JPT HOA 1 Greek architecture
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
262 Terms
8th Century B.C. to 2nd Century
Greek Architecture
The rugged nature of the greek peninsula & its widespread islands, made communication difficult. It was bounded on two sides by Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, Athens as its center kingdom contains the upper city known as Citadel
Geographical influence
Marble - chief building material, they also had ample amount of building stones
Geological influence
Climate was intermediate between "Cold & hot" which favored an outdoor life, dramatic presentations, most of public ceremonies took place in an open air, even in religious rites, due to limited public buildings other than temples.
Climactic influence
Aegeans
Worship "nature", priestesses rather than priests conducted the religious rites
Greeks
Represents their deities by large statues. They worship natural phenomena
1. Aphrodite - Venus
2. Apollo - Apollo
3. Ares - Mars
4. Artemis - Diana
5. Athena - Minerva
6. Demeter - Ceres
7. Dionysus - Bacchus
8. Hephaestus - Vulcan
9. Hera - Juno
10. Heracles - Hercules
11. Hermes - Mercury
12. Hestia - Vesta
13. Nike - Victoria
14. Pan - Pan
15. Poseidon - Neptune
16. Zeus - Jupiter
Greek Deities - Roman Deities
Aphrodite/Venus
Greek/Roman god/goddess of commerce, love and beauty
Apollo/Apollo
Greek/Roman god/goddess of law and reason, art, music and poetry
Ares/Mars
Greek/Roman god/goddess of war
Artemis/Diana
Greek/Roman god/goddess of chastity
Athena/Minerva
Greek/Roman god/goddess of leaning and wisdom
Demeter/Ceres
Greek/Roman god/goddess of earth and agriculture
Dionysus/Bacchus
Greek/Roman god/goddess of wine and feasting
Hephaestus/Vulcan
Greek/Roman god/goddess of fire, flame and forgery
Hera/Juno
Greek/Roman god/goddess of marriage; wife of zeus
Heracles/Hercules
Greek/Roman god/goddess; son of zeus; mythical half god & man
Hermes/Mercury
Greek/Roman god/goddess; messenger of the gods
Hestia/Vesta
Greek/Roman god/goddess of hearth and home
Nike/Victoria
Greek/Roman god/goddess of victory
Pan/Pan
Greek/Roman god/goddess of flock
Poseidon/Neptune
Greek/Roman god/goddess of the sea
Zeus/Jupiter
Greek/Roman god/goddess; supreme god, ruler of the sky, chief god
Chief diversion were music, dancing, wrestling, boxing, gymnastic, and bull-fighting often w/ religious connection. Women took part in hunting and more strenuous games, as well as in craftwork. Tyrannic, aristrocratic, & democratic were the forms of government. Pericles - one of the leaders in Athens
Social and political influence
1. Early Period
2. Hellenic Period
Periods of development
Early period
(3000 B.C. to 700 B.C.) period of development wherein Aegeans, Minoans, and Myceneans were the only people in Greece.
Hellenic period
period of development; essentially columnar & trabeated in Acropolis which was crowned by Parthenon. By the 16th century, Parthenon was converted into a christian church
1. Low pitch or flat roof on multi-storey structure
2. Stairway was developed for vertical circulation
3. Houses termed as Megaron & palaces were principal building types
Characteristic feature of Aegean architecture or early period
1. Enclosed porch
2. Living apartment or megaron proper
3. Thalamus or sleeping room
Megaron areas
1. Cyclopean
2. Polygonal
3. Rectangular
4. Inclined blocks
4 methods of walling surface finishes
Cyclopean
A masonry made-up of huge stone blocks laid on mortar
Polygonal
A masonry which is constructed with stones having polygonal faces
Rectangular
Block of stone cut into rectangular shapes
Inclined blocks
Stones with inclined blocks
1. Simplicity and harmony
2. Purity of lines
3. Perfection of proportions
4. Refinement of details
Characteristics of greek architecture
temples which were built towards the rising sun (east)
Chief building type of hellenic period
1. rectangular plan
2. propylaea gateways
3. Collonade surrounds the temple
4. Ceiling were omitted & treated with timber panelled coffers lacunaria
5. Stone walls
6. Marble sculptures
7. Murals
8. Entasis, optical illusion correctoin
Characteristic features of temples
1. Gate of lions, Mycenae
2. Palaces
3. Tombs
Examples of architectural structures (aegean architecture or early period)
Gate of lions, Mycenae
Most ancient stone sculpture in europe
1. Palace of King Minos, Knossos
2. The Palace, Tyrins
3. The Palace, Mycenae
Examples of palaces of the aegean or early period
1. Tholos
2. Rock-cut or chamber tomb
2 types of aegean tomb
Tholos
A stone vaulted construction shaped like an old fashion beehive. It consists of a long passage known as Dromos leading to the domed chamber
Rock-cut or chamber tomb
rectangular chamber, cut within the slope. Hill side approach by Dromos
1. Tremenos
2. Civic square
3. Temples
4. Propylaea
5. Theater
6. Public building
Examples of architectural structures (Greek architecture or hellenic period)
Tremenos
- or sacred enclosure, also known as citadel or acropolis or upper city
1. Principal temple
2. Pinacotheca (picture gallery)
3. Glypthotheca (sculpture gallery)
4. Statue of Athena
5. The Erectheion
6. Old Temple of Athena
7. The Parthenon
8. Theater of Dionysos
9. Stoa of Eumenes
10. Odeion of Herodes Atticus
11. Temple of Nike Apteros
Important structures found in acropolis
Civic square
City square or market place, the greeks's political, business and economic life
Agora
Greek civic square
Piazza
Italian civic square
Market
English civic square
Forum
Roman civic square
Place
French civic square
1. Civic square at Miletus
2. Civic square at Ephesus
3. Civic square at Priene
Examples of civic square (agora)
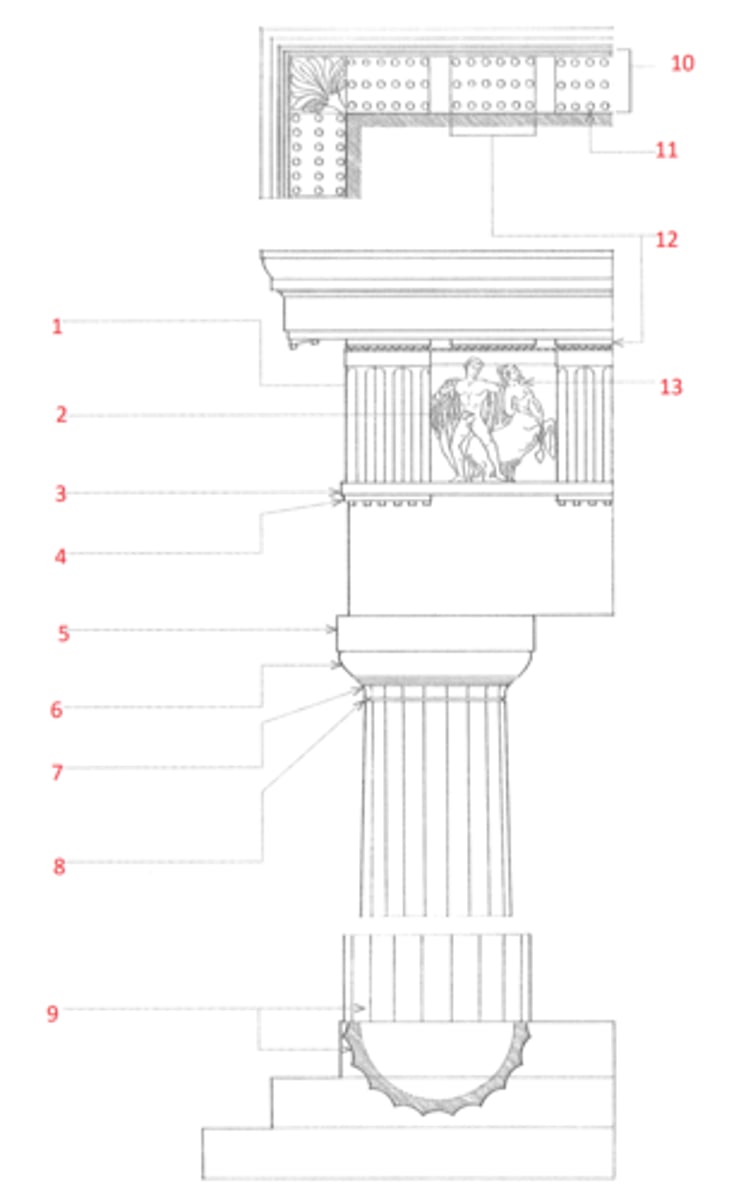
Temples
Were the chief building. Usually the plan is rectangular in shape.
1. Naos
2. Pronaos
3. Epinaos or Opisthdomus
Parts of a greek temple
Naos
Part of a Greek temple; principal chamber containing the statue of the god or goddess with porticoes & colonnades
Pronaos
Part of a Greek temple; the inner portico in front of the naos, or cella of the naos
Epinaos or Opisthodomus
Part of a Greek temple; posticum which serves as the treasury chamber.
1. According to the number of columns on the entrance front
2. By the arrangement of the exterior columns of the temple in relation to naos
2 ways of describing temples (rectangular)
columniation
The use or arrangement of columns in a structure
1. Henostyle - 1 column
2. Distyle - 2 columns
3. Tristyle - 3 columns
4. Tetrastyle - 4 columns
5. Pentastyle - 5 columns
6. Hexastyle - 6 columns
7. Heptastyle - 7 columns
8. Octastyle - 8 columns
9. Enneastyle - 9 columns
10. Decastyle - 10 columns
11. Dodecastyle - 12 columns
Type of temple by the arrangement of the exterior columns of the temple in relation to naos (columniation)
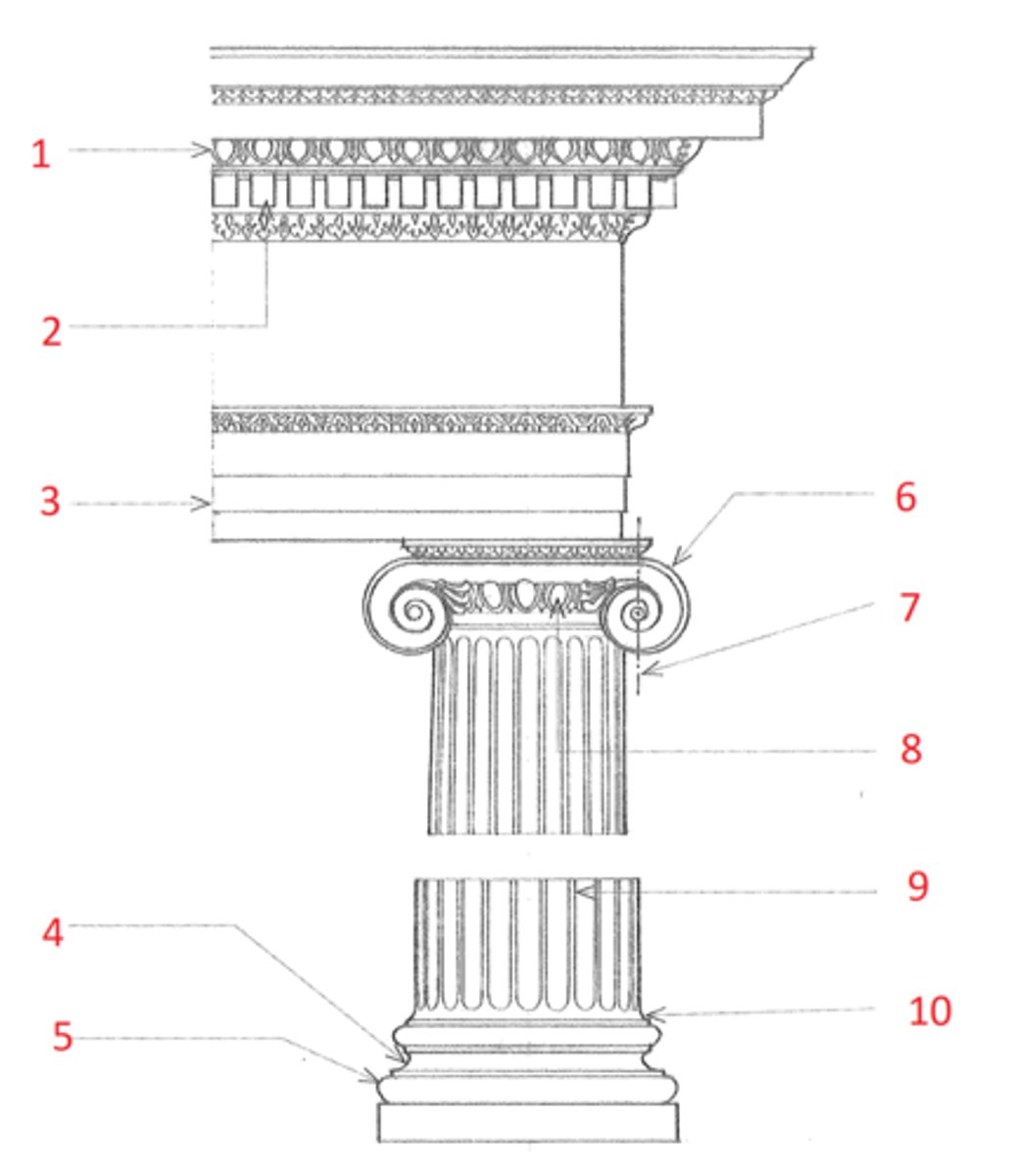
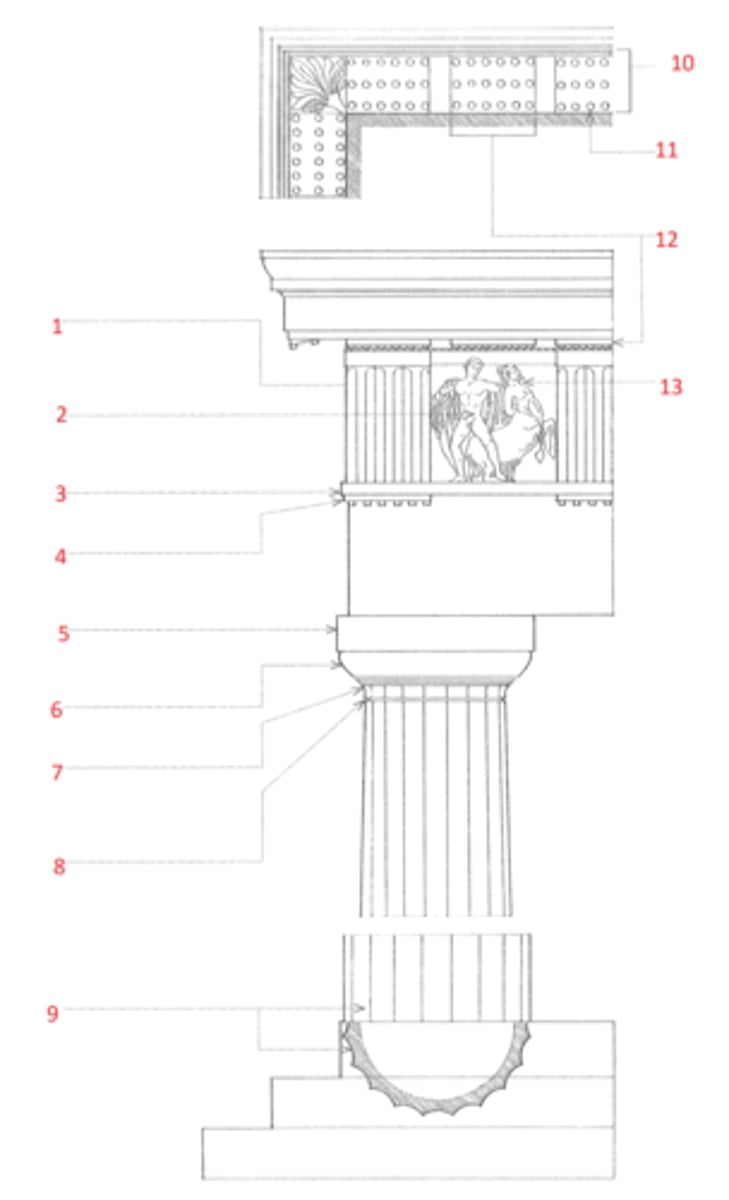
1. cymatium
2. corona
3. bed molding
4. cornice
5. frieze
6. architrave
7. capital
8. shaft
9. base
10. cornice or cap
11. dado
12. base moulding
13. plinth
14. entablature
15. column
16. pedestal
Identify
cymatium
(1) The crowning member of a classical cornice, usually a cyma recta.
corona
(2) The projecting, slablike member of a classical cornice, supported by the bed molding and crowned by the cymatium.

bed molding
(3) The molding or group of moldings immediately beneath the corona of a cornice.
cornice
(4) The uppermost member of a classical entablature, consisting typiclly of a cymatium, corona, and bed molding
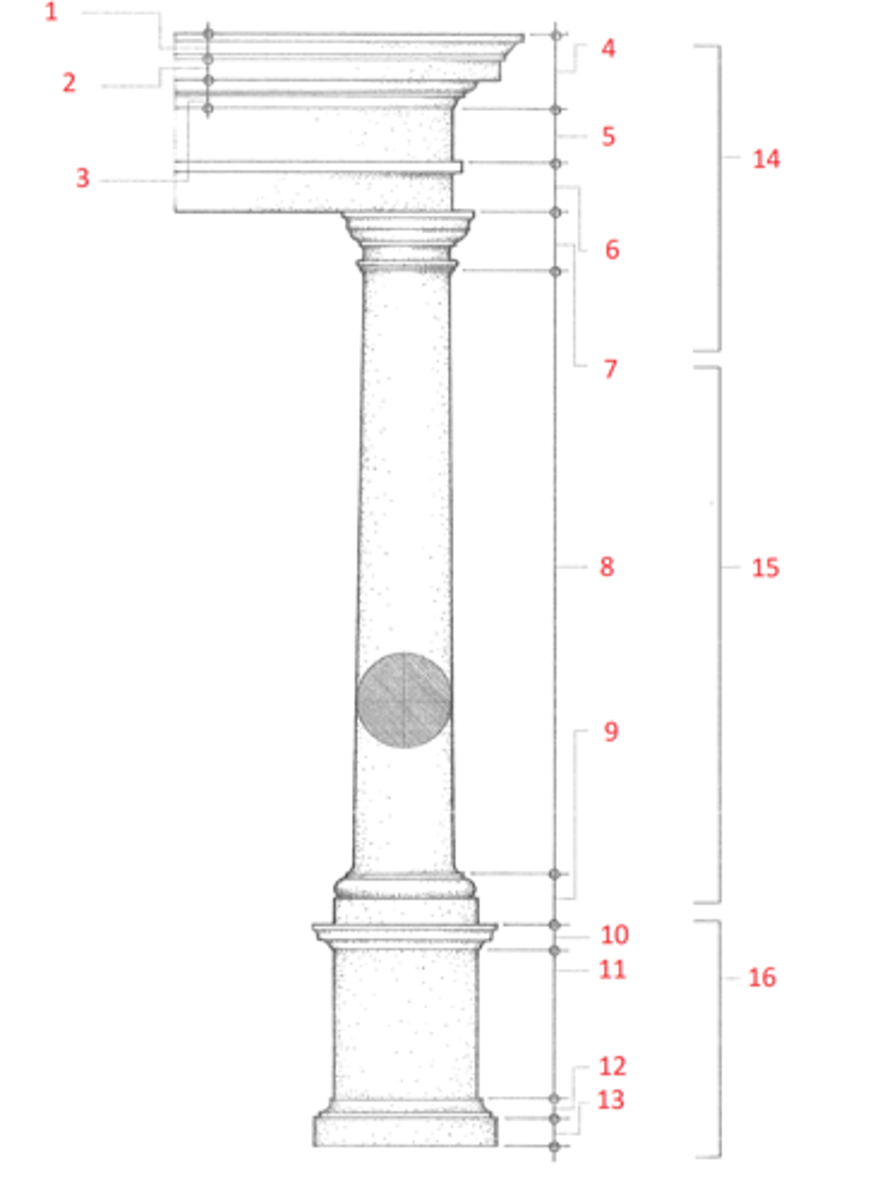
frieze
(5) The horizontal part of a classical entablature between the cornice and architrave, often decorated with sculpture in low relief.
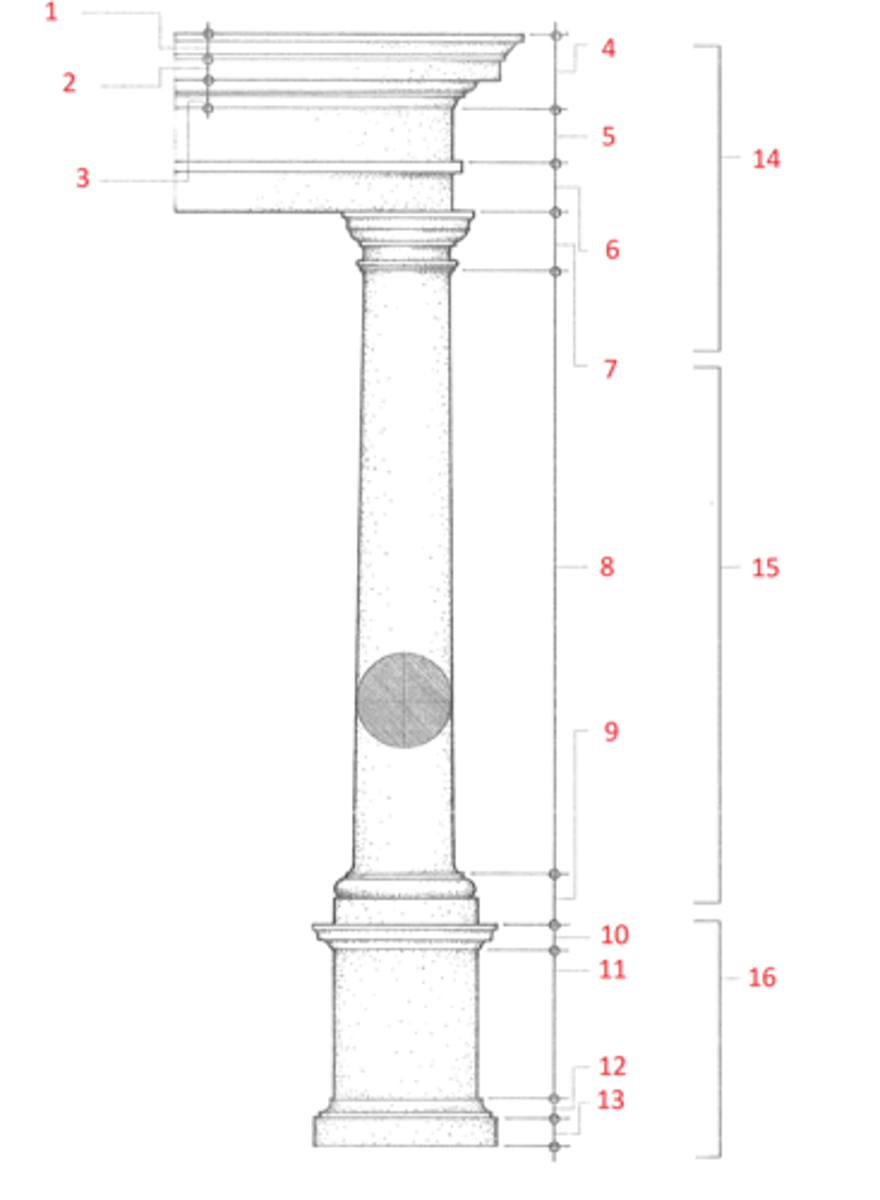
architrave
(6) The lowermost division of a classical entablature, resting directly on the column capitals and supporting the frieze.
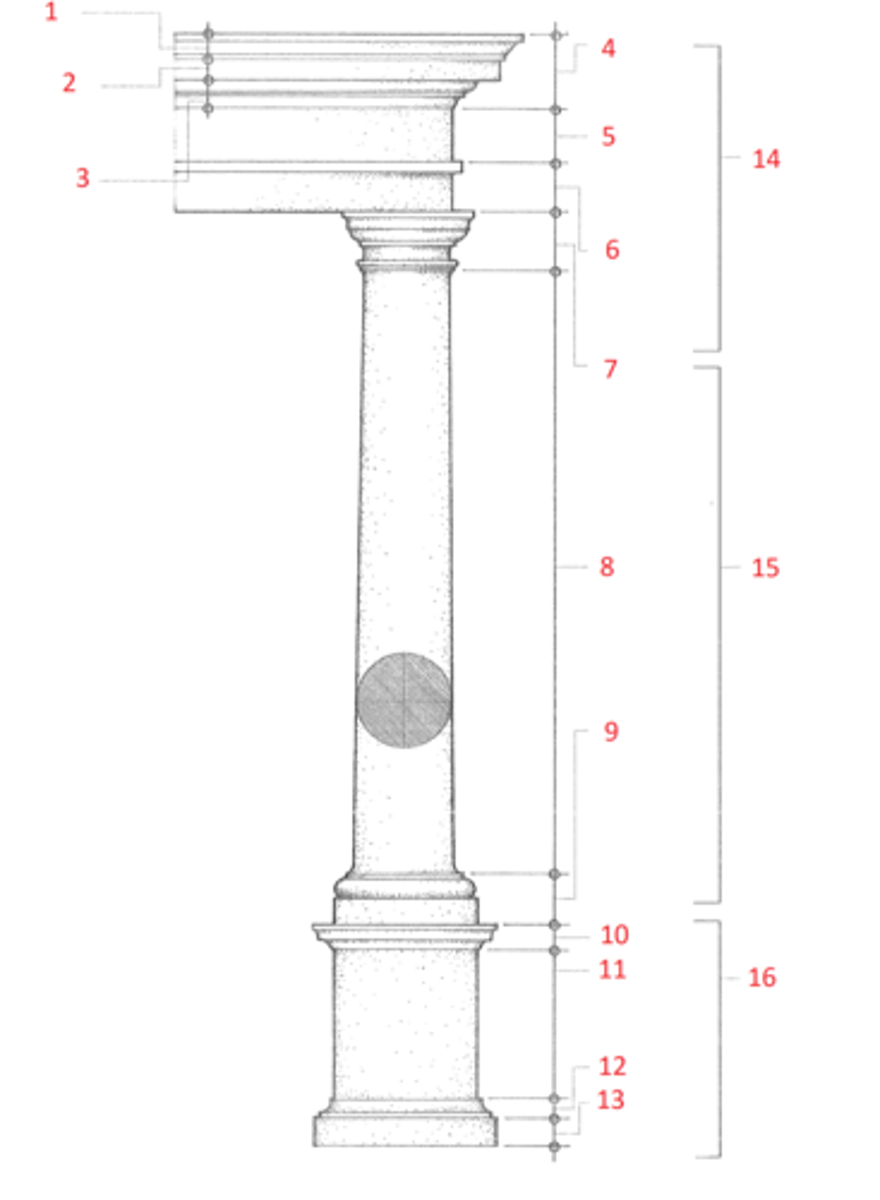
capital
(7) The distinctively treated upper end of a column, pillar, or pier, crowning the shaft and taking the weight of the entablature or architrave.
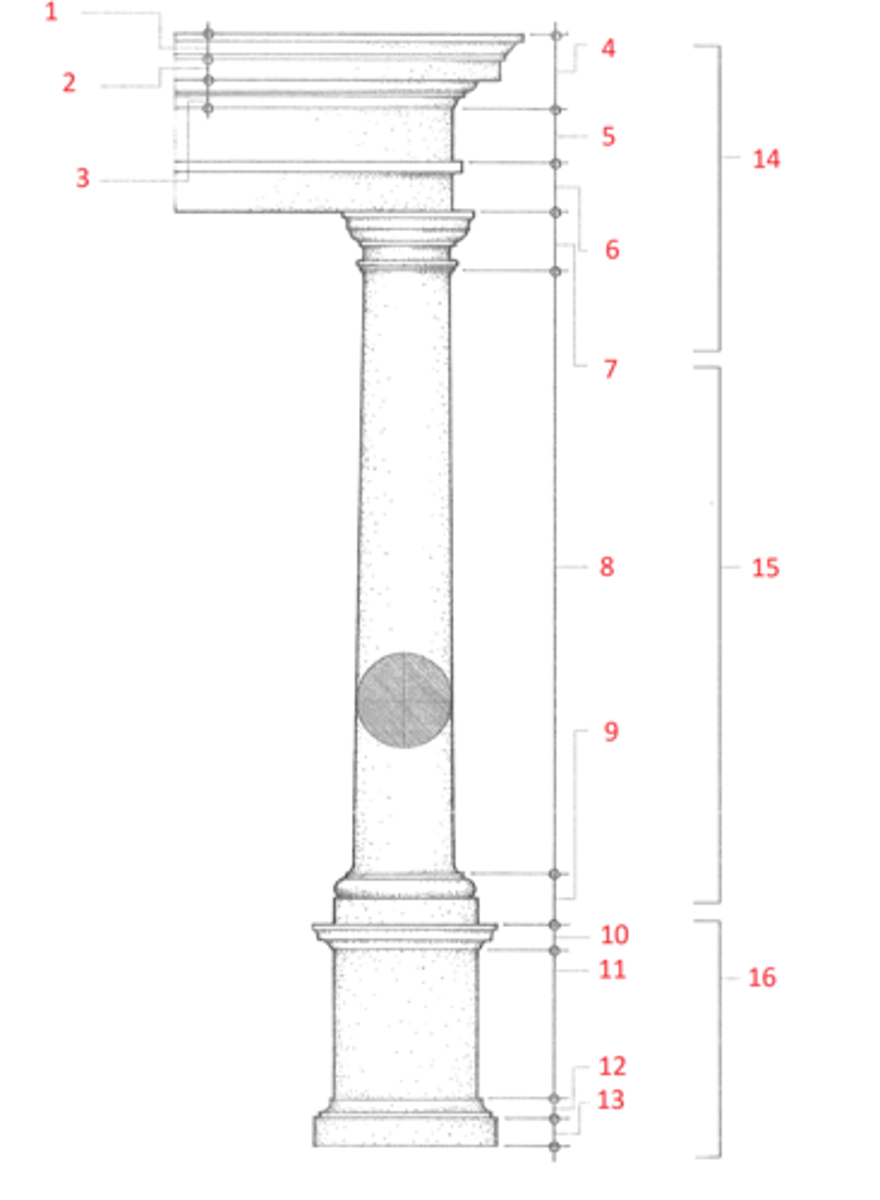
shaft
(8) The central part of a column or pier between the capital and the base.
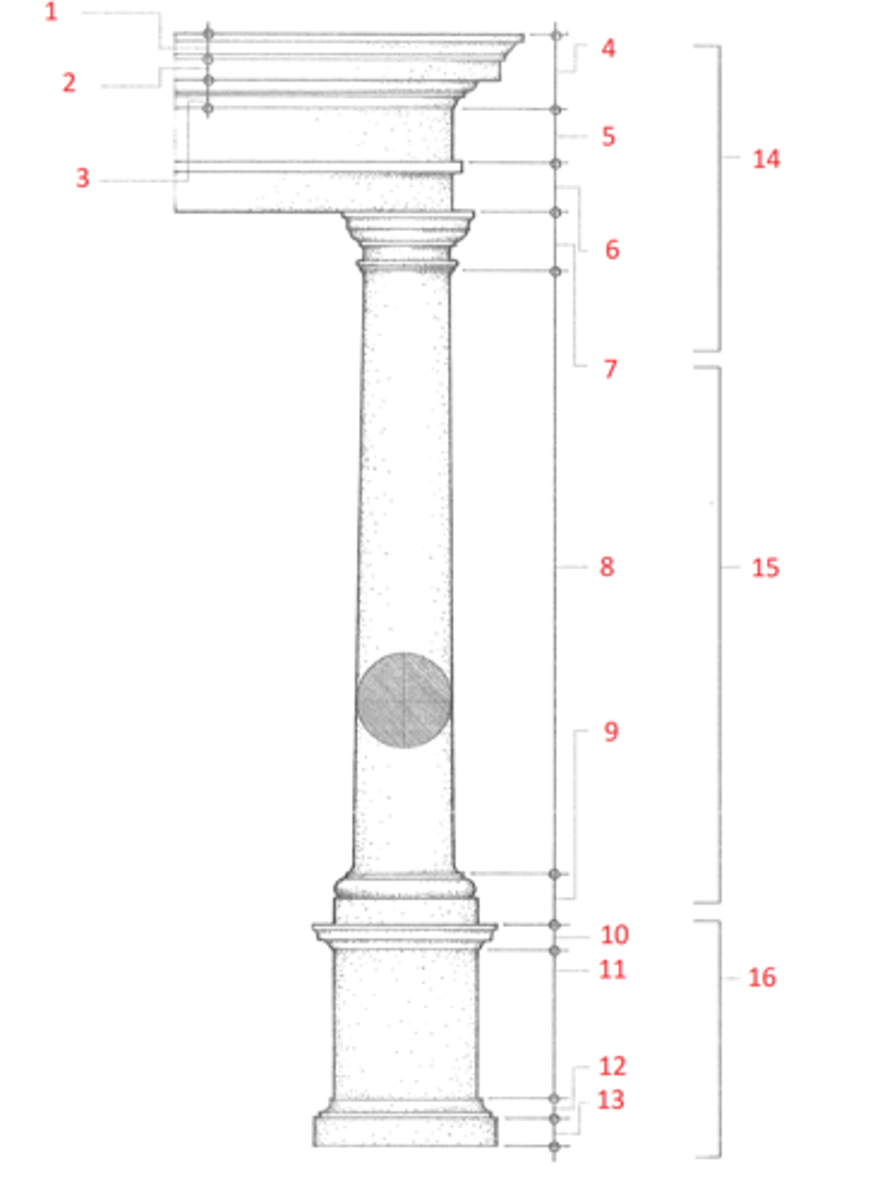
base
(9) The lowermost portion of a wall, column, pier, or other structure, usually distinctively treated and considered as an architectural unit.
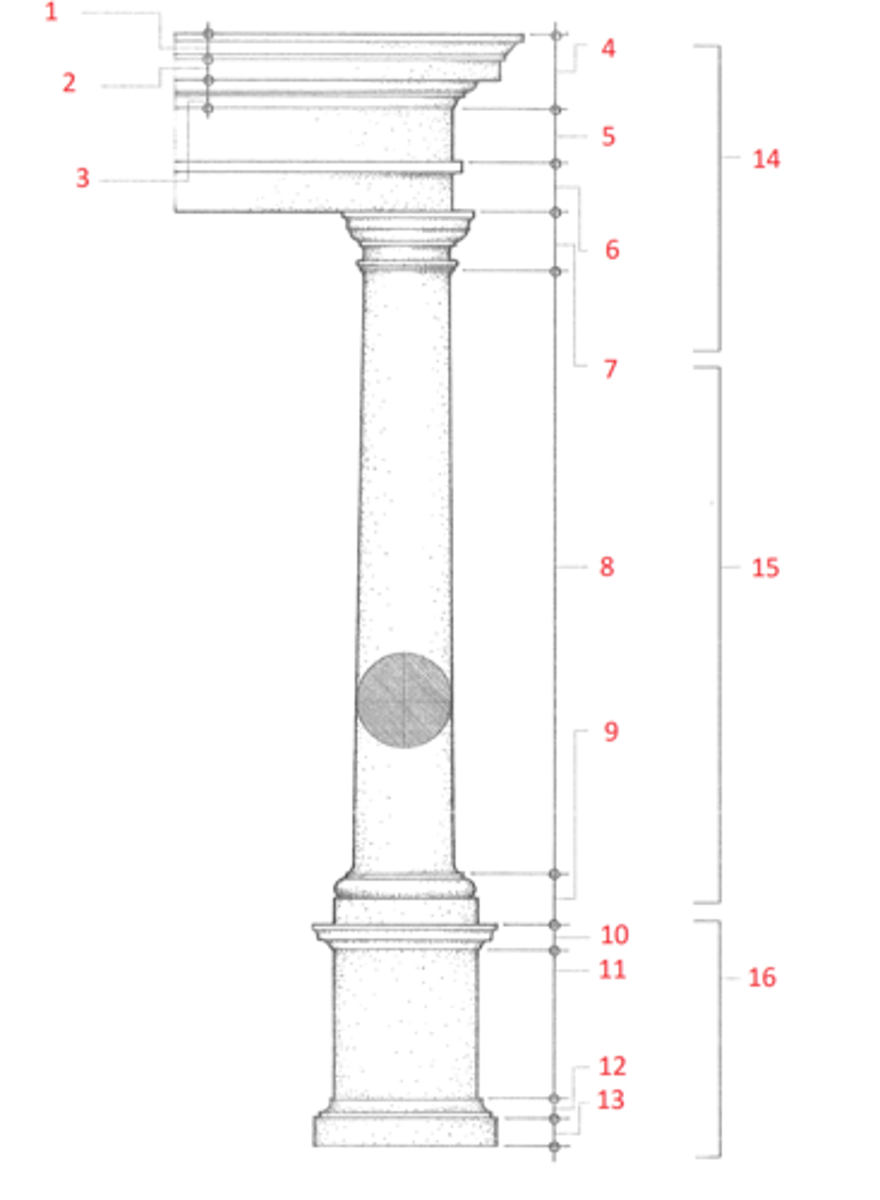
dado
(11) The part of a pedestal between the base and the cornice or cap. Also called die.
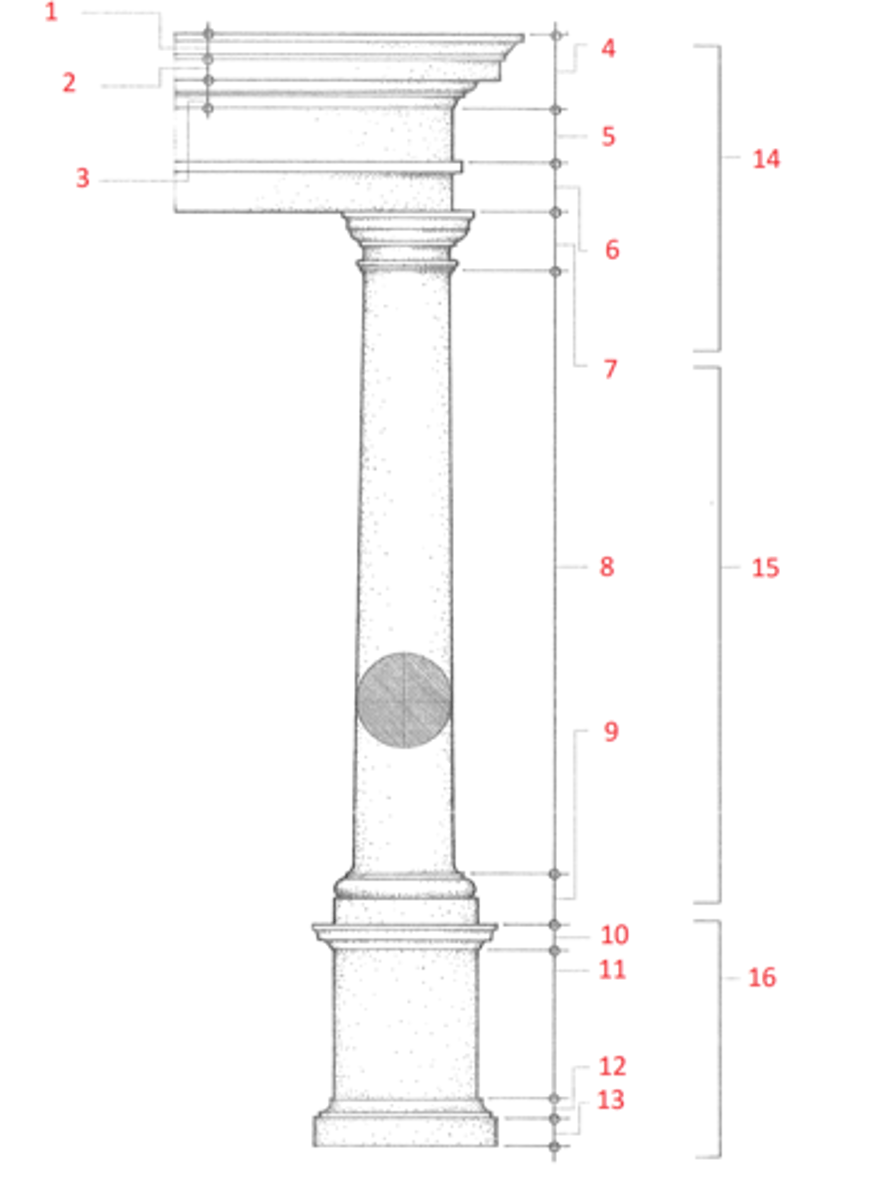
plinth
(13) The usually square slab beneath the base of a column, pier, or pedestal.
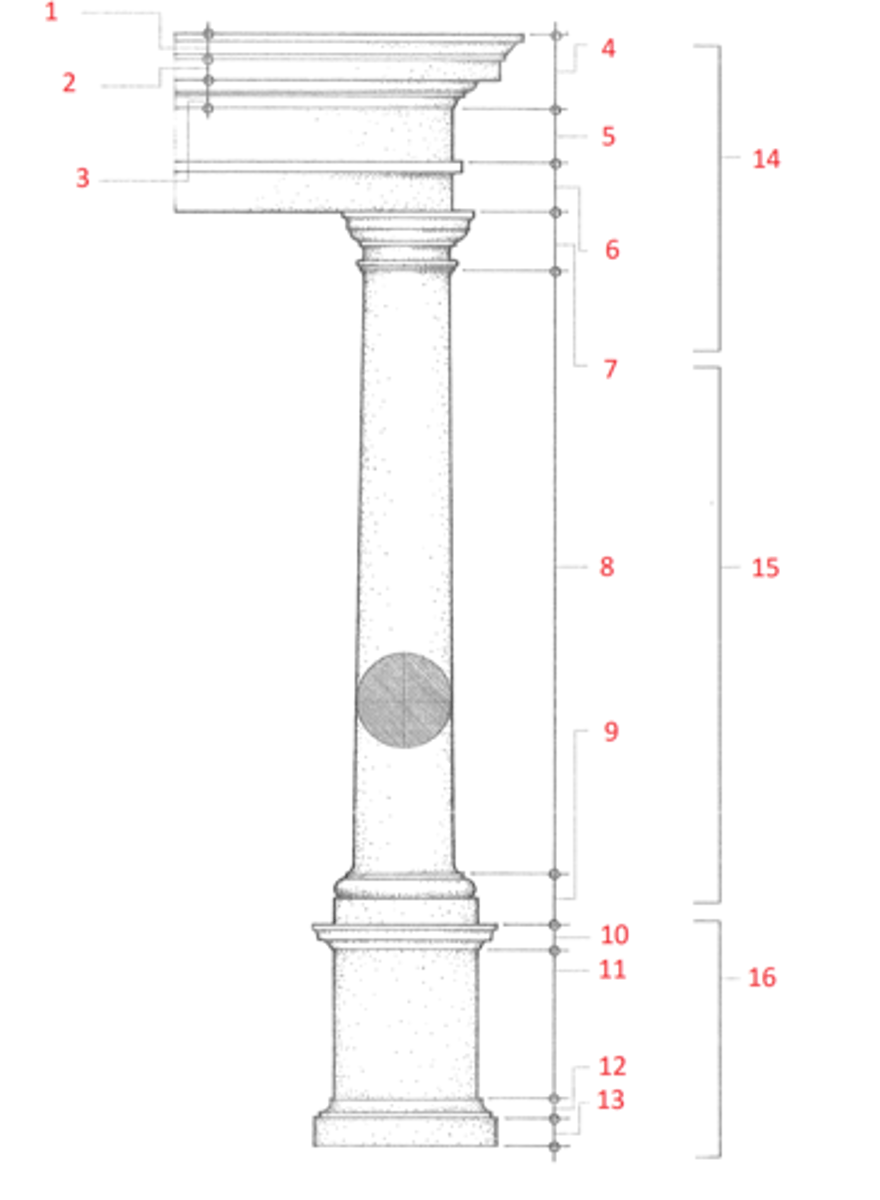
entablature
(14) The horizontal section of a classical order that rests on the columns, usually composed of a cornice, frieze, and architrave.
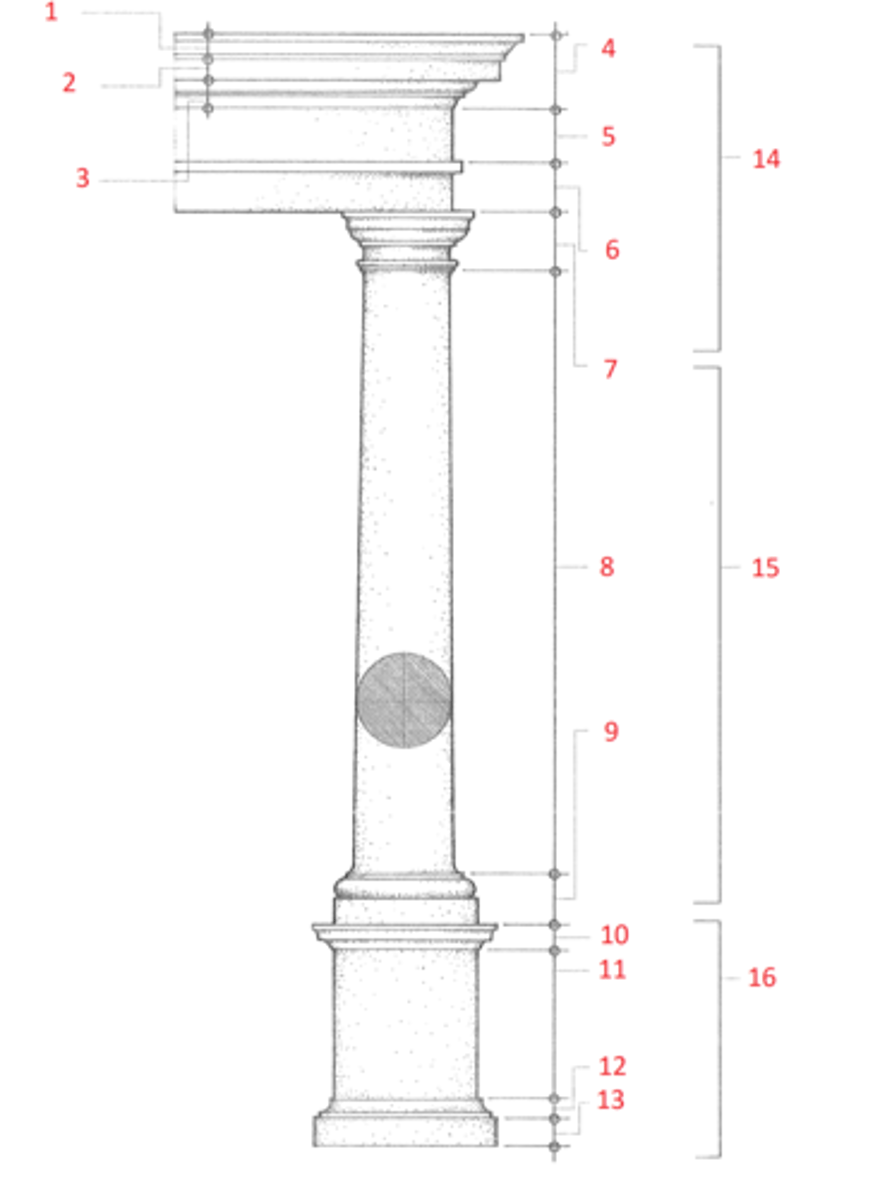
column
(15) A cylindrical support in classical architecture, consisting of a capital, shaft, and usually a base, either monolithic or built up of drums the full diameter of the shaft.
pedestal
(16) A construction upon which a column, statue, memorial shaft, or the like, is elevated, usually consisting of a base, a dado, and a cornice or cap.
intercolumniation
The space between two adjacent columns, usually the clear space between the lower parts of the shafts, measured in column diameters. Also, a system for spacing columns in a colonnade based on this measurement.
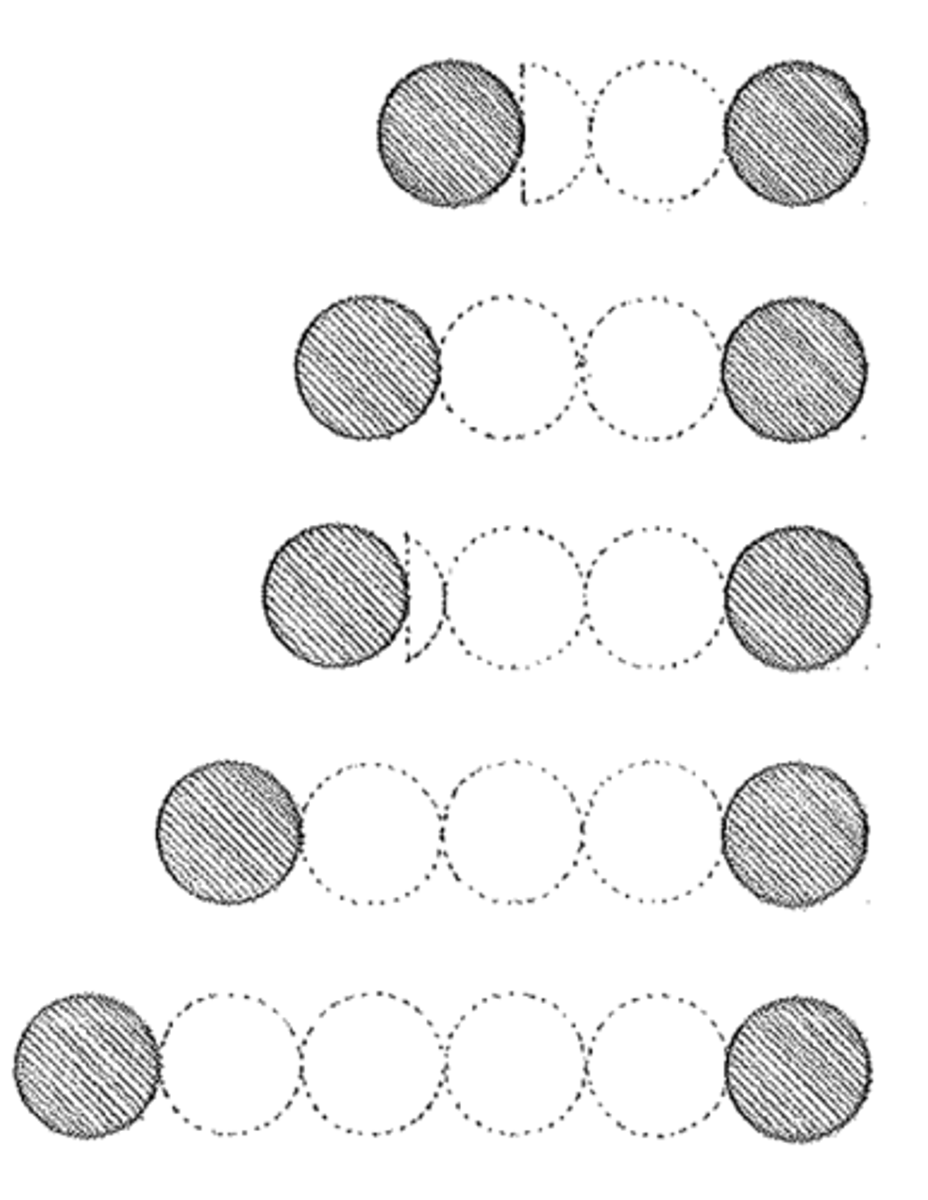
pycnostyle
Having an intercolumniation of 1½ diameters
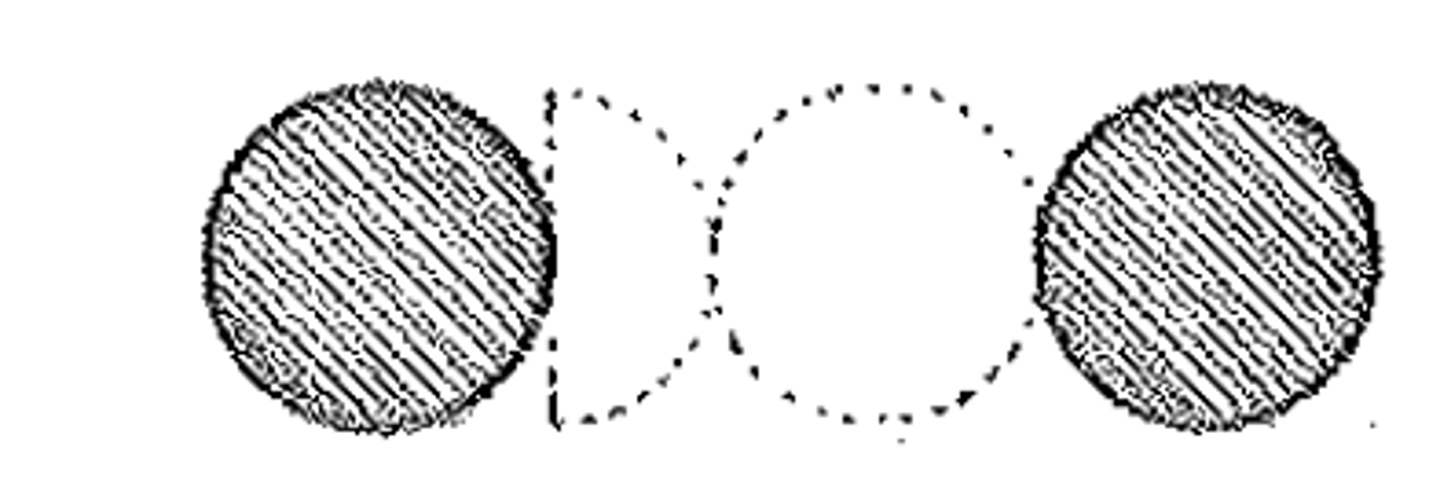
systyle
Having an intercolumniation of 2 diameters
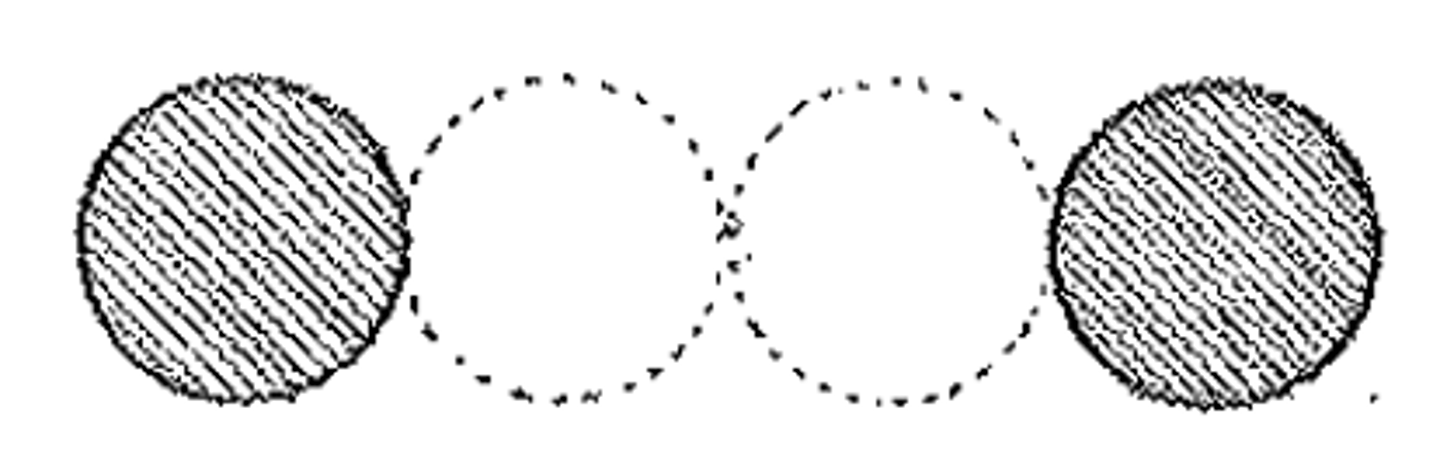

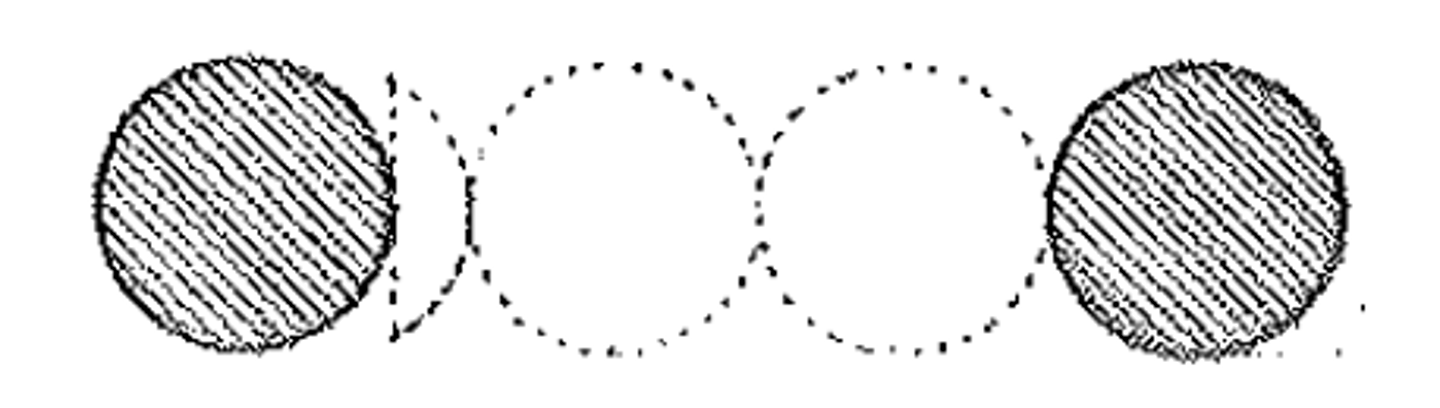
eustyle
Having an intercolumniation of 2¼ diameters
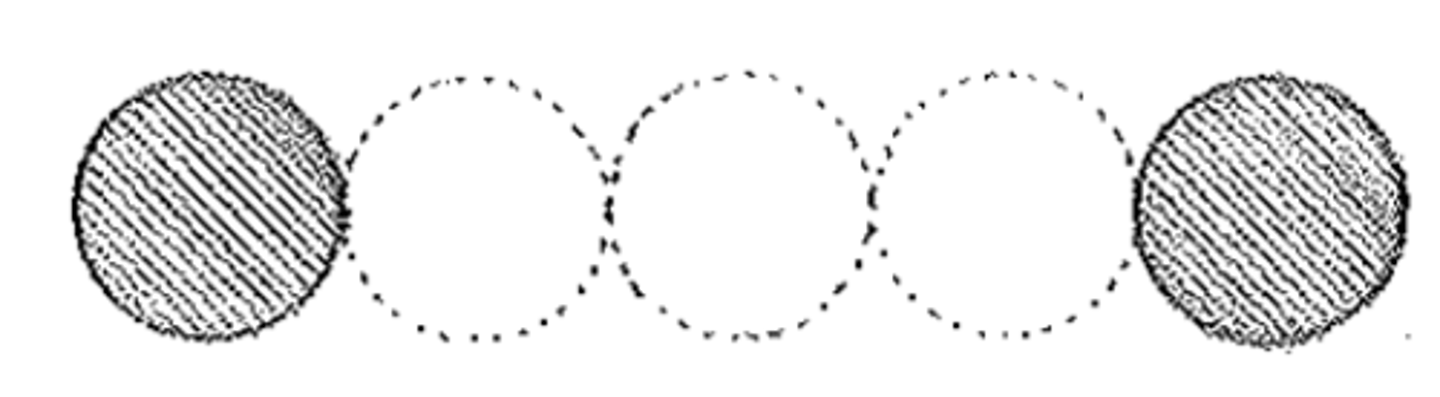
diastyle
Having an intercolumniation of 3 diameters
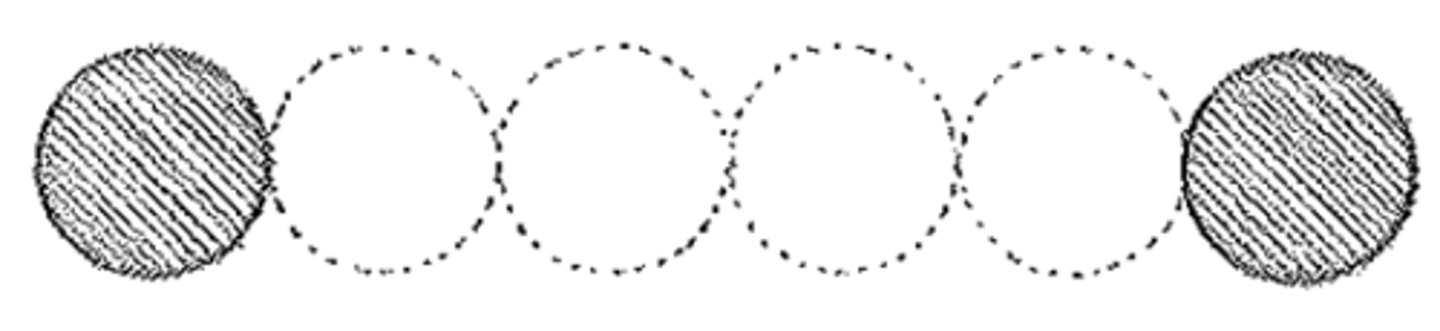
araeostyle
Having an intercolumniation of 4 diameters. Also areostyle
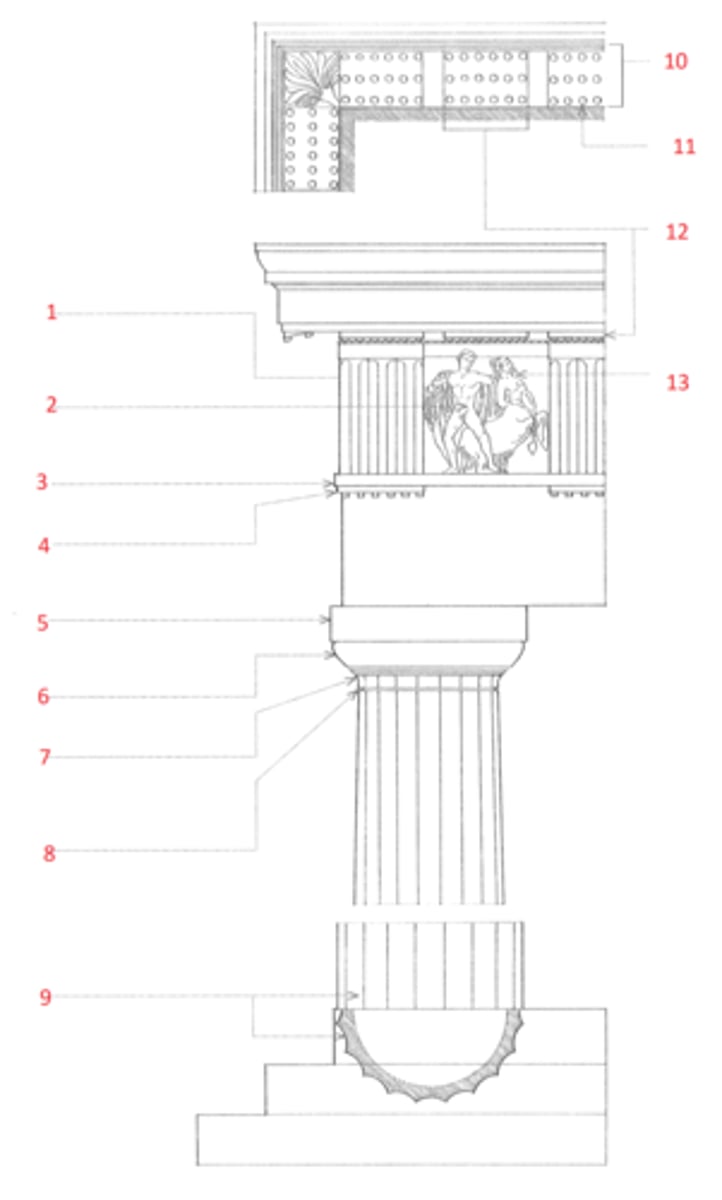
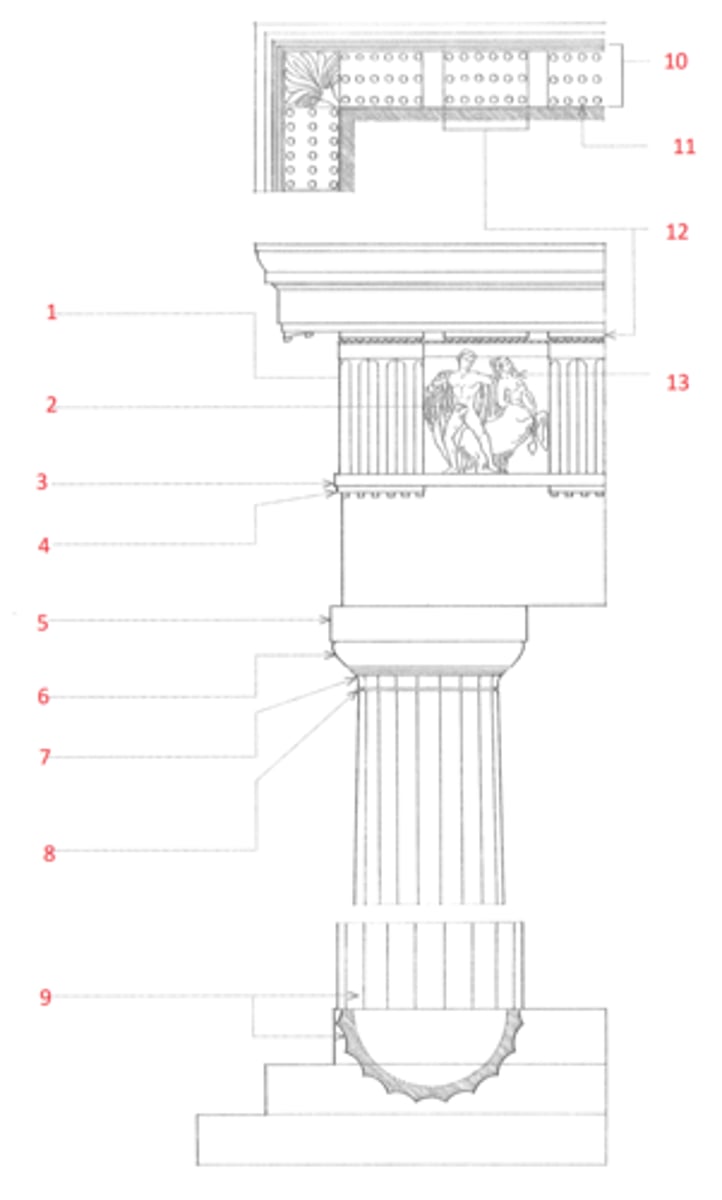
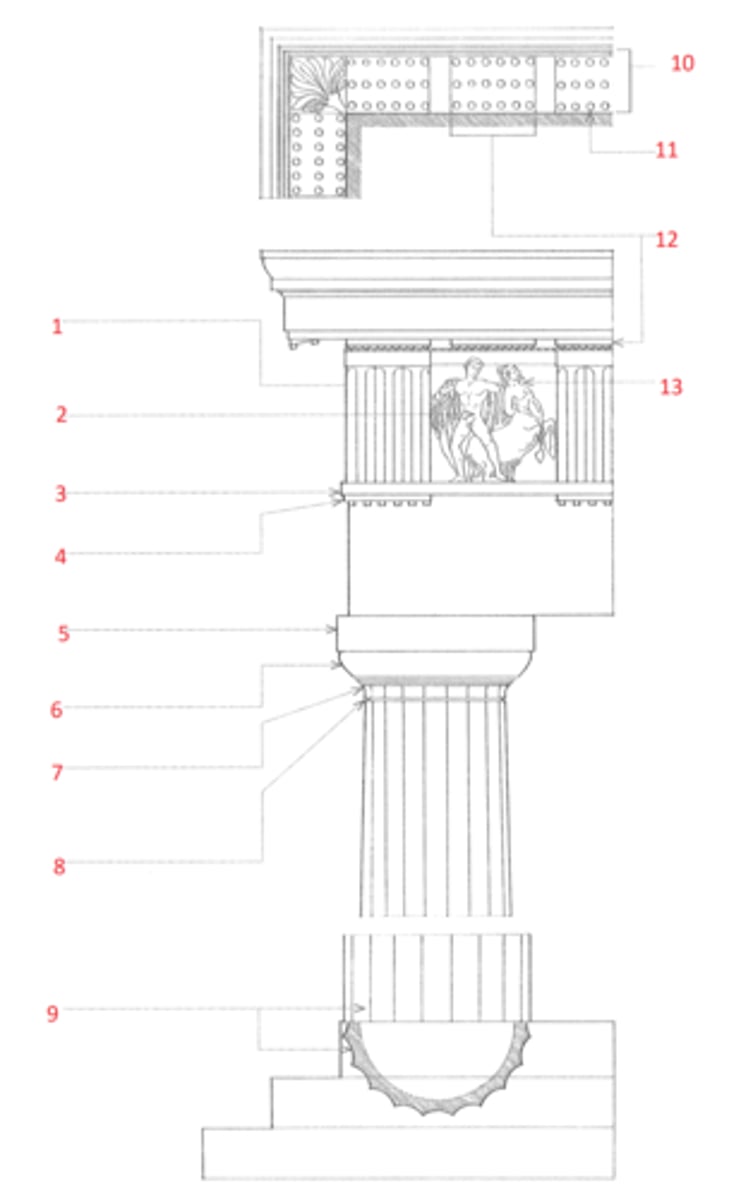
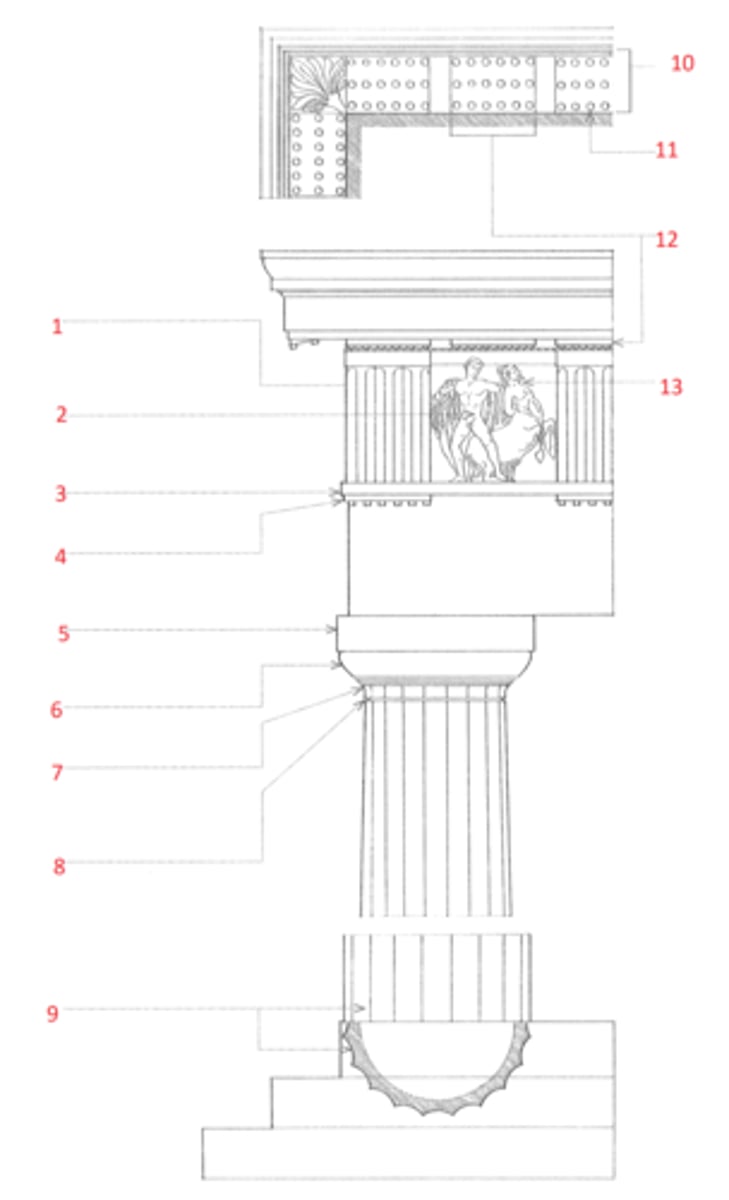
Doric order
The oldest and simplest of the five classical orders, developed in Greece in the 7th century BCE and later imitated by the Romans, characterized by a fluted column having no base, a plain cushion-shaped capital supporting a square abacus, and an entablature consisting of a plain architrave, a frieze of triglyphs and metopes, and a cornice, the corona of which has mutules on its soffit. In the Roman Doric order, the columns are more slender and usually have bases, the channeling is sometimes altered or omitted, and the capital consists of a bandlike necking, an echinus, and a molded abacus.
1. triglyph
2. metope
3. taenia
4. regula
5. abacus
6. echinus
7. necking
8. annulet
9. fluting
10. soffit
11. gutta
12. mutule
13. zophorus
Identify (Doric order)
triglyph
(1) One of the vertical blocks separating the metopes in a Doric frieze, typically having two vertical grooves or glyphs on its face, and two chamfers or hemiglyphs at the sides
metope
(2) Any of the panels, either plain or decorated, between triglyphs in the Doric frieze. Also called intertriglyph.
taenia
(3) A raised band or fillet separating the frieze from the architrave on a Doric entablature. Also, tenia.
regula
(4) A fillet beneath the taenia in a Doric entablature, corresponding to a triglyph above and from which guttae are suspended. Also called guttae band.
abacus
(5) The flat slab forming the top of a column capital plain in the Doric style, but molded or otherwise enriched in other styles
echinus
(6) The prominent circular molding supporting the abacus of a Doric or Tuscan capital.
necking
(7) The upper part of a column, just above the shaft and below the projecting part of the capital, when differentiated by a molding, groove, or the omission of fluting.
annulet
(8) An encircling band, molding, or fillet, on a capital or shaft of a column.
fluting
(9) A decorative motif consisting of a series of long, rounded, parallel grooves, as on the shaft of a classical column.
soffit
(10) The underside of an architectural element, as that of an arch, beam, cornice, or staircase
gutta
(11) One of a series of small, droplike ornaments, attached to the undersides of the mutules and regulae of a Doric entablature. Also called drop.
mutule
(12) A projecting flat block under the corona of a Doric cornice, corresponding to the modillion of other orders
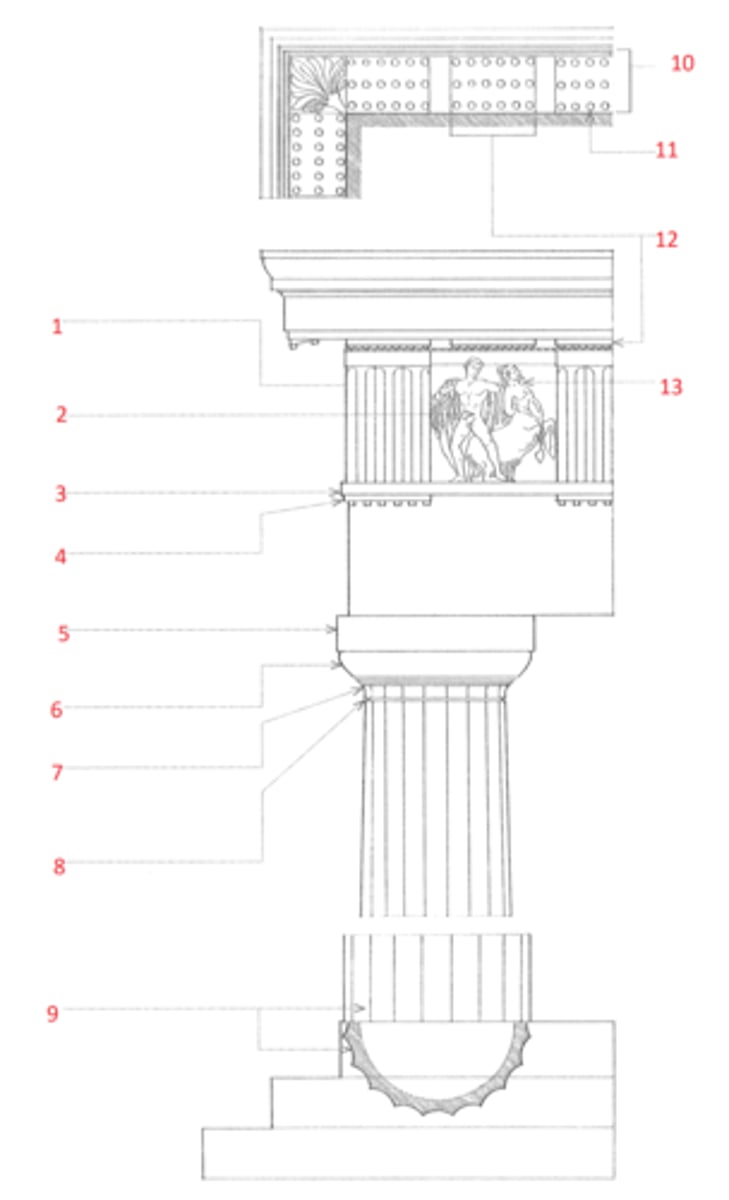
zophorus
(13) A frieze bearing carved figures of people or animals. Also, zoophorus.
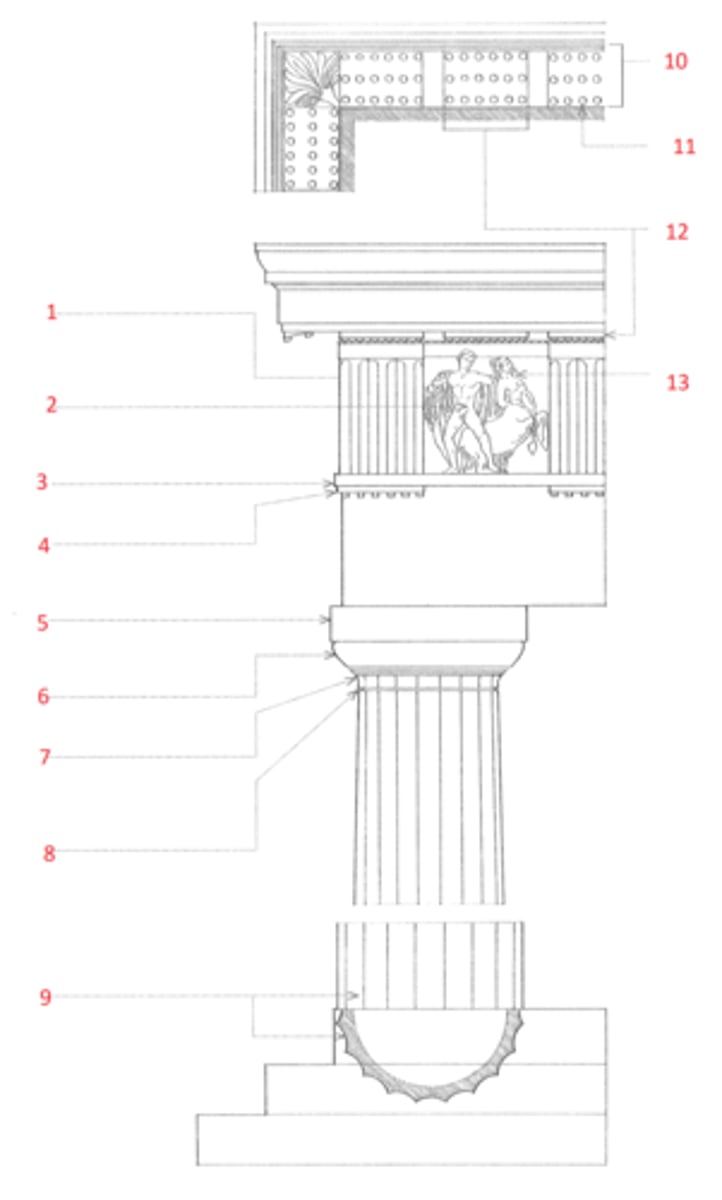
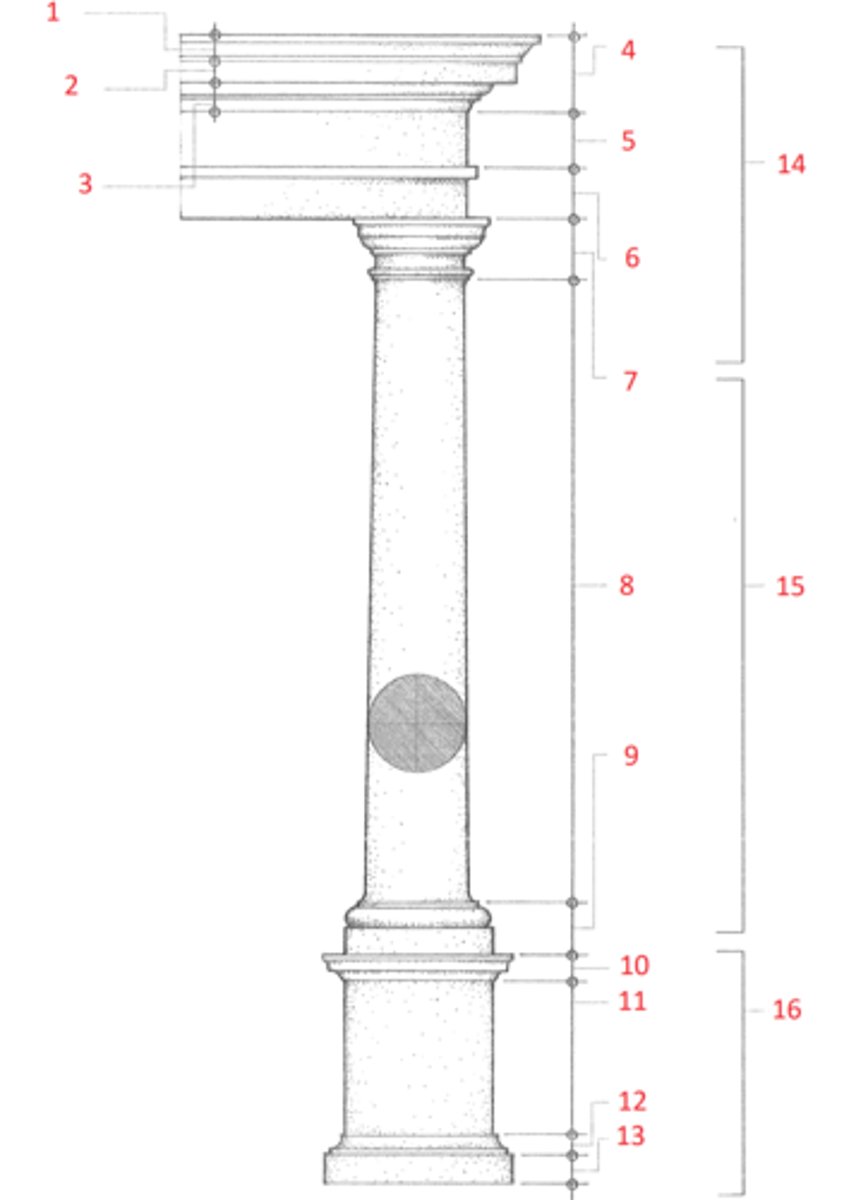
Ionic order
A classical order that developed in the Greek colonies of Asia Minor in the 6th century BCE, characterized esp. by the spiral volutes of its capital. The fluted columns typically had molded bases and supported an entablature consisting of an architrave of three fascias, a richly ornamented frieze, and a cornice corbeled out on egg-and-dart and dentil moldings. Roman and Renaissance examples are often more elaborate, and usually set the volutes of the capitals 45º to the architrave
1. egg and dart
2. dentil
3. fascia
4. scotia
5. torus
6. volute
7. cathetus
8. echinus
9. fillet
10. apohyge
Identify (Ionic order)
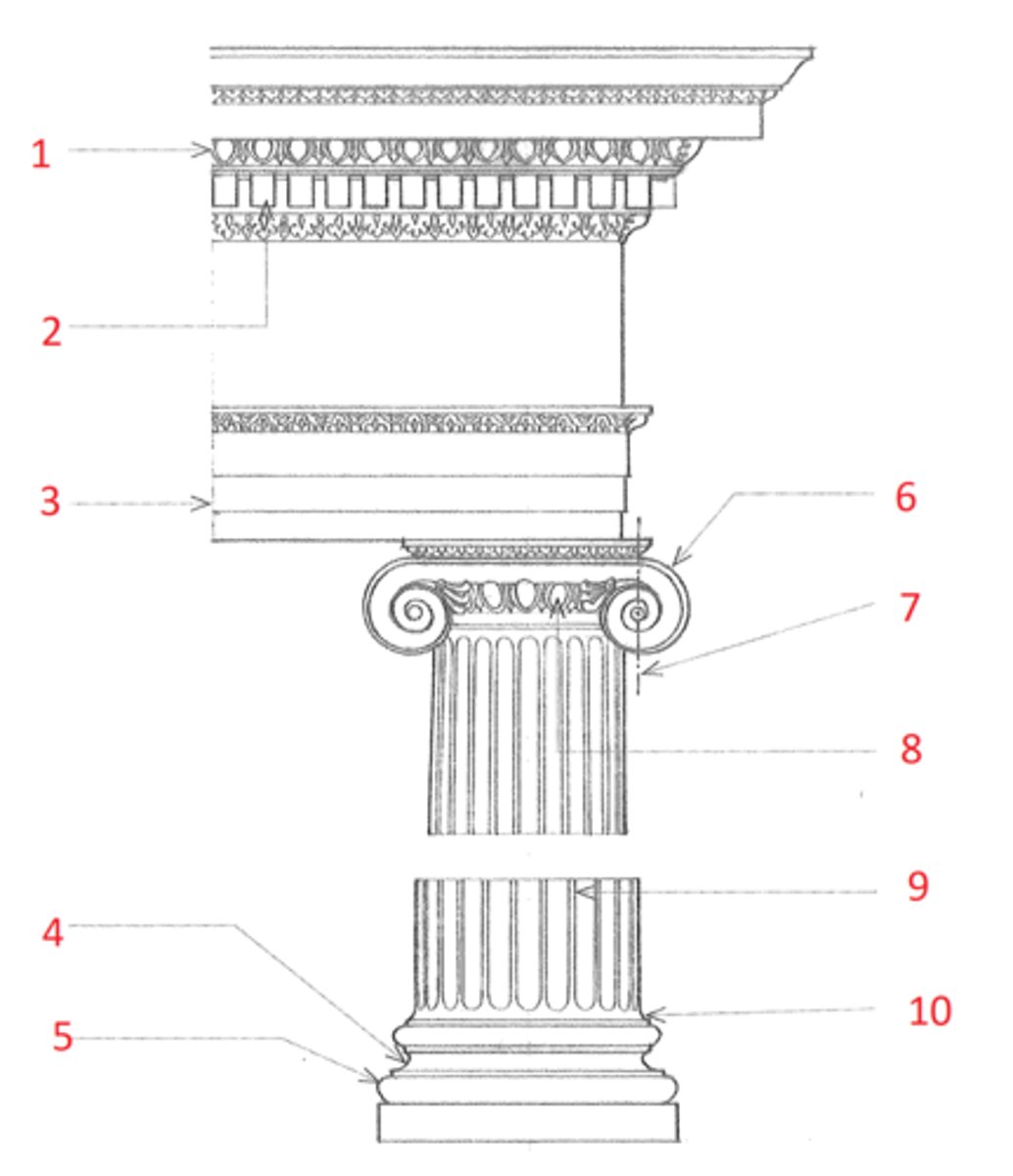
egg and dart
(1) An ornamental motif for enriching an ovolo or echinus, consisting of a closely set, alternating series of oval and pointed forms. Also called egg and tongue.