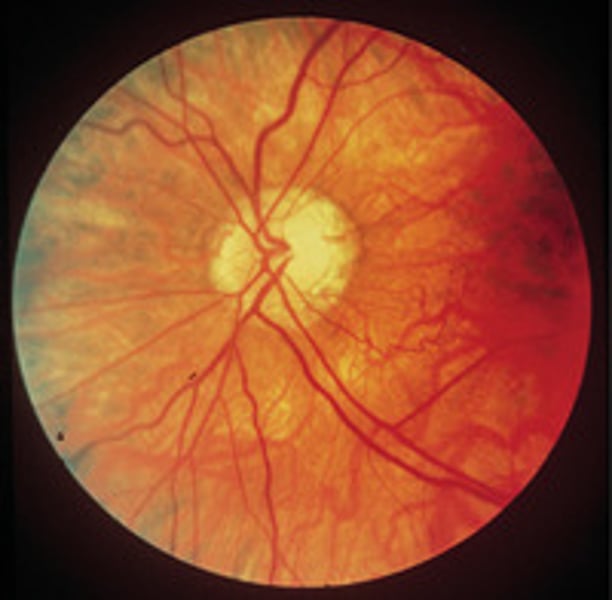
night blindness
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin D
Made by our skin when exposed to sunlight. Also found in eggs and oily fish

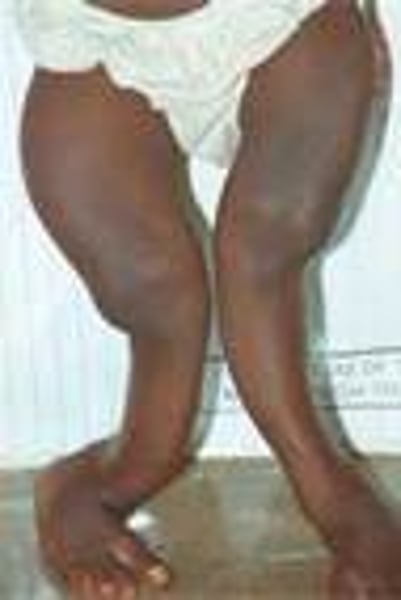
Rickets
Bendy bones, caused by vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin C
Also called ascorbic acid. Needed to help heal wounds. Found in citrus fruit (lemons, oranges).

Scurvy
Vitamin C deficiency

Calcium
Mineral ion, found in dairy, helps to build bones and teeth.

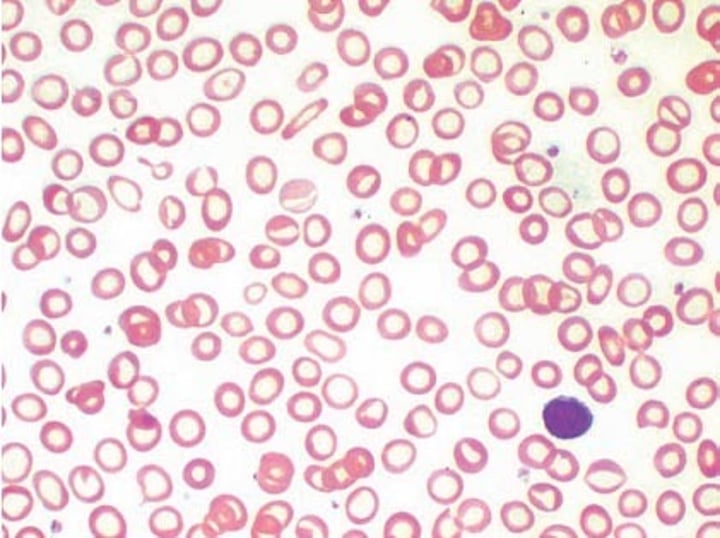
Iron
Found in red meat, liver, bean. Makes hemoglobin (in red blood cells)

Anaemia
lack of iron
water
found in the cytoplasm of our cells

Fibre
helps the intestines move food down the tube. Found in fruit & veg

constipation
difficulty in passing faeces (poop)

balanced diet
appropriate proportions of carbohydrate, protein, lipid, vitamins, minerals, water and dietary fibre.

Energy requirements
How many calories a person needs, depends on activity level, age and pregnancy
Calories
unit of energy

sedentary
Taking little or no physical activity as part of everyday living.

Fish are a good source of protein in the human diet. Describe what happens to fish protein in the gut of a human
digested / broken down;
amino acids / (poly)peptides; stomach;
protease / named protease enzyme (ONCE);
HCl / acid / low pH / eq;
small intestine / duodenum / ileum; bile / neutralise /alkaline / eq; optimum pH (ONCE)
Explain what is meant by the term saprotrophic nutrition (2)
1 (feed on) dead / rotting / decomposing / eq;
2 enzyme(s);
3 extracellular / outside / external / eq;
4 digests / digestion / digestive;
5 absorption
What is meant by the term organ
tissue(s) that carry out (same) function / different cell types that carry out (same) function / eq;
Molecule used to store carbohydrates in fungi
Glycogen
Describe the role of the liver in digestion
bile;
emulsifies / large drops to small drops / eq;
neutralise / optimum pH / alkaline;
Describe the process of digestion in the mouth (3)
1. Amylase produced
2. Starch digested
3. Maltose / glucose
4. Physical digestion / mechanical digestion / chewing...
Describe how food is moved through the gut
peristalsis;
contraction;
muscles;
pushed / squeezed / waves / eq
Explain how egestion differs from excretion
faeces versus named excretory product; undigested food versus metabolic waste product; anus versus kidney/lung/skin;
not in cells versus in cells
Suggest what happens to starch in the gut of a parakeet
digested / broken down
amylase / carbohydrase
maltose / glucose / sugar
Describe and explain how the structure of the small intestine is adapted for absorbing digested food.
1. long;
2. villi / villus / microvilli;
3. increase surface area / eq;
4. diffusion / active transport / osmosis;
5. capillaries;
6. (blood flow) maintains concentration gradient / maintains diffusion gradient;
7. thin walls / one cell thick / short distance; (applies to villi or capillaries)
8. lacteal(s);
Suggest the consequences of having a diet that lacks fresh fruit and fibre.
1. lack vitamin C / antioxidant / scurvy / bleeding gums / eq;
2. constipation / less food movement / bowel cancer / raised cholesterol / increase heart disease / eq
Suggest the consequences of having a diet that contains too much fat.
1. obesity / increase in weight / eq;
2. blockage of arteries;
3. high blood pressure / stroke / heart disease / raised cholesterol / eq;
4. diabetes;
5. joint damage / arthritis / eq; 6. gall stones
Description of egestion
removal of undigested food / faeces / waste from anus
Description of digestion
break down large molecules / large molecules to small molecules / insoluble to soluble molecules;
Cells do not store glucose. Instead it is converted into glycogen to be stored. Suggest why cells do not store glucose.
1. soluble / dissolves; 2. osmotic effect / eq;
Give three ways in which villi are adapted to absorb small food molecules.
1. large surface area / microvilli;
2. thin / short diffusion distance / eq; 3. blood / capillaries / eq;
4. permeable;
5. lacteal;
Molecule used to store carbohydrates in animals
Glycogen
Molecule used to store carbohydrates in plants
Starch
Molecule used to store carbohydrates in fungi
Glycogen
Growth hormone is a protein.
It might be present in the milk produced by the cows and then be consumed by humans. Some people are worried that this may harm humans. Other people say that this is not a problem for two reasons.
Firstly, the milk is pasteurised (heated to high temperatures).
Secondly, the growth hormone is destroyed in the human stomach.
(i) Suggest what happens to the growth hormone when milk is pasteurised.
Denatured
Describe how the growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach
1. HCl / hydrochloric acid;
2. enzyme / protease / pepsin
3. Breakdown/ digest
4. (acid) denatures growth hormone
Explain how the villi are adapted to absorb glucose
1. large surface area;
2. microvilli ;
3. capillaries;
4. movement of blood / concentration gradient / eq;
5. one cell thick / thin wall / thin / short distance;
6. diffusion;
7. active transport;
Descibe the two chemical tests someone could use to identify each type of carbohydrate, starch and glucose
1. iodine;
2. Browny orange to blue black colour- starch
3. Benedict's / eq;
4. heat / use water bath / eq;
5. Blue to brick red = glucose
Molecule used to store carbohydrate in animals
Glycogen
Molecule used to store carbohydrate in plants
Starch
Name the chemical used to test for starch
Iodine
Explain what happens in a leaf when it is destarched
starch removed / starch used / no starch / eq; (converted to) glucose;
respiration / energy
acid
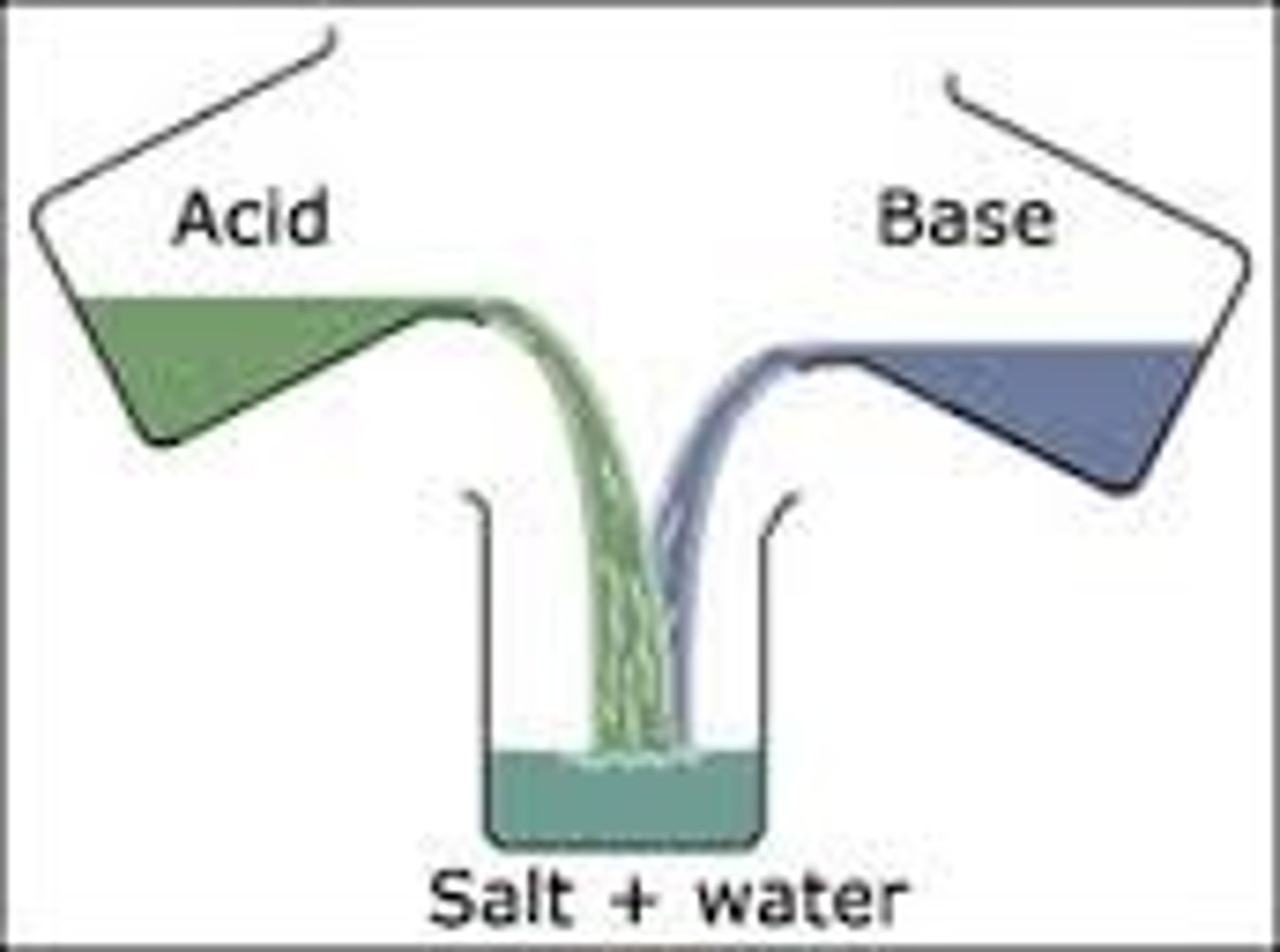
Corrosive substance which has a pH lower than 7. Acidity is caused by a high concentration of hydrogen ions.

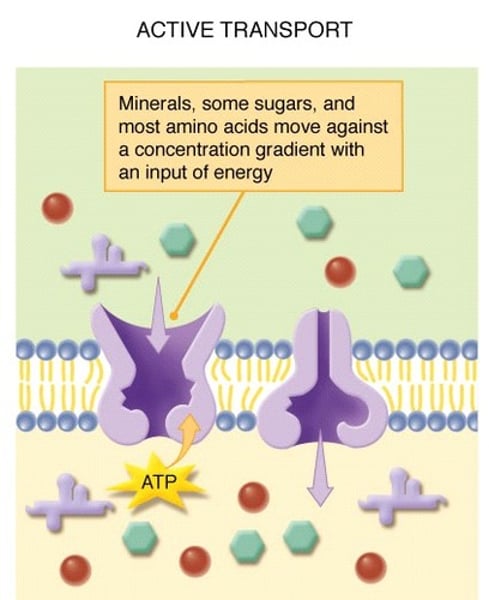
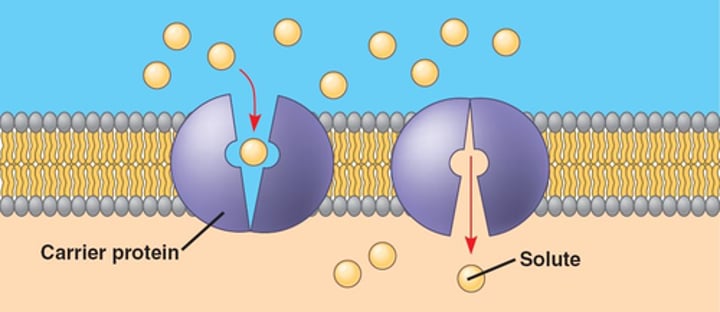
active transport
The transport of molecules against their concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration.
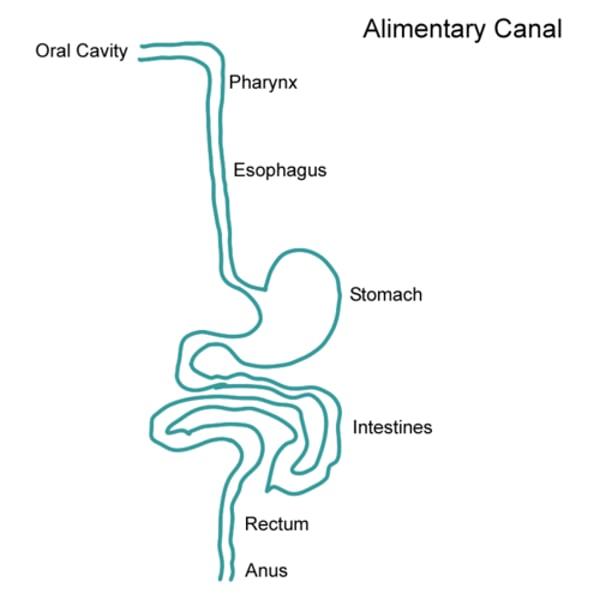
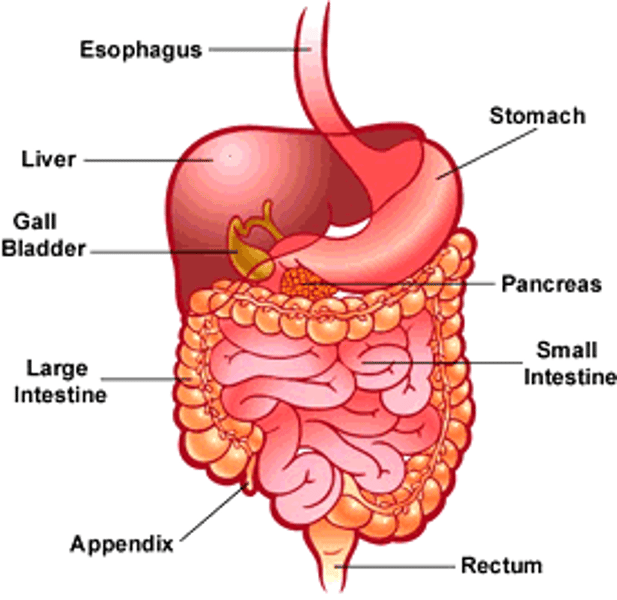
alimentary canal
The digestive tract which runs from mouth to anus.
alkaline
having a pH greater than 7

amino acid
Building blocks of protein

amylase
enzyme that breaks down starch into sugar. Found in saliva.

bile
A substance produced in the liver. It emulsifies fats to prepare them for digestion.
catalyst
A substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction itself.
cellulose
A carbohydrate. It forms the cell wall in plant cells.
compound
A substance formed by the chemical union of two or more elements.
diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
digestion
The breakdown of large insoluble food molecules to smaller soluble ones.
egestion
The process of passing out the remains of food that has not been digested, as faeces, through the anus.

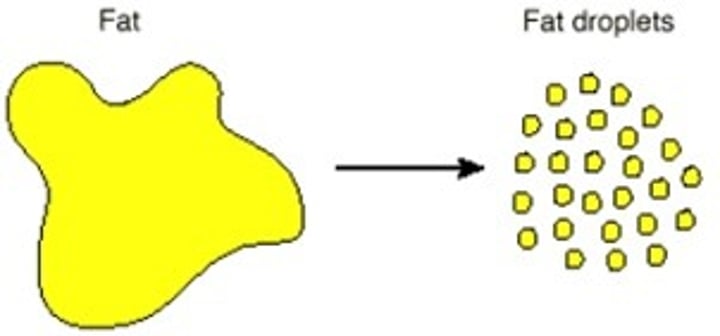
emulsify
To mix water with fats and oils to produce a cloudy mixture called an emulsion.
enzyme
A protein which catalyses or speeds up a chemical reaction.
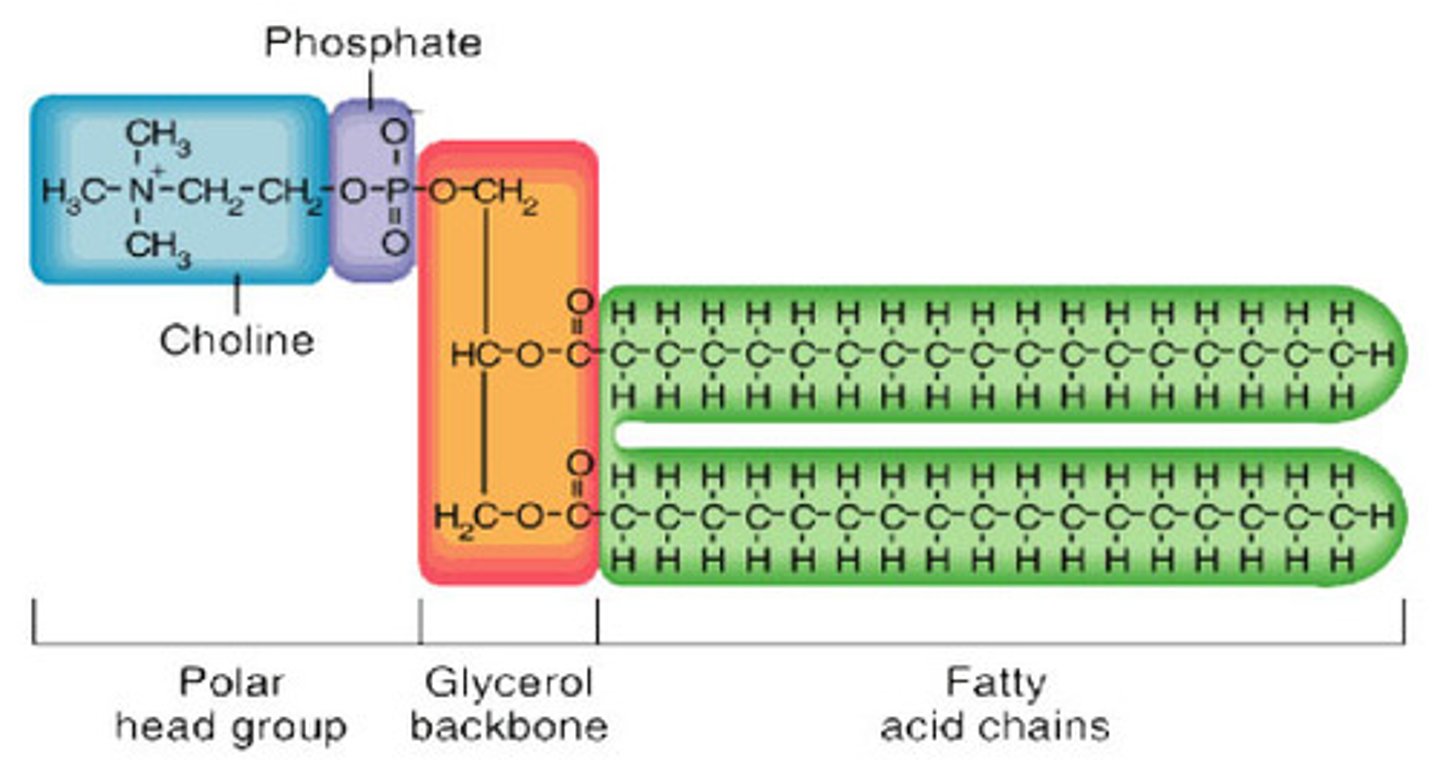
fatty acids
Building blocks of Lipids (fats)
glucose
A simple sugar used by cells for respiration.

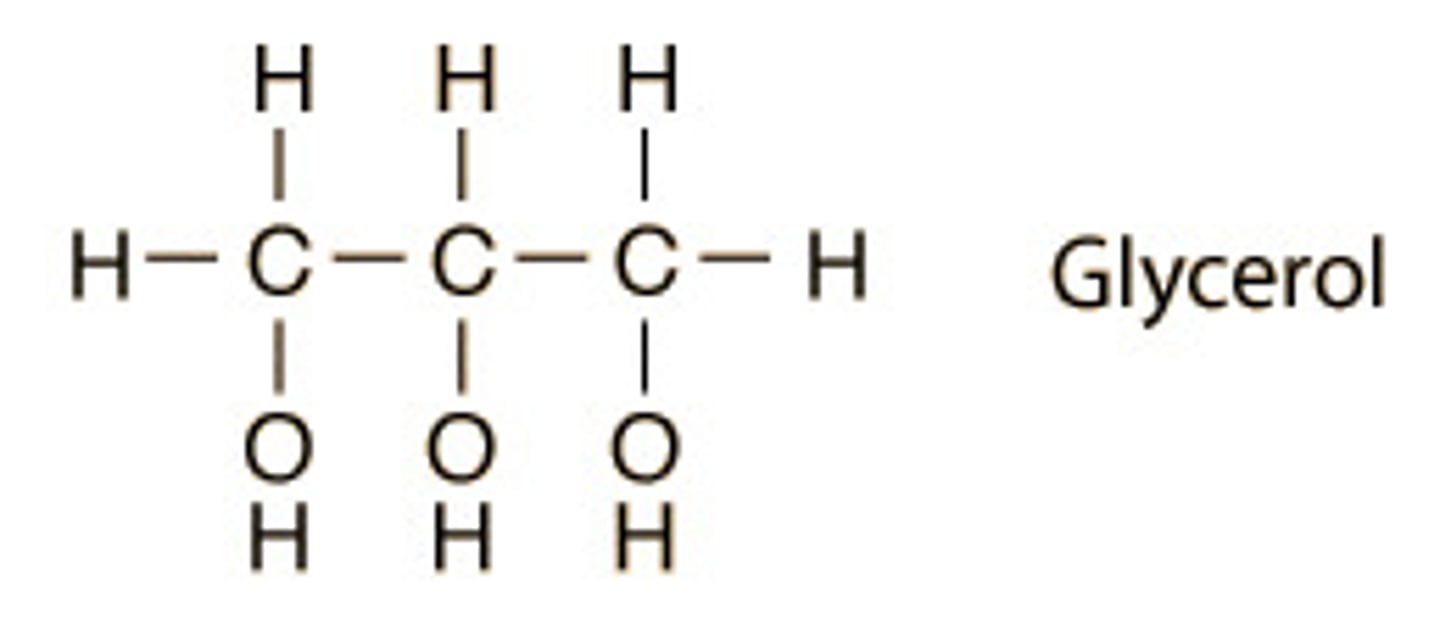
glycerol
A soluble carbohydrate which is coverted into glucose by the liver.
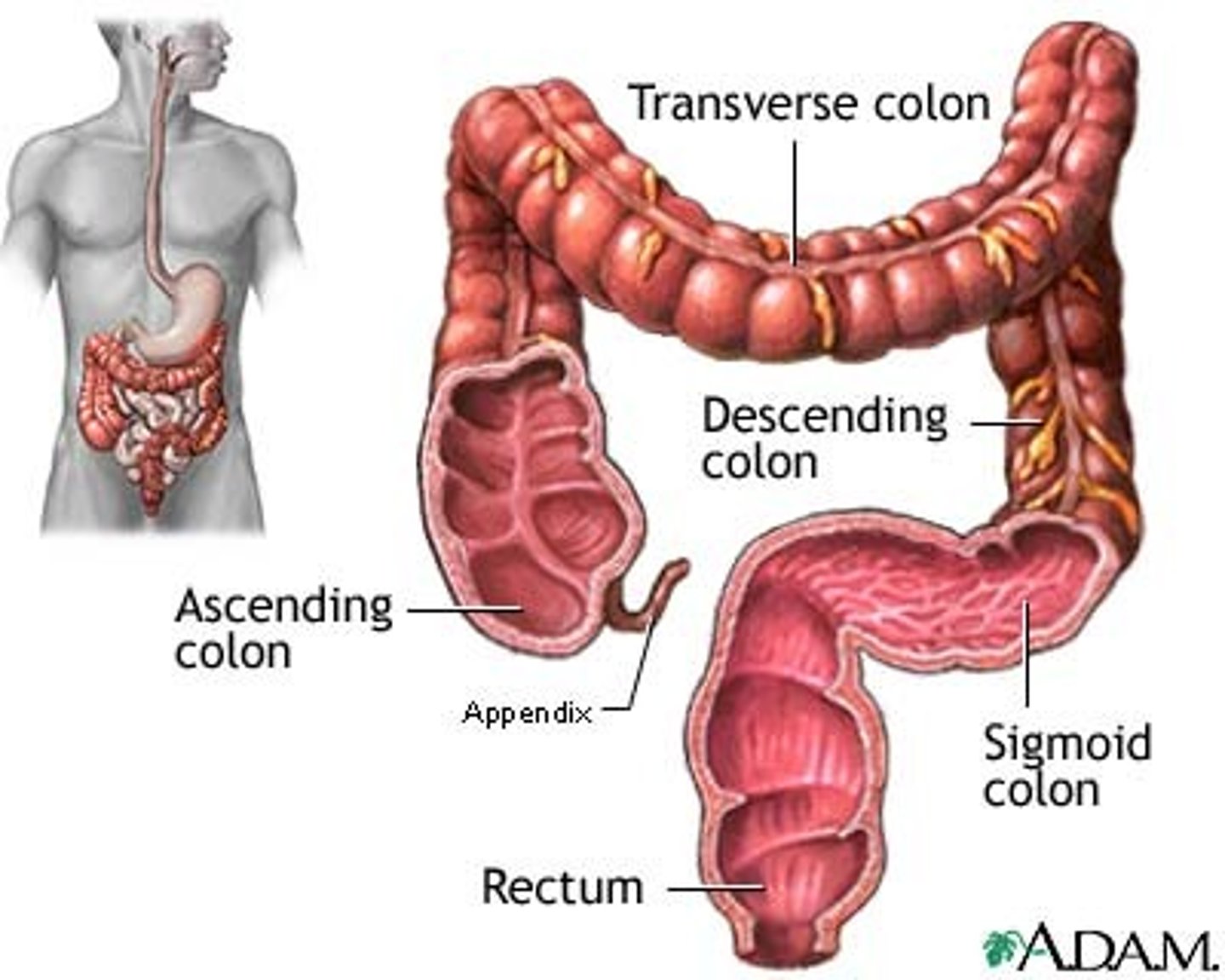
large intestine
The lower part of the alimentary canal (gut) where absorption of water and production of faeces happens. Includes the colon and rectum.
lymph
The liquid which circulates within a mammal's body transporting the products of fat digestion from the lacteals.
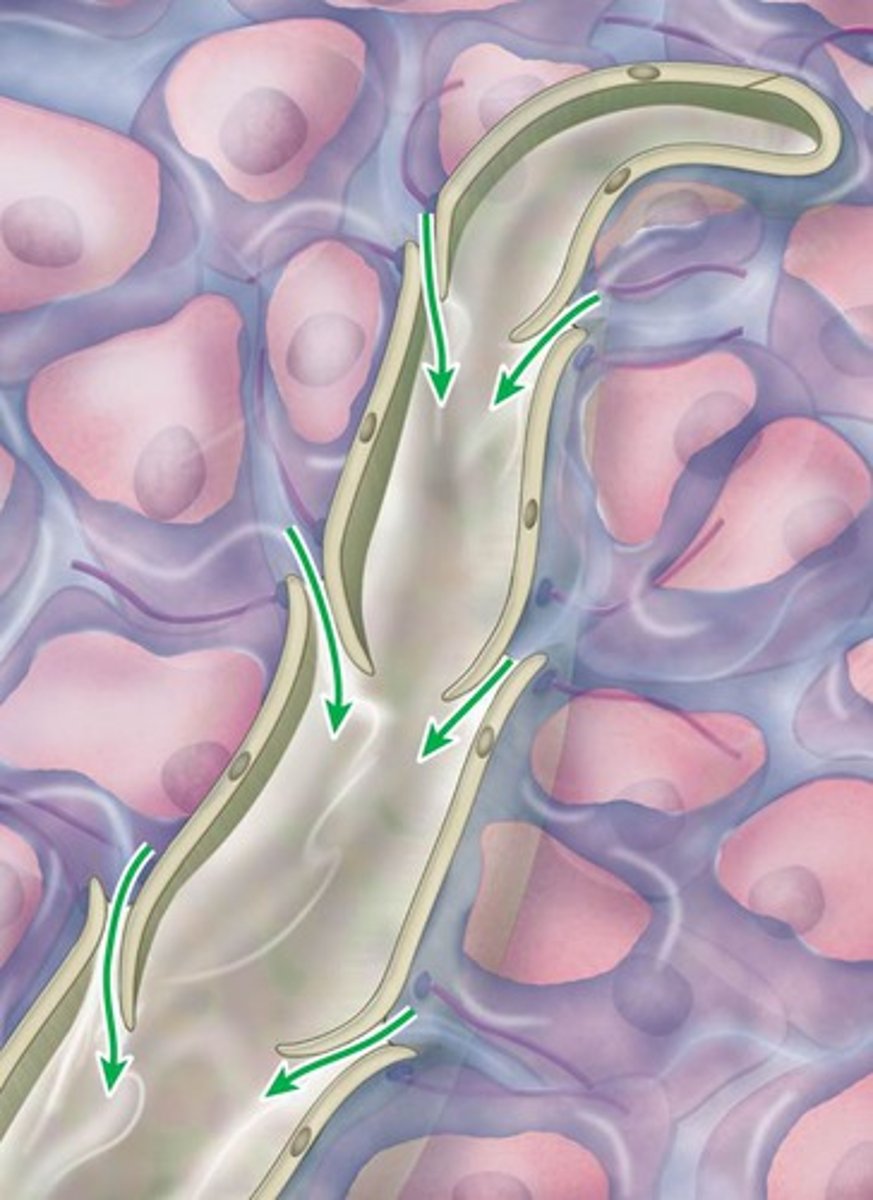
maltase
An enzyme that converts maltose (a disaccharide, two sugars stuck together) into glucose (a monosaccharide, one sugar).
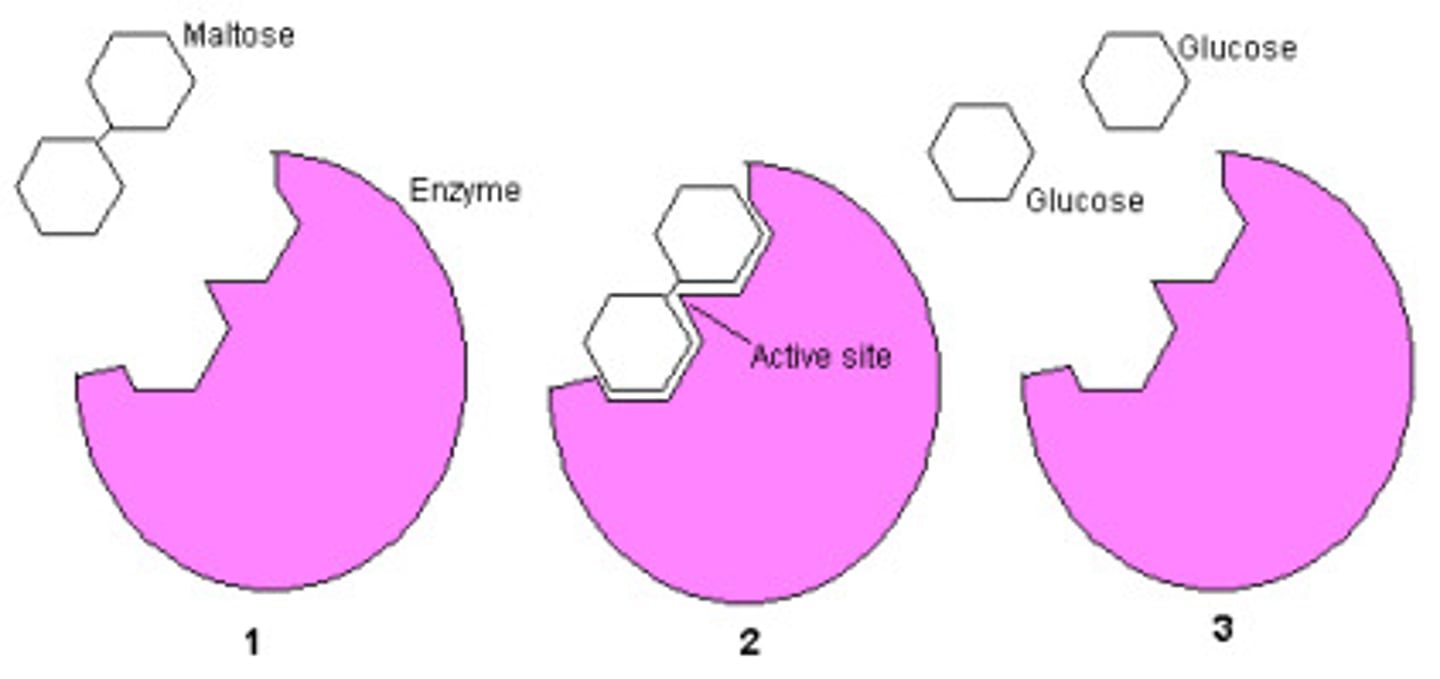
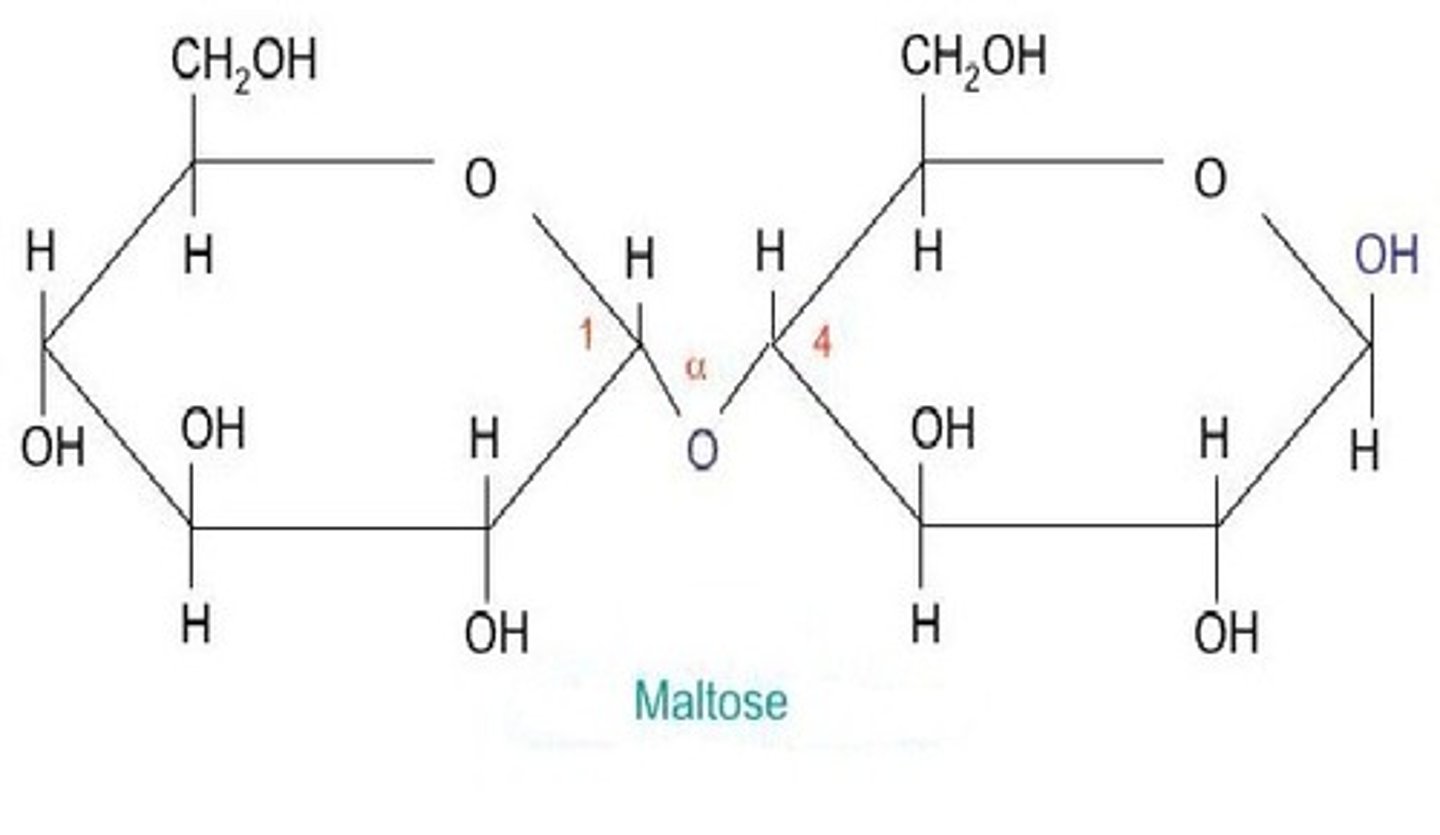
maltose
A disaccharide (two sugars stuck together) made from two glucose molecules joined together.
micro organisms
Microscopic living things such as archaea, bacteria and some species of eukaryotes.
neutralise
To be made neutral (pH 7).
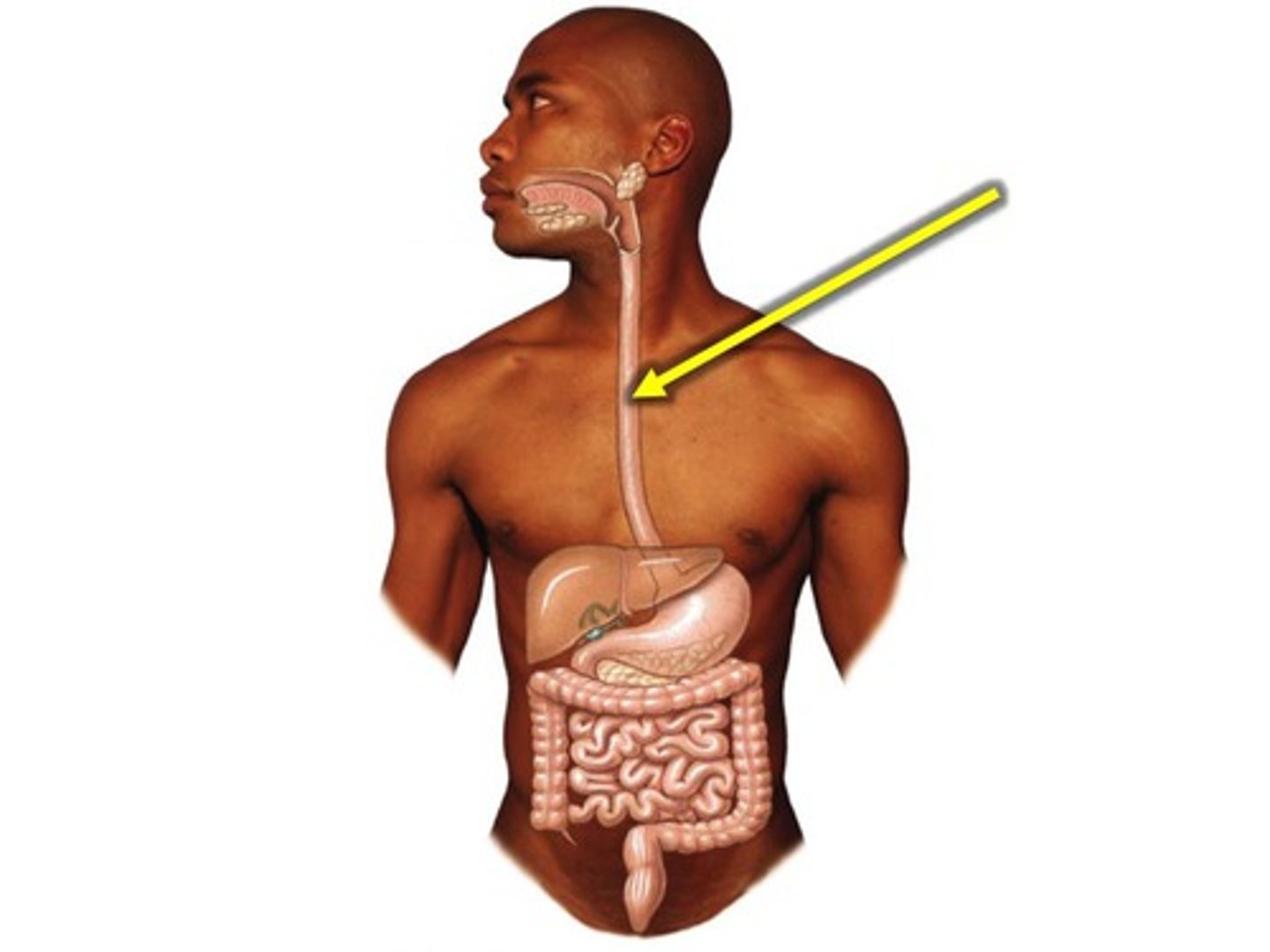
oesophagus
The gullet, the tube that leads from the mouth to the stomach.
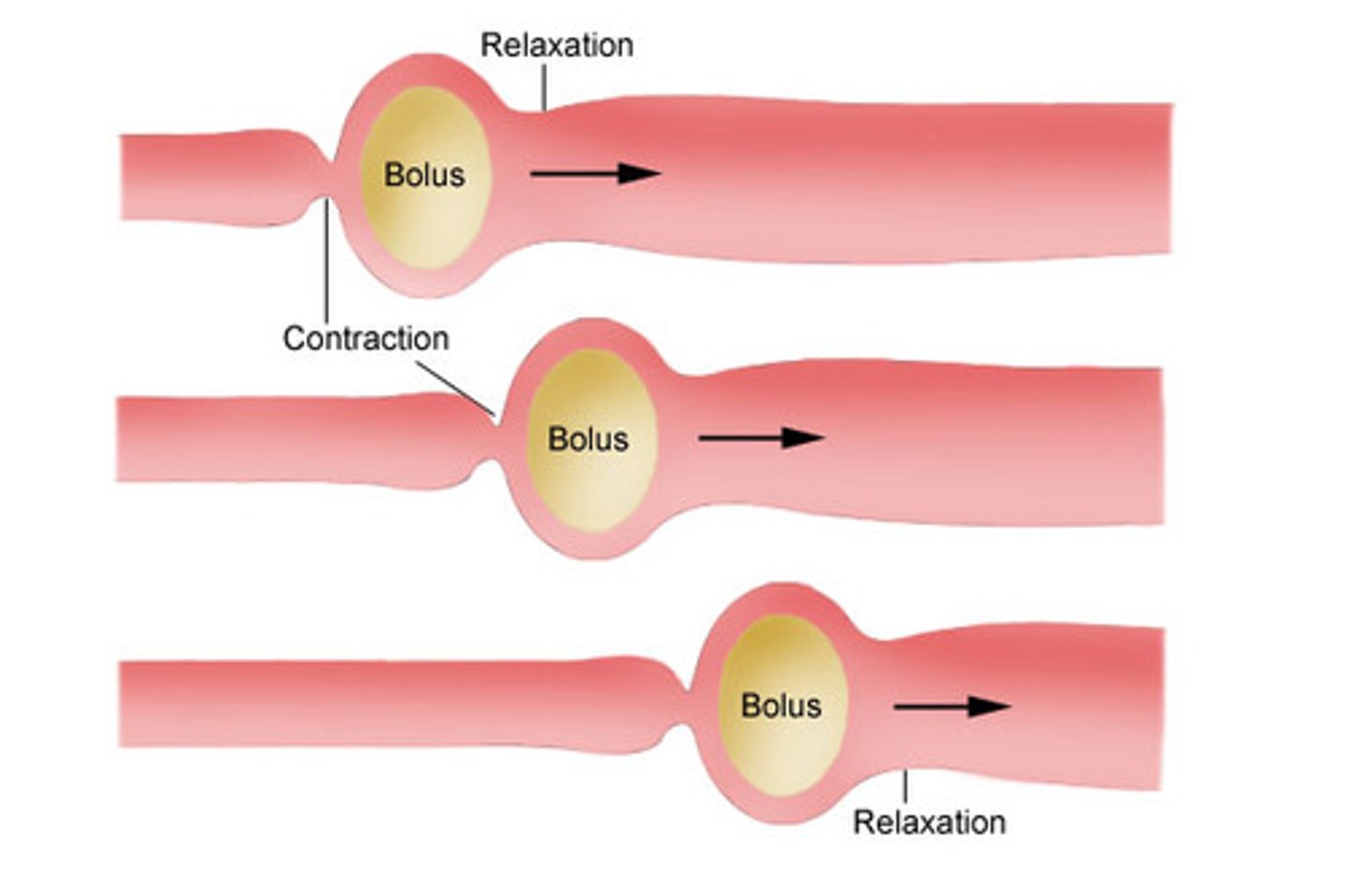
peristalsis
Wave-like muscular contractions in the smooth wall of the gut which move food through the alimentary canal.
pH
Scale of acidity or alkalinity. A power of hydrogen value below 7 is acidic, a pH value above 7 is alkaline.
